Electrochemical Nickel-Catalyzed Synthesis of Unsymmetrical Diorganyl Selanes from Diaryl Diselanes and Aryl and Alkyl Iodides
Abstract
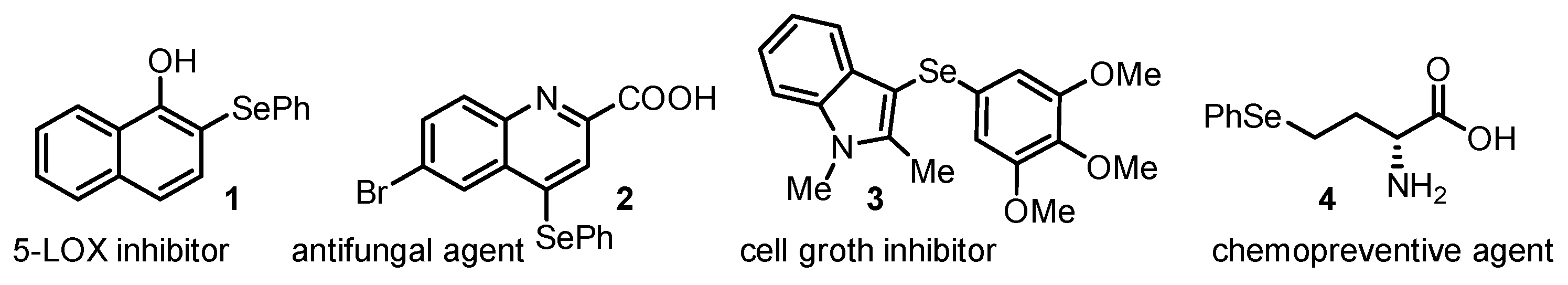
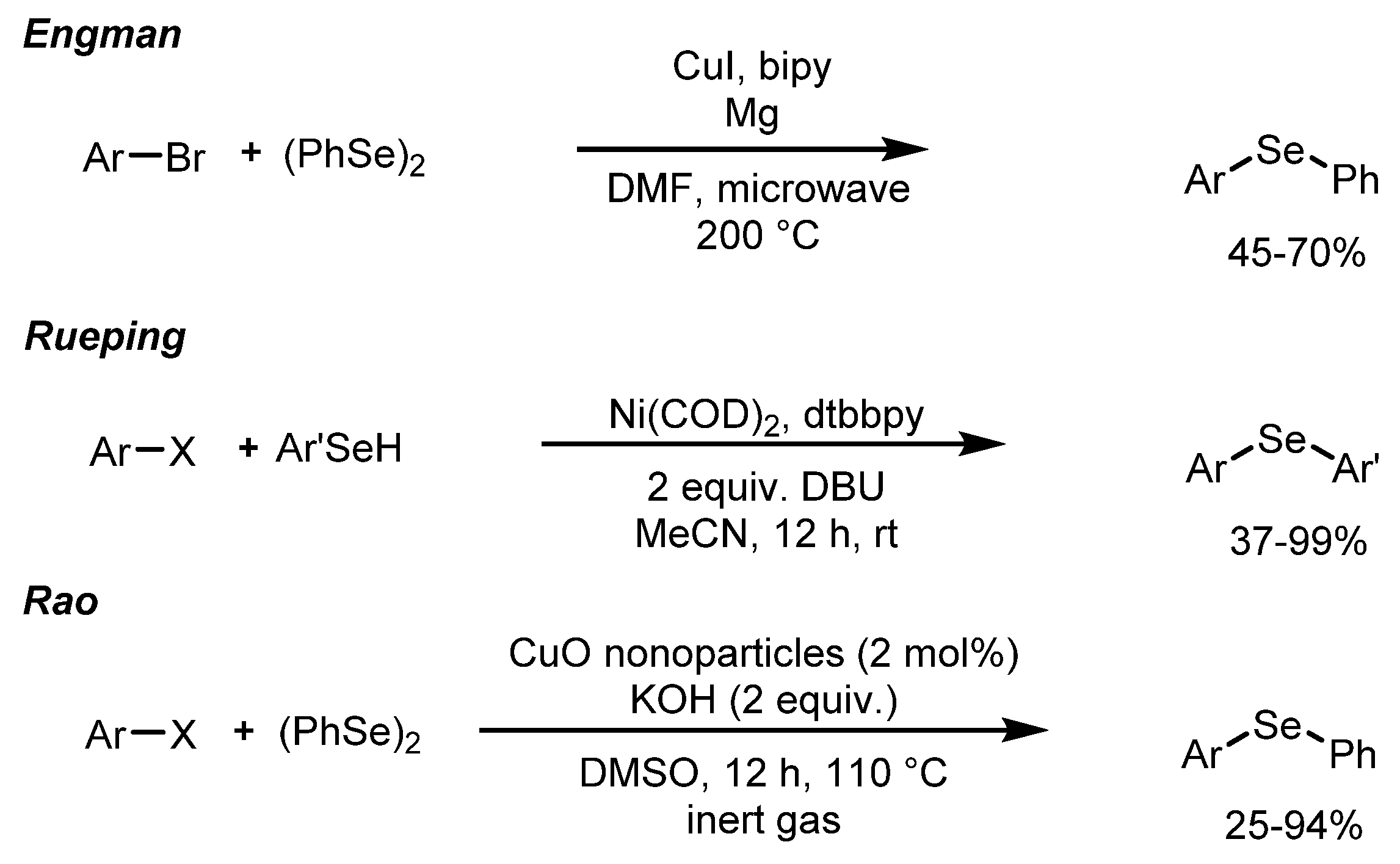
1. Introduction
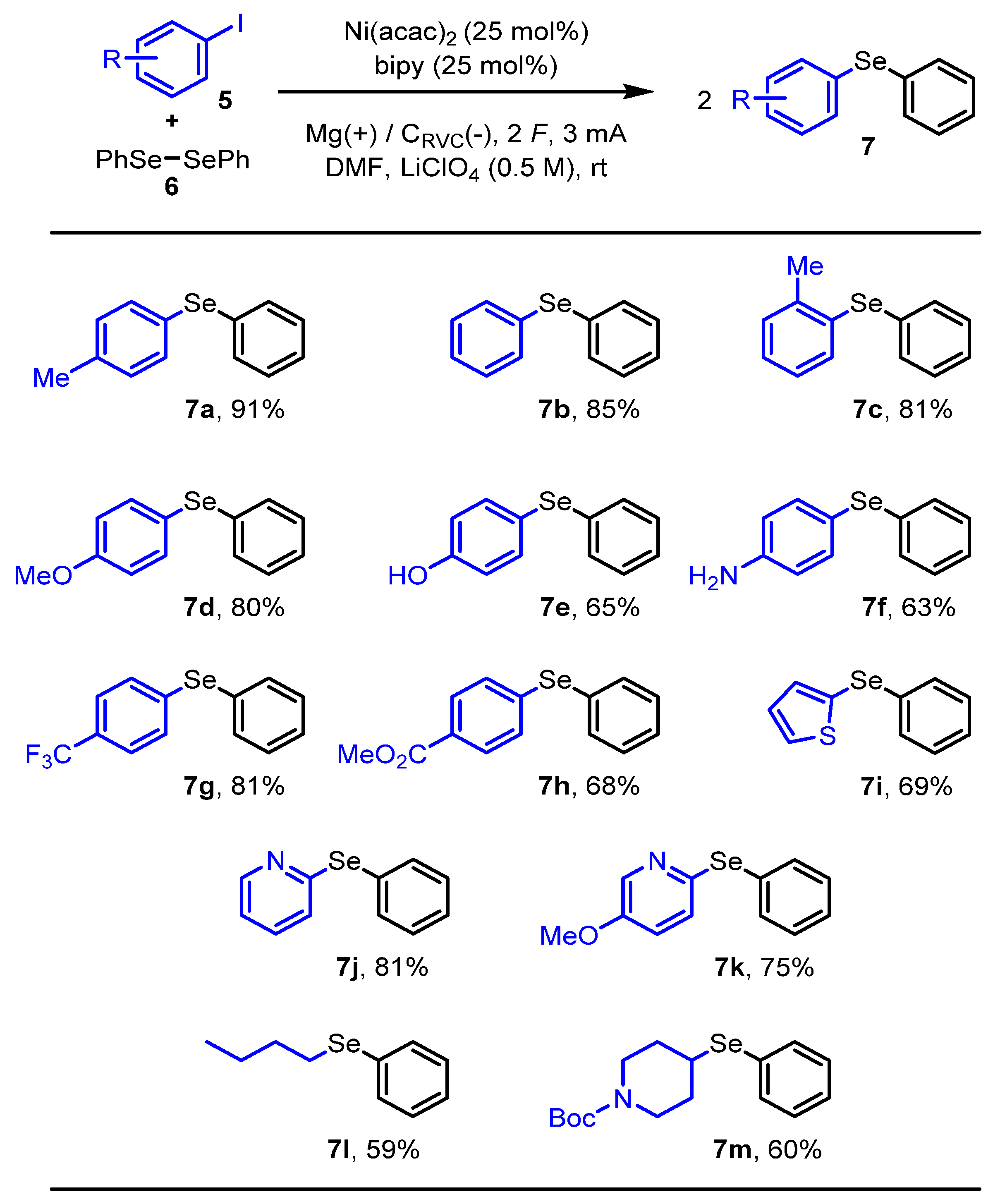
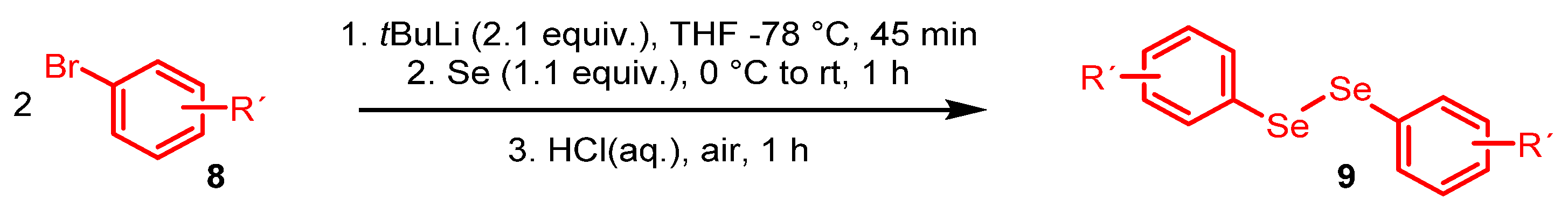
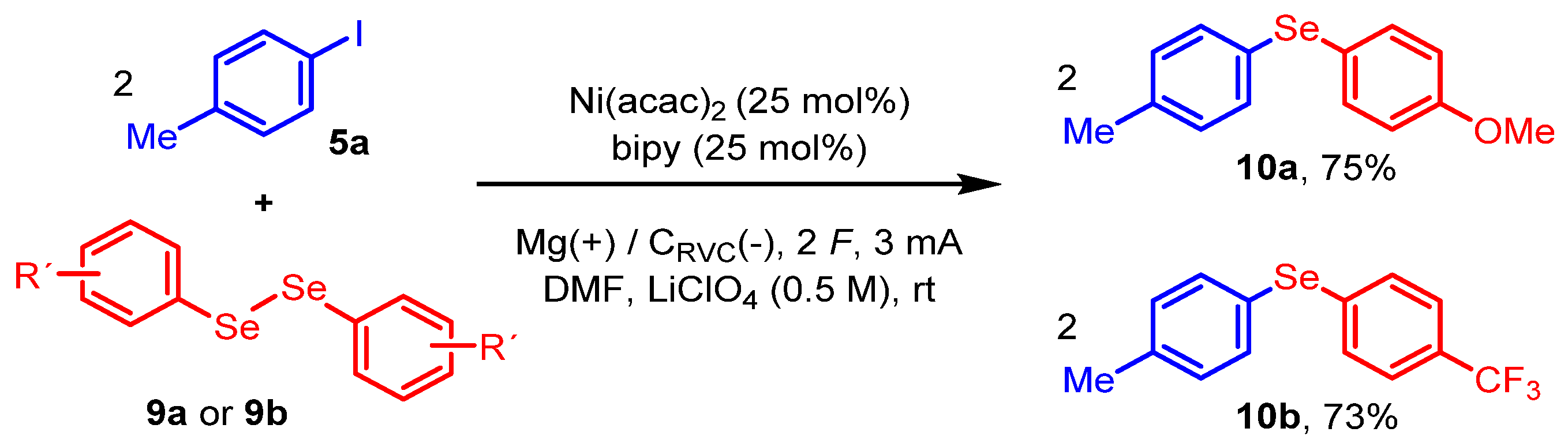
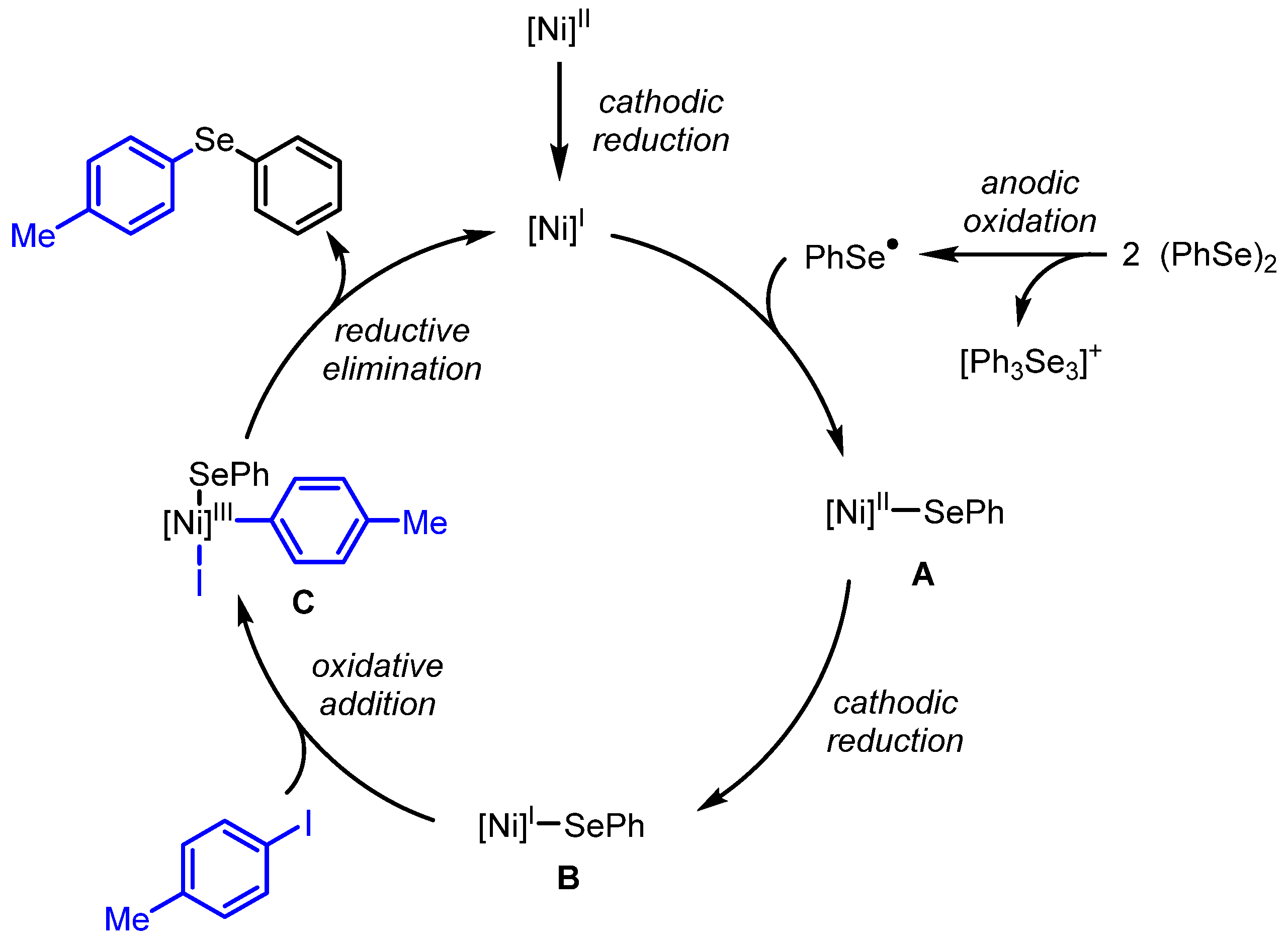
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. The General Procedure
3.3. Characterization Data of Novel Compounds
5-Methoxy-2-(phenylselanyl)pyridine (7k)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nogueira, C.W.; Zeni, G.; Rocha, J.B.T. Organoselenium and organotellurium compounds: Toxicology and pharmacology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6255–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonego, J.M.; de Diego, S.I.; Szajnman, S.H.; Gallo-Rodriguez, C.; Rodriguez, J.B. Organoselenium compounds: Chemistry and applications in organic synthesis. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 52, e202300030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamata, Y.; Hashimotot, T.; Maruoka, K. A chiral electrophilic selenium catalyst for highly enantioselective oxidative cyclization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5206–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadel, J.T.; Back, T.G. Asymmetric synthesis with organoselenium compounds—The past twelve years. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 31, e202304074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, N. Convenient synthesis of unsymmetrical organochalcogenides using organoboronic acids with dichalcogenides via cleavage of the S-S, Se-Se, or Te-Te bond by a copper catalyst. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Engman, L. Microwave-assisted copper-catalyzed preparation of diaryl chalcogenides. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 5400–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, N.; Onami, T. Copper-catalyzed synthesis of diaryl selenide from aryl iodide and diphenyl diselenide using magnesium metal. Synlett 2003, 2003, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhumagazy, S.; Zhu, C.; Yue, H.F.; Rueping, M. Nickel-catalyzed carbon–selenium bond formations under mild conditions. Synlett 2023, 34, 1381–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonciolini, S.; Pulcinella, A.; Leone, M.; Schiroli, D.; Ruiz, A.L.; Sorato, A.; Dubois, M.A.J.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Masson, G.; Ca’, N.D.; et al. Metal-free photocatalytic cross-electrophile coupling enables C1 homologation and alkylation of carboxylic acids with aldehydes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Mao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, B.; Yang, X.-Y.; Li, J. Metal-free photochemical C-Se cross-coupling of aryl halides with diselenides. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.P.; Kumar, A.V.; Swapna, K.; Rao, K.R. Copper oxide nanoparticle-catalyzed coupling of diaryl diselenide with aryl halides under ligand-free conditions. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 951–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Qui, Y. Electroreductive cross-electrophile coupling (eXEC) reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ware, S.D.; Mondragon, J.; Rein, J.; Strotman, N.; Lehnherr, D.; See, K.A.; et al. Electrochemically driven cross-electrophile coupling of alkyl halides. Nature 2022, 604, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, Z.; Wang, M. Nickel-catalyzed asymmetric propargyl-aryl cross-electrophile coupling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 63, e202313655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Su, P.-F.; Shu, X.-Z. Reductive cross-coupling of unreactive electrophiles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2491–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-M.; Lui, X.-T.; Xu, L.-L.; Shang, M. Electrochemical Ni-catalyzed decarboxylative C(sp3)-N cross-electrophile coupling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202315222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queder, J.; Hilt, G. The electrochemical trans-chloroformyloxylation of unactivated alkenes. Synlett 2024, 34. in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.E.; Jarvo, E.R. Stereospecific and stereoconvergent cross-couplings between alkyl electrophiles. Nat. Chem. Rev. 2017, 1, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Weix, D.J. Mechanism and Selectivity in Nickel-Catalyzed Cross-Electrophile Coupling of Aryl Halides with Alkyl Halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16192–16197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.S.; Rentaria-Gomez, A.; Ton, S.J.; Gogoi, A.R.; Gutierrez, O.; Martin, R. Elucidating electron-transfer events in polypyridine nickel complexes for reductive coupling reactions. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Beromi, M.M.; Banerjee, G.; Brudvig, G.W.; Hazari, N.; Mercado, B.Q. Nickel (I) Aryl species: Synthesis, properties, and catalytic activity. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Hu, J.; Qui, C.; Gong, H. Insights into recent nickel-catalyzed reductive and redox C-C coupling of electrophiles, C(sp3)-H bonds and alkenes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, L.; Wang, Q.; Tang, H.-T.; Mo, Z.-Y.; Pan, Y.-M. Recent advances in electrochemically mediated reactions of diselenides. SynOpen 2023, 7, 521–534. [Google Scholar]

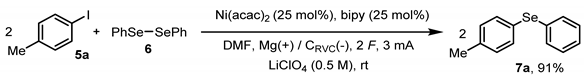
| Entry | Change to the Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bu4NPF6 as supporting electrolyte | 58% |
| 2 | LiClO4 (0.5 M) as supporting electrolyte, glassy carbon cathode | 66% |
| 3 | LiClO4 (0.24 M) as supporting electrolyte, glassy carbon cathode | 48% |
| 4 | NiCl2·6H2O as nickel catalyst precursor | 62% |
| 5 | NiBr2 as nickel catalyst precursor | 52% |
| 6 | NiI2 as nickel catalyst precursor | 57% |
| 7 | Ni(acac)2 (20 mol%) | 43% |
| 8 | Ni(acac)2 (30 mol%) | 44% |
| 9 | 1,10-phananthroline as ligand | 46% |
| 10 | 1,2-(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe) as ligand | 2% |
| 11 | Dimethylaminoacetamide (DMA) as solvent | 50% |
| 12 | Acetonitrile (MeCN) as solvent | 36% |
| 13 | 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol as solvent | 0% |
| 14 | Divided cell (P4 frit) (2 F) | 12% |
| 15 | Pseudo-divided cell (Pt wire anode) | 0% |
| 16 | Glassy carbon cathode | 57% |
| 17 | Magnesium cathode | 56% |
| 18 | Platinum cathode | 0% |
| 19 | Zinc anode | 20% |
| 20 | Platinum anode | 0% |
| 21 | 1.5 F of electricity | 42% |
| 22 | 2.5 F of electricity | 27% |
| 23 | None | 91% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Queder, J.; Hilt, G. Electrochemical Nickel-Catalyzed Synthesis of Unsymmetrical Diorganyl Selanes from Diaryl Diselanes and Aryl and Alkyl Iodides. Molecules 2024, 29, 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194669
Queder J, Hilt G. Electrochemical Nickel-Catalyzed Synthesis of Unsymmetrical Diorganyl Selanes from Diaryl Diselanes and Aryl and Alkyl Iodides. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194669
Chicago/Turabian StyleQueder, Jona, and Gerhard Hilt. 2024. "Electrochemical Nickel-Catalyzed Synthesis of Unsymmetrical Diorganyl Selanes from Diaryl Diselanes and Aryl and Alkyl Iodides" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194669
APA StyleQueder, J., & Hilt, G. (2024). Electrochemical Nickel-Catalyzed Synthesis of Unsymmetrical Diorganyl Selanes from Diaryl Diselanes and Aryl and Alkyl Iodides. Molecules, 29(19), 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194669





