On Water Arrangements in Right- and Left-Handed DNA Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Structures and Their Patterns of Hydration
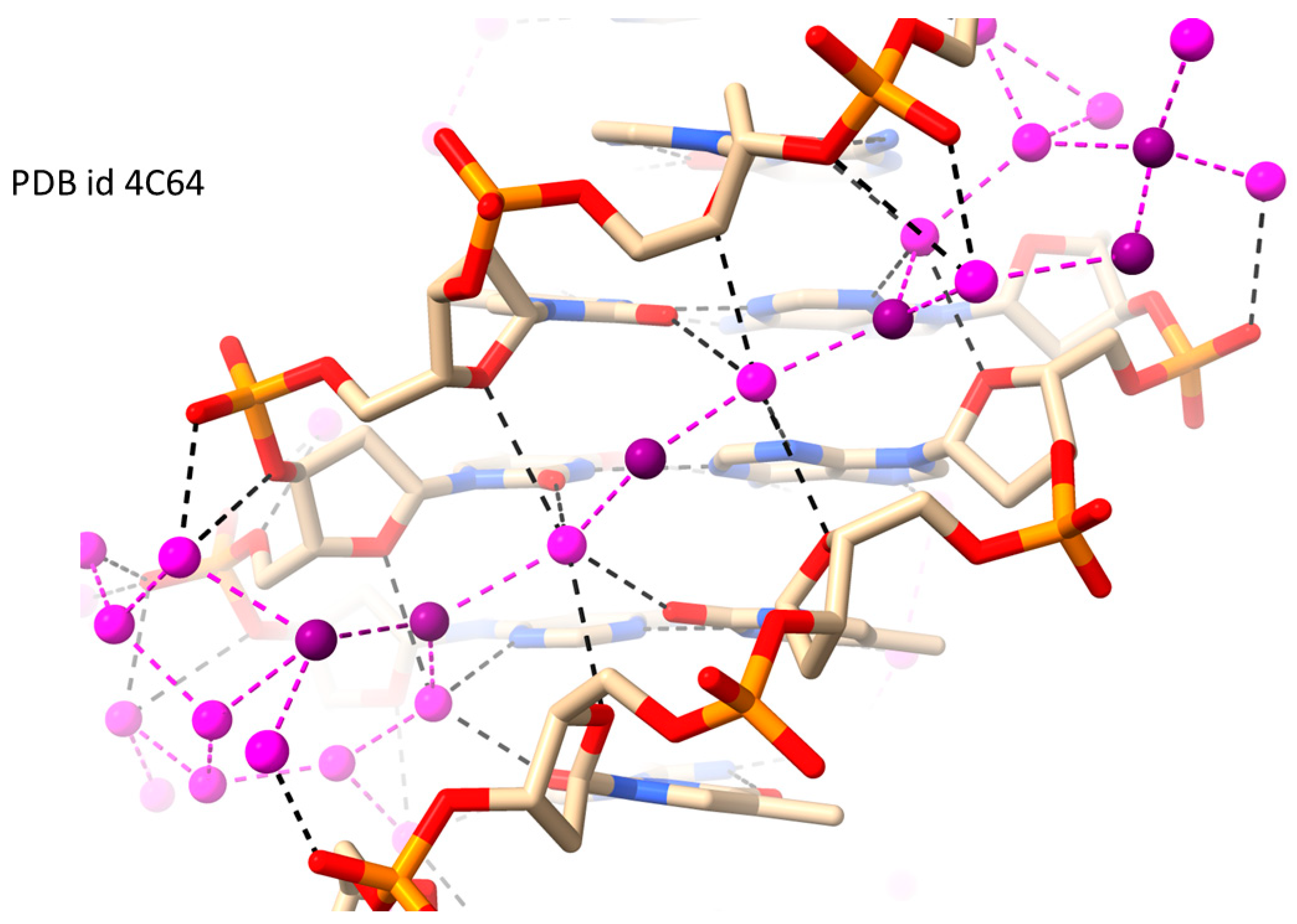
2.1. RH-Duplex DNAs
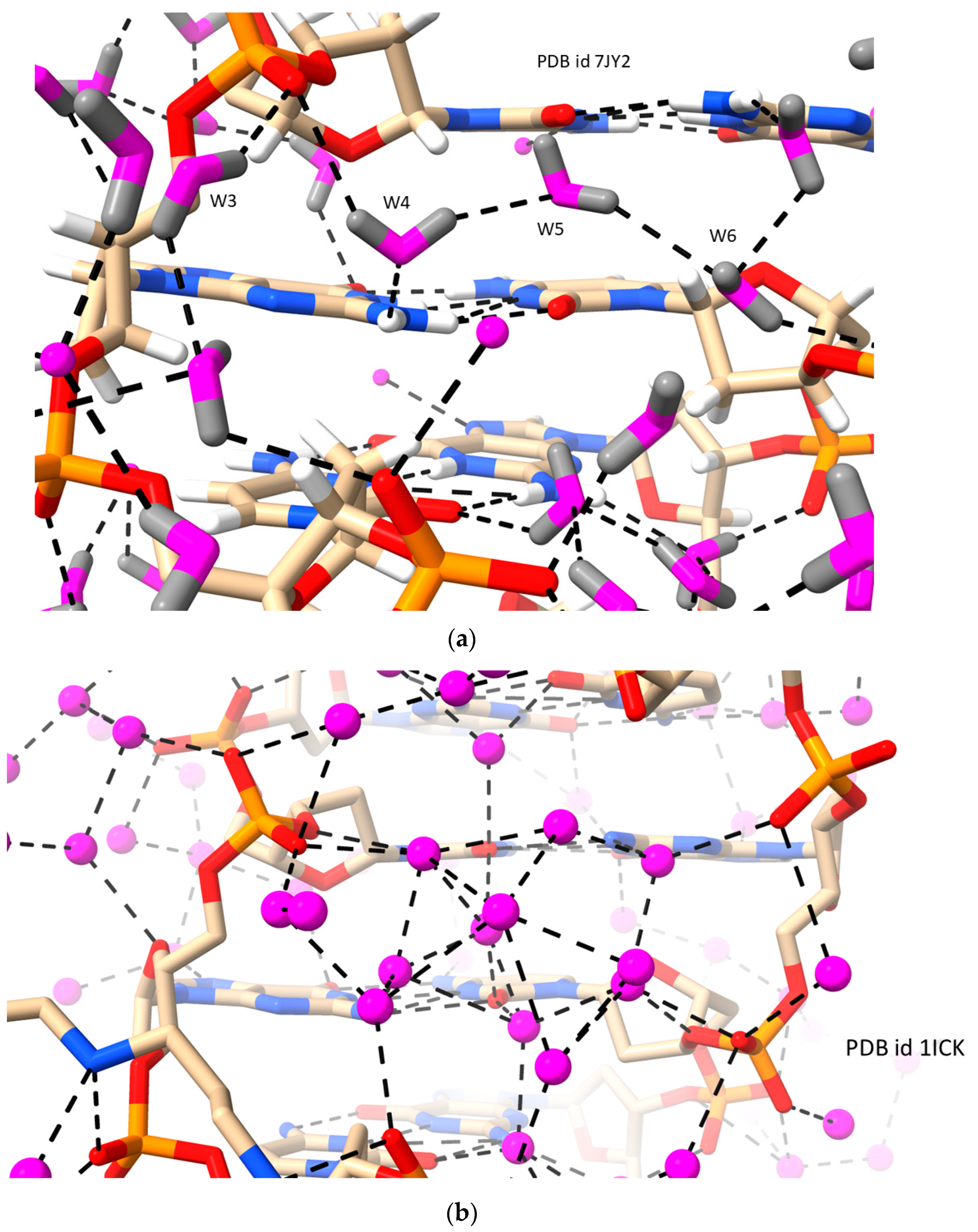
2.2. LH Duplex DNAs (i.e., Z-DNA)
2.3. RH-G4s
- Two adjacent strands running in the same direction generate a medium groove.
- Two adjacent strands running in opposite directions will generate either narrow or wide grooves.
- A narrow groove has all phosphate groups oriented into the groove; thus, in the adjacent groove, all phosphates on the shared strand between the two grooves are forced to be oriented away from the groove, making it either wide or medium but not narrow.
- Adjacent narrow grooves do not exist.
- Wide grooves have all phosphates oriented away from the groove.
2.4. RH i-Motifs
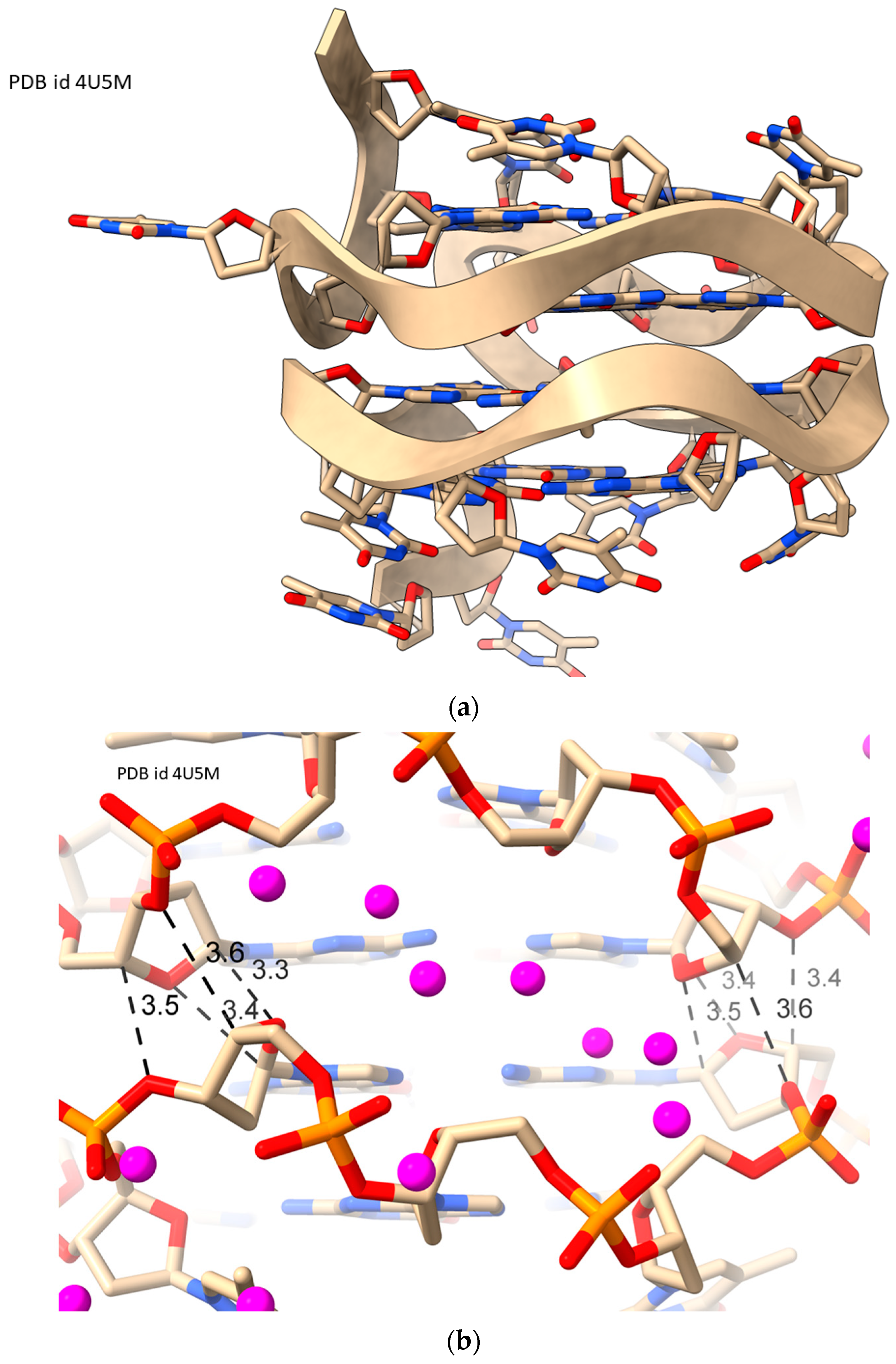
2.5. LH-G4s
3. Discussion
4. Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Westhof, E. Water: An integral part of nucleic acid structure. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 1988, 17, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M. Hydration of DNA. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1991, 1, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, M.; Portmann, S.; Usman, N. RNA hydration: A detailed look. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 8489–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermannová, L.; Schneider, B. Hydration of proteins and nucleic acids: Advances in experiment and theory. A review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laage, D.; Elsaesser, T.; Hynes, J.T. Water dynamics in the hydration shells of biomolecules. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10694–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, M.L.; Vanselous, H.; Corcelli, S.A.; Petersen, P.B. DNA’s chiral spine of hydration. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giambaşu, G.M.; Case, D.A.; York, D.M. Predicting site-binding modes of ions and water to nucleic acids using molecular solvation theory. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harp, J.M.; Coates, L.; Sullivan, B.; Egli, M. Water structure around a left-handed Z-DNA fragment analyzed by cryo neutron crystallography. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 4782–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermannová, L.; Černý, J.; Malý, M.; Nekardová, M.; Schneider, B. Knowledge-based prediction of DNA hydration using hydrated dinucleotides as building blocks. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2022, 78, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, W.K.; Li, Y.; Fenley, M.O. Insights into DNA solvation found in protein-DNA structures. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 121, 4749–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubon, T.; Zdorevskyi, O.; Perepelytsya, S. Molecular dynamics study of collective water vibrations in a DNA hydration shell. Eur. Biophys. J. 2023, 52, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.E.; Gosling, R.G. The structure of sodium thymonucleate fibres. I. The influence of water content. Acta Crystallogr. 1953, 6, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.D.; Crick, F.H.C. Molecular structure of nucleic acids: A structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature 1953, 171, 737–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, W.; Wilkins, M.H.; Wilson, H.R.; Hamilton, L.D. the molecular configuration of deoxyribonucleic acid. iv. X-ray diffraction study of the A form. J. Mol. Biol. 1965, 12, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broomhead, J.M. The structures of pyrimidines and purines. IV. The crystal structure of guanine hydrochloride and its relation to that of adenine hydrochloride. Acta Crystallogr. 1951, 4, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopka, M.L.; Fratini, A.V.; Drew, H.R.; Dickerson, R.E. Ordered water structure around a B-DNA dodecamer: A quantitative study. J. Mol. Biol. 1983, 163, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.K.; Zhao, L.; Zewail, A.H. Water at DNA surfaces: Ultrafast dynamics in minor groove recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8113–8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, K.J.; Brown, D.G.; Spink, N.; Skelly, J.V.; Neidle, S. Molecular structure of the B-DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG)2. An examination of propeller twist and minor-groove water structure at 2.2Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 226, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minasov, G.; Tereshko, V.; Egli, M. Atomic-resolution crystal structures of B-DNA reveal specific influences of divalent metal ions on conformation and packing. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 291, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liepinsh, E.; Otting, G.; Wȕthrich, K. NMR observation of individual molecules of hydration water bound to DNA duplexes: Direct evidence for a spine of hydration water present in aqueous solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 6549–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlieghe, D.; Turkenburg, J.P.; Van Meervelt, L. B-DNA at atomic resolution reveals extended hydration patterns. Acta Crystallogr. D 1999, 55, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-López, M.; Malinina, L.; Liu, J.; Huynh-Dinh, T.; Subirana, J.A. Water and ions in a high resolution structure of B-DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 23683–23686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, G.R.; Squire, C.J.; Baker, L.J.; Martin, R.F.; White, J. Intermolecular interactions and water structure in a condensed phase B-DNA crystal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhumalar, A.; Bansal, M. Structural insights into the effect of hydration and ions on A-tract DNA: A molecular dynamics study. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, K.K.; Maehigashi, T.; Howerton, S.B.; Sines, C.C.; Tannenbaum, S.; Williams, L.D. High-resolution structure of an extended A-tract: [d(CGCAAATTTGCG)]2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15330–15331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, S.; Chatake, T.; Ohhara, T.; Kurihara, K.; Tanaka, I.; Suzuki, N.; Fujimoto, Z.; Mizuno, H.; Niimura, N. Complicated water orientations in the minor groove of the B-DNA decamer d(CCATTAATGG)2 observed by neutron diffraction measurements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 3017–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Schatz, G.C. Molecular dynamics study of the role of the spine of hydration in DNA A-tracts in determining nucleosome occupancy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 13672–13681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubon, T.L.; Perepelytsya, S.M. Low-frequency vibrations of water molecules in DNA minor groove. Eur. Phys. J. E Soft Matter 2021, 44, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.; Neidle, S.; Wilson, W.D. A role for water molecules in DNA-ligand minor groove recognition. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, A.; Depauw, S.; Nhili, R.; David-Cordonnier, M.H.; Lee, M.P.; Ismail, M.A.; Farahat, A.A.; Say, M.; Chackal-Catoen, S.; et al. Water-mediated binding of agents that target the DNA minor groove. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10171–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Wilson, W.D.; Neidle, S. Small-molecule binding to the DNA minor groove is mediated by a conserved water cluster. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangir, D.K.; Kundu, S.; Mehrotra, R. Role of minor groove width and hydration pattern on amsacrine interaction with DNA. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlitzki, N.; Huang, K.; Xhani, S.; Farahat, A.A.; Kumar, A.; Boykin, D.W.; Poon, G.M.K. Investigation of the electrostatic and hydration properties of DNA minor groove-binding by a heterocyclic diamidine by osmotic pressure. Biophys. Chem. 2017, 231, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, G.A.; Hambley, T.W.; McAuley-Hecht, K.; Brown, T.; Hunter, W.N. Anthracycline-DNA interactions at unfavourable base-pair triplet-binding sites: Structures of d(CGGCCG)/daunomycin and d(TGGCCA)/adriamycin complexes. Acta Crystallogr D 1993, 49, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidle, S.; Berman, H.M.; Shieh, H.S. Highly structured water network in crystals of a deoxydinucleoside-drug complex. Nature 1980, 288, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellert, M.; Lipsett, M.N.; Davies, D.R. Helix formation by guanylic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1962, 48, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge, S.; Parkinson, G.N.; Hazel, P.; Todd, A.K.; Neidle, S. Quadruplex DNA: Sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochman, M.L.; Paeschke, K.; Zakian, V.A. DNA secondary structures: Stability and function of G-quadruplex structures. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 13, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, J.; Adhikari, S.; Balasubramanian, S. The structure and function of DNA G-quadruplexes. Trends Chem. 2019, 2, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnerdy, F.R.; Phan, A.T. Quadruplex structure and diversity. Ann. Rep. Med. Chem. 2020, 54, 45–73. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, A.K.; Johnston, M.; Neidle, S. Highly prevalent putative quadruplex sequence motifs in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2901–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Prevalence of quadruplexes in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2908–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. G-quadruplexes in promoters throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel-Hertsch, R.; Beraldi, D.; Lensing, S.V.; Marsico, G.; Zyner, K.; Parry, A.; Di Antonio, M.; Pike, J.; Kimura, H.; Narita, M.; et al. G-quadruplex structures mark human regulatory chromatin. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte-Reche, E.; Serrano-Chacón, I.; Gonzalez, C.; Gallo, J.; Bañobre-López, M. Potential G-quadruplexes and i-Motifs in the SARS-CoV-2. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.C.; Buscaglia, R.; Chaires, J.B.; Lane, A.N.; Trent, J.O. Hydration Is a major determinant of the G-quadruplex stability and conformation of the human telomere 3′ sequence of d(AG3(TTAG3)3). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17105–17107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petraccone, L.; Pagano, B.; Giancola, C. Studying the effect of crowding and dehydration on DNA G-quadruplexes. Methods 2012, 57, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Takahashi, S.; Bhowmik, S.; Ohyama, T.; Sugimoto, N. Volumetric strategy for quantitatively elucidating a local hydration network around a G-quadruplex. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 7400–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.-M.; Tu, Y.; Wu, Y.-Y. Heterogeneous hydration patterns of G-quadruplex DNA. Chin. Phys. B 2023, 32, 028702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yatsunyk, L.; Neidle, S. Water spines and networks in G-quadruplex structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.J.; Heddi, B.; Schmitt, E.; Lim, K.W.; Mechulam, Y.; Phan, A.T. Structure of a left-handed DNA G-quadruplex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2729–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Winnerdy, F.R.; Maity, A.; Mechulam, Y.; Phan, A.T. A novel minimal motif for left-handed G-quadruplex formation. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 2527–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Ngo, K.H.; Winnerdy, F.R.; Maity, A.; Bakalar, B.; Mechulam, Y.; Schmitt, E.; Phan, A.T. Bulges in left-handed G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 1724–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakalar, B.; Heddi, B.; Schmitt, E.; Mechulam, Y.; Phan, A.T. A minimal sequence for left-handed G-quadruplex formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2331–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnerdy, F.R.; Bakalar, B.; Maity, A.; Vandana, J.J.; Mechulam, Y.; Schmitt, E.; Phan, A.T. NMR solution and X-ray crystal structures of a DNA molecule containing both right- and left-handed parallel-stranded G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 8272–8281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, N.Q.; Chung, W.J.; Truong, T.H.A.; Heddi, B.; Phan, A.T. G-quadruplex structure of an anti-proliferative DNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 7487–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.; Messaoudi, C.; Mouawad, L. ASC-G4, an algorithm to calculate advanced structural characteristics of G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 2087–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lercher, L.; McDonough, M.A.; El-Sagheer, A.H.; Thalhammer, A.; Kriaucionis, S.; Brown, T.; Schofield, C.J. Structural insights into how 5-hydroxymethylation influences transcription factor binding. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1794–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauter, Z.; Adamiak, D.A. Anomalous signal of phosphorus used for phasing DNA oligomer: Importance of data redundancy. Acta Crystallogr. D 2001, 57, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, K.; Brzuszkiewicz, A.; Dauter, M.; Kubicki, M.; Jaskolski, M.; Dauter, Z. High regularity of Z-DNA revealed by ultra high-resolution crystal structure at 0.55 Å. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 6238–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatake, T.; Tanaka, I.; Umino, H.; Arai, S.; Niimura, N. The hydration structure of a Z-DNA hexameric duplex determined by a neutron diffraction technique. Acta Crystallogr. 2005, D61, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessner, R.V.; Quigley, G.J.; Egli, M. Comparative studies of high resolution Z-DNA crystal structures. Part 1: Common hydration patterns of alternating dC-dG. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 236, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, S.; Parkinson, G.N.; Neidle, S. Crystal structure of the potassium form of an Oxytricha nova G-quadruplex. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 320, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, B.; Cai, Q.; Miao, H.; Shi, X.; Xu, N.; You, Y.; Fung, C.P.; Din, R.U.; et al. The crystal structure of an antiparallel chair-type G-quadruplex formed by bromo-substituted human telomeric DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 5395–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidle, S.; Sanderson, M. Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Beseiso, D.; Chen, E.V.; McCarthy, S.E.; Martin, K.N.; Gallagher, E.P.; Miao, J.; Yatsunyk, L.A. The first crystal structures of hybrid and parallel four-tetrad intramolecular G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 2959–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.S.; Jordan, D.; Lin, L.Y.; McCarthy, S.E.; Schneekloth, J.S., Jr.; Yatsunyk, L.A. Crystal structure of an i-motif from the HRAS oncogene promoter. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202301666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, K.; Lech, C.J.; Heddi, B.; Phan, A.T. High-resolution AFM structure of DNA G-wires in aqueous solution. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidle, S. Structured waters mediate small molecule binding to G-quadruplex nucleic acids. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, B.; Jain, T. The role of water in protein-DNA recognition. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Mol. Struct. 2004, 33, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privalov, P.L.; Crane-Robinson, C. Role of water in the formation of macromolecular structures. Eur. Biophys. J. 2017, 46, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, C.A.; Sargent, D.F.; Luger, K.; Maeder, A.W.; Richmond, T.J. solvent mediated interactions in the structure of the nucleosome core particle at 1.9 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 319, 1097–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




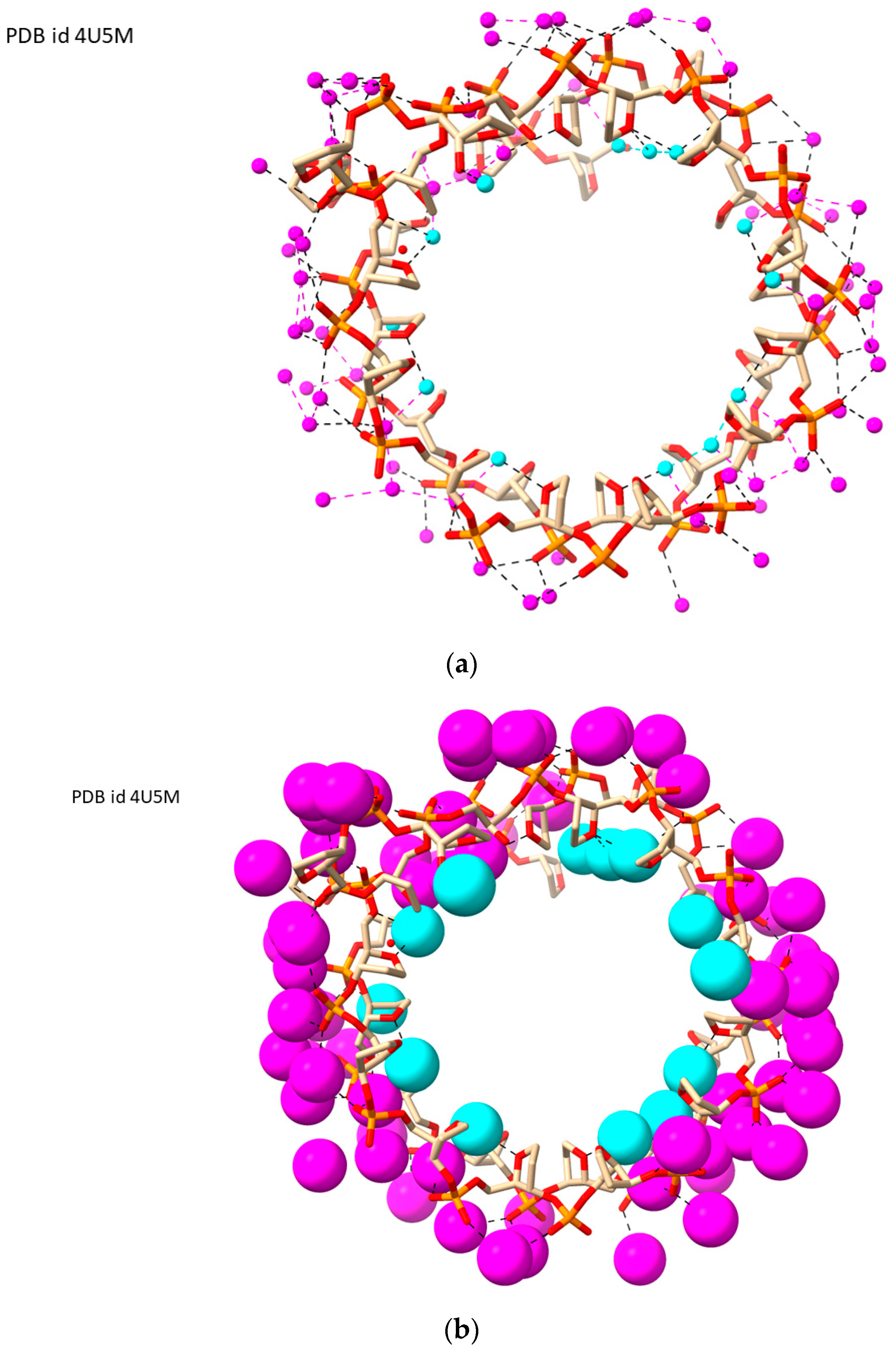
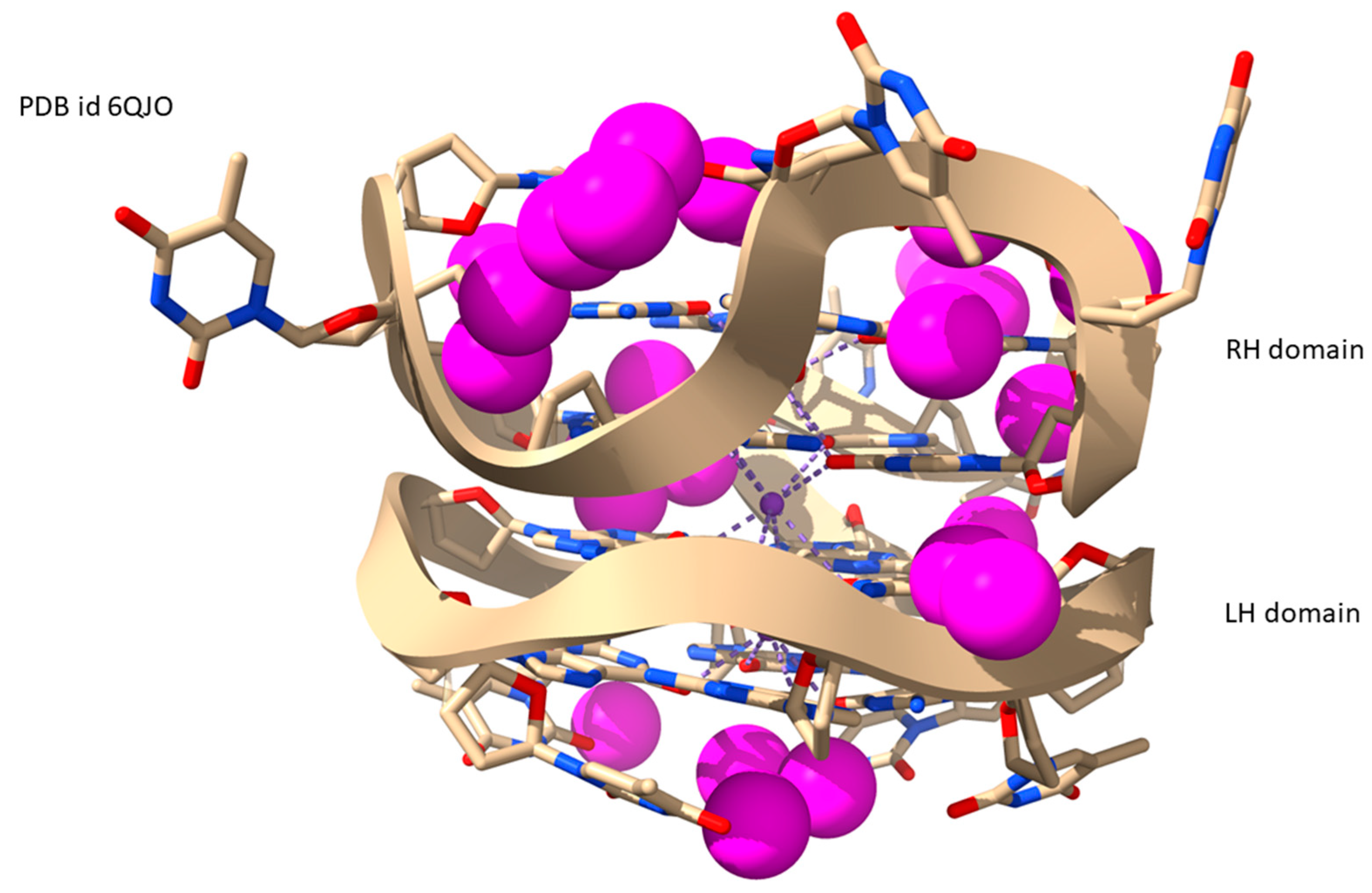

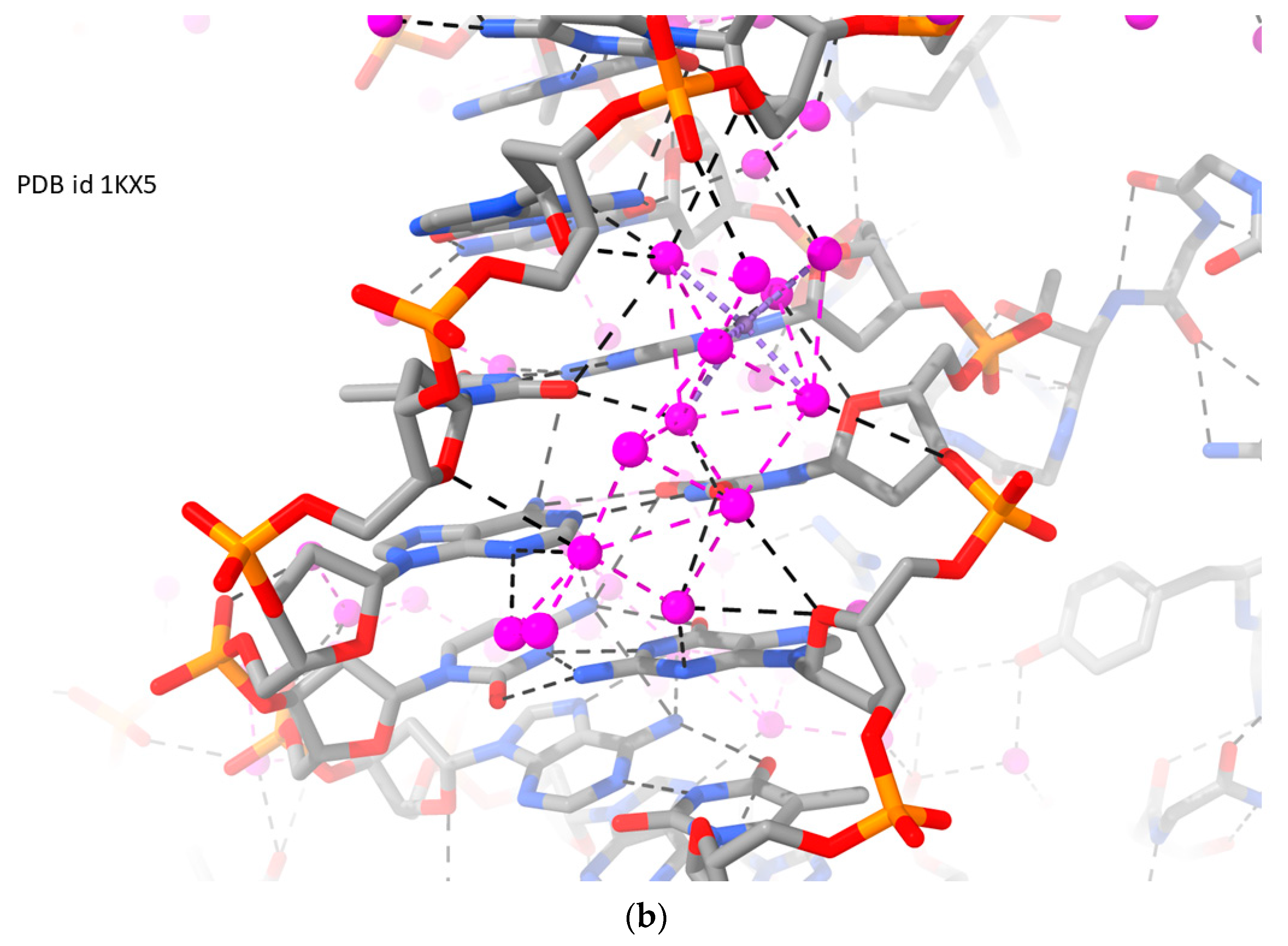
| Sequence | DNA Structure | Resolution (Å) | R Factor | No. of Solvent Atoms | PDB ID | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d[CGCGAATTCGCG] | RH-B-DNA | 1.32 | 0.139 | 131 | 4C64 | [58] |
| Nucleosome core particle 1 | RH-B-DNA | 1.94 | 0.208 | 3130 | 1KX5 | [72] |
| d[CGCGCG]2 | LH-Z-DNA | 1.00/1.50 | 0.156/ 0.277 | 77 | 7JY2 | [8] |
| d[CGCGCG]2 | LH-Z-DNA | 0.95 | 0.086 | 83 | 1ICK | [59] |
| d[CGCGCG]2 | LH-Z-DNA | 0.55 | 0.068 | 78.6 | 3P4J | [60] |
| d[CGCGCG]2 | LH-Z-DNA | 1.80 | 0.222 | 44 | 1V9G | [61] |
| d[GGGGTTTTGGGG] | RH-G4 Antiparallel dimer | 1.60 | 0.225 | 131 | 1JPQ | [63] |
| d[GGGTTAGGBrGTTAGGGTTAGGBrG] | RH-G4 Telomeric antiparallel | 1.40 | 0.159 | 119 | 6JKN | [64] |
| d[G(TTGGGG)4] | RH-G4 Telomeric hybrid | 1.56 | 0.154 | 379 | 6XT7 | [66] |
| d[CGC3GTGC3TGCGC3GCAAC3GA] | RH i-motif | 1.77 | 0.221 | 73 | 8CXF | [67] |
| d[(TGG)4TTG(TGG)3TGTT] | LH-G4 | 1.50 | 0.143 | 94 | 4U5M | [50] |
| d[GG(TGG)2TGTGTTGG(TGG)3TGTG] | LH-G4 | 1.69 | 0.20 | 80 | 7DFY | [51] |
| d[GT(GGT)3GTGGTGTGTGGTGG] | LH-G4 + 1 bulge | 1.18 | 0.119 | 158 | 7D5D | [52] |
| d[GT(GGT)3GTGGTGTGTGTGTGG] | LH-G4 + 2 bulges | 1.30 | 0.184 | 208 | 7D5E | [52] |
| d[G(TGG)3TG] | Minimal LH-G4 | 2.31 | 0.20 | 24 | 6FQ2 | [53] |
| d[GT(GGT)3GTTGT(GGT)3GT] | LH-G4 | 2.01 | 0.185 | 10 | 6GZ6 | [53] |
| d[GGTTGGTGTGGTTGGTTGT(GGT)3G | LH/RH-G4 | 1.80 | 0.164 | 166 | 6QJO | [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yatsunyk, L.A.; Neidle, S. On Water Arrangements in Right- and Left-Handed DNA Structures. Molecules 2024, 29, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020505
Yatsunyk LA, Neidle S. On Water Arrangements in Right- and Left-Handed DNA Structures. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020505
Chicago/Turabian StyleYatsunyk, Liliya A., and Stephen Neidle. 2024. "On Water Arrangements in Right- and Left-Handed DNA Structures" Molecules 29, no. 2: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020505
APA StyleYatsunyk, L. A., & Neidle, S. (2024). On Water Arrangements in Right- and Left-Handed DNA Structures. Molecules, 29(2), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020505