The Development of an Extraction Method for Simultaneously Analyzing Fatty Acids in Macroalgae Using SPE with Derivatization for LC–MS/MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
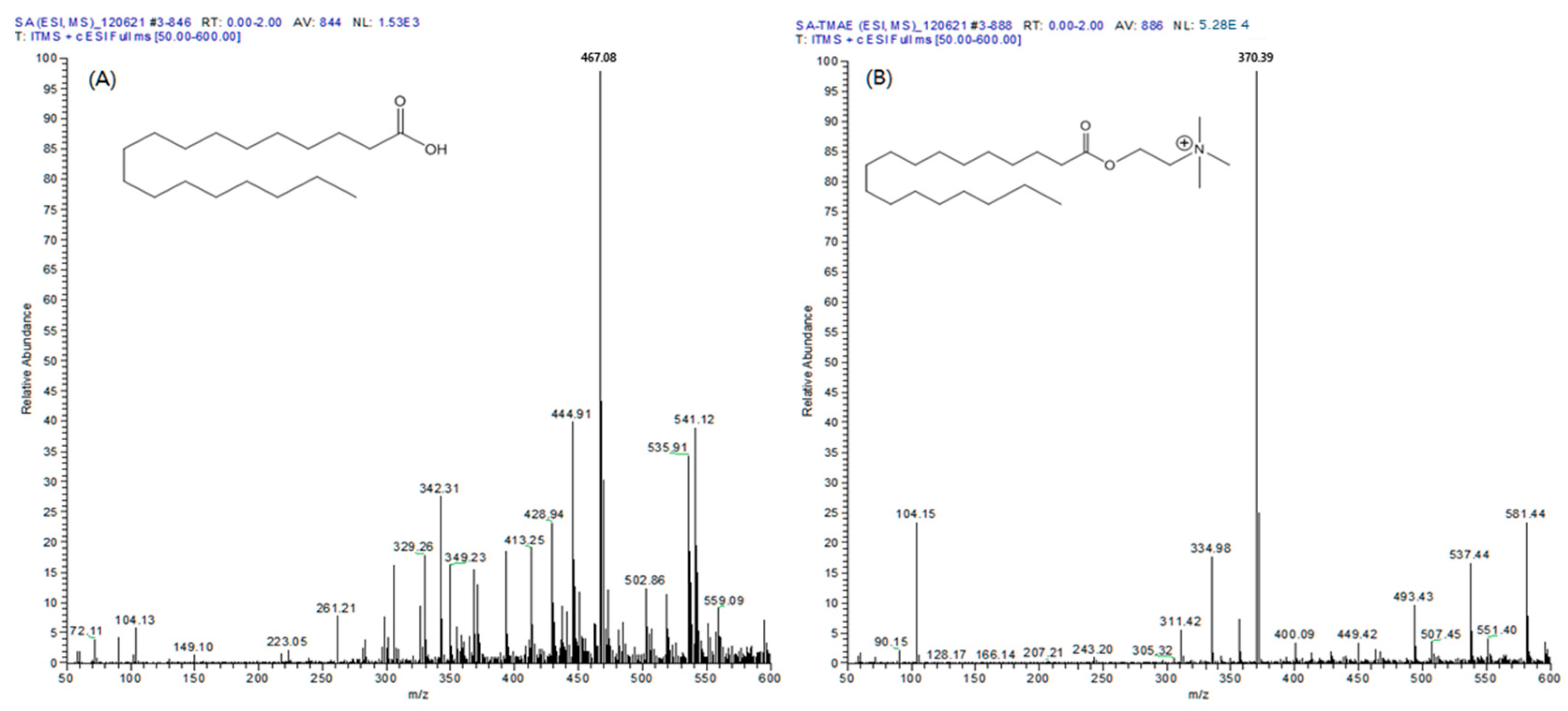
2.1. Derivatization Performance
2.2. Selection of Ionization Method-ESI vs APCI
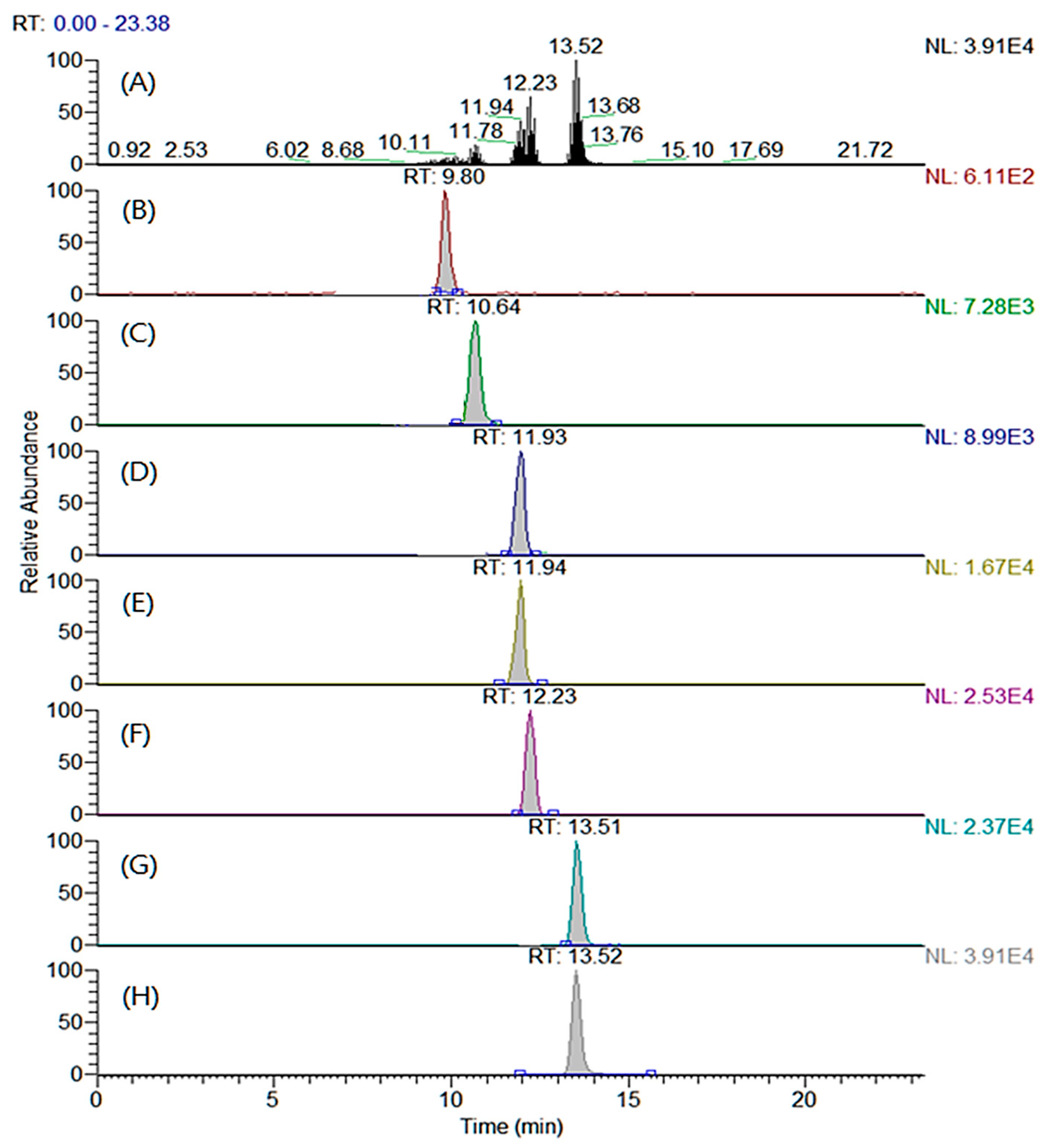
2.3. Optimization of LC–MS/MS Conditions
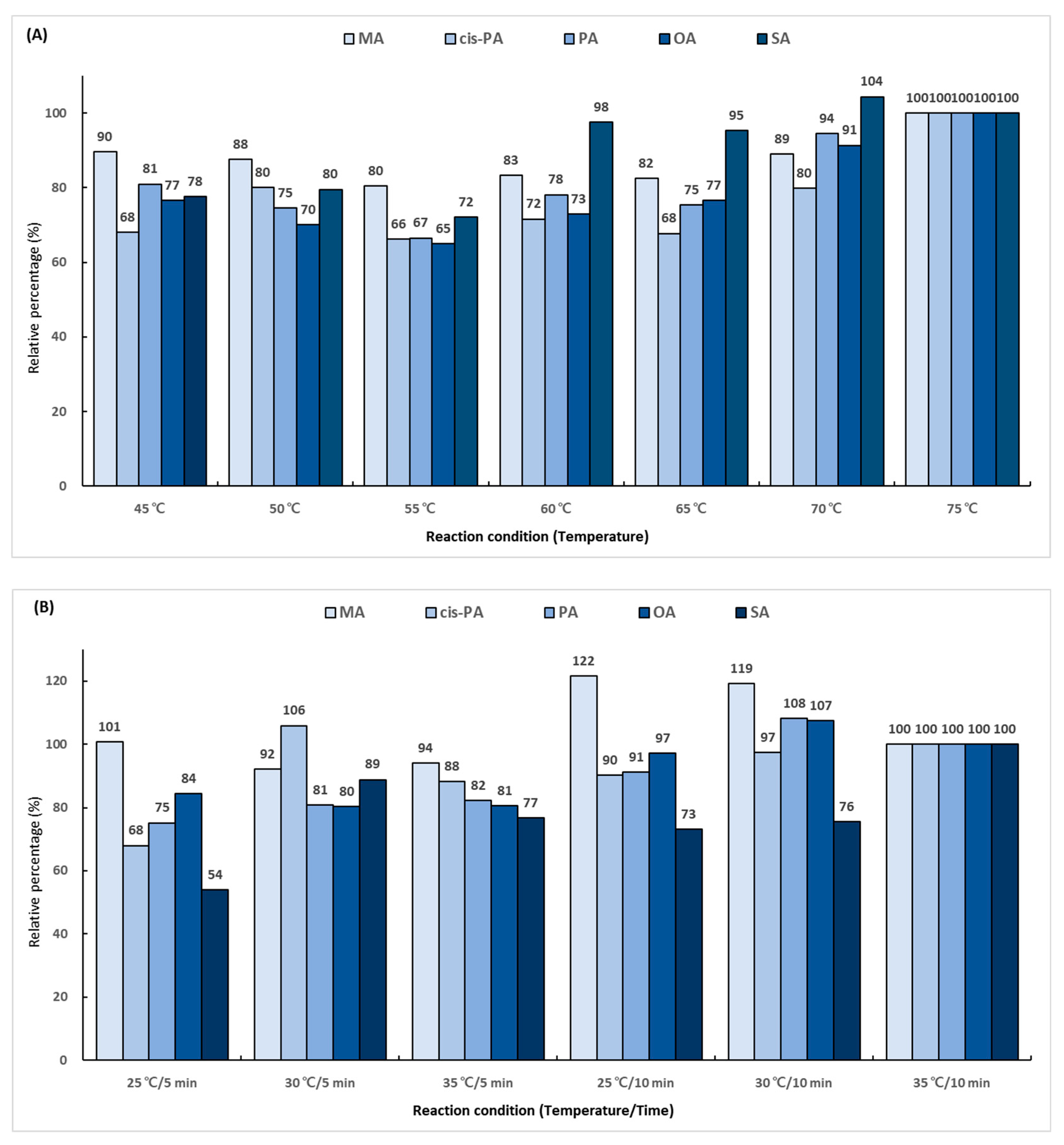
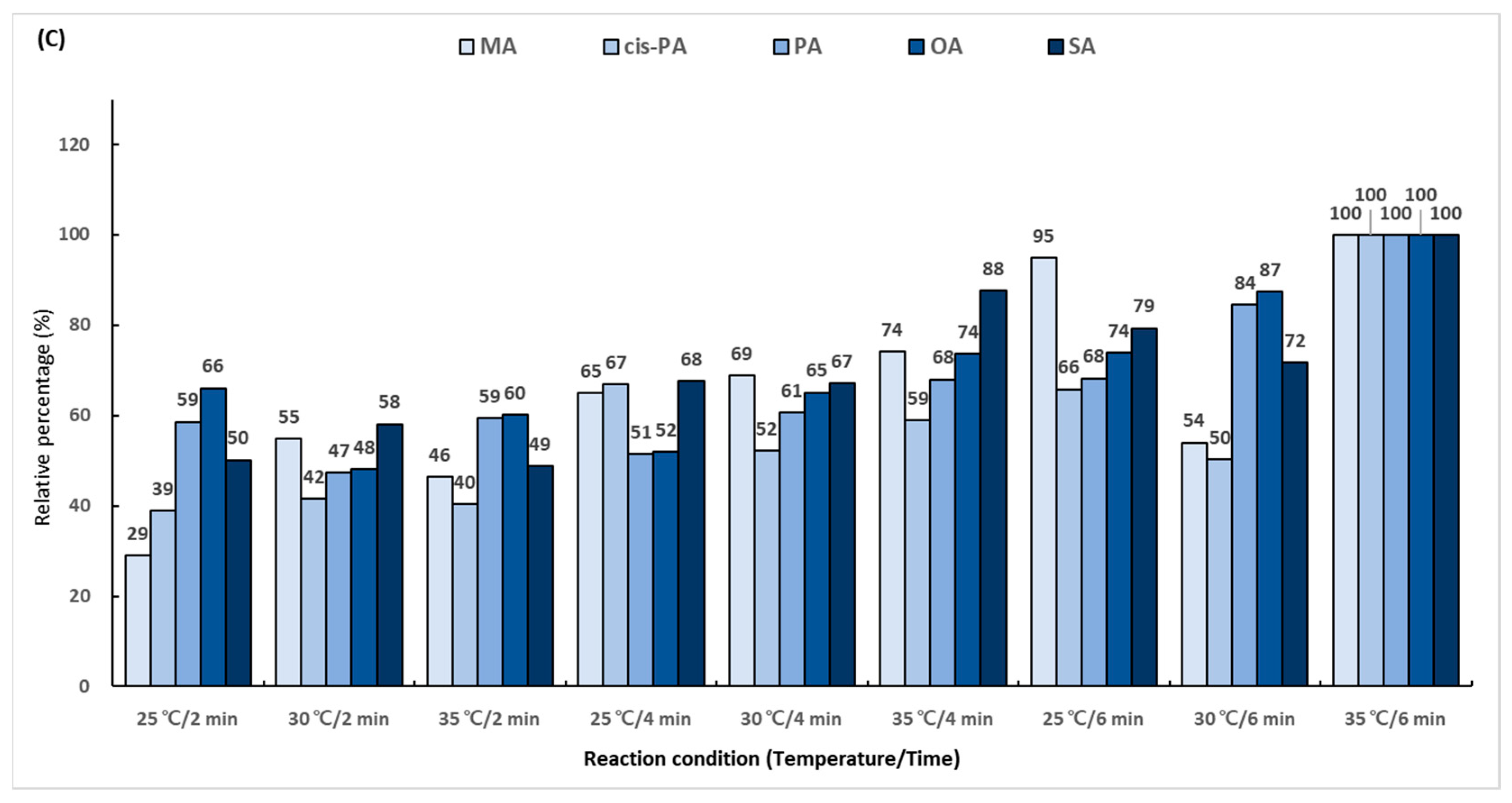
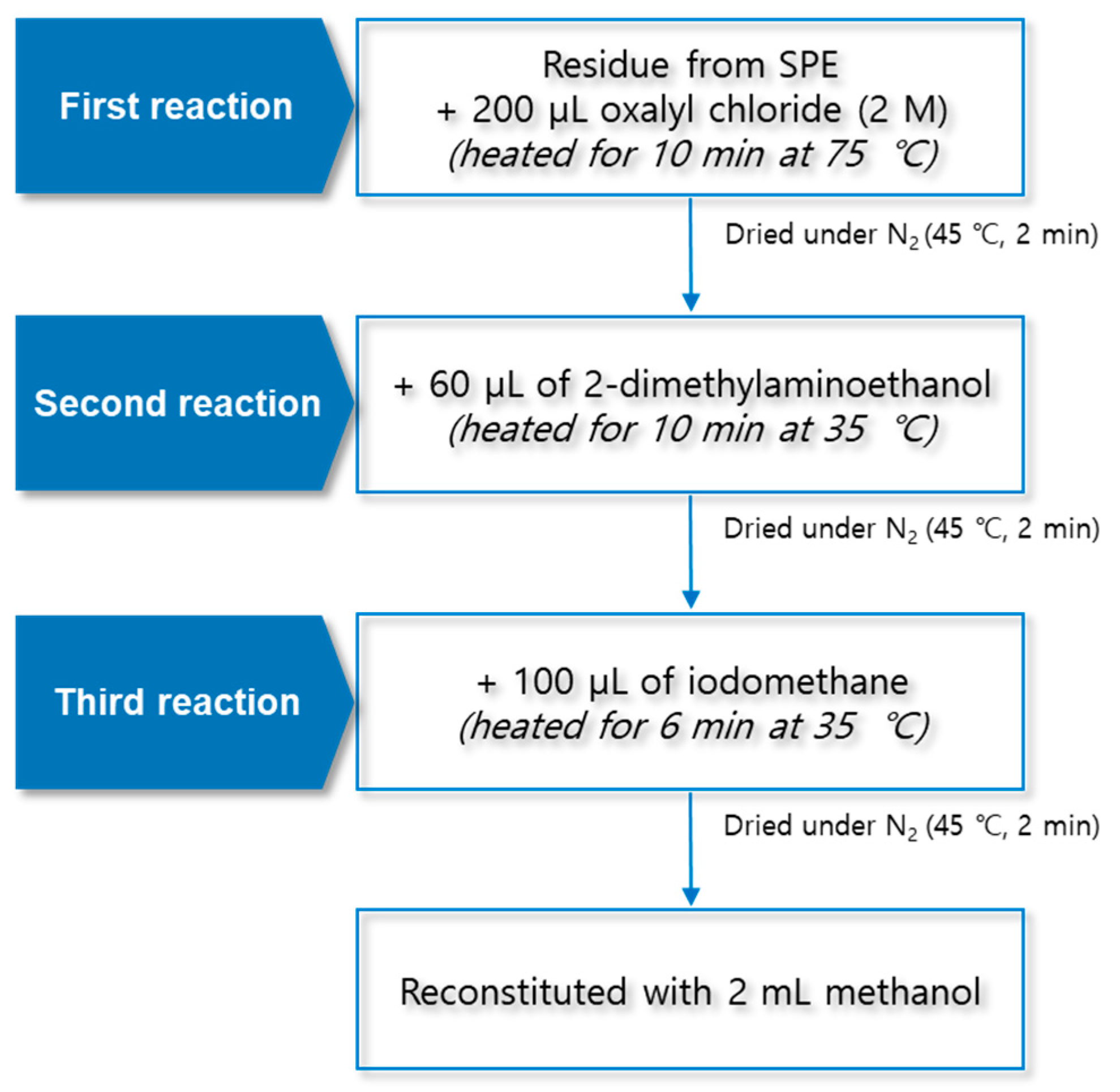
2.4. Optimization of Trimethylaminoethyl Derivatization Conditions
2.5. Optimization of Solid-Phase Extraction Conditions
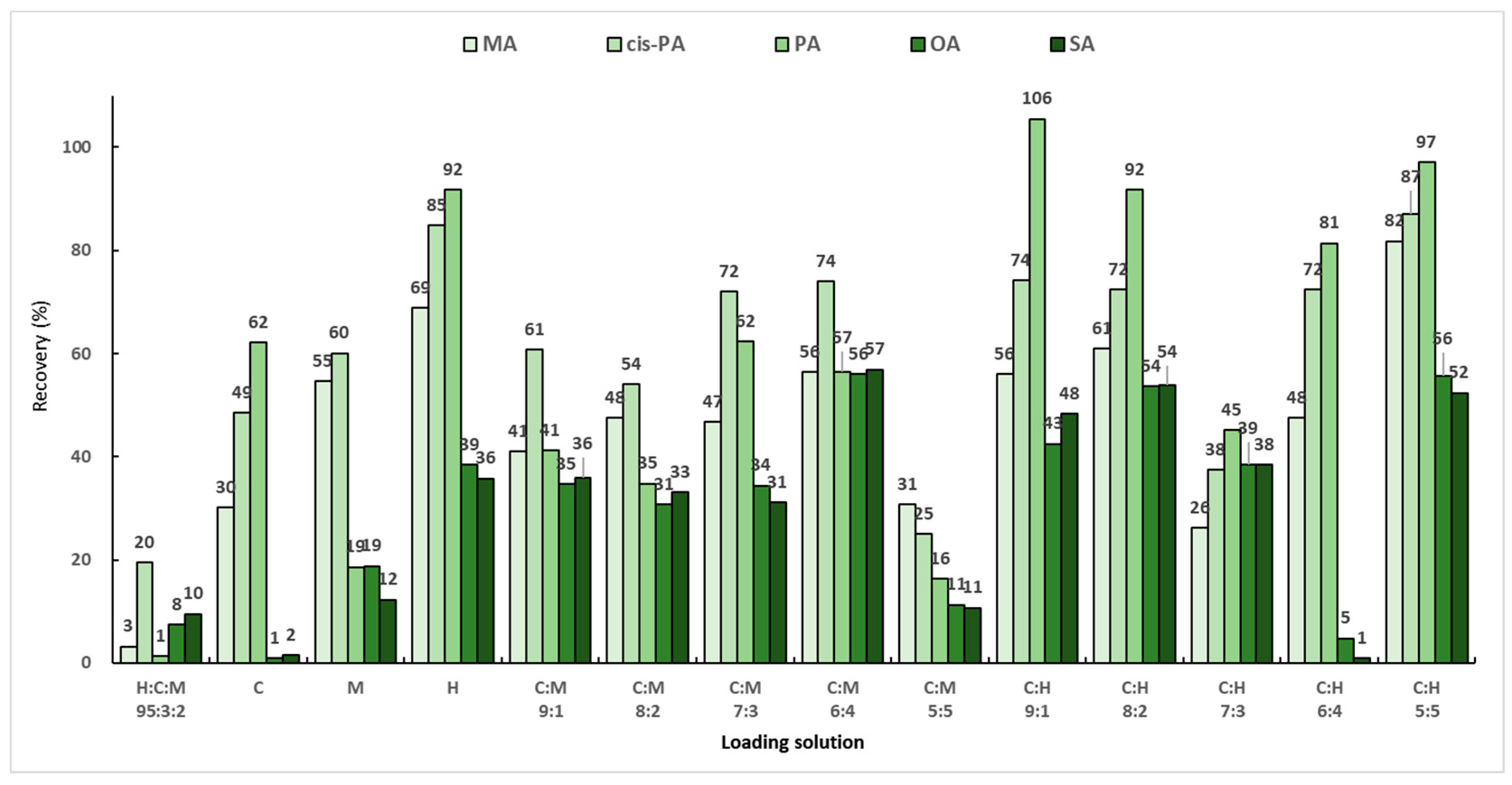
2.5.1. Optimization of Loading Solution
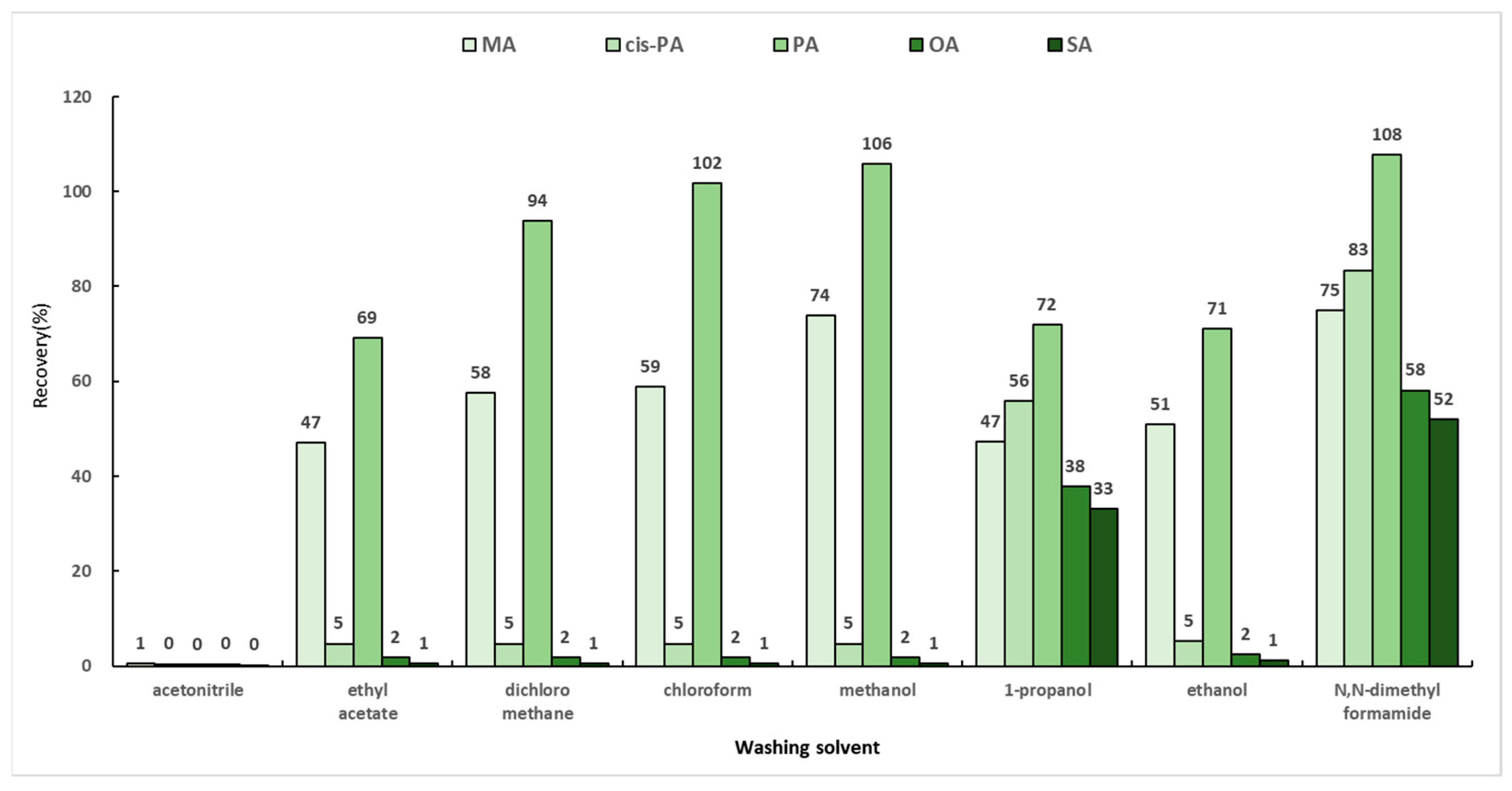
2.5.2. Optimization of Washing Solvent
2.5.3. Optimized Final Conditions
2.6. Recovery
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Sample Preparation (Lyophilization and Solid-Phase Extraction)
3.3. Derivatization
3.4. LC–MS/MS Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheehan, J.; Dunabay, T.; Benemann, J.; Roessler, P. A Look Back at the US Department of Energy Aquatic Species Program: Biodiesel from Algae; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 1998.
- Ragauskas, A.J.; Williams, C.K.; Davison, B.H.; Britovsek, G.; Cairney, J.; Eckert, C.A.; Frederick, W.J.; Hallett, J.P.; Leak, D.J.; Liotta, C.L.; et al. The Path Forward for Biofuels and Biomaterials. Science 2006, 311, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, R.E.H.; Mabee, W.; Saddler, J.N.; Taylor, M. An overview of second generation biofuel technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1570–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, R.P.; Anisha, G.S.; Nampoothiri, K.M.; Pandey, A. Micro and macroalgal biomass: A renewable source for bioethanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Duan, P.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Fan, Y. Co-liquefaction of micro- and macroalgae in subcritical water. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L.; Owende, P. Biofuels from microalgae-A review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: A review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, G.B.; Abdelaziz, A.E.M.; Hallenbeck, P.C. Algal biofuels: Challenges and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawczynski, C.; Schubert, R.; Jahreis, G. Amino acids, fatty acids, and dietary fibre in edible seaweed products. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlotterbeck, J.; Kolb, A.; Lämmerhofer, M. Free fatty acid profiling in marine algae extract by LC-MS/MS and isolation as well as quantification of the ω-3 fatty acid hexadeca-4,7,10,13-tetraenoic acid. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 4286–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, K.; Jeon, Y.J. Bio-functionalities of proteins derived from marine algae—A review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceiras, R.; Rodríguez, M.; Cancela, A.; Urrejola, S.; Sanchez, A. Macroalgae: Raw material for biodiesel production. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3318–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Guihéneuf, F.; Stengel, D.B. Fatty acid contents and profiles of 16 macroalgae collected from the Irish Coast at two seasons. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ginneken, V.J.; Helsper, J.P.; de Visser, W.; van Keulen, H.; Brandenburg, W.A. Polyunsaturated fatty acids in various macroalgal species from north Atlantic and tropical seas. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratana-arporn, P.; Chirapart, A. Nutritional evaluation of tropical green seaweeds Caulerpa lentillifera and Ulva reticulata. Nat. Sci. 2006, 40, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, W.H.; Tornabene, T.G.; Weissman, J. Screening for Lipid Yielding Microalgae: Activities for 1983; STR-231-2207; SERI: Golden, CO, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, L.; Oliveira, A.C. Microalgae as a raw material for biofuels production. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angers, P.; Arul, J. A simple method for regiospecific analysis of triacylglycerols by gas chromatography. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Fuentes, B.; Rodríguez, K.E.; Brito, A.; Díaz, L. Analysis of the Content of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters in Biodiesel by Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: Method and Comparison with Gas Chromatography. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, K.; Masumura, T.; Kohsaka, C.; Yamamoto, Y. Simultaneous Determination of Free Fatty Acids and Esterified Fatty Acids in Rice Oil by Gas Chromatography. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazmi, B.; Beygisangchin, M.; Rashid, U.; Mokhtar, W.N.A.W.; Tsubota, T.; Alsalme, A.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C. Glycerol-Based Retrievable Heterogeneous Catalysts for Single-Pot Esterification of Palm Fatty Acid Distillate to Biodiesel. Molecules 2022, 27, 7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczna, M.; Olzog, M.; Heipieper, H.J.; Naether, D.J.; Chrzanowski, L. Membrane fatty acid composition and cell surface hydrophobicity of marine hydrocarbonoclastic alcanivorax borkumensis SK2 grown on diesel, biodiesel and rapeseed oil as carbon sources. Molecules 2018, 23, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guihéneuf, F.; Schmid, M.; Stengel, D.B. Lipids and Fatty Acids in Algae: Extraction, Fractionation into Lipid Classes, and Analysis by Gas Chromatography Coupled with Flame Ionization Detector (GC-FID). In Natural Products from Marine Algae: Methods and Protocols; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1308, pp. 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hira, K.; Farhat, H.; Sohail, N.; Ansari, M.; Ara, J.; Ehteshamul-Haque, S. Hepatoprotective activity against acetaminophen-induced liver dysfunction and GC-MS profiling of a brown algae Sargassum ilicifolium. Clin. Phytoscience 2021, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Watanabe, N.; Baldermann, S.; Yoshikawa, K.; Fujita, A.; Mase, N. Determination of volatile compounds in four commercial samples of japanese green algae using solid phase microextraction gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Sci. World J. 2014, 8, 289780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brondz, I. Development of fatty acid analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, and related techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 465, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzourani, C.; Kokotou, M.G. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Derivatization-Based Methods for the Determination of Fatty Acids in Biological Samples. Molecules 2022, 27, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Antequera, T.; Andres, A.I.; Petron, M.J.; Muriel, E. Improvement of a solid phase extraction method for analysis of lipid fractions in muscle foods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 500, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Salem, N., Jr. Separation of lipid classes by solid phase extraction. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 2285–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| RT (min) | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Capillary Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMAE–Myristic Acid | 9.8 | 314.4 | 255.3 | 22 | 28 |
| TMAE–cis-Palmitvaccenic Acid | 10.7 | 340.4 | 281.3 | 24 | 28 |
| TMAE–Palmitic Acid | 11.9 | 342.4 | 283.4 | 24 | 28 |
| TMAE–Palmitic Acid-d2 | 11.9 | 344.4 | 285.3 | 20 | 28 |
| TMAE–Oleic Acid | 12.2 | 368.3 | 309.3 | 46 | 30 |
| TMAE–Stearic Acid | 13.5 | 370.4 | 311.4 | 34 | 32 |
| TMAE–Stearic-d2 Acid | 13.5 | 372.4 | 313.4 | 26 | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yum, T.; Kim, E.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Choi, S.; Paeng, K.-J. The Development of an Extraction Method for Simultaneously Analyzing Fatty Acids in Macroalgae Using SPE with Derivatization for LC–MS/MS. Molecules 2024, 29, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020430
Yum T, Kim E-Y, Kim Y, Choi S, Paeng K-J. The Development of an Extraction Method for Simultaneously Analyzing Fatty Acids in Macroalgae Using SPE with Derivatization for LC–MS/MS. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020430
Chicago/Turabian StyleYum, Taewoo, Eun-Yong Kim, Yeongeun Kim, Sukyoung Choi, and Ki-Jung Paeng. 2024. "The Development of an Extraction Method for Simultaneously Analyzing Fatty Acids in Macroalgae Using SPE with Derivatization for LC–MS/MS" Molecules 29, no. 2: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020430
APA StyleYum, T., Kim, E.-Y., Kim, Y., Choi, S., & Paeng, K.-J. (2024). The Development of an Extraction Method for Simultaneously Analyzing Fatty Acids in Macroalgae Using SPE with Derivatization for LC–MS/MS. Molecules, 29(2), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020430






