Sensory Quality, Volatile Compounds, and Physical Properties of Sheep’s Milk Cheese with Herbs (Allium ursinum L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Composition, Acidity and Water Activity of Cheese
2.2. Sensory Quality of Cheese
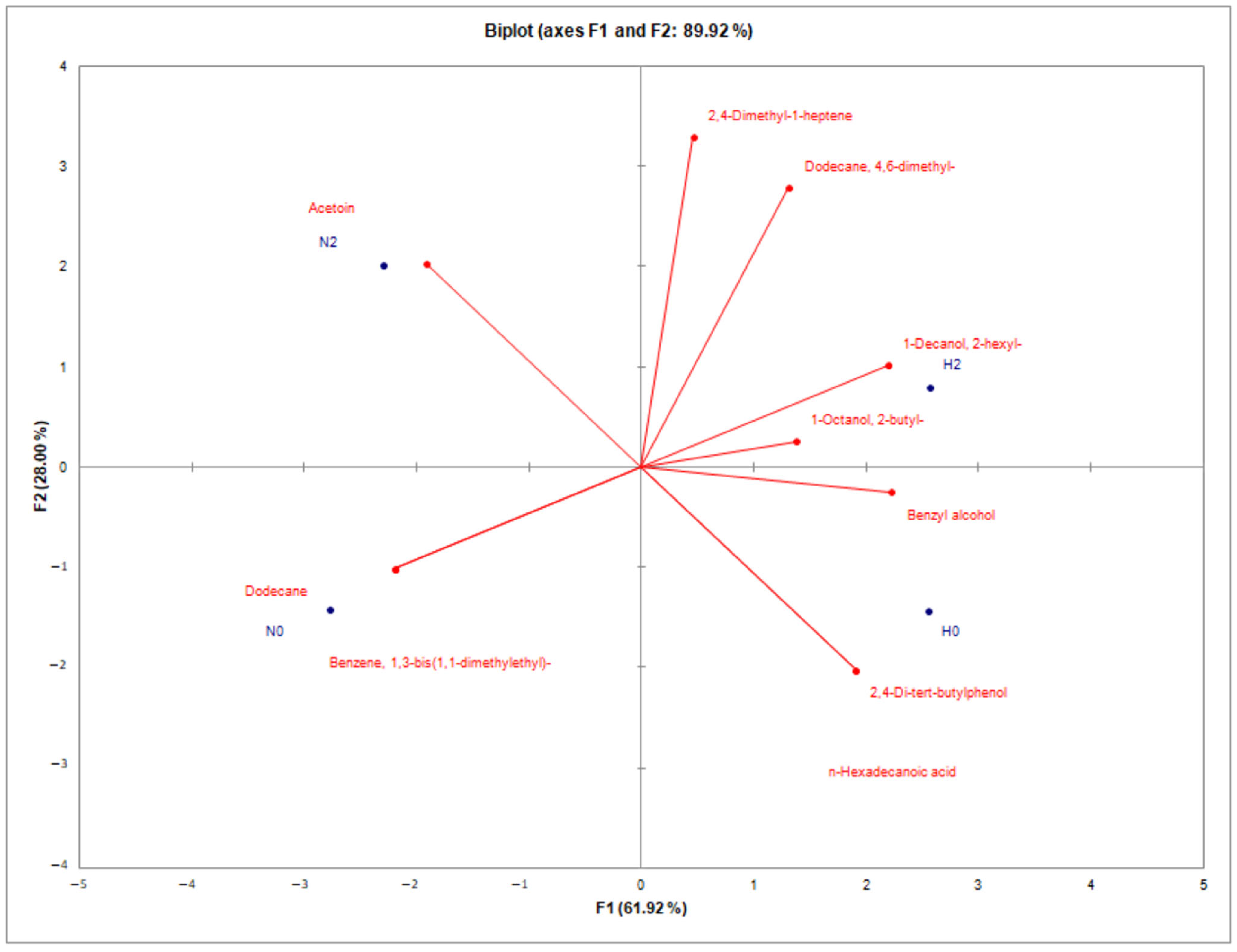
2.3. Volatile Compounds in Cheese
2.4. Physical Properties of Cheese
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Chemical Composition, Acidity, and Water Activity Evaluation
3.3. Sensory Quality Assessment
3.4. Volatile Compounds Analysis
3.5. Physical Properties Analysis
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balthazar, C.F.; Pimentel, T.C.; Ferrão, L.L.; Almada, C.N.; Santillo, A.; Albenzio, M.; Mollakhalili, N.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Nascimento, J.S.; Silva, M.C.; et al. Sheep Milk: Physicochemical Characteristics and Relevance for Functional Food Development. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta-Kubica, A.; Jamróz, E.; Kawecka, A.; Juszczak, L.; Krzyściak, P. Active Edible Furcellaran/Whey Protein Films with Yerba Mate and White Tea Extracts: Preparation, Characterization and Its Application to Fresh Soft Rennet-Curd Cheese. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarakci, Z.; Temiz, H.; Aykut, U.; Turhan, S. Influence of Wild Garlic on Color, Free Fatty Acids, and Chemical and Sensory Properties of Herby Pickled Cheese. Int. J. Food Prop. 2011, 14, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptasińska-Marcinkiewicz, J. Hodowla Owiec i Produkcja Mleka Owczego w Polsce i Na Świecie. Zesz. Nauk. Uniw. Ekon. w Krakowie 2014, 3, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najgebauer- Lejko, D.; Domagała, J.; Walczycka, M. Traditional Cheeses from the Malopolska Region. In Cultural Heritage—Possibilities for Land-Centered Societal Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Sonmezdag, A.S. Characterization of Aroma and Aroma-Active Composition of Gaziantep Cheese by Solvent-Assisted Flavor Evaporation (SAFE) and Aroma Extract Dilution Analysis (AEDA). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębczyński, P.; Bernaś, E.; Słupski, J. Usage of Wild-Growing Plants as Foodstuff. In Cultural Heritage—Possibilities for Land-centered Societal Development; Hernik, J., Walczycka, M., Sankowski, E., Harris, B.J., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 269–283. ISBN 9783030580919. [Google Scholar]
- Znamirowska, A.; Szajnar, K.; Rożek, P.; Kalicka, D.; Kuzacutẽniar, P.; Hanus, P.; Kotula, K.; Obirek, M.; Kluz, M. Effect of Addition of Wild Garlic (Allium Ursinum) on the Quality of Kefirs from Sheep’s Milk. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2017, 16, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Radusin, T.; Torres-Giner, S.; Stupar, A.; Ristic, I.; Miletic, A.; Novakovic, A.; Lagaron, J.M. Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Properties of Electrospun Polylactide Films Containing Allium Ursinum L. Extract. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupar, A.; Vidović, S.; Vladić, J.; Radusin, T.; Mišan, A. A Sustainable Approach for Enhancing Stability and Bioactivity of Allium Ursinum Extract for Food Additive Applications. Separations 2024, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolewska, D.; Podolak, I.; Makowska-Wąs, J. Allium Ursinum: Botanical, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Overview. Phytochem. Rev. 2015, 14, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štajner, D.; Popović, B.M.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Štajner, M. Antioxidant and Scavenger Activities of Allium Ursinum. Fitoterapia 2008, 79, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta-Kubica, A.; Najgebauer-Lejko, D.; Domagała, J.; Štefániková, J.; Golian, J. The Effect of Cow Breed and Wild Garlic Leaves (Allium Ursinum L.) on the Sensory Quality, Volatile Compounds, and Physical Properties of Unripened Soft Rennet-Curd Cheese. Foods 2022, 11, 3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliguem, H.; Ben Hassine, D.; Ben Haj Said, L.; Ben Tekaya, I.; Rahmani, R.; Bellagha, S. Supplementation of Double Cream Cheese with Allium Roseum: Effects on Quality Improvement and Shelf-Life Extension. Foods 2021, 10, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szołtysik, M.; Dâbrowska, A.; Babij, K.; Pokora, M.; Zambrowicz, A.; Połomska, X.; Wojtatowicz, M.; Chrzanowska, J. Biochemical and Microbiological Changes in Cheese Inoculated with Yarrowia Lipolytica Yeast. Zywn. Nauk. Technol. Jakosc/Food. Sci. Technol. Qual. 2013, 20, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CODEX STAN 283-1978; Codex Alimentarius Commission General Standard for Cheese 283-1978. Codex Aliment: Rome, Italy, 2013; pp. 1–6.
- Znamirowska, A.; Rożek, P.; Buniowska, M.; Kalicka, D.; Kuźniar, P. Using Wild Garlic (Allinum Ursinum L.) in Production of Milk Fermented with Bifidobacterium Animalis Ssp. Lactis BB-12. Zywn. Nauk. Technol. Jakosc Food. Sci. Technol. Qual. 2018, 25, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryłko-Pikielna, N.; Matuszewska, I. Rozdział 13. Sensoryczne Badania Konsumenckie—Metody. In Sensoryczne Badania Żywności. Podstawy—Metody-Zastosowania; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PTTŻ: Kraków, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Naibaho, F.G.; Hartanto, A.; Bintang, M.; Jamilah, I.; Priyani, N.; Putra, E.D. GC-MS Analysis and Antimicrobial Activity of the Aqueous Extract from the Bulbs of Allium Chinense G. Don. Cultivated in North Sumatra, Indonesia. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolma, N.; Shahar, B.; Chongtham, N. Determination of Mineral Elements, Antioxidant Activity and Bio-Active Compounds of Allium Prezewalskianum Regel, an Underutilized Plant of Ladakh, India Using ICP-AES, AAS and GC-MS. Meas. Food 2024, 13, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítová, E.; Mokáňová, R.; Babák, L.; Zemanová, J.; Sklenářová, K. The Changes of Flavour and Aroma Active Compounds Content during Produgtion of Edam Cheese. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendelianae Brun. 2011, 59, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues Galli, B.; Trossolo, E.; Carafa, I.; Squara, S.; Caratti, A.; Filannino, P.; Cordero, C.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Effectiveness of Modified Atmosphere and Vacuum Packaging in Preserving the Volatilome of Stelvio PDO Cheese over Time. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneberry, S.; Wilkinson, M.G.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Kelly, P.M.; Guinee, T.P. Interactive Effects of Salt and Fat Reduction on Composition, Rheology and Functional Properties of Mozzarella-Style Cheese. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 613–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO5534:2004; Cheese and Processed Cheese—Determination of the Total Solids Content. ISO: Geneva, Switzerlands, 2004.
- ISO3433:2008; Cheese—Determination of Fat Content—Van Gulik Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerlands, 2008; p. 3433.
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; Chapter 33, Dairy Products; AOAC: Rockville, ML, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ISO18787:2017; Foodstuffs—Determination of Water Activity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerlands, 2017.
- Gawęcka, J.; Jędryka, T. Rozdział 5. Metody Punktowe. In Analiza Sensoryczna: Wybrane Metody I Przykłady Zastosowań; Wydawnictwo Akademii Ekonomicznej w Poznaniu: Poznań, Poland, 2001; pp. 57–76. ISBN 838876019X. [Google Scholar]
- Baryłko-Pikielna, N.; Matuszewska, I. Rozdział 10. Metody Sensorycznej Analizy Opisowej. In Sensoryczne Badania Żywności. Podstawy—Metody—Zastosowania; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PTTŻ: Kraków, Poland, 2014; pp. 181–226. ISBN 978-83-935421-3-0. [Google Scholar]
- Štefániková, J.; Martišová, P.; Šnirc, M.; Kunca, V.; Árvay, J. The Effect of Amanita Rubescens Pers Developmental Stages on Aroma Profile. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najgebauer-Lejko, D.; Liszka, K.; Tabaszewska, M.; Domagała, J. Probiotic Yoghurts with Sea Buckthorn, Elderberry, and Sloe Fruit Purees. Molecules 2021, 26, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla, P.; Beltrán, M.C.; Molina, A.; Escriche, I.; Molina, M.P. Characteristics of Ripened Tronchón Cheese from Raw Goat Milk Containing Legally Admissible Amounts of Antibiotics. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domagała, J.; Pluta-Kubica, A.; Wieteska-Śliwa, I.; Duda, I. The Influence of Milk Protein Cross-Linking by Transglutaminase on Technology, Composition and Quality Properties of Gouda-Type Cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 130, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XLSTAT Addinsoft. Analyse de Données et Statistique Avec MS Excel; Addinsoft: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
| Feature | Type of Cheese and Storage Duration (Weeks) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H | |||||
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | A | T | |
| Water content [%] | 53.55 ± 5.25 | 54.38 ± 1.45 | 49.67 ± 2.91 | 50.38 ± 0.82 | ** | NS |
| pH | 4.58 ± 0.25 | 4.82 ± 0.03 | 4.64 ± 0.20 | 4.72 ± 0.19 | * | * |
| Water activity | 0.971 ± 0.002 | 0.976 ± 0.004 | 0.966 ± 0.006 | 0.971 ± 0.005 | NS | * |
| Fat content [%] | 23.42 ± 0.92 | ne | 23.17 ± 3.11 | ne | NS | ne |
| Protein content [%] | 17.95 ± 1.35 | ne | 19.13 ± 1.43 | ne | NS | ne |
| Ash content [%] | 2.49 ± 0.22 | ne | 2.76 ± 0.22 | ne | NS | ne |
| NaCl content [%] | 0.94 ± 0.05 | ne | 0.89 ± 0.05 | ne | NS | ne |
| Feature | Type of Cheese and Storage Duration (Weeks) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H | |||||
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | A | T | |
| Sensory quality on a five-point scale | ||||||
| Color | 4.93 ± 0.24 | 4.73 ± 0.53 | 4.98 ± 0.11 | 4.73 ± 0.53 | NS | * |
| Appearance | 4.75 ± 0.41 | 4.60 ± 0.48 | 4.58 ± 0.49 | 4.48 ± 0.57 | NS | NS |
| Texture | 4.85 ± 0.33 | 4.75 ± 0.38 | 4.63 ± 0.46 | 4.78 ± 0.34 | NS | NS |
| Odor | 4.85 ± 0.33 | 4.65 ± 0.46 | 4.93 ± 0.24 | 4.68 ± 0.44 | NS | ** |
| Taste | 4.80 ± 0.41 | 4.60 ± 0.58 | 4.80 ± 0.41 | 4.68 ± 0.57 | NS | NS |
| Overall quality | 4.83 ± 0.21 | 4.65 ± 0.36 | 4.79 ± 0.24 | 4.66 ± 0.32 | NS | * |
| Intensity of the discriminants of odor and taste | ||||||
| Sheep milk odor | 4.00 ± 0.92 | 4.05 ± 1.00 | 2.85 ± 1.23 | 2.80 ± 1.61 | *** | NS |
| Sour odor | 2.15 ± 1.31 | 1.95 ± 1.28 | 1.95 ± 1.23 | 1.05 ± 1.00 | * | * |
| Wild garlic odor | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 4.30 ± 0.73 | 4.20 ± 1.01 | *** | NS |
| Desirable odor | 4.55 ± 0.83 | 4.35 ± 0.75 | 4.50 ± 0.76 | 4.30 ± 0.80 | NS | NS |
| Rancid odor | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.30 ± 0.66 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.15 ± 0.37 | NS | ** |
| Foreign odor | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.25 ± 0.55 | 0.20 ± 0.41 | 0.20 ± 0.41 | NS | NS |
| Sheep milk taste | 4.15 ± 0.99 | 4.20 ± 0.89 | 3.30 ± 1.17 | 3.20 ± 1.47 | *** | NS |
| Sour taste | 2.65 ± 1.23 | 2.30 ± 1.22 | 2.10 ± 0.97 | 1.90 ± 1.07 | NS | NS |
| Bitter taste | 0.10 ± 0.31 | 0.75 ± 0.97 | 0.25 ± 0.44 | 0.75 ± 1.12 | NS | * |
| Piquant taste | 0.60 ± 1.14 | 0.25 ± 0.44 | 1.60 ± 1.47 | 1.15 ± 1.39 | *** | NS |
| Salty taste | 2.90 ± 1.17 | 2.75 ± 1.29 | 2.70 ± 1.03 | 2.25 ± 1.12 | NS | NS |
| Wild garlic taste | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 4.00 ± 0.92 | 4.20 ± 0.70 | *** | NS |
| Desirable taste | 4.55 ± 0.60 | 4.40 ± 0.88 | 4.60 ± 0.60 | 4.15 ± 1.35 | NS | NS |
| Rancid taste | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.31 | 0.05 ± 0.22 | 0.10 ± 0.31 | NS | NS |
| Foreign taste | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.22 | 0.35 ± 0.67 | 0.40 ± 0.68 | *** | NS |
| Compounds | Sensory Descriptors 1 | Type of Cheese and Storage Duration (Weeks) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H | ||||
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | ||
| 1,2-Propanediol, 1-phenyl- | Plastic, pungent, buttery, honey | + | |||
| 11-Methyldodecanol | - | + | + | + | |
| 1-Decanol, 2-hexyl- | Mild and sweet | + | + | + | + |
| 1-Decanol, 2-methyl- | Sweet and fat-like | + | |||
| 1-Decene, 2,4-dimethyl- | - | + | |||
| 1-Dodecanol | Fatty and waxy | + | |||
| 1-Dodecanol, 2-hexyl- | Fatty and waxy | + | |||
| 1-Dodecanol, 2-octyl- | Faint | + | |||
| 1-Dodecene | Mild and pleasant | + | + | + | |
| 1-Octanol, 2-butyl- | Pungent, mild, sweet, fishy | + | + | + | + |
| 1-Pentadecene | - | + | |||
| 1-Tetradecanol | Coconut, weak oily, fatty | + | |||
| 1-Tetradecene | Mild and pleasant | + | + | ||
| 2,4-Dimethyl-1-heptene | Pungent and plastic | + | + | + | + |
| 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol | Phenolic and herbal | + | + | + | + |
| 2-Decenal, (E)- | Fatty, green, orange, tallowy | + | + | ||
| 2-Isopropyl-5-methyl-1-heptanol | - | + | + | + | + |
| 3-Ethyl-3-methylheptane | Coffee | + | + | ||
| 3-Octadecene, (E)- | - | + | |||
| 4-Decene, 7-methyl-, (E)- | Creamy | + | |||
| Acetoin | Butter, coffee, creamy | + | + | + | + |
| Benzaldehyde | Almond, burnt sugar, fruity, woody | + | + | + | + |
| Benzene, 1,3-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)- | - | + | + | + | + |
| Benzyl alcohol | Aromatic, floral, fruity, sweet | + | + | + | + |
| Carbonic acid, eicosyl vinyl ester | Sweet | + | |||
| Cyclopentane, 1-butyl-2-propyl- | - | + | + | ||
| Decane | Alkane, fruity, fuel, sweet | + | + | + | + |
| Decane, 4-methyl- | Pungent, acrid, green and ripe fruits, dried pericarp of Japanese pepper | + | + | + | |
| Decane, 5-ethyl-5-methyl- | - | + | + | + | |
| Dichloroacetic acid, undecyl ester | Pungent and acetic | + | |||
| Dodecane | Alkane and fuel-like | + | + | + | + |
| Dodecane, 4,6-dimethyl- | - | + | + | + | + |
| Ethane, 1,1,2,2-tetrachloro- | Sweet | + | |||
| Ethanol, 2-(dodecyloxy)- | - | + | + | ||
| Heptane, 2,4-dimethyl- | Pungent and plastic | + | + | + | |
| Heptane, 4-methyl- | Sweet and fruity | + | + | + | + |
| Hexadecane | Alkane, fruity, fuel, sweet | + | + | + | + |
| n-Hexadecanoic acid | Rancid and pungent | + | + | + | + |
| Nonane, 2,6-dimethyl- | - | + | |||
| Nonane, 4-methyl- | Meaty and fatty | + | + | + | |
| Octane, 3,3-dimethyl- | - | + | |||
| Octane, 3,5-dimethyl- | Acidic and pungent | + | |||
| Octane, 4-methyl- | Faint hydrocarbon swell | + | + | ||
| Tetradecane | Alkane, fuel, mild herbaceous, sweet | + | + | + | + |
| Tetradecanoic acid | Waxy, fatty, soapy | + | + | ||
| Tetrachloroethylene | Chloroform, sweet, ether-like | + | + | ||
| Undecane, 3,8-dimethyl- | Gasoline-like to odorless | + | |||
| Feature | Type of Cheese and Storage Duration | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H | |||||
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | A | T | |
| Color parameters | ||||||
| L* | 81.69 ± 1.39 | 82.06 ± 1.93 | 75.83 ± 5.96 | 75.91 ± 5.24 | *** | NS |
| a* | −1.85 ± 0.24 | −1.96 ± 0.19 | −2.38 ± 0.32 | −2.52 ± 0.25 | *** | * |
| b* | 11.76 ± 0.89 | 13.06 ± 1.51 | 12.86 ± 1.20 | 13.87 ± 1.12 | *** | *** |
| h | 98.91 ± 0.67 | 89.04 ± 9.52 | 100.57 ± 1.79 | 91.14 ± 9.51 | NS | *** |
| C* | 11.91 ± 0.91 | 7.78 ± 0.75 | 13.09 ± 1.17 | 8.20 ± 0.55 | *** | *** |
| Textural parameters | ||||||
| Hardness [kG] | 1.29 ± 0.26 | 1.58 ± 0.34 | 2.16 ± 0.44 | 2.13 ± 0.39 | *** | NS |
| Adhesiveness [kG s] | 0.10 ± 0.08 | 0.13 ± 0.07 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | 0.13 ± 0.07 | NS | NS |
| Springiness [-] | 0.61 ± 0.07 | 0.50 ± 0.07 | 0.63 ± 0.09 | 0.45 ± 0.08 | NS | *** |
| Cohesiveness [-] | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | NS | *** |
| Chewiness [kG] | 0.19 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.11 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | *** | *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pluta-Kubica, A.; Najgebauer-Lejko, D.; Domagała, J.; Lakatošová, J.; Šnirc, M.; Golian, J. Sensory Quality, Volatile Compounds, and Physical Properties of Sheep’s Milk Cheese with Herbs (Allium ursinum L.). Molecules 2024, 29, 5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29245999
Pluta-Kubica A, Najgebauer-Lejko D, Domagała J, Lakatošová J, Šnirc M, Golian J. Sensory Quality, Volatile Compounds, and Physical Properties of Sheep’s Milk Cheese with Herbs (Allium ursinum L.). Molecules. 2024; 29(24):5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29245999
Chicago/Turabian StylePluta-Kubica, Agnieszka, Dorota Najgebauer-Lejko, Jacek Domagała, Jana Lakatošová, Marek Šnirc, and Jozef Golian. 2024. "Sensory Quality, Volatile Compounds, and Physical Properties of Sheep’s Milk Cheese with Herbs (Allium ursinum L.)" Molecules 29, no. 24: 5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29245999
APA StylePluta-Kubica, A., Najgebauer-Lejko, D., Domagała, J., Lakatošová, J., Šnirc, M., & Golian, J. (2024). Sensory Quality, Volatile Compounds, and Physical Properties of Sheep’s Milk Cheese with Herbs (Allium ursinum L.). Molecules, 29(24), 5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29245999







