Novel Dihydrocoumarins Induced by Radiolysis as Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Newly Generated Dihydrocoumarins
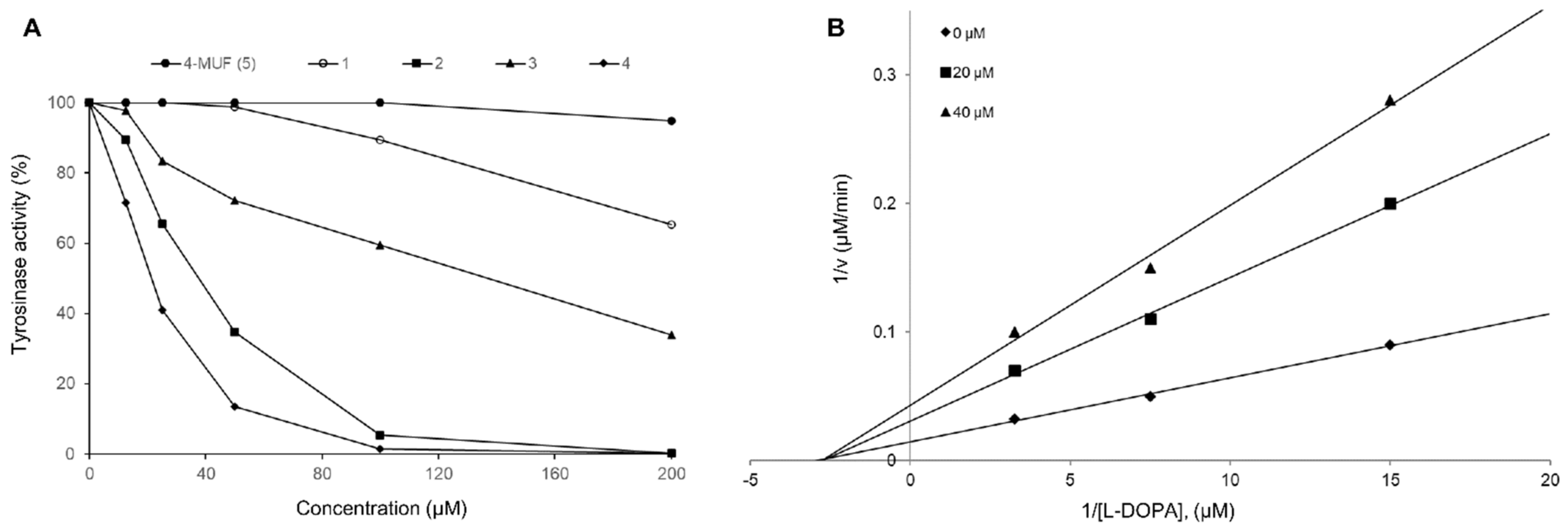
2.2. Inhibition Effects of Mushroom Tyrosinase
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Sample Preparation and New Compound Isolation
3.3. Inhibitory Effects of Mushroom Tyrosinase
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seo, S.Y.; Sharma, V.K.; Sharma, N. Mushroom tyrosinase: Recent prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearing, V.J.; Jimenez, M. Mammalian tyrosinase--the critical regulatory control point in the melanocyte pigmentation. Int. J. Biochem. 1987, 19, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Luo, Y.; Chen, P. Elucidation of the mechanism of enzymatic browning inhibition by sodium chlorite. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, N.P.M.; Vicanova, J.; Pavel, S.B. The hunt for natural skin whitening agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5326–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolghadri, S.; Bahrami, A.; Khan, M.T.S.; Munoz-Munoz, J.; Garcia-Molina, F.; Carcia-Canovas, F.; Saboury, A.A. A comprehensive review on tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzyme. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 279–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Anzai, K.; Kuwahara, N.; Komaki, H.; Miyadoh, S.; Harayama, S.; Ando, K. Physicochemical characters of a tyrosinase inhibitor produced by Streptomyces roseolilacinus NBRC 12815. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, F.; Roleira, F.; Mihanzes, N.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E. Simple coumarins and analogues in medicinal chemistry: Occurrence, synthesis and biological activity. Cur. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 887–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Jiang, J.G. Pharmacological and nutritional effects of natural coumarins and their structure-activity relationships. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1701073–1701096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanachi, A.; Leonetti, F.; Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Carotti, A. Coumarin: A natural, privileged and versatile scaffold for bioactive compounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 250–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikrishna, D.; Godugu, C.; Dubey, P.K. Review on pharmacological properties of coumarins. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 18, 113–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.Y.; Kim, K.I.; Han, J.M.; Park, W.Y.; Seo, H.S.; Lim, S.; Byun, E.B. Ionizing radiation technology to improve the physicochemical and biological properties of natural compounds by molecular modification: A review. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 194, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.H.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.K.; Choi, H.J.; Chung, B.Y.; Bai, H.W. Inhibitory effect of γ-ray-modified hydroxymethylated baicalins on NO production. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 96, 129491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.H.; Park, H.S.; Jang, S.H.; Won, C.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, T.H.; Cho, J.H. Rotenoisin A is a novel anti-adipogenic compound. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, S.; Qureshi, R.N. Gamma radiolytic degradation of flouranthene and monitoring of radiolytic products using GC-MS and HPLC. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2008, 77, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, N.; Awang, K.; Yahya, M.A. New coumarin from the bark of Cryptocarya bracteolate. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 803–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.G.; Moura Bordado, J.C.; Mateus, M.M. 1H-NMR dataset for hydroxycoumarins–Aesculetin, 4-Methylumbelliferone, and umbelliferone. Data Brief 2016, 30, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jung, H.J.; Park, H.R.; Jung, U.; Jo, S.K. Radiolysis study of genistein in methanolic solution. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2009, 78, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Song, H.Y.; Han, J.M.; Byun, E.B. GLM, a novel luteolin derivative, attenuates inflammatory responses in dendritic cells: Therapeutic potential against ulcerative colitis. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2019, 518, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Hebert, D.N. Tyrosinase maturation through the mammalian secretory pathway: Bringing color to life. Pigment Cell Res. 2006, 19, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Kim, M.H.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.H. Whitening effect of Hizikia fusiformis ethanol extract and its fractions. Food Chem. 2012, 22, 889–896. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.X.; Kubo, I. Kinetics of mushroom tyrosinase inhibition by quercetin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4108–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, E.C.; Hansen, W.H.; Fitzhugh, O.G.; Jenner, P.M.; Jones, W.I.; Taylor, J.M.; Brouwer, J.B. Food flavourings and compounds of related structure. II. Subacute and chronic toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1967, 5, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
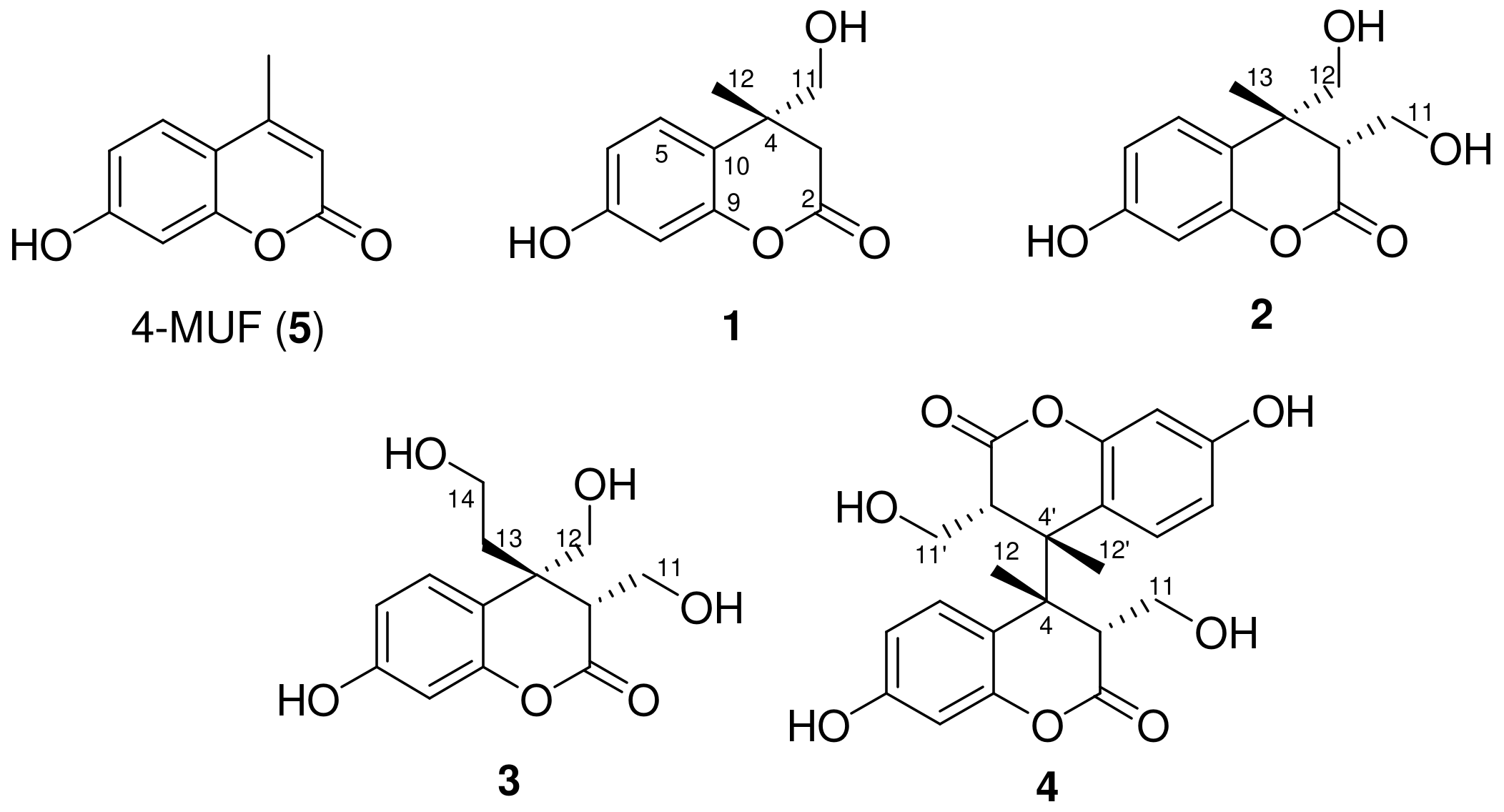
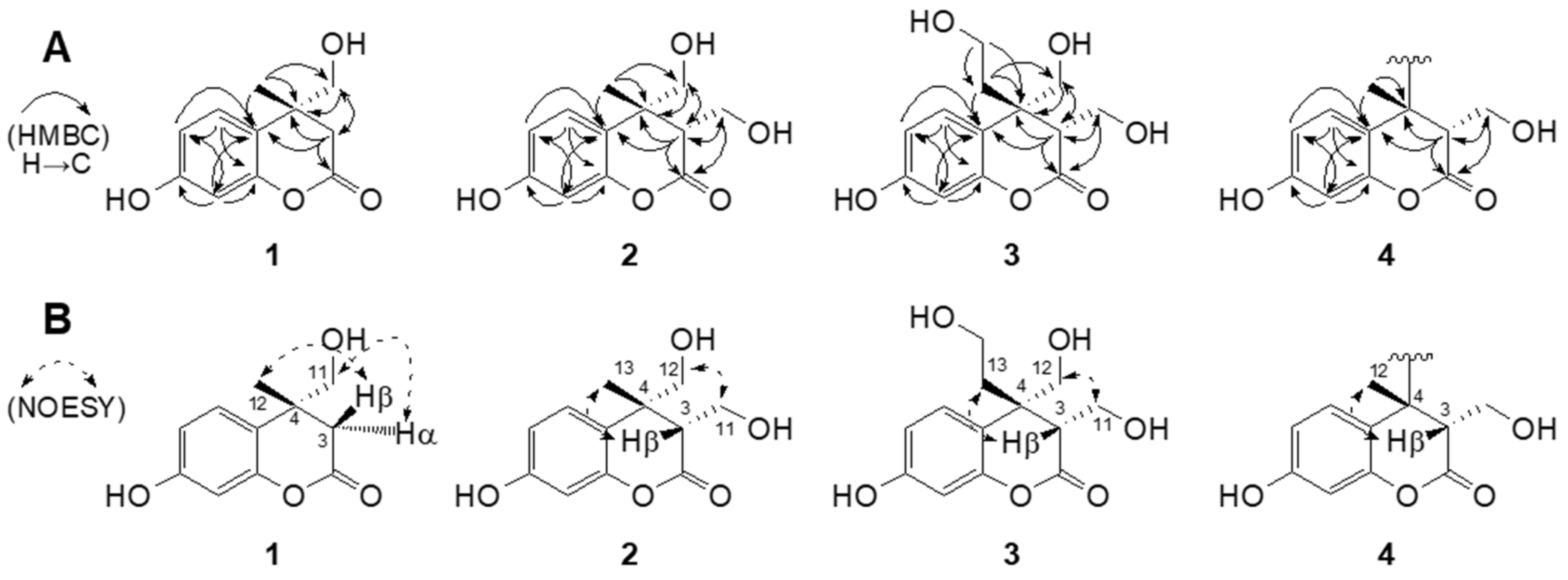
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δH (J in Hz) 2 | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type |
| 2 | — | 178.6, C | — | 180.9, C | — | 180.2, C |
| 3β | 3.05 (d, 16.8) | 41.5, CH2 | 2.91 (t, 4.2) | 53.6, CH | 3.06 (t, 4.2) | 52.6, CH |
| 3α | 2.63 (d, 16.8) | |||||
| 4 | — | 42.5, C | — | 44.3, C | — | 47.1, C |
| 5 | 6.86 (d, 8.4) | 127.0, CH | 6.72 (d, 8.4) | 126.9, CH | 7.08 (d, 8.4) | 127.3, CH |
| 6 | 6.28 (dd, 8.4, 2.4) | 106.1, CH | 6.31 (dd, 8.4, 2.4) | 106.4, CH | 6.30 (dd, 8.4, 2.4) | 105.8, CH |
| 7 | — | 157.2, C | — | 157.1, C | — | 157.4, C |
| 8 | 6.31 (d, 2.4) | 102.7, CH | 6.35 (d, 2.4) | 102.8, CH | 6.34 (d, 2.4) | 103.3, CH |
| 9 | — | 155.9, C | — | 155.5, C | — | 156.2, C |
| 10 | — | 121.5, C | — | 119.3, C | — | 119.1, C |
| 11 | 4.59 (d, 9.0) | 79.1, CH2 | 3.79 (dd, 11.4, 4.2) | 60.3, CH2 | 4.13 (dd, 11.4, 4.2) | 59.0, CH2 |
| 4.47 (d, 9.0) | 3.66 (dd, 11.4, 4.2) | 4.06 (dd, 11.4, 4.2) | ||||
| 12 | 1.45 (s) | 24.8, CH3 | 4.84 (d, 7.8) | 77.9, CH2 | 4.80 (d, 9.0) | 76.0, CH2 |
| 4.32 (d, 7.8) | 4.61 (d, 9.0) | |||||
| 13 | 1.45 (s) | 26.4, CH3 | 2.63 (m) | 34.2, CH2 | ||
| 2.10 (m) | ||||||
| 14 | 3.42 (m) | 58.8, CH2 | ||||
| 3.29 (m) | ||||||
| Position | δH (J in Hz) 2 | δC, Type | Position | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | — | 169.7, C | 2′ | — | 169.7, C |
| 3β | 3.22 (dd, 7.2, 5.4) | 48.0, CH | 3β′ | 3.22 (dd, 7.2, 5.4) | 48.0, CH |
| 4 | — | 46.5, C | 4′ | — | 46.5, C |
| 5 | 6.47 (d, 8.4) | 131.0, CH | 5′ | 6.47 (d, 8.4) | 131.0, CH |
| 6 | 6.43 (dd, 8.4, 2.4) | 110.9, CH | 6′ | 6.43 (dd, 8.4, 2.4) | 110.9, CH |
| 7 | — | 158.2, C | 7′ | — | 158.2, C |
| 8 | 6.36 (d, 2.4) | 102.5, CH | 8′ | 6.36 (d, 2.4) | 102.5, CH |
| 9 | — | 152.2, C | 9′ | — | 152.2, C |
| 10 | — | 115.4, C | 10′ | — | 115.4, C |
| 11 | 3.85 (dd, 11.4, 5.4) | 60.9, CH2 | 11′ | 3.85 (dd, 11.4, 5.4) | 60.9, CH2 |
| 3.49 (dd, 11.4, 7.2) | 3.49 (dd, 11.4, 7.2) | ||||
| 12 | 1.28 (s) | 19.5, CH3 | 12′ | 1.28 (s) | 19.5, CH3 |
| Compound | Tyrosinase IC50 Value (μM) 1 | Inhibition Type (Ki, μM) |
|---|---|---|
| Gamma-ray treated 4-MUF (50 kGy) | 86.7 ± 1.6 2 | NT 3 |
| 4-MUF (5) | >500 a | NT |
| 1 | 142.9 ± 1.5 b | NT |
| 2 | 49.0 ± 1.3 c | NT |
| 3 | 254.6 ± 2.1 a | NT |
| 4 | 19.8 ± 0.5 d | Non-competitive (16.0 ± 0.2) |
| Kojic acid 4 | 131.7 ± 1.7 b | NT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, G.H.; Yadav, M.; Lee, S.S.; Chung, B.Y.; Cho, J.-H.; Lee, I.-C.; Bai, H.-W.; Kim, T.H. Novel Dihydrocoumarins Induced by Radiolysis as Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2024, 29, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020341
Jeong GH, Yadav M, Lee SS, Chung BY, Cho J-H, Lee I-C, Bai H-W, Kim TH. Novel Dihydrocoumarins Induced by Radiolysis as Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020341
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Gyeong Han, Manisha Yadav, Seung Sik Lee, Byung Yeoup Chung, Jae-Hyeon Cho, In-Chul Lee, Hyoung-Woo Bai, and Tae Hoon Kim. 2024. "Novel Dihydrocoumarins Induced by Radiolysis as Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors" Molecules 29, no. 2: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020341
APA StyleJeong, G. H., Yadav, M., Lee, S. S., Chung, B. Y., Cho, J.-H., Lee, I.-C., Bai, H.-W., & Kim, T. H. (2024). Novel Dihydrocoumarins Induced by Radiolysis as Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Molecules, 29(2), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020341






