The Combined Anti-Aging Effect of Hydrolyzed Collagen Oligopeptides and Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Human Skin Fibroblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
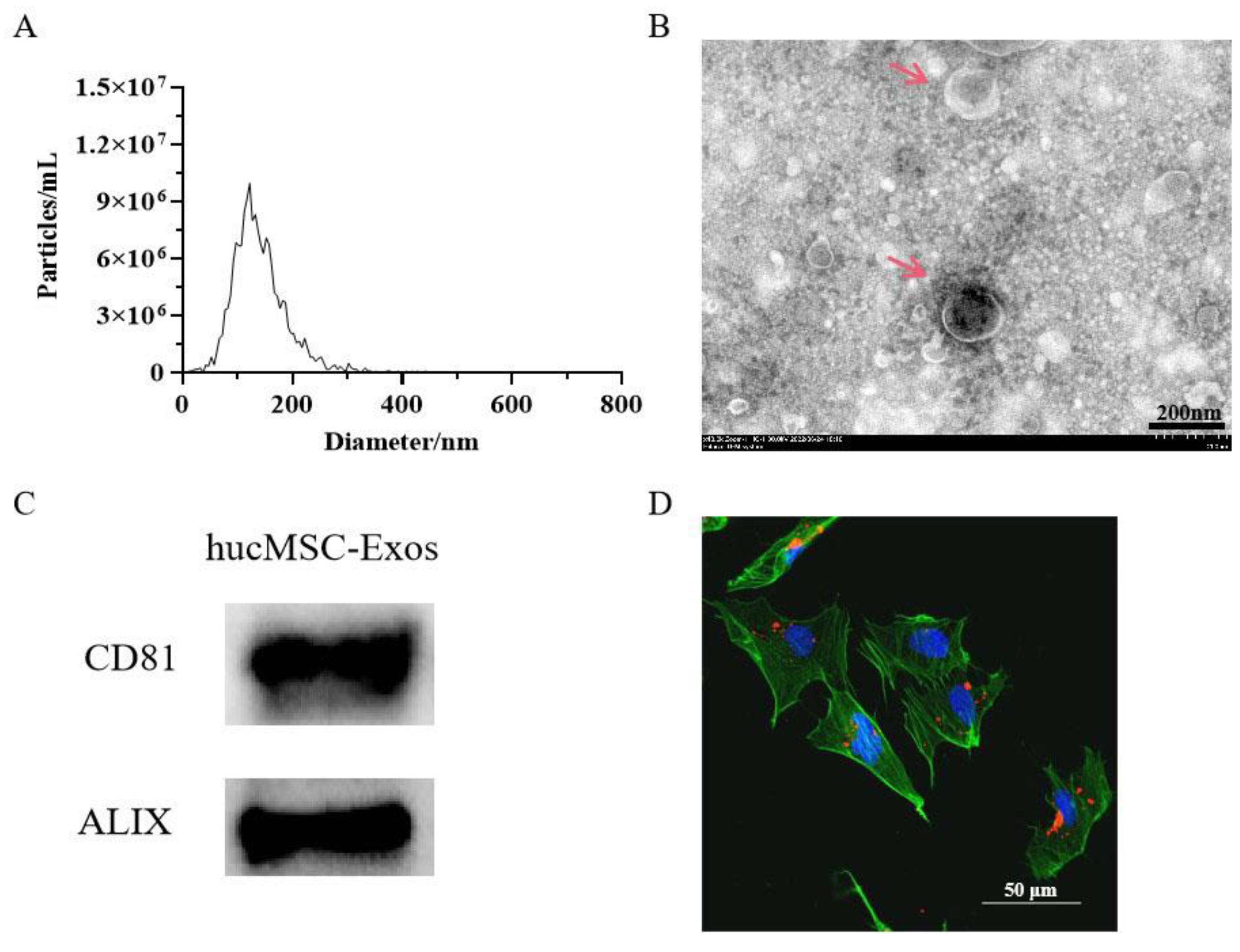
2.1. Characterization of Exosomes
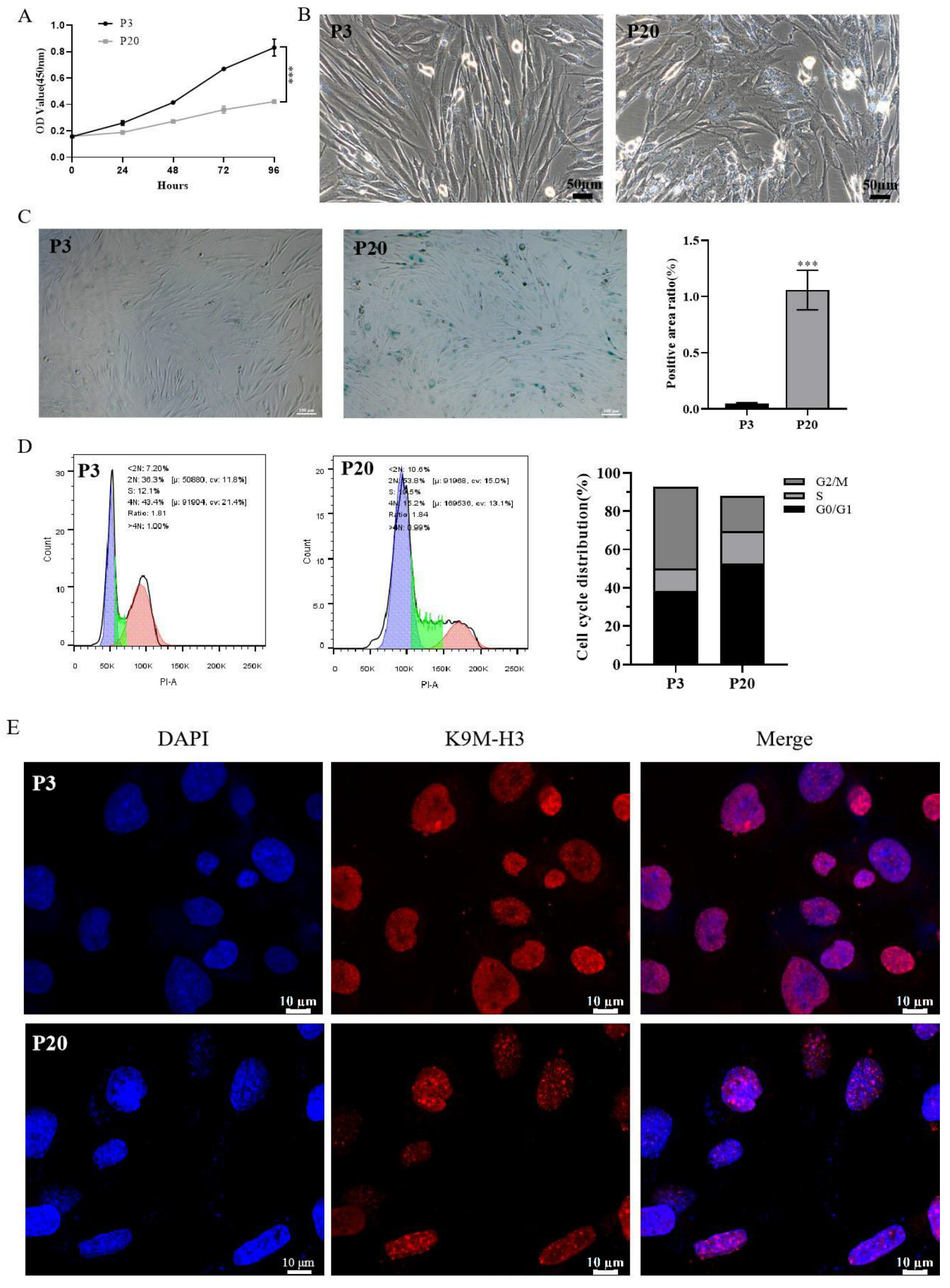
2.2. Establishment of a Model of Replicative Senescence of HSFs
2.3. Effect of Different Concentrations of HucMSC-Exos or HCOPs on the Proliferation of Senescent HSFs
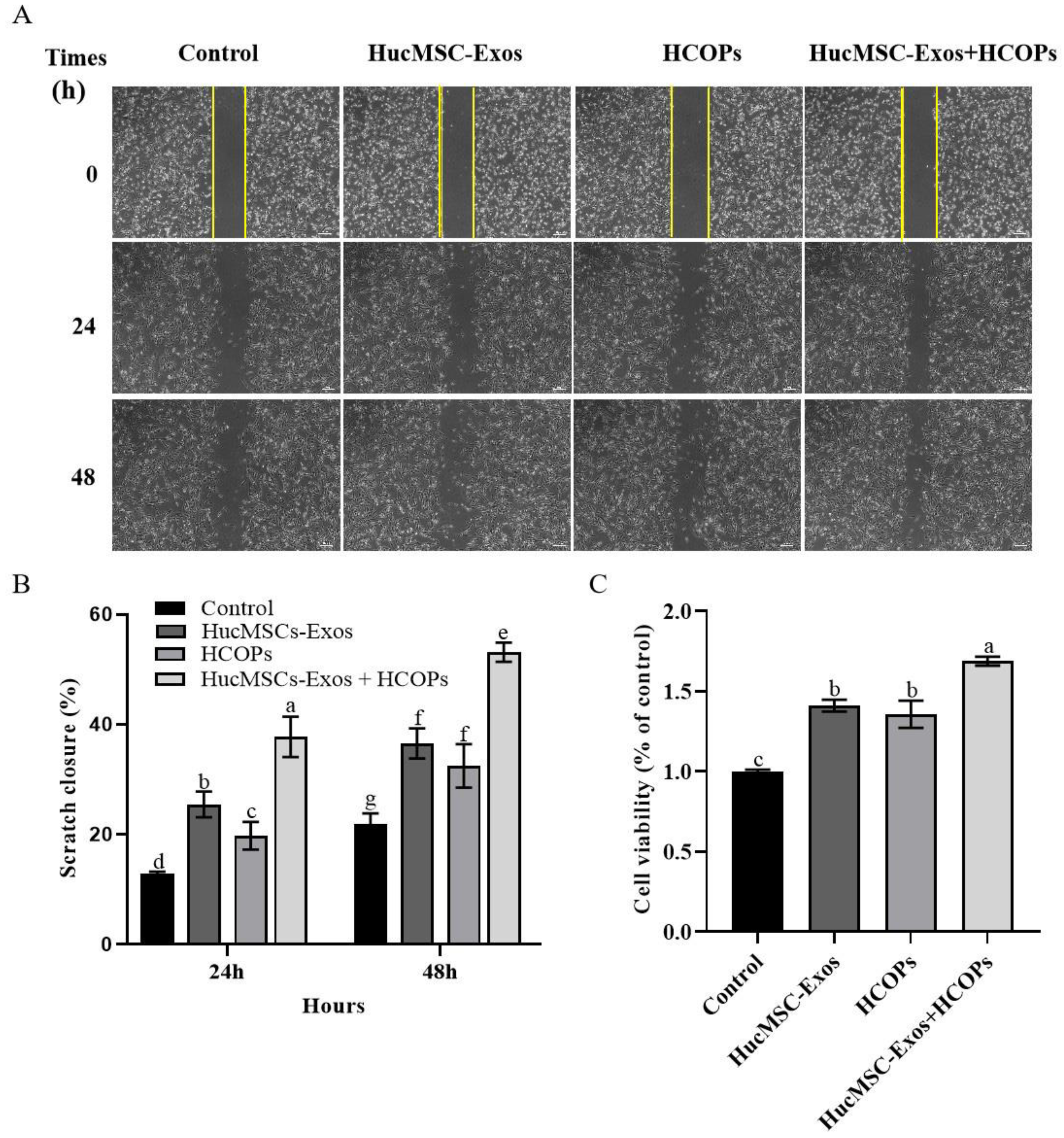
2.4. Combined Effect of HCOPs and HucMSC-Exos at the Selected Concentrations on the Proliferation and Migration of HSFs
2.5. Combined Effect of HCOPs and HucMSC-Exos at the Selected Concentrations on the Expression of ROS and SA-β-Gal Activity in HSFs
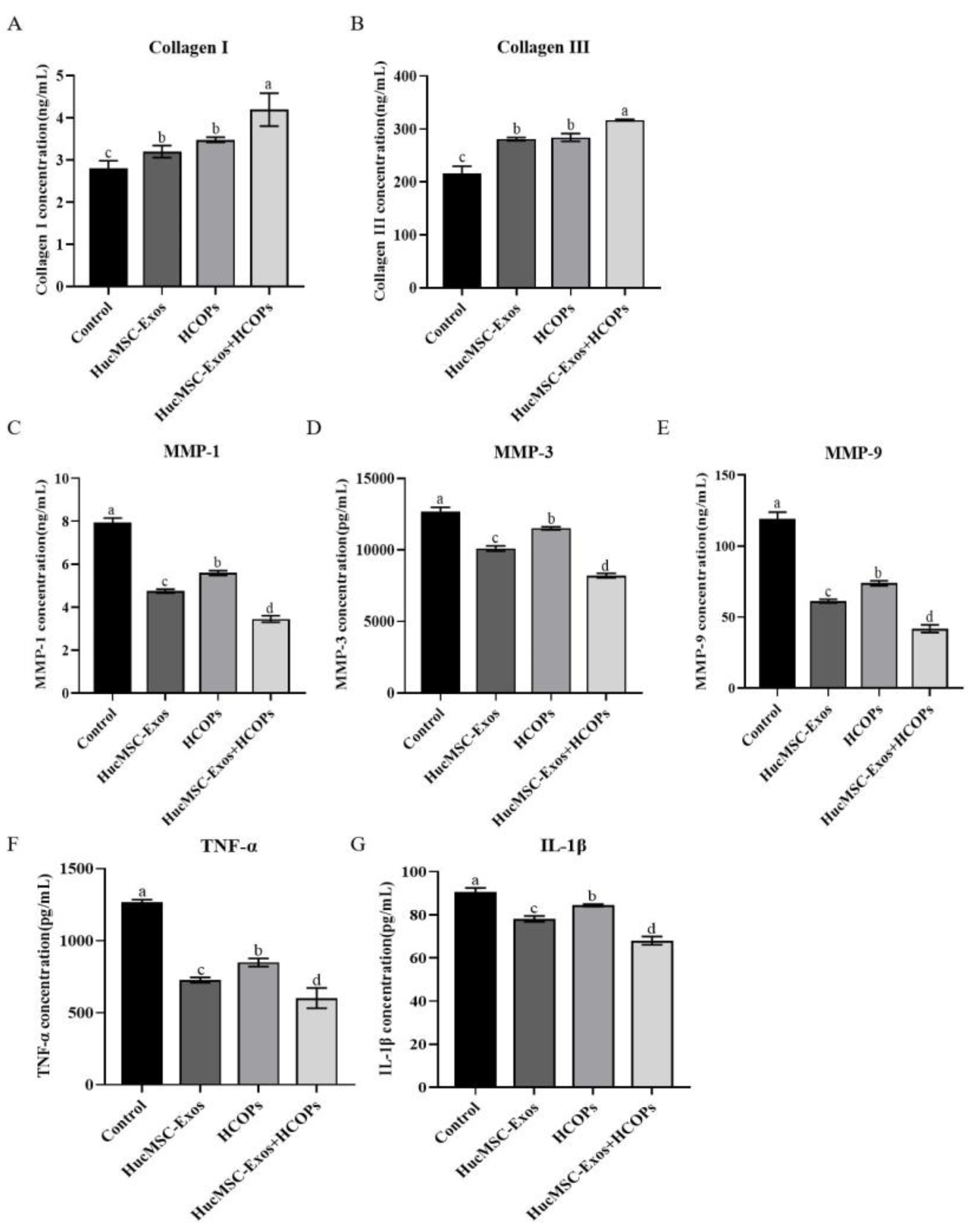
2.6. Combined Effect of HCOPs and HucMSC-Exos at Selected Concentrations on ECM Construction-Related Proteins and Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) in HSFs
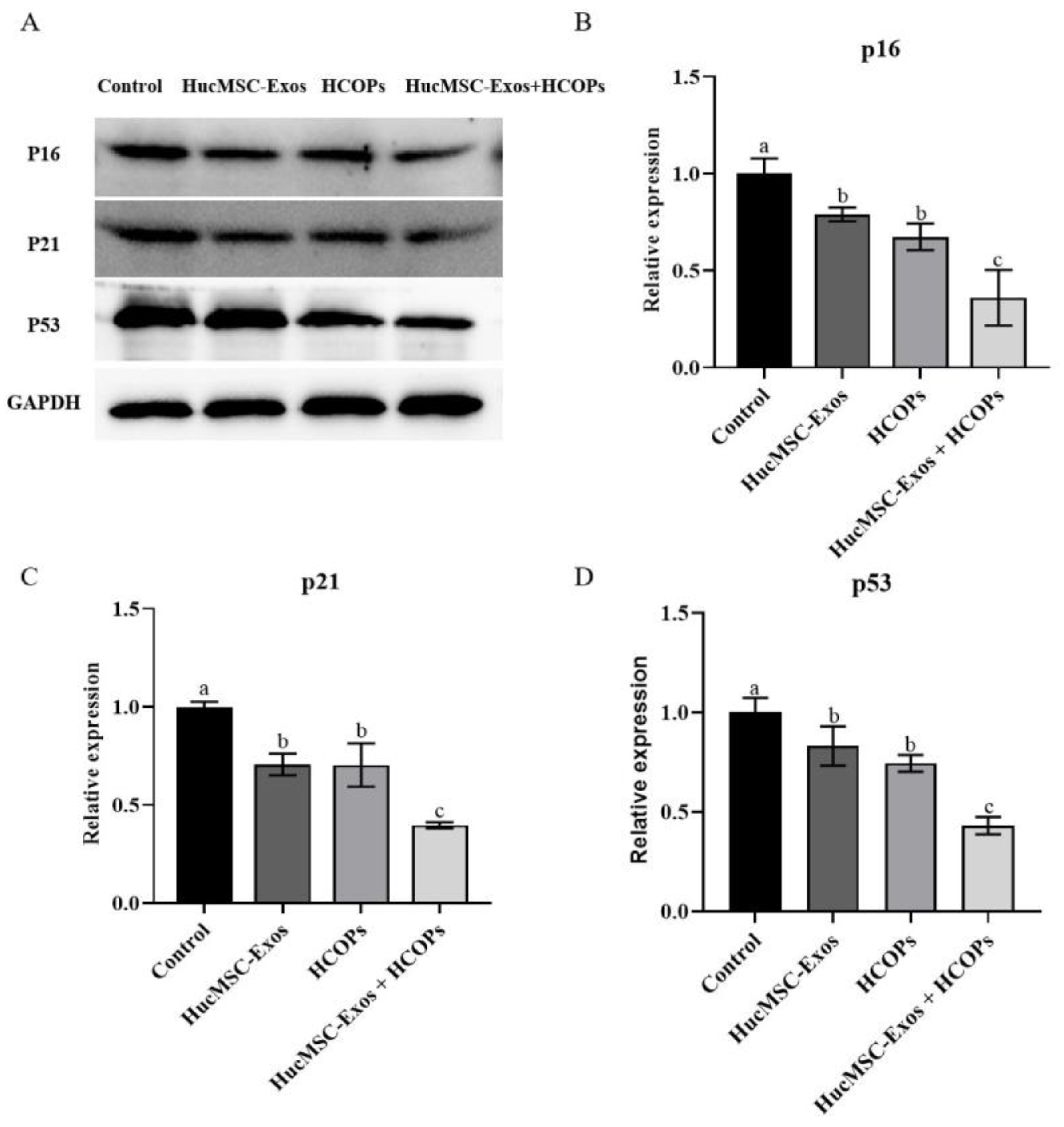
2.7. Combined Effect of HCOPs and HucMSC-Exos at the Selected Concentrations on Senescence-Associated Regulators
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Exosome Isolation
4.3. Characterization of HucMSC-Exos
4.4. In Vitro Exosome Uptake Assay
4.5. Proliferation Assay
4.6. Cell Cycle Assay
4.7. Migration Assay
4.8. SA-β-Gal Staining
4.9. ROS Content
4.10. SAHF Assay
4.11. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.12. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.13. Western Blotting Analysis
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Low, E.; Alimohammadiha, G.; Smith, L.A.; Costello, L.F.; Przyborski, S.A.; von Zglinicki, T.; Miwa, S. How good is the evidence that cellular senescence causes skin ageing? Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 71, 101456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.-W.; Kwon, S.-H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Na, J.-I.; Huh, C.-H.; Choi, H.-R.; Park, K.-C. Molecular mechanisms of dermal aging and antiaging approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Rhee, W.J.; Park, J.H. Exosomes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells ameliorate the aging of skin fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, K.; Kishi, K. Regulation of ENPP5, a senescence-associated secretory phenotype factor, prevents skin aging. Biogerontology 2024. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, Z.; Cores, J.; Huang, K.; Su, T.; Dinh, P.-U.; Cheng, K. Needle-free injection of exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblast spheroids ameliorates skin photoaging. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11273–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxson, S.; Lopez, E.A.; Yoo, D.; Danilkovitch-Miagkova, A.; LeRoux, M.A. Concise review: Role of mesenchymal stem cells in wound repair. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.V.; Schoenberg, E.; Zaya, R.; Rohrer, T.; Zachary, C.B.; Saedi, N. The rise of stem cells in skin rejuvenation: A new frontier. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 38, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, Q.; Liang, Y.; Xu, X.; Halbiyat, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, T.; Peng, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Sodium alginate hydrogel integrated with type III collagen and mesenchymal stem cell to promote endometrium regeneration and fertility restoration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendt, M.; Rezvani, K.; Shpall, E. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-A.; Yu, P.-J.; Yang, D.-Q.; Chen, W. The antisenescence effect of exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells on skin fibroblasts. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1034316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, F.; Ekstrom, K.; Nazarenko, I.; Maugeri, M.; Valadi, H.; Hill, A.F.; Camussi, G.; Nawaz, M. Non-coding RNAs in mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Deciphering regulatory roles in stem cell potency, inflammatory resolve, and tissue regeneration. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Tan, Y.; Zou, S.; Zhang, H.; Mao, F.; Gong, A.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. hucMSC exosome-derived GPX1 is required for the recovery of hepatic oxidant injury. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, H.; Su, P.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; He, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote skin wound healing in diabetic mice by regulating epidermal autophagy. Burn. Trauma 2024, 12, tkae001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.X. Intervention Study of HUMSCs-Derived Exosomes Combined with Collagen Peptides on Osteoarthritis. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Chen, Q.; Wen, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q. A therapeutic microneedle patch made from hair-derived keratin for promoting hair regrowth. Acs Nano 2019, 13, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, P.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xie, H. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes combined with gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel to promote fractional laser injury wound healing. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 4040–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.N.; Vu, D.M.; Vo, N.; Tran, N.H.B.; Ho, D.T.K.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, T.A.; Nguyen, H.N.; Tu, L.N. Skin rejuvenation and photoaging protection using adipose-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles loaded with exogenous cargos. Ski. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, e13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.-Y.; Huang, Y.-L.; Pu, C.-M.; Kang, Y.-N.; Hoang, K.D.; Chen, K.-H.; Chen, C. Effects of Oral Collagen for Skin Anti-Aging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Cruz, G.; León-López, A.; Cruz-Gómez, V.; Jiménez-Alvarado, R.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Collagen hydrolysates for skin protection: Oral administration and topical formulation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotphruethipong, L.; Hutamekalin, P.; Nilsuwan, K.; Sukketsiri, W.; Aluko, R.E.; Abdul, N.R.; Benjakul, S. Combined effects of defatted hydrolyzed collagen from salmon skin and vitamin c on proliferation and migration of human fibroblast cell. Fishes 2022, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debacq-Chainiaux, F.; Erusalimsky, J.D.; Campisi, J.; Toussaint, O. Protocols to detect senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA-βgal) activity, a biomarker of senescent cells in culture and in vivo. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Kajiya, H.; Ozeki, S.; Okabe, K.; Ikebe, T. Corrigendum to “Reactive oxygen species promotes cellular senescence in normal human epidermal keratinocytes through epigenetic regulation of p16(INK4a)” [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 452 (2014) 622–628]. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Wu, S.-N.; Zhang, L.-P.; Zhao, X.-S.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.-Y.; Yuan, R.-Y.; Liu, J.-L.; Mao, H.-J.; Zhu, N.-W. Stem cell-derived exosomes: A new method for reversing skin aging. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 19, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Cho, W.L.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.D.; Park, H.-A.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Jo, D.-G.; Cho, Y.W. Functional recovery in photo-damaged human dermal fibroblasts by human adipose-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1565885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, K.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Jeon, B. Oral administration of a novel hydrolyzed chicken sternal cartilage extract (BioCell Collagen®) reduces UVB-induced photoaging in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, S.; Lu, S.; Xiao, G.; Zhao, M. Effects of collagen hydrolysates on UV-induced photoaging mice: Gly-Pro-Hyp as a potent anti-photoaging peptide. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3008–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Cai, Y.; Wei, Y. mTOR signaling from cellular senescence to organismal aging. Aging Dis. 2014, 5, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Q. Preparation of NAMPT Gene Engineering Exosomes and Its Anti-Aging Effect. Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz, J.-F.; de Isla, N.; Li, Y.; Bensoussan, D.; Zhang, L.; Huselstein, C.; Chen, Y.; Decot, V.; Magdalou, J.; Li, N. Stem cells and regenerative medicine: Myth or reality of the 21th century. Stem Cells Int. 2015, 2015, 734731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troyer, D.L.; Weiss, M.L. Concise review: Wharton’s jelly-derived cells are a primitive stromal cell population. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Qian, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, W. Isolation of cancer stem cells from transformed human mesenchymal stem cell line F6. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 88, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Kwon, H.H.; Park, G.-H.; Yang, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Choi, H.; Lee, J.H.; Sung, S. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes for immunomodulatory therapeutics and skin regeneration. Cells 2020, 9, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Gao, F.; Liu, T.; Ren, W.; Chen, L.; Cao, Y.; Chen, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W. Extracellular vesicles deposit PCNA to rejuvenate aged bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells and slow age-related degeneration. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaaz8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazaki, M.; Ito, Y.; Yamada, M.; Goulas, S.; Teramoto, S.; Nakaya, M.; Ohno, S.; Yamaguchi, K. Oral ingestion of collagen hydrolysate leads to the transportation of highly concentrated Gly-Pro-Hyp and its hydrolyzed form of Pro-Hyp into the bloodstream and skin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2315–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, E.; Rajapakse, N.; Byun, H.-G.; Kim, S.-K. Investigation of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) skin gelatin peptides for their in vitro antioxidant effects. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-López, A.; Fuentes-Jiménez, L.; Hernández-Fuentes, A.D.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Hydrolysed collagen from sheepskins as a source of functional peptides with antioxidant activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Bian, W.; Liu, N.; Yin, S.; Yang, M.; Luo, M.; Tang, J.; Yang, X. A short peptide potentially promotes the healing of skin wound. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotphruethipong, L.; Binlateh, T.; Hutamekalin, P.; Aluko, R.E.; Tepaamorndech, S.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Impact of hydrolyzed collagen from defatted sea bass skin on proliferation and differentiation of preosteoblast MC3T3-E1 cells. Foods 2021, 10, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Cai, X.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Jin, J.; Qin, T.; Li, Y. Bovine collagen oligopeptides accelerate wound healing by promoting fibroblast migration via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 90, 104981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotphruethipong, L.; Binlateh, T.; Hutamekalin, P.; Sukketsiri, W.; Aluko, R.E.; Benjakul, S. In vitro antioxidant and wound-healing activities of hydrolyzed collagen from defatted Asian sea bass skin as influenced by different enzyme types and hydrolysis processes. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18144–18151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Luo, Z.; Tang, J.; Lin, L.; Du, Z.; Dong, C. The effects and mechanism of collagen peptide and elastin peptide on skin aging induced by D-galactose combined with ultraviolet radiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 210, 111964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.M. Exosomes secreted from induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerate skin cell proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabbir, A.; Cox, A.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; Salgado, M.; Badiavas, E.V. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes induce proliferation and migration of normal and chronic wound fibroblasts, and enhance angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2015, 24, 1635–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, E.K.; Zhang, Q.; Yoon, B.S.; Moon, J.-H.; Lee, G.; Park, G.; Kang, P.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, A.; You, S. Hypoxic conditioned medium from human amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerates skin wound healing through TGF-β/SMAD2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woonnoi, W.; Chotphruethipong, L.; Tanasawet, S.; Benjakul, S.; Sutthiwong, N.; Sukketsiri, W. Hydrolyzed collagen from salmon skin increases the migration and filopodia formation of skin keratinocytes by activation of FAK/Src pathway. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2021, 71, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xue, R.; Mao, Z.; Lu, W.; Jiang, Y. Lycorine hydrochloride suppresses stress-induced premature cellular senescence by stabilizing the genome of human cells. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPak, K.M.; Burd, C.E. The molecular balancing act of p16INK4a in cancer and aging. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wu, W.; Huang, H.; Huang, R.; Xie, L.; Su, A.; Liu, S.; Zheng, R.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, H.l. The p53/miRNAs/Ccna2 pathway serves as a novel regulator of cellular senescence: Complement of the canonical p53/p21 pathway. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, H.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno Mengual, E. Exosomes in the Real World of Medical Aesthetics: A Review. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

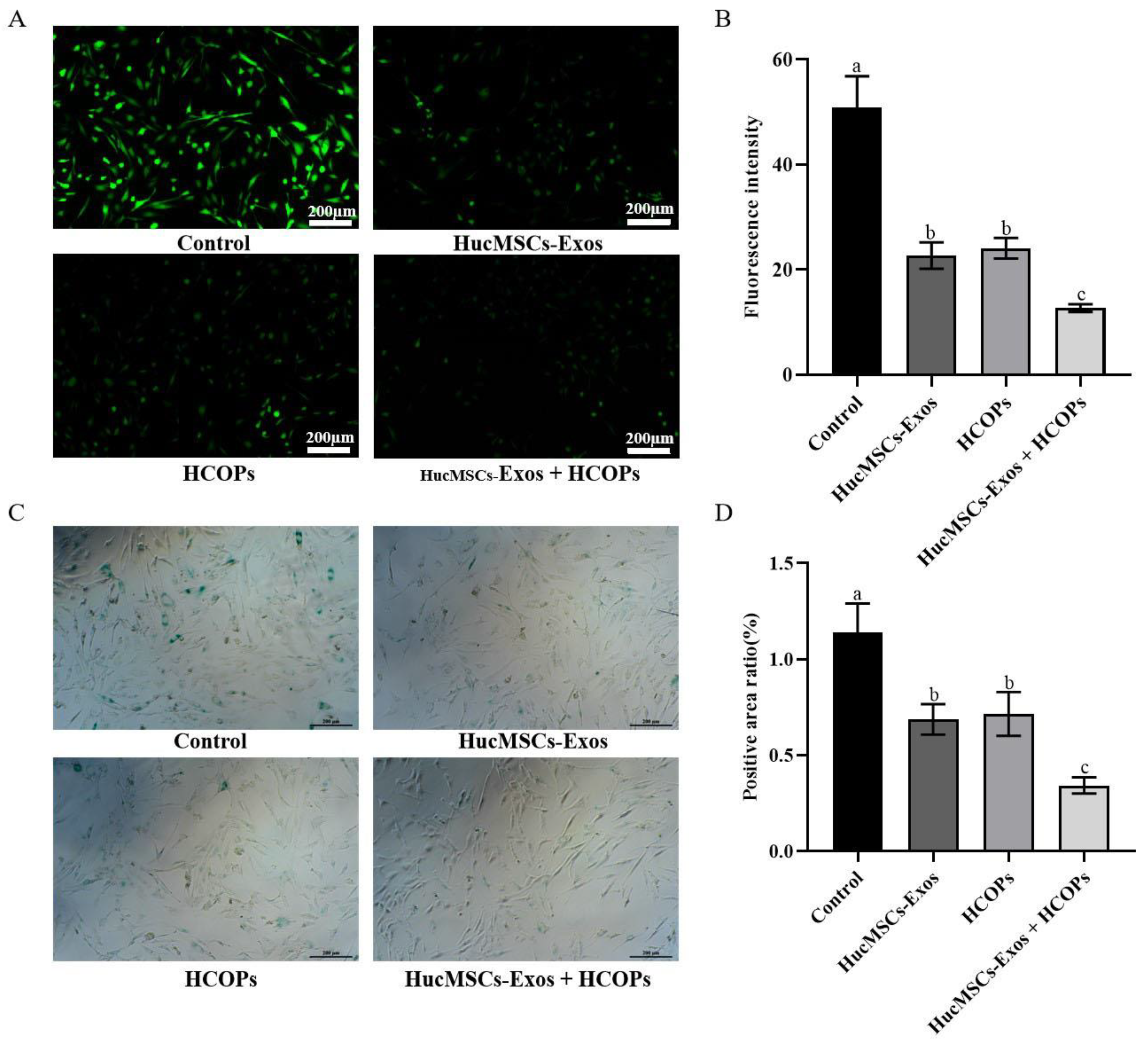

| Groups | ROS | SA-β-Gal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorescence Intensity | Percentage of Control % | Positive Rate of SA-β-Gal | Percentage of Control % | |
| Control | 50.9 ± 6.0 a | 100.0 ± 11.7 a | 1.14 ± 0.15 a | 100.0 ± 13.3 a |
| Exos | 22.7 ± 2.5 b | 44.6 ± 5.0 b | 0.69 ± 0.08 b | 60.3 ± 7.0 b |
| HCOPs | 24.1 ± 2.0 b | 47.3 ± 3.9 b | 0.72 ± 0.11 b | 62.8 ± 10.0 b |
| Exos + HCOPs | 12.7 ± 0.7 c | 24.9 ± 1.4 c | 0.34 ± 0.04 c | 30.1 ± 3.7 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Khan, A.; Pang, Y.; Song, H.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Qiao, H.; Xie, J. The Combined Anti-Aging Effect of Hydrolyzed Collagen Oligopeptides and Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Human Skin Fibroblasts. Molecules 2024, 29, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071468
Zhu H, Guo X, Zhang Y, Khan A, Pang Y, Song H, Zhao H, Liu Z, Qiao H, Xie J. The Combined Anti-Aging Effect of Hydrolyzed Collagen Oligopeptides and Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Human Skin Fibroblasts. Molecules. 2024; 29(7):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071468
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Huimin, Xin Guo, Yongqing Zhang, Ajab Khan, Yinuo Pang, Huifang Song, Hong Zhao, Zhizhen Liu, Hua Qiao, and Jun Xie. 2024. "The Combined Anti-Aging Effect of Hydrolyzed Collagen Oligopeptides and Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Human Skin Fibroblasts" Molecules 29, no. 7: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071468
APA StyleZhu, H., Guo, X., Zhang, Y., Khan, A., Pang, Y., Song, H., Zhao, H., Liu, Z., Qiao, H., & Xie, J. (2024). The Combined Anti-Aging Effect of Hydrolyzed Collagen Oligopeptides and Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Human Skin Fibroblasts. Molecules, 29(7), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071468






