Figure 1.
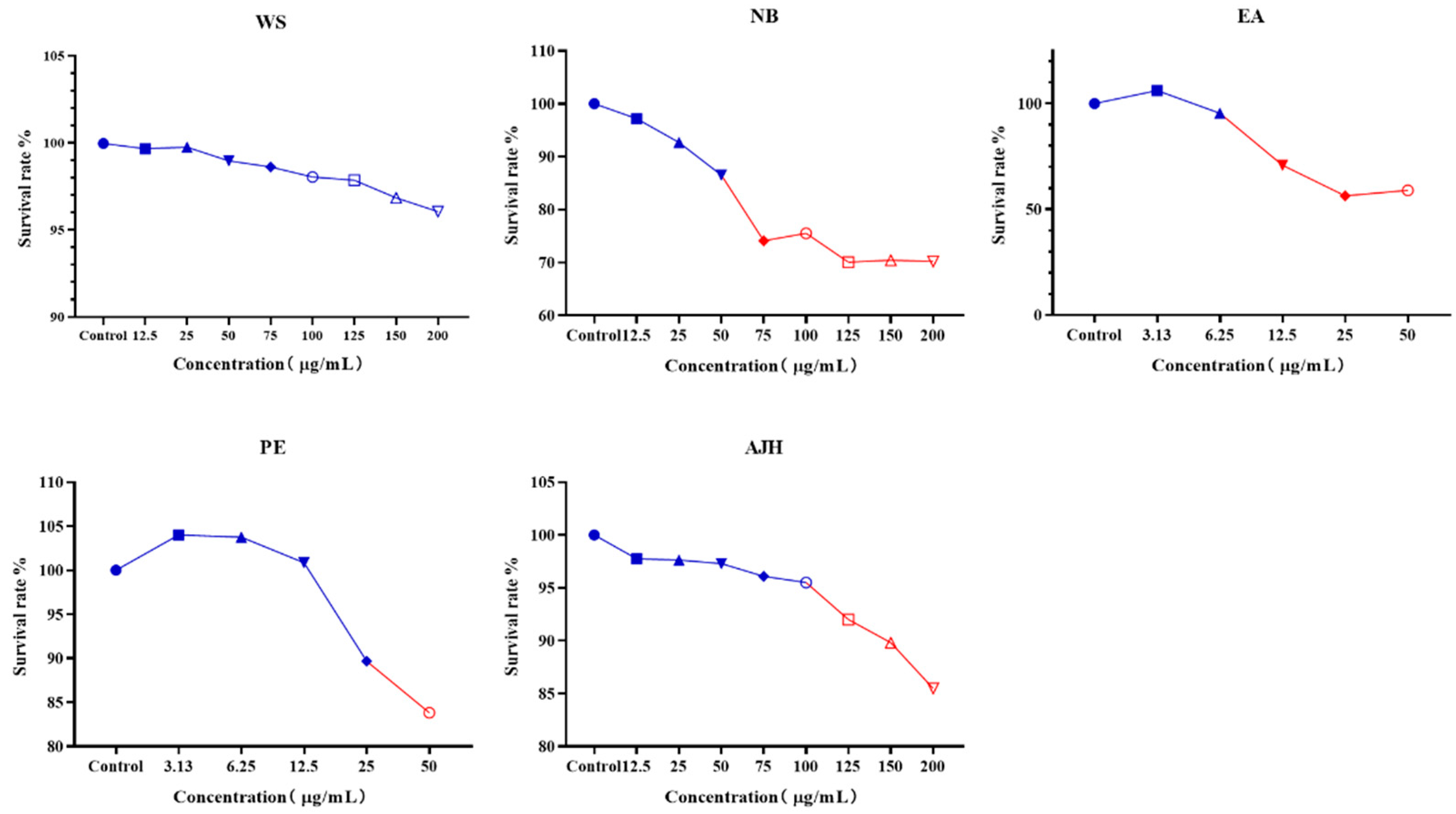
The non-toxic concentration results of different extraction parts of AJH on MH-S cells ( ± SD, n = 8). The color in blue represent the safe concentration and the red illucidate the harmful concentration. The shape of the points represent always the same mean.
Figure 1.
The non-toxic concentration results of different extraction parts of AJH on MH-S cells ( ± SD, n = 8). The color in blue represent the safe concentration and the red illucidate the harmful concentration. The shape of the points represent always the same mean.
Figure 2.
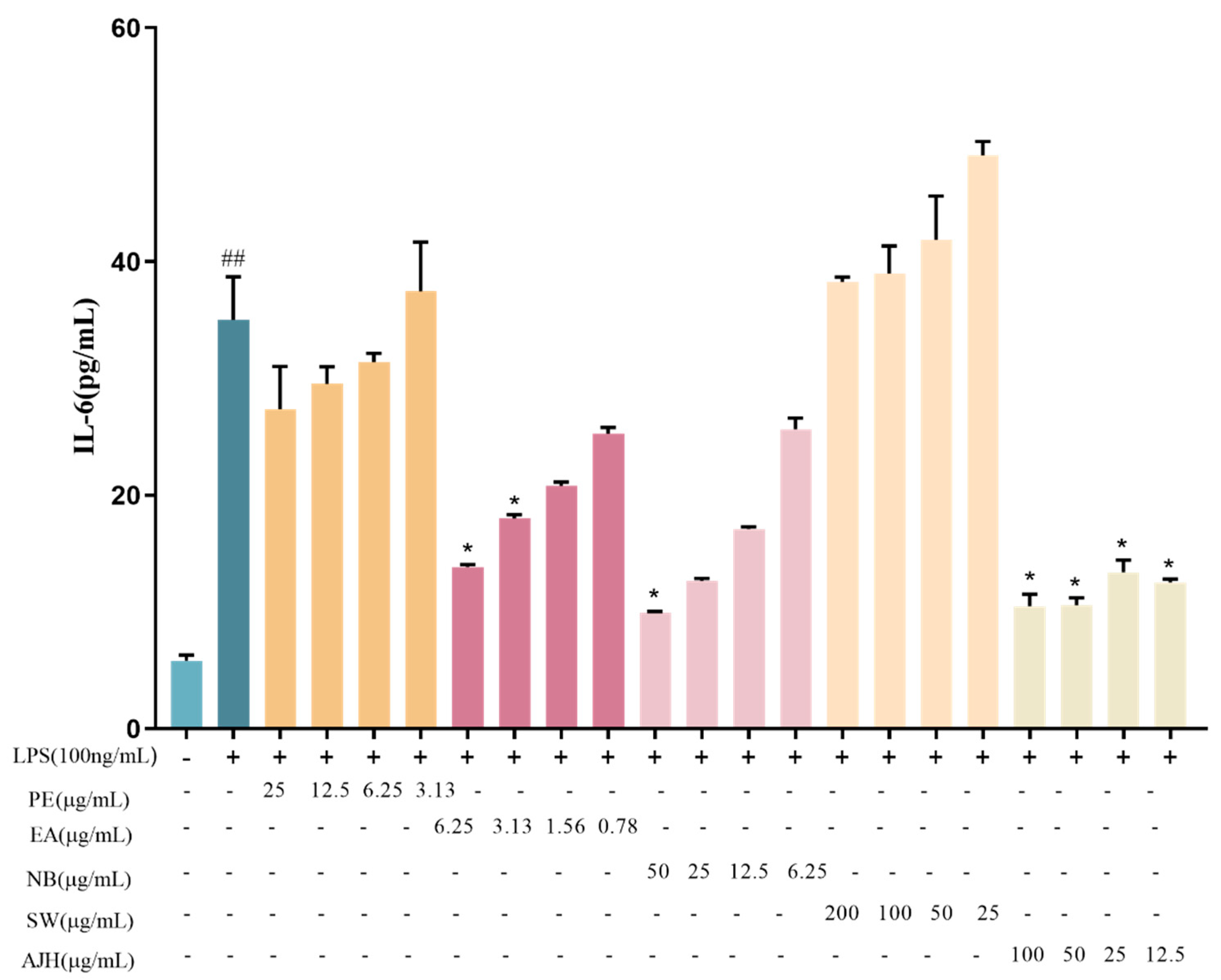
Effects of AJH and different extraction sites on the expression level of IL-6 in MH-S cells ( ± SD, n = 6). Note: compared with the blank group: ## p < 0.01; compared with the model group: * p < 0.05. Each color represents a test group, such as PE, EA, NB, WS and AJH.
Figure 2.
Effects of AJH and different extraction sites on the expression level of IL-6 in MH-S cells ( ± SD, n = 6). Note: compared with the blank group: ## p < 0.01; compared with the model group: * p < 0.05. Each color represents a test group, such as PE, EA, NB, WS and AJH.
Figure 3.
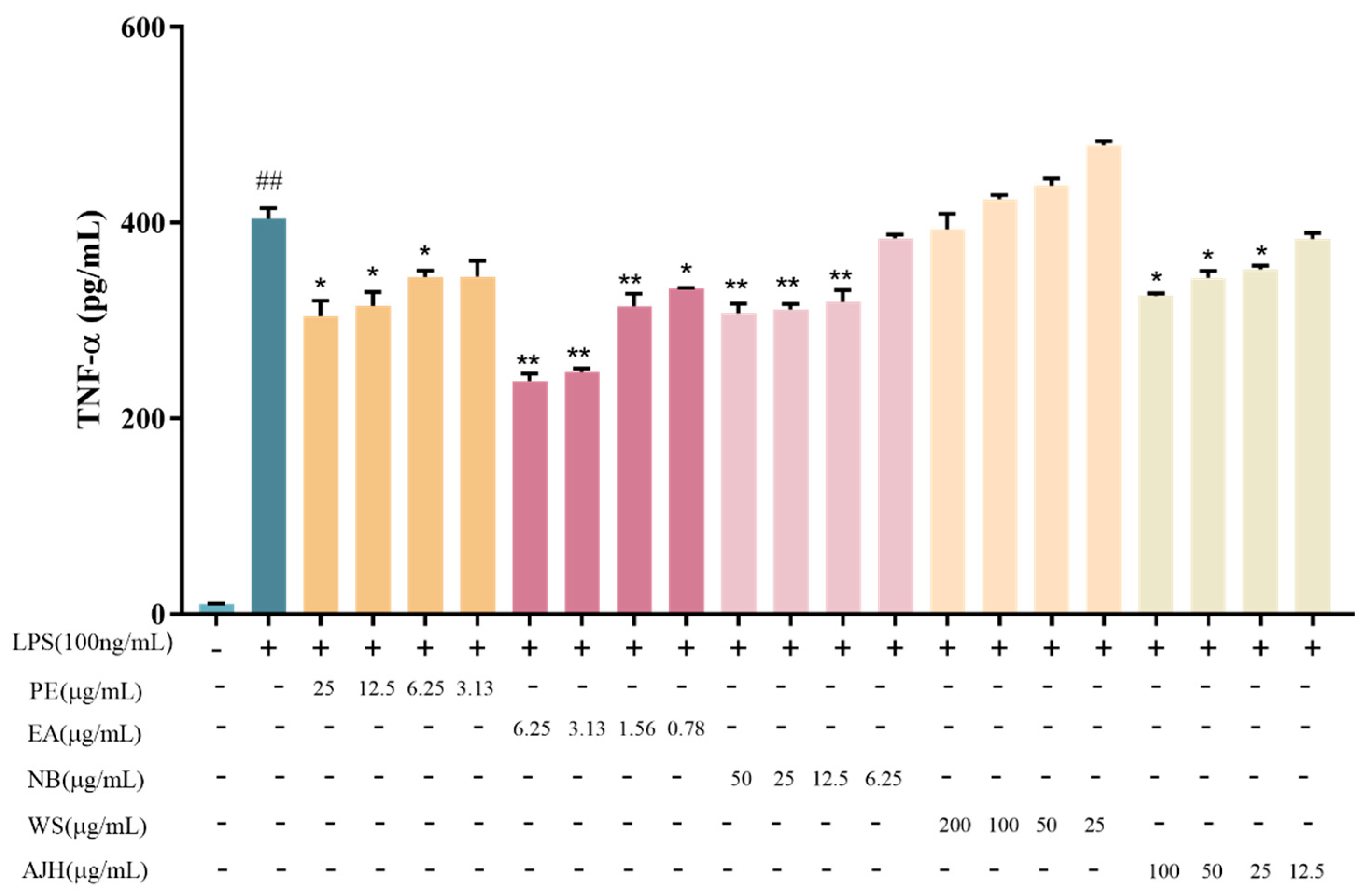
Effects of AJH and different extraction sites on the expression level of TNF-α in MH-S cells ( ± SD, n = 6). Note: compared with the blank group: ## p < 0.01; compared with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Each color represents a test group, such as PE, EA, NB, WS and AJH.
Figure 3.
Effects of AJH and different extraction sites on the expression level of TNF-α in MH-S cells ( ± SD, n = 6). Note: compared with the blank group: ## p < 0.01; compared with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Each color represents a test group, such as PE, EA, NB, WS and AJH.
Figure 4.
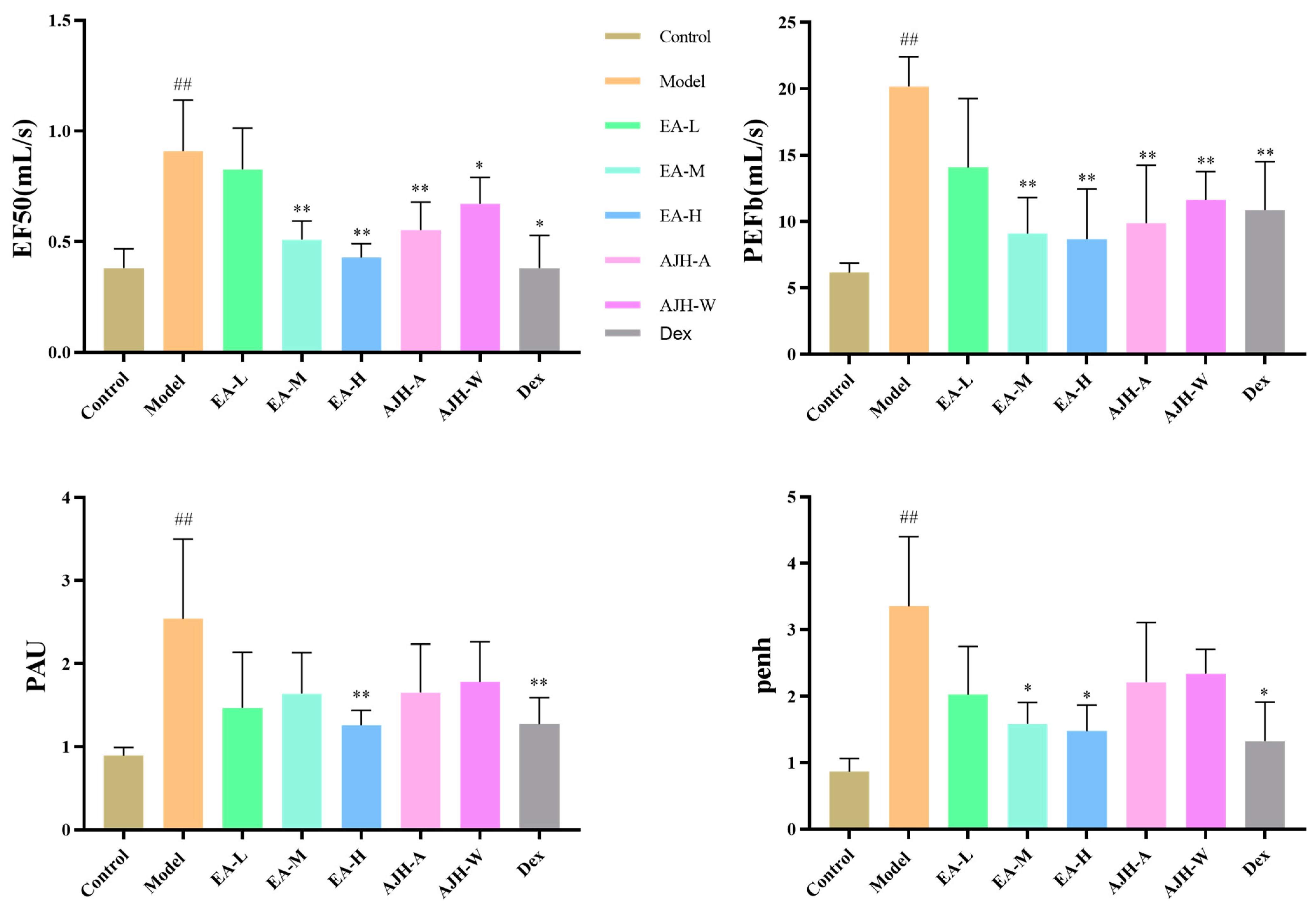
Effects of EA of AJH on the lung function of ALI model rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: ## p < 0.01; comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group, EA-L: EA low-dose group; EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: AJH 70% alcohol extract group, AJH-W: AJH aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
Figure 4.
Effects of EA of AJH on the lung function of ALI model rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: ## p < 0.01; comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group, EA-L: EA low-dose group; EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: AJH 70% alcohol extract group, AJH-W: AJH aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
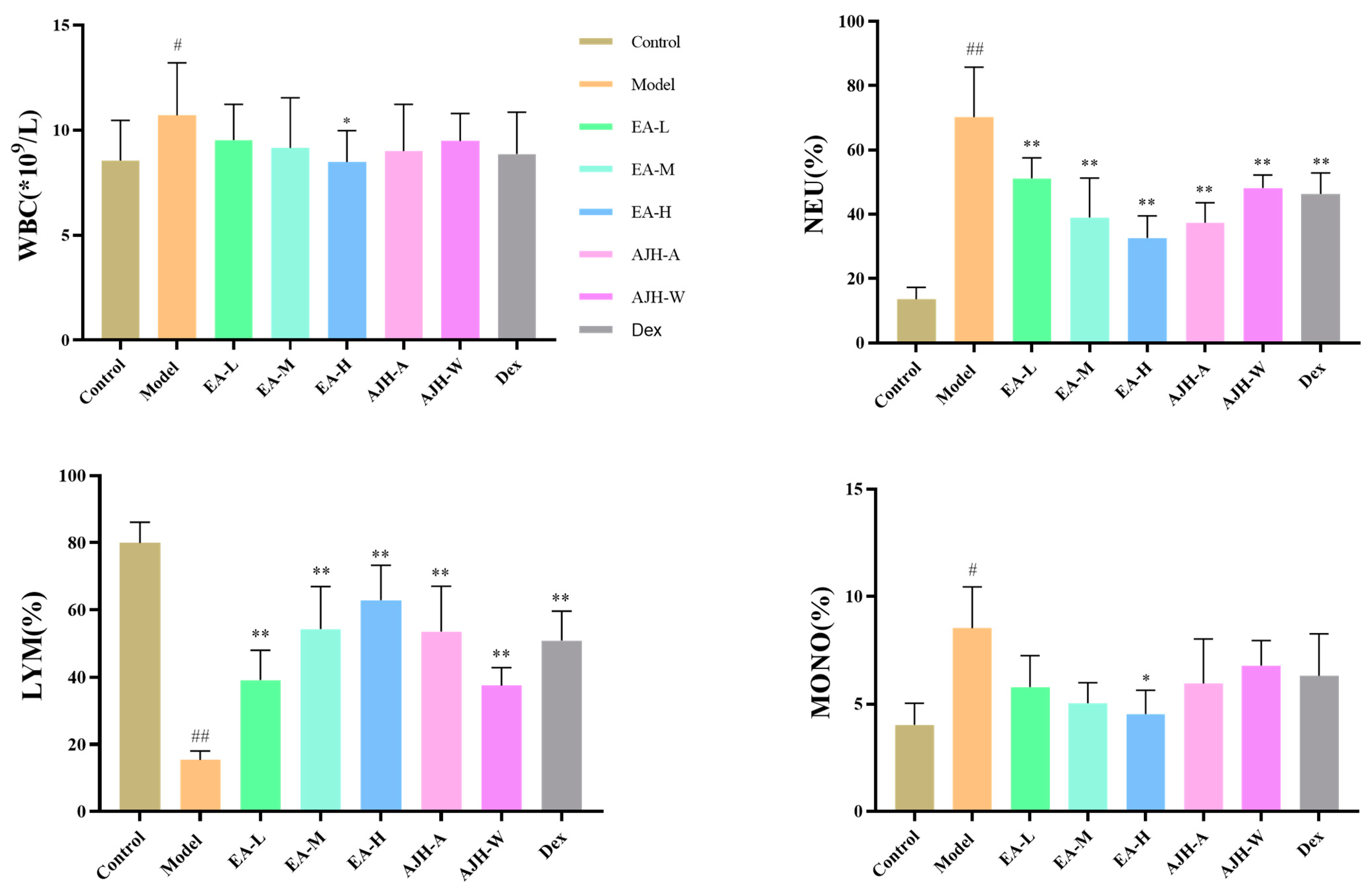
Figure 5.
Effects of the EA site of AJH on the blood routine of ALI model rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01; comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group, EA-L: EA low-dose group, EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: AJH 70% alcohol extract group, AJH-W: AJH aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
Figure 5.
Effects of the EA site of AJH on the blood routine of ALI model rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01; comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group, EA-L: EA low-dose group, EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: AJH 70% alcohol extract group, AJH-W: AJH aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
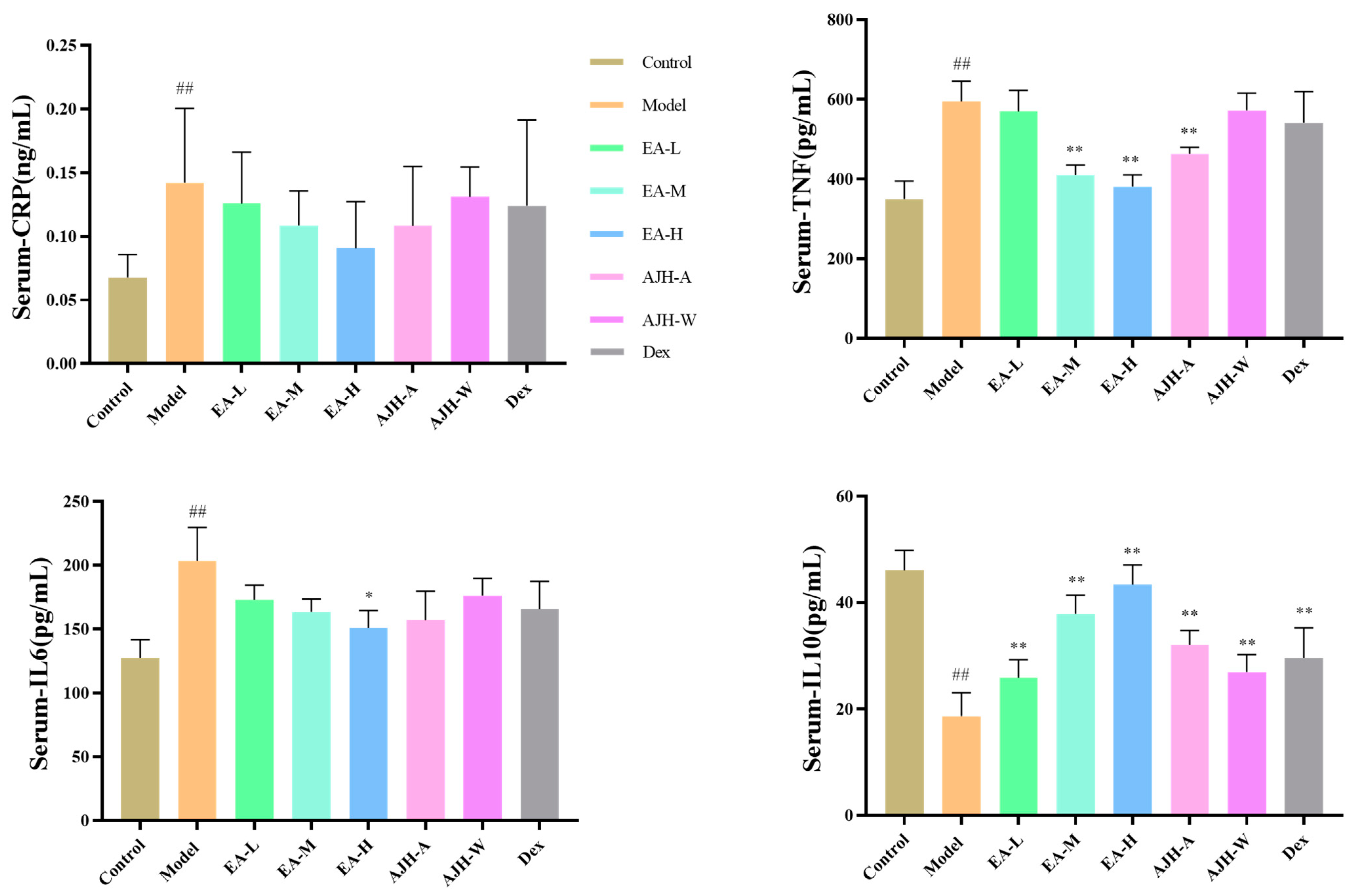
Figure 6.
Effects of the EA site of AJH on serum levels of CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in ALI model rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: ## p < 0.01, comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group; EA-L: EA low-dose group, EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: AJH 70% alcohol extract group, AJH-W: AJH aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
Figure 6.
Effects of the EA site of AJH on serum levels of CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in ALI model rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: ## p < 0.01, comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group; EA-L: EA low-dose group, EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: AJH 70% alcohol extract group, AJH-W: AJH aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
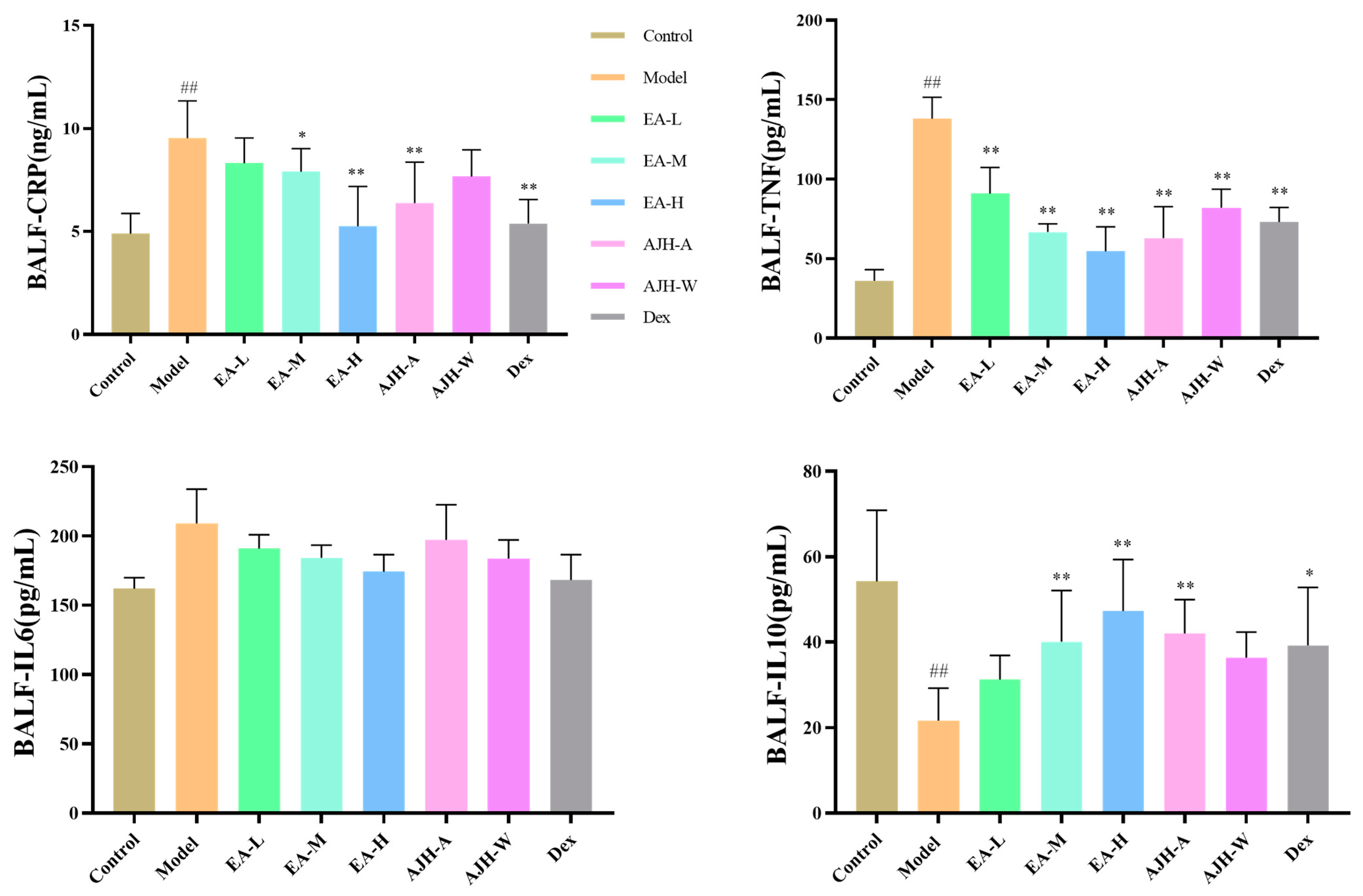
Figure 7.
Effects of the EA of AJH on the levels of CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in the BALF of ALI model rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: ## p < 0.01, comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group, EA-L: EA low-dose group, EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: AJH 70% alcohol extract group, AJH-W: AJH aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
Figure 7.
Effects of the EA of AJH on the levels of CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in the BALF of ALI model rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: ## p < 0.01, comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group, EA-L: EA low-dose group, EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: AJH 70% alcohol extract group, AJH-W: AJH aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
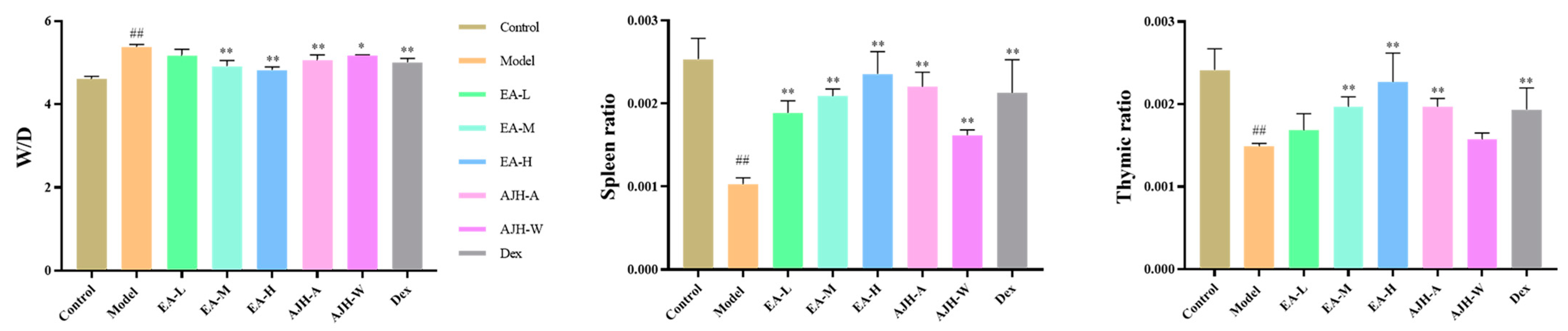
Figure 8.
Effects of EA of AJH on lung wet–dry weight ratio and organ index of ALI rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: ## p < 0.01; comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group, EA-L: EA low-dose group, EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: 70% alcoholic extract group, AJH-W: aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
Figure 8.
Effects of EA of AJH on lung wet–dry weight ratio and organ index of ALI rats ( ± SD, n = 8). Note: comparison with the blank group: ## p < 0.01; comparison with the model group: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Control: blank group, Model: model group, EA-L: EA low-dose group, EA-M: EA medium-dose group, EA-H: EA high-dose group, AJH-A: 70% alcoholic extract group, AJH-W: aqueous extract group, Dex: dexamethasone group.
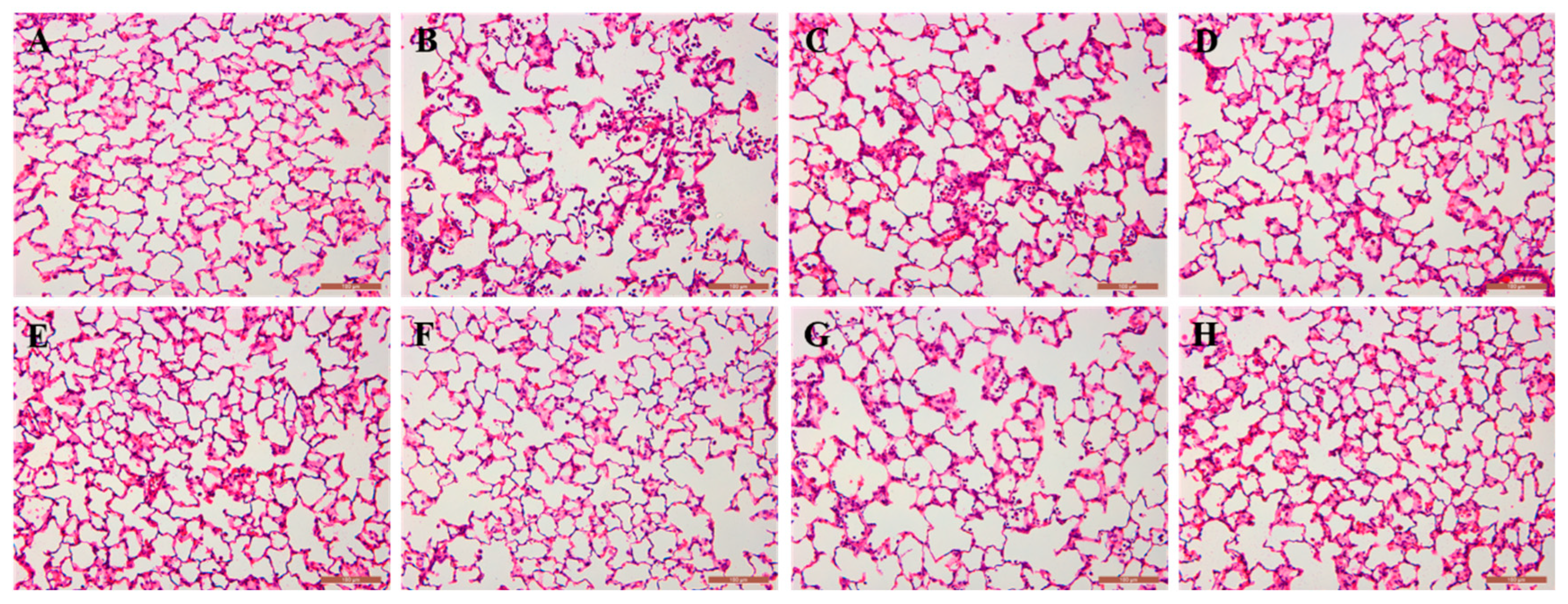
Figure 9.
Histopathologic morphology of rat lungs in each group (HE staining, ×200). Note: (A): blank group; (B): model group; (C): low-dose group at EA; (D): medium-dose group at EA; (E): high-dose group at EA; (F): AJH 70% alcoholic extract group; (G): AJH aqueous extract group; (H): dexamethasone group.
Figure 9.
Histopathologic morphology of rat lungs in each group (HE staining, ×200). Note: (A): blank group; (B): model group; (C): low-dose group at EA; (D): medium-dose group at EA; (E): high-dose group at EA; (F): AJH 70% alcoholic extract group; (G): AJH aqueous extract group; (H): dexamethasone group.
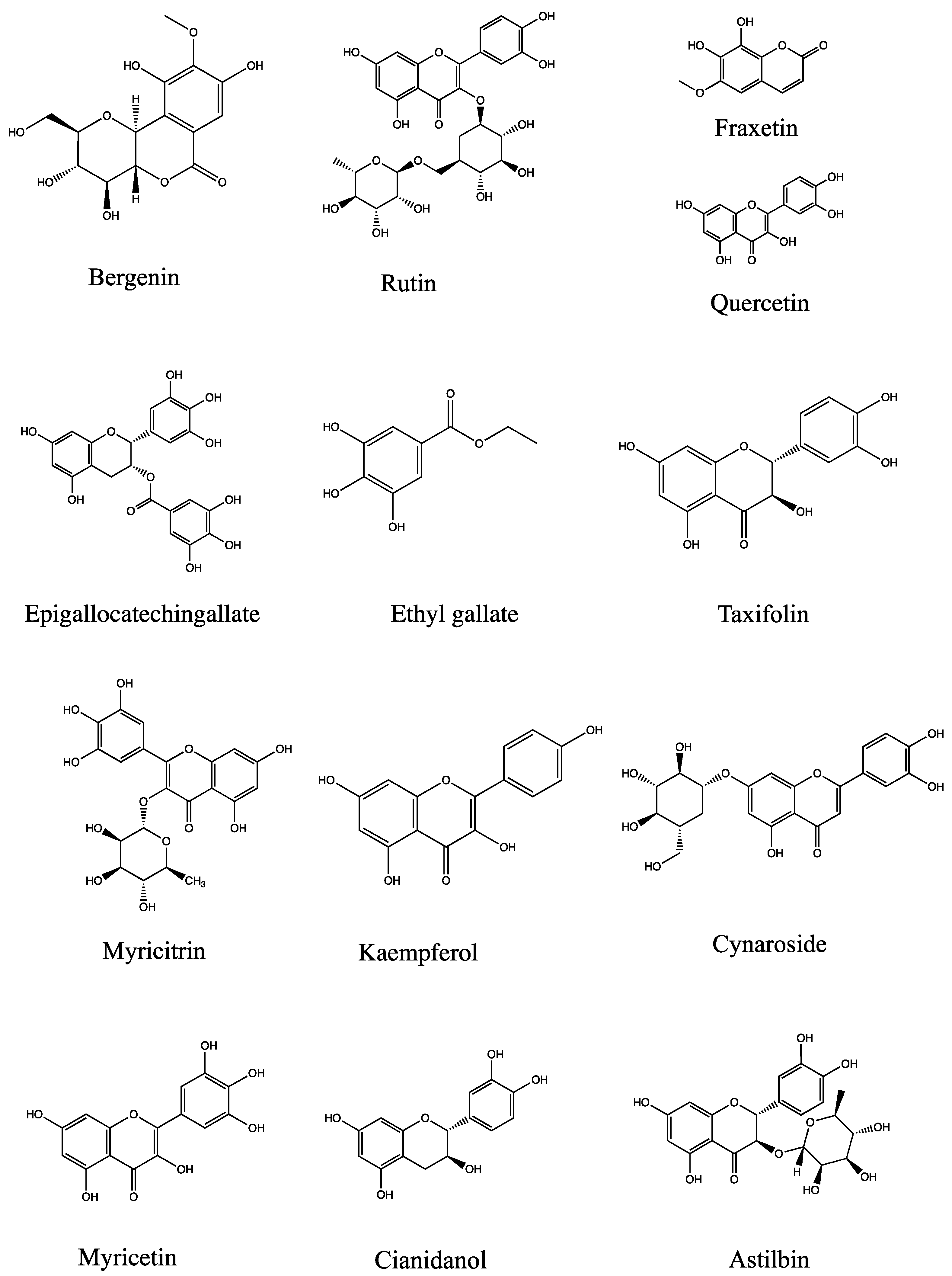
Figure 10.
Chemical structure of 13 main compounds (bergenin, quercetin, epigallocatechingallate, rutin, cianidanol, myricitrin, ethyl gallate, kaempferol, taxifolin, cynaroside, myricetin, fraxetin, astilbin).
Figure 10.
Chemical structure of 13 main compounds (bergenin, quercetin, epigallocatechingallate, rutin, cianidanol, myricitrin, ethyl gallate, kaempferol, taxifolin, cynaroside, myricetin, fraxetin, astilbin).
Table 1.
Compositional enrichment results of PE, EA, NB, and WS.
Table 1.
Compositional enrichment results of PE, EA, NB, and WS.
| Sites | Phenylpropanoid | Terpene | Flavonoid | Steroid | Quinone | Phenolic Acids, Carboxylic Acids, and Their Derivatives | Total |
|---|
| PE | 23 | 33 | 4 | 16 | 5 | 134 | 215 |
| EA | 40 | 31 | 31 | 13 | 7 | 167 | 289 |
| NB | 21 | 13 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 81 | 128 |
| WS | 11 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 49 | 69 |
| Total | 63 | 59 | 35 | 28 | 14 | 329 | 528 |
Table 2.
Design of optimal dosing concentration for each dosing group (μg/mL).
Table 2.
Design of optimal dosing concentration for each dosing group (μg/mL).
| Sites | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|
| AJH | 100 | 50 | 25 | 12.5 |
| PE | 25 | 12.5 | 6.25 | 3.13 |
| EA | 6.25 | 3.13 | 1.56 | 0.78 |
| NB | 50 | 25 | 12.5 | 6.25 |
| WS | 200 | 100 | 50 | 25 |
Table 3.
Comprehensive scoring results of PE, EA, NB, and WS on the expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in AJH.
Table 3.
Comprehensive scoring results of PE, EA, NB, and WS on the expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in AJH.
| Sites | IL-6 | TNF-α | P0IL-6 + P0TNF-α |
|---|
| p1 | p2 | p0 | SUMP0 | p1 | p2 | p0 | SUMP0 |
|---|
| PE 25 μg/mL | 0.374 | 0.039 | 0.104 | 0.136 | 0.01 | 0.004 | 0.400 | 0.806 | 0.942 |
| PE 12.5 μg/mL | 0.475 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.01 | 0.003 | 0.300 |
| PE 6.25 μg/mL | 0.740 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.056 |
| PE 3.13 μg/mL | 0.997 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.06 | 0.003 | 0.050 |
| EA 6.25 μg/mL | 0.031 | 0.014 | 0.452 | 0.525 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 2.000 | 2.429 | 2.954 |
| EA 3.13 μg/mL | 0.039 | 0.002 | 0.051 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| EA 1.56 μg/mL | 0.059 | 0.001 | 0.017 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.429 |
| EA 0.78 μg/mL | 0.184 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.032 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| NB 50 μg/mL | 0.043 | 0.001 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.667 | 0.952 | 0.975 |
| NB 25 μg/mL | 0.065 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| NB 12.5 μg/mL | 0.091 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.286 |
| NB 6.25 μg/mL | 0.181 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.333 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| WS 200 μg/mL | −0.807 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −0.039 | −0.017 | 0.002 | 0.118 | −0.118 | −0.157 |
| WS 100 μg/mL | −0.794 | 0.006 | 0.008 | −0.1 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| WS 50 μg/mL | −0.483 | 0.015 | 0.031 | −0.335 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| WS 25 μg/mL | −0.076 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −0.976 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| AJH 100 μg/mL | 0.024 | 0.037 | 1.542 | 2.127 | 0.02 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.059 | 2.186 |
| AJH 50 μg/mL | 0.029 | 0.005 | 0.172 | 0.017 | 0.001 | 0.059 |
| AJH 25 μg/mL | 0.031 | 0.012 | 0.387 | 0.045 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| AJH12.5 μg/mL | 0.038 | 0.001 | 0.026 | 0.315 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Table 4.
Results of the determination of the content of AJH and EA ( ± SD, n = 3).
Table 4.
Results of the determination of the content of AJH and EA ( ± SD, n = 3).
| Compounds | EA | AJH (Obversion) | AJH |
|---|
| Content (μg/g EA Powder) | Content (μg/g Raw AJH) |
|---|
| Isoeugenol | 758.18 ± 4.75 | 13.98 ± 0.11 | 100.33 ± 0.02 |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 453.91 ± 1.84 | 8.27 ± 0.1 | 81.32 ± 1.54 |
| Quercetin | 6057.59 ± 71.5 | 112.15 ± 0.08 | 155.49 ± 1.93 |
| Taxifolin | 662.33 ± 8.79 | 12.07 ± 0.21 | 11.18 ± 0.07 |
| Myricetin | 4521.58 ± 9.77 | 83.15 ± 0.89 | 80.89 ± 0.25 |
| Gallic acid | 8300.42 ± 23.04 | 153.48 ± 0.35 | 174.36 ± 1.01 |
| Ethyl gallate | 1398.6 ± 1.67 | 24.24 ± 1.28 | 30.86 ± 0.03 |
| Fraxetin | 918.08 ± 10.3 | 16.34 ± 0.09 | 18.34 ± 0.12 |
| Palmitic acid | 15,525.36 ± 39.26 | 282.86 ± 0.61 | 269.68 ± 0.06 |
| Kaempferol | 23,916.89 ± 42.79 | 439.05 ± 2.34 | 476.97 ± 1.09 |
| Eriodictyol | 446.7 ± 1.78 | 8.23 ± 0.04 | 8.2 ± 0.03 |
| Cianidanol | 2897.69 ± 6.14 | 52.52 ± 0.01 | 49.02 ± 0.1 |
| Bergenin | 285,582.94 ± 2309.97 | 5064.71 ± 59.58 | 5150.12 ± 23.68 |
| Cynaroside | 17,346.17 ± 88.96 | 318.37 ± 1.35 | 311.3 ± 0.36 |
| Astilbin | 2343.77 ± 1.24 | 43.11 ± 0.16 | 54.9 ± 0.09 |
| Epigallocatechingallate | 12,936.53 ± 55.07 | 238.32 ± 0.14 | 234.04 ± 0.69 |
| Myricitrin | 12,030.85 ± 8.51 | 220.46 ± 0.28 | 265.71 ± 4.68 |
| Nictoflorin | 397.4 ± 2.15 | 7.27 ± 0.03 | 8.71 ± 0.02 |
| Rutin | 618.27 ± 0.82 | 11.28 ± 0.02 | 6.73 ± 0.03 |
Table 5.
Results of the correlation between the content of 19 chemical components in the EA and anti-inflammatory activity.
Table 5.
Results of the correlation between the content of 19 chemical components in the EA and anti-inflammatory activity.
| Compounds | Correlation | Range | Compounds | Correlation | Range |
|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | 1 | 1 | Taxifolin | 0.833 | 11 |
| Bergenin | 0.878 | 2 | Isoeugenol | 0.831 | 12 |
| Gallic acid | 0.863 | 3 | Palmitic acid | 0.828 | 13 |
| Quercetin | 0.86 | 4 | Luteolin-7-O-glucoside | 0.824 | 14 |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | 0.846 | 5 | Myricetin | 0.824 | 15 |
| Rutin | 0.84 | 6 | Fraxetin | 0.821 | 16 |
| Catechin | 0.84 | 7 | Astilbin | 0.82 | 17 |
| Myricitrin | 0.839 | 8 | Eriodictyol | 0.753 | 18 |
| Ethyl gallate | 0.836 | 9 | Nicotiflorin | 0.626 | 19 |
| Kaempferide | 0.835 | 10 | | | |
Table 6.
Different concentration designs of dosing groups (μg/mL).
Table 6.
Different concentration designs of dosing groups (μg/mL).
| Sites | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|
| AJH | 200 | 150 | 125 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 12.5 |
| PE | 50 | 25 | 12.5 | 6.25 | 3.13 | - | - | - |
| EA | 50 | 25 | 12.5 | 6.25 | 3.13 | - | - | - |
| NB | 200 | 150 | 125 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 12.5 |
| WS | 200 | 150 | 125 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 12.5 |
Table 7.
Ion information of the components to be measured for quantitative analysis.
Table 7.
Ion information of the components to be measured for quantitative analysis.
| Compounds | Test Mode | Test Ion | m/z | Rt (min) |
|---|
| Isoeugenol | [M + H]+ | C10H13O2+ | 165.0910 | 15.73 |
| Caryophyllene oxide | [M + H]+ | C15H25O+ | 221.1900 | 17.01 |
| Quercetin | [M + H]+ | C15H11O7+ | 303.0499 | 8.67 |
| Taxifolin | [M + H]+ | C15H13O7+ | 305.0656 | 9.19 |
| Myricetin | [M + H]+ | C15H11O8+ | 319.0448 | 8.86 |
| Gallic acid | [M − H]− | C7H5O5− | 169.0142 | 2.34 |
| Ethyl gallate | [M − H]− | C9H9O5− | 197.0455 | 8.89 |
| Fraxetin | [M − H]− | C10H7O5− | 207.0299 | 8.15 |
| Palmiticacid | [M − H]− | C16H31O2− | 255.2330 | 20.25 |
| Kaempferol | [M − H]− | C15H9O6− | 285.0405 | 9.3 |
| Eriodictyol | [M − H]− | C15H11O6− | 287.0561 | 11.37 |
| Cianidanol | [M − H]− | C15H13O6− | 289.0718 | 6.95 |
| Bergenin | [M − H]− | C14H15O9− | 327.0722 | 6.42 |
| Cynaroside | [M − H]− | C21H19O11− | 447.0933 | 8.98 |
| Astilbin | [M − H]− | C21H21O11− | 449.1089 | 9.24 |
| Epigallocatechingallate | [M − H]− | C22H17O11− | 457.0776 | 7.86 |
| Myricitrin | [M − H]− | C21H19O12− | 463.0882 | 8.8 |
| Nictoflorin | [M − H]− | C27H29O15− | 593.1512 | 9.09 |
| Rutin | [M − H]− | C27H29O16− | 609.1461 | 8.66 |