Degradation Product-Promoted Depolymerization Strategy for Chemical Recycling of Poly(bisphenol A carbonate)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Depolymerization of PC under Solvent-Free Conditions
2.2. Effect of Solvent Type on the Reaction
2.3. Probe into the Role of DMI
2.4. Optimization of DMI Equivalent
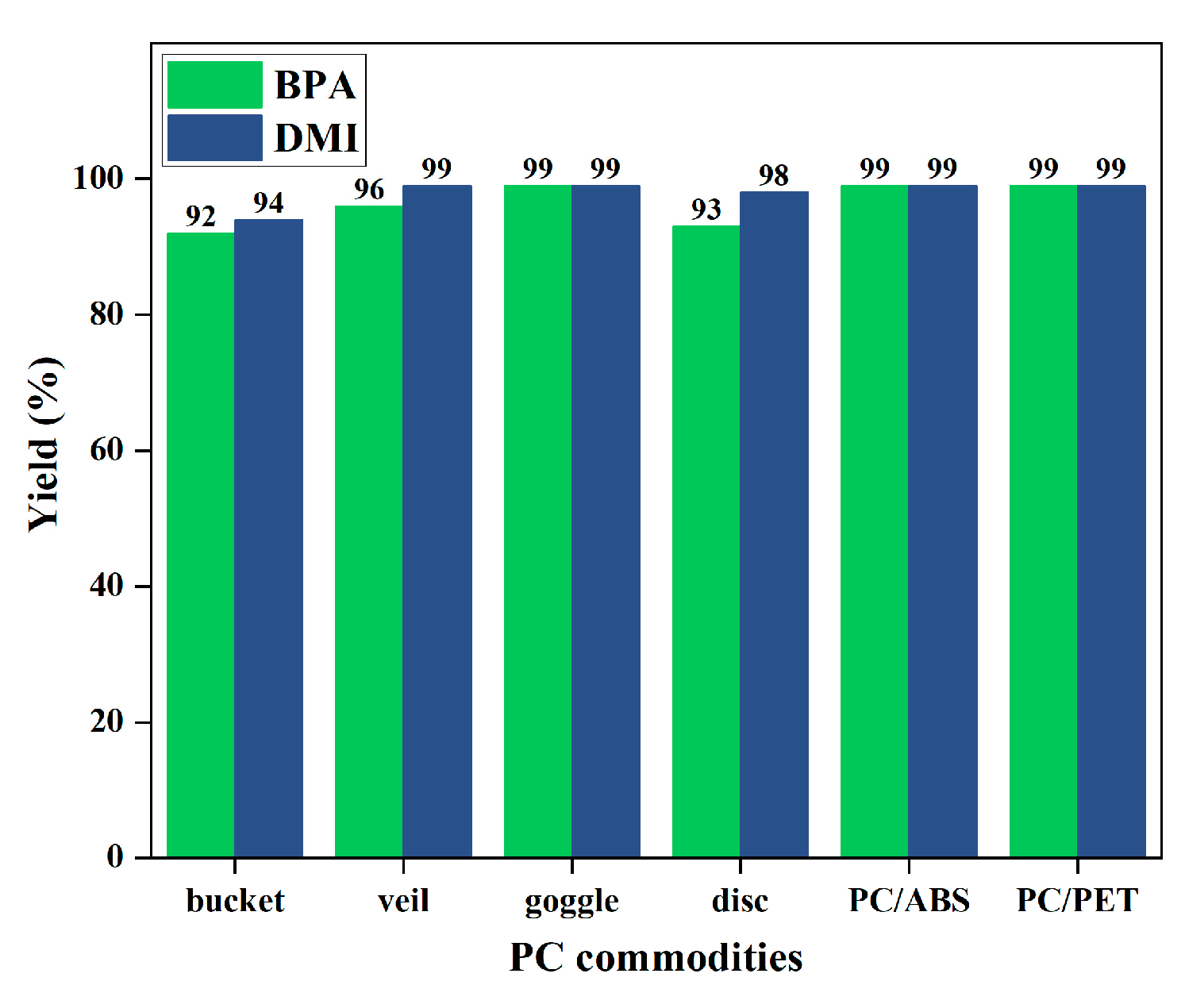
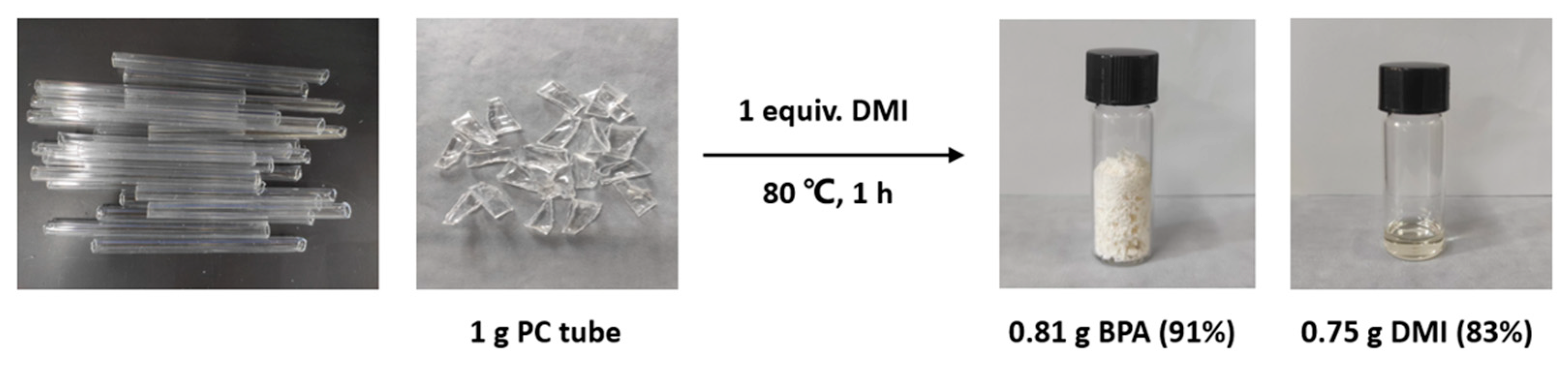
2.5. Degradation of Common PC Waste Plastics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Depolymerization of PC
3.3. The Determination of the Binding Constant
3.4. Product Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potter, H.V. Plastics and some recent applications. Nature 1939, 143, 785–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Collard, F.; Fabres, J.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Provencher, J.F.; Rochman, C.M.; Sebille, E.; Tekman, M.B. Plastic pollution in the arctic. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.V.; Jiang, P.; Tan, R.R.; Aviso, K.B.; You, F.; Zhao, X.; Lee, C.T.; Klemeš, J.J. Forecasting plastic waste generation and interventions for environmental hazard mitigation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; You, F. Life cycle assessment of microplastics reveals their greater environmental hazards than mismanaged polymer waste losses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 11780–11797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Korey, M.; Li, K.; Copenhaver, K.; Tekinalp, H.; Celik, S.; Kalaitzidou, K.; Ruan, R.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Ozcan, S. Plastic waste upcycling toward a circular economy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.M.; Robertson, M.L. The future of plastics recycling. Science 2017, 358, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatyev, I.A.; Thielemans, W.; Vander Beke, B. Recycling of polymers: A review. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, I.; Jenks, M.J.F.; Roelands, M.C.P.; White, R.J.; Harmelen, T.; Wild, P.; Laan, G.P.; Meirer, F.; Keurentjes, J.T.F.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Beyond mechanical recycling: Giving new life to plastic waste. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15402–15423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Ribes-Greus, A. Mechanical recycling of polylactide, upgrading trends and combination of valorization techniques. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 84, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrus, R.; Bykowski, D.; Sobota, P. Solvothermal alcoholysis routes for recycling polylactide waste as lactic acid esters. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5222–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, Q. Chemically recyclable polymer materials: Polymerization and depolymerization cycles. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 2321–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, P.; Kamran, M.; Davidson, M.G.; Jones, M.D.; Román-Ramírez, L.A.; Wood, J. Organocatalysis for versatile polymer degradation. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 3721–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Recent progress in the chemical upcycling of plastic wastes. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 4137–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Waste to wealth: Chemical recycling and chemical upcycling of waste plastics for a great future. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 4123–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Gong, S.; Liu, P.; et al. Depolymerization of polyesters by a binuclear catalyst for plastic recycling. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, L.; Wohlert, J.; Olsén, P.; Hakkarainen, M.; Odelius, K. “Like recycles like”: Selective ring-closing depolymerization of poly(L-lactic acid) to L-lactide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202204531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, W.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Long, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.-Z. Water-solvent regulation on complete hydrolysis of thermosetting polyester and complete separation of degradation products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höcker, H.; Keul, H. Ring-opening polymerization and ring-closing depolymerization. Adv. Mater. 1994, 6, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Nagai, D. A novel construction of ring-opening polymerization and chemical recycling system. Macromol. Symp. 2005, 226, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsén, P.; Odelius, K.; Albertsson, A.-C. Thermodynamic presynthetic considerations for ring-opening polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsén, P.; Undin, J.; Odelius, K.; Keul, H.; Albertsson, A.-C. Switching from controlled ring-opening polymerization (cROP) to controlled ring-closing depolymerization (cRCDP) by adjusting the reaction parameters that determine the ceiling temperature. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3995–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Chang, W.; Shi, D.; Yang, L.; Tian, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, E.-Q.; Lu, H. Geminal dimethyl substitution enables controlled polymerization of penicillamine-derived β-thiolactones and reversed depolymerization. Chem 2020, 6, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, G.; Dong, B.; Hou, H.; Wang, Q. A “polymer to polymer” chemical recycling of PLA plastics by the “DE–RE polymerization” strategy. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, G.; Yang, R.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q. Chemical upcycling of poly(lactide) plastic waste to lactate ester, lactide and new poly(lactide) under Mg-catalysis condition. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, G.; Dong, B.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q. Selective, sequential, and “one-pot” depolymerization strategies for chemical recycling of commercial plastics and mixed plastics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 9860–9871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chai, M.; Xu, G.; Yang, R.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q. Catalyst-free amino-alcoholysis depolymerization strategy: A facile and powerful tool for chemical recycling of poly(bisphenol A carbonate). Green Chem. 2023, 5, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, M.R.; Prévost, S.; List, B. Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of thiols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16982–16985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, M.R.; Poladura, B.; Diaz de Los Bernardos, M.; Leutzsch, M.; Goddard, R.; List, B. Activation of carboxylic acids in asymmetric organocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7063–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y.; Che, P.; Nie, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, J. Understanding and measurement for the binding energy of hydrogen bonds of biomass-derived hydroxyl compounds. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, D.; Che, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Gao, J.; Xu, J. Binding energy as driving force for controllable reconstruction of hydrogen bonds with molecular scissors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6085–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiner, S. Assessment of the presence and strength of H-Bonds by means of corrected NMR. Molecules 2016, 21, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, S.; Goto, H.; Yamada, E.; Oku, A. Chemical conversion of poly(carbonate) to 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone (DMI) and bisphenol A: A practical approach to the chemical recycling of plastic wastes. Polymer 2002, 43, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Shah, S.M.; Cao, R.; Chen, J. Novel sponge-like molecularly imprinted mesoporous silica material for selective isolation of bisphenol A and its analogues from sediment extracts. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, T.; Nakai, T.; Mihara, M. Efficient solvent-free synthesis of urea derivatives using selenium-catalyzed carbonylation of amines with carbon monoxide and oxygen. Synthesis 2010, 2010, 4251–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
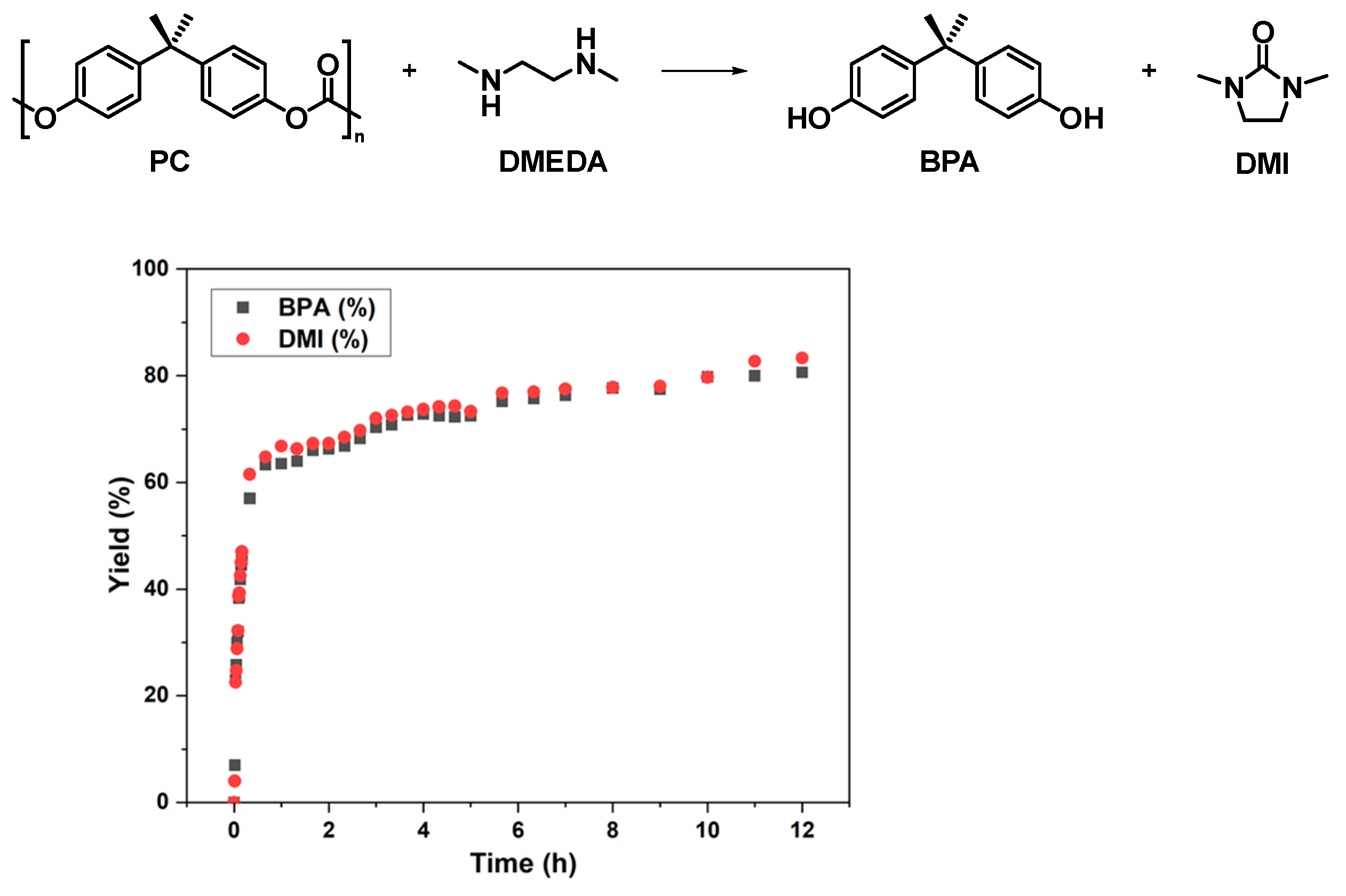

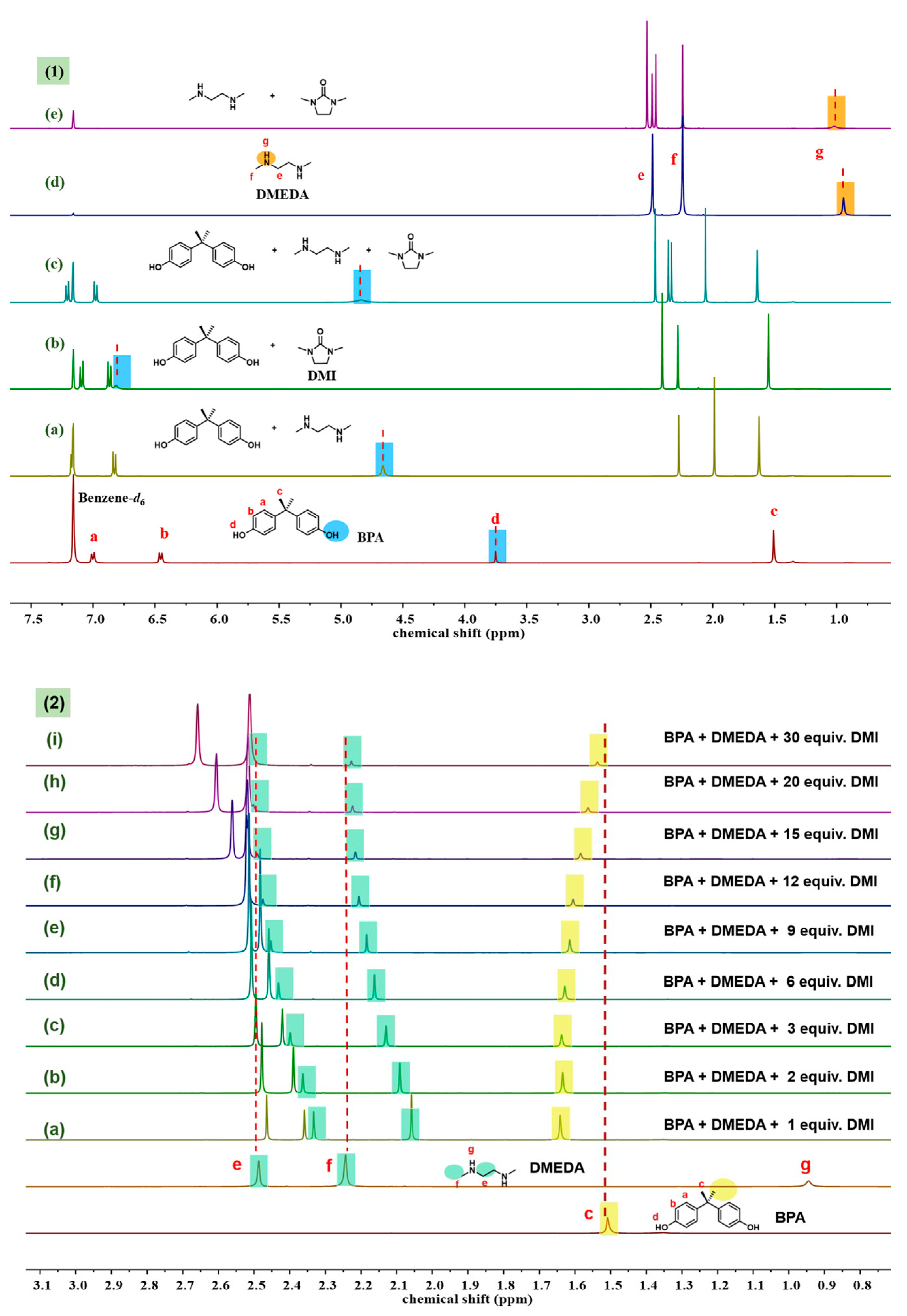
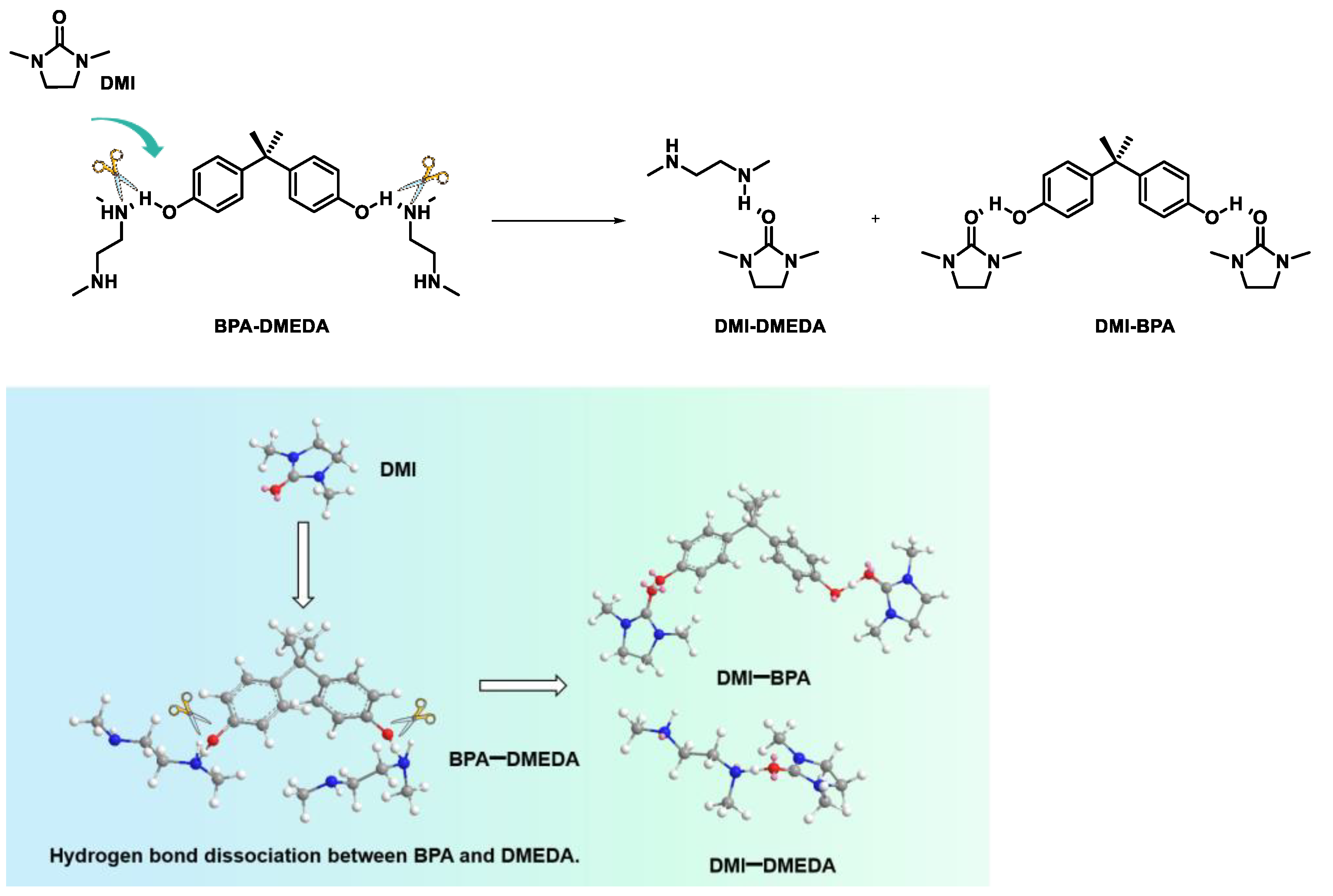
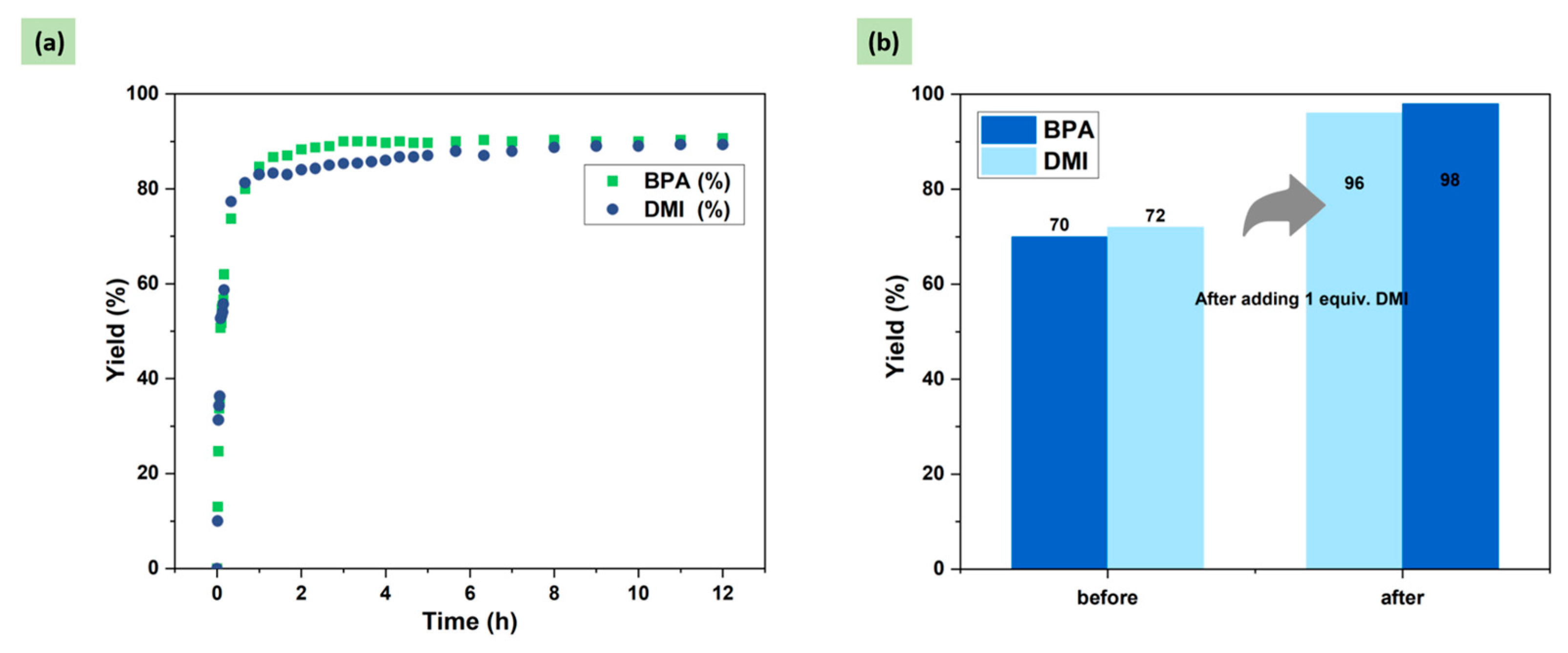
| Entry | Solvent | Yield of BPA (%) | Yield of DMI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DCM | 77 | 79 |
| 2 | THF | 68 | 66 |
| 3 | EtOAc | 75 | 75 |
| 4 | Tol. | 72 | 71 |
| 5 | Ace. | 70 | 68 |
| 6 | DMI | 87 | 85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, M.; Xu, G.; Yang, R.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q. Degradation Product-Promoted Depolymerization Strategy for Chemical Recycling of Poly(bisphenol A carbonate). Molecules 2024, 29, 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030640
Chai M, Xu G, Yang R, Sun H, Wang Q. Degradation Product-Promoted Depolymerization Strategy for Chemical Recycling of Poly(bisphenol A carbonate). Molecules. 2024; 29(3):640. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030640
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Maoqing, Guangqiang Xu, Rulin Yang, Hongguang Sun, and Qinggang Wang. 2024. "Degradation Product-Promoted Depolymerization Strategy for Chemical Recycling of Poly(bisphenol A carbonate)" Molecules 29, no. 3: 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030640
APA StyleChai, M., Xu, G., Yang, R., Sun, H., & Wang, Q. (2024). Degradation Product-Promoted Depolymerization Strategy for Chemical Recycling of Poly(bisphenol A carbonate). Molecules, 29(3), 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030640






