1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives: Physicochemical Properties, Antileishmanial Potential, Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations of Leishmania infantum Target Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
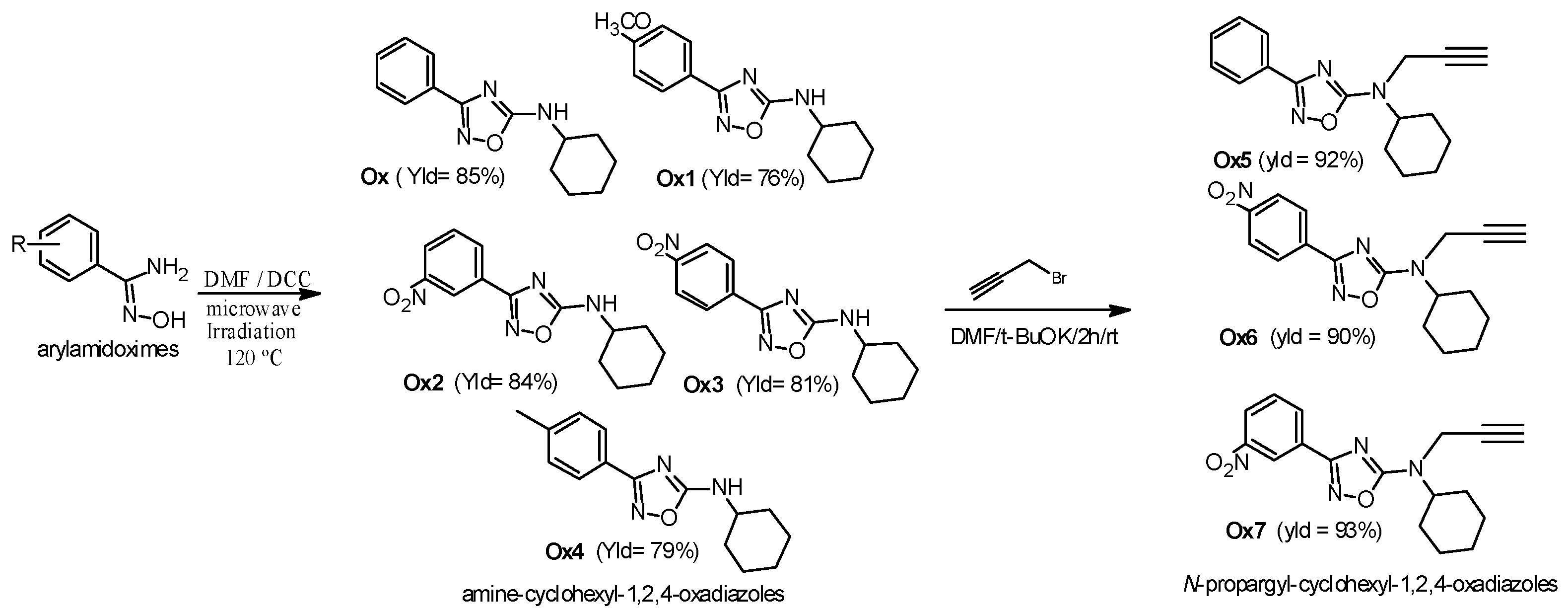
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Physicochemical Properties
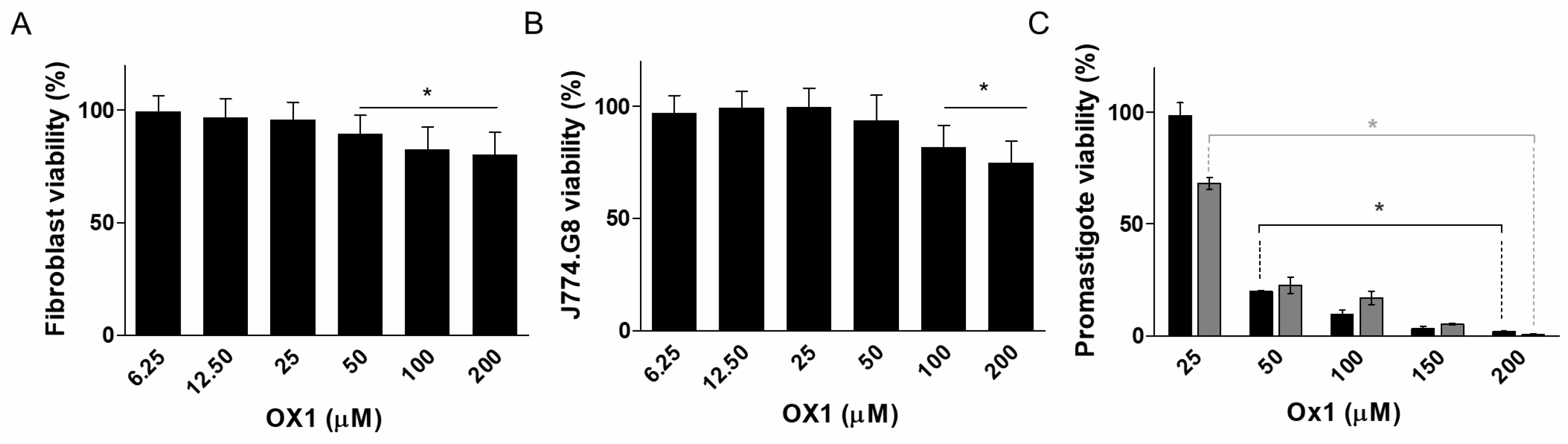
2.3. Cytotoxicity in Mammalian Cells and Effects of Ox1–Ox7 on L. infantum Promastigotes
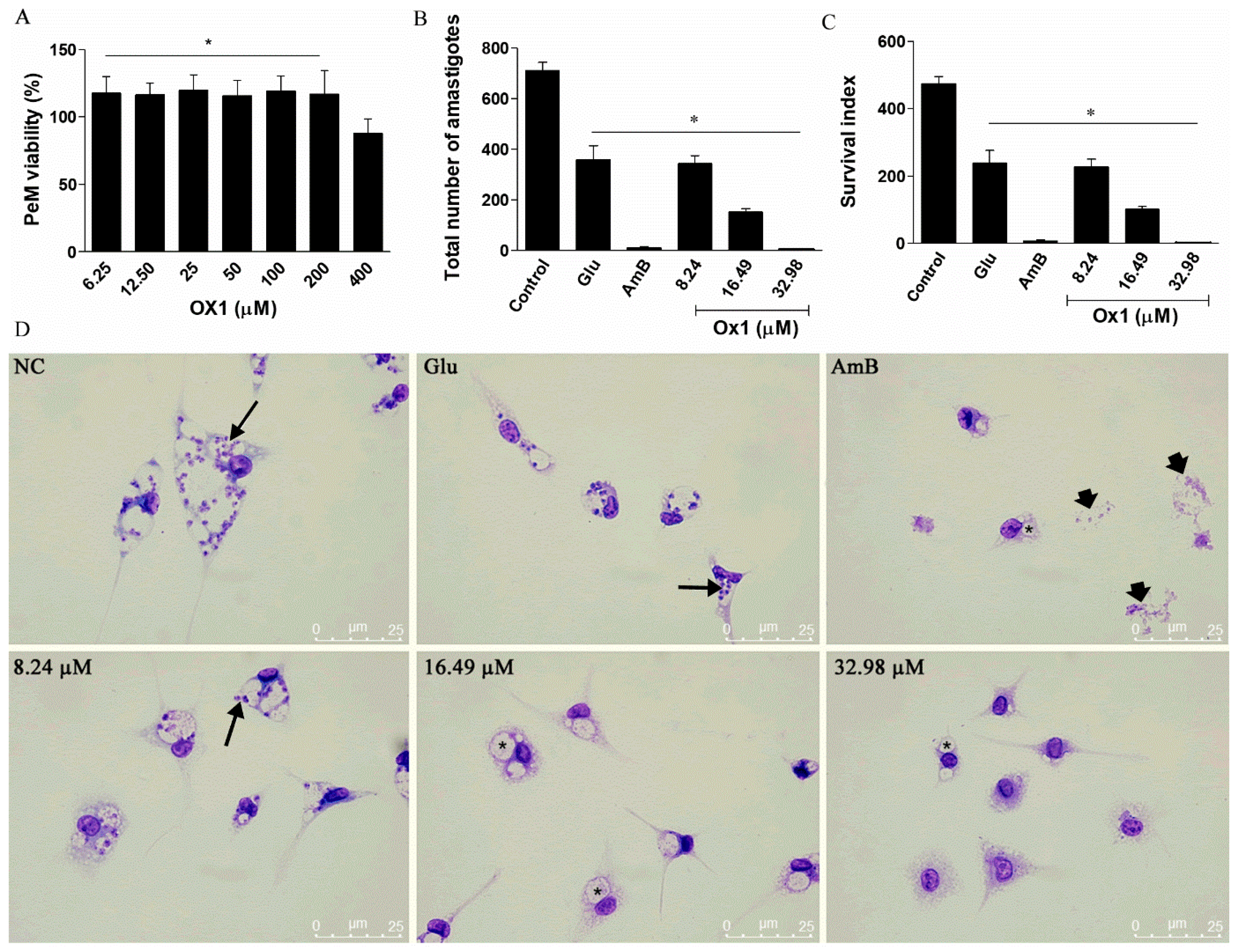
2.4. The Effects of Ox1 on L. infantum Amastigotes
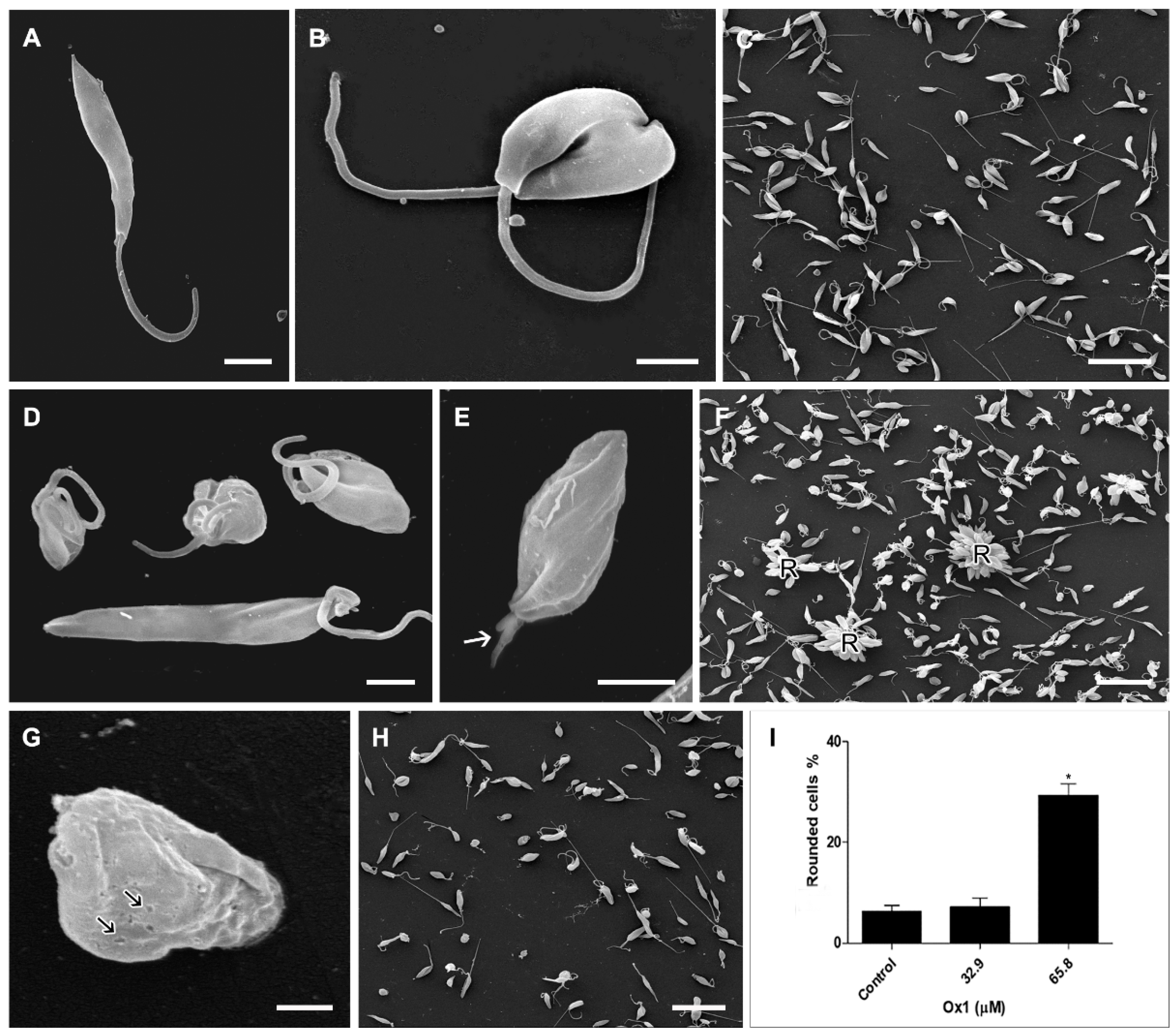
2.5. Effects of Ox1 on Ultrastructure of L. infantum Promastigotes
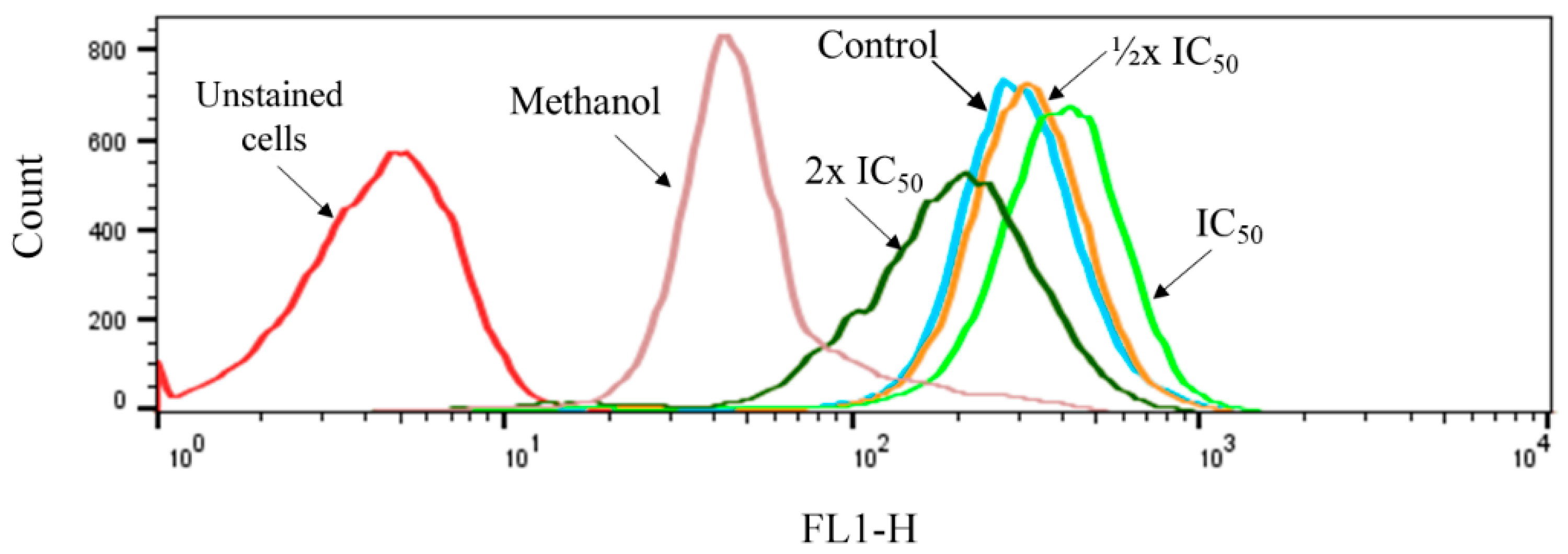
2.6. Effects of Ox1 on the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential of Promastigotes
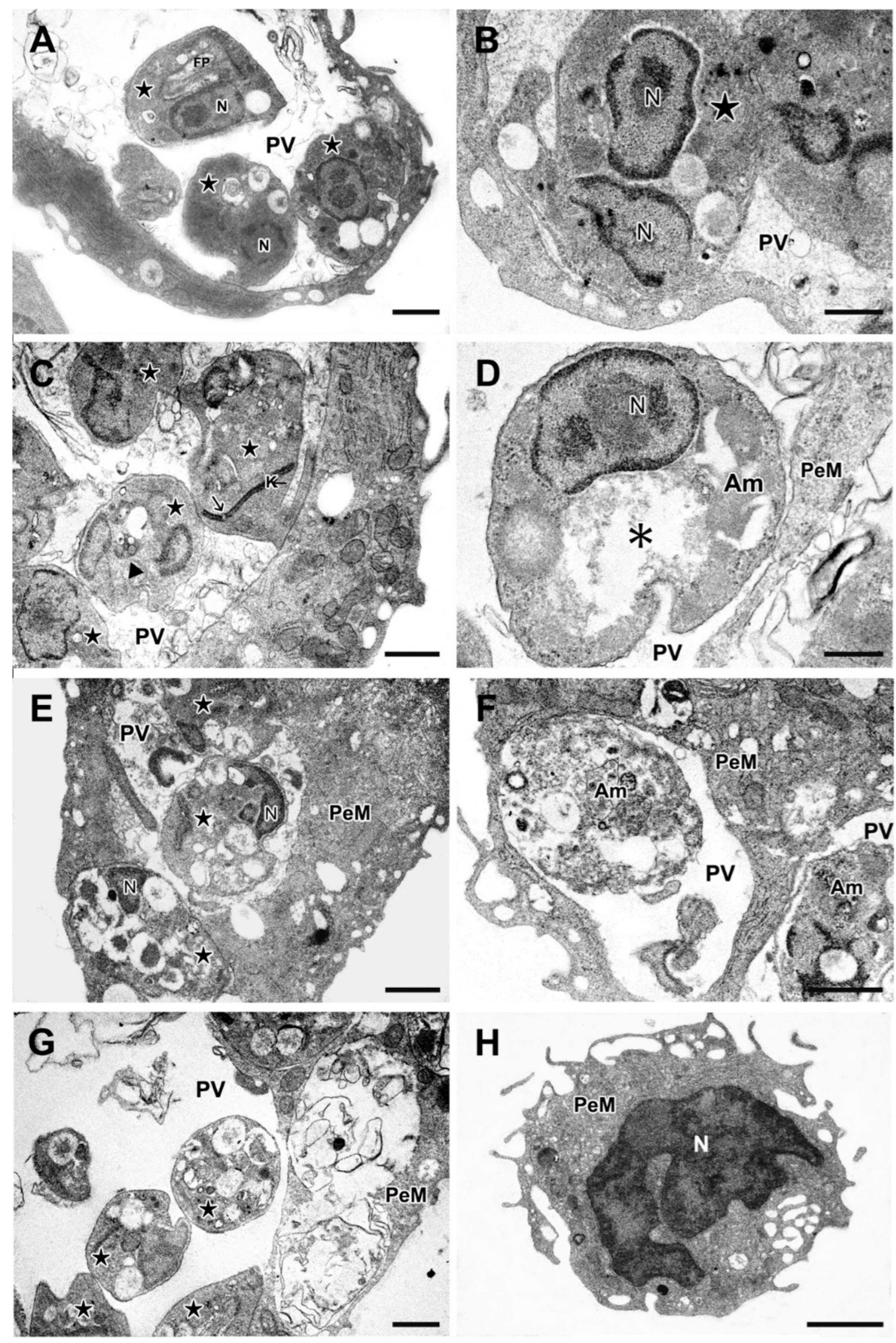
2.7. Effects of Ox1 on the Ultrastructure of L. infantum Amastigotes
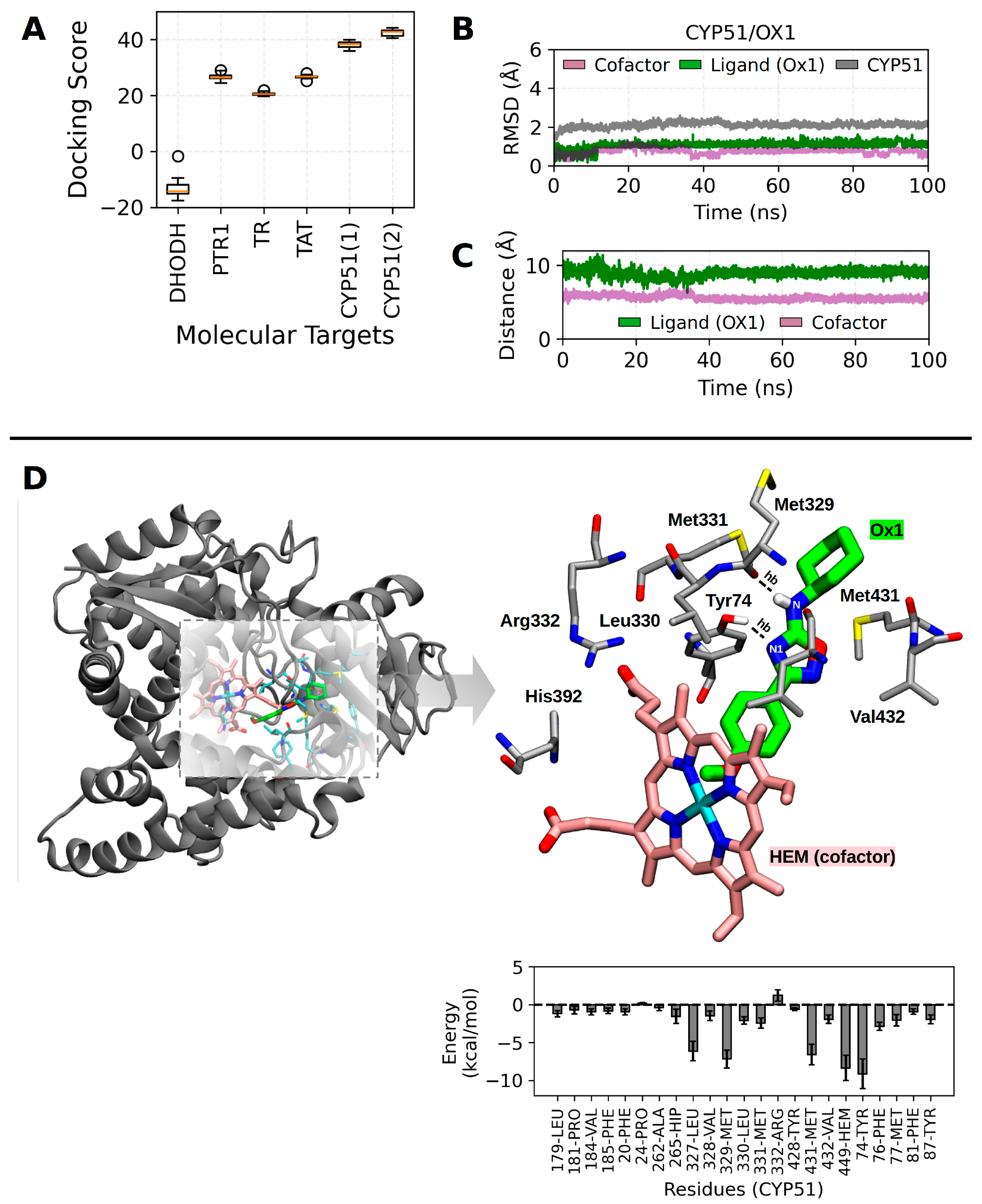
2.8. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Calculations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.1.1. Synthesis of 3-Aryl-5-cyclohexylamino-1,2,4-oxadiazole Derivatives (Ox, Ox1, Ox2, Ox3, Ox4) [28]
3.1.2. Synthesis of the N-Propargyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole Derivatives (Ox5, Ox6, Ox7) [20]
3.2. Physiochemical Assay
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay in Mammalian Cells
3.4. Promastigotes Culture
3.5. In Vitro Assay of the Effects of Ox1–Ox7 on L. infantum Promastigotes
3.6. The Effects of 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Selected Derivative on Amastigote Forms
3.7. Ultrastructural Assay
3.8. Effects of Ox1 on the Parasite Mitochondria
3.9. Molecular Docking
3.10. MD Simulations and MD Trajectory Analysis
3.11. Statistical Assays
3.12. Ethical Considerations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wamai, R.G.; Kahn, J.; McGloin, J.; Ziaggi, G. Visceral Leishmaniasis: A Global Overview. J. Glob. Health Sci. 2020, 2, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Griensven, J.; Diro, E. Visceral Leishmaniasis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, V.; Chandel, S.; Pandey, V.; Asati, S.; Jain, P.; Jain, A.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 8—Novel Therapeutic Approaches for the Treatment of Leishmaniasis. In Biomaterials and Bionanotechnology; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Advances in Pharmaceutical Product Development and Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 263–300. ISBN 978-0-12-814427-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, S.; Frasca, K.; Scherrer, S.; Henao-Martínez, A.F.; Newman, S.; Ramanan, P.; Suarez, J.A. A Review of Leishmaniasis: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2021, 8, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Leishmaniasis. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Yasmin, H.; Adhikary, A.; Al-Ahdal, M.N.; Roy, S.; Kishore, U. Host–Pathogen Interaction in Leishmaniasis: Immune Response and Vaccination Strategies. Immuno 2022, 2, 218–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.M.; Lockwood, D.N. Treatment of Visceral Leishmaniasis. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2010, 2, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, M.C.; Horn, D.; Fairlamb, A.H.; Ferguson, M.A.J.; Gray, D.W.; Read, K.D.; De Rycker, M.; Torrie, L.S.; Wyatt, P.G.; Wyllie, S.; et al. Anti-Trypanosomatid Drug Discovery: An Ongoing Challenge and a Continuing Need. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.S.; de Araújo, R.V.; Giarolla, J.; Seoud, O.E.; Ferreira, E.I. Searching for Drugs for Chagas Disease, Leishmaniasis and Schistosomiasis: A Review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, S.; Singh, P.K.; Silakari, O. An Update on Small Molecule Strategies Targeting Leishmaniasis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 339–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhameliya, T.M.; Chudasma, S.J.; Patel, T.M.; Dave, B.P. A Review on Synthetic Account of 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles as Anti-Infective Agents. Mol. Divers. 2022, 26, 2967–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.; Verma, A.; Mishra, P. Significance of Nitrogen Heterocyclic Nuclei in the Search of Pharmacological Active Compounds. In New Perspective in Agricultural and Human Health; Bharti Publishers: Delhi, India, 2017; pp. 100–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraja, O.; Bodke, Y.D.; Pushpavathi, I.; Ravi Kumar, S. Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Investigations of Potentially Bioactive Heterocyclic Compounds Containing 4-Hydroxy Coumarin. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbuceanu, S.-F.; Rosca, E.-V.; Apostol, T.-V.; Socea, L.-I.; Draghici, C.; Farcasanu, I.C.; Ruta, L.L.; Nitulescu, G.M.; Iscrulescu, L.; Pahontu, E.-M.; et al. New Heterocyclic Compounds from Oxazol-5(4H)-One and 1,2,4-Triazin-6(5H)-One Classes: Synthesis, Characterization and Toxicity Evaluation. Molecules 2023, 28, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biological Activity of Oxadiazole and Thiadiazole Derivatives|Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00253-022-11969-0 (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Biernacki, K.; Daśko, M.; Ciupak, O.; Kubiński, K.; Rachon, J.; Demkowicz, S. Novel 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives in Drug Discovery. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Li, Y.; Irace, C.; Mollo, E.; Castelluccio, F.; Di Pascale, A.; Cimino, G.; Santamaria, R.; Guo, Y.-W.; Gavagnin, M. Structure and Cytotoxicity of Phidianidines A and B: First Finding of 1,2,4-Oxadiazole System in a Marine Natural Product. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2516–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Boulos, J.C.; Omer, E.A.; Klauck, S.M.; Efferth, T. Modes of Action of a Novel C-MYC Inhibiting 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivative in Leukemia and Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaram Upare, A.; Gadekar, P.K.; Sivaramakrishnan, H.; Naik, N.; Khedkar, V.M.; Sarkar, D.; Choudhari, A.; Mohana Roopan, S. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of (E)-5-Styryl-1,2,4-Oxadiazoles as Anti-Tubercular Agents. Bioorgan. Chem. 2019, 86, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, V.N.M.; do Amaral Moura, C.F.; dos Santos Peixoto, A.; Ferreira, V.P.G.; Araújo, H.M.; Pimentel, L.M.L.M.; do Ó Pessoa, C.; Nicolete, R.; Dos Anjos, J.V.; Sharma, P.P.; et al. Synthesis of Alkynylated 1,2,4-Oxadiazole/1,2,3-1H-Triazole Glycoconjugates: Discovering New Compounds for Use in Chemotherapy against Lung Carcinoma and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 220, 113472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.F.A.; Marzouk, A.A.; Nafady, A.; El-Gamal, D.A.; Allam, R.M.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.-D.A.; El Subbagh, H.I.; Moustafa, A.H. Design, Synthesis and Molecular Modeling of Novel Aryl Carboximidamides and 3-Aryl-1,2,4-Oxadiazoles Derived from Indomethacin as Potent Anti-Inflammatory iNOS/PGE2 Inhibitors. Bioorgan. Chem. 2020, 105, 104439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, P.H.; Timaniya, J.B.; Patel, M.J.; Patel, K.P. Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of Novel Substituted 1,2,4-Oxadiazole and Their Biological Broadcast. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, D.M.; Capers, J.; Salem, M.M.; DeLuca-Fradley, K.; Croft, S.L.; Werbovetz, K.A. Antikinetoplastid Activity of 3-Aryl-5-Thiocyanatomethyl-1,2,4-Oxadiazoles. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 2815–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.S.; Santos, H.; Lima, S.R.; Conti, C.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Zeoly, L.A.; Ferreira, L.L.G.; Krogh, R.; Andricopulo, A.D.; Coelho, F. Discovery of Highly Potent and Selective Antiparasitic New Oxadiazole and Hydroxy-Oxindole Small Molecule Hybrids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 201, 112418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Ge, S.; Shi, Y.; Fang, Y.; Ling, Y. Design, Synthesis, and Bioactivities of Novel Oxadiazole-Substituted Pyrazole Oximes. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meher, D.K.; Nayak, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Pathak, M. Synthesis, Evaluation & Pharmacological Action of Oxadiazole Derivatives. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2020, 9, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, C.V.G.; da Silva, W.M.B.; Rodrigues, J.P.V.; Rocha, Y.M.; Teixeira, M.J.; de Oliveira, R.N.; de Souza, N.V.; Nicolete, R. Anti-Leishmania infantum in Vitro Effect of n-Cyclohexyl-1,2,4-Oxadiazole and Its ADME/TOX Parameters. J. Parasit. Dis. 2022, 46, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, V.N.M.; dos Santos, F.G.; Ferreira, V.P.G.; Araújo, H.M.; do Ó Pessoa, C.; Nicolete, R.; de Oliveira, R.N. Focused Microwave Irradiation-Assisted Synthesis of N-Cyclohexyl-1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives with Antitumor Activity. Synth. Commun. 2018, 48, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, A.; Buscemi, S.; Piccionello, A.P.; Pibiri, I. Recent Advances in the Chemistry of 1,2,4-Oxadiazolesa. In Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Scriven, E.F.V., Ramsden, C.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 116, pp. 85–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mezeiova, E.; Janockova, J.; Andrys, R.; Soukup, O.; Kobrlova, T.; Muckova, L.; Pejchal, J.; Simunkova, M.; Handl, J.; Micankova, P.; et al. 2-Propargylamino-Naphthoquinone Derivatives as Multipotent Agents for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 211, 113112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsenko, K.; Hagenow, S.; Affini, A.; Reiner, D.; Stark, H. Rasagiline Derivatives Combined with Histamine H3 Receptor Properties. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 126612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoso, K.T.; Menorca, A.; Cheung, C.-Y.; Cook, G.M.; Stocker, B.L.; Timmer, M.S.M. The Synthesis and Evaluation of Quinolinequinones as Anti-Mycobacterial Agents. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3532–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, R.M.; Pérez-Pertejo, Y.; Gutiérrez-Corbo, C.; Domínguez-Asenjo, B.; Ordóñez, C.; García-Estrada, C.; Martínez-Valladares, M.; Balaña-Fouce, R. Current and Promising Novel Drug Candidates against Visceral Leishmaniasis. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 1385–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyoto, T.; Potet, J.; Boelaert, M. Why Miltefosine—A Life-Saving Drug for Leishmaniasis—Is Unavailable to People Who Need It the Most. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e000709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnielli, J.B.T.; Monti-Rocha, R.; Costa, D.L.; Molina Sesana, A.; Pansini, L.N.N.; Segatto, M.; Mottram, J.C.; Costa, C.H.N.; Carvalho, S.F.G.; Dietze, R. Natural Resistance of Leishmania infantum to Miltefosine Contributes to the Low Efficacy in the Treatment of Visceral Leishmaniasis in Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 101, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temraz, M.G.; Elzahhar, P.A.; El-Din, A.; Bekhit, A.; Bekhit, A.A.; Labib, H.F.; Belal, A.S.F. Anti-Leishmanial Click Modifiable Thiosemicarbazones: Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and in Silico Studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.-Y.; He, J.-H.; Lu, A.-P.; Hou, T.-J.; Cao, D.-S. Application of Negative Design To Design a More Desirable Virtual Screening Library. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 4411–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante-Costa, V.S.; Queiroz-Oliveira, T.; Horta, M.F.; Castro-Gomes, T. Leishmania and Their Vertebrate Host Cells. In Lifecycles of Pathogenic Protists in Humans; de Souza, W., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 143–165. ISBN 978-3-030-80682-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan, C.; Donhauser, N.; Döring, R.; Röllinghoff, M.; Diefenbach, A.; Rittig, M.G. Fibroblasts as Host Cells in Latent Leishmaniosis. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valigurová, A.; Kolářová, I. Unrevealing Mystery Latent Leishmaniasis: What Cells Can Host Leishmania? Pathogens 2023, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsadze, S.Z.; Loginova, Y.D.; dos Passos Gomes, G.; Alabugin, I.V. Stereoelectronic Chameleons: The Donor–Acceptor Dichotomy of Functional Groups. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 3225–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderer, T.; McConville, M.J. The Leishmania–Macrophage Interaction: A Metabolic Perspective. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Cuca, L.E.; Delgado, G. Antileishmanial and Immunomodulatory Activity of Xylopia Discreta. Parasite Immunol. 2009, 31, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machín, L.; Nápoles, R.; Gille, L.; Monzote, L. Leishmania amazonensis Response to Artemisinin and Derivatives. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 80, 102218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrence, L.M.; Gajula, A.; Jones, M.A. Surprising Effects of Rocking Motion on Leishmania tarentolae Behavior in Culture and Implications for Cell Stress. Stresses 2023, 3, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovannisci, D.M.; Paul Plested, C.; Moe, G.R. Evidence for Rosettes as an Unrecognized Stage in the Life Cycle of Leishmania Parasites. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2010, 57, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes Rodrigues, J.C.; Souza, W. de Ultrastructural Alterations in Organelles of Parasitic Protozoa Induced by Different Classes of Metabolic Inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, F.D.; Sanchez, M.A.; Landfear, S.M. Touching the Surface: Diverse Roles for the Flagellar Membrane in Kinetoplastid Parasites. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, e00079-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, F.D.; Yates, P.A.; Landfear, S.M. Nutrient Sensing in Leishmania: Flagellum and Cytosol. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 115, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagger, F.; Valdivieso, E.; Marcano, A.K.; Ayesta, C. Regulatory Volume Decrease in Leishmania mexicana: Effect of Anti-Microtubule Drugs. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oliveira, S.S.C.; Marques, C.S.F.; de Sousa, D.P.; Andrade, L.N.; Fricks, A.T.; Jain, S.; Branquinha, M.H.; Souto, E.B.; Santos, A.L.S.; Severino, P. Analysis of the Mechanisms of Action of Isopentenyl Caffeate against Leishmania. Biochimie 2021, 189, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antinarelli, L.M.R.; Midlej, V.; da Silva, E.D.S.; Coelho, E.A.F.; da Silva, A.D.; Coimbra, E.S. Exploring the Repositioning of the Amodiaquine as Potential Drug against Visceral Leishmaniasis: The in Vitro Effect against Leishmania infantum Is Associated with Multiple Mechanisms, Involving Mitochondria Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress and Loss of Cell Cycle Control. Chem.—Biol. Interact. 2023, 371, 110333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkov, S.M. Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Is the General Reason for Apoptosis Induced by Different-Valence Heavy Metals in Cells and Mitochondria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, E.S.; de Jesus, J.A.; Bezerra-Souza, A.; Brito, J.R.; Lago, J.H.G.; Laurenti, M.D.; Passero, L.F.D. Tolnaftate Inhibits Ergosterol Production and Impacts Cell Viability of Leishmania sp. Bioorgan. Chem. 2020, 102, 104056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Silva Nunes, D.C.; Costa, M.S.; Bispo-da-Silva, L.B.; Ferro, E.A.V.; Zóia, M.A.P.; Goulart, L.R.; Rodrigues, R.S.; de Melo Rodrigues, V.; Yoneyama, K.A.G. Mitochondrial Dysfunction on Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis Induced by Ketoconazole: Insights into Drug Mode of Action. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2022, 117, e210157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.; Roy, P.K.; Babu, N.K.; Singh, S. Clotrimazole Causes Membrane Depolarization and Induces Sub G0 Cell Cycle Arrest in Leishmania donovani. Acta Trop. 2024, 252, 107139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Macedo-Silva, S.T.; Visbal, G.; Souza, G.F.; dos Santos, M.R.; Cämmerer, S.B.; de Souza, W.; Rodrigues, J.C.F. Benzylamines as Highly Potent Inhibitors of the Sterol Biosynthesis Pathway in Leishmania amazonensis Leading to Oxidative Stress and Ultrastructural Alterations. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duszenko, M.; Ginger, M.L.; Brennand, A.; Gualdrón-López, M.; Colombo, M.I.; Coombs, G.H.; Coppens, I.; Jayabalasingham, B.; Langsley, G.; Lisboa de Castro, S.; et al. Autophagy in Protists. Autophagy 2011, 7, 127–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, P.S.; Akematsu, T.; Besteiro, S.; Bindschedler, A.; Carruthers, V.B.; Chahine, Z.; Coppens, I.; Descoteaux, A.; Lopes Alberto Duque, T.; He, C.Y.; et al. Autophagy in Protists and Their Hosts: When, How and Why? Autophagy Rep. 2023, 2, 2149211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedra-Rezende, Y.; Macedo, I.S.; Midlej, V.; Mariante, R.M.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S. Different Drugs, Same End: Ultrastructural Hallmarks of Autophagy in Pathogenic Protozoa. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 856686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandes, J.M.; de Figueiredo, R.C.B.Q. The Endoplasmic Reticulum of Trypanosomatids: An Unrevealed Road for Chemotherapy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1057774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.d.A.; Gomes, P.S.; Midlej, V.; Coimbra, E.S.; de Matos Guedes, H.L. PF-429242, a Subtilisin Inhibitor, Is Effective in Vitro Against Leishmania infantum. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 583834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna-Barreto, R.F.S. Cell Death Pathways in Pathogenic Trypanosomatids: Lessons of (over)Kill. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamotte, S.; Späth, G.F.; Rachidi, N.; Prina, E. The Enemy within: Targeting Host–Parasite Interaction for Antileishmanial Drug Discovery. PLoS Neglect. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, B.; Madhubala, R. Drug Targets in Leishmania. J. Parasit. Dis. 2010, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Hortelano, I.; Alcolea, V.; Font, M.; Pérez-Silanes, S. Examination of Multiple Trypanosoma cruzi Targets in a New Drug Discovery Approach for Chagas Disease. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2022, 58, 116577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Basu, S.; Feng, M.; Ning, Y.; Munasinghe, I.; Joachim, A.M.; Li, J.; Madden, R.; Burks, H.; Gao, P.; et al. CYP5122A1 Encodes an Essential Sterol C4-Methyl Oxidase in Leishmania donovani and Determines the Antileishmanial Activity of Antifungal Azoles. Res. Sq. 2023, 1, rs.3.rs-3185204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto Pinheiro, M.; da Silva Emery, F.; Cristina Nonato, M. Target Sites for the Design of Anti-Trypanosomatid Drugs Based on the Structure of Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 2615–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, T.; Colotti, G.; Ilari, A.; Fiorillo, A. Targeting Trypanothione Reductase, a Key Enzyme in the Redox Trypanosomatid Metabolism, to Develop New Drugs against Leishmaniasis and Trypanosomiases. Molecules 2020, 25, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, S.; Saudagar, P. Knockout of Tyrosine Aminotransferase Gene by Homologous Recombination Arrests Growth and Disrupts Redox Homeostasis in Leishmania Parasite. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 3229–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panecka-Hofman, J.; Poehner, I. Structure and Dynamics of Pteridine Reductase 1: The Key Phenomena Relevant to Enzyme Function and Drug Design. Eur. Biophys. J. 2023, 52, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourbeli, V.; Chontzopoulou, E.; Moschovou, K.; Pavlos, D.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Papanastasiou, I.P. An Overview on Target-Based Drug Design against Kinetoplastid Protozoan Infections: Human African Trypanosomiasis, Chagas Disease and Leishmaniases. Molecules 2021, 26, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, E.J.F.; Padilha, I.Q.M.; Araújo, D.A.M.; Rocha, G.B. Determining the Relative Binding Affinity of Ricin Toxin A Inhibitors by Using Molecular Docking and Nonequilibrium Work. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guterres, H.; Im, W. Improving Protein-Ligand Docking Results with High-Throughput Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, S.F.L.S.; Sant’Anna, C.M.R. A Procedure Combining Molecular Docking and Semiempirical Method PM7 for Identification of Selective Shp2 Inhibitors. Biopolymers 2019, 110, e23320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryde, U.; Söderhjelm, P. Ligand-Binding Affinity Estimates Supported by Quantum-Mechanical Methods. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5520–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepesheva, G.I.; Friggeri, L.; Waterman, M.R. CYP51 as Drug Targets for Fungi and Protozoan Parasites: Past, Present and Future. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1820–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepesheva, G.I.; Villalta, F.; Waterman, M.R. Targeting Trypanosoma cruzi Sterol 14α-Demethylase (CYP51). In Advances in Parasitology; Weiss, L.M., Tanowitz, H.B., Kirchhoff, L.V., Eds.; Chagas Disease, Part A; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 75, pp. 65–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoldo, F.R.P.; Carta, F.; Angeli, A.; Cardoso, V.d.S.; Supuran, C.T.; Vermelho, A.B. Chagas Disease: Perspectives on the Past and Present and Challenges in Drug Discovery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalta, F.; Dobish, M.C.; Nde, P.N.; Kleshchenko, Y.Y.; Hargrove, T.Y.; Johnson, C.A.; Waterman, M.R.; Johnston, J.N.; Lepesheva, G.I. VNI Cures Acute and Chronic Experimental Chagas Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes-da-Silva, F.H.; Batista, D.d.G.J.; Da Silva, C.F.; Pavão, B.P.; Batista, M.M.; Moreira, O.C.; Souza, L.R.Q.; Britto, C.; Rachakonda, G.; Villalta, F.; et al. Successful Aspects of the Coadministration of Sterol 14α-Demethylase Inhibitor VFV and Benznidazole in Experimental Mouse Models of Chagas Disease Caused by the Drug-Resistant Strain of Trypanosoma cruzi. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ispikoudi, M.; Amvrazis, M.; Kontogiorgis, C.; Koumbis, A.E.; Litinas, K.E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Fylaktakidou, K.C. Convenient Synthesis and Biological Profile of 5-Amino-Substituted 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5635–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais-Teixeira, E.; de Carvalho, A.S.; da Costa, J.C.; Duarte, S.L.; Mendonça, J.S.; Boechat, N.; Rabello, A. In Vitro and in Vivo Activity of Meglumine Antimoniate Produced at Farmanguinhos-Fiocruz, Brazil, against Leishmania (Leishmania) Amazonensis, L (L.) Chagasi and L (Viannia) Braziliensis. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2008, 103, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, F.C.M.; Bevilaqua, C.M.L.; Accioly, M.P.; de Morais, S.M.; de Andrade-Júnior, H.F.; de Carvalho, C.A.; Lima, J.C.; Magalhães, H.C.R. In Vitro Efficacy of Coriandrum Sativum, Lippia Sidoides and Copaifera Reticulata against Leishmania chagasi. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2012, 21, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, V.N.; da Silva, W.V.; do Nascimento, P.H.; Silva, S.R.B.; Cabral Filho, P.E.; Assis, S.P.d.O.; da Silva, C.A.; de Oliveira, R.N.; de Figueiredo, R.C.B.Q.; Lima, V.L.d.M. Antileishmanial Activity of 4-Phenyl-1-[2-(Phthalimido-2-Yl)Ethyl]-1H-1,2,3-Triazole (PT4) Derivative on Leishmania amazonensis and Leishmania braziliensis: In Silico ADMET, in Vitro Activity, Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations. Bioorgan. Chem. 2020, 105, 104437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrove, T.Y.; Wawrzak, Z.; Liu, J.; Nes, W.D.; Waterman, M.R.; Lepesheva, G.I. Substrate Preferences and Catalytic Parameters Determined by Structural Characteristics of Sterol 14α-Demethylase (CYP51) from Leishmania infantum. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26838–26848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.A.; Abramov, A.; Abendroth, J.; Alonso, A.; Zhang, S.; Alcolea, P.J.; Edwards, T.; Lorimer, D.; Myler, P.J.; Larraga, V. Structure of Tyrosine Aminotransferase from Leishmania infantum. Acta Crystall. Sect. F 2014, 70, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilari, A.; Baiocco, P.; Messori, L.; Fiorillo, A.; Boffi, A.; Gramiccia, M.; Di Muccio, T.; Colotti, G. A Gold-Containing Drug against Parasitic Polyamine Metabolism: The X-Ray Structure of Trypanothione Reductase from Leishmania infantum in Complex with Auranofin Reveals a Dual Mechanism of Enzyme Inhibition. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandakrishnan, R.; Aguilar, B.; Onufriev, A.V. H++ 3.0: Automating pK Prediction and the Preparation of Biomolecular Structures for Atomistic Molecular Modeling and Simulations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W537–W541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Hardy, D.J.; Maia, J.D.C.; Stone, J.E.; Ribeiro, J.V.; Bernardi, R.C.; Buch, R.; Fiorin, G.; Hénin, J.; Jiang, W.; et al. Scalable Molecular Dynamics on CPU and GPU Architectures with NAMD. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 044130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and Validation of a Genetic Algorithm for Flexible Docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Belfon, K.A.A.; Raguette, L.; Huang, H.; Migues, A.N.; Bickel, J.; Wang, Y.; Pincay, J.; Wu, Q.; et al. ff19SB: Amino-Acid-Specific Protein Backbone Parameters Trained against Quantum Mechanics Energy Surfaces in Solution. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2020, 16, 528–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassetti, D.; Pagliai, M.; Procacci, P. Assessment of GAFF2 and OPLS-AA General Force Fields in Combination with the Water Models TIP3P, SPCE, and OPC3 for the Solvation Free Energy of Druglike Organic Molecules. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E.I. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for Processing and Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectory Data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Schaeffer, R.D.; et al. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Lipinski Rules | MW (≤500) g/mol | HBA (≤10) | HBD (≤5) | LogP (≤5) | n-ROTB (≤10) | TPSA (≤140 A2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ox1 | Yes | 273.33 | 4 | 1 | 3.10 | 4 | 60.18 |
| Ox2 | Yes | 288.30 | 5 | 1 | 2.64 | 4 | 96.77 |
| Ox3 | Yes | 288.30 | 5 | 1 | 2.73 | 4 | 96.77 |
| Ox4 | Yes | 257.33 | 3 | 1 | 3.32 | 3 | 50.95 |
| Ox5 | Yes | 267.33 | 3 | 0 | 3.57 | 3 | 42.16 |
| Ox6 | Yes | 326.35 | 5 | 0 | 3.26 | 5 | 87.98 |
| Ox7 | Yes | 326.35 | 5 | 0 | 3.28 | 5 | 87.98 |
| Miltefosine | Yes | 407.57 | 4 | 0 | 3.35 | 20 | 68.40 |
| Compound | Mammalian Cell Type | Pro | SI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC50 (µM) | IC50 (µM) | Pro/L929 | Pro/J774.G8 | ||
| L929 | J774.G8 | ||||
| Ox1 | 320 ± 4.7 | 293.1 ± 5.5 | 32.9 ± 2.2 | 9.7 | 8.9 |
| Ox2 | 364 ± 6.1 | 285.4 ± 7.0 | 220 ± 3.6 | 1.7 | 1.2 |
| Ox3 | 356 ± 6.2 | >200 | 336 ± 12.1 | 1.1 | n.d. |
| Ox4 | 290 ± 10.0 | >200 | 174.4 ± 12.3 | 1.7 | n.d. |
| Ox5 | 375 ± 15.3 | 160 ± 6.5 | 84.7 ± 3.6 | 4.4 | 1.8 |
| Ox6 | 338 ± 31.1 | 231 ± 8.1 | 92.2 ± 1.9 | 3.7 | 2.5 |
| Ox7 | >200 | 197 ± 6.0 | 98.2 ± 1.4 | n.d. | 2.0 |
| Receptor | Docking Score | ΔGbind (MM/GBSA) | ΔHbind (PM7) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CYP51 | 36.43 (a), 39.77 (b) (1) | −42.686 ± 0.636 (1) | −50.060 ± 0.875 (1) |
| TAT | 27.30 (2) | −14.663 ± 0.593 (4) | −18.702 ± 0.885 (4) |
| PTR1 | 26.17 (3) | −37.946 ± 0.822 (2) | −40.471 ± 1.076 (2) |
| TR | 20.40 (4) | −25.632 ± 0.811 (3) | −25.588 ± 0.765 (3) |
| DHODH | −9.59 (5) | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbosa, D.C.S.; Holanda, V.N.; Lima, E.M.A.; Cavalcante, M.K.A.; Brelaz-de-Castro, M.C.A.; Chaves, E.J.F.; Rocha, G.B.; Silva, C.J.O.; Oliveira, R.N.; Figueiredo, R.C.B.Q. 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives: Physicochemical Properties, Antileishmanial Potential, Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations of Leishmania infantum Target Proteins. Molecules 2024, 29, 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194654
Barbosa DCS, Holanda VN, Lima EMA, Cavalcante MKA, Brelaz-de-Castro MCA, Chaves EJF, Rocha GB, Silva CJO, Oliveira RN, Figueiredo RCBQ. 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives: Physicochemical Properties, Antileishmanial Potential, Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations of Leishmania infantum Target Proteins. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194654
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbosa, Deyzi C. S., Vanderlan N. Holanda, Elton M. A. Lima, Marton K. A. Cavalcante, Maria Carolina A. Brelaz-de-Castro, Elton J. F. Chaves, Gerd B. Rocha, Carla J. O. Silva, Ronaldo N. Oliveira, and Regina C. B. Q. Figueiredo. 2024. "1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives: Physicochemical Properties, Antileishmanial Potential, Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations of Leishmania infantum Target Proteins" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194654
APA StyleBarbosa, D. C. S., Holanda, V. N., Lima, E. M. A., Cavalcante, M. K. A., Brelaz-de-Castro, M. C. A., Chaves, E. J. F., Rocha, G. B., Silva, C. J. O., Oliveira, R. N., & Figueiredo, R. C. B. Q. (2024). 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives: Physicochemical Properties, Antileishmanial Potential, Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations of Leishmania infantum Target Proteins. Molecules, 29(19), 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194654









