The Effect of Bacterial AHL on the Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Content in Plants According to High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Analysis
2.1. Selection of the Chromatographic Conditions
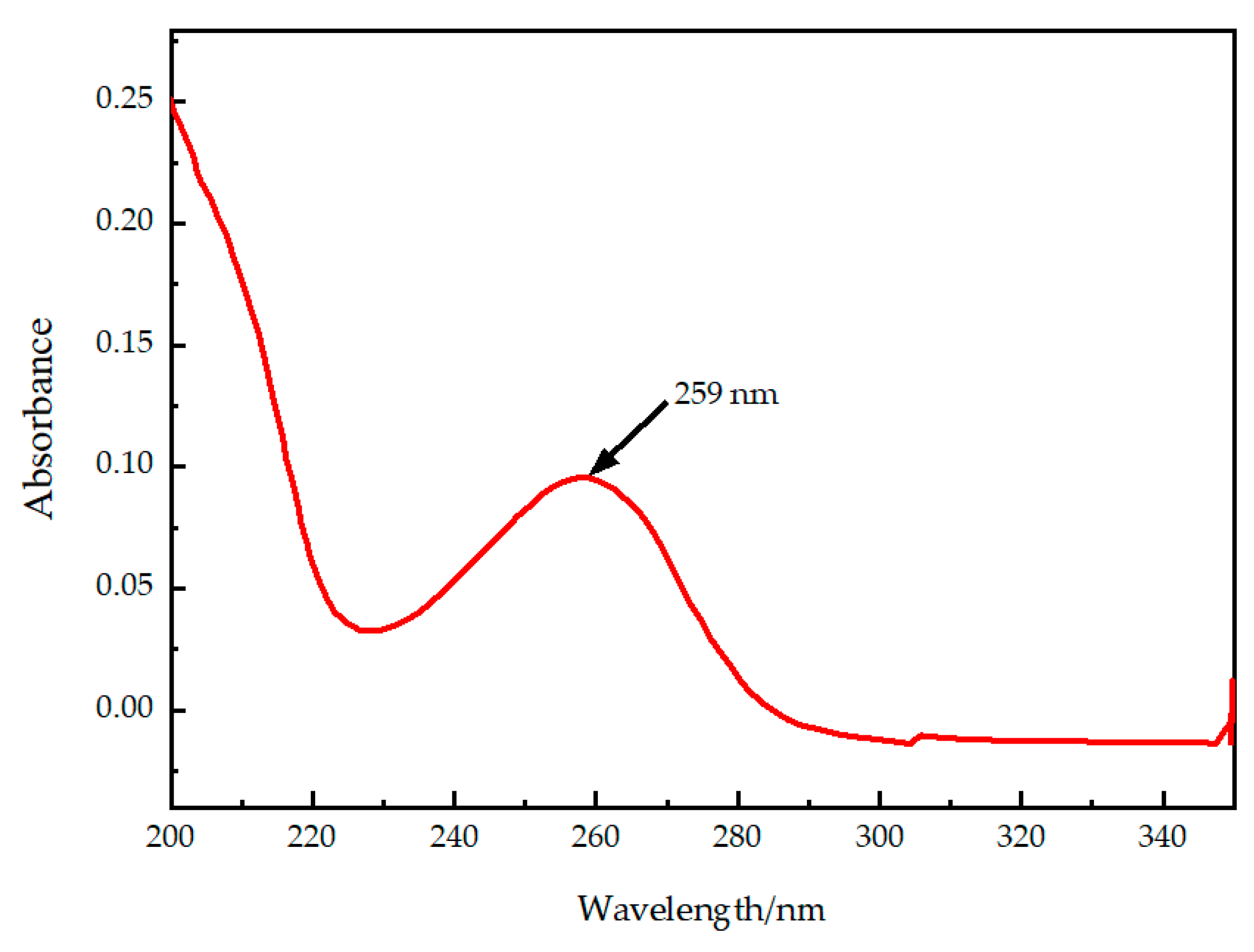
2.1.1. Selection of Detection Wavelength
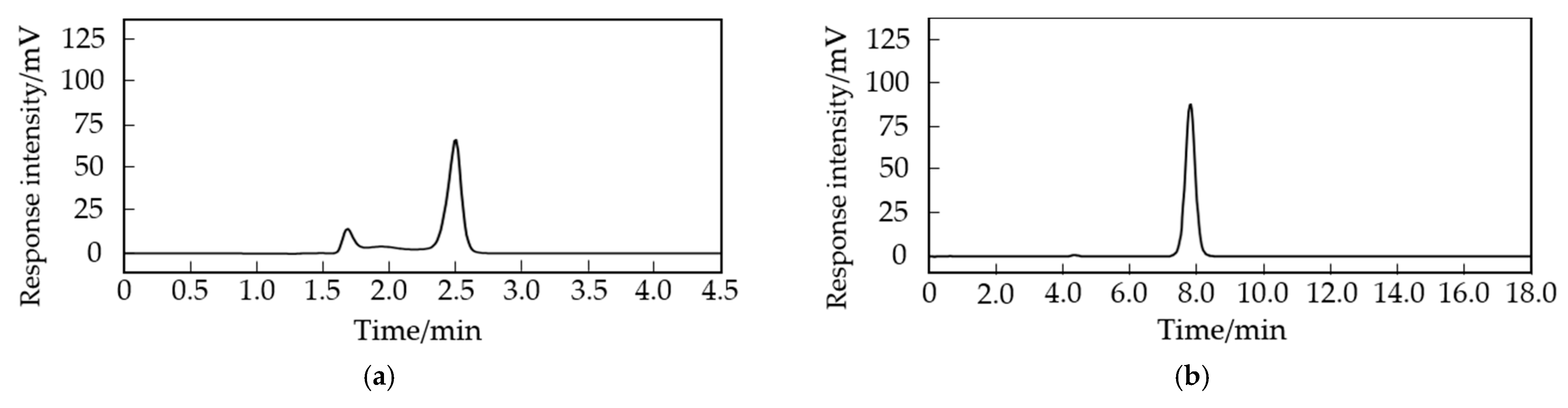
2.1.2. Selection of the Mobile Phase
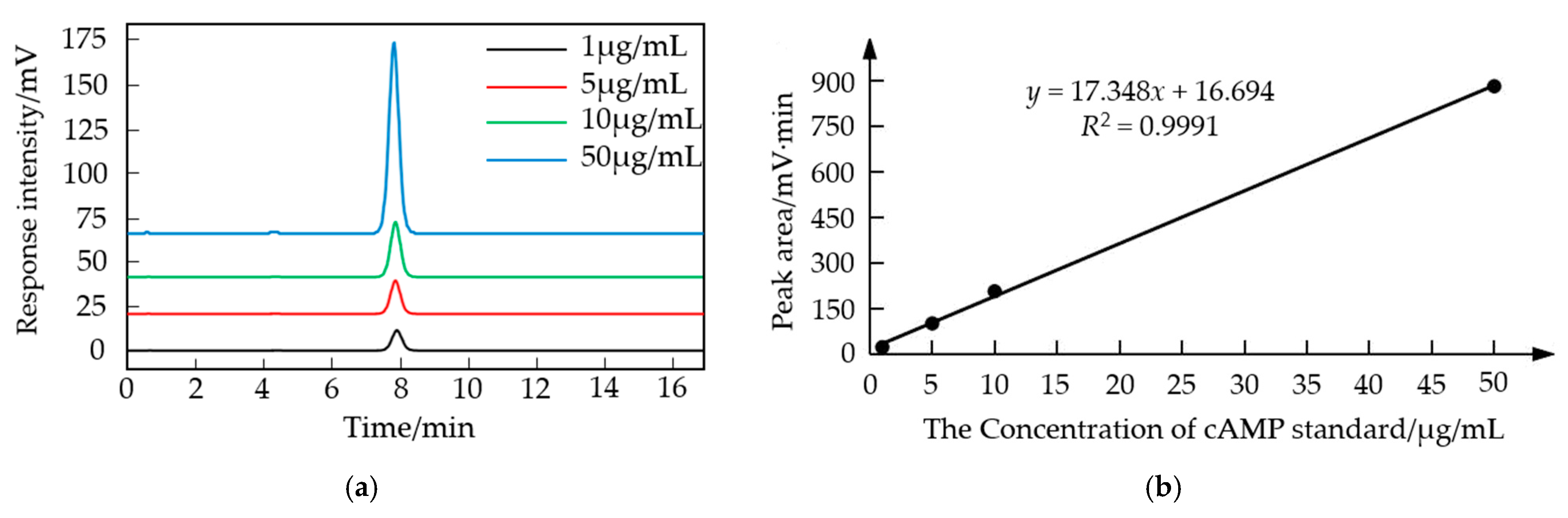
2.1.3. Plotting the Standard Curve
2.2. Selection of the Optimal Extraction Method for Arabidopsis cAMP
2.3. Precision Testing
2.4. Recovery Rate Testing
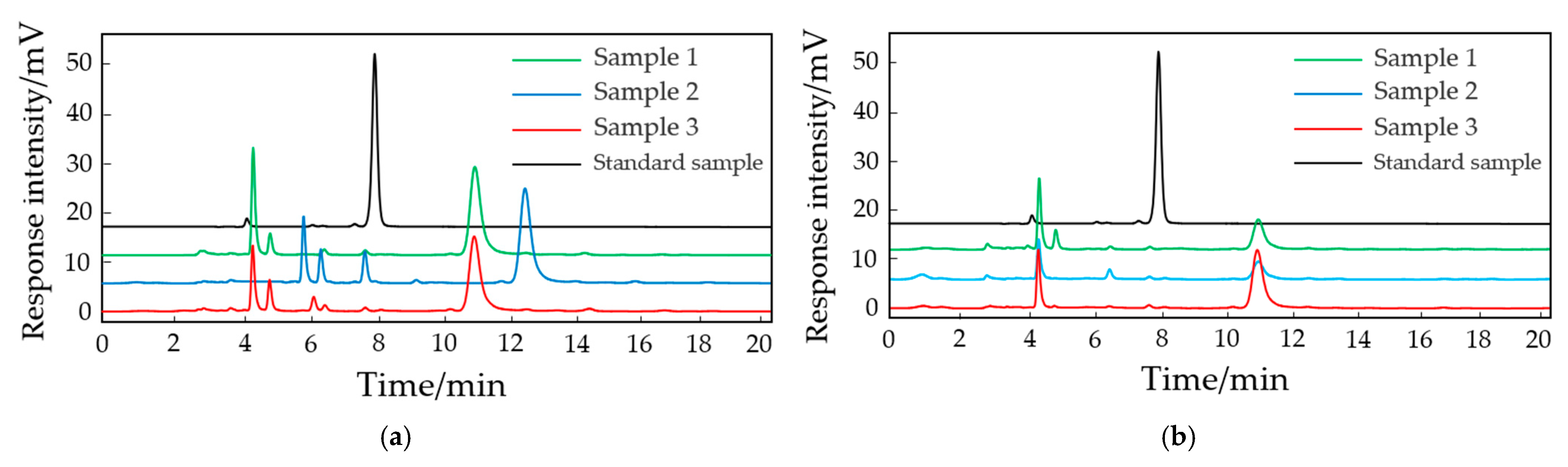
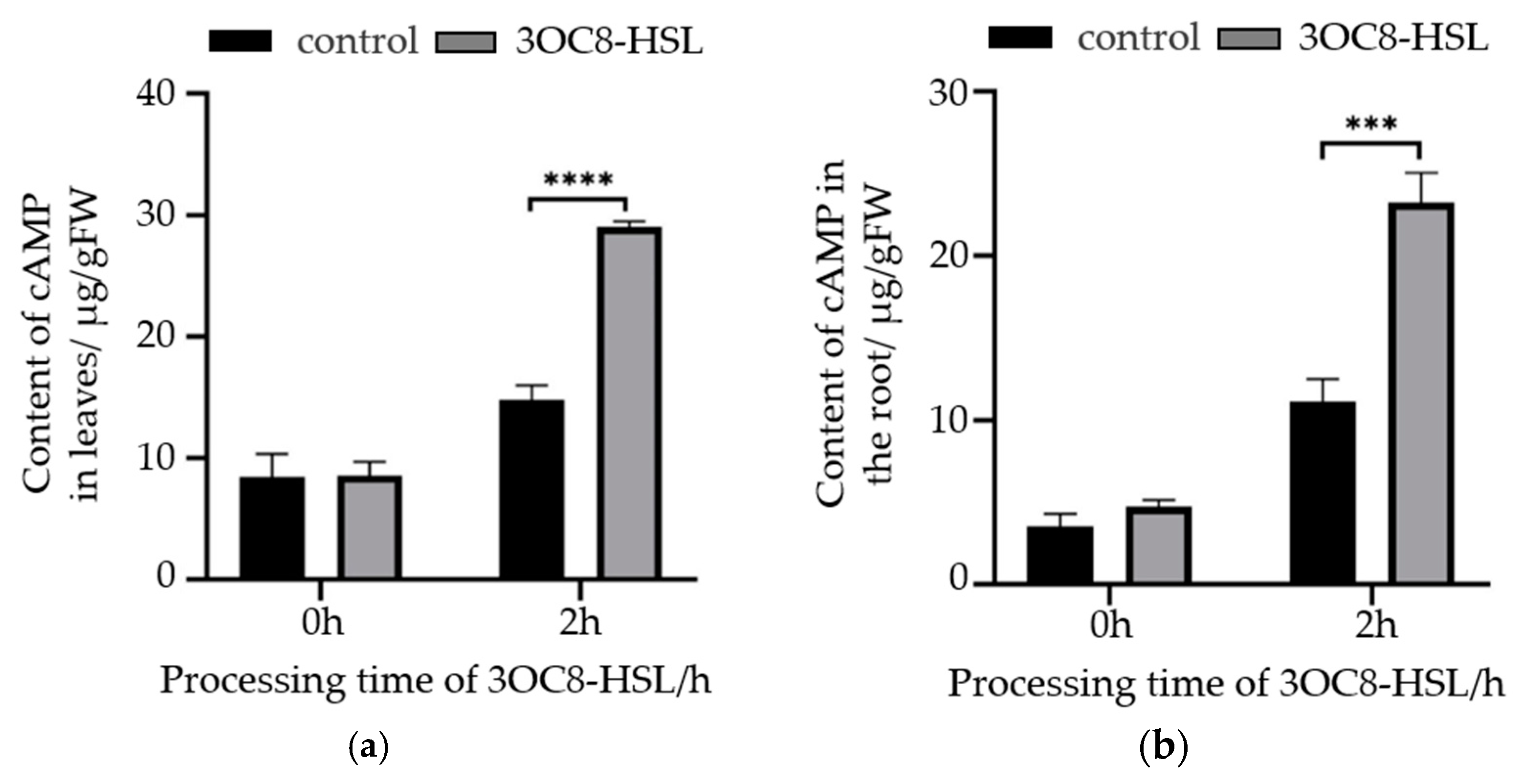
2.5. The Increase in the Plant cAMP Levels Induced by Bacterial AHL
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Samples and Reagents
4.1.2. Experimental Instruments
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Preparation of cAMP Standard
4.2.2. Selection of Chromatographic Conditions
4.2.3. Standard Curve Plotting
4.2.4. Arabidopsis Thaliana Cultivation
4.2.5. Preparation and Treatment of the AHL Molecule Solutions
4.2.6. Extraction of cAMP
4.2.7. Precision Experiment
4.2.8. Sample Recovery Rate Experiment
4.2.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y. Extraction and Quantitative Detection of Adenosine Monophosphate in Chinese Jujube from Ningxia. Ningxia Agric. For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Guo, X. Regulatory Role of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase in Animal Lipid Metabolism. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 29, 4287–4294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Lü, J. Effects of Adenosine Monophosphate on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Black Bean. Chin. Hortic. Abstr. 2017, 33, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lü, S.; Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, H.; Tian, Z.; Hu, X. Research Progress on the Regulatory Role of cAMP in Plant Growth, Development, and Stress Adaptation. J. Henan Agric. Univ. 2023, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Liu, J. The Role of cAMP Signaling in Higher Plants. Chin. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 36, 494–503. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Ye, Z.; Ping, W.; Ge, Q. Research Progress on the Mediation of Plant Growth and Defense Mechanisms by Quorum Sensing Signal Molecules AHLs. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2022, 58, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Xing, M.; Lin, Y.; Yao, H.; Mao, A.; Tang, D. Research Progress on AHL Analogs as Quorum Sensing System Enhancers in Bacteria. J. Microbiol. 2023, 43, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.-S.; Jia, Z.-H.; Xu, J.-Z.; Zhang, Z.; Bian, Z. N-butyryl-homoserine lactone, a bacterial quorum-sensing signaling molecule, induces intracellular calcium elevation in Arabidopsis root cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, S.-T.; Hernandez-reyes, C.; Samans, B.; Stein, E.; Neumann, C.; Schikora, M.; Reichelt, M.; Mithöfer, A.; Becker, A.; Kogel, K.H.; et al. N-acyl-homoserine lactone primes plants for cell wall reinforcement and induces resistance to bacterial pathogens via the salicylic acid/oxylipin pathway. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2708–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, X.-Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Cao, X.Y.; Jia, Z.H.; Song, S.S. N-3-oxo-hexanoyl-homoserine lactone, a bacterial quorum sensing signal, enhances salt tolerance in Arabidopsis and wheat. Bot. Stud. 2020, 61, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, Z.-H.; Song, C.; Huang, Y.; Ma, H.; Song, S. N-3-oxo-octanoyl-homoserine lactone-mediated priming of resistance to Pseudomonas syringae requires the salicylic acid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, Z.-H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Song, S.; Jia, Y. N-3-oxo-octanoyl homoserine lactone primes plant resistance against necrotrophic pathogen pectobacterium carotovorum by coordinating jasmonic acid and auxin-signaling pathways. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 886268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.-M.; Han, M.; Grimm, M.; Ponath, J.; Reichelt, M.; Mithöfer, A.; Schikora, A. Combination of bacterial N-acyl homoserine lactones primes Arabidopsis defenses via jasmonate metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 2027–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomovatskaya, L.-A.; Romanenko, A.-S.; Filinova, N.-V.; Dudareva, L.V. Determination of cAMP in plant cells by a modified enzyme immunoassay method. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 30, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludivine, T.; Claudius, M.; Luisa, E.; Pasqualini, S.; Gehring, C. Proteomic signatures implicate cAMP in light and temperature responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Proteom. 2013, 83, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, V.-D.; Dieter, B.; Pauline, C.; Van Der Straeten, D.; Sandra, P.; Lynen, F. Wounding stress causes rapid increase in concentration of the naturally occurring 2′,3′-isomers of cyclic guanosine- and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cGMP and cAMP) in plant tissues. Phytochemistry 2014, 103, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, L.; Meier, S.; Gehring, C. The Arabidopsis cyclic nucleotide interactome. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2016, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetta, W.; Vannini, C.; Sgobba, A.; Marsoni, M.; Paradiso, A.; Ortolani, F.; Bracale, M.; Viggiano, L.; Blanco, E.; de Pinto, M.C. Cyclic AMP deficiency negatively affects cell growth and enhances stress-related responses in tobacco Bright Yellow-2 cells. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.-Q.; Guo, Y.-H.; Peng, S.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Jia, W.; Zhao, J. Molecular targets and biological functions of cAMP signaling in Arabidopsis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.-X.; Zhang, M.-L.; Qu, Y.-Y.; Yuan, Y.; Ehsan, S.; Gao, M.-J.; Zhao, R.-Y.; Qi, C.-F.; Guo, X.-X.; et al. A cyclic effect of cAMP and calcium signaling contributes to jujube growth and development. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2094–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, T.; Li, X.; Pang, X.; Liu, L. Analysis of the Basic Principles and Considerations of ELISA. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2009, 37, 2357–2358. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, C. Principles of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its Application in the Detection of Food Preservatives. China Food Ind. 2021, 8, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. The Use of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in the Detection of Food Additives. Food Saf. Guide 2023, 14, 143–145. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, H. Fluorescent Dyes and Their Applications in Detection. Shanghai Dye. 2021, 49, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, R.-P.; Smith, C.-J. Cyclic nucleotides. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 2423–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, C. Adenyl cyclases and cAMP in plant signaling-past and present. Cell Commun. Signal. 2010, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L. Research on the Analysis and Detection Method of cAMP in Hotan Jade Jujube. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 36, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Li, J.; Shi, F.; Ouyang, Y. Simultaneous Rapid Determination of Residues of 91 Pesticides in Apples by Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. Jiangsu J. Prev. Med. 2023, 34, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Liu, M.; Yang, R.; Gao, L.; Ding, Z.; Chen, D. Determination of Tannic Acid Content in Ripe Pu’er Tea by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. China Tea Process. 2022, 2, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Shan, C. Process Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Low Eutectic Solvent Extraction of Adenosine in Xinjiang Red Dates. Food Ind. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Song, J.; Lu, C.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Influence of Different Microbial Agents on cAMP Content in Xinjiang Grey Jujube. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 32, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Cui, L.; Li, N.; Zhong, Y.; Hua, X.; Zhao, X. Process Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Water Bath Extraction of Adenosine in Jujube. China Food Addit. 2019, 30, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, P.; Tian, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, P. Effects of Exogenous Hormones on Adenosine and Ascorbic Acid Content in Jujube Fruits. Sichuan Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 1, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, S.; Sun, Z.; Qiu, H. Determination of Adenosine Content in Northern Chinese Red Dates by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Test. Technol. Instrum. 2020, 26, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.-L.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Chen, H.-H.; Hoermayer, L.; Sinclair, S.; Zou, M.; Del Genio, C.I.; Kubeš, M.F.; Napier, R.; Jaworski, K.; et al. Adenylate cyclase activity of TIR1/AFB auxin receptors in plants. Nature 2022, 611, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molchan, O.; Sokolovsky, S.; Volotovsky, I. The phytochrome control of the cAMP endogenous level in oat seedlings. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2000, 47, 463–467. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Han, X.-W.; Wu, J.-H.; Zheng, S.; Shang, Z.; Sun, D.; Zhou, R.; Li, B. A heat-activated calcium-permeable channel—Arabidopsis cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 6--is involved in heat shock responses. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 70, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormann, J.; Boenisch, M.-J.; Bruckner, E.; First, D.; Schäfer, W. The adenylyl cyclase plays a regulatory role in the morphogenetic switch from vegetative to pathogenic lifestyle of Fusarium graminearum on wheat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetta, W.; Vandelle, E.; Locoto, V.; Costa, A.; Cimini, S.; Bittencourt Moura, A.; Luoni, L.; Graf, A.; Viggiano, L.; De Gara, L.; et al. Genetic buffering of cyclic AMP in Arabidopsis thaliana compromises the plant immune response triggered by an avirulent strain of Pseudomonas syringae pv. Tomato. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 98, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Bian, Z.-R.; Jia, Z.-H.; Zhao, Q.; Song, S. The GCR1 and GPA1 Participate in Promotion of Arabidopsis Primary Root Elongation Induced by N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactones, the Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Signals. MPMI 2012, 25, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Bian, Z.-R.; Song, S. 3-Oxo-octanoyl homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C8-HSL) induces Ca2+ influx in Arabidopsis thaliana root cells. Plant Physiol. J. 2011, 47, 872–878. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Davis, N.-G. Feedback phosphorylation of the yeast a-factor receptor requires activation of the downstream signaling pathway from G protein through mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Serial Number | Standard Determination | Sample Determination | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cAMP Content/μg/mL | Relative Standard Deviation/% | cAMP Content/μg/mL | Relative Standard Deviation/% | |
| 1 | 49.83773 | 1.791772 | 2.974983 | 1.133876 |
| 2 | 49.68457 | 3.021732 | ||
| 3 | 49.64117 | 2.977173 | ||
| 4 | 47.93290 | 2.933018 | ||
| 5 | 48.35555 | 3.004900 | ||
| Serial Number | cAMP Content in the Sample/μg | Amount of cAMP Added/μg | HPLC Results/μg/mL | Rate of Recovery/% | Average Recovery Rate/% | Relative Standard Deviation/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.926504 | 0.5 | 4.825110 | 101.4742 | 101.067 | 1.553644 |
| 2 | 0.777231 | 4.388229 | 103.0721 | |||
| 3 | 0.612843 | 3.662785 | 98.7413 | |||
| 4 | 0.570371 | 3.591480 | 100.6608 | |||
| 5 | 1.253136 | 5.924833 | 101.3869 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Jia, Z.; Song, S.; Zhao, Q. The Effect of Bacterial AHL on the Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Content in Plants According to High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules 2024, 29, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051074
Zhao X, Li W, Li X, Jia Z, Song S, Zhao Q. The Effect of Bacterial AHL on the Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Content in Plants According to High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051074
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xuemeng, Wen Li, Xiliu Li, Zhenhua Jia, Shuishan Song, and Qian Zhao. 2024. "The Effect of Bacterial AHL on the Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Content in Plants According to High-Performance Liquid Chromatography" Molecules 29, no. 5: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051074
APA StyleZhao, X., Li, W., Li, X., Jia, Z., Song, S., & Zhao, Q. (2024). The Effect of Bacterial AHL on the Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Content in Plants According to High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules, 29(5), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051074







