Optimizing Analysis Methods: Rapid and Accurate Determination of Cuaminosulfate Residues with LC-MS/MS Based on Box–Behnken Design Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.2. Optimization of Chromatography
2.3. Optimization of Column
2.4. Optimization of Extraction and Cleanup Procedure
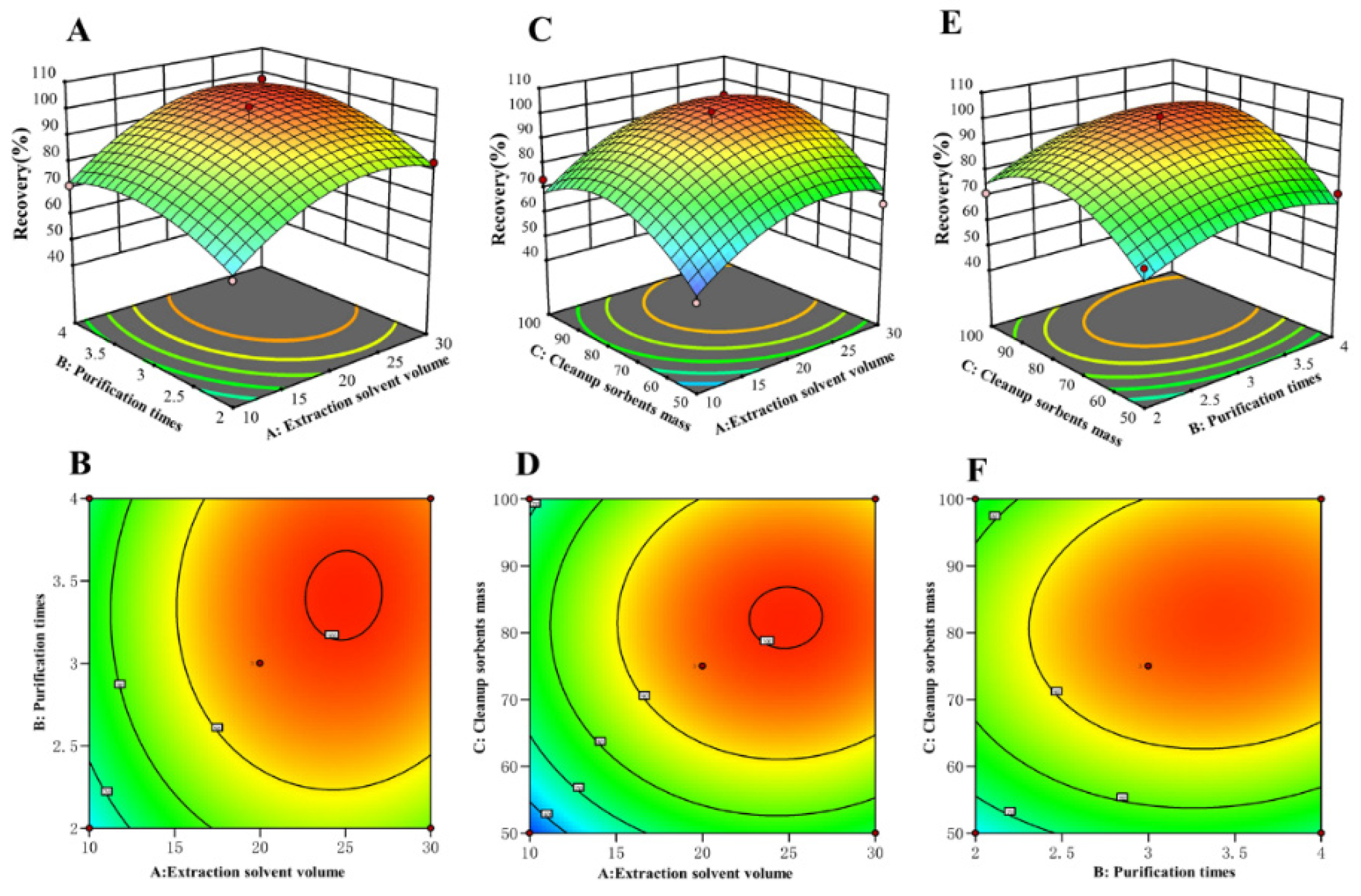
2.5. BBD Studies
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. Dissipation and Terminal Residue of Cuaminosulfate under Field Conditions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Chemicals
3.2. Standard Solution Preparation
3.3. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Conditions
3.4. Sample Preparation
3.5. Field Trial Design and Sample Collection
3.6. Method Validation
3.7. Statistical Analysis
3.7.1. Matrix Effect and Recovery
3.7.2. Dissipation Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorokina, M.; McCaffrey, K.S.; Deaton, E.E.; Ma, G.Y.; Ordovás, J.M.; Perkins-Veazie, P.M.; Steinbeck, C.; Levi, A.; Parnell, L.D. A Catalog of Natural Products Occurring in Watermelon—Citrullus lanatus. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 729822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivannan, A.; Lee, E.S.; Han, K.; Lee, H.E.; Kim, D. Versatile Nutraceutical Potentials of Watermelon—A Modest Fruit Loaded with Pharmaceutically Valuable Phytochemicals. Molecules 2020, 25, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. World Food and Agriculture—Statistical Yearbook 2022; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shamary, N.M.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Al-Shaikh, I.; Al-Meer, S.H.; Ahmad, T.A. Evaluation of pesticide residues of organochlorine in vegetables and fruits in Qatar: Statistical analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.; Han, L.; Wang, Q.; Kong, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.; Shen, Y.; Gao, G.; et al. Determination and risk assessment of 31 pesticide residues in apples from China’s major production regions. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 118, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, V.; Eslami, Z.; Molaee-Aghaee, E.; Peivasteh-Roudsari, L.; Sadighara, P.; Van Nam, T.; Fakhri, Y.; Ravanlou, A.A. Evaluation of pesticide residues and risk assessment in apple and grape from western Azerbaijan Province of Iran. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, J.R.; Osdaghi, E.; Behlau, F.; Köhl, J.; Jones, J.B.; Aubertot, J.N. Thirteen decades of antimicrobial copper compounds applied in agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, E.M. Antifouling: Regulation of biocides in the UK before and after Brexit. Mar. Policy 2018, 92, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capinera, J.L.; Dickens, K. Some effects of copper-based fungicides on plant-feeding terrestrial molluscs: A role for repellents in mollusc management. Crop Prot. 2016, 83, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, J.; Cantrell, F.L. Death by Copper Ammonium Complex-Containing Fungicide. Am. J. Foren. Med. Path 2021, 42, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celar, F.A.; Kos, K. In vitro compatibility of strain ATCC 74040 with copper fungicides. J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 144, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giller, K.E.; Witter, E.; McGrath, S.P. Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: A review. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1389–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauert, S.; Knauer, K. The role of reactive oxygen species in copper toxicity to two freshwater green algae. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, L.; Thuerig, B.; Apostolov, S.; Blogg, H.; Borgo, E.; Corneo, P.E.; Fittje, S.; de Palma, M.; Donko, A.; Experton, C.; et al. Use of Copper-Based Fungicides in Organic Agriculture in Twelve European Countries. Agronomy 2022, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, Z. Degradation Dynamics of Cuaminosul-Fate in Tobacco and Soil. Henan Sci. 2016, 34, 1444–1447. [Google Scholar]
- Syrgabek, Y.; Alimzhanova, M. Modern Analytical Methods for the Analysis of Pesticides in Grapes: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Curbelo, M.Á.; Varela-Martínez, D.A.; Riaño-Herrera, D.A. Pesticide-residue analysis in soils by the QuEChERS method: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, S.; Muzammil, K.; Nasir, N.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, M.F.; Khalid, M.; Ahmad, W.; Dawria, A.; Reddy, L.K.; Busayli, A.M. Advancement and new trends in analysis of pesticide residues in food: A comprehensive review. Plants 2022, 11, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picó, Y.; Blasco, C.; Font, G. Environmental and food applications of LC–tandem mass spectrometry in pesticide-residue analysis: An overview. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2004, 23, 45–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Shan, W.; Zheng, Y. Simultaneous determination of five pyrazole fungicides in cereals, vegetables and fruits using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1262, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dong, F.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Kong, Z.; Chen, X.; Liang, X.; Zheng, Y. Simultaneous enantioselective determination of triazole fungicides in soil and water by chiral liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1224, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brookhart, A.; Arora, M.; McCullagh, M.; Wilson, I.D.; Plumb, R.S.; Vissers, J.P.C.; Tanna, N. Understanding mobile phase buffer composition and chemical structure effects on electrospray ionization mass spectrometry response. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1696, 463966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, N.; Miyazaki, S.; Ohira, M.; Tanaka, N.; Felinger, A. Comparison of the kinetic performance of different columns for fast liquid chromatography, emphasizing the contributions of column end structure. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1473, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumberg, L.M. Methodology of quantitative comparison of practically achievable kinetic performance of differently structured liquid chromatography columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1672, 463039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehotay, S.J.; Son, K.A.; Kwon, H.; Koesukwiwat, U.; Fu, W.S.; Mastovska, K.; Hoh, E.; Leepipatpiboon, N. Comparison of QuEChERS sample preparation methods for the analysis of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2548–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Qiao, H.O.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.L.; Xia, X.D. Determination of nitrofurans metabolites residues in aquatic products by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu-Ping, Z.; Lin, M.; Lan-Qi, H.; Jian-Bo, C.; Li, Z. The optimization and establishment of QuEChERS-UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneously detecting various kinds of pesticides residues in fruits and vegetables. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1060, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, T.K.; Ho, T.D.; Behra, P.; Nhu-Trang, T.T. Determination of 400 pesticide residues in green tea leaves by UPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS combined with QuEChERS extraction and mixed-mode SPE clean-up method. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Li, J.Z. Determination of forchlorfenuron residues in watermelon by solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Duan, H.L.; Ma, S.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.Q. Solidification of a Switchable Solvent-Based QuEChERS Method for Detection of 16 Pesticides in Some Fruits and Vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8045–8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manirakiza, P.; Covaci, A.; Schepens, P. Improved analytical procedure for determination of chlorinated pesticide residues in human serum using solid phase disc extraction (SPDE), single-step clean-up and gas chromatography. Chromatographia 2002, 55, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Huang, J.; Cai, J.; Yu, C.; Jiang, S.; Ye, Q.; Yang, S.; Pan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Microwave-ultrasonic technique development coupled with natural deep eutectic solvents in anthocyanin extraction from perilla leaves (Perilla frutescens var. Acuta). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 3006–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Kaw, H.Y.; Zhao, J.; Zou, Y.; He, M.; Li, Z.; Li, D. NLow matrix effect pretreatment method based on gas-liquid micro-extraction technique for determining multi-class pesticides in crops. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1675, 463178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.L.; Olomukoro, A.A.; Emmons, R.V.; Goodage, N.H.; Gionfriddo, E. Matrix effects demystified: Strategies for resolving challenges in analytical separations of complex samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, e2300571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Qiao, T.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D. Dissipation and safety evaluation of afidopyropen and its metabolite residues in supervised cotton field. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Liu, X. Dissipation behavior, residues distribution and dietary risk assessment of tembotrione and its metabolite in maize via QuEChERS using HPLC-MS/MS technique. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M.; Pena-Pereira, F.; Psillakis, E. AGREEprep—Analytical Greenness Metric for Sample Preparation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 149, 116553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalia, M.; Wojciech, W.; Justyna, P.; Victoria, S. Blue applicability grade index (BAGI) and software: A new tool for the evaluation of method practicality. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 7598. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska, M.; Lozowicka, B. The processing factors of canning and pasteurization for the most frequently occurring fungicides and insecticides in apples and their application into dietary risk assessment. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Liu, Y.N.; Fan, B.; Lu, J.; He, Y.; Kong, Z.Q.; Zhu, Y.L.; Jian, Q.; Wang, F.Z. A chemometric processing-factor-based approach to the determination of the fates of five pesticides during apple processing. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 31270.1-2014; Test Guidelines for Environmental Safety Evaluation of Chemical Pesticides Part 4: Soil Adsorption/Deabsorption. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Zhao, J.L.; Tan, Z.H.; Wen, Y.; Fan, S.; Liu, C.L. Dissipation of fluazinam in citrus groves and a risk assessment for its dietary intake. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2052–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
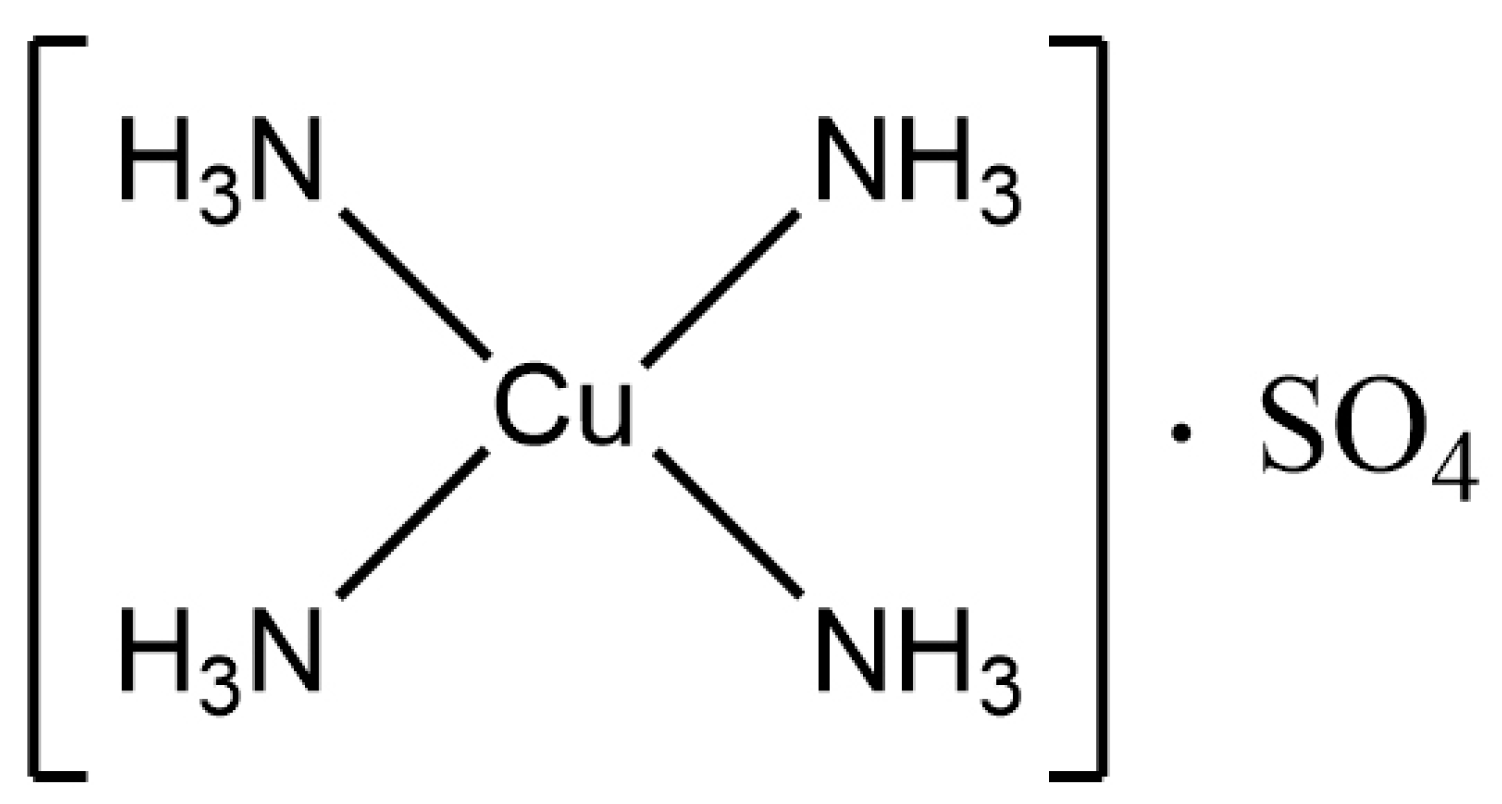
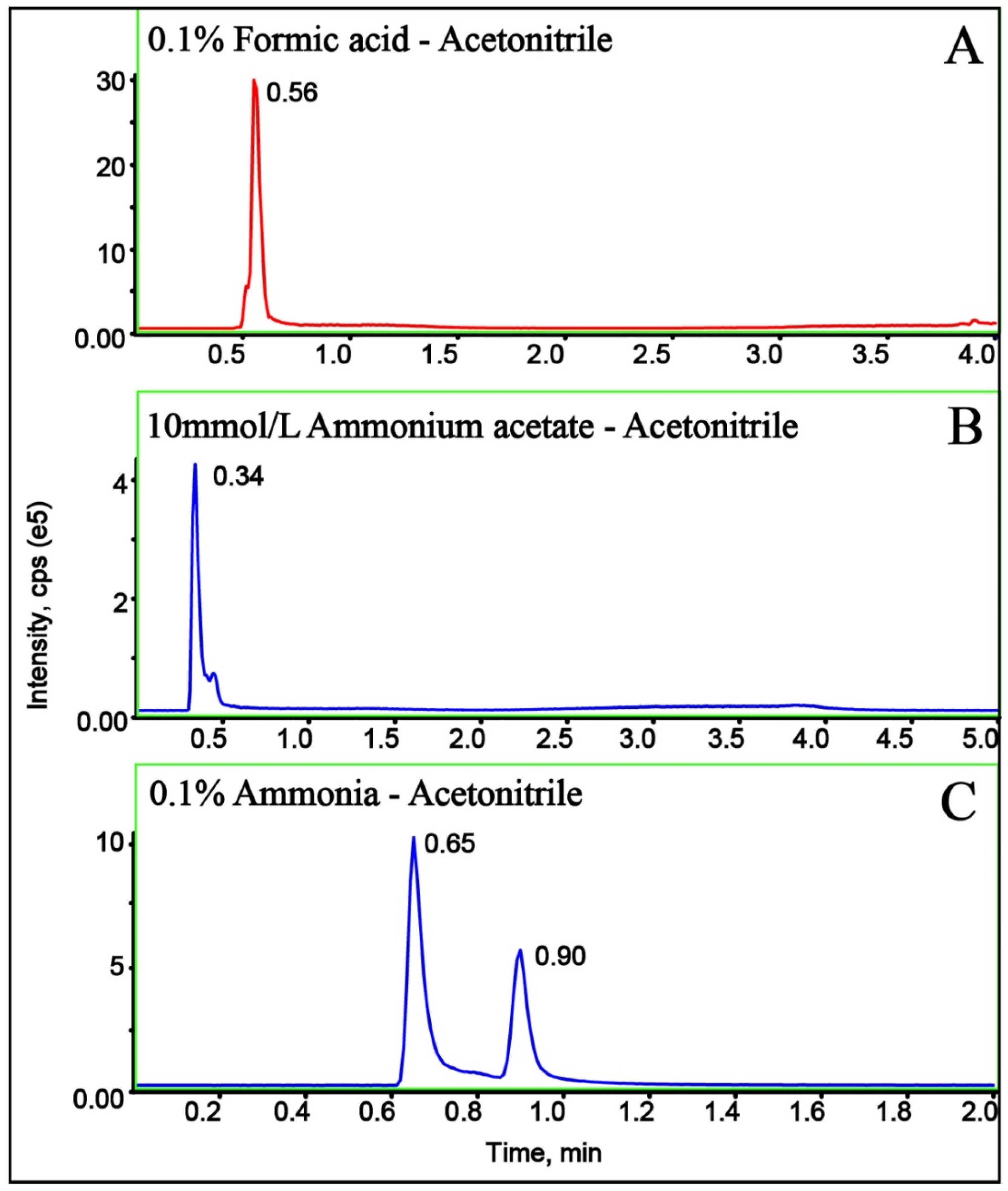
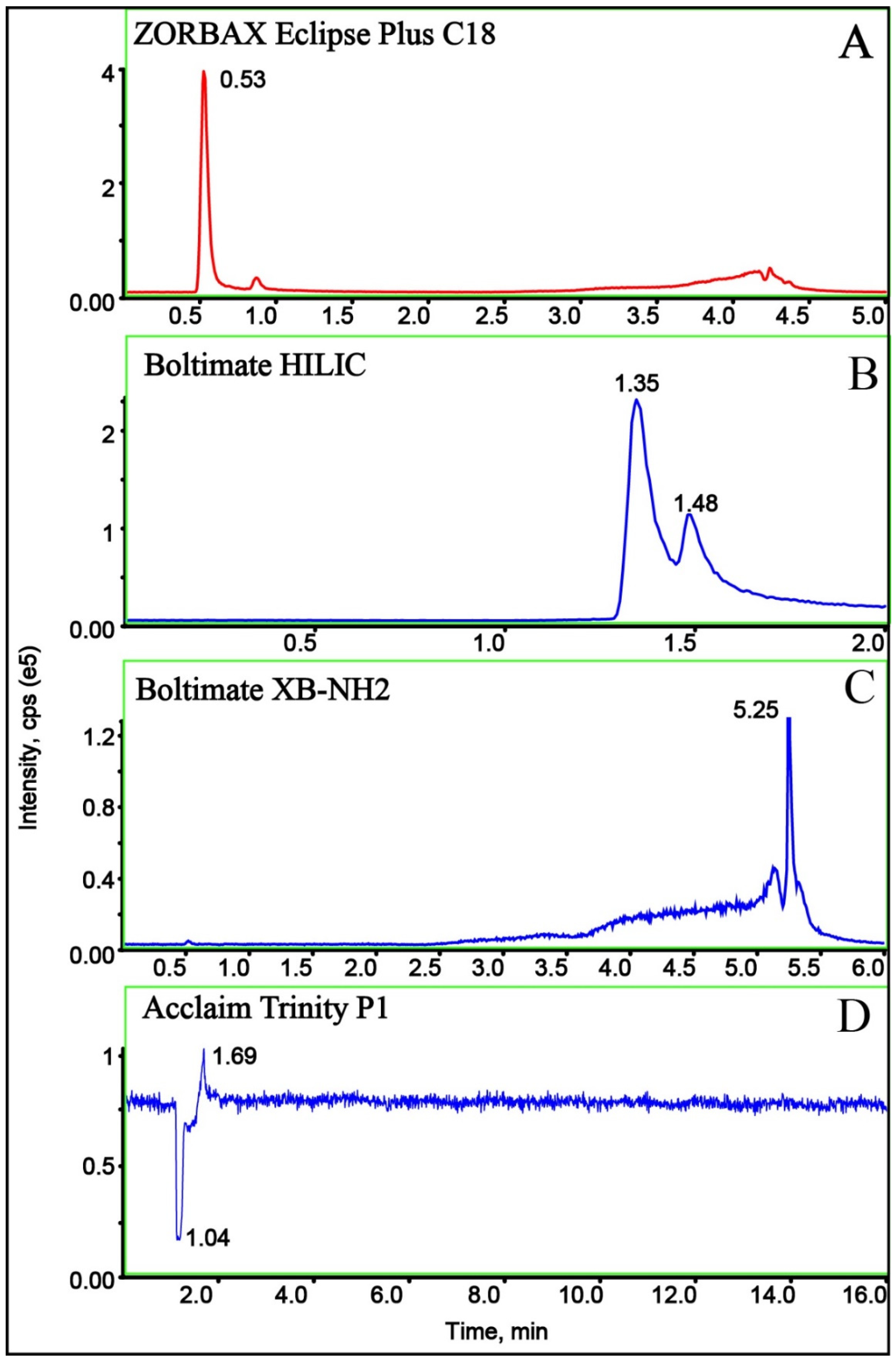
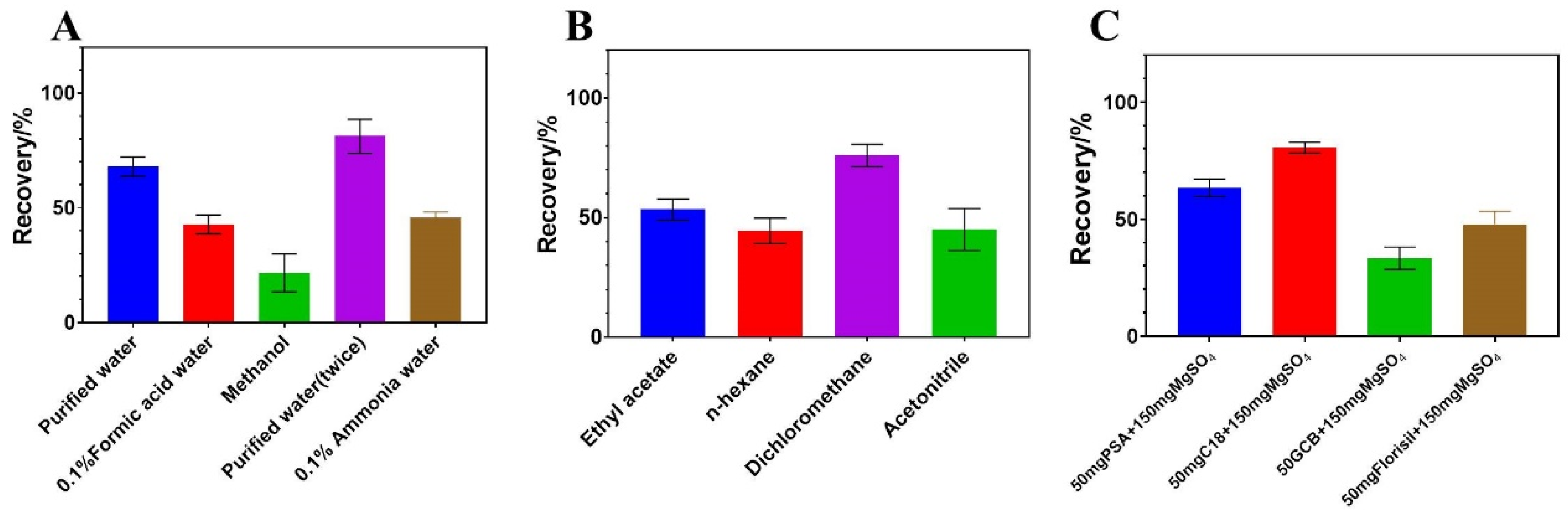

| MW | tR (min) | DP (V) | Quantification Ion Transition | CE1 (eV) | Diagnostic Ion Transition | CE2 (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 131.67 | 0.51 | 67/65 | 131.9→104.0 | 10 | 131.9→122.0 | 6 |
| Matrix | Calibration Curve | R2 | Matrix Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1% Ammonium hydroxide | y = 1,699,198.0640x + 19,444.5177 | 0.9991 | - |
| Watermelon | y = 105,377.7778x + 4980.2778 | 0.9998 | −93.8 |
| Soil | y = 736,731.1573x +5217.1344 | 0.9981 | −56.6 |
| Sample | Spiked Level (mg/kg) | Intra-Day Recovery (%) | RSDr (%) | Inter-Day Recovery (%) | RSDR (%) | LOQ (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Watermelon | 0.05 | 95.1 | 5.3 | 88.3 | 6.3 | 0.05 |
| 0.5 | 79.6 | 5.4 | 93.2 | 9.4 | ||
| 1 | 80.0 | 9.9 | 89.4 | 4.9 | ||
| 2 | 88.3 | 6.5 | 101.1 | 3.5 | ||
| Soil | 0.05 | 93.1 | 6.3 | 92.4 | 7.3 | 0.05 |
| 0.5 | 88.5 | 7.4 | 87.5 | 4.1 | ||
| 5 | 80.8 | 7.8 | 83.9 | 4.9 | ||
| 20 | 81.1 | 3.4 | 801.3 | 6.7 |
| Fujian | Guangxi | Shanxi | Anhui | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection Points | Residue (mg/kg) | Degradation Rate | Residue (mg/kg) | Degradation Rate | Residue (mg/kg) | Degradation Rate | Residue (mg/kg) | Degradation Rate | ||||||||
| 1 | 2 | Mean | (%) | 1 | 2 | Mean | (%) | 1 | 2 | Mean | (%) | 1 | 2 | Mean | (%) | |
| 0 | 8.4 | 9.8 | 9.1 | - | 12.8 | 7.6 | 10.2 | - | 3.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | - | 11.0 | 8.0 | 9.5 | - |
| 7 | 6.7 | 8.1 | 7.4 | 18.9 | 9.6 | 7.4 | 8.5 | 16.6 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 49.8 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 6.5 | 31.5 |
| 14 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 77.3 | 4.1 | 7.1 | 5.6 | 45.3 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 62.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 47.3 |
| 21 | 2.6 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 74.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 75.2 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 37.8 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 78.8 |
| 28 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 91.6 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 85.1 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 50.3 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 73.7 |
| Regression Equation | Y = 9.640−0.07386x | Y = 10.85−0.05616x | - | Y = 9.581−0.05508x | ||||||||||||
| R2 | 0.8856 | 0.7615 | - | 0.8734 | ||||||||||||
| T1/2(d) | 9.4 | 12.3 | - | 12.6 | ||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mao, L.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, C. Optimizing Analysis Methods: Rapid and Accurate Determination of Cuaminosulfate Residues with LC-MS/MS Based on Box–Behnken Design Study. Molecules 2024, 29, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040794
He M, Wang Y, Zhang L, Mao L, Zhu L, Zheng Y, Liu X, Wu C. Optimizing Analysis Methods: Rapid and Accurate Determination of Cuaminosulfate Residues with LC-MS/MS Based on Box–Behnken Design Study. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040794
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Mingyuan, Yuzhu Wang, Lan Zhang, Liangang Mao, Lizhen Zhu, Yongquan Zheng, Xingang Liu, and Chi Wu. 2024. "Optimizing Analysis Methods: Rapid and Accurate Determination of Cuaminosulfate Residues with LC-MS/MS Based on Box–Behnken Design Study" Molecules 29, no. 4: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040794
APA StyleHe, M., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Mao, L., Zhu, L., Zheng, Y., Liu, X., & Wu, C. (2024). Optimizing Analysis Methods: Rapid and Accurate Determination of Cuaminosulfate Residues with LC-MS/MS Based on Box–Behnken Design Study. Molecules, 29(4), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040794








