Pharmacological Characters and Toxicity Evaluation of Coumarin Derivative LP4C as Lead Compound against Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LP4C Inhibits the P. aeruginosa Biofilm without Bactericidal Activity
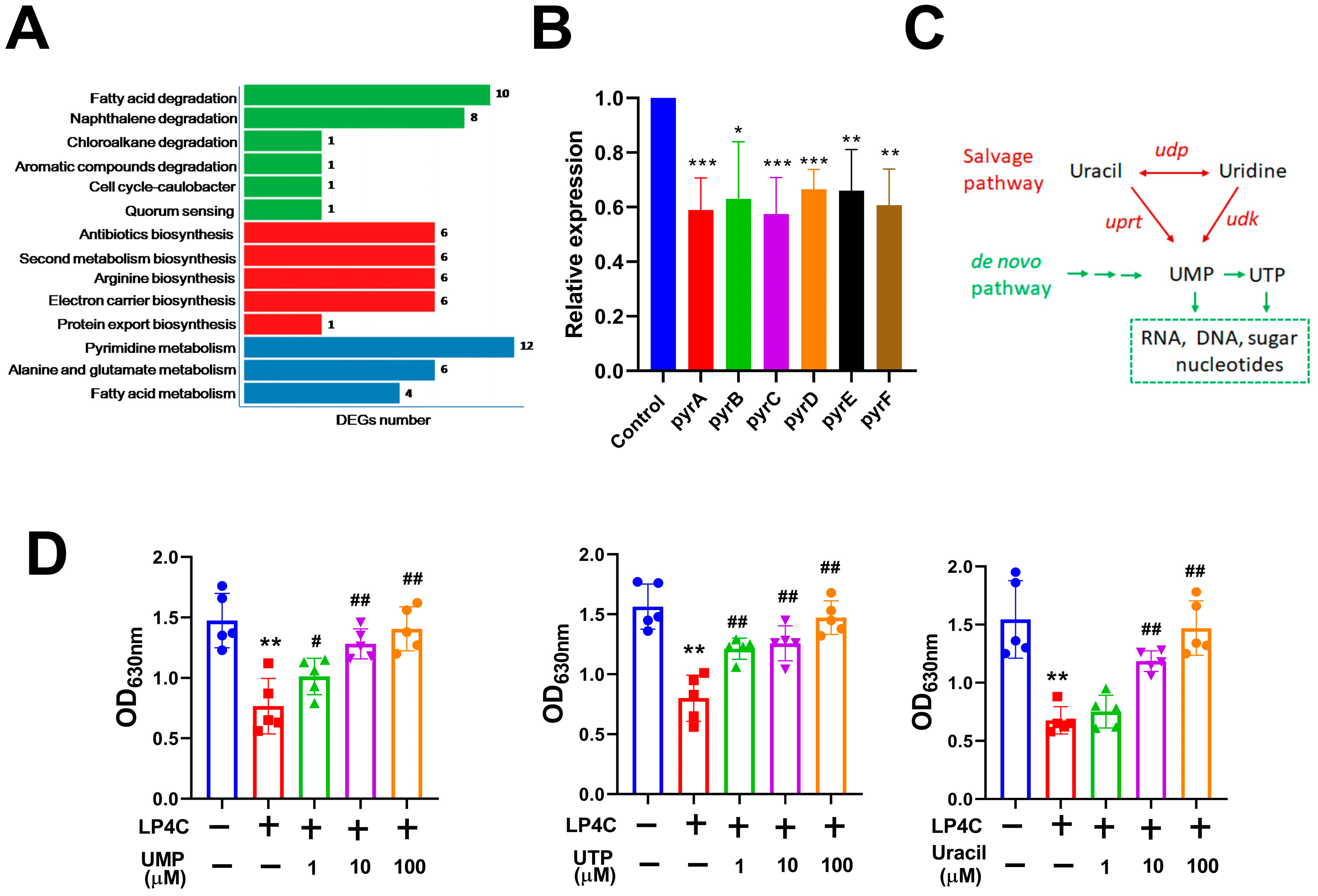
2.2. Bacterial Pyrimidine Involved the Inhibitory Activity of LP4C
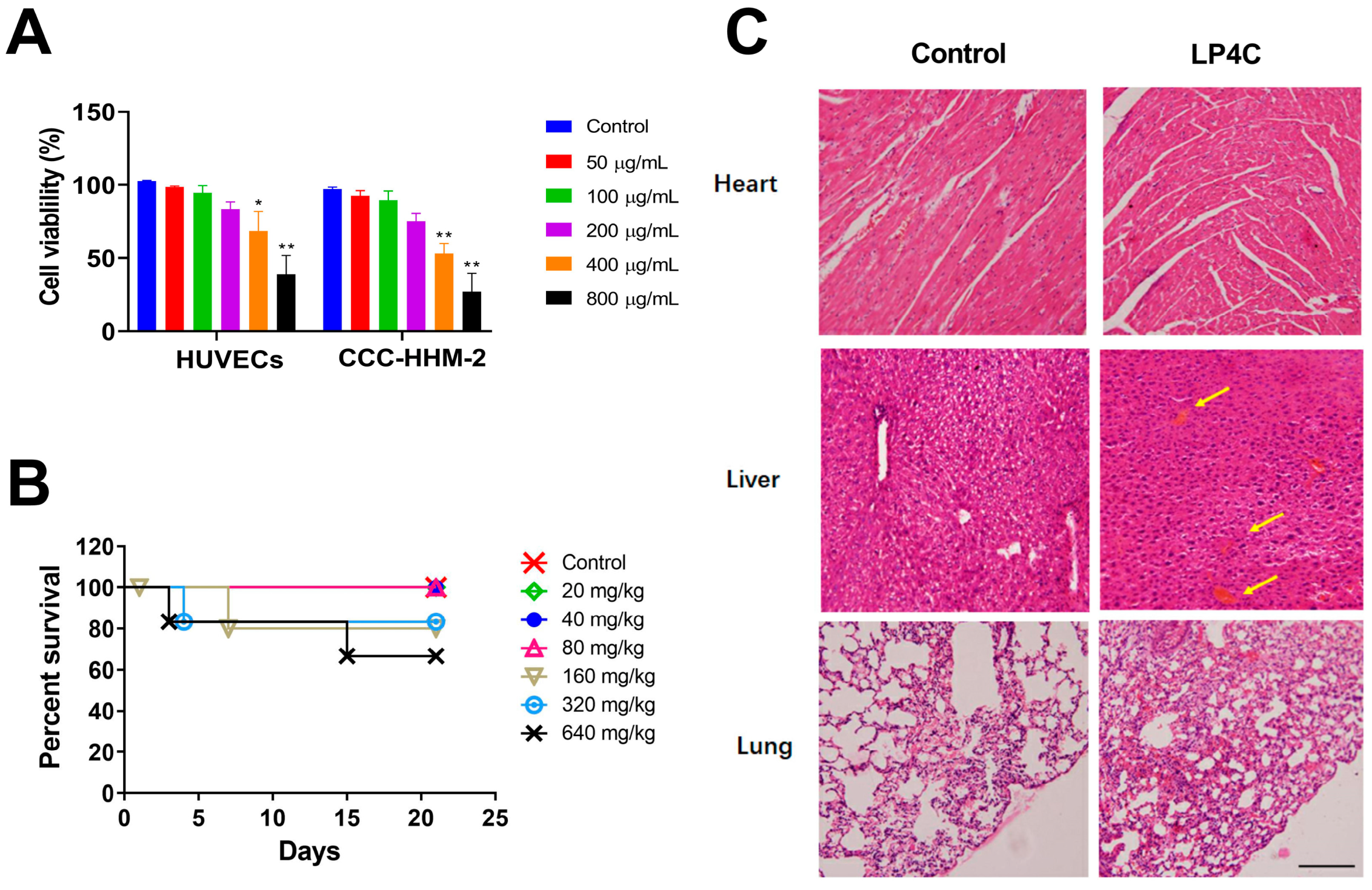
2.3. Cytotoxicity and Acute Toxicity of LP4C
2.4. The Bacterial Reverse Mutation Assay of LP4C
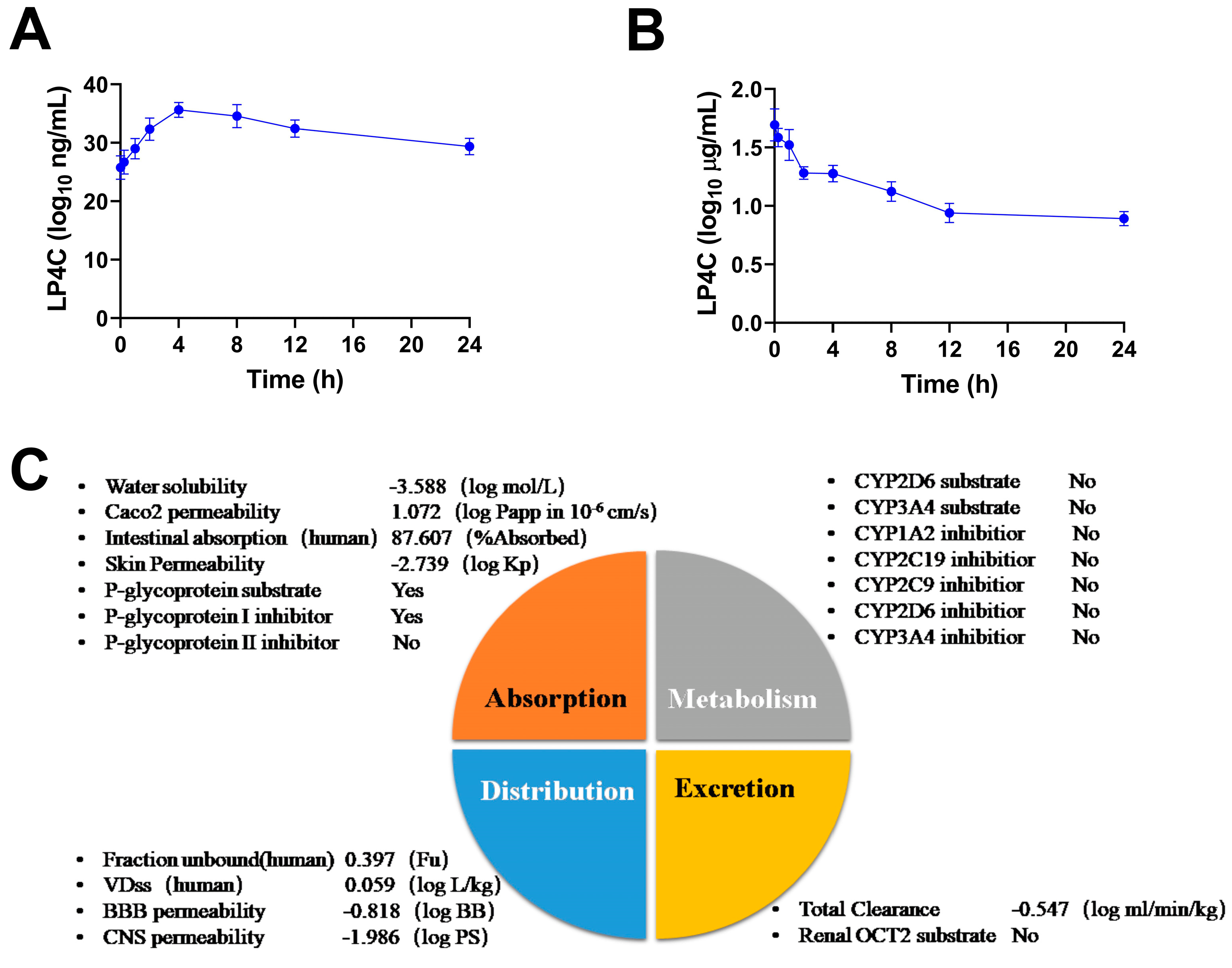
2.5. Pharmacokinetics and ADME Properties of LP4C
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Bacterial Strain and Animals
4.3. Anti-Bacterial Activity Measurement
4.4. Growth and Measurement of Bacterial Biofilm
4.5. RNA Isolation and RNA-seq
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
4.7. Cytotoxicity Test
4.8. Acute Toxicity Assay
4.9. Ames Test
4.10. Pharmacokinetics Measurement
4.11. ADME Properties Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, D.J.; Spratt, D.; Liddle, A.D. Implant materials and prosthetic joint infection: The battle with the biofilm. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.H. Biofilm dispersion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, M.T.T.; Wibowo, D.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellatly, S.L.; Hancock, R.E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: New insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathog. Dis. 2013, 67, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D., Jr.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic Fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The Host-Microbe Interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00138-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzo, J.R.; Devaraj, A.; Gloag, E.S.; Jurcisek, J.A.; Robledo-Avila, F.; Kesler, T.; Wilbanks, K.; Mashburn-Warren, L.; Balu, S.; Wickham, J.; et al. Z-form extracellular DNA is a structural component of the bacterial biofilm matrix. Cell 2021, 184, 5740–5758.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karygianni, L.; Ren, Z.; Koo, H.; Thurnheer, T. Biofilm Matrixome: Extracellular Components in Structured Microbial Communities. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilton, M.; Charron-Mazenod, L.; Moore, R.; Lewenza, S. Extracellular DNA Acidifies Biofilms and Induces Aminoglycoside Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condinho, M.; Carvalho, B.; Cruz, A.; Pinto, S.N.; Arraiano, C.M.; Pobre, V. The role of RNA regulators, quorum sensing and c-di-GMP in bacterial biofilm formation. FEBS Open Bio 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, R.T.; Blasco, L.; Ambroa, A.; Gonzalez-Pedrajo, B.; Fernandez-Garcia, L.; Lopez, M.; Bleriot, I.; Bou, G.; Garcia-Contreras, R.; Wood, T.K.; et al. Relationship Between Quorum Sensing and Secretion Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yin, B.; Qian, L.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, S. Screening for novel quorum-sensing inhibitors to interfere with the formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; van Gennip, M.; Phipps, R.K.; Shanmugham, M.S.; Christensen, L.D.; Alhede, M.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Friedrich, K.; Uthe, F.; et al. Ajoene, a sulfur-rich molecule from garlic, inhibits genes controlled by quorum sensing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihua, L.; Jianhuit, W.; Jialini, Y.; Yayin, L.; Guanxin, L. Effects of allicin on the formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofinm and the production of quorum-sensing controlled virulence factors. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, C.A.; Freundorfer, M.; Mah, T.F.; Otarola-Rojas, M.; Garcia, M.; Sanchez-Vindas, P.; Poveda, L.; Maschek, J.A.; Baker, B.J.; Adonizio, A.L.; et al. Inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing and biofilm formation by extracts of neotropical rainforest plants. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Hou, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Su, S.; Ye, Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; et al. A new coumarin compound DCH combats methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm by targeting arginine repressor. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, S.; Yu, M.; Zhai, D.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ma, X.; Jia, M.; Xue, X.; Li, M. Pyrancoumarin derivative LP4C targeting of pyrimidine de novo synthesis pathway inhibits MRSA biofilm and virulence. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 959736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Yin, P.; Li, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Qu, D.; Li, Z.; Xue, X.; Luo, X.; Li, M. In vitro and in vivo anti-biofilm activity of pyran derivative against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domakonda, A.; West, T.P. Control of pyrimidine nucleotide formation in Pseudomonas aurantiaca. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Das, M.C.; Das, A.; Bhowmik, S.; Sandhu, P.; Akhter, Y.; Bhattacharjee, S.; De, U.C. Modulation of S. aureus and P. aeruginosa biofilm: An in vitro study with new coumarin derivatives. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qais, F.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I.; Husain, F.M.; Khan, R.A.; Hassan, I.; Shahzad, S.A.; AlHarbi, W. Coumarin Exhibits Broad-Spectrum Antibiofilm and Antiquorum Sensing Activity against Gram-Negative Bacteria: In Vitro and In Silico Investigation. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 18823–18835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Ray, S.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Nandi, D. Insights into coumarin-mediated inhibition of biofilm formation in Salmonella Typhimurium. Biofouling 2020, 36, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Qian, L.; Cao, L.; Tan, H.; Huang, Y.; Xue, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, S. Virtual screening for novel quorum sensing inhibitors to eradicate biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murahari, E.C.; West, T.P. The pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway and its regulation in Pseudomonas jessenii. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villela, A.D.; Sanchez-Quitian, Z.A.; Ducati, R.G.; Santos, D.S.; Basso, L.A. Pyrimidine salvage pathway in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavaglia, M.; Rossi, E.; Landini, P. The pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway modulates production of biofilm determinants in Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, A.; Attila, C.; Whiteley, M.; Wood, T.K. Uracil influences quorum sensing and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and fluorouracil is an antagonist. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kohli, S.; Sandhu, S.; Bansal, Y.; Bansal, G. Coumarin: A promising scaffold for anticancer agents. Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1032–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanachi, A.; Leonetti, F.; Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Carotti, A. Coumarin: A Natural, Privileged and Versatile Scaffold for Bioactive Compounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineo, G.; Hull, R.D. Coumarin therapy in thrombosis. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 17, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugosz, A.; Janecka, A. Novobiocin Analogs as Potential Anticancer Agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, L.; Gu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Deng, J.Y. CycA-Dependent Glycine Assimilation Is Connected to Novobiocin Susceptibility in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0250122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Fujii, W.; Hori, H.; Kitagawa, Y.; Ozaki, K. Relationship between coumarin-induced hepatocellular toxicity and mitochondrial function in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y. Synthesis of Furanocoumarin, Benzofuran and Coumarin Derivatives Possessing an Inhibitory Effect on Human CYP, and Elucidation of the Inhibitory Mechanism. Yakugaku Zasshi 2017, 137, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, L.; Cai, L. Transcriptome Sequencing: RNA-Seq. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1754, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, D.E.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group (μg/plate) | TA97 | TA98 | TA100 | TA102 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −S9 | +S9 | −S9 | +S9 | −S9 | +S9 | −S9 | +S9 | |
| LP4C 5000 μg/plate | 112 ± 9.83 | 141 ± 7.65 | 24 ± 3.5 | 31 ± 5.2 | 122 ± 7.67 | 130 ± 5.69 | 256 ± 9.21 | 273 ± 12.6 |
| LP4C 2000 μg/plate | 120 ± 8.53 | 140 ± 6.47 | 26 ± 6.7 | 32 ± 5.8 | 120 ± 5.71 | 132 ± 6.95 | 262 ± 8.44 | 280 ± 11.3 |
| LP4C 1000 μg/plate | 119 ± 8.52 | 142 ± 5.96 | 25 ± 5.4 | 32 ± 4.7 | 120 ± 8.33 | 131 ± 6.75 | 267 ± 8.35 | 279 ± 10.6 |
| LP4C 200 μg/plate | 122 ± 7.42 | 140 ± 8.55 | 26 ± 4.8 | 33 ± 4.1 | 116 ± 6.42 | 133 ± 7.34 | 271 ± 5.68 | 281 ± 9.36 |
| LP4C 50 μg/plate | 123 ± 5.92 | 142 ± 7.13 | 26 ± 2.2 | 32 ± 3.6 | 117 ± 5.96 | 130 ± 7.68 | 260 ± 10.3 | 276 ± 11.2 |
| DMSO 100 μL/plate | 122 ± 8.44 | 139 ± 8.26 | 24 ± 3.4 | 32 ± 3.8 | 119 ± 5.83 | 130 ± 4.58 | 261 ± 12.1 | 280 ± 8.87 |
| Positive control | 2014 ± 105 | 1354 ± 135 | 2027 ± 126 | 2036 ± 124 | 1376 ± 206 | 1273 ± 195 | 1673 ± 215 | 954 ± 63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, M.; Xin, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y.; Jia, M.; Wang, B.; Li, M. Pharmacological Characters and Toxicity Evaluation of Coumarin Derivative LP4C as Lead Compound against Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 2023, 28, 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073138
Yu M, Xin J, Liu Y, Chen Y, Zhao H, Li Y, Hou Y, Jia M, Wang B, Li M. Pharmacological Characters and Toxicity Evaluation of Coumarin Derivative LP4C as Lead Compound against Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073138
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Moxi, Jiajia Xin, Yongsheng Liu, Yamiao Chen, Hui Zhao, Yaoyao Li, Yachen Hou, Min Jia, Bin Wang, and Mingkai Li. 2023. "Pharmacological Characters and Toxicity Evaluation of Coumarin Derivative LP4C as Lead Compound against Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073138
APA StyleYu, M., Xin, J., Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Zhao, H., Li, Y., Hou, Y., Jia, M., Wang, B., & Li, M. (2023). Pharmacological Characters and Toxicity Evaluation of Coumarin Derivative LP4C as Lead Compound against Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules, 28(7), 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073138






