Delayed Effect of Superheated Steam Treatment on Starch Retrogradation of Rice Cake After Storage by Modifying Starch Chain-Length Distribution in Rice Flour
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of SS Treatment on the Composition and Particle Size Distribution of Rice Flour
2.2. Effect of SS Treatment on Rheological Properties of Rice Flour and Rice Paste
2.3. Effect of SS Treatment on Pasting Properties of Rice Flour
2.4. Amylopectin Chain-Length Distribution and Weight-Average Molecular Weight of Rice Starch
2.5. Microstructure Analysis of Rice and Rice Flour
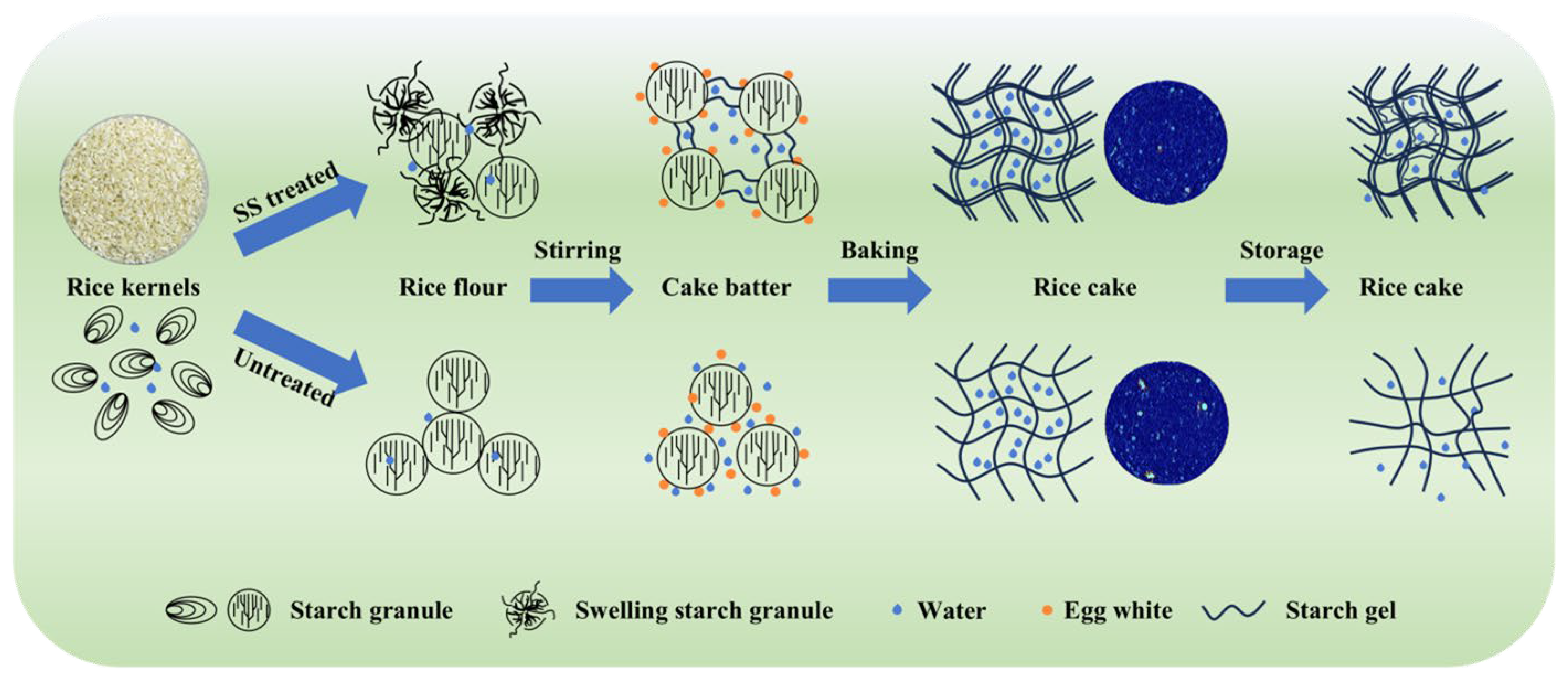
2.6. Effect of SS Treatments on Rice Cake Quality
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. SS Treatment of Rice Kernels
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of Rice Flour
3.3. The Pasting Properties of Rice Flour
3.4. The Amylopectin Chain-Length Distribution and Weight-Average Molecular Weight of Rice Starch
3.5. Rheological Properties of Rice Flour and Rice Paste
3.6. Microstructure of Rice Flour
3.7. The Preparation of Rice Cake
3.8. Baking Properties of Rice Cake
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nespeca, L.D.S.; Da Silva Paulino, H.F.; Barlati Vieira Da Silva, T.; Bona, E.; Leimann, F.V.; Marques, L.L.M.; Cardoso, F.A.R.; Droval, A.A.; Fuchs, R.H.B. How Does the Replacement of Rice Flour with Flours of Higher Nutritional Quality Impact the Texture and Sensory Profile and Acceptance of Gluten-free Chocolate Cakes? Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 2019–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, R.S.; Paz, G.; Morris, A.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Moncada, M.; King, J.M. High Protein Brown Rice Flour, Tapioca Starch & Potato Starch in the Development of Gluten-Free Cupcakes. LWT 2021, 152, 112326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.-X.; Lin, Q.-L.; Liu, G.-Q.; Yu, F.-X. A Comparative Study of the Characteristics of Cross-Linked, Oxidized and Dual-Modified Rice Starches. Molecules 2012, 17, 10946–10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purhagen, J.K.; Sjöö, M.E.; Eliasson, A.-C. The Anti-Staling Effect of Pre-Gelatinized Flour and Emulsifier in Gluten-Free Bread. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Retrogradation Properties of High Amylose Rice Flour and Rice Starch by Physical Modification. LWT 2010, 43, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Cui, S.W.; Qiu, J. Different Thermal Treatments of Highland Barley Kernel Affect Its Flour Physicochemical Properties by Structural Modification of Starch and Protein. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Xiong, Y.; Lu, H.; Luo, S.; Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Liu, C. Preparation and Characterization of Rice Starch Citrates by Superheated Steam: A New Strategy of Producing Resistant Starch. LWT 2022, 154, 112890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Z.; Kumrungsee, T.; Huang, W.; Cao, R. Effect of Pressure Cooking on Phenolic Compounds of Quinoa. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2023, 6, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, A.; Qiu, J.; Li, Z. Effects of Superheated Steam on Starch Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Buckwheat Flour during Storage. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 99, 103221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Luo, S.; Liu, C. Improvement in Storage Stability of Lightly Milled Rice Using Superheated Steam Processing. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 71, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zuo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Wang, L. Pre-Gelatinization Phenomenon and Protein Structural Changes in Rice Quality Modification by Superheated Steam Treatment. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-T.; Zhou, D.-N.; Jin, Z.-Y.; Xu, X.-M.; Chen, H.-Q. Effect of Repeated Heat-Moisture Treatments on Digestibility, Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Sweet Potato Starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Bian, K.; Guan, E.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y. Reduction of Deoxynivalenol in Wheat with Superheated Steam and Its Effects on Wheat Quality. Toxins 2019, 11, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.-N.; Rahman, M.S.; Lee, K.-Y.; Choi, S.-G. Superheated Steam Pretreatment of Rice Flours: Gelatinization Behavior and Functional Properties during Thermal Treatment. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 101013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, E.; Li, M.; Bian, K.; Wen, J.; Ren, C. Improvement of Cake Quality by Superheated Steam Treatment of Wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z. Superheated Steam Treatment Improved Flour Qualities of Wheat in Suitable Conditions. J. Food Process Preserv. 2017, 41, e13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, A.; Qiu, J.; Li, Z. Inhibiting Effect of Superheated Steam Processing on Milling Characteristics Deterioration Induced by Storage of Common Buckwheat. LWT 2021, 145, 111375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burešová, I.; Lullien-Pellerin, V.; Červenka, L.; Mlček, J.; Šebestíková, R.; Masaříková, L. The Comparison of the Effect of Flour Particle Size and Content of Damaged Starch on Rice and Buckwheat Slurry, Dough, and Bread Characteristics. Foods 2023, 12, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sang, S.; Xu, D.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X. The Contribution of Superheated Steam Treatment of Wheat Flour to the Cake Quality. LWT 2021, 141, 110958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sang, S.; Wu, F.; Xu, X. Insight into the Thermal Stability, Structural Change and Rheological Property of Wheat Gluten Treated by Superheated Steam during Hydration. Food Struct. 2023, 36, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Oyedeji, A.B.; Ogundele, O.M.; Adebo, O.A.; Njobeh, P.B.; Kayitesi, E. Infrared Heating under Optimized Conditions Enhanced the Pasting and Swelling Behaviour of Cowpea Starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, D.; Sang, S.; Jin, Y.; Xu, X.; Cui, B. Effect of Superheated Steam Treatment on the Structural and Digestible Properties of Wheat Flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, H.; Wan, C.; Leng, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, P.; Gao, X.; Gao, J. Structural, Pasting and Thermal Properties of Common Buckwheat (Fagopyrum Esculentum Moench) Starches Affected by Molecular Structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Li, C.; Bai, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X. A Starch Molecular Basis for Aging-Induced Changes in Pasting and Textural Properties of Waxy Rice. Food Chem. 2019, 284, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Qiu, J. Multi-Scale Structure, Rheological and Digestive Properties of Starch Isolated from Highland Barley Kernels Subjected to Different Thermal Treatments. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cao, S.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, W. Modification in Physicochemical, Structural and Digestive Properties of Pea Starch during Heat-Moisture Process Assisted by Pre- and Post-Treatment of Ultrasound. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.-P.; Zhou, H.-M.; Zhu, K.-R.; Li, Q. Effect of Thermal Treatment on the Physicochemical, Ultrastructural and Nutritional Characteristics of Whole Grain Highland Barley. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavareze, E.D.R.; Storck, C.R.; De Castro, L.A.S.; Schirmer, M.A.; Dias, A.R.G. Effect of Heat-Moisture Treatment on Rice Starch of Varying Amylose Content. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Lin, Z.; Wang, A.; Xiao, T.; He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.-T. Influence of Damaged Starch on the Properties of Rice Flour and Quality Attributes of Gluten-Free Rice Bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 101, 103296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiraghi, M.; De La Hera, E.; Pérez, G.T.; Gómez, M. Effect of Wheat Flour Character-istics on Sponge Cake Quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, L.; Tong, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Effect of Milling Methods on the Properties of Rice Flour and Gluten-Free Rice Bread. LWT 2019, 108, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC International Method 56.11.02; Solvent Retention Capacity Profile; AACC: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000.
- Wang, H.; Li, D.; Ma, Q.; Wu, E.; Gao, L.; Yang, P.; Gao, J.; Feng, B. Nitrogen Fertilizer Affects Starch Synthesis to Define Non-Waxy and Waxy Proso Millet Quality. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Kuang, J. Rheological, Thermal, and Structural Properties of Heat-Induced Gluten Gel: Effects of Starch with Varying Degrees of Debranching. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 272, 132678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, J.; Torbica, A.; Belović, M. Effect of Non-Gluten Proteins and Transglutaminase on Dough Rheological Properties and Quality of Bread Based on Millet (Panicum miliaceum) Flour. LWT 2020, 118, 108852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xiong, W.; Wang, L.; Ju, X. Insight into the Effect of Gluten-Starch Ratio on the Properties of Chinese Steamed Bread (Mantou). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


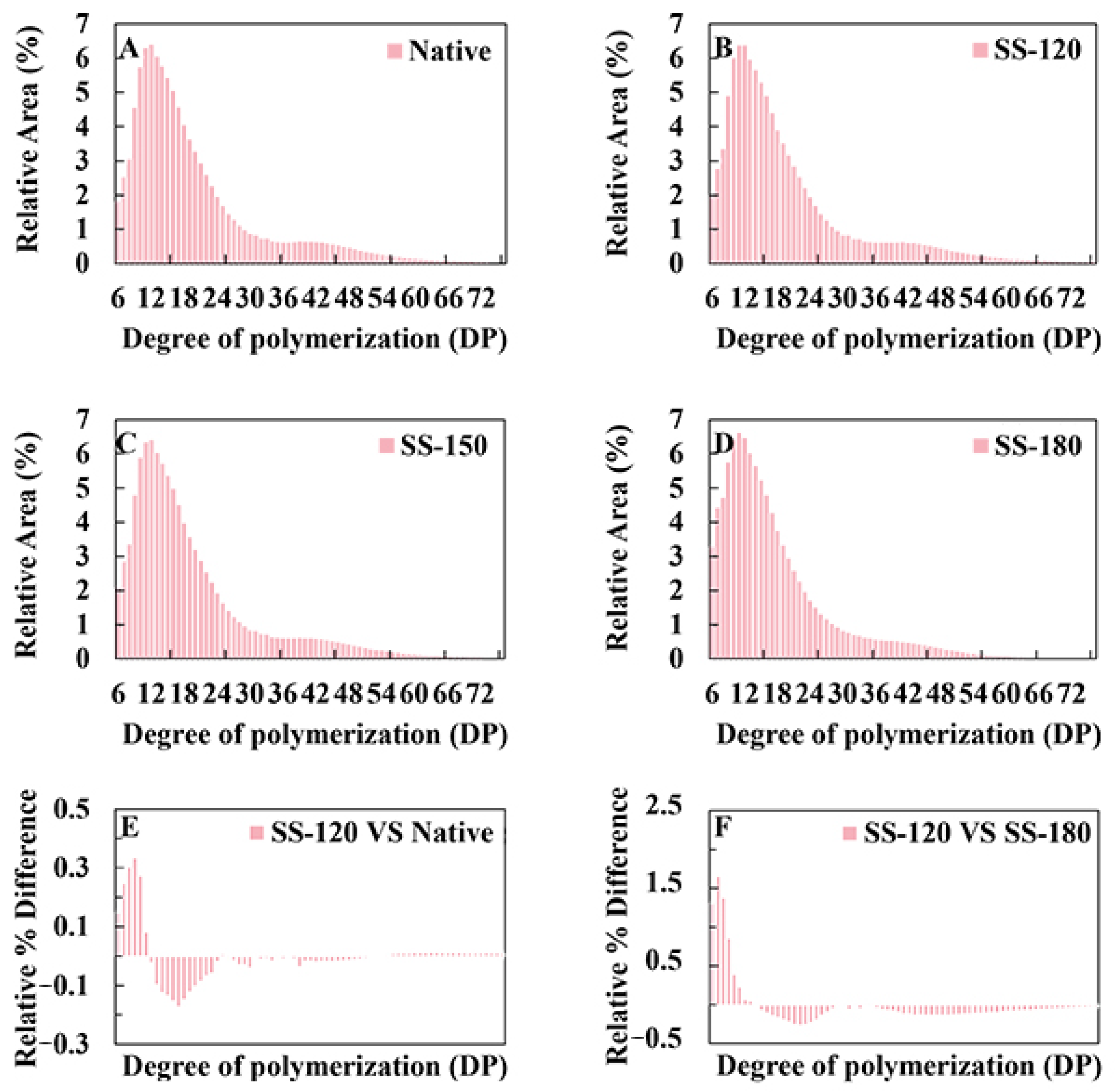


| Pasting Properties | Native | SS-120 | SS-150 | SS-180 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak viscosity (Pa·s) | 3044 ± 41 a | 2649 ± 93 c | 2722 ± 42 bc | 2767 ± 63 b |
| Trough viscosity (Pa·s) | 596 ± 22 a | 446 ± 17 b | 372 ± 35 c | 363 ± 33 c |
| Breakdown (Pa·s) | 2448 ± 46 a | 2203 ± 100 c | 2350 ± 34 b | 2404 ± 35 ab |
| Final viscosity (Pa·s) | 3202 ± 7.6 a | 2994 ± 177 b | 3221 ± 75 a | 3320 ± 51 a |
| Setback (Pa·s) | 2606 ± 27 b | 2549 ± 182 b | 2849 ± 81 a | 2957 ± 23 a |
| Pasting time (min) | 9.49 ± 0.05 b | 9.61 ± 0.15 ab | 9.68 ± 0.16 a | 9.73 ± 0.07 a |
| Pasting temperature (°C) | 81.31 ± 0.19 c | 82.11 ± 0.27 b | 82.65 ± 0.47 a | 82.72 ± 0.32 a |
| Native | SS-120 | SS-150 | SS-180 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP6-12 (%) | 30.40 ± 0.01 c | 31.75 ± 0.11 b | 31.67 ± 0.05 b | 37.59 ± 0.12 a |
| DP13-24 (%) | 47.50 ± 0.11 a | 46.25 ± 0.21 b | 46.81 ± 0.05 c | 44.35 ± 0.16 d |
| DP25-36 (%) | 11.40 ± 0.02 a | 11.27 ± 0.06 b | 11.22 ± 0.01 b | 10.63 ± 0.05 c |
| DP ≥ 37 (%) | 10.70 ± 0.09 a | 10.73 ± 0.10 a | 10.31 ± 0.02 b | 7.42 ± 0.08 c |
| Mw (kDa) | 88,127.87 ± 5299.20 c | 127,439.13 ± 1406.56 b | 142,088.03 ± 5482.78 a | 122,115.39 ± 8838.54 b |
| PDI | 2.88 ± 0.26 a | 2.88 ± 0.18 a | 2.71 ± 0.09 a | 2.28 ± 0.29 b |
| Time | Crumb Structure | Native | SS-120 | SS-150 | SS-180 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 day | Cell area (%) | 50.57 ± 0.25 bc | 50.15 ± 0.73 c | 51.27 ± 0.21 a | 51.18 ± 0.29 a |
| 0 day | Cell diameter (mm) | 1.71 ± 0.04 b | 1.73 ± 0.11 ab | 1.83 ± 0.00 a | 1.79 ± 0.07 ab |
| 0 day | Cell wall thickness (mm) | 0.42 ± 0.01 a | 0.43 ± 0.01 a | 0.44 ± 0.01 a | 0.44 ± 0.01 a |
| 0 day | Specific volume (mL/g) | 2.86 ± 0.08 b | 2.96 ± 0.06 ab | 3.08 ± 0.05 a | 3.09 ± 0.09 a |
| 0 day | Hardness (N) | 1.81 ± 0.07 b | 2.03 ± 0.15 a | 1.30 ± 0.29 d | 1.59 ± 0.13 c |
| 0 day | Cohesiveness | 0.73 ± 0.02 a | 0.71 ± 0.02 b | 0.70 ± 0.01 b | 0.71 ± 0.02 b |
| 0 day | Springiness (mm) | 7.33 ± 0.25 b | 7.64 ± 0.24 ab | 6.92 ± 1.36 b | 8.51 ± 0.41 a |
| 0 day | Gumminess (N) | 1.32 ± 0.05 a | 1.44 ± 0.12 a | 0.90 ± 0.20 c | 1.11 ± 0.10 b |
| 0 day | Chewiness (mJ) | 9.65 ± 0.50 a | 10.98 ± 1.19 a | 6.43 ± 2.52 c | 9.51 ± 1.28 a |
| 7 day | Hardness (N) | 6.05 ± 0.51 a | 5.77 ± 0.14 ab | 5.83 ± 0.21 ab | 5.30 ± 0.30 b |
| 7 day | Cohesiveness | 0.60 ± 0.06 b | 0.60 ± 0.03 b | 0.59 ± 0.01 b | 0.71 ± 0.07 a |
| 7 day | Springiness (mm) | 9.20 ± 0.10 b | 9.52 ± 0.06 a | 9.49 ± 0.14 a | 9.14 ± 0.14 b |
| 7 day | Gumminess (N) | 3.65 ± 0.61 a | 3.47 ± 0.19 a | 3.44 ± 0.15 a | 3.77 ± 0.16 a |
| 7 day | Chewiness (mJ) | 34.70 ± 5.06 a | 33.08 ± 1.99 a | 32.66 ± 1.12 a | 34.40 ± 1.00 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Xia, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, J. Delayed Effect of Superheated Steam Treatment on Starch Retrogradation of Rice Cake After Storage by Modifying Starch Chain-Length Distribution in Rice Flour. Molecules 2024, 29, 5253. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225253
Cao R, Zhang Z, Wang X, Xia C, Cheng Y, Wang Z, Qiu J. Delayed Effect of Superheated Steam Treatment on Starch Retrogradation of Rice Cake After Storage by Modifying Starch Chain-Length Distribution in Rice Flour. Molecules. 2024; 29(22):5253. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225253
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Ruge, Zixiu Zhang, Xishuang Wang, Chen Xia, Yongqiang Cheng, Zhiwei Wang, and Ju Qiu. 2024. "Delayed Effect of Superheated Steam Treatment on Starch Retrogradation of Rice Cake After Storage by Modifying Starch Chain-Length Distribution in Rice Flour" Molecules 29, no. 22: 5253. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225253
APA StyleCao, R., Zhang, Z., Wang, X., Xia, C., Cheng, Y., Wang, Z., & Qiu, J. (2024). Delayed Effect of Superheated Steam Treatment on Starch Retrogradation of Rice Cake After Storage by Modifying Starch Chain-Length Distribution in Rice Flour. Molecules, 29(22), 5253. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225253








