Naturally Inspired Coumarin Derivatives in Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Discovery: Latest Advances and Current Challenges
Abstract
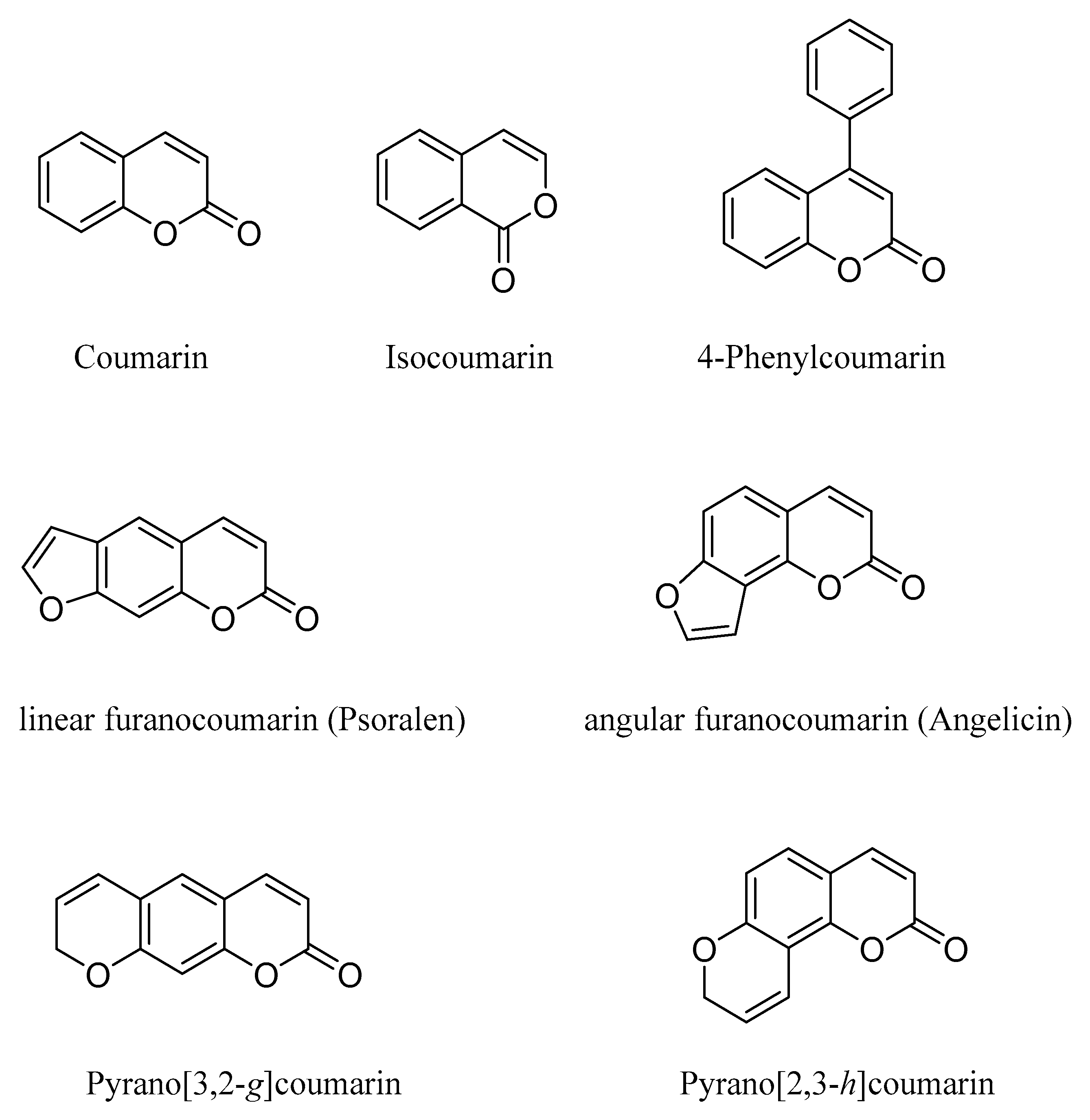
1. Introduction
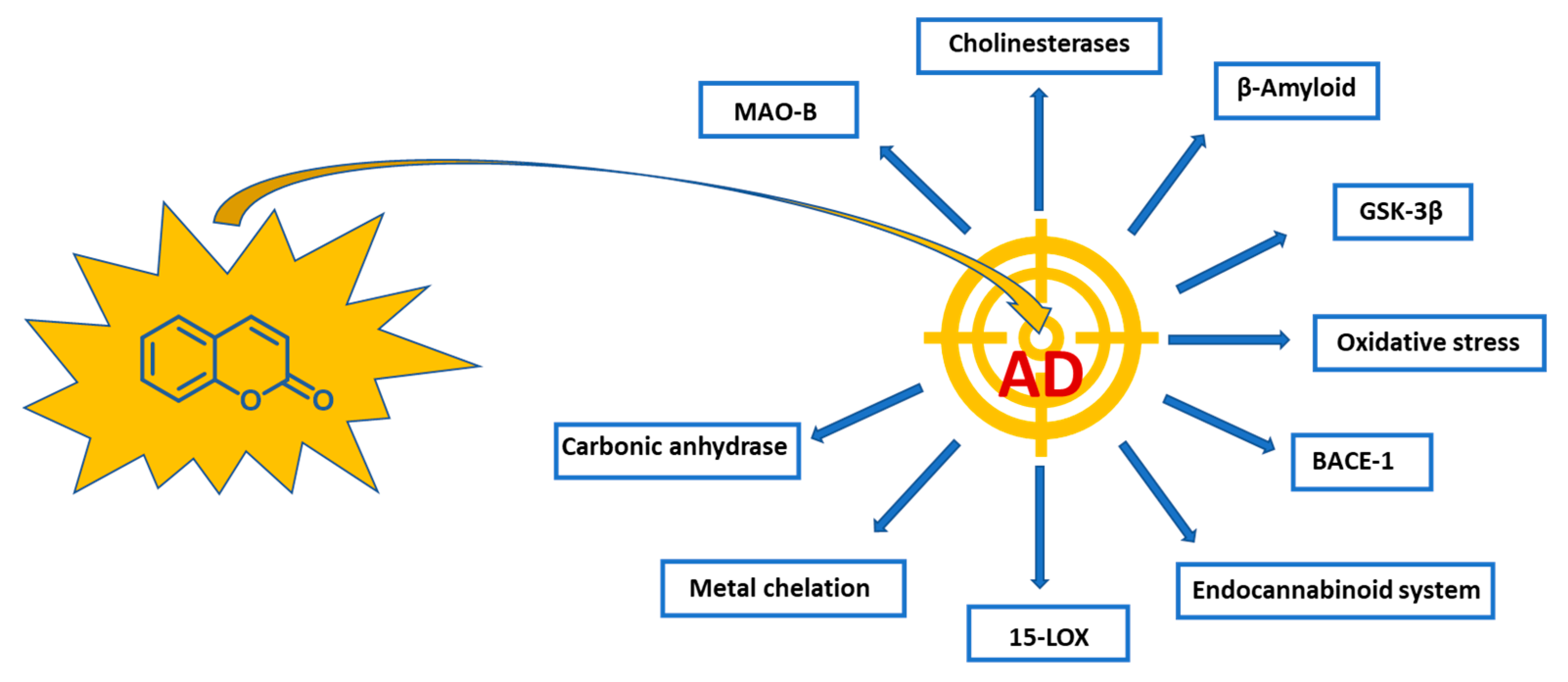
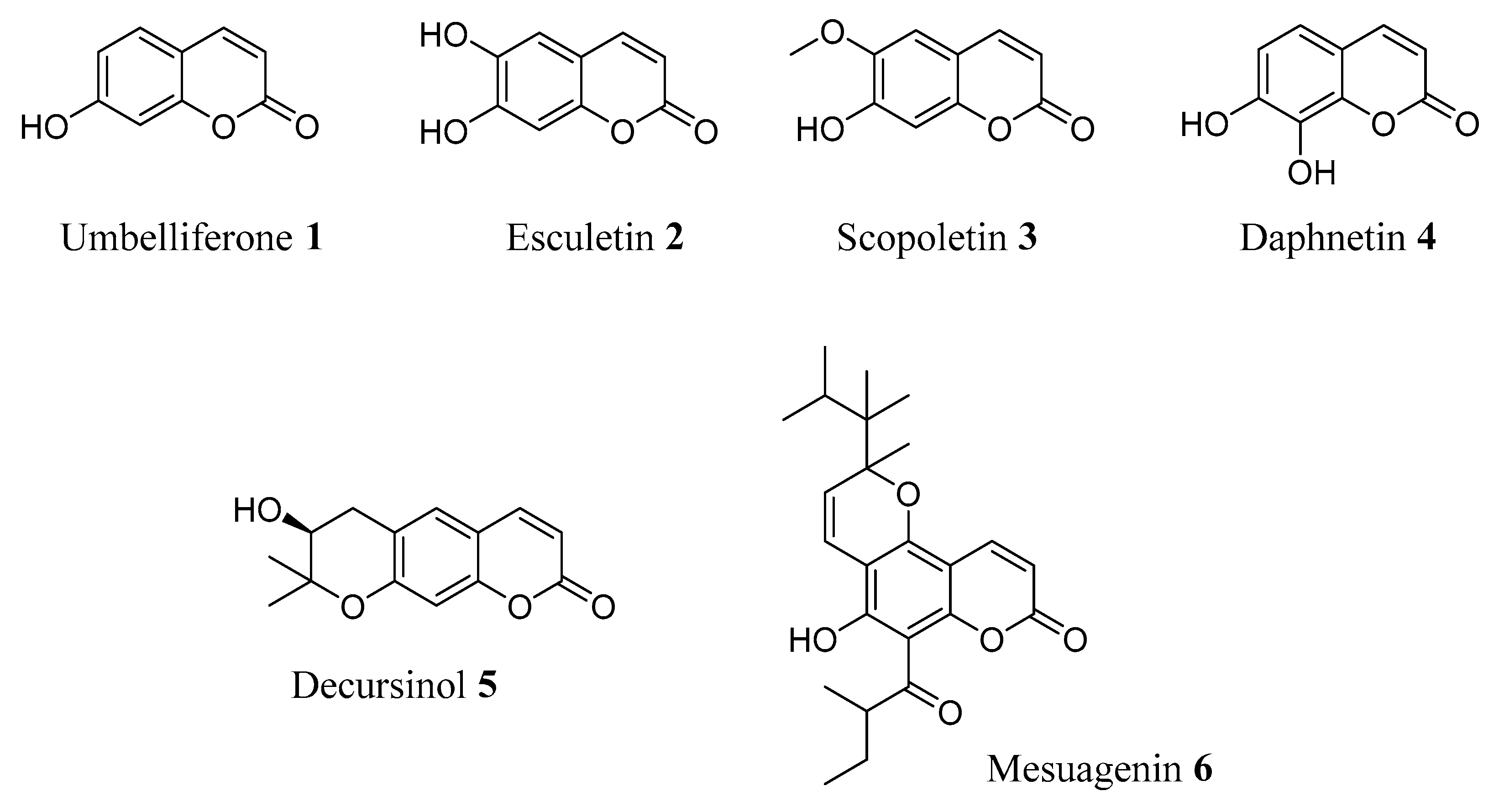
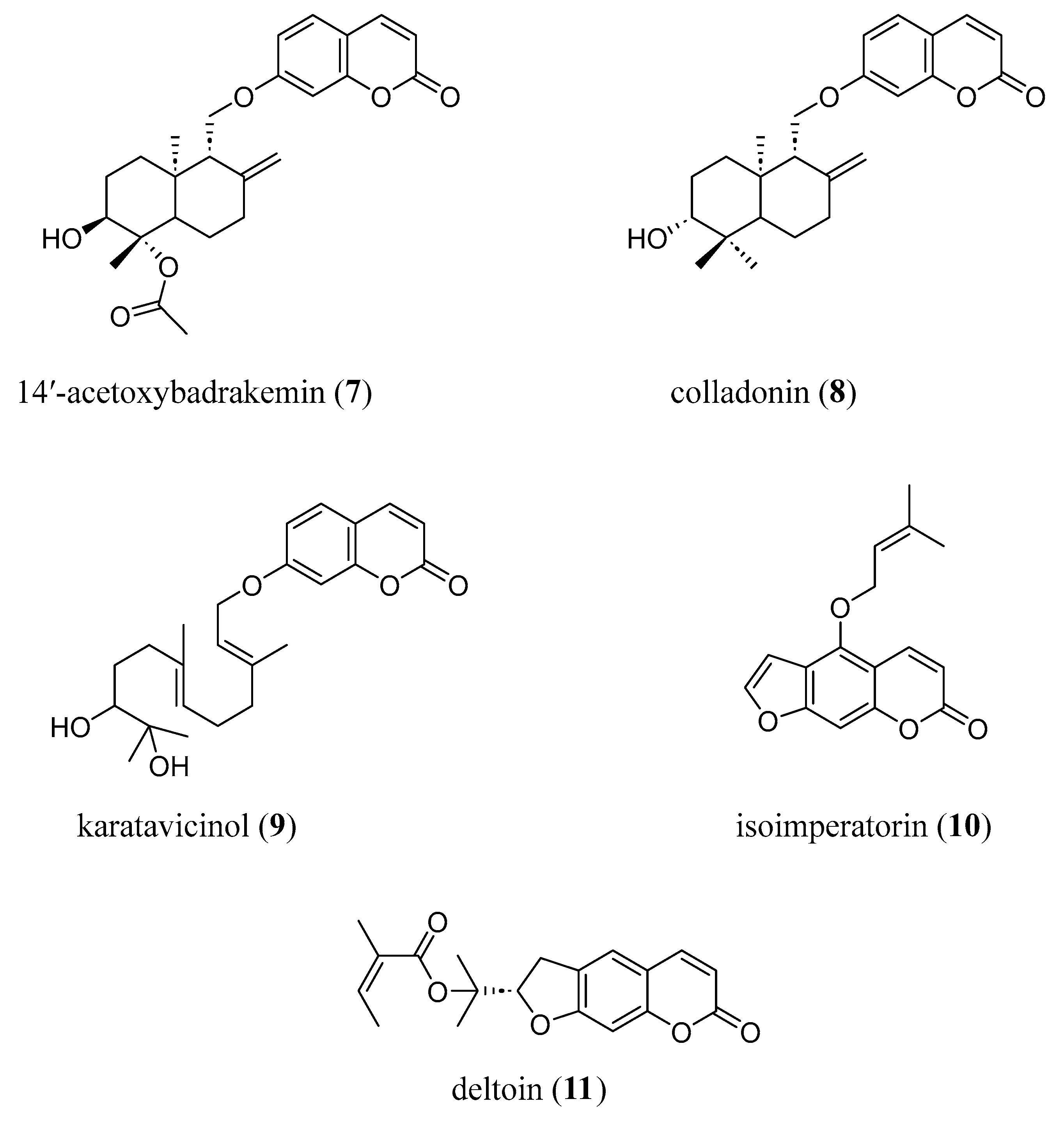
2. Natural Coumarin Derivatives in AD
3. Synthetic Coumarin Derivatives in AD
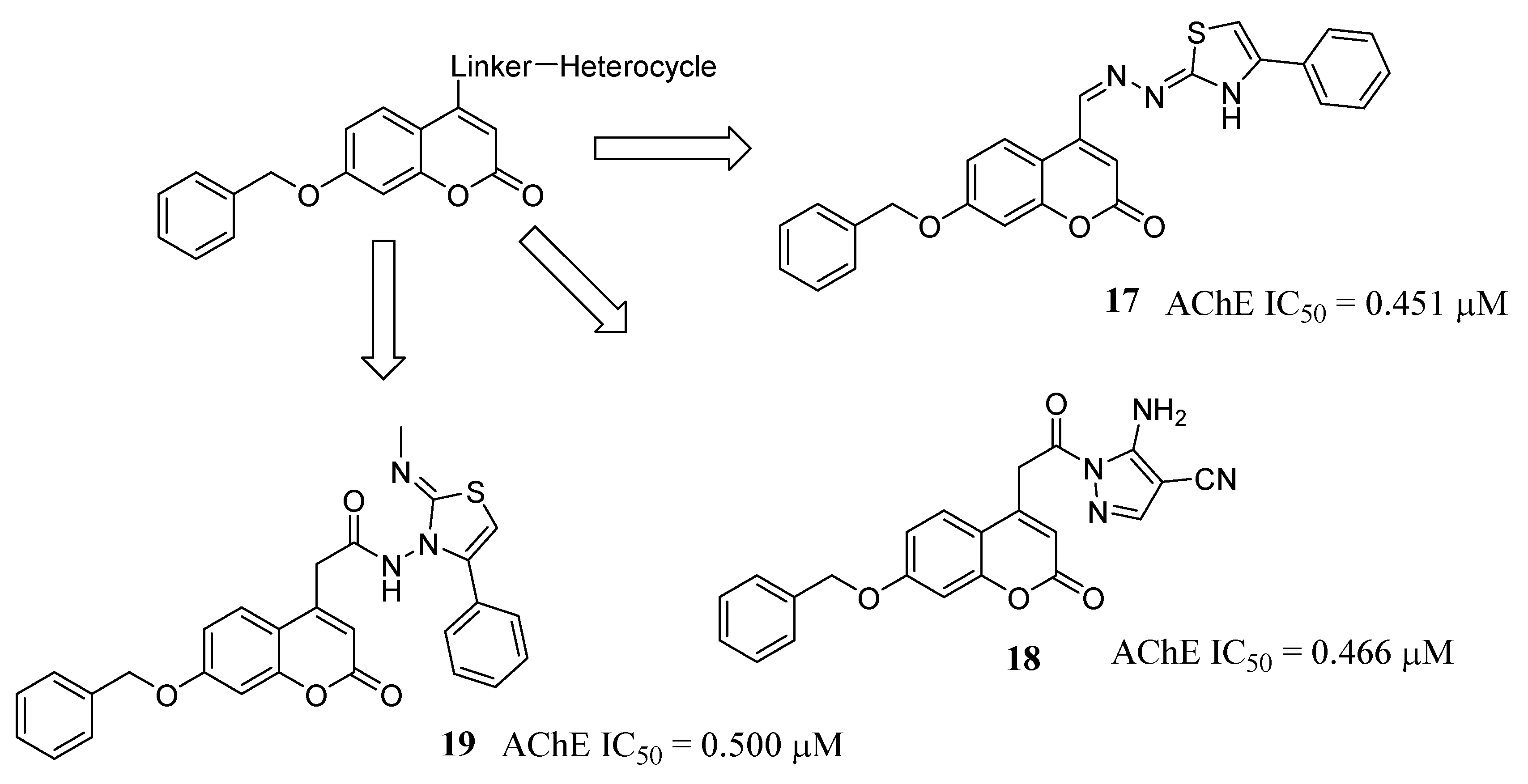
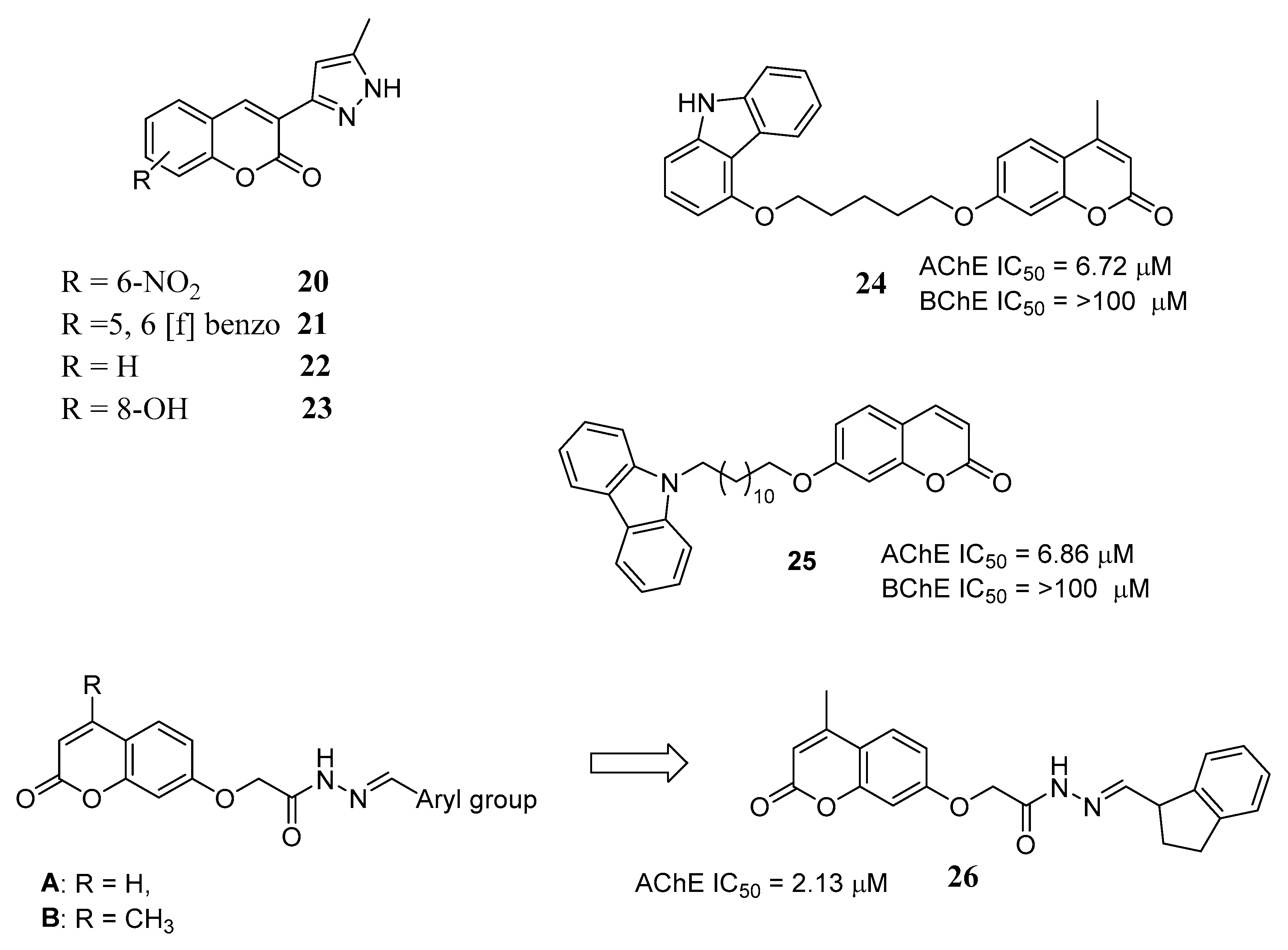
3.1. Multipotent Coumarin-Based Derivatives Mainly Focused on ChEs Inhibition
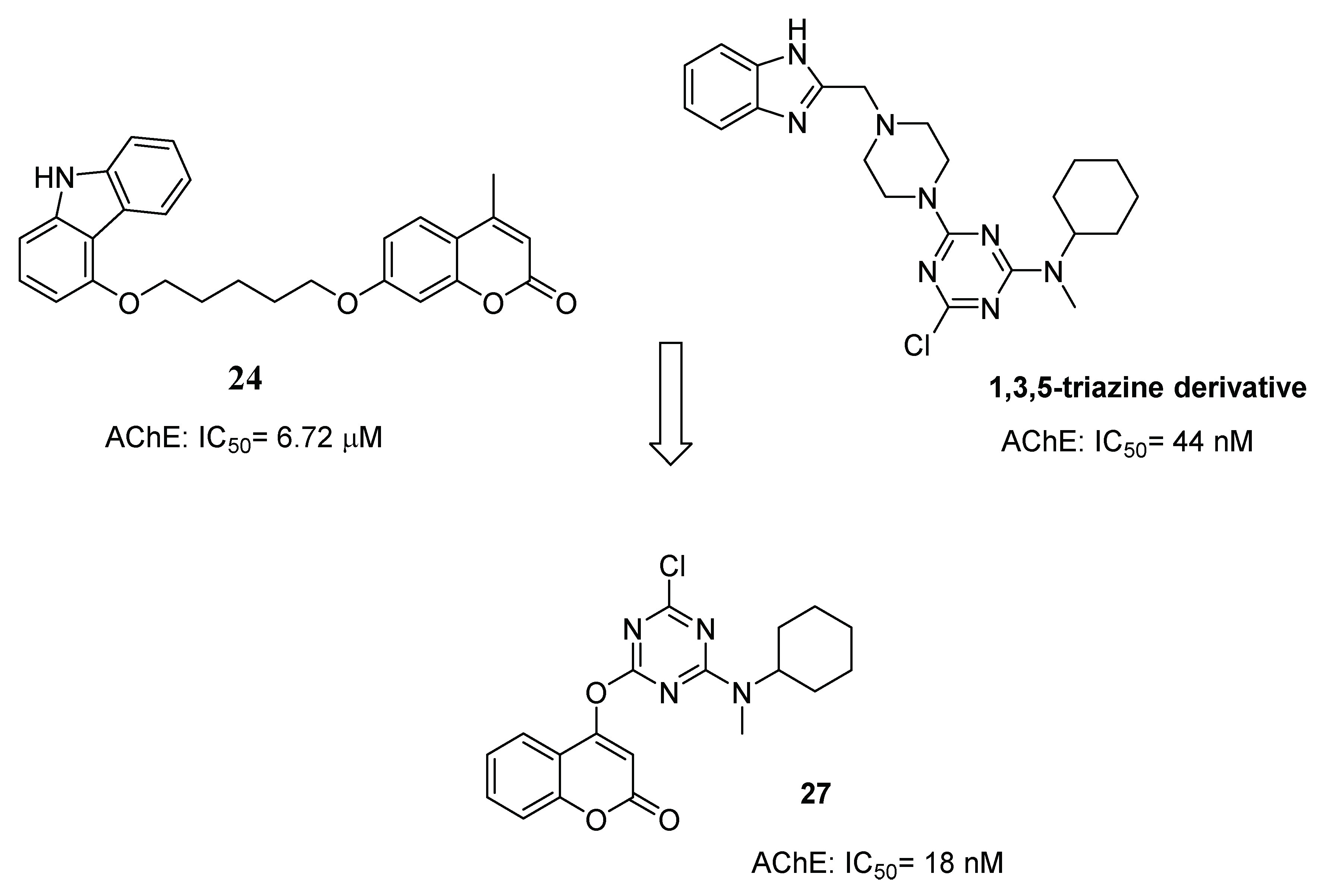
3.2. Coumarins Acting on Different Selected Targets
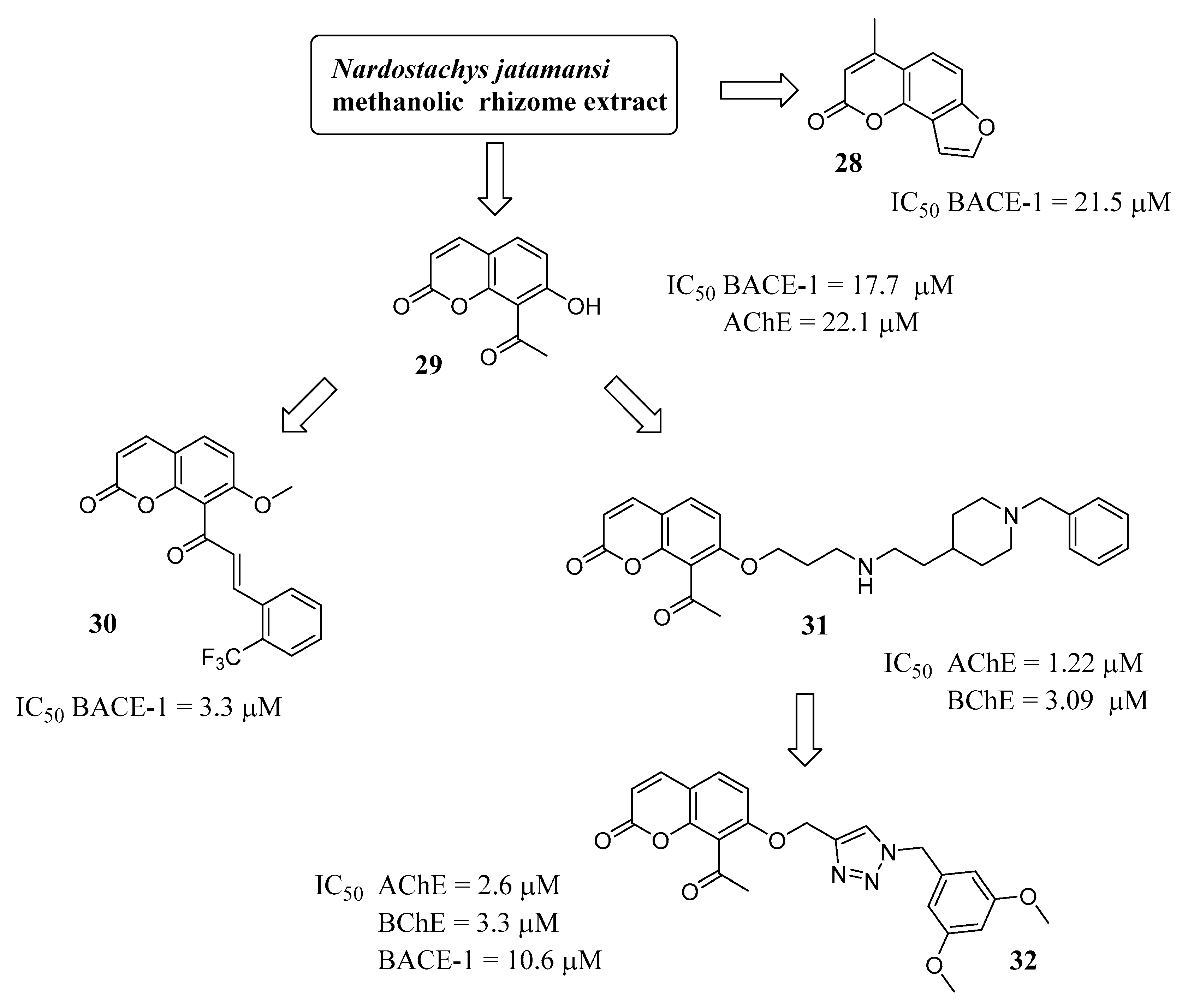
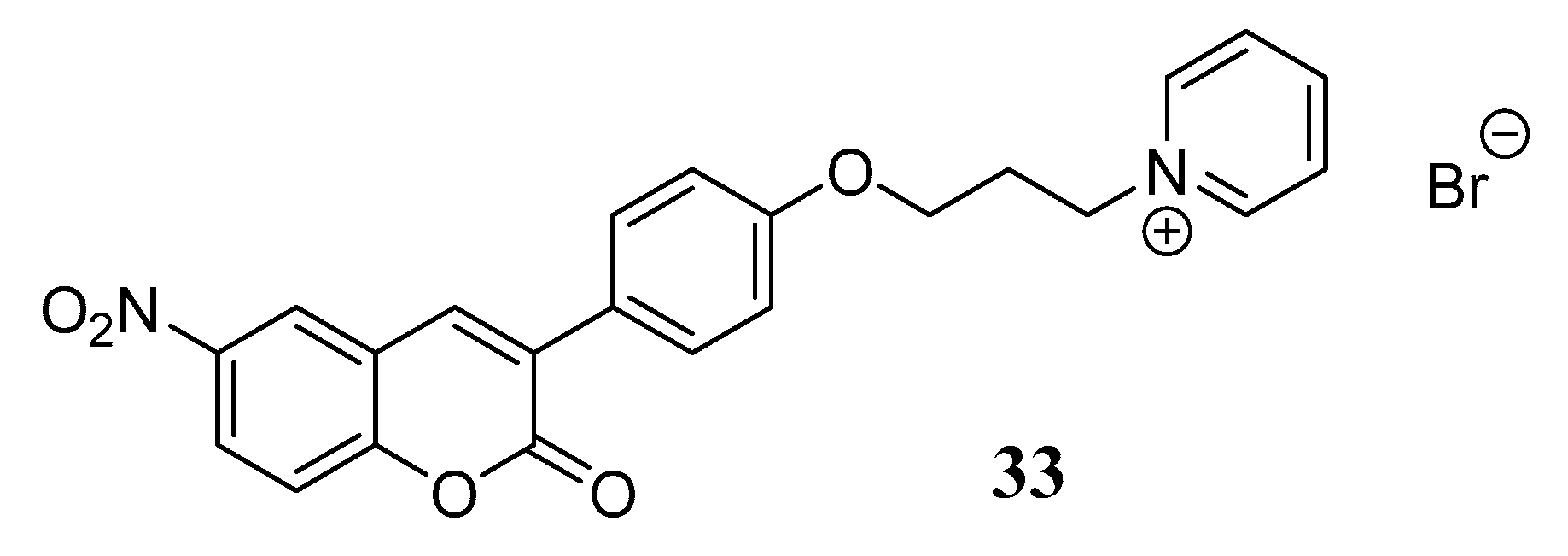
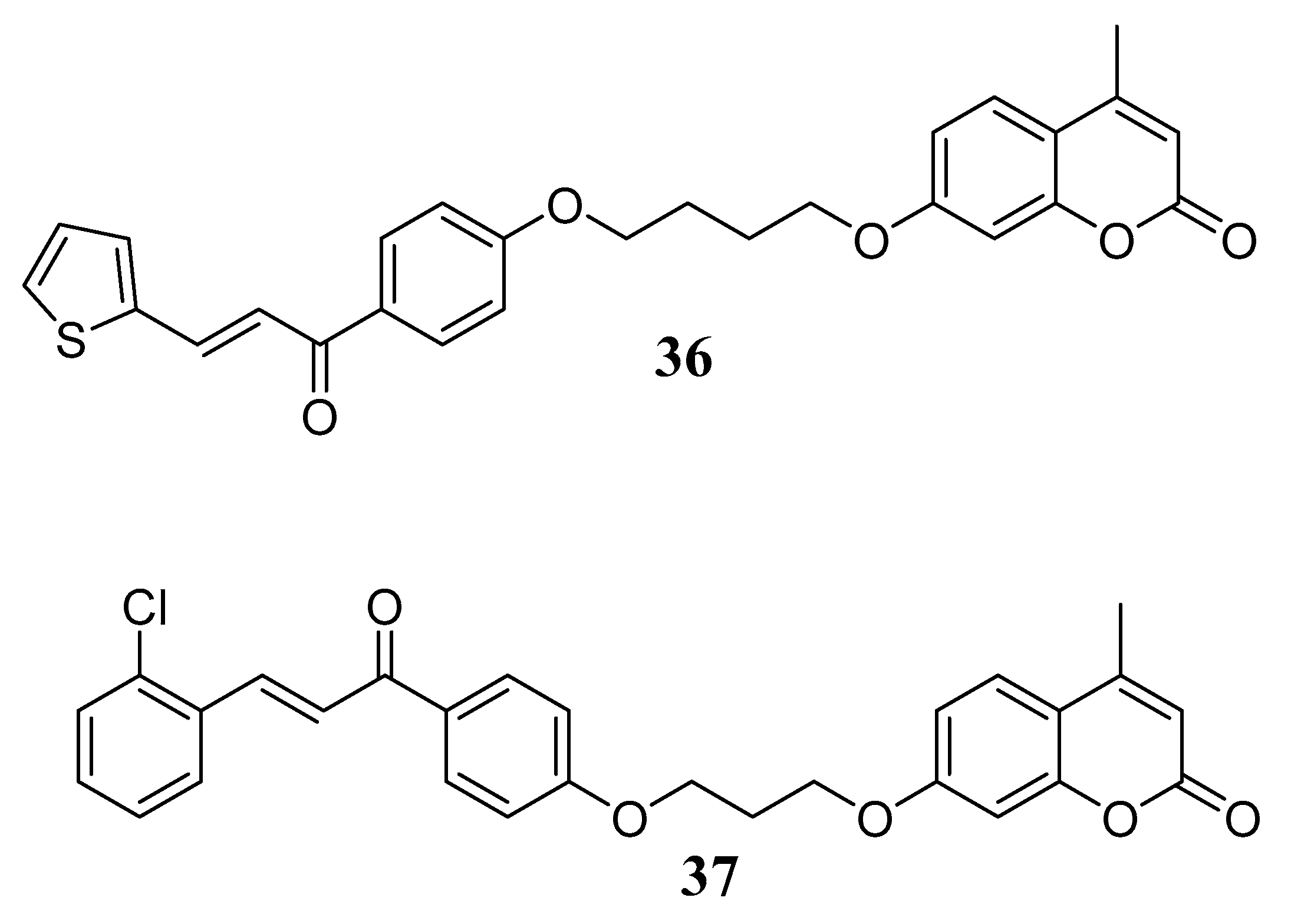
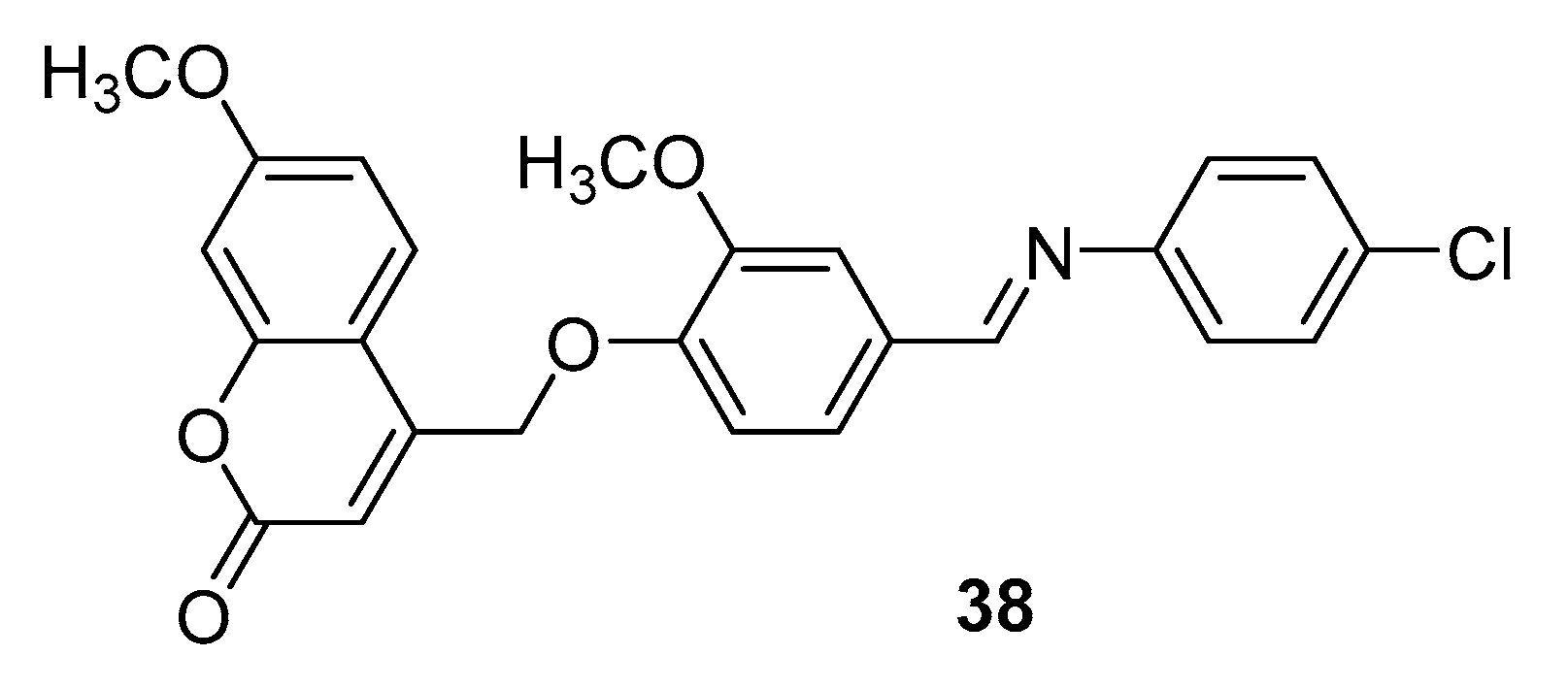
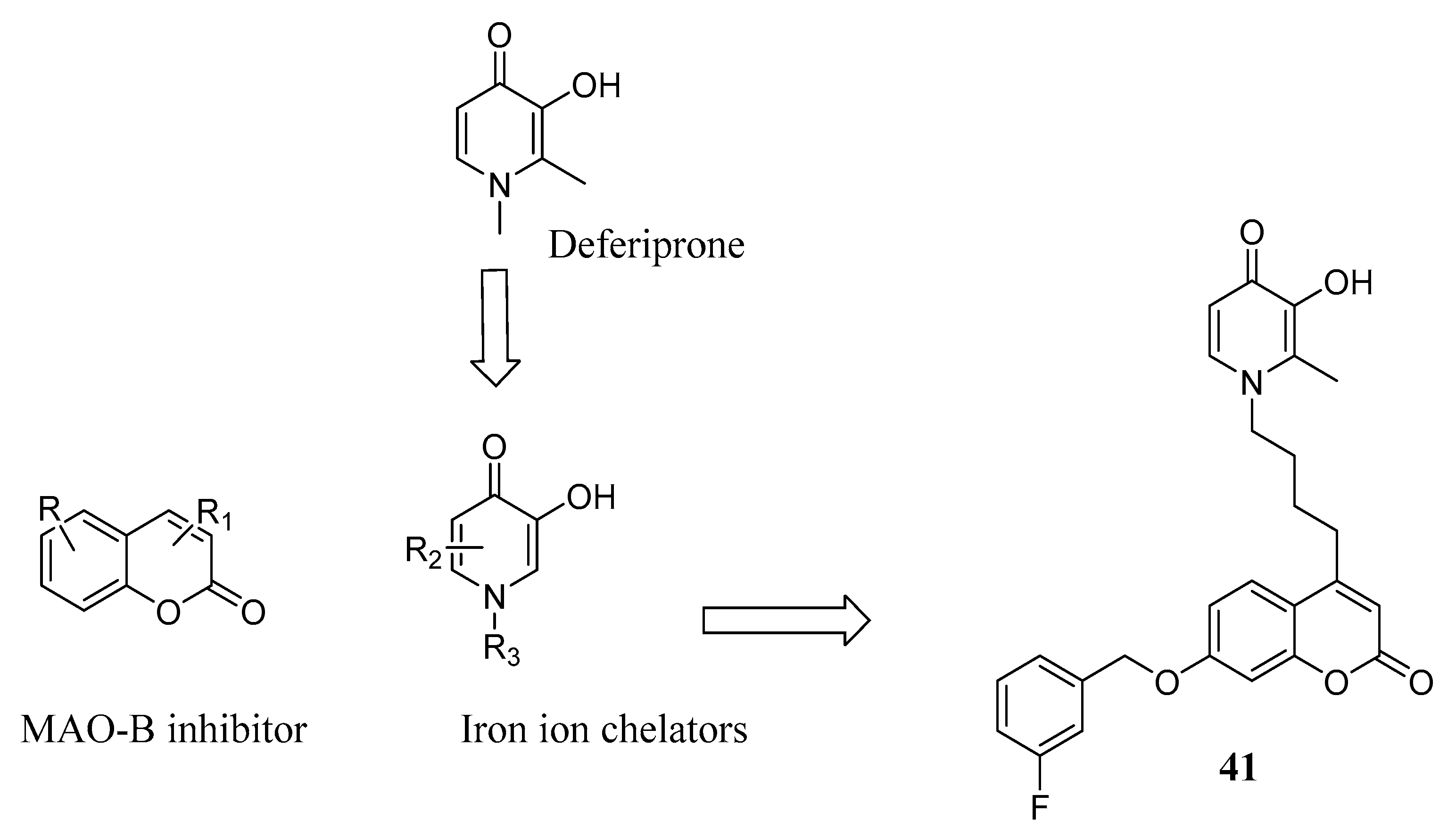
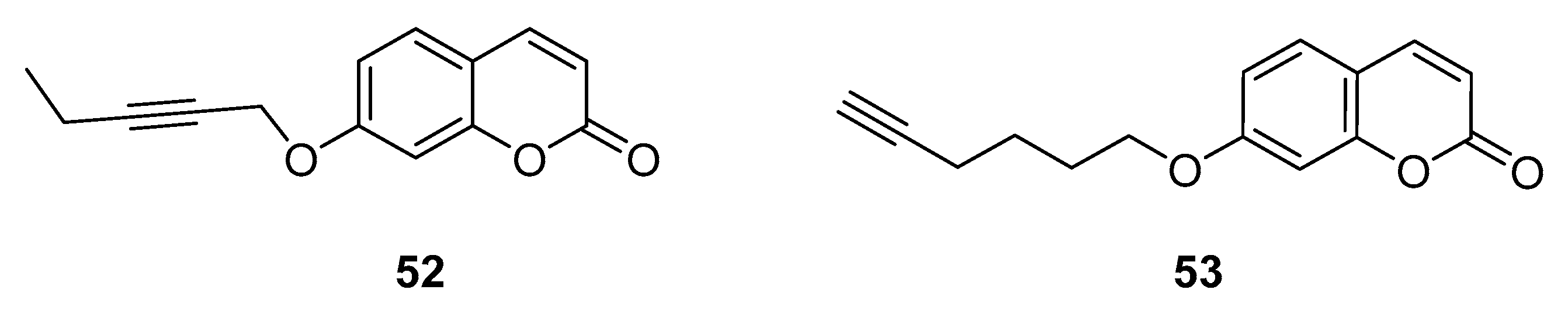
3.3. Coumarins as MTDLs for Emerging Targets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borges, F.; Roleira, F.; Milhazes, N.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E. Simple Coumarins and Analogues in Medicinal Chemistry: Occurrence, Synthesis and Biological Activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 887–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoult, J.R.S.; Payá, M. Pharmacological and biochemical actions of simple coumarins: Natural products with therapeutic potential. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1996, 27, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, F.; Pinna, C.; Dallavalle, S.; Tamborini, L.; Pinto, A. An Overview of Coumarin as a Versatile and Readily Accessible Scaffold with Broad-Ranging Biological Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Poyraz, S.; Ersatir, M. Recent advances on biologically active coumarin-based hybrid compounds. Med. Chem. Res. 2023, 32, 617–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.S.; Gupta, J.; Sharma, S.; Sahu, D. An insight into the therapeutic applications of coumarin compounds and their mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Muncipinto, G.; Nicolotti, O.; Carrieri, A.; Rullo, M.; Stefanachi, A.; Leonetti, F.; Altomare, C. A twenty-year journey exploring coumarin-based derivatives as bioactive molecules. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1002547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameel, E.; Umar, T.; Kumar, J.; Hoda, N. Coumarin: A Privileged Scaffold for the Design and Development of Antineurodegenerative Agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 87, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, A.; Al Balushi, K.; Akhtar, M.J.; Khan, S.A. Coumarin linked heterocyclic hybrids: A promising approach to develop multi target drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1241, 130618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, D.M.; Morris, J.C.; Goate, A.M. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Challenge of the Second Century. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 77sr1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y. A β 42 and A β 40: Similarities and differences. J. Pept. Sci. 2015, 21, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, C.; Killick, R.; Lovestone, S. The GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioffi, F.; Adam, R.H.I.; Broersen, K. Molecular Mechanisms and Genetics of Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 72, 981–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrekar-Colucci, S.; Landreth, G.E. Microglia and Inflammation in Alzheimers Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2010, 9, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Gu, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z. The FDA-approved anti-amyloid-β monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikrishna, D.; Godugu, C.; Dubey, P.K. A Review on Pharmacological Properties of Coumarins. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 113–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chiu, Y.J.; Yang, S.M.; Chen, C.M.; Huang, C.C.; Lee-Chen, G.J.; Lin, W.; Chang, K.H. Novel synthetic chalcone-coumarin hybrid for Aβ aggregation reduction, antioxidation, and neuroprotection. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, S.; Hoda, N. A comprehensive review of monoamine oxidase inhibitors as Anti-Alzheimer’s disease agents: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riederer, P. Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibition in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotoxicology 2004, 25, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors: Promising therapeutic agents for Alzheimer’s disease (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyiparambath, V.P.; Rajappan, K.P.; Rangarajan, T.M.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Pannipara, M.; Bhaskar, V.; Nair, A.S.; Sudevan, S.T.; Kumar, S.; Mathew, B. Deciphering the detailed structure–activity relationship of coumarins as Monoamine oxidase enzyme inhibitors—An updated review. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 98, 655–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Liu, R.; Lv, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y. Latest advances in dual inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase B against Alzheimer’s disease. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Z.; Alagöz, M.A.; Bahçecioğlu, Ö.F.; Gök, S. Monoamine Oxidase-B (MAO-B) Inhibitors in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 6045–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, N.N.; Aly, H.F.; Fouad, G.I.; El-Karim, S.S.A.; Anwar, M.M.; Syam, Y.M.; Elseginy, S.A.; Ahmed, K.A.; Booles, H.F.; Shalaby, M.B.; et al. Anti-Alzheimer activity of new coumarin-based derivatives targeting acetylcholinesterase inhibition. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 18496–18510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
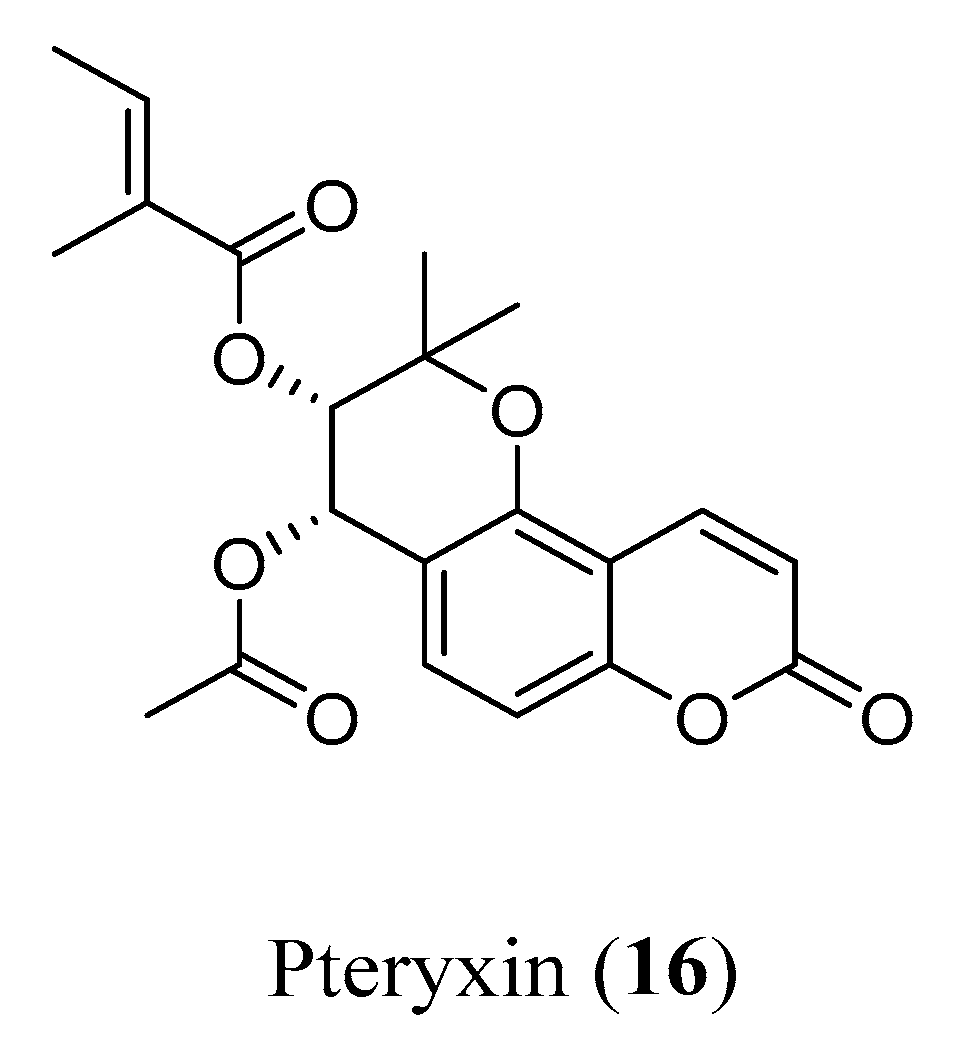
- Kiris, I.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Basar, M.K.; Sahin, B.; Gurel, B.; Baykal, A.T. Molecular Effects of Pteryxin and Scopoletin in the 5xFAD Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 29, 2937–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.E.; Tosun, F.; Deniz, F.S.S.; Eren, G.; Mıhoğlugil, F.; Akalgan, D.; Miski, M. Butyrylcholinesterase-inhibiting natural coumarin molecules as potential leads. Phytochem. Lett. 2021, 44, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Khan, W.; Zia, K.; Azizuddin; Ahsan, W.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Najmi, A.; Khan, A.; Bouyahya, A.; et al. Natural coumarins from Murraya paniculata as mixed-type inhibitors of cholinesterases: In vitro and in silico investigations. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1133809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomohiro, N.; Yasuko, K.; Sei-Itsu, M. Inhibitory effect of esculetin on 5-lipoxygenase and leukotriene biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Lipids Lipid Metab. 1983, 753, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Park, B.-K.; Kim, Y.H.; Shim, I.; Kang, I.-C.; Lee, M.Y. Antidepressant Effect of Fraxinus rhynchophylla Hance Extract in a Mouse Model of Chronic Stress-Induced Depression. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8249563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, Q.; Li, X. Esculetin: A review of its pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q. Role of Nrf2 in Oxidative Stress and Toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzezewa, S.C.; Omoruyi, S.I.; Zondagh, L.S.; Malan, S.F.; Ekpo, O.E.; Joubert, J. Design; synthesis and evaluation of 3,7-substituted coumarin derivatives as multifunctional Alzheimer’s disease agents. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 1606–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; Mattsson, N.; Schöll, M.; Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H. Amyloid biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulaamane, Y.; Kandpal, P.; Chandra, A.; Britel, M.R.; Maurady, A. Chemical library design QSAR modeling and molecular dynamics simulations of naturally occurring coumarins as dual inhibitors of MAO-B and AChE. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 42, 1629–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Wang, Z.; Lei, M.; Che, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Shi, L.; Cui, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Daphnetin ameliorates Aβ pathogenesis via STAT3/GFAP signaling in an APP/PS1 double-transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 180, 106227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, N.H.; Suwanjang, W.; Ruankham, W.; Songtawee, N.; Wongchitrat, P.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Pra-chayasittikul, S.; Phopin, K. Butein, isoliquiritigenin, and scopoletin attenuate neurodegeneration via an-tioxidant enzymes and SIRT1/ADAM10 signaling pathway. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 16593–16606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; Tsai, S.-H.; Chen, C.-S.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-M.; Lai, Z.-Y.; Lin, C.-M. Structure–activity relationship of coumarin derivatives on xanthine oxidase-inhibiting and free radical-scavenging activities. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.E.; Senol, F.S.; Shekfeh, S.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Banoglu, E. Pteryxin—A promising butyrylcholinesterase-inhibiting coumarin derivative from Mutellina purpurea. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigalunas, M.; Brakmann, S.; Waldmann, H. Chemical Evolution of Natural Product Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3314–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaveta; Mishra, S.; Singh, P. Hybrid molecules: The privileged scaffolds for various pharmaceuticals. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 500–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citarella, A.; Vittorio, S.; Dank, C.; Ielo, L. Syntheses, reactivity, and biological applications of coumarins. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1362992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.M.; Rahman, D.E.A.; Allam, H.A.; El-Zoheiry, H.H. Design and synthesis of novel coumarin derivatives as potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 110, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Tu, Z. Pyrazole Scaffold Synthesis, Functionalization, and Applications in Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease Treatment (2011–2020). Molecules 2021, 26, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouz-Touami, A.; Chouh, A.; Halit, S.; Terrachet-Bouaziz, S.; Makhloufi-Chebli, M.; Ighil-Ahriz, K.; Silva, A.M.S. New Coumarin-Pyrazole hybrids: Synthesis, Docking studies and Biological evaluation as potential cholinesterase inhibitors. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1249, 131591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.-H.; Min, W.; Song, M.; Si, X.-X.; Li, M.-C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.-W.; Liu, W.-W. Synthesis, characterization, crystal structure and evaluation of four carbazole-coumarin hybrids as multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1209, 127897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.Q.; Min, W.; Wang, J.; Si, X.X.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, Y.W.; Shi, D.H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new carbazole-coumarin hybrids as dual binding site inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1229, 129784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharamak, S.; Wisarutwanit, T.; Songoen, W.; Saparpakorn, P.; Pluempanupat, W. Synthesis and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Evaluation of Coumarin-Linked Carbazole Derivatives. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202303879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharat, R.; Prabhu, A.; Khambete, M.P. Potential of triazines in Alzheimer’s disease: A versatile privileged scaffold. Arch. Pharm. 2022, 355, 2100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-L.; Wen, Z.-Y.; Qian, J.-J.; Zou, J.-P.; Liu, S.-M.; Yang, S.; Qin, T.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liu, W.-W.; et al. Design, synthesis, characterization and evaluation of 1,3,5-triazine-benzimidazole hybrids as multifunctional acetylcholinesterases inhibitors. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1257, 132498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zou, J.; Cao, Y.; Xu, X.; Ding, B.; Liu, W.; Ma, S.; Shi, D. Design, Synthesis and Anticholinesterase Activity of Coumarin-1,3,5-triazine Derivatives. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202303428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Nuthakki, V.K.; Gairola, S.; Singh, B.; Bharate, S.B. A Coumarin−Donepezil Hybrid as a Blood−Brain Barrier Permeable Dual Cholinesterase Inhibitor: Isolation, Synthetic Modifications, and Biological Evaluation of Natural Coumarins. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202200300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Bharate, S.B. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Coumarin Triazoles as Dual Inhibitors of Cholinesterases and β-Secretase. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 11161–11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, T.; Ashfaq, M.; Saleem, M.; Rafiq, M.; Shahzad, M.I.; Kotwica-Mojzych, K.; Mojzych, M.; Scaffolds, P. Phenols and Derivatives of Azo Moiety: Current Therapeutic Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepehri, S.; Saeedi, M.; Larijani, B.; Mahdavi, M. Recent developments in the design and synthesis of benzylpyridinium salts: Mimicking donepezil hydrochloride in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 936240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnl, J.; Roggenkamp, D.; Gehrke, S.A.; Stäb, F.; Wenck, H.; Kolbe, L.; Neufang, G. Licochalcone A activates Nrf2 in vitro and contributes to licorice extract-induced lowered cutaneous oxidative stress in vivo. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Fan, H.; Tang, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, W.-K. Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of chalcone derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 6124–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.H.; Chang, K.H.; Chiu, Y.J.; Weng, Z.K.; Sun, Y.C.; Lin, W.; Lee-Chen, G.J.; Chen, C.M. Neuroprotective Action of Coumarin Derivatives through Activation of TRKB-CREB-BDNF Pathway and Reduction of Caspase Activity in Neuronal Cells Expressing Pro-Aggregated Tau Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.H.; Shakya, S.; Hussain, F.H.S.; Murugesan, S.; Chander, S.; Pratama, M.R.F.; Jamil, S.; Das, B.; Biswas, S.; Jamalis, J. Design, synthesis, anti-acetylcholinesterase evaluation and molecular modelling studies of novel coumarin-chalcone hybrids. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 11450–11462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.H.; Abdulrahman, F.A.; Obaidullah, A.J.; Alotaibi, H.F.; Alanazi, M.M.; Noamaan, M.A.; Murugesan, S.; Amran, S.I.; Bhat, A.R.; Jamalis, J. Discovery of Novel Coumarin-Schiff Base Hybrids as Potential Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Enzyme Inhibition, and Computational Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Das, S.S.; Srivastava, A.; Choudhury, A.; Bhattacharjee, R.; De, S.; Perveen, A.; Iqbal, D.; Gupta, P.K.; et al. Molecular Insights into Therapeutic Potentials of Hybrid Compounds Targeting Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 3512–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sena Murteira Pinheiro, P.; Franco, L.S.; Montagnoli, T.L.; Fraga, C.A.M. Molecular hybridization: A powerful tool for multitarget drug discovery. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2024, 19, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Mi, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Z.; Li, L.; Gu, J.; Zhou, T.; Bai, R.; Xie, Y. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of potential anti-AD hybrids with monoamine oxidase B inhibitory and iron-chelating effects. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.; Brunskill, S.; Doree, C.; Williams, S.; Howard, J.; Hyde, C. Oral deferiprone for iron chelation in people with thalassaemia. In Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; Roberts, D., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, L.; Liu, W.; Tian, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Qiu, J.; Feng, X.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel coumarin derivatives as multifunctional ligands for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 242, 114689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourabdi, L.; Küçükkılınç, T.T.; Khoshtale, F.; Ayazgök, B.; Nadri, H.; Alashti, F.F.; Forootanfar, H.; Akbari, T.; Shafiei, M.; Foroumadi, A.; et al. Synthesis of New 3-Arylcoumarins Bearing N-Benzyl Triazole Moiety: Dual Lipoxygenase and Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors With Anti-Amyloid Aggregation and Neuroprotective Properties Against Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Chem. 2022, 9, 810233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mphahlele, M.J.; Agbo, E.N.; Gildenhuys, S.; Setshedi, I.B. Exploring Biological Activity of 4-Oxo-4H-furo [2,3-h]chromene Derivatives as Potential Multi-Target-Directed Ligands Inhibiting Cholinesterases, β-Secretase, Cyclooxygenase-2, and Lipoxygenase-5/15. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Kwon, H.; Park, Y.; Kim, K.S.; Song, C.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.-H.; Yu, H.-J.; Henkel, J.S.; et al. Epigallocatechin gallate protects nerve growth factor differentiated PC12 cells from oxidative-radical-stress-induced apoptosis through its effect on phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and glycogen synthase kinase-3. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 118, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Akhtar, M.J.; Gogoi, U.; Meenakshi, D.U.; Das, A. An Overview of 1,2,3-triazole-Containing Hybrids and Their Potential Anticholinesterase Activities. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, M.; Shi, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, A.; Shen, R. Design, Synthesis, Calculation and Biological Activity Studies Based on Privileged Coumarin Derivatives as Multifunctional Anti-AD Lead Compound. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202200867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V. Endocannabinoids: Synthesis and degradation. In Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampa, A.; Bartolini, M.; Bisi, A.; Belluti, F.; Gobbi, S.; Andrisano, V.; Ligresti, A.; Di Marzo, V. The first dual ChE/FAAH inhibitors: New perspectives for Alzheimer’s disease? ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 3, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, S.; Allarà, M.; Scalvini, L.; Kostrzewa, M.; Belluti, F.; Gobbi, S.; Naldi, M.; Rivara, S.; Bartolini, M.; Ligresti, A.; et al. New Coumarin derivatives as cholinergic and cannabinoid system modulators. Molecules 2021, 26, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, S.; Scalvini, L.; Bartolini, M.; Belluti, F.; Gobbi, S.; Andrisano, V.; Ligresti, A.; Di Marzo, V.; Rivara, S.; Mor, M.; et al. Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH), Acetylcholinesterase (AChE), and Butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE): Networked Targets for the Development of Carbamates as Potential Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6387–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canepa, E.; Parodi-Rullan, R.; Vazquez-Torres, R.; Gamallo-Lana, B.; Guzman-Hernandez, R.; Lemon, N.L.; Angiulli, F.; Debure, L.; Ilies, M.A.; Østergaard, L.; et al. FDA-approved carbonic anhydrase inhibitors reduce amyloid β pathology and improve cognition, by ameliorating cerebrovascular health and glial fitness. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 5048–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedi, N.A.; Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani, M.; Rezaei, P.; Askarzadeh, M.; Alikhani, M.; Adib, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Larijani, B.; Niakan, S.; Tehrani, M.B.; et al. Dual functional cholinesterase and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Design, synthesis, in vitro, and in silico evaluations of coumarin-dihydropyridine derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1276, 134767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrino, E.; Carradori, S.; Carta, F.; Melfi, F.; Gallorini, M.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; López, Ó.; Petzer, J.P.; et al. A Multitarget Approach against Neuroinflammation: Alkyl Substituted Coumarins as Inhibitors of Enzymes Involved in Neurodegeneration. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orioli, R.; Belluti, F.; Gobbi, S.; Rampa, A.; Bisi, A. Naturally Inspired Coumarin Derivatives in Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Discovery: Latest Advances and Current Challenges. Molecules 2024, 29, 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153514
Orioli R, Belluti F, Gobbi S, Rampa A, Bisi A. Naturally Inspired Coumarin Derivatives in Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Discovery: Latest Advances and Current Challenges. Molecules. 2024; 29(15):3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153514
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrioli, Rebecca, Federica Belluti, Silvia Gobbi, Angela Rampa, and Alessandra Bisi. 2024. "Naturally Inspired Coumarin Derivatives in Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Discovery: Latest Advances and Current Challenges" Molecules 29, no. 15: 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153514
APA StyleOrioli, R., Belluti, F., Gobbi, S., Rampa, A., & Bisi, A. (2024). Naturally Inspired Coumarin Derivatives in Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Discovery: Latest Advances and Current Challenges. Molecules, 29(15), 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153514








