Effect of Sulfuric Acid Corrosion on Flotation Performance of Calcite by Changing Surface Roughness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
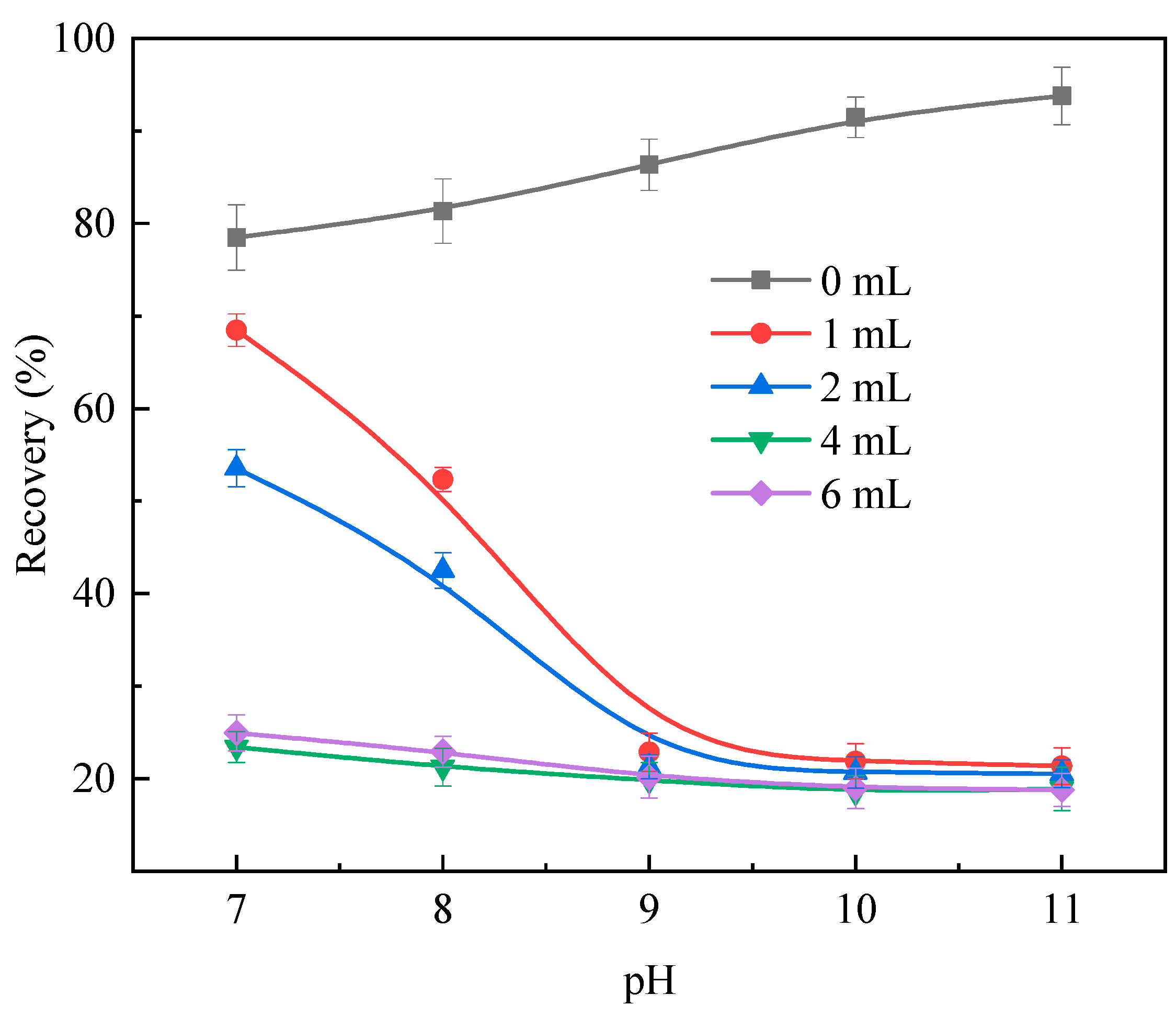
2.1. Microflotation Results
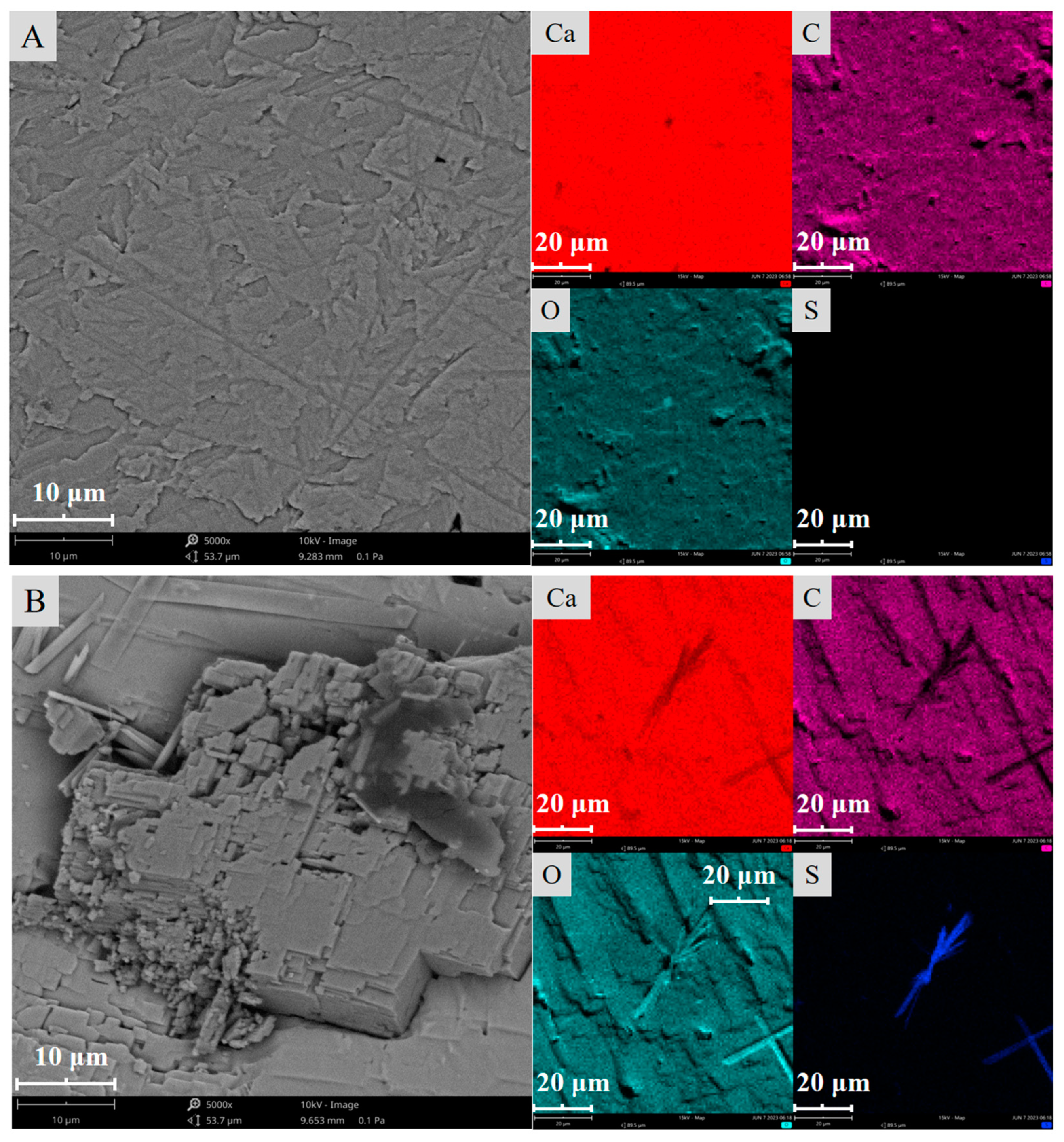
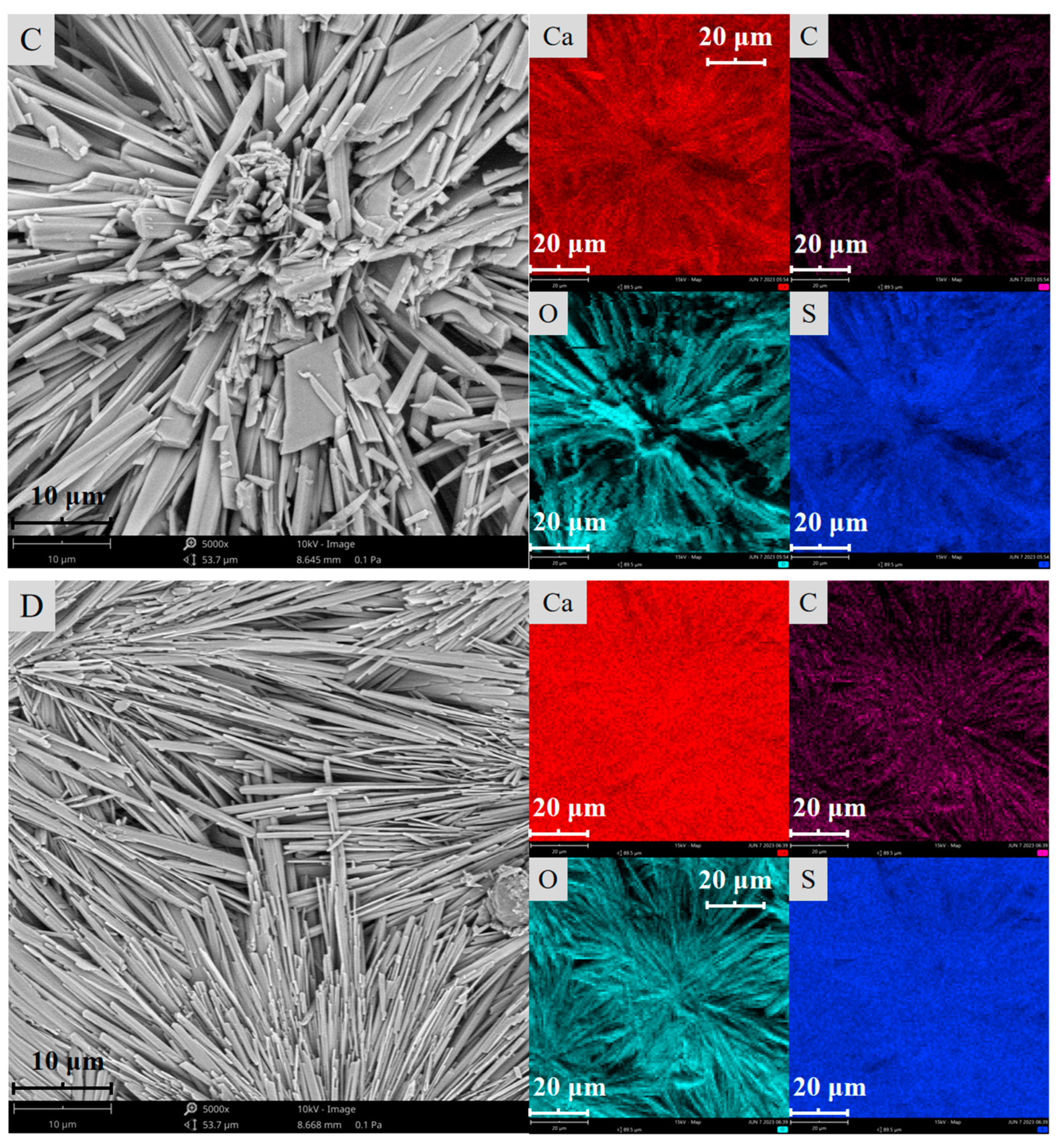
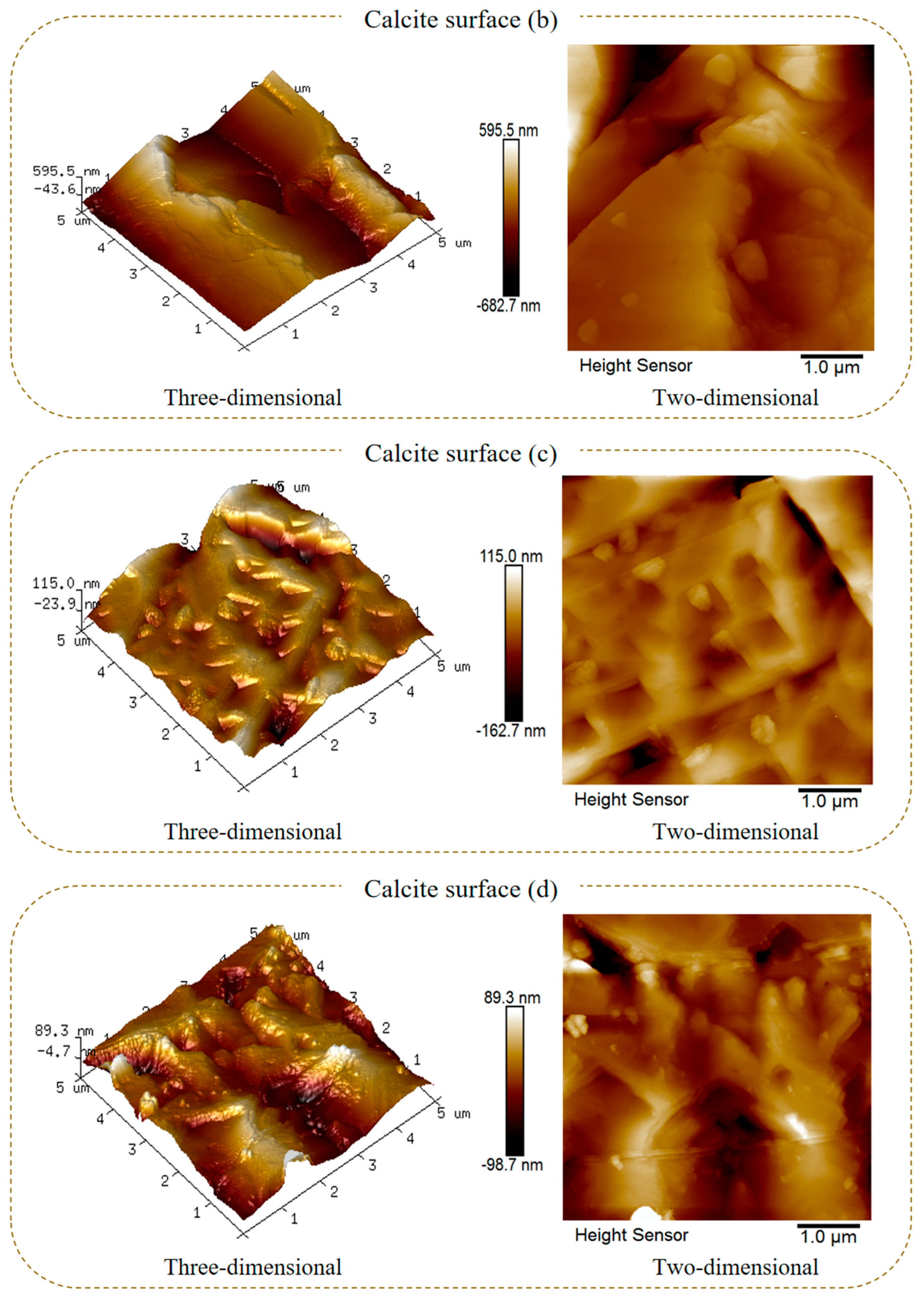
2.2. Surface Morphology Characterization
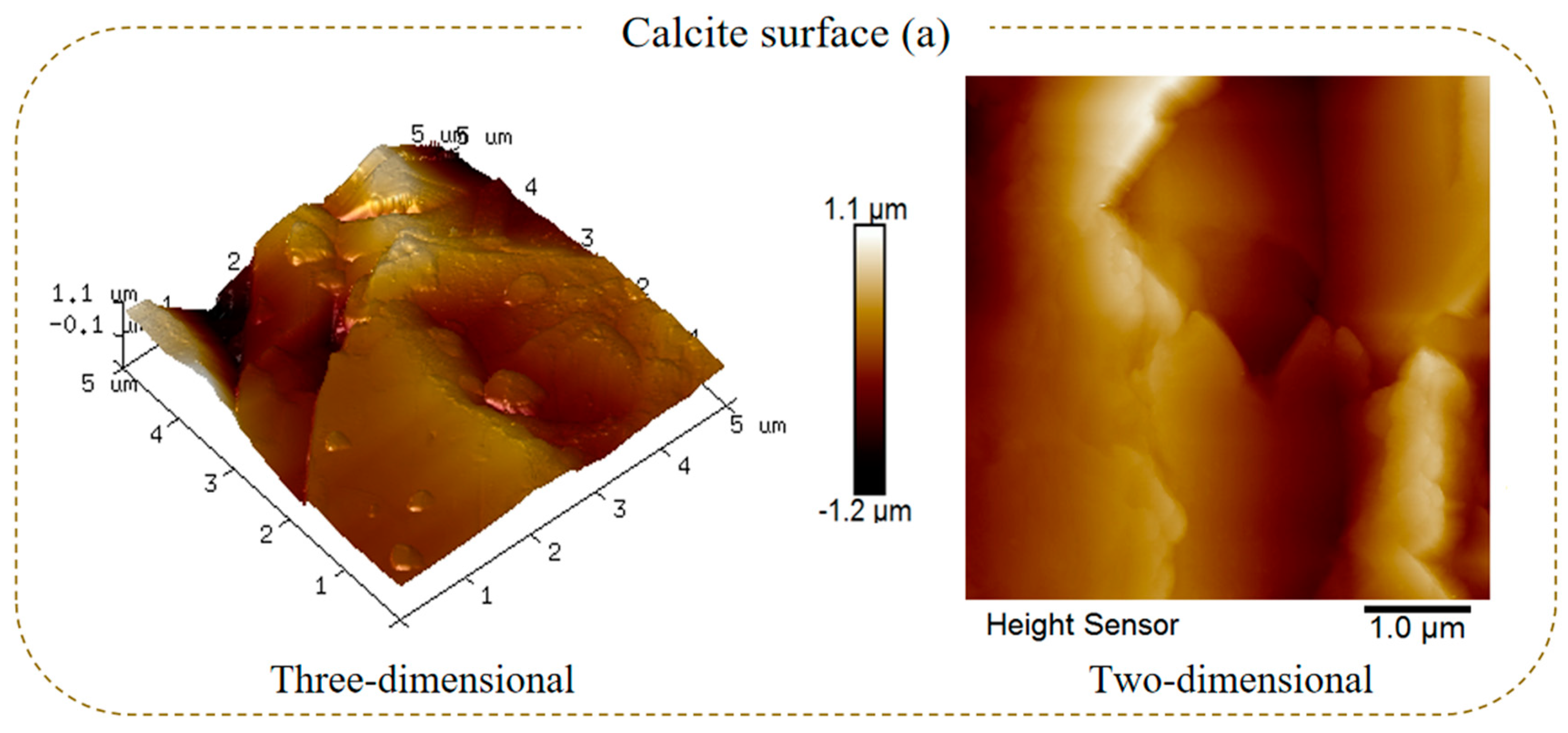
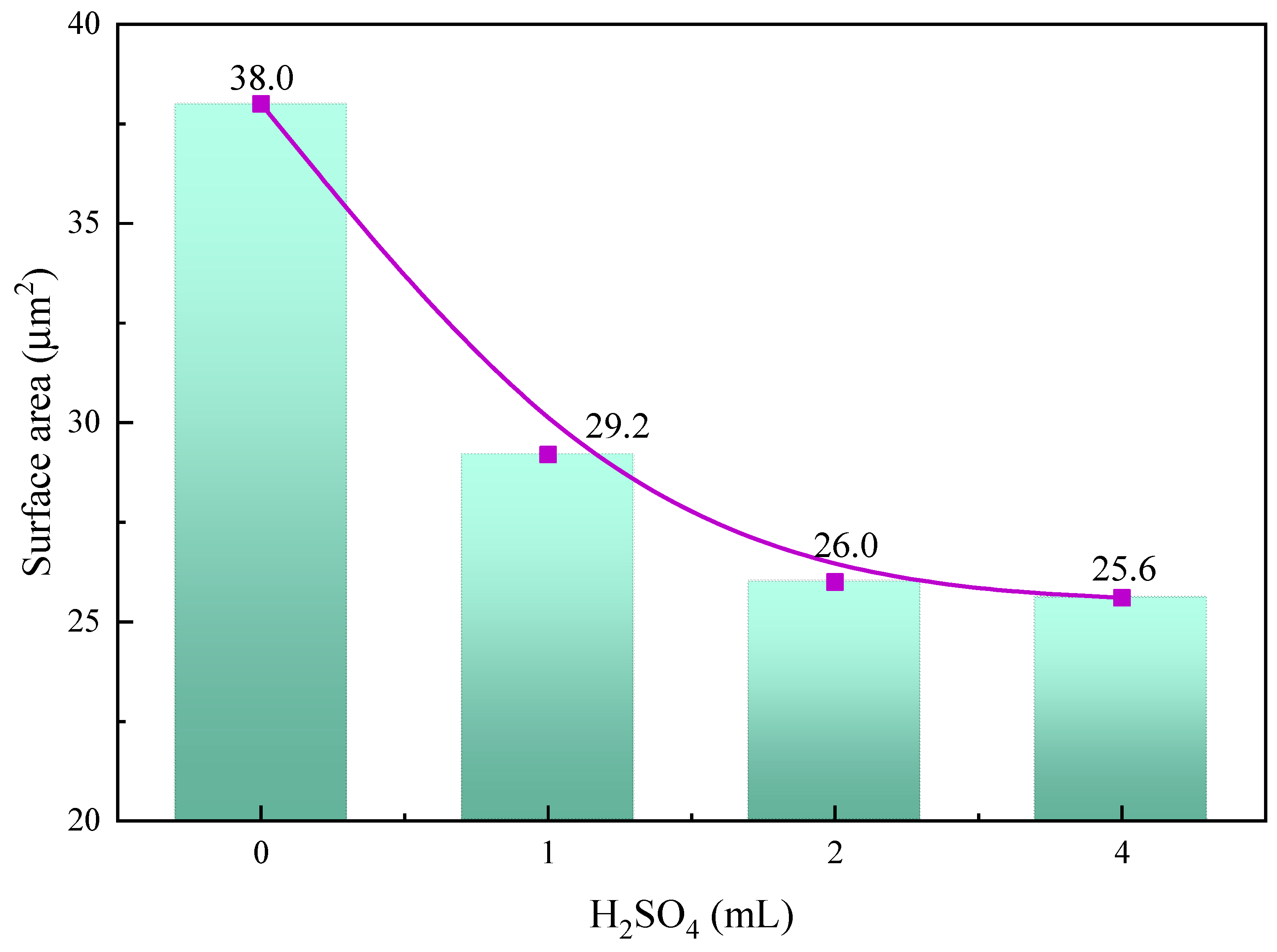
2.3. Surface Roughness Characterization
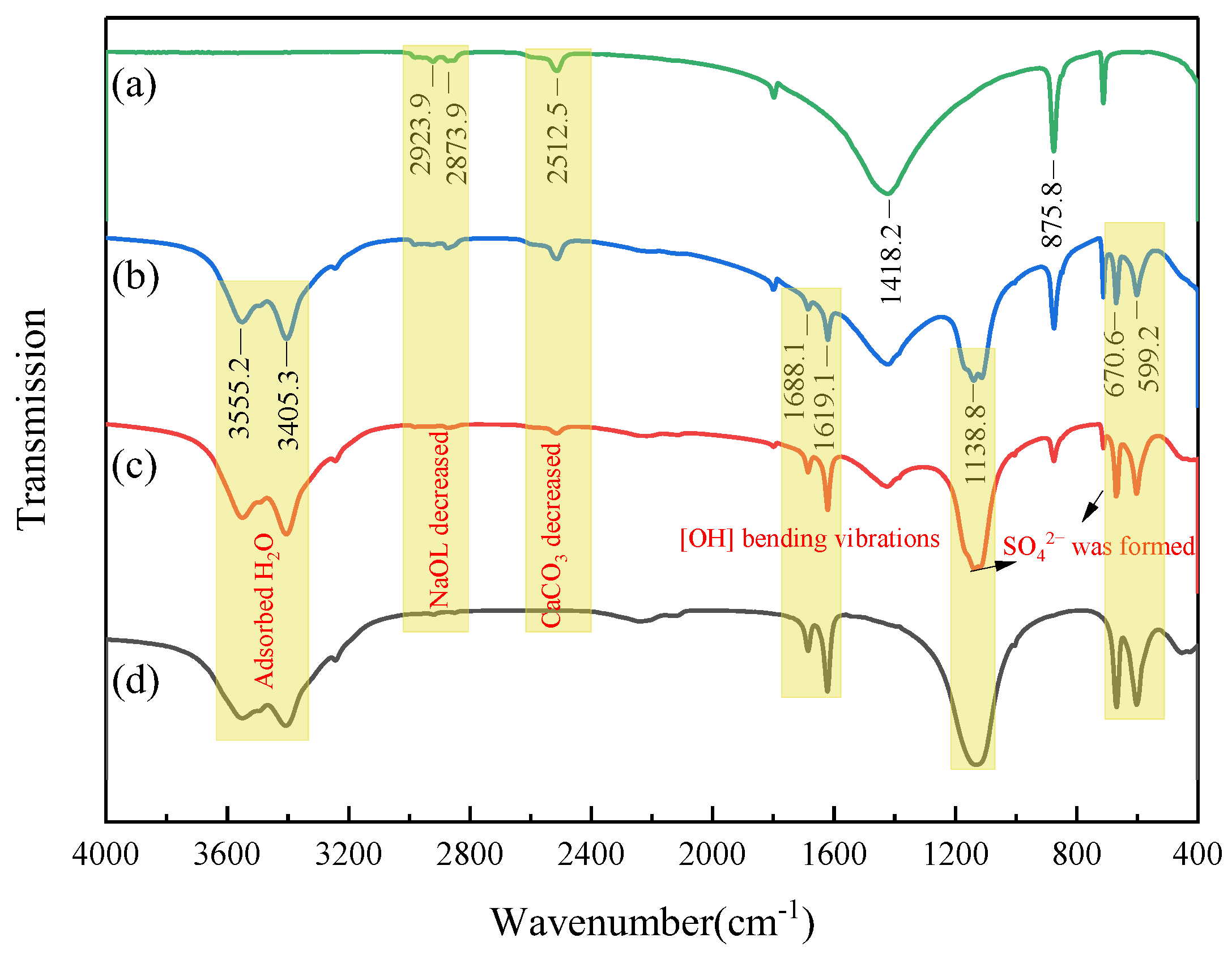
2.4. Surface Composition Analysis
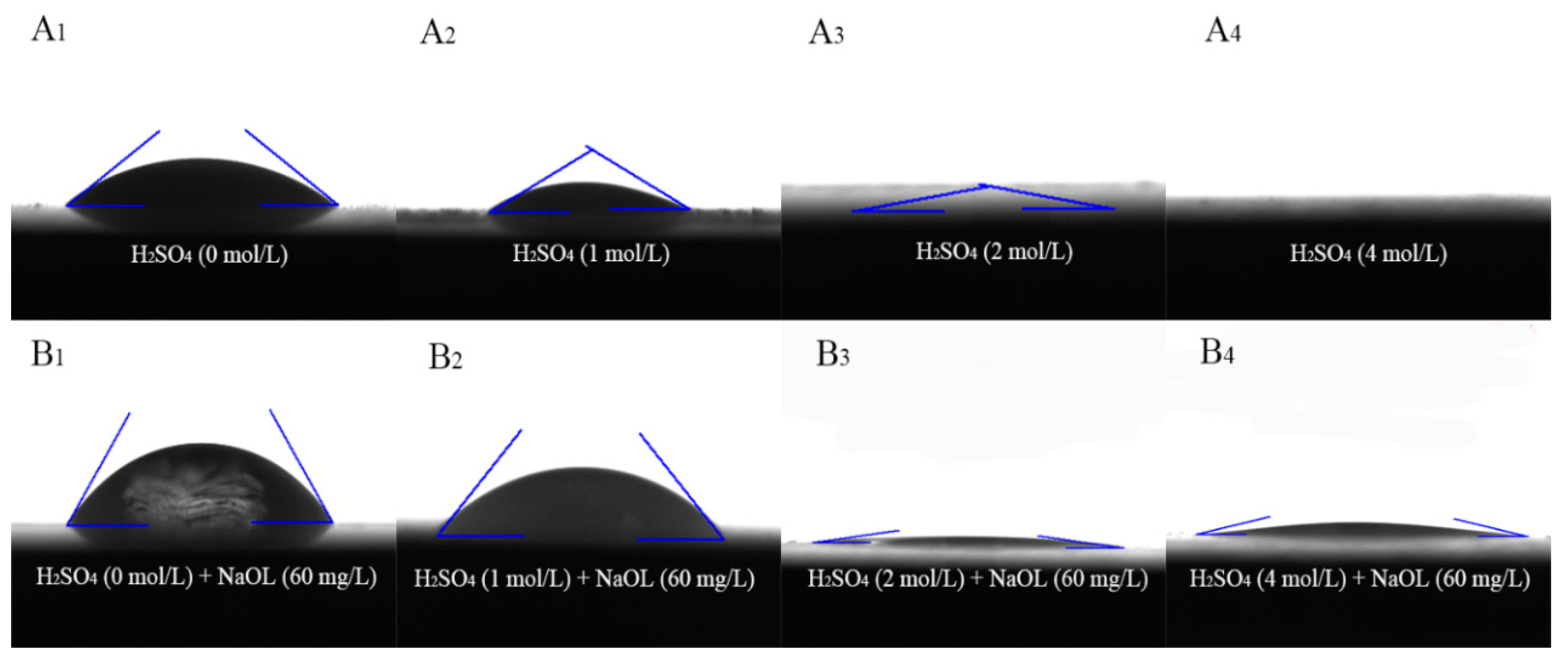
2.5. Surface Wettability Measurements
2.6. Possible Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Microflotation Experiments
3.3. AFM Measurements
3.4. SEM–EDS Analysis
3.5. FT-IR Measurement
3.6. Contact Angle Measurements
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The results of the microflotation experiments suggest that sulfuric acid treatment can significantly reduce the floatability of calcite, and the flotation recovery of calcite was stable at approximately 19% when the acid dosage was greater than 2 mL;
- (2)
- The SEM and AFM results reveal that after the sulfuric acid reaction of calcite, its surface changes from stepped CaCO3 to crystalline cluster CaSO4, which significantly reduces the average surface roughness and surface area of calcite and the active sites Ca2+;
- (3)
- The FT-IR results and contact angle measurements reveal that the surface of calcite treated with sulfuric acid exhibits strong hydrophilicity. Moreover, the acid treatment reduces the adsorption of NaOL, which makes it difficult for NaOL to enhance the hydrophobicity of the calcite surface.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Role of surface roughness in the wettability, surface energy and flotation kinetics of calcite. Powder Technol. 2020, 371, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y. Anisotropic surface properties of calcite: A consideration of surface broken bonds. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 520, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Deng, J.; Geng, H.; Bai, Z.; Gui, X.; Ma, Z.; Miao, Z. An exploratory study on strategic metal recovery of coal gangue and sustainable utilization potential of recovery residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, S.M.; Ezzati, E.; Rashidnejad-Omran, N.; Moradzadeh, A. Geoeconomics of fluorspar as strategic and critical mineral in Iran. Resour. Policy 2017, 52, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xing, D.; Deng, J.; Jin, D.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Qin, G.; Liu, X. Effect of sulfuric acid pretreatment on flotation performance of calcite and fluorite. Miner. Eng. 2023, 203, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ma, Z.; Qin, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, B. A residue reutilization strategy on fluorine-containing water purification. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 371, 133613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, S. Beneficiation of fluorite by flotation in a new chemical scheme. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lyu, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, H. The role of sodium phytate in the flotation separation of smithsonite from calcite. Miner. Eng. 2022, 187, 107775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzpour, A.; Samadzadeh Yazdi, M.R.; Mohammadi, B.; Chelgani, S.C. Calcite in froth flotation—A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shean, B.J.; Cilliers, J.J. A review of froth flotation control. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 100, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Wu, B.; Chen, J.; Deng, J.; Sun, X.; Hu, M.; Cai, J.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, C. Selective depression of marmatite by sodium alginate in flotation separation of galena and marmatite. Miner. Eng. 2023, 201, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, P. The flotation separation of scheelite from calcite using acidified sodium silicate as depressant. Miner. Eng. 2015, 80, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Peng, J.; Guo, W.; Luo, G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. The depression behavior and mechanism of carboxymethyl chitosan on calcite flotation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Sun, W.; Liu, X. Anisotropic surface energies and adsorption behaviors of scheelite crystal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 415, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Sun, R.; Wang, G.; Deng, J.; Zhang, X. Flotation separation of fluorite and calcite using anhydrous glucose and aluminum sulfate as a combined depressant. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 624, 157089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Deng, J.; Ni, C.; Wang, D.; Xue, K.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X. Reverse froth flotation separation of limonite and quartz with cationic gemini surfactant. Miner. Eng. 2022, 177, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, C.; Sun, W.; Gao, Y.; Kowalczuk, P.B. Froth flotation of fluorite: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 290, 102382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Moreno, J.; Torres, R.; Valle, H.; Song, S. Flotation of fluorite from ores by using acidized water glass as depressant. Miner. Eng. 2013, 45, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lopez-Valdivieso, A.; Martinez-Martinez, C.; Torres-Armenta, R. Improving fluorite flotation from ores by dispersion processing. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, W.; Zeng, X.; Fang, S.; Han, H.; Hong, K.; Hu, Y. Use of Al2(SO4)3 and acidified water glass as mixture depressants in flotation separation of fluorite from calcite and celestite. Miner. Eng. 2019, 137, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Laskowski, J.S. The adsorption of polysaccharides onto mineral surfaces: An acid/base interaction. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2000, 60, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, D. Room Temperature Cleaner Flotation Technique for Scheelite Rough Concentrate. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 1997, 7, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, S.; Hu, Y.; Tang, H.; Gao, J.; Yin, Z.; Guan, Q. Selective adsorption of tannic acid on calcite and implications for separation of fluorite minerals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 512, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, R.; Backfolk, K.; Rosenholm, J.B.; Nurmi, K. Flocculation of calcite dispersions induced by the adsorption of highly cationic starch. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 219, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y.; Tang, H.; Yin, Z.; Guan, Q.; Gao, J. Investigation of two-stage depressing by using hydrophilic polymer to improve the process of fluorite flotation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarquís, P.E.; Menéndez-Aguado, J.M.; Mahamud, M.M.; Dzioba, R. Tannins: The organic depressants alternative in selective flotation of sulfides. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 84, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aro, T.; Fatehi, P.J.C. Production and Application of Lignosulfonates and Sulfonated Lignin. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Liu, D.; Tian, X.; Zuo, Q.; Wang, D.; Wen, S. The role of copper ion and soluble starch used as a combined depressant in the flotation separation of fluorite from calcite: New insights on the application of modified starch in mineral processing. Miner. Eng. 2022, 181, 107550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.W.; Marmur, A.J.S.I. Meaningful contact angles in flotation systems: Critical analysis and recommendations. Surf. Innov. 2017, 6, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, T.; Kong, D. Knowledge-based neural network for surface roughness prediction of ball-end milling. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 194, 110282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yin, W.; Wang, D.; Sun, H.; Chen, K.; Yang, B. The role of surface roughness in the wettability and floatability of quartz particles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 527, 146799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M. Effect of comminution on particle shape and surface roughness and their relation to flotation process. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 94, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, R.; Gu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, X. Identification of a promoter element mediating kisspeptin-induced increases in GnRH gene expression in sheep. Gene 2019, 699, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicyilmaz, C.; Ulusoy, U.; Bilgen, S.; Yekeler, M. Flotation responses to the morphological properties of particles measured with three-dimensional approach. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2005, 75, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, U.; Yekeler, M. Correlation of the surface roughness of some industrial minerals with their wettability parameters. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2005, 44, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ku, J.; Zuo, W.; Yin, W. Study of reverse flotation of calcite from scheelite in acidic media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Q. Investigations on flotation separation of scheelite from calcite by using a novel depressant: Sodium phytate. Miner. Eng. 2018, 126, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Wen, S. Influence of lead ion pretreatment surface modification on reverse flotation separation of fluorite and calcite. Miner. Eng. 2021, 171, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.; Deng, W. Selective flotation separation of ilmenite from titanaugite using mixed anionic/cationic collectors. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 166, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Teng, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, S. Use of NaOL and CTAB mixture as collector in selective flotation separation of enstatite and magnetite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 570, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böke, H.; Akkurt, S.; Özdemir, S.; Göktürk, E.H.; Saltik, E.N. Quantification of CaCO3–CaSO3·0.5H2O–CaSO4·2H2O mixtures by FTIR analysis and its ANN model. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.Y.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’na, D.A.; Qiblawey, H.; Zouari, N. Investigating the effect of temperature on calcium sulfate scaling of reverse osmosis membranes using FTIR, SEM-EDX and multivariate analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potapova, E.; Yang, X.; Westerstrand, M.; Grahn, M.; Holmgren, A.; Hedlund, J. Interfacial properties of natural magnetite particles compared with their synthetic analogue. Miner. Eng. 2012, 36–38, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Corona-Arroyo, M.A.; López-Valdivieso, A.; Song, S. Contact angle and vacuum floatability of ultrafine size particles. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, S.; Mousavinezhad, S.K.; Gharabaghi, M. Chemical and colloidal aspects of collectorless flotation behavior of sulfide and non-sulfide minerals. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 225, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Feng, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Gao, Z. Flotation separation of apatite and calcite using gum arabic as a depressant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| H2SO4 Dosage (mL) | Surface Element Weight Percentage (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | C | O | S | |
| 0 | 34.47 | 15.13 | 50.40 | - |
| 1 | 33.76 | 14.68 | 51.09 | 0.37 |
| 2 | 20.16 | 7.51 | 58.90 | 13.43 |
| 4 | 20.88 | 7.79 | 56.35 | 14.98 |
| Treatment Conditions | A1 | A2 | A3 | A3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact angle (θA) | 37.14 | 29.47 | 5.16 | None |
| Treatment conditions | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 |
| Contact angle (θA) | 58.93 | 49.26 | 7.71 | 12.72 |
| Chemical | Conc. % | Supplier | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2SO4 | 98.0 | Sinopharm Chemical | pH adjuster |
| NaOH | 96.0 | Shiyi Chemical Reagent | pH adjuster |
| NaOL | 99.0 | Macleans Biochemical | Collector |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, D.; Sun, R.; Ma, S.; Wen, H.; Wang, Z.; Deng, J. Effect of Sulfuric Acid Corrosion on Flotation Performance of Calcite by Changing Surface Roughness. Molecules 2024, 29, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051062
Xing D, Sun R, Ma S, Wen H, Wang Z, Deng J. Effect of Sulfuric Acid Corrosion on Flotation Performance of Calcite by Changing Surface Roughness. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051062
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Dingquan, Ruofan Sun, Shuai Ma, Heping Wen, Zhongchi Wang, and Jiushuai Deng. 2024. "Effect of Sulfuric Acid Corrosion on Flotation Performance of Calcite by Changing Surface Roughness" Molecules 29, no. 5: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051062
APA StyleXing, D., Sun, R., Ma, S., Wen, H., Wang, Z., & Deng, J. (2024). Effect of Sulfuric Acid Corrosion on Flotation Performance of Calcite by Changing Surface Roughness. Molecules, 29(5), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051062








