New Progress on London Dispersive Energy, Polar Surface Interactions, and Lewis’s Acid–Base Properties of Solid Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. New Approach for the Calculation of the Deformation Polarizability and the Indicator Parameter
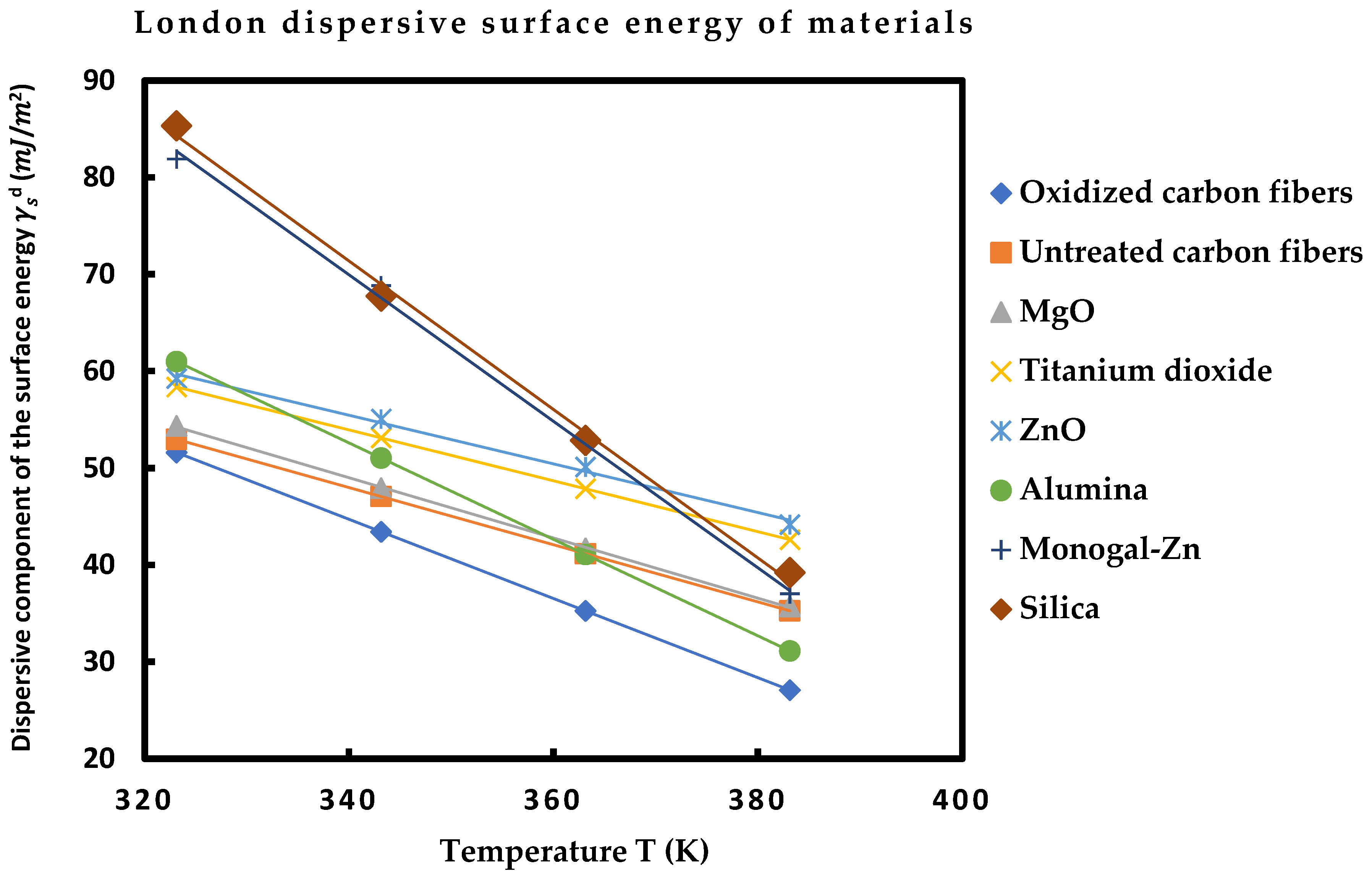
2.2. London Dispersive Surface Energy of Solid Particles by Using the Thermal Model
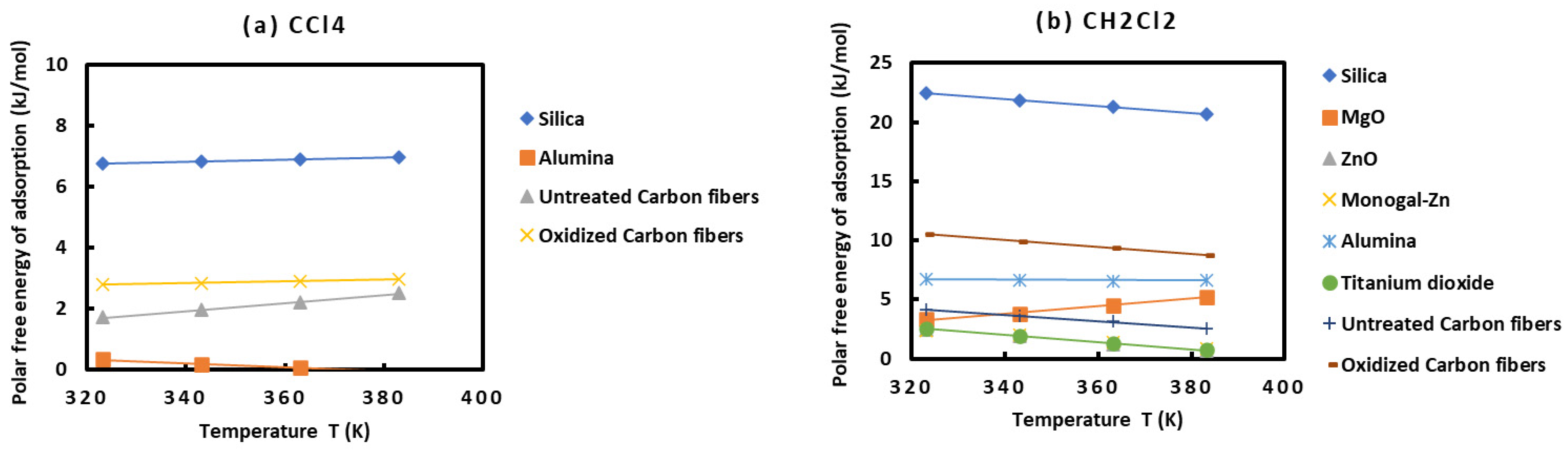
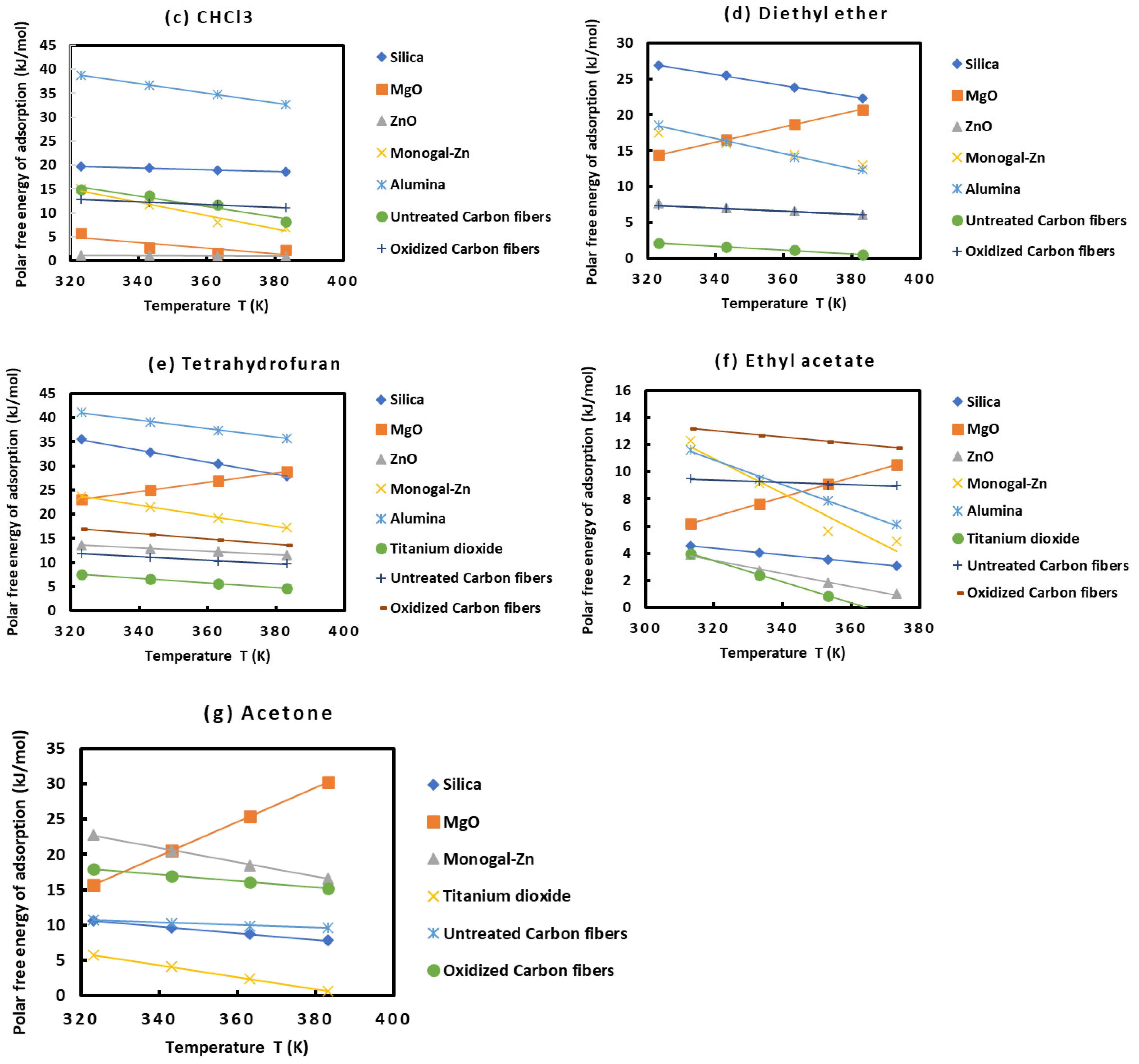
2.3. Polar Surface Interactions between Solid Materials and Organic Molecules
- ○
- With CCl4: alumina < untreated carbon fibers < oxidized carbon fibers < silica;
- ○
- With CH2Cl2: Monogal-Zn < ZnO < TiO2 < MgO < untreated carbon fibers < alumina < oxidized carbon fibers < silica;
- ○
- With CHCl3: ZnO < MgO < oxidized carbon fibers < untreated carbon fibers < Monogal-Zn < silica < alumina;
- ○
- With diethyl ether: untreated carbon fibers < oxidized carbon fibers < ZnO < MgO < Monogal-Zn < alumina < silica;
- ○
- With tetrahydrofuran: TiO2 < untreated carbon fibers < ZnO < oxidized carbon fibers < MgO < Monogal-Zn < silica < alumina;
- ○
- With ethyl acetate: TiO2 < ZnO < silica < MgO < untreated carbon fibers < alumina < monogal-Zn < oxidized carbon fibers;
- ○
- With acetone: TiO2 < silica < untreated carbon fibers < MgO < oxidized carbon fibers.
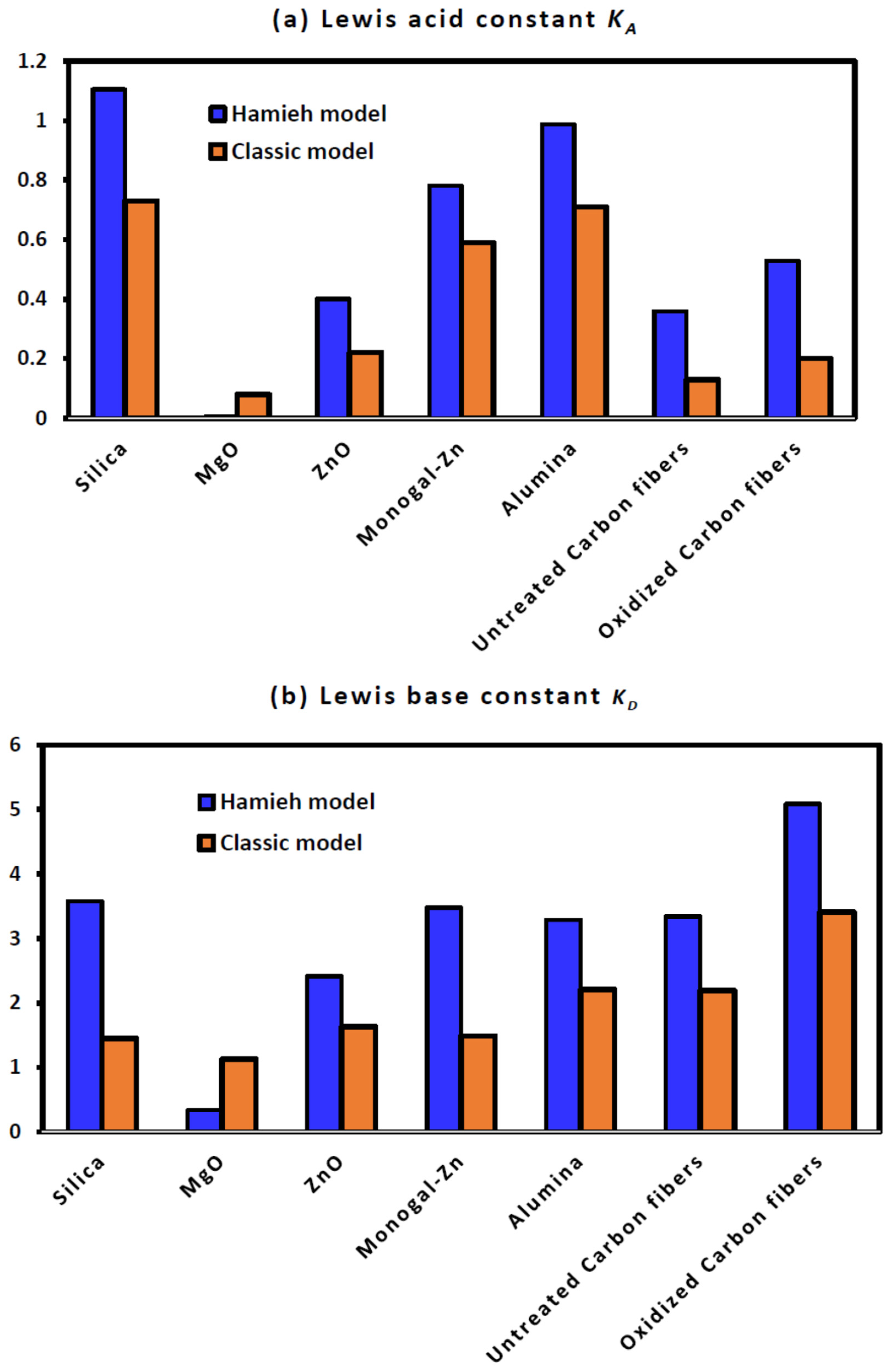
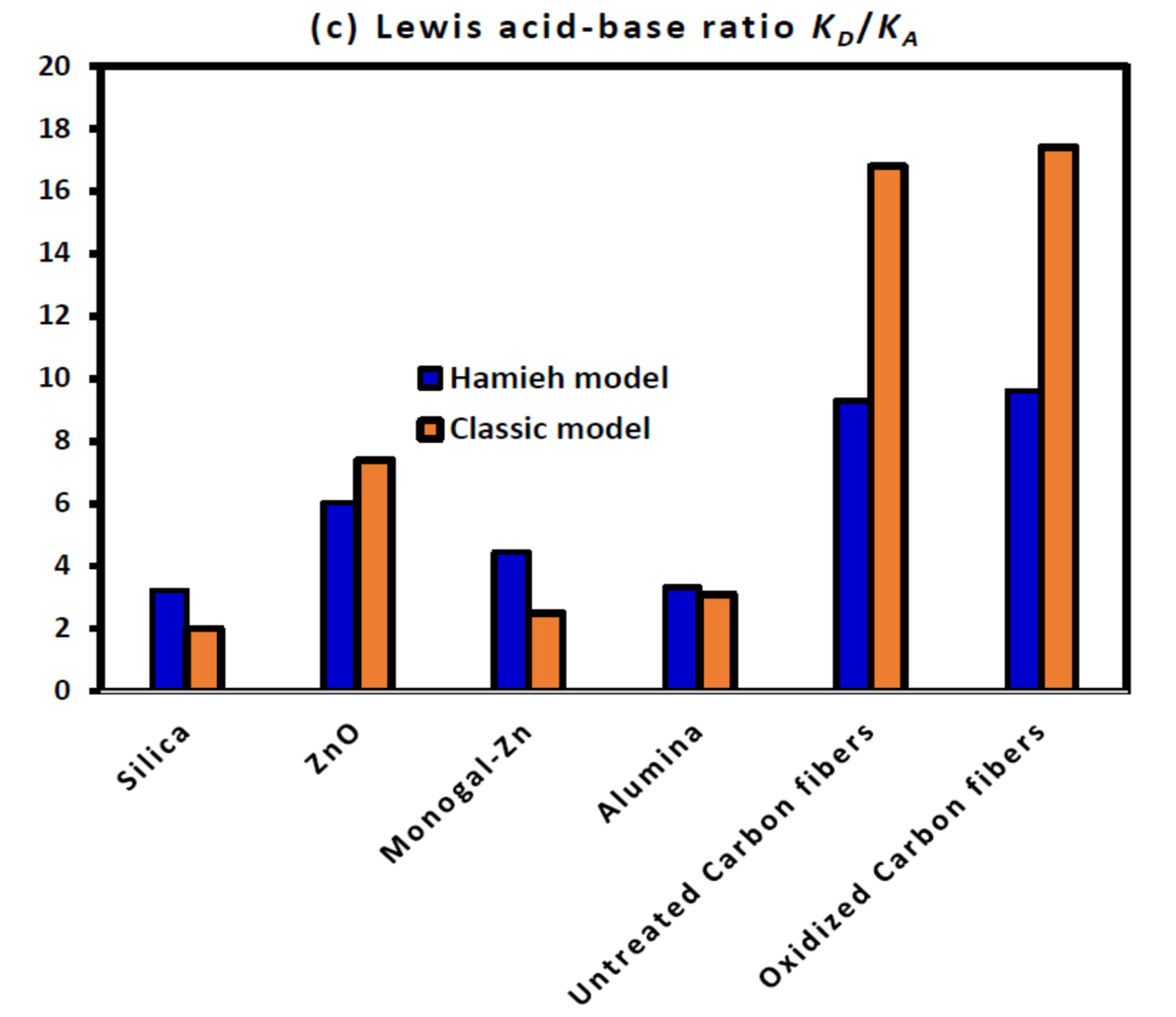
2.4. Lewis’s Enthalpic and Entropic Acid–Base Parameters
2.5. Consequences of the Application of the New Method
3. Methods and Models
3.1. London Dispersion Interaction Energy [33]
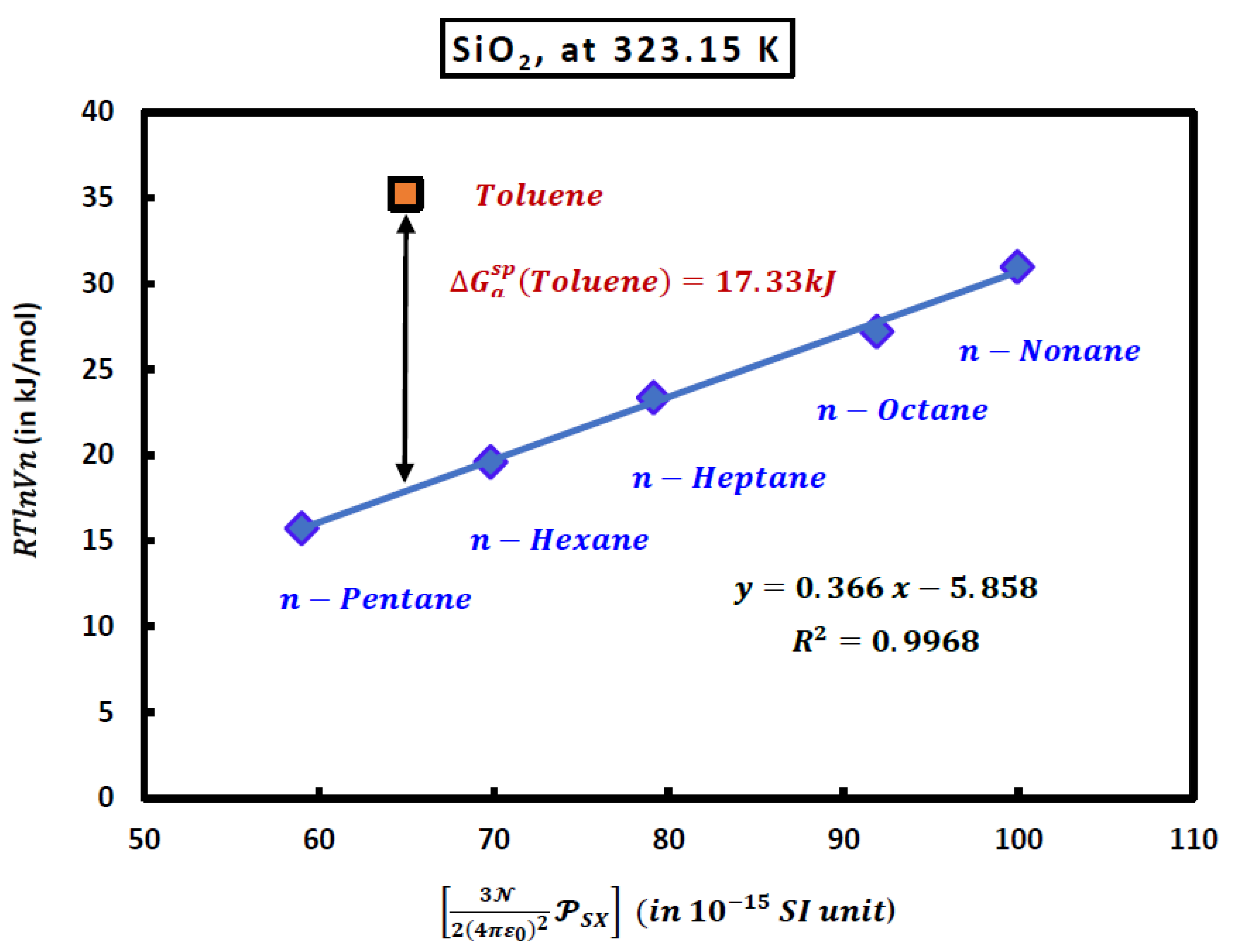
3.2. London Free Dispersion Energy in IGC at Infinite Dilution
4. Materials and Solvents
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saint-Flour, C.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography. A method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short carbon fibers. 1. Through adsorption isotherms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Flour, C.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography: Method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short fibers. 2. Through retention volumes measured near zero surface coverage. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Flour, C.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography: A quick method of estimating surface free energy variations induced by the treatment of short glass fibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 91, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.; Lavielle, L.; Martin, C. The role of the interface in carbon fibre-epoxy composites. J. Adhes. 1987, 23, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, J.-B.; Park, S.; Balard, H. Evaluation of specific interactions of solid surfaces by inverse gas chromatography. Chromatographia 1991, 31, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendlé, E.E.; Papirer, E. A new topological index for molecular probes used in inverse gas chromatography for the surface nanorugosity evaluation, 2. Application for the Evaluation of the Solid Surface Specific Interaction Potential. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 194, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendlé, E.E.; Papirer, E. A new topological index for molecular probes used in inverse gas chromatography for the surface nanorugosity evaluation, 1. Method of Evaluation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 194, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, D.T.; Brookman, D.J. Thermodynamically based gas chromatographic retention index for organic molecules using salt-modified aluminas and porous silica beads. Anal. Chem. 1968, 40, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehimi, M.M.; Pigois-Landureau, E. Determination of acid–base properties of solid materials by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. A novel empirical method based on the dispersive contribution to the heat of vaporization of probes. J. Mater. Chem. 1994, 4, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, J.-B.; Ridaoui, H.; Balard, H.; Barthel, H.; Gottschalk-Gaudig, T. Evolution of the surface polar character of pyrogenic silicas, with their grafting ratios by dimethylchlorosilane, studied by microcalorimetry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 325, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagiełło, J.; Ligner, G.; Papirer, E. Characterization of silicas by inverse gas chromatography at finite concentration: Determination of the adsorption energy distribution function. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1990, 137, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rückriem, M.; Inayat, A.; Enke, D.; Gläser, R.; Einicke, W.-D.; Rockmann, R. Inverse gas chromatography for determining the dispersive surface energy of porous silica. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 357, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Meyer, R.; Czihal, S.; Bertmer, M.; Decker, U.; Naumov, S.; Uhlig, H.; Steinhart, M.; Enke, D. Functionalization of porous siliceous materials, Part 2: Surface characterization by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1603, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Wu, D.; Heng, J.Y.Y.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Hadjittofis, E.; Su, W.; Tang, J.; Zhao, H.; Wu, W. Comparative study of surface properties determination of colored pearl-oyster-shell-derived filler using inverse gas chromatography method and contact angle measurements. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 78, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidqi, M.; Balard, H.; Papirer, E.; Tuel, A.; Hommel, H.; Legrand, A. Study of modified silicas by inverse gas chromatography. Influence of chain length on the conformation of n-alcohols grafted on a pyrogenic silica. Chromatographia 1989, 27, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyda, M.M.; Guiochon, G. Surface properties of silica-based adsorbents measured by inverse gas–solid chromatography at finite concentration. Langmuir 1997, 13, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielmann, F.; Baumgarten, E. Characterization of Microporous Aluminas by Inverse Gas Chromatography. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 229, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onjia, A.E.; Milonjić, S.K.; Todorović, M.; Loos-Neskovic, C.; Fedoroff, M.; Jones, D.J. An inverse gas chromatography study of the adsorption of organics on nickel- and copper-hexacyanoferrates at zero surface coverage. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 251, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyszewska, M.; Krzywania, A.; Zaborski, M.; Szynkowska, M.I. Surface properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles studied by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 5284–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, N.; Arvanitopoulou, E.; Roubani-Kalantzopoulou, F.; Kalantzopoulos, A. Time distribution of adsorption energies, local monolayer capacities, and local isotherms on heterogeneous surfaces by inverse gas chromatography. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Heng, J.; Nikolaev, A.; Waters, K. Introducing inverse gas chromatography as a method of determining the surface heterogeneity of minerals for flotation. Powder Technol. 2013, 249, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Bertóti, I.; Pukánszky, B.; Rosa, R.; Lazzeri, A. Structure and surface coverage of water-based stearate coatings on calcium carbonate nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, M.; Reng, Y.; Pu, B.; Li, J. Variation of surface characteristics of silica-coated calcium carbonate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 273, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandosz, T.J.; Putyera, K.; Jagiełło, J.; Schwarz, J.A. Application of inverse gas chromatography to the study of the surface properties of modified layered minerals. Microporous Mater. 1993, 1, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Gong, M. Preparation of Toluene-Imprinted Homogeneous Microspheres and Determination of Their Molecular Recognition Toward Template Vapor by Inverse Gas Chromatography. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauenhofer, E.; Cho, J.; Yu, J.; Al-Saigh, Z.Y.; Kim, J. Adsorption of hydrocarbons commonly found in gasoline residues on household materials studied by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1594, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paloglou, A.; Martakidis, K.; Gavril, D. An inverse gas chromatographic methodology for studying gas-liquid mass transfer. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1480, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamieh, T. Study of the temperature effect on the surface area of model organic molecules, the dispersive surface energy and the surface properties of solids by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1627, 461372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Ahmad, A.A.; Roques-Carmes, T.; Toufaily, J. New approach to determine the surface and interface thermodynamic properties of H-β-zeolite/rhodium catalysts by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. New Methodology to Study the Dispersive Component of the Surface Energy and Acid–Base Properties of Silica Particles by Inverse Gas Chromatography at Infinite Dilution. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2021, 60, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. New physicochemical methodology for the determination of the surface thermodynamic properties of solid particles. Appliedchem 2023, 3, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Schultz, J. Study of the adsorption of n-alkanes on polyethylene surface—State equations, molecule areas and covered surface fraction. Comptes Rendus L’acad. Sci. Sér. IIb 1996, 323, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- London, F. The general theory of molecular forces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1937, 33, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. (Ed.) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 87th ed.; Internet Version 2007; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss, C.J.; Good, R.J.; Chaudhury, M.K. Additive and nonadditive surface tension components and the interpretation of contact angles. Langmuir 1988, 4, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Locke, D.C.; Purnell, J.H. Concurrent solution and adsorption phenomena in chromatography. I. J. Phys. Chem. 1969, 73, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Purnell, J.H. Gas chromatography at finite concentrations. Part 2.—A generalized retention theory. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1968, 64, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Purnell, J.H. Gas chromatography at finite concentrations. Part 3.—Theory of frontal and elution techniques of thermodynamic measurement. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1969, 65, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Purnell, J.H. Gas chromatography at finite concentrations. Part 4.—Experimental evaluation of methods for thermodynamic study of solutions. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1969, 65, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Purnell, J.H. Gas chromatography at finite concentrations. Part 1.—Effect of gas imperfection on calculation of the activity coefficient in solution from experimental data. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1968, 64, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.; Papirer, E.; Jiao, W.M.; Donnet, J.B. Modification of silica surfaces by grafting of alkyl chains. I—Characterization of silica surfaces by inverse gas–solid chromatography at zero surface coverage. Chromatographia 1987, 23, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papirer, E.; Balard, H.; Vidal, A. Inverse gas chromatography: A valuable method for the surface characterization of fillers for polymers (glass fibres and silicas). Eur. Polym. J. 1988, 24, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelkel, A. Inverse gas chromatography: Characterization of polymers, fibers, modified silicas, and surfactants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1991, 22, 411–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillet, J.E.; Romansky, M.; Price, G.J.; Van der Mark, R. Studies of polymer structure and interactions by automated inverse gas chromatography. In ACS Symposium N° 391; Lloyd, D.R., Schreiber, T.C., Pizana, C.C., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 20–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann, V. The Donor-Acceptor Approach to Molecular Interactions; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Riddle, F.L.; Fowkes, F.M. Spectral shifts in acid-base chemistry. Van der Waals contributions to acceptor numbers, Spectral shifts in acid-base chemistry. 1. van der Waals contributions to acceptor numbers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 3259–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Rageul-Lescouet, M.; Nardin, M.; Haidara, H.; Schultz, J. Study of acid-base interactions between some metallic oxides and model organic molecules. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1997, 125, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Molecule | (eV) | (in 10−30 m3) | (in 10−40 C m2/V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-pentane | 10.28 | 9.99 | 11.12 |
| n-hexane | 10.13 | 11.90 | 13.24 |
| n-heptane | 9.93 | 13.61 | 15.14 |
| n-octane | 9.80 | 15.90 | 17.69 |
| n-nonane | 9.71 | 17.36 | 19.32 |
| n-decane | 9.65 | 19.10 | 21.25 |
| CCl4 | 11.47 | 10.85 | 12.07 |
| Nitromethane | 11.08 | 7.37 | 8.20 |
| CH2Cl2 | 11.32 | 7.21 | 8.02 |
| CHCl3 | 11.37 | 8.87 | 9.86 |
| Diethyl ether | 9.51 | 9.47 | 10.54 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 9.38 | 8.22 | 9.15 |
| Ethyl acetate | 10.01 | 9.16 | 10.19 |
| Acetone | 9.70 | 6.37 | 7.09 |
| Acetonitrile | 12.20 | 4.44 | 4.94 |
| Toluene | 8.83 | 11.80 | 13.13 |
| Benzene | 9.24 | 10.35 | 11.52 |
| Methanol | 10.85 | 3.28 | 3.65 |
| SiO2 | 8.15 | 5.42 | 6.04 |
| MgO | 7.65 | 5.47 | 6.09 |
| ZnO | 4.35 | 5.27 | 5.86 |
| Zn | 9.39 | 5.82 | 6.47 |
| Al2O3 | 5.99 | 5.36 | 5.96 |
| TiO2 | 9.50 | 7.12 | 7.92 |
| Carbon | 11.26 | 1.76 | 1.96 |
| Molecule | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−15 SI) |
|---|---|---|
| n-pentane | 7.274 | 58.992 |
| n-hexane | 7.226 | 69.814 |
| n-heptane | 7.162 | 79.135 |
| n-octane | 7.119 | 91.901 |
| n-nonane | 7.089 | 99.919 |
| n-decane | 7.069 | 109.623 |
| CCl4 | 7.623 | 67.151 |
| Nitromethane | 7.513 | 44.956 |
| CH2Cl2 | 7.582 | 44.379 |
| CHCl3 | 7.596 | 54.666 |
| Diethyl ether | 7.022 | 53.988 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 6.977 | 46.564 |
| Ethyl acetate | 7.188 | 53.453 |
| Acetone | 7.087 | 36.652 |
| Acetonitrile | 7.818 | 28.180 |
| Toluene | 6.780 | 64.955 |
| Benzene | 6.930 | 58.231 |
| Methanol | 7.447 | 19.829 |
| Molecule | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−15 SI) |
|---|---|---|
| n-pentane | 7.018 | 56.917 |
| n-hexane | 6.974 | 67.374 |
| n-heptane | 6.914 | 76.393 |
| n-octane | 6.874 | 88.735 |
| n-nonane | 6.846 | 96.490 |
| n-decane | 6.828 | 105.872 |
| CCl4 | 7.343 | 64.680 |
| Nitromethane | 7.241 | 43.325 |
| CH2Cl2 | 7.304 | 42.754 |
| CHCl3 | 7.317 | 52.662 |
| Diethyl ether | 6.783 | 52.153 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 6.742 | 44.991 |
| Ethyl acetate | 6.938 | 51.595 |
| Acetone | 6.844 | 35.395 |
| Acetonitrile | 7.523 | 27.117 |
| Toluene | 6.557 | 62.820 |
| Benzene | 6.697 | 56.277 |
| Methanol | 7.179 | 19.116 |
| Molecule | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−15 SI) |
|---|---|---|
| n-pentane | 4.891 | 39.665 |
| n-hexane | 4.869 | 47.041 |
| n-heptane | 4.840 | 53.478 |
| n-octane | 4.820 | 62.224 |
| n-nonane | 4.807 | 67.745 |
| n-decane | 4.797 | 74.392 |
| CCl4 | 5.046 | 44.451 |
| Nitromethane | 4.998 | 29.904 |
| CH2Cl2 | 5.028 | 29.431 |
| CHCl3 | 5.034 | 36.231 |
| Diethyl ether | 4.776 | 36.716 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 4.755 | 31.732 |
| Ethyl acetate | 4.852 | 36.080 |
| Acetone | 4.806 | 24.852 |
| Acetonitrile | 5.131 | 18.494 |
| Toluene | 4.662 | 44.666 |
| Benzene | 4.733 | 39.769 |
| Methanol | 4.968 | 13.230 |
| Molecule | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−15 SI) |
|---|---|---|
| n-pentane | 7.852 | 63.683 |
| n-hexane | 7.797 | 75.326 |
| n-heptane | 7.722 | 85.324 |
| n-octane | 7.672 | 99.042 |
| n-nonane | 7.638 | 107.648 |
| n-decane | 7.615 | 118.076 |
| CCl4 | 8.261 | 72.769 |
| Nitromethane | 8.132 | 48.658 |
| CH2Cl2 | 8.212 | 48.070 |
| CHCl3 | 8.228 | 59.222 |
| Diethyl ether | 7.560 | 58.122 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 7.508 | 50.105 |
| Ethyl acetate | 7.752 | 57.650 |
| Acetone | 7.635 | 39.486 |
| Acetonitrile | 8.490 | 30.603 |
| Toluene | 7.280 | 69.743 |
| Benzene | 7.453 | 62.627 |
| Methanol | 8.054 | 21.447 |
| Molecule | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−15 SI) |
|---|---|---|
| n-pentane | 6.056 | 49.114 |
| n-hexane | 6.023 | 58.186 |
| n-heptane | 5.978 | 66.053 |
| n-octane | 5.948 | 76.784 |
| n-nonane | 5.927 | 83.541 |
| n-decane | 5.913 | 91.697 |
| CCl4 | 6.296 | 55.460 |
| Nitromethane | 6.221 | 37.222 |
| CH2Cl2 | 6.268 | 36.687 |
| CHCl3 | 6.277 | 45.177 |
| Diethyl ether | 5.880 | 45.209 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 5.849 | 39.033 |
| Ethyl acetate | 5.996 | 44.590 |
| Acetone | 5.926 | 30.646 |
| Acetonitrile | 6.428 | 23.171 |
| Toluene | 5.710 | 54.699 |
| Benzene | 5.816 | 48.867 |
| Methanol | 6.175 | 16.443 |
| Molecule | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−15 SI) |
|---|---|---|
| n-pentane | 7.900 | 64.071 |
| n-hexane | 7.844 | 75.781 |
| n-heptane | 7.768 | 85.834 |
| n-octane | 7.718 | 99.631 |
| n-nonane | 7.683 | 108.285 |
| n-decane | 7.660 | 118.773 |
| CCl4 | 8.314 | 73.236 |
| Nitromethane | 8.183 | 48.965 |
| CH2Cl2 | 8.264 | 48.376 |
| CHCl3 | 8.281 | 59.600 |
| Diethyl ether | 7.604 | 58.462 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 7.552 | 50.396 |
| Ethyl acetate | 7.799 | 57.996 |
| Acetone | 7.680 | 39.719 |
| Acetonitrile | 8.546 | 30.804 |
| Toluene | 7.321 | 70.137 |
| Benzene | 7.496 | 62.988 |
| Methanol | 8.104 | 21.581 |
| Molecule | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−15 SI) |
|---|---|---|
| n-pentane | 8.598 | 69.736 |
| n-hexane | 8.532 | 82.430 |
| n-heptane | 8.443 | 93.286 |
| n-octane | 8.384 | 108.220 |
| n-nonane | 8.342 | 117.574 |
| n-decane | 8.314 | 128.928 |
| CCl4 | 9.091 | 80.082 |
| Nitromethane | 8.935 | 53.465 |
| CH2Cl2 | 9.032 | 52.869 |
| CHCl3 | 9.052 | 65.147 |
| Diethyl ether | 8.249 | 63.421 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 8.188 | 54.640 |
| Ethyl acetate | 8.479 | 63.053 |
| Acetone | 8.339 | 43.125 |
| Acetonitrile | 9.369 | 33.772 |
| Toluene | 7.917 | 75.847 |
| Benzene | 8.122 | 68.249 |
| Methanol | 8.841 | 23.543 |
| Molecule | (in 10−40 C m2/V) (Donnet Values) | (in 10−40 C m2/V) (Our Values) | Relative Error (in %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-nonane | 19.75 | 19.32 | 2.2 |
| n-decane | - | 21.25 | - |
| CCl4 | 11.68 | 12.07 | 3.2 |
| CH2Cl2 | - | 8.02 | - |
| CHCl3 | 10.57 | 9.86 | 7.2 |
| Diethyl ether | 9.71 | 10.54 | 8.0 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 8.77 | 9.15 | 4.2 |
| Ethyl acetate | 10.79 | 10.19 | 5.9 |
| Acetone | 7.12 | 7.09 | 0.4 |
| Acetonitrile | 5.43 | 4.94 | 10.0 |
| Toluene | 13.68 | 13.13 | 4.2 |
| Benzene | 11.95 | 11.52 | 3.7 |
| Methanol | - | 3.65 | - |
| SiO2 | - | 6.04 | - |
| MgO | - | 6.09 | - |
| ZnO | - | 5.86 | - |
| Zn | - | 6.47 | - |
| Al2O3 | - | 5.96 | - |
| TiO2 | - | 7.92 | - |
| Carbon | - | 1.96 | - |
| Temperature T (K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 | Equation of |
| Oxidized carbon fibers | 51.59 | 43.42 | 35.25 | 27.08 | = −0.408 T + 183.6 |
| Untreated carbon fibers | 52.96 | 47.06 | 41.16 | 35.27 | = −0.295 T + 148.2 |
| MgO | 54.35 | 47.92 | 41.71 | 35.71 | = −0.311 T + 154.6 |
| MgO | 58.37 | 53.12 | 47.87 | 42.62 | = −0.262 T + 143.2 |
| ZnO | 59.25 | 55.07 | 50.12 | 44.16 | = −0.251 T + 140.8 |
| Al2O3 | 60.98 | 51.03 | 41.08 | 31.13 | = −0.497 T + 221.7 |
| Monogal-Zn | 81.90 | 68.84 | 52.26 | 37.03 | = −0.756 T + 327.0 |
| SiO2 | 85.34 | 67.75 | 52.86 | 39.23 | = −0.766 T + 331.8 |
| Silica | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| CCl4 | 6.752 | 6.810 | 6.881 | 6.968 |
| Nitromethane | 13.573 | 12.367 | 11.273 | 10.191 |
| CH2Cl2 | 22.490 | 21.846 | 21.269 | 20.716 |
| CHCl3 | 19.752 | 19.304 | 18.925 | 18.546 |
| Diethyl ether | 26.838 | 25.462 | 23.802 | 22.314 |
| THF | 35.506 | 32.787 | 30.435 | 27.908 |
| Ethyl Acetate | 4.566 | 4.015 | 3.530 | 3.079 |
| Acetone | 10.612 | 9.608 | 8.703 | 7.816 |
| Acetonitrile | 16.734 | 15.304 | 14.016 | 12.738 |
| Toluene | 17.330 | 16.724 | 16.168 | 15.598 |
| Benzene | 5.640 | 5.170 | 4.745 | 4.328 |
| MgO | ||||
| T(K) | 323.1500 | 343.1500 | 363.1500 | 383.15 |
| CH2Cl2 | 3.3120 | 3.7860 | 4.5320 | 5.211 |
| CHCl3 | 5.833 | 2.693 | 1.560 | 2.176 |
| Diethyl ether | 14.415 | 16.559 | 18.671 | 20.721 |
| THF | 23.053 | 25.004 | 26.928 | 28.797 |
| Acetone | 15.723 | 20.520 | 25.354 | 30.243 |
| Ethyl acetate | 6.224 | 7.620 | 9.112 | 10.523 |
| ZnO | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| CH2Cl2 | 2.4490 | 1.9151 | 1.2231 | 0.6320 |
| CHCl3 | 1.1506 | 1.0611 | 0.9988 | 0.9325 |
| Diethyl ether | 7.7211 | 7.0452 | 6.5940 | 6.0373 |
| THF | 13.5961 | 12.9006 | 12.2948 | 11.5175 |
| Ethyl acetate | 3.9554 | 2.7149 | 1.8004 | 1.0420 |
| Benzene | 0.8696 | 0.6900 | 0.5367 | 0.3535 |
| Monogal-Zn | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| CH2Cl2 | 2.354 | 1.965 | 1.426 | 0.854 |
| CHCl3 | 15.001 | 11.698 | 7.938 | 6.927 |
| Diethyl ether | 17.481 | 15.950 | 14.408 | 12.982 |
| THF | 23.786 | 21.503 | 19.298 | 17.285 |
| Acetone | 22.779 | 20.603 | 18.500 | 16.582 |
| Ethyl acetate | 12.287 | 9.154 | 5.642 | 4.895 |
| Alumina | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| CCl4 | 0.334 | 0.163 | 0.084 | - |
| CH2Cl2 | 6.751 | 6.654 | 6.575 | 6.648 |
| CHCl3 | 38.808 | 36.648 | 34.670 | 32.613 |
| Ether | 18.559 | 16.226 | 14.028 | 12.322 |
| THF | 41.085 | 39.144 | 37.268 | 35.790 |
| Ethyl acetate | 11.624 | 9.452 | 7.875 | 6.125 |
| Toluene | 40.532 | 38.377 | 36.371 | 34.878 |
| TiO2 | ||||
| T(K) | 313.15 | 333.15 | 353.15 | 373.15 |
| CH2Cl2 | 2.546 | 1.924 | 1.254 | 0.723 |
| CHCl3 | 3.146 | 2.019 | 0.893 | - |
| THF | 7.620 | 6.620 | 5.620 | 4.620 |
| Ethyl Acetate | 3.979 | 2.417 | 0.857 | - |
| Acetone | 5.776 | 4.068 | 2.362 | 0.651 |
| Benzene | 5.564 | 4.199 | 2.834 | 1.463 |
| Nitromethane | 10.394 | 9.024 | 7.657 | 6.283 |
| Acetonitrile | 4.615 | 2.524 | 0.433 | -1.661 |
| Untreated Carbon fibers | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| CCl4 | 1.723 | 1.956 | 2.203 | 2.518 |
| CH2Cl2 | 4.096 | 3.645 | 3.129 | 2.548 |
| CHCl3 | 14.829 | 13.537 | 11.761 | 8.193 |
| Ether | 2.112 | 1.633 | 1.131 | 0.546 |
| THF | 11.852 | 11.079 | 10.310 | 9.748 |
| C6H6 | 8.577 | 8.315 | 8.055 | 8.011 |
| Ethyl acetate | 9.500 | 9.251 | 9.019 | 8.975 |
| Acetone | 10.723 | 10.282 | 9.865 | 9.647 |
| Oxidized Carbon fibers | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| CCl4 | 2.785 | 2.843 | 2.911 | 2.974 |
| CH2Cl2 | 10.546 | 9.952 | 9.379 | 8.800 |
| CHCl3 | 12.788 | 12.228 | 11.685 | 11.134 |
| Ether | 7.399 | 6.965 | 6.548 | 6.124 |
| THF | 17.020 | 15.878 | 14.753 | 13.623 |
| C6H6 | 10.429 | 9.943 | 9.473 | 8.995 |
| Ethyl acetate | 13.212 | 12.718 | 12.242 | 11.758 |
| Acetone | 17.928 | 16.999 | 16.094 | 15.183 |
| Silica | ||
|---|---|---|
| Polar Solvent | () | () |
| CCl4 | −4.6 | 5.2514 |
| Nitromethane | 52.8 | 30.543 |
| CH2Cl2 | 27.7 | 31.377 |
| CHCl3 | 18.8 | 25.788 |
| Diethyl ether | 77.4 | 51.914 |
| THF | 123.5 | 75.304 |
| Ethyl acetate | 23 | 11.944 |
| Acetone | 43.6 | 24.624 |
| Acetonitrile | 62.2 | 36.719 |
| Toluene | 27.1 | 26.027 |
| Benzene | 20.4 | 12.173 |
| MgO | ||
| CH2Cl2 | 32.2 | 7.1665 |
| CHCl3 | −60.5 | −24.435 |
| Diethyl ether | 105.1 | 19.543 |
| Ethyl acetate | 71.9 | 17.038 |
| THF | 95.8 | 7.8791 |
| Acetone | 242 | 62.489 |
| Acetonitrile | 81.6 | 2.0138 |
| Toluene | −13.8 | 15.211 |
| ZnO | ||
| CH2Cl2 | 20.9 | 8.9949 |
| CHCl3 | −11.4 | 1.0743 |
| Diethyl ether | 18.5 | 18.218 |
| THF | 23.8 | 26.647 |
| Ethyl acetate | 38.2 | 17.176 |
| Benzene | −1.0 | 6.7082 |
| Monogal | ||
| CH2Cl2 | 25.2 | 10.547 |
| CHCl3 | 139.9 | 59.803 |
| Diethyl ether | 75.2 | 41.760 |
| THF | 108.5 | 58.796 |
| Ethyl acetate | 44.2 | 21.674 |
| Acetone | 103.5 | 56.155 |
| Acetonitrile | 110.8 | 54.921 |
| Toluene | 99.9 | 54.474 |
| Alumina | ||
| CCl4 | 6.2 | 2.314 |
| CH2Cl2 | 1.9 | 7.3421 |
| CHCl3 | 102.8 | 71.989 |
| Diethyl ether | 104.6 | 52.207 |
| THF | 88.8 | 69.683 |
| Ethyl acetate | 90.4 | 40.683 |
| Toluene | 94.9 | 71.036 |
| Titanium dioxide | ||
| CH2Cl2 | 30.7 | 12.146 |
| CHCl3 | 56.4 | 20.818 |
| THF | 10.0 | 23.277 |
| Ethyl Acetate | 78.1 | 28.448 |
| Acetone | 85.4 | 32.518 |
| Benzene | 68.3 | 26.965 |
| Nitromethane | 68.5 | 31.846 |
| Acetonitrile | 104.6 | 37.370 |
| Untreated carbon fibers | ||
| CCl4 | −13.2 | −2.4181 |
| CH2Cl2 | 25.8 | 12.209 |
| CHCl3 | 108.4 | 49.284 |
| Benzene | 9.8 | 11.602 |
| Diethyl ether | 26 | 10.275 |
| THF | 35.4 | 22.895 |
| Ethyl acetate | 9 | 12.289 |
| Acetone | 18.2 | 16.380 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers | ||
| CCl4 | 3.2 | 1.7876 |
| CH2Cl2 | 29.1 | 19.639 |
| CHCl3 | 27.5 | 21.406 |
| Benzene | 23.9 | 17.897 |
| Diethyl ether | 21.2 | 14.038 |
| THF | 56.6 | 34.733 |
| Ethyl acetate | 24.2 | 20.782 |
| Acetone | 45.7 | 32.230 |
| Solid Surfaces | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica | 0.73 | 1.45 | 2.0 | 0.6509 | 1.23 | 1.45 | 1.2 | 0.651 |
| MgO | 0.08 | 1.13 | 14.0 | 0.1722 | 1.16 | 0.57 | 0.5 | 0.8126 |
| ZnO | 0.22 | 1.63 | 7.4 | 0.422 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.3 | 0.8761 |
| Monogal-Zn | 0.59 | 1.49 | 2.5 | 0.7296 | 1.07 | 3.08 | 2.9 | 0.7295 |
| Alumina | 0.71 | 2.21 | 3.1 | 0.7301 | 0.92 | 4.21 | 4.6 | 0.7739 |
| Titanium dioxide | 0.25 | 0.87 | 3.5 | 0.9874 | 0.86 | 1.80 | 2.1 | 0.9804 |
| Untreated Carbon fibers | 0.13 | 2.19 | 16.8 | 0.0799 | 0.30 | 1.56 | 5.2 | 0.3195 |
| Oxidized Carbon fibers | 0.20 | 3.41 | 17.4 | 0.0779 | 0.37 | 4.32 | 11.6 | 0.141 |
| Solid Surfaces | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica | 1.105 | 3.572 | 0.186 | 3.23 |
| MgO | 0.005 | 0.336 | −0.045 | 71.66 |
| ZnO | 0.401 | 2.418 | 0.089 | 6.03 |
| Monogal-Zn | 0.782 | 3.477 | 0.113 | 4.45 |
| Alumina | 0.988 | 3.291 | 0.136 | 3.33 |
| Untreated Carbon fibers | 0.359 | 3.339 | 0.110 | 9.29 |
| Oxidized Carbon fibers | 0.529 | 5.085 | 0.161 | 9.61 |
| Results by Using Donnet et al.’s Method | |||||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 | 403.15 | () | () |
| CCl4 | 34.616 | 31.401 | 28.904 | 26.818 | 24.489 | 124.2 | 74.643 |
| Nitromethane | 34.014 | 30.151 | 27.038 | 24.328 | 21.424 | 155 | 83.687 |
| CH2Cl2 | 53.122 | 48.974 | 45.622 | 42.692 | 39.626 | 166.4 | 106.43 |
| CHCl3 | 48.598 | 44.795 | 41.775 | 39.150 | 36.312 | 151.1 | 96.995 |
| Diethyl ether | 53.703 | 49.136 | 44.982 | 41.394 | 37.319 | 202.5 | 118.86 |
| THF | 57.922 | 52.382 | 47.865 | 43.564 | 39.053 | 232.8 | 132.69 |
| Ethyl Acetate | 33.315 | 29.418 | 26.298 | 23.608 | 20.724 | 155 | 82.944 |
| Acetone | 25.935 | 22.701 | 20.154 | 18.016 | 15.527 | 127.5 | 66.771 |
| Acetonitrile | 25.145 | 22.059 | 19.641 | 17.621 | 15.228 | 121.4 | 64.011 |
| Toluene | 55.833 | 51.069 | 47.157 | 43.631 | 40.161 | 193.9 | 117.99 |
| Benzene | 38.564 | 34.399 | 31.032 | 28.069 | 25.006 | 167.2 | 92.143 |
| Results by using our new method | |||||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 | 403.15 | () | () |
| CCl4 | 6.752 | 6.810 | 6.881 | 6.968 | 7.129 | 5.2514 | 6.752 |
| Nitromethane | 13.573 | 12.367 | 11.273 | 10.191 | 9.378 | 30.543 | 13.573 |
| CH2Cl2 | 22.490 | 21.846 | 21.269 | 20.716 | 20.287 | 31.377 | 22.490 |
| CHCl3 | 19.752 | 19.304 | 18.925 | 18.546 | 18.250 | 25.788 | 19.752 |
| Diethyl ether | 26.838 | 25.462 | 23.802 | 22.314 | 20.676 | 51.914 | 26.838 |
| THF | 35.506 | 32.787 | 30.435 | 27.908 | 25.593 | 75.304 | 35.506 |
| Ethyl Acetate | 4.566 | 4.015 | 3.530 | 3.079 | 2.732 | 11.944 | 4.566 |
| Acetone | 10.612 | 9.608 | 8.703 | 7.816 | 7.144 | 24.624 | 10.612 |
| Acetonitrile | 16.734 | 15.304 | 14.016 | 12.738 | 11.793 | 36.719 | 16.734 |
| Toluene | 17.330 | 16.724 | 16.168 | 15.598 | 15.187 | 26.027 | 17.330 |
| Benzene | 5.640 | 5.170 | 4.745 | 4.328 | 4.026 | 12.173 | 5.640 |
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 | 403.15 | () | () |
| CCl4 | 5.1 | 4.6 | 4.2 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 23.7 | 11.1 |
| Nitromethane | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 5.1 | 6.2 |
| CH2Cl2 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 5.3 | 4.7 |
| CHCl3 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 5.9 | 4.9 |
| Diethyl ether | 2.0 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 3.9 | 4.4 |
| THF | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 3.1 | 3.7 |
| Ethyl Acetate | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.5 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 13.0 | 18.2 |
| Acetone | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 5.2 | 6.3 |
| Acetonitrile | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 3.3 | 3.8 |
| Toluene | 3.2 | 3.1 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 7.4 | 6.8 |
| Benzene | 6.8 | 6.7 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.2 | 13.7 | 16.3 |
| Molecule | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−19 J) | (in 10−10 J1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-pentane | 7.27 | 7.02 | 4.89 | 7.85 | 6.06 | 7.90 | 8.60 | 12.83 |
| n-hexane | 7.23 | 6.97 | 4.87 | 7.80 | 6.02 | 7.84 | 8.53 | 12.73 |
| n-heptane | 7.16 | 6.91 | 4.84 | 7.72 | 5.98 | 7.77 | 8.44 | 12.61 |
| n-octane | 7.12 | 6.87 | 4.82 | 7.67 | 5.95 | 7.72 | 8.38 | 12.52 |
| n-nonane | 7.09 | 6.85 | 4.81 | 7.64 | 5.93 | 7.68 | 8.34 | 12.46 |
| n-decane | 7.07 | 6.83 | 4.80 | 7.62 | 5.91 | 7.66 | 8.31 | 12.43 |
| CCl4 | 7.62 | 7.34 | 5.05 | 8.26 | 6.30 | 8.31 | 9.09 | 13.55 |
| Nitromethane | 7.51 | 7.24 | 5.00 | 8.13 | 6.22 | 8.18 | 8.94 | 13.32 |
| CH2Cl2 | 7.58 | 7.30 | 5.03 | 8.21 | 6.27 | 8.26 | 9.03 | 13.46 |
| CHCl3 | 7.60 | 7.32 | 5.03 | 8.23 | 6.28 | 8.28 | 9.05 | 13.49 |
| Diethyl ether | 7.02 | 6.78 | 4.78 | 7.56 | 5.88 | 7.60 | 8.25 | 12.34 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 6.98 | 6.74 | 4.76 | 7.51 | 5.85 | 7.55 | 8.19 | 12.25 |
| Ethyl acetate | 7.19 | 6.94 | 4.85 | 7.75 | 6.00 | 7.80 | 8.48 | 12.66 |
| Acetone | 7.09 | 6.84 | 4.81 | 7.64 | 5.93 | 7.68 | 8.34 | 12.46 |
| Acetonitrile | 7.82 | 7.52 | 5.13 | 8.49 | 6.43 | 8.55 | 8.60 | 13.97 |
| Toluene | 6.78 | 6.56 | 4.66 | 7.28 | 5.71 | 7.32 | 8.53 | 11.89 |
| Benzene | 6.93 | 7.02 | 4.73 | 7.45 | 5.82 | 7.50 | 8.44 | 12.16 |
| Methanol | 7.45 | 6.97 | 4.97 | 8.05 | 6.18 | 8.10 | 8.38 | 13.18 |
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| SiO2 | 5.05 | 5.12 | 5.19 | 5.27 |
| MgO | 5.23 | 5.27 | 5.31 | 5.35 |
| ZnO | 4.87 | 4.88 | 4.89 | 4.90 |
| Monogal | 5.18 | 5.24 | 5.33 | 5.44 |
| Al2O3 | 5.03 | 5.08 | 5.13 | 5.16 |
| TiO2 | 5.51 | 5.53 | 5.54 | 5.56 |
| Untreated carbon fibers | 4.45 | 4.48 | 4.50 | 4.52 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers | 4.49 | 4.54 | 4.59 | 4.64 |
| () of Dichloromethane | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| SiO2 | 22.49 | 21.846 | 21.269 | 20.716 |
| MgO | 3.312 | 3.786 | 4.532 | 5.211 |
| ZnO | 2.449 | 1.9151 | 1.2231 | 0.632 |
| Monogal | 2.354 | 1.965 | 1.426 | 0.854 |
| Al2O3 | 6.751 | 6.654 | 6.575 | 6.648 |
| TiO2 | 2.546 | 1.924 | 1.254 | 0.723 |
| Untreated carbon fibers | 4.096 | 3.645 | 3.129 | 2.548 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers | 10.546 | 9.952 | 9.379 | 8.8 |
| () of ethyl acetate | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| SiO2 | 4.566 | 4.015 | 3.53 | 3.079 |
| MgO | 6.224 | 7.62 | 9.112 | 10.523 |
| ZnO | 3.9554 | 2.7149 | 1.8004 | 1.042 |
| Monogal | 12.287 | 9.154 | 5.642 | 4.895 |
| Al2O3 | 11.624 | 9.452 | 7.875 | 6.125 |
| TiO2 | 3.979 | 2.417 | 0.857 | - |
| Untreated carbon fibers | 9.500 | 9.251 | 9.019 | 8.975 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers | 13.212 | 12.718 | 12.242 | 11.758 |
| Values of (in mJ/m2) | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| SiO2 | 8.11 | 6.15 | 4.66 | 3.47 |
| MgO | 15.07 | 22.14 | 31.03 | 40.57 |
| ZnO | 6.08 | 2.81 | 1.21 | 0.40 |
| Monogal | 58.72 | 31.95 | 11.90 | 8.78 |
| Al2O3 | 52.55 | 34.06 | 23.18 | 13.75 |
| TiO2 | 6.16 | 2.23 | 0.27 | 0.03 |
| Untreated carbon fibers | 33.54 | 31.08 | 28.63 | 26.18 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers | 64.04 | 57.33 | 50.62 | 43.91 |
| Values of (in mJ/m2) | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| SiO2 | 275.18 | 254.53 | 236.49 | 219.94 |
| MgO | 5.97 | 7.64 | 10.74 | 13.92 |
| ZnO | 3.26 | 1.96 | 0.78 | 0.20 |
| Monogal | 3.01 | 2.06 | 1.06 | 0.37 |
| Al2O3 | 24.80 | 23.61 | 22.60 | 22.65 |
| TiO2 | 3.53 | 1.97 | 0.82 | 0.27 |
| Untreated carbon fibers | 8.01 | 5.99 | 3.98 | 1.96 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers | 55.89 | 48.21 | 40.53 | 32.85 |
| Values of (in mJ/m2) | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| SiO2 | 94.46 | 79.11 | 66.37 | 55.27 |
| MgO | 18.96 | 26.02 | 36.51 | 47.52 |
| ZnO | 8.91 | 4.69 | 1.95 | 0.57 |
| Monogal | 26.61 | 16.22 | 7.11 | 3.62 |
| Al2O3 | 65.95 | 56.00 | 46.05 | 36.11 |
| TiO2 | 9.32 | 4.19 | 0.95 | 0.17 |
| Untreated carbon fibers | 32.75 | 27.04 | 21.32 | 15.61 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers | 119.64 | 105.11 | 90.58 | 76.04 |
| Values of (in mJ/m2) | ||||
| T(K) | 323.15 | 343.15 | 363.15 | 383.15 |
| SiO2 | 179.80 | 146.86 | 119.23 | 94.50 |
| MgO | 76.31 | 77.15 | 81.42 | 86.23 |
| ZnO | 71.12 | 61.88 | 54.11 | 47.71 |
| Monogal | 116.87 | 91.36 | 67.14 | 48.53 |
| Al2O3 | 128.31 | 106.07 | 86.64 | 67.71 |
| TiO2 | 70.06 | 60.18 | 51.74 | 45.15 |
| Untreated carbon fibers | 85.71 | 74.10 | 62.49 | 50.87 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers | 171.23 | 148.53 | 125.83 | 103.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamieh, T. New Progress on London Dispersive Energy, Polar Surface Interactions, and Lewis’s Acid–Base Properties of Solid Surfaces. Molecules 2024, 29, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050949
Hamieh T. New Progress on London Dispersive Energy, Polar Surface Interactions, and Lewis’s Acid–Base Properties of Solid Surfaces. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050949
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamieh, Tayssir. 2024. "New Progress on London Dispersive Energy, Polar Surface Interactions, and Lewis’s Acid–Base Properties of Solid Surfaces" Molecules 29, no. 5: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050949
APA StyleHamieh, T. (2024). New Progress on London Dispersive Energy, Polar Surface Interactions, and Lewis’s Acid–Base Properties of Solid Surfaces. Molecules, 29(5), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050949







