Imidazole-Based Lithium Salt LiHDI as a Solid Electrolyte Interphase-Stabilising Additive for Lithium-Conducting Electrolytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
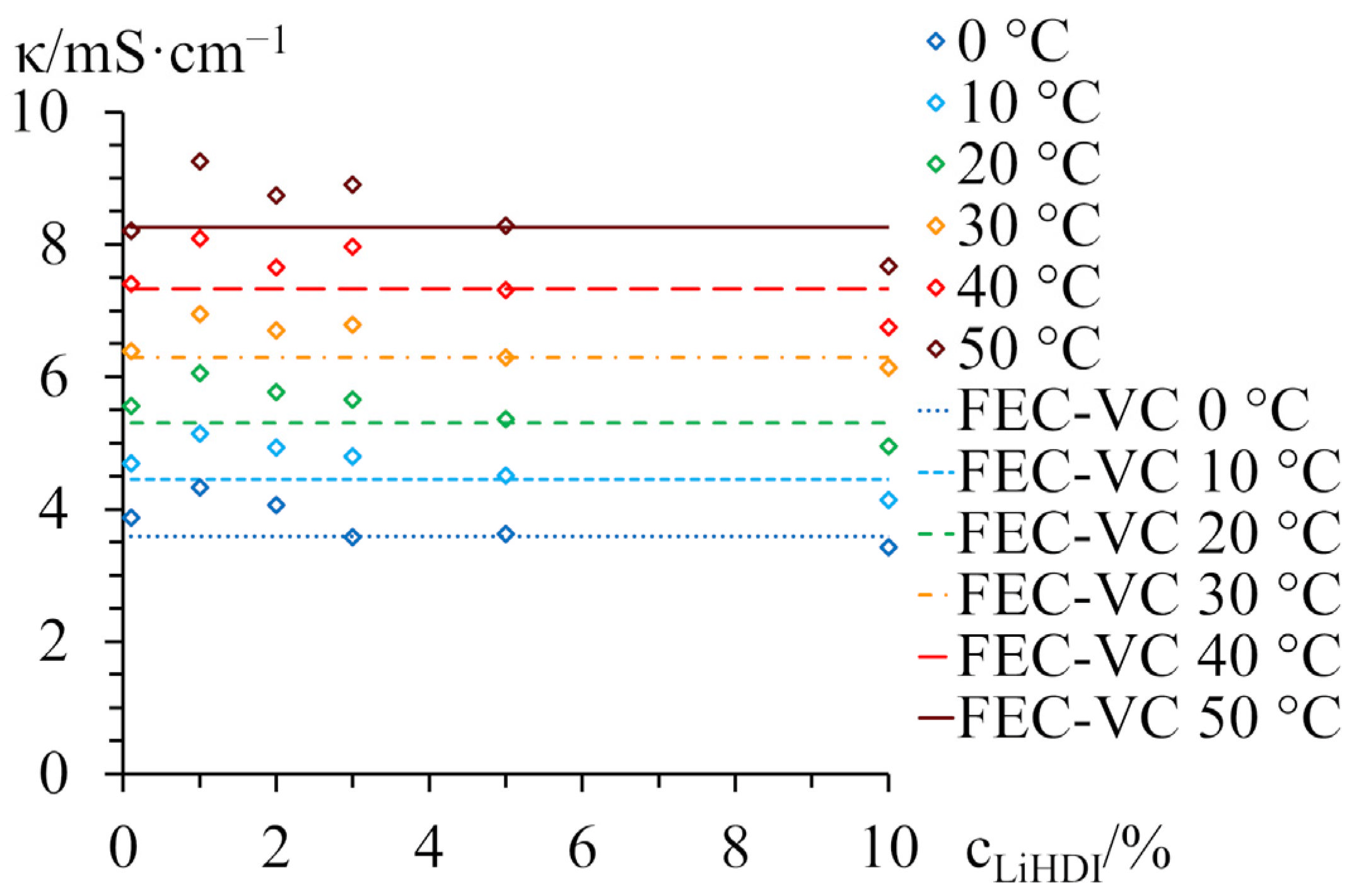
2.1. Conductivity
2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry
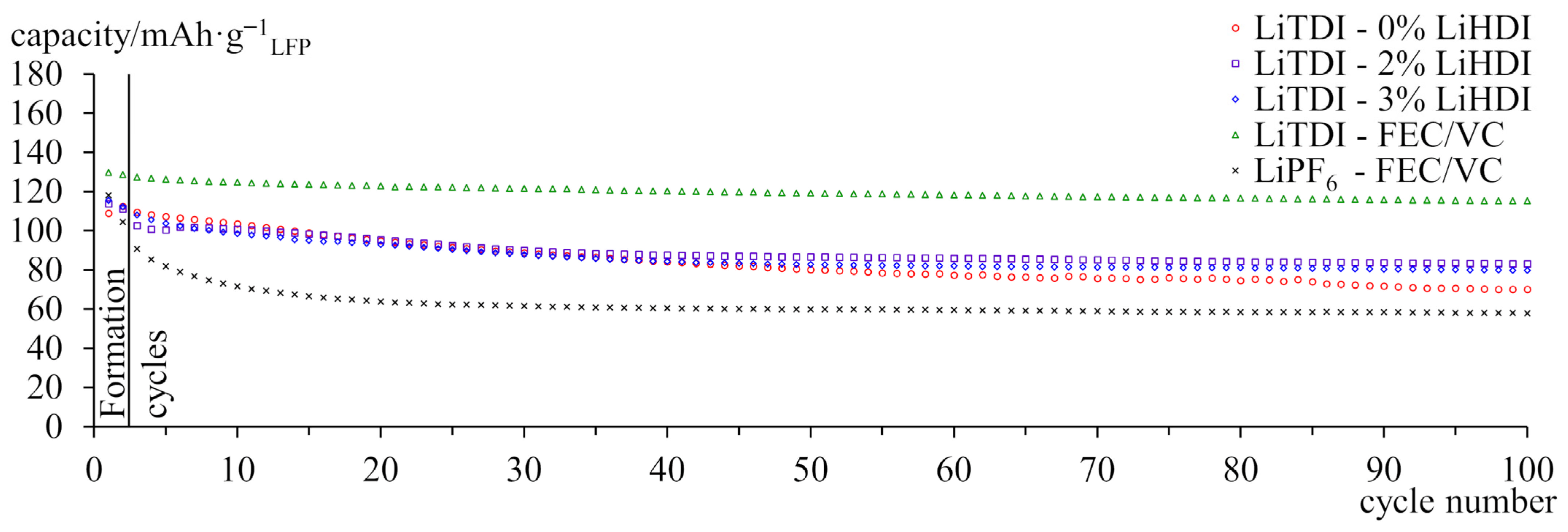
2.3. Galvanostatic Cycling at 25 °C
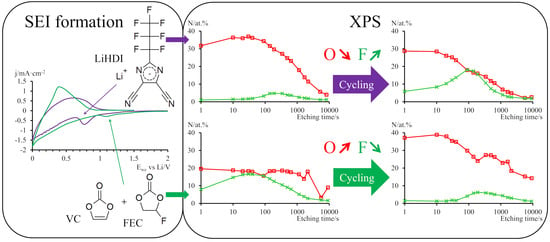
2.4. XPS Studies
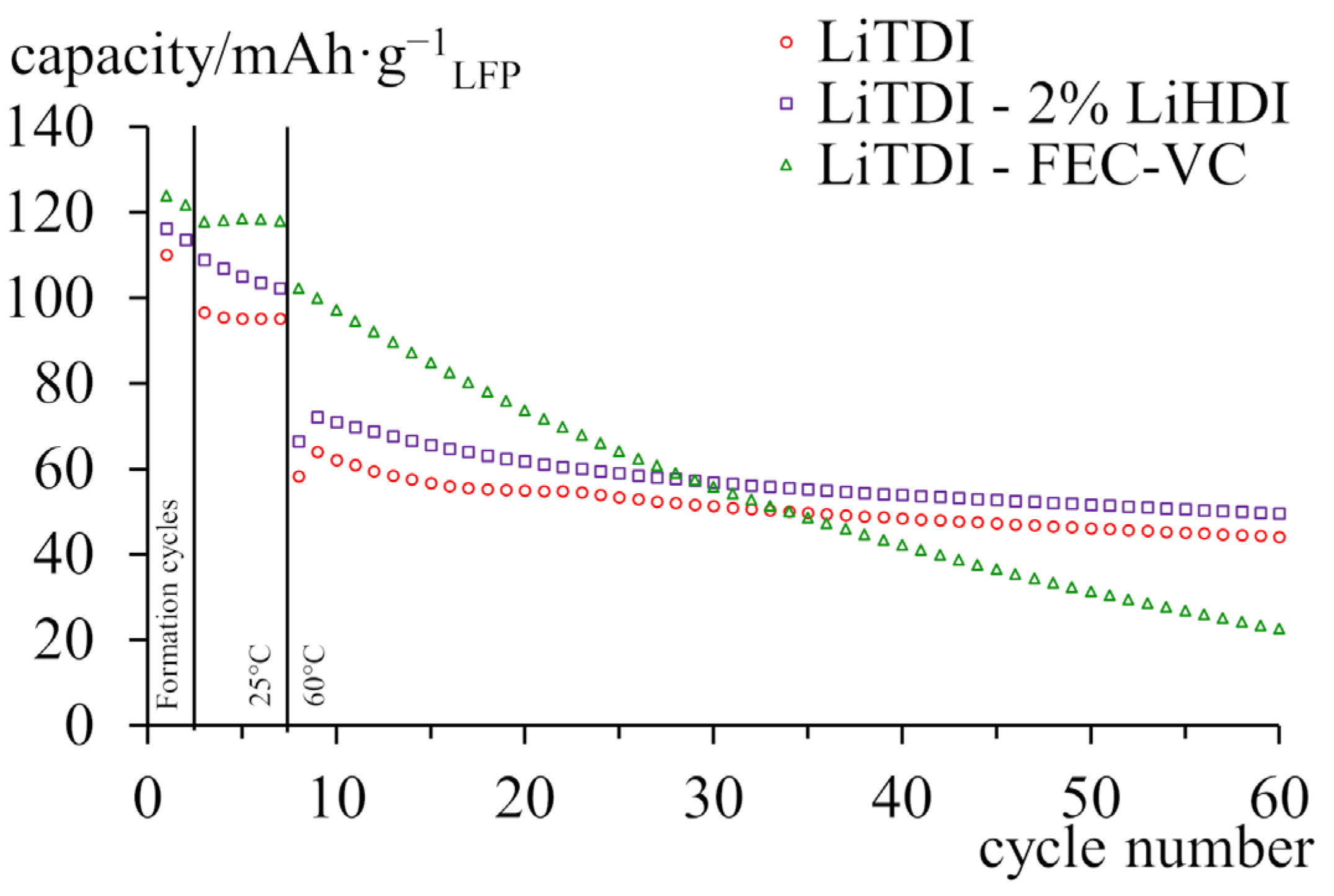
2.5. Galvanostatic Cycling at 60 °C
2.6. Thermal Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in 1:2 weight ratio EC/DMC mixture;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in 1:2 weight ratio EC/DMC mixture with 2% of LiHDI additive;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in 1:2 weight ratio EC/DMC mixture with 3% of LiHDI additive;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in 1:2 weight ratio EC/DMC mixture with 2% of VC and 10% of FEC additives;
- 1 mol·kg−1 LiPF6 in 1:2 weight ratio EC/DMC mixture with 2% of VC and 10% of FEC additives.
- Graphite;
- LiFePO4;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in EC:2DMC with 2% of LiHDI;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in EC:2DMC with 2% of VC and 10% of FEC;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in EC:2DMC with 2% of LiHDI + graphite;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in EC:2DMC with 2% of VC and 10% of FEC + graphite;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in EC:2DMC with 2% of LiHDI + LiFePO4;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in EC:2DMC with 2% of VC and 10% of FEC + LiFePO4;
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in EC:2DMC with 2% of LiHDI + graphite (lithiated);
- 0.63 mol·kg−1 LiTDI in EC:2DMC with 2% of VC and 10% of FEC + graphite (lithiated).
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, K. Electrolytes and Interphases in Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S. The Great Battery Race. Foreign Policy 2010, 182, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K. Nonaqueous Liquid Electrolytes for Lithium-Based Rechargeable Batteries. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, L.; Gambaretto, G.; Caporiccio, G.; Alessandrini, F.; Passerini, S. Perfluoroalkanesulfonylimides and their lithium salts: Synthesis and characterisation of intermediates and target compounds. J. Fluorine Chem. 2004, 125, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Jow, T.R.; Amine, K.; Henriksen, G.L. LiPF6–EC–EMC electrolyte for Li-ion battery. J. Power Sources 2002, 107, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanaraj, J.S.; Zinigrad, E.; Levi, M.D.; Aurbach, D.; Schmidt, M. A comparison among LiPF6, LiPF3(CF2CF3)3 (LiFAP), and LiN(SO2CF2CF3)2 (LiBETI) solutions: Electrochemical and thermal studies. J. Power Sources 2003, 119–121, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhuang, G.V.; Ross, P.N., Jr. Thermal stability of LiPF6 salt and Li-ion battery electrolytes containing LiPF6. J. Power Sources 2006, 161, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heider, U.; Oesten, R.; Jungnitz, M. Challenge in manufacturing electrolyte solutions for lithium and lithium ion batteries quality control and minimizing contamination level. J. Power Sources 1999, 81–82, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plakhotnyk, A.V.; Ernst, L.; Schmutzler, R. Hydrolysis in the system LiPF6—propylene carbonate—dimethyl carbonate—H2O. J. Fluorine Chem. 2005, 126, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueguen, A.; Streich, D.; He, M.; Mendez, M.; Chesneau, F.F.; Novak, P.; Berg, E.J. Decomposition of LiPF6 in High Energy Lithium-Ion Batteries Studied with Online Electrochemical Mass Spectrometry. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, B.; Dedryvere, R.; Gorgoi, M.; Rensmo, H.; Gonbeau, D.; Edström, K. Role of the LiPF6 Salt for the Long-Term Stability of Silicon Electrodes in Li-Ion Batteries—A Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McOwen, D.W.; Delp, S.A.; Henderson, W.A. A Thermally Stable Li-ion Battery Electrolyte Using LiTDI. In ECS Meeting Abstracts; MA2013-02; The Electrochemical Society: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2013; p. 1182. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.S.; Xu, K.; Jow, T.R. Tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphite as a co-solvent for nonflammable electrolytes in Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2003, 113, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Naito, H.; Sone, Y.; Segami, G.; Kuwajima, S. New Additives to Improve the First-Cycle Charge–Discharge Performance of a Graphite Anode for Lithium-Ion Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Campion, C.; Lucht, B.L.; Ravdel, B.; DiCarlo, J.; Abraham, K.M. Additives for Stabilizing LiPF6-Based Electrolytes against Thermal Decomposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Coating Material-Induced Acidic Electrolyte Improves LiCoO2 Performances. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2006, 9, A552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Gamolsky, K.; Markovsky, B.; Gofer, Y.; Schmidt, M.; Heider, U. On the use of vinylene carbonate (VC) as an additive to electrolyte solutions for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ufheil, J.; Baertsch, M.C.; Würsig, A.; Novak, P. Maleic anhydride as an additive to γ-butyrolactone solutions for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, R.; Inaba, M.; Jeong, S.K.; Iriyama, Y.; Abe, T.; Ogumia, Z. Effects of Some Organic Additives on Lithium Deposition in Propylene Carbonate. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, A1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.X.; McMillan, R.S.; Murray, J.J.; Davidson, I.J. Use of Chloroethylene Carbonate as an Electrolyte Solvent for a Lithium Ion Battery Containing a Graphitic Anode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, L161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedzicki, L.; Żukowska, G.Z.; Bukowska, M.; Szczeciński, P.; Grugeon, S.; Laruelle, S.; Armand, M.; Panero, S.; Scrosati, B.; Marcinek, M.; et al. New type of imidazole based salts designed specifically for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkrob, I.; Pupek, K.Z.; Gilbert, J.A.; Trask, S.E.; Abraham, D.P. Chemical Stability of Lithium 2-Trifluoromethyl-4,5-dicyanoimidazolide, an Electrolyte Salt for Li-Ion Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 28463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polu, A.R.; Rhee, H.-W.; Kim, D.K. New solid polymer electrolytes (PEO20–LiTDI–SN) for lithium batteries: Structural, thermal and ionic conductivity studies. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 8548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillet, S.; Schmidt, G.; Ladouceur, S.; Frechette, J.; Barray, F.; Clement, D.; Hovington, P.; Guerfi, A.; Vijh, A.; Cayrefourcq, I.; et al. Determination of the electrochemical performance and stability of the lithium-salt, lithium 4,5-dicyano-2-(trifluoromethyl) imidazolide, with various anodes in Li-ion cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 299, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Renault, S.; Ebadi, M.; Wang, Z.; Björklund, E.; Guyomard, D.; Brandell, D.; Edström, K.; Gustafsson, T. LiTDI: A Highly Efficient Additive for Electrolyte Stabilization in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhaut, C.L.; Dedryvere, R.; Timperman, L.; Schmidt, G.; Lemordant, D.; Anouti, M. A new solvent mixture for use of LiTDI as electrolyte salt in Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 305, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S.; Hernández, G.; Wagner, N.P.; Svensson, A.M.; Brandell, D. Modelling capacity fade in silicon-graphite composite electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 377, 138067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillet, S.; Schmidt, G.; Ladouceur, S.; Frechette, J.; Barray, F.; Clement, D.; Hovington, P.; Guerfi, A.; Vijh, A.; Cayrefourcq, I.; et al. Power capability of LiTDI-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 294, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownrigg, A.W.; Mountjoy, G.; Chadwick, A.V.; Alfredsson, M.; Bras, W.; Billaud, J.; Armstrong, A.R.; Bruce, P.G.; Dominko, R.; Kelder, E.M. In situ Fe K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy study during cycling of Li2FeSiO4 and Li2.2Fe0.9SiO4 Li ion battery materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, F.; Xu, C.; Niedzicki, L.; Marcinek, M.; Gustafsson, T.; Björefors, F.; Edström, K.; Younesi, R. SEI Formation and Interfacial Stability of a Si Electrode in a LiTDI-Salt Based Electrolyte with FEC and VC Additives for Li-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgren, F.; Rehnlund, D.; Pan, R.; Pettersson, J.; Younesi, R.; Xu, C.; Gustafsson, T.; Edström, K.; Nyholm, L. On the Capacity Losses Seen for Optimized Nano-Si Composite Electrodes in Li-Metal Half-Cells. Adv. Energy Matter. 2019, 9, 1901608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedzicki, L.; Karpierz, E.; Bitner, A.; Kasprzyk, M.; Zukowska, G.Z.; Marcinek, M.; Wieczorek, W. Optimization of the lithium-ion cell electrolyte composition through the use of the LiTDI salt. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 117, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Tow, D.; Peled, E.; Burstein, L. A Study of Highly Oriented Pyrolytic Graphite as a Model for the Graphite Anode in Li-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chusid, O.Y.; Ely, E.E.; Aurbach, D.; Babai, M.; Carmeli, Y. Electrochemical and spectroscopic studies of carbon electrodes in lithium battery electrolyte systems. J. Power Sources 1993, 43, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassol, H.; Buthker, J.W.; Ferguson, G.A.; Curtiss, L.A.; Gewirth, A.A. Solvent Oligomerization during SEI Formation on Model Systems for Li-Ion Battery Anodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michan, A.L.; Parimalam, B.S.; Leskes, M.; Kerber, R.N.; Yoon, T.; Grey, C.P.; Lucht, B.L. Fluoroethylene Carbonate and Vinylene Carbonate Reduction: Understanding Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolyte Additives and Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formation. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, H.; Sakata, Y.; Inoue, A.; Yamaguchi, S. Analysis of Vinylene Carbonate Derived SEI Layers on Graphite Anode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkrob, I.A.; Wishart, J.F.; Abraham, D.P. What Makes Fluoroethylene Carbonate Different? J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 14954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaumann, T.; Balach, J.; Langklotz, U.; Sauchuk, V.; Fritsch, M.; Michaelis, A.; Teltevskij, V.; Mikhailova, D.; Oswald, S.; Klose, M.; et al. Lifetime vs. rate capability: Understanding the role of FEC and VC in high-energy Li-ion batteries with nano-silicon anodes. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Anouti, M.; Caillon-Caravanier, M.; Willmann, P.; Lemordant, D. Thermodynamic of LiF dissolution in alkylcarbonates and some of their mixtures with water. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2009, 285, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedzicki, L.; Kasprzyk, M.; Kuziak, K.; Żukowska, G.Z.; Marcinek, M.; Wieczorek, W.; Armand, M. Liquid electrolytes based on new lithium conductive imidazole salts. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, R.; Slegr, H.; Shu, Z.X.; Wang, W. Fluoroethylene carbonate electrolyte and its use in lithium ion batteries with graphite anodes. J. Power Sources 1999, 81–82, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profatilova, I.A.; Kim, S.-S.; Choi, N.-S. Enhanced thermal properties of the solid electrolyte interphase formed on graphite in an electrolyte with fluoroethylene carbonate. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lindgren, F.; Philippe, B.; Gorgoi, M.; Björefors, F.; Edström, K.; Gustafsson, T. Improved Performance of the Silicon Anode for Li-Ion Batteries: Understanding the Surface Modification Mechanism of Fluoroethylene Carbonate as an Effective Electrolyte Additive. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Yang, G.; Rajput, N.N.; Self, J.; Park, S.-W.; Nanda, J.; Persson, K.A. The influence of FEC on the solvation structure and reduction reaction of LiPF6/EC electrolytes and its implication for solid electrolyte interphase formation. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Han, X.; Xiang, Y.; Zhong, G.; Wang, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y. Identification of the Solid Electrolyte Interface on the Si/C Composite Anode with FEC as the Additive. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Ohtsuka, H.; Akuto, K.; Sakurai, Y. Confirmation of Long-Term Cyclability and High Thermal Stability of LiFePO4 in Prismatic Lithium-Ion Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, L.J.; Marcinek, M.; Beer, L.; Kerr, J.B.; Kostecki, R. An Investigation of the Effect of Graphite Degradation on Irreversible Capacity in Lithium-ion Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, A442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Cao, Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, H.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Capacity fade of LiFePO4/graphite cell at elevated temperature. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2013, 17, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, C.L.; Li, W.; Lucht, B.L. Thermal Decomposition of LiPF6-Based Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.P.C.; Okasinski, J.S.; Kalaga, K.; Shkrob, I.A.; Abraham, D.P. Quantifying lithium concentration gradients in the graphite electrode of Li-ion cells using operando energy dispersive X-ray diffraction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.M.; Herstedt, M.; Bishop, A.G.; Edström, K. The influence of lithium salt on the interfacial reactions controlling the thermal stability of graphite anodes. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Anouti, M.; Caillon-Caravanier, M.; Willmann, P.; Sizaret, P.-Y.; Lemordant, D. Solubilization of SEI lithium salts in alkylcarbonate solvents. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2011, 305, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Huang, J.; Peng, X.; Cao, D.; Galaska, A.; Qiu, S.; Liu, J.; Khan, M.A.; Joung, D.P.; Ryu, J.E.; et al. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) derived fluorine-doped magnetic carbon nanoadsorbents for enhanced chromium removal. Carbon 2017, 115, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, P.; Sobola, D.; Částková, K.; Knápek, A.; Burda, D.; Orudzhev, F.; Dallaev, R.; Tofel, P.; Trčka, T.; Grmela, L.; et al. Characterization of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Electrospun Fibers Doped by Carbon Flakes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Park, I.; Ha, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Woo, M.-H.; Jeong, M.-H.; Shin, W.C.; Ue, M.; Hong, S.Y.; Choi, N.-S. Understanding the thermal instability of fluoroethylene carbonate in {LiPF6}-based electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 225, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufl, T.; Pritzl, D.; Hartmann, L.; Solchenbach, S.; Mendez, M.A.; Gasteiger, H.A. Implications of the thermal stability of FEC-based electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 020531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhaut, C.L.; Porion, P.; Timperman, L.; Schmidt, G.; Lemordant, D.; Anouti, M. LiTDI as electrolyte salt for Li-ion batteries: Transport properties in EC/DMC. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 180, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.S.; Jow, T.R. Conductivity and Viscosity of PC-DEC and PC-EC Solutions of LiPF6. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, A620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.A. A nonlinear least squares fit procedure for analysis of immittance data of electrochemical systems. Solid State Ionics 1986, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Broszkiewicz, M.; Brzozowski, B.; Trzeciak, T.; Zalewska, A.; Ryl, J.; Niedzicki, L. Imidazole-Based Lithium Salt LiHDI as a Solid Electrolyte Interphase-Stabilising Additive for Lithium-Conducting Electrolytes. Molecules 2024, 29, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040804
Broszkiewicz M, Brzozowski B, Trzeciak T, Zalewska A, Ryl J, Niedzicki L. Imidazole-Based Lithium Salt LiHDI as a Solid Electrolyte Interphase-Stabilising Additive for Lithium-Conducting Electrolytes. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040804
Chicago/Turabian StyleBroszkiewicz, Marek, Bartosz Brzozowski, Tomasz Trzeciak, Aldona Zalewska, Jacek Ryl, and Leszek Niedzicki. 2024. "Imidazole-Based Lithium Salt LiHDI as a Solid Electrolyte Interphase-Stabilising Additive for Lithium-Conducting Electrolytes" Molecules 29, no. 4: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040804
APA StyleBroszkiewicz, M., Brzozowski, B., Trzeciak, T., Zalewska, A., Ryl, J., & Niedzicki, L. (2024). Imidazole-Based Lithium Salt LiHDI as a Solid Electrolyte Interphase-Stabilising Additive for Lithium-Conducting Electrolytes. Molecules, 29(4), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040804