Engineering of Green Carbon Dots for Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of Green CDs
2.1. Hydrothermal Treatment
2.2. Microwave Irradiation
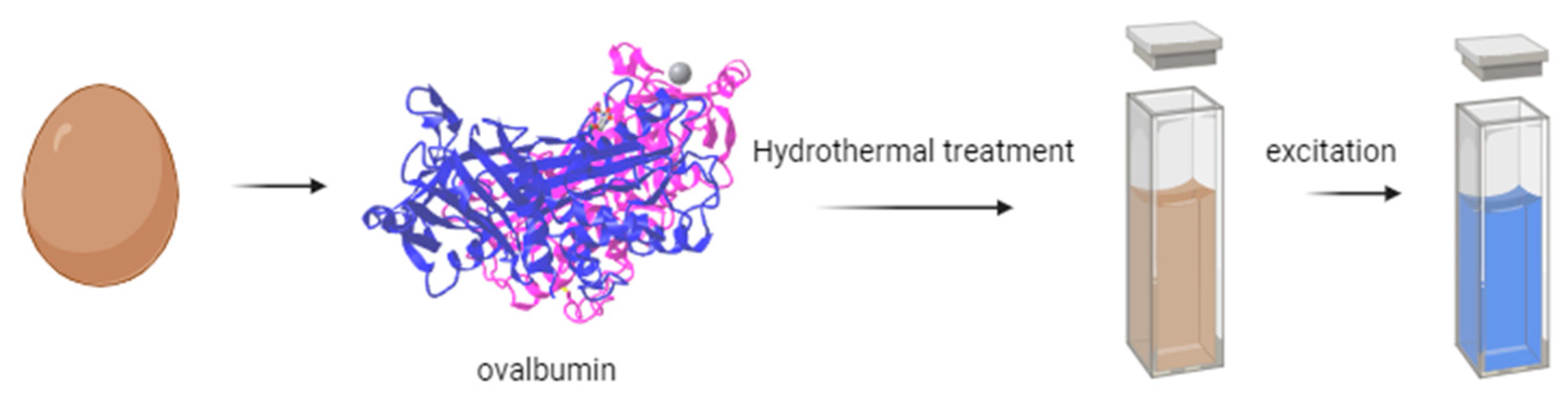
2.3. Heating
2.4. Extraction
2.5. Other Methods
3. Optical Properties
3.1. Absorbance
3.2. Photoluminescence
3.3. Up-Conversion Fluorescence
4. Bio-Applications
4.1. Bioimaging
4.2. Biosensing
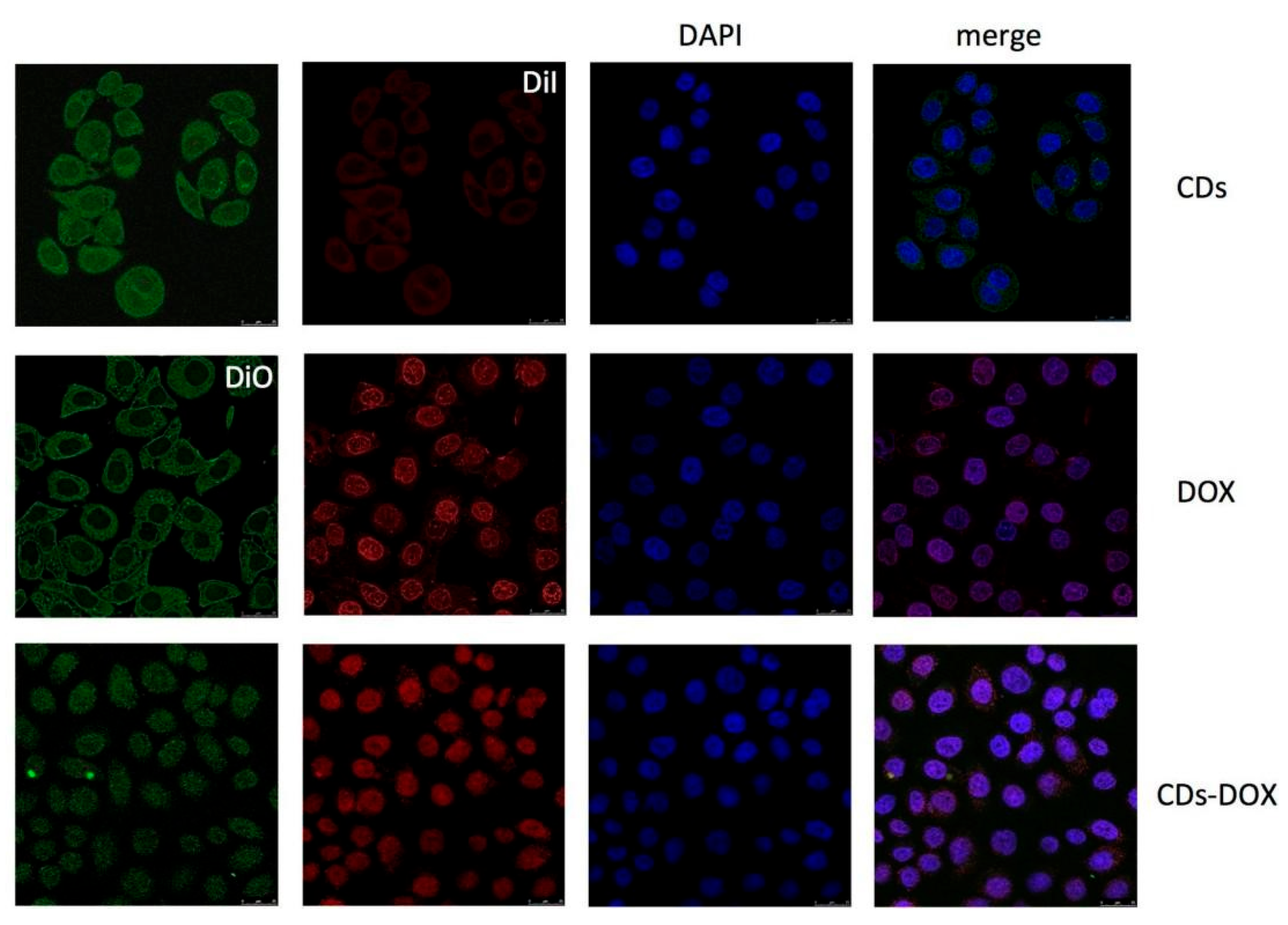
4.3. Drug/Gene Delivery
4.4. Antimicrobial and Antiviral Effects
4.5. Formatting of Mathematical Components
4.6. Cancer Diagnosis
4.7. Pharmaceutical Formulations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ackermann, J.; Metternich, J.T.; Herbertz, S.; Kruss, S. Biosensing with Fluorescent Carbon Nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Kollie, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, W.; Ying, X.; Zhu, J.; Yang, S.; Yu, M. Antitumor Activity and Potential Mechanism of Novel Fullerene Derivative Nanoparticles. Molecules 2021, 26, 3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimaneepong, V.; Skallevold, H.E.; Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S.; Rokaya, D.; Sapkota, J. Graphene for Antimicrobial and Coating Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barati, F.; Avatefi, M.; Moghadam, N.B.; Asghari, S.; Ekrami, E.; Mahmoudifard, M. A review of graphene quantum dots and their potential biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 37, 1137–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajith, M.P.; Pardhiya, S.; Rajamani, P. Carbon Dots: An Excellent Fluorescent Probe for Contaminant Sensing and Remediation. Small 2022, 18, 2105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Lanceta, A.; Medrano-Bosch, M.; Melgar-Lesmes, P. Single-Walled Carbon Nanohorns as Promising Nanotube-Derived Delivery Systems to Treat Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, H.; Bincoletto, V.; Arpicco, S.; Giordani, S. Supramolecular Functionalisation of B/N Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions for Novel Nanocarrier Systems. Materials 2022, 15, 5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Macairan, J.-R.; Yousefi, N.; Tufenkji, N.; Naccache, R. Green synthesis of carbon dots and their applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25354–25363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, Ł.; Piątkowski, M.; Radwan-Pragłowska, J.; Bogdał, D.; Matysek, D. Chitosan-Based Carbon Quantum Dots for Biomedical Applications: Synthesis and Characterization. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Bardakci, F.; Akgöl, S.; Kusat, K.; Adnan, M.; Alam, M.; Gupta, R.; Sahreen, S.; Chen, Y.; Gopinath, S.; et al. Green Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties and Biomedical Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, A.; Bibi, N.; Hyder, S.; Muhammad, A.; Ren, H.; Liu, J.; Lei, Z. Recent advances in green carbon dots (2015–2022): Synthesis, metal ion sensing, and biological applications. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 1068–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintz, K.J.; Zhou, Y.; Leblanc, R.M. Recent development of carbon quantum dots regarding their optical properties, photoluminescence mechanism, and core structure. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4634–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, D.K.; Praveenkumar, V.; Si, S.; Panigrahi, H.; Mishra, S. Carbon Dots and Their Polymeric Nanocomposites: Insight into Their Synthesis, Photoluminescence Mechanisms, and Recent Trends in Sensing Applications. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 11050–11080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, C.; Li, G.; Lu, M.; Han, J.; Cao, S.; Chen, L.; et al. Green synthesis of chlorella-derived carbon dots and their fluorescence imaging in zebrafish. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Qureshi, A.; Azhar, M.; Hassan, Z.U.; Gul, S.; Ahmad, S. Recent Progress of Fluorescent Carbon Dots and Graphene Quantum Dots for Biosensors: Synthesis of Solution Methods and their Medical Applications. J. Fluoresc. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, A.; Hoffman, J.; Morgiel, J.; Mościcki, T.; Stobiński, L.; Szymański, Z.; Małolepszy, A. Luminescent Carbon Dots Synthesized by the Laser Ablation of Graphite in Polyethylenimine and Ethylenediamine. Materials 2021, 14, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutroneo, M.; Silipigni, L.; Malinsky, P.; Slepicka, P.; Franco, D.; Torrisi, L. Polyvinylalcohol Composite Filled with Carbon Dots Produced by Laser Ablation in Liquids. Polymers 2024, 16, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Song, Y.; Heller, M.J. Seamless aqueous arc discharge process for producing graphitic carbon nanostructures. Carbon 2017, 120, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Wu, H.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J. Photo-Fenton Reaction of Graphene Oxide: A New Strategy to Prepare Graphene Quantum Dots for DNA Cleavage. ACS NANO 2012, 6, 6592–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Dou, Y.; Yang, H.; Xing, H.; Zhu, C.; Wang, T.; Xuan, Z.; Yang, M. Ce6-modified Fe ions-doped carbon dots as multifunctional nanoplatform for ferroptosis and photodynamic synergistic therapy of melanoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.-A.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Dai, T.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Q. Commercially activated carbon as the source for producing multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots by chemical oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, G.; Belal, F.; Elmansi, H. Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as fluorescent nanosensors for the spectrofluorimetric determination of palbociclib: Application for cellular imaging and selective probing in living cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 4156–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monte-Filho, S.S.; Andrade, S.I.E.; Lima, M.B.; Araujo, M.C.U. Synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon dots from lemon and onion juices for determination of riboflavin in multivitamin/mineral supplements. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laddha, H.; Yadav, P.; Sharma, M.; Agarwal, M.; Gupta, R. Waste to value transformation: Converting Carica papaya seeds into green fluorescent carbon dots for simultaneous selective detection and degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride in water. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasa, S.K.; Ha, S.; Baek, S.H.; Phan, L.M.T.; Kim, S.; Kwak, K.; Park, T.J. Tuning of carbon dots emission color for sensing of Fe3+ ion and bioimaging applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 98, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liao, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H.; Tan, M. Fluorescent carbon dots from beer for breast cancer cell imaging and drug delivery. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 8911–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Cheng, S.; Tan, M. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots with antibacterial activity and their application in Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) storage. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liao, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X. Facile green and one-pot synthesis of purple perilla derived carbon quantum dot as a fluorescent sensor for silver ion. Talanta 2019, 201, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkal, A.; Allawadhi, P.; Pradhan, R.; Khurana, A.; Bharani, K.K.; Packirisamy, G. Allium sativum derived carbon dots as a potential theranostic agent to combat the COVID-19 crisis. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdev, A.; Gopinath, P. Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots from coriander leaves and their potential application as antioxidants, sensors and bioimaging agents. Analyst 2015, 140, 4260–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.K.; Choudhary, B.; Yadav, A.; Patidar, R.; Mishra, A.; Kulshrestha, V. Green-synthesized, pH-stable and biocompatible carbon nanosensor for Fe3+: An experimental and computational study. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Qin, D.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, X.; Deng, B. N-doped carbon quantum dots from osmanthus fragrans as a novel off-on fluorescent nanosensor for highly sensitive detection of quercetin and aluminium ion, and cell imaging. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Bao, L.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y. The Application of Green-Synthesis-Derived Carbon Quantum Dots to Bioimaging and the Analysis of Mercury(II). J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 8183134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Qi, N.; Li, K.; Cheng, D.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Green fluorescent nanomaterials for rapid detection of chromium and iron ions: Wool keratin-based carbon quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 8108–8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, G. Application and Research Status of Long-Wavelength Fluorescent Carbon Dots. Molecules 2023, 28, 7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Vincy, A.; Rani, K.; Jain, N.; Singh, S.; Agarwal, A.; Vankayala, R. Facile Synthesis of Multifunctional Carbon Dots Derived from Camel Milk for Mn7+ Sensing and Antiamyloid and Anticancer Activities. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 36521–36533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, P. An overview on animal/human biomass-derived carbon dots for optical sensing and bioimaging applications. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 35088–35126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lu, F.; Zhang, M.; Kong, H.; Cheng, J.; Luo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, H. The neuroprotective effect of pretreatment with carbon dots from Crinis Carbonisatus (carbonized human hair) against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.; Kasouni, A.; Sygellou, L.; Leonardos, I.; Troganis, A.; Stalikas, C. Human fingernails as an intriguing precursor for the synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur-doped carbon dots with strong fluorescent properties: Analytical and bioimaging applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 267, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essner, J.B.; Laber, C.H.; Ravula, S.; Polo-Parada, L.; Baker, G.A. Pee-dots: Biocompatible fluorescent carbon dots derived from the upcycling of urine. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Ding, Y.; Hua, J.; Tang, B.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Qin, K.; Li, B. Bacteria-derived fluorescent carbon dots for highly selective detection of p-nitrophenol and bioimaging. Analyst 2019, 144, 5497–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, K.; Zhang, D.; Ding, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xiang, Y.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, X.; Li, B.; Wei, Y. Applications of hydrothermal synthesis of Escherichia coli derived carbon dots in in vitro and in vivo imaging and p-nitrophenol detection. Analyst 2019, 145, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kousheh, S.A.; Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Molaei, R. Preparation of antimicrobial/ultraviolet protective bacterial nanocellulose film with carbon dots synthesized from lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, N.K.; Jana, G.C.; Aktara, M.N.; Das, S.; Nayim, S.; Patra, A.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Bhadra, K.; Hossain, M. Carbon dots derived from lychee waste: Application for Fe(3+) ions sensing in real water and multicolor cell imaging of skin melanoma cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 108, 110429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiyan, S.; Arumugam, L.; Srirengan, S.P.; Pitchan, R.; Sevugan, P.; Kannan, K.; Pitchan, G.; Hegde, T.A.; Gandhirajan, V. Biocompatible Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Sugarcane Industrial Wastes for Effective Nonlinear Optical Behavior and Antimicrobial Activity Applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30363–30372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, W.; Yang, D.S.; Yang, F. Soybean-derived blue photoluminescent carbon dots. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, M.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Synthesis, applications and biosafety evaluation of carbon dots derived from herbal medicine. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 18, 042004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatahi, Z.; Esfandiari, N.; Ehtesabi, H.; Bagheri, Z.; Tavana, H.; Ranjbar, Z.; Latifi, H. Physicochemical and cytotoxicity analysis of green synthesis carbon dots for cell imaging. EXCLI J. 2019, 18, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, K.; Wu, Y.; Li, D.; Song, Y.; Prakash, S.; Tan, M. Fluorescent nanoparticles in the popular pizza: Properties, biodistribution and cytotoxicity. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2408–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anpalagan, K.; Karakkat, J.V.; Jelinek, R.; Kadamannil, N.N.; Zhang, T.; Cole, I.; Nurgali, K.; Yin, H.; Lai, D.T.H. A Green Synthesis Route to Derive Carbon Quantum Dots for Bioimaging Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Cao, L.; Guo, H.; Dong, W.; Li, L. Green Synthesis of Phosphorescent Carbon Dots for Anticounterfeiting and Information Encryption. Sensors 2022, 22, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.; Li, L.; Jiang, C.; Mei, Q.; Dong, W.-F.; Yan, R. Riboflavin-based carbon dots with high singlet oxygen generation for photodynamic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7972–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Liang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Xia, K.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Sustainable Silk-Derived Multimode Carbon Dots. Small 2021, 17, 2103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolanowska, A.; Dzido, G.; Krzywiecki, M.; Tomczyk, M.M.; Łukowiec, D.; Ruczka, S.; Boncel, S. Carbon Quantum Dots from Amino Acids Revisited: Survey of Renewable Precursors toward High Quantum-Yield Blue and Green Fluorescence. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 41165–41176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Liu, Q.; Jin, X.; Ding, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, P.; Chen, S. Magnetic Carbon Quantum Dots/Iron Oxide Composite Based on Waste Rice Noodle and Iron Oxide Scale: Preparation and Photocatalytic Capability. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.-Y.; Ying, W.-Y.; Che, R.-J.; Xiao, P.; Zhou, Y.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.-Y.; Chen, S.-P. CQDs/ZnO composites based on waste rice noodles: Preparation and photocatalytic capability. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 23692–23703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Dong, P.; Huang, J. A Mini Review on Carbon Quantum Dots: Preparation, Properties, and Electrocatalytic Application. Front Chem. 2019, 7, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wen, Y.; Kang, X. Halogen-Doped Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Application, and Prospects. Molecules 2022, 27, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathap, N.; Balla, P.; Shivakumar, M.S.; Periyasami, G.; Karuppiah, P.; Ramasamy, K.; Venkatesan, S. Prosopis juliflora hydrothermal synthesis of high fluorescent carbon dots and its antibacterial and bioimaging applications. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholipour, A.; Rahmani, S. The Green Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots through One-step Hydrothermal Approach by Orange Juice for Rapid, and Accurate Detection of Dopamine. J. Fluoresc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.-M.; Park, B.-Y.; Ghouri, Z.K.; Park, M.; Kim, H.-Y. Synthesis of carbon quantum dots from cabbage with down- and up-conversion photoluminescence properties: Excellent imaging agent for biomedical applications. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3791–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Fu, X.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Z. Ovalbumin as a Precursor for Green Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Cell Imaging. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Ga, L.; Ai, J. A fluorescent biosensor based on carbon quantum dots and single-stranded DNA for the detection of Escherichia coli. Analyst 2023, 148, 3892–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghataty, D.S.; Amer, R.I.; Amer, M.A.; Abdel Rahman, M.F.; Shamma, R.N. Green Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Bovine Serum Albumin for Linezolid Drug Delivery as Potential Wound Healing Biomaterial: Bio-Synergistic Approach, Antibacterial Activity, and In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangmora, R.; Kemacheevakul, P.; Chuangchote, S. Fiberglass cloth coated by coffee ground waste-derived carbon quantum dots/titanium dioxide composite for removal of caffeine and other pharmaceuticals from water. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almufarij, R.S.; Mohamed, M.E. Green Synthesis of a Carbon Quantum Dots-Based Superhydrophobic Membrane for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. Materials 2023, 16, 5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
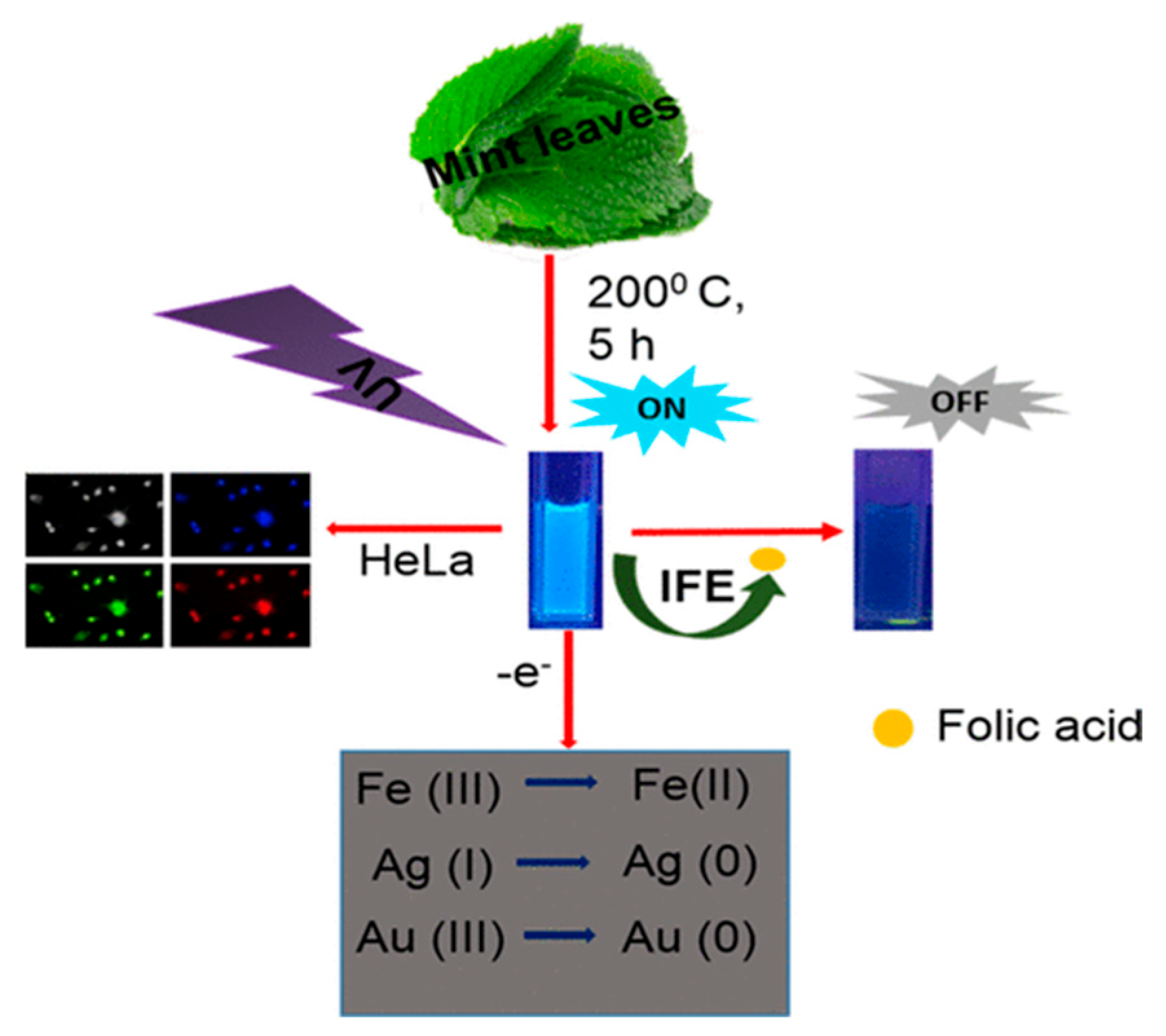
- Architha, N.; Ragupathi, M.; Shobana, C.; Selvankumar, T.; Kumar, P.; Lee, Y.S.; Kalai Selvan, R. Microwave-assisted green synthesis of fluorescent carbon quantum dots from Mexican Mint extract for Fe3+ detection and bio-imaging applications. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu Nu, T.T.; Thi Tran, N.H.; Truong, P.L.; Phan, B.T.; Nguyen Dinh, M.T.; Dinh, V.-P.; Phan, T.S.; Go, S.; Chang, M.; Loan Trinh, K.T.; et al. Green synthesis of microalgae-based carbon dots for decoration of TiO2 nanoparticles in enhancement of organic dye photodegradation. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkeumaleu, A.T.; Benetti, D.; Haddadou, I.; Di Mare, M.; Ouellet-Plamondon, C.M.; Rosei, F. Brewery spent grain derived carbon dots for metal sensing. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 11621–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Kumar, K.; Saini, P.; Mahawar, D.K.; Rathore, K.S.; Kumar, S.; Dandia, A.; Parewa, V. Sustainable synthesis of biomass-derived carbon quantum dots and their catalytic application for the assessment of α,β-unsaturated compounds. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 32619–32629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavika, J.P.; Shobana, C.; Ragupathi, M.; Kumar, P.; Lee, Y.S.; Govarthanan, M.; Selvan, R.K. A sustainable green synthesis of functionalized biocompatible carbon quantum dots from Aloe barbadensis Miller and its multifunctional applications. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Semary, M.S.; El-Emam, A.A.; Belal, F.; El-Masry, A.A. Microwave assisted synthesis of fluorescent hetero atom doped carbon dots for determination of betrixaban with greenness evaluation. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 11044–11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SalİM, F.S.; Sargin, İ.; Arslan, G. Carbon quantum dots and chitosan-based heterogeneous silver catalyst for reduction of nitroaromatic compounds. Turk. J. Chem. 2023, 47, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.S.; Singh, V.; Sharma, C.P.; Vyas, A.; Pandey, P.; Singh, J.; Gupta, N.M.; Sachdev, M.; Goel, A. Picomolar Detection of Lead Ions (Pb2+) by Functionally Modified Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots from Watermelon Juice and Their Imaging in Cancer Cells. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohamy, H.A.S.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Kamel, S. Eco-friendly Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots as an Effective Adsorbent. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 33, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
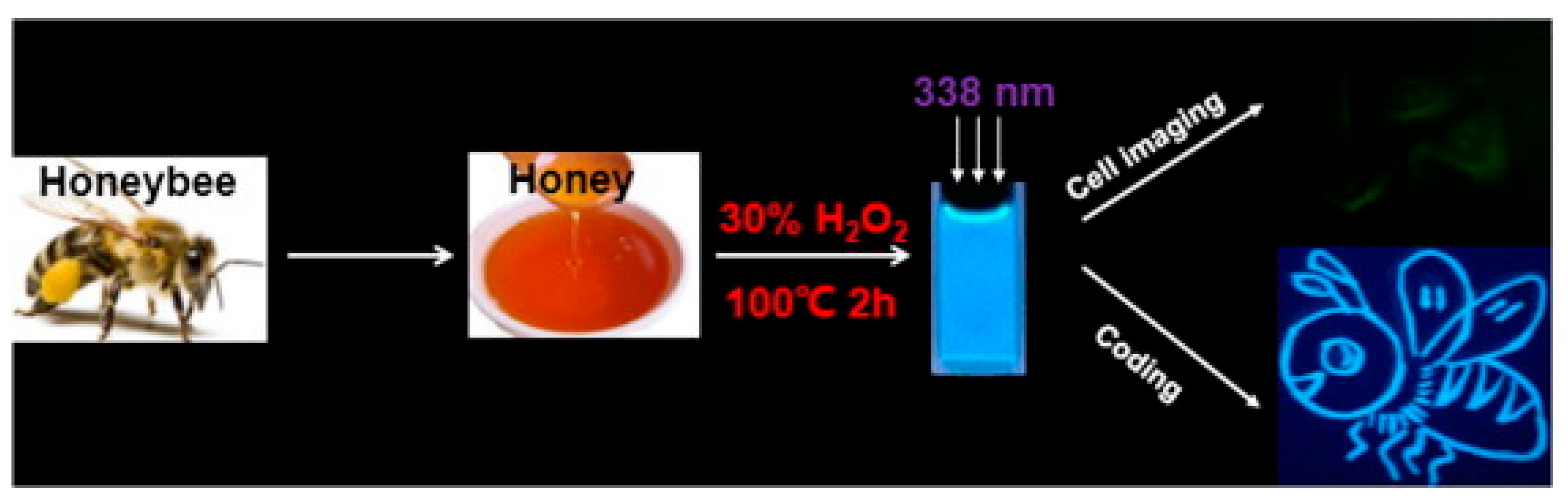
- Yang, X.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhu, S.; Luo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Dou, Y. Novel and green synthesis of high-fluorescent carbon dots originated from honey for sensing and imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, C.; Wang, H.; Cong, S.; Tan, M. Fluorescent nanoparticles present in Coca-Cola and Pepsi-Cola: Physiochemical properties, cytotoxicity, biodistribution and digestion studies. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, H.; Song, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Tan, M. Presence of photoluminescent carbon dots in Nescafe® original instant coffee: Applications to bioimaging. Talanta 2014, 127, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
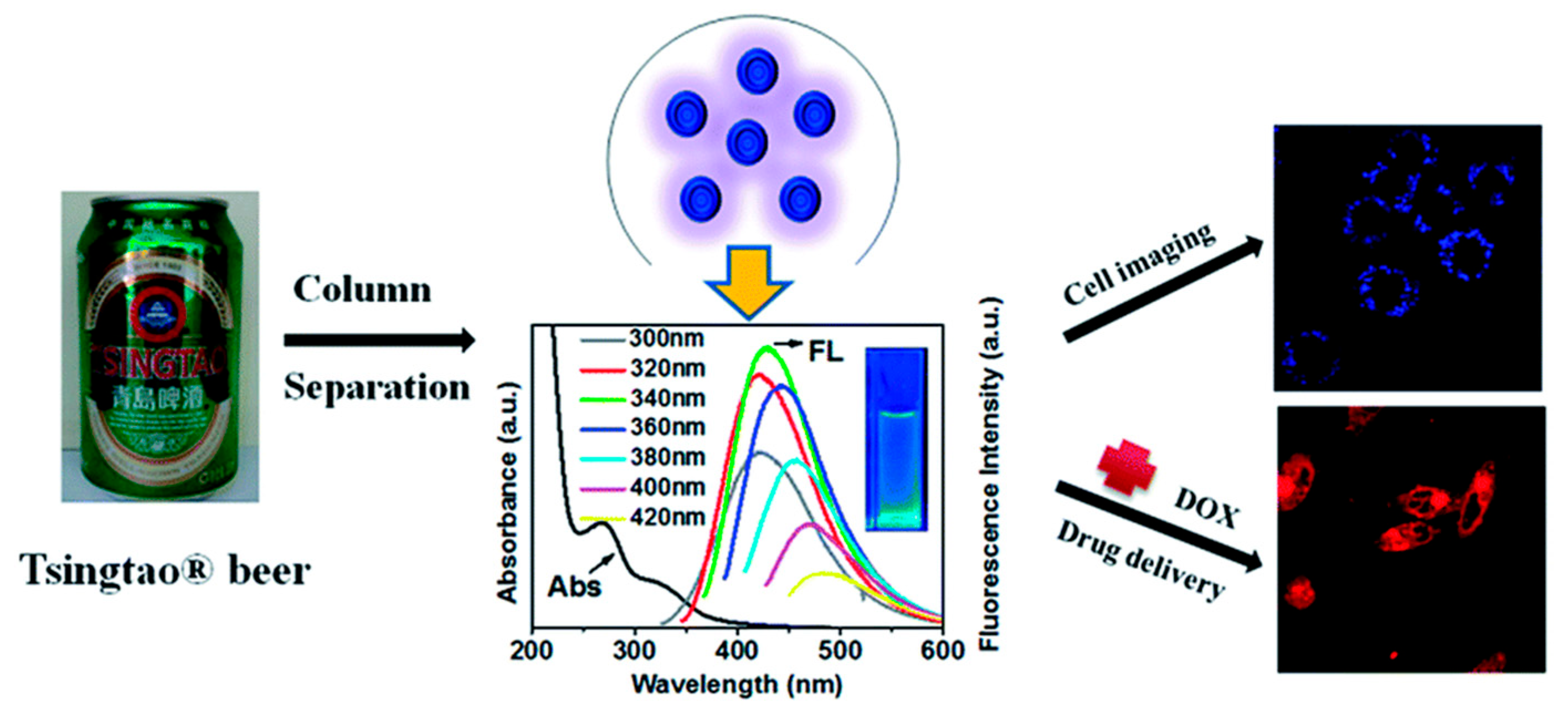
- Liao, H.; Jiang, C.; Liu, W.; Vera, J.M.; Seni, O.D.; Demera, K.; Yu, C.; Tan, M. Fluorescent Nanoparticles from Several Commercial Beverages: Their Properties and Potential Application for Bioimaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8527–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Na, X.; Lai, B.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Tan, M. Effects of fluorescent carbon dots from the baked lamb on energy and lipid metabolism. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sahu, S.; Sonkar, S.K.; Tackett Ii, K.N.; Sun, K.W.; Liu, Y.; Maimaiti, H.; Anilkumar, P.; Sun, Y.-P. Versatility with carbon dots—From overcooked BBQ to brightly fluorescent agents and photocatalysts. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 15604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Song, Y.; Liu, K.; Tan, M. Interaction of Carbon Dots from Grilled Spanish Mackerel with Human Serum Albumin, γ-Globulin and Fibrinogen. Foods 2021, 10, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
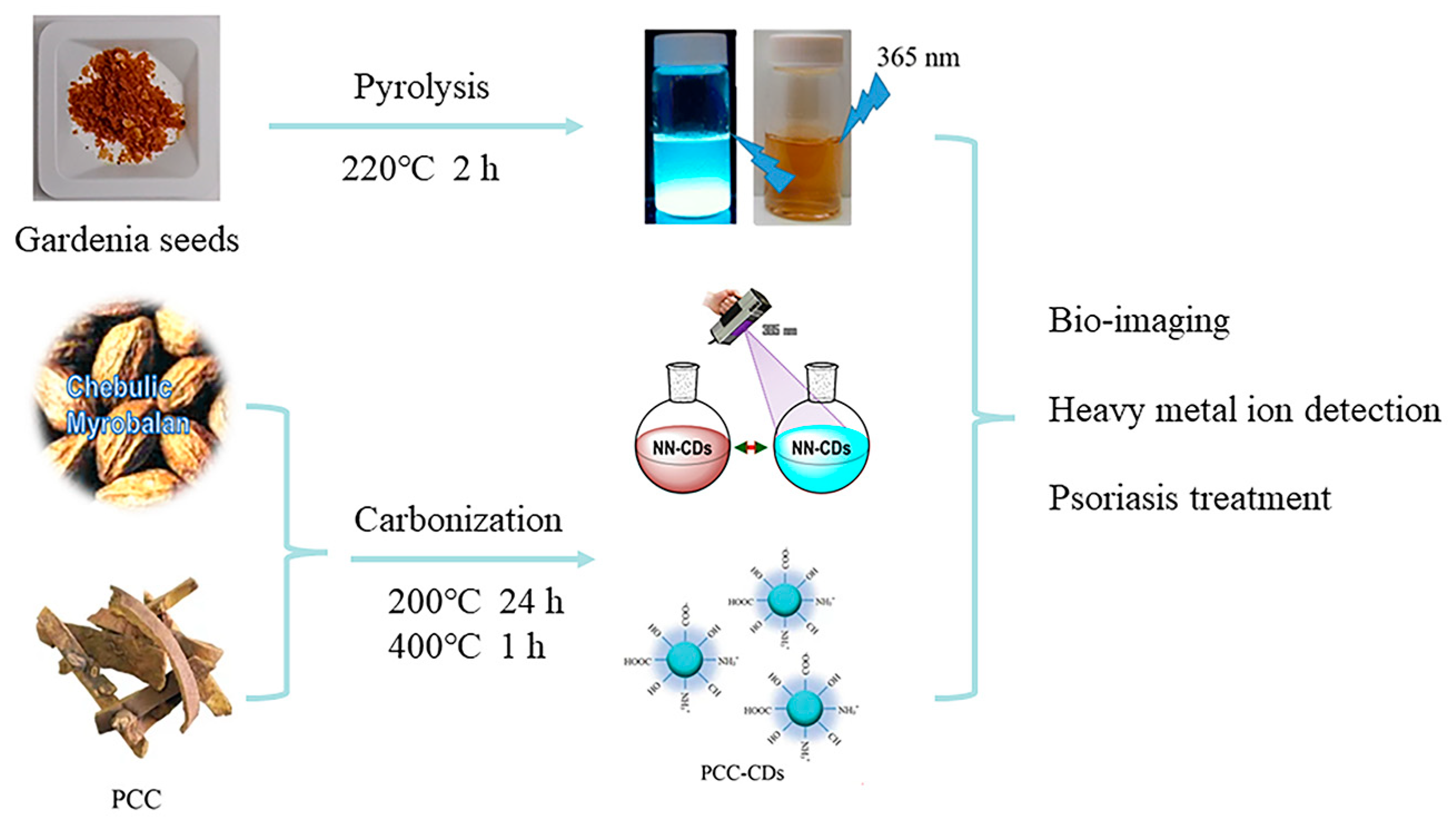
- Tsai, H.-W.; Wu, T.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Fu, S.-F.; Wu, M.-Y.; Lin, Y.-W. Green synthesis of gardenia seeds-based carbon dots for bacterial imaging and antioxidant activity in aqueous and oil samples. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 29283–29290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Perumal, S.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Vinodh, R.; Sangaraju, S.; Kishore, S.C.; Lee, Y.R. Natural Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots Obtained from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Chebulic Myrobalan and Their Sensing Ability toward Heavy Metal Ions. Sensors 2023, 23, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cheng, J.; Hu, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, F.; Kong, H.; Qu, H.; Zhao, Y. Green Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex-based carbon dots for ameliorating imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation in mice. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandarkuzhali, S.A.A.; Jeyalakshmi, V.; Sivaraman, G.; Singaravadivel, S.; Krishnamurthy, K.R.; Viswanathan, B. Highly fluorescent carbon dots from Pseudo-stem of banana plant: Applications as nanosensor and bio-imaging agents. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimarkou, A.; Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Kasouni, A.; Sygellou, L.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Stalikas, C.D. Selective FRET-based sensing of 4-nitrophenol and cell imaging capitalizing on the fluorescent properties of carbon nanodots from apple seeds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, T.; Kumar, S. Turning date palm fronds into biocompatible mesoporous fluorescent carbon dots. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.J.; Roy, A.K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.-E.; Jeong, J.H.; In, I.; Park, S.Y. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from natural materials of mango fruit for bio-imaging probes. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 15196–15202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, F.G.; Gonzales, K.N.; Troncoso, O.P.; Cañedo, V.S. Carbon Quantum Dots Based on Marine Polysaccharides: Types, Synthesis, and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Liu, J.; Yao, J.; Wang, R.; Shi, W.; Lu, C. Photoluminescence Mechanism of Carbon Dots: Triggering Multiple Color Emissions through Controlling the Degree of Protonation. Molecules 2022, 27, 6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Chang, J.; Tang, Z.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Insights into photoluminescence mechanisms of carbon dots: Advances and perspectives. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jia, L.; Guo, X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Green synthesis of up- and down-conversion photoluminescent carbon dots from coffee beans for Fe3+ detection and cell imaging. Analyst 2019, 144, 7421–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
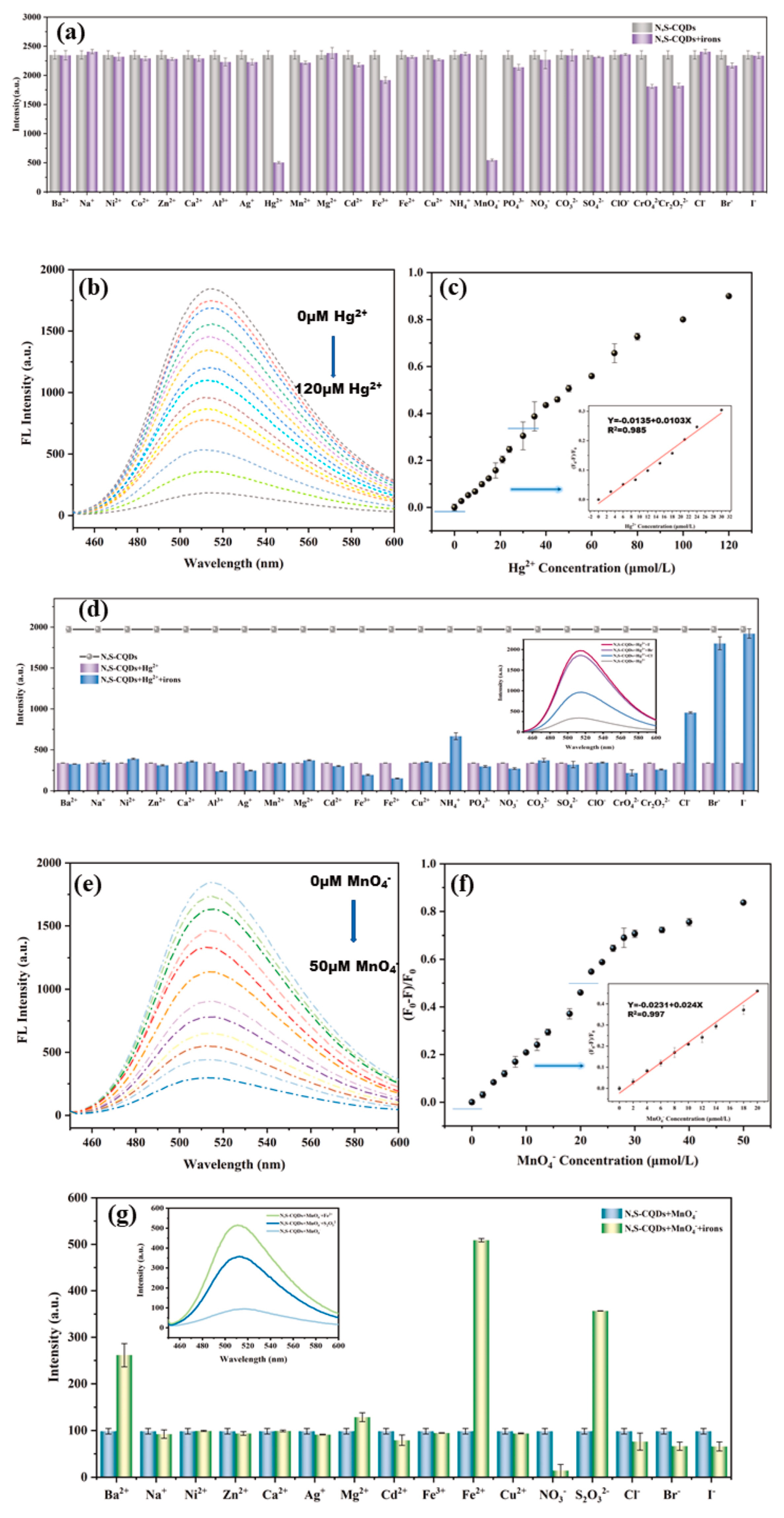
- Gao, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Cui, J.; Lu, Y.; Rong, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, C. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon quantum dots as “on-off-on” fluorescence probes to detect Hg2+ and MnO4− and improving the photostability of Rhodamine B. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1277, 341683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, B.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D.; Jing, L.; Gao, C.; Li, J.; He, Z.; Wang, J. Bioinspired Cryoprotectants of Glucose-Based Carbon Dots. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 3785–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chatterjee, S.; Palecha, M.; Sen, P.; Ateeq, B.; Verma, V. Chickpea peel waste as sustainable precursor for synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanotubes for bioimaging application. Carbon Lett. 2020, 31, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Yu, L.; Li, H.; Cheng, F.; Yi, X.; He, J.; Li, B. Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Gynostemma for Bioimaging and Antioxidant in Zebrafish. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9832–9840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; ChawPattnayak, B.; Dash, P.; Nayak, B.; Mohapatra, S. Papaya-Derived Carbon-Dot-Loaded Fluorescent Hydrogel for NIR-Stimulated Photochemotherapy and Antibacterial Activity. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 4, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Jiao, X.-Y.; Xu, L. The N,S co-doped carbon dots with excellent luminescent properties from green tea leaf residue and its sensing of gefitinib. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsai, N.; Tanawannapong, N.; Praneerad, J.; Kladsomboon, S.; Jaiyong, P.; Paoprasert, P. Real-time detection of alcohol vapors and volatile organic compounds via optical electronic nose using carbon dots prepared from rice husk and density functional theory calculation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, V.; Kizhakayil, R.N. Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Biosensor, Green Reductant, and Biomarker. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 23475–23484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Suresh Kumar, G.; Sujatha Devi, P. Egg-shell derived carbon dots for base pair selective DNA binding and recognition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 20476–20488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, J.; Wu, Z.; Qiao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Gao, Y.; Yan, H.; Liu, W. Enhanced Antibacterial Activity against Escherichia coli Based on Cationic Carbon Dots Assembling with 5-Aminolevulinic Acid. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 7034–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Xia, S. Valorization of Expired Passion Fruit Shell by Hydrothermal Conversion into Carbon Quantum Dot: Physical and Optical Properties. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 12, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Coy, E.; Li, J.j.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, P.; Wang, G. Fe-Doped Carbon Dots as NIR-II Fluorescence Probe for In Vivo Gastric Imaging and pH Detection. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, Z.; Qu, L.; Zhu, C.; Ye, R.; Li, S.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots derived from linseed and their applications in cellular imaging and sensing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3181–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Akanda, M.R.; Park, B.-Y.; Kim, H.Y. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from carrot juice for in vitro cellular imaging. Carbon Lett. 2017, 21, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.; Afkhami, A.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Madrakian, T. Green and cost-effective synthesis of carbon dots from date kernel and their application as a novel switchable fluorescence probe for sensitive assay of Zoledronic acid drug in human serum and cellular imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1030, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, Y.; Shen, J.; Huang, P.; Guo, S.; Pan, J.; Feng, B. Dual functional carbon dots derived from cornflour via a simple one-pot hydrothermal route. Mater. Lett. 2014, 123, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaraki, R.; Sadeghinejad, N. Microwave assisted synthesis of doped carbon dots and their application as green and simple turn off-on fluorescent sensor for mercury (II) and iodide in environmental samples. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, S.K.; D’Souza, A.; Suhail, B. Blue light-emitting carbon dots (CDs) from a milk protein and their interaction with Spinacia oleracea leaf cells. Int. Nano Lett. 2019, 9, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, Q.; He, L.; Zhou, R.; Liao, L.; Xue, J.; Xiao, X. Green synthesis of CQDs for determination of iron and isoniazid in pharmaceutical formulations. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, M.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yan, X.; Liu, M.; Zhuo, S.; Wang, S.; Min, X.; Gao, C.; et al. Synchronous and rapid preparation of lignin nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots from natural lignocellulose. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 3414–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, B.I.; Hassan, A.I.; Batakoushy, H.A.; Saraya, R.E.; Abdel-Aal, M.A.A.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Ibrahim, A.E.; Hassan, Y.F. Design, Characterization, and Bioanalytical Applications of Green Terbium- and Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as a Fluorescent Nanoprobe for Omadacycline Analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 2024, 78, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalani, N.; Nezhad-Mokhtari, P.; Jabbari, E. Microwave-assisted and one-step synthesis of PEG passivated fluorescent carbon dots from gelatin as an efficient nanocarrier for methotrexate delivery. Artif Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Qu, H.; Zhao, Y. Novel mulberry silkworm cocoon-derived carbon dots and their anti-inflammatory properties. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 48, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhou, S.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Yu, S. Folic acid functionalized gadolinium-doped carbon dots as fluorescence/magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent for targeted imaging of liver cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 234, 113721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Guo, X.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lonshakov, F. Green preparation of carbon dots with mangosteen pulp for the selective detection of Fe3+ ions and cell imaging. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Cong, S.; Zhao, H.; Tan, M. Nuclear-targeted of TAT peptide-conjugated carbon dots for both one-and two-photon fluorescence imaging. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 180, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhamore, J.R.; Jha, S.; Park, T.J.; Kailasa, S.K. Green synthesis of multi-color emissive carbon dots from Manilkara zapota fruits for bioimaging of bacterial and fungal cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 191, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayda, S.; Hadla, M.; Palazzolo, S.; Kumar, V.; Caligiuri, I.; Ambrosi, E.; Pontoglio, E.; Agostini, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Benedetti, A.; et al. Bottom-up synthesis of carbon nanoparticles with higher doxorubicin efficacy. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2017, 248, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Tian, J.; Jia, L.; Yu, J.-S. Waste frying oil as a precursor for one-step synthesis of sulfur-doped carbon dots with pH-sensitive photoluminescence. Carbon 2014, 77, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.; Sahoo, G.; Das, R.; Prusty, G.; Swain, S.K. Carbon quantum dot tailored calcium alginate hydrogel for pH responsive controlled delivery of vancomycin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gu, D.; Su, Y.; Ji, D.; Yang, Y.; Chen, K.; Pan, H.; Pan, W. Easy Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Carbon Dots Using the One-Pot Green Method for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Shu, Q.-W.; Liang, J.-M.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.-P.; Deng, X.-Y.; Swihart, M.T.; Tan, K.-J. One-Pot Hydrothermal Synthesis of Carbon Dots with Efficient Up- and Down-Converted Photoluminescence for the Sensitive Detection of Morin in a Dual-Readout Assay. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.-L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.-Y.; Xu, J.-J. Nucleolin-Targeted Ratiometric Fluorescent Carbon Dots with a Remarkably Large Emission Wavelength Shift for Precise Imaging of Cathepsin B in Living Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4042–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, G.; Luo, W.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, N.; Guo, M.; Fan, X. Tryptophan-sorbitol based carbon quantum dots for theranostics against hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Chinnathambi, S.; Bakhori, N.; Abu, N.; Etezadi, F.; Thangavel, V.; Packwood, D.; Sivaniah, E.; Pandian, G.N. Biomass-derived carbon dots as fluorescent quantum probes to visualize and modulate inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W.; Luo, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Pang, Q. Pb(ii) detection and versatile bio-imaging of green-emitting carbon dots with excellent stability and bright fluorescence. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 2472–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, G.; Li, L.; Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zuo, S.; Zeng, Z.; Xiong, W.; Guo, C. Green Synthesis of Nitrogen–Doped Carbon Dots from Fresh Tea Leaves for Selective Fe3+ Ions Detection and Cellular Imaging. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Guo, B.; Hao, L.; Liu, N.; Lin, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, X.; Gu, B. Doxorubicin-loaded environmentally friendly carbon dots as a novel drug delivery system for nucleus targeted cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, A.; Hashemi, E. A pseudohomogeneous nanocarrier based on carbon quantum dots decorated with arginine as an efficient gene delivery vehicle. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, T.; Hu, H.; Zhou, J.; Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Tang, W.; Fang, L.; Xiao, S.; Liang, J. Glycyrrhizic-Acid-Based Carbon Dots with High Antiviral Activity by Multisite Inhibition Mechanisms. Small 2020, 16, 1906206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-J.; Zhao, H.-P.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Guo, L.; Liu, J.-Y.; Pu, J.; Lv, J. Updates on global epidemiology, risk and prognostic factors of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2452–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, W.; Qiu, L.; Jiang, X.; Zuo, D.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. One pot synthesis of highly luminescent polyethylene glycol anchored carbon dots functionalized with a nuclear localization signal peptide for cell nucleus imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6104–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
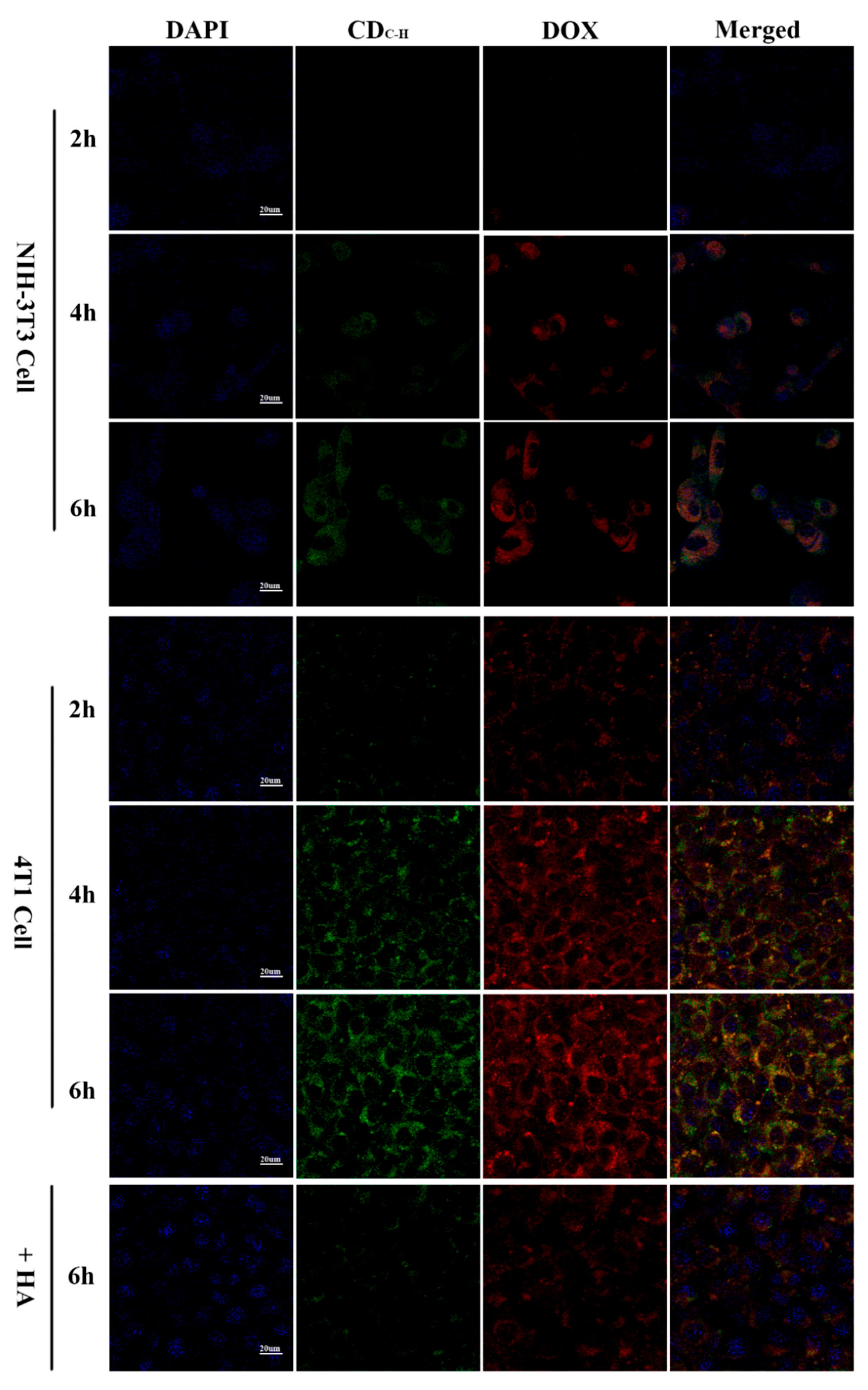
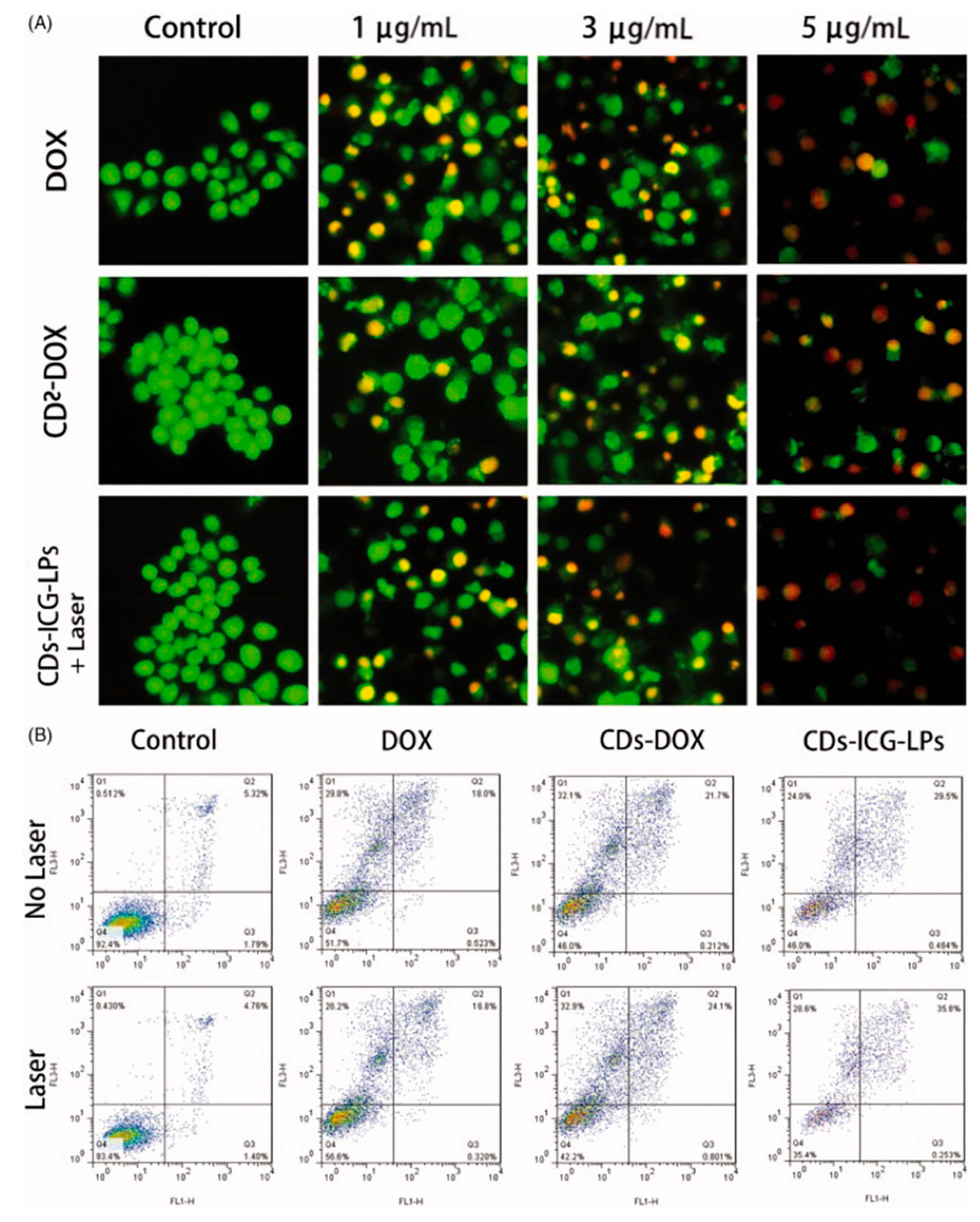
- Xue, X.; Fang, T.; Yin, L.; Jiang, J.; He, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, D. Multistage delivery of CDs-DOX/ICG-loaded liposome for highly penetration and effective chemo-photothermal combination therapy. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1826–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Cai, Q.; Zhao, S.; Ling, F.; Xiang, G.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, X. CDs-ICG@BSA nanoparticles for excellent phototherapy and in situ bioimaging. Talanta 2024, 271, 125661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, E.; Esfandiari, N.; Ranjbar, Z.; Alvandi, N.; Fatahi, Z. Designing of a pH-activatable carbon dots as a luminescent nanoprobe for recognizing folate receptor-positive cancer cells. Nanotechnology 2021, 33, 075103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, B.; Liu, K.; Xie, W.; Cui, J.; Li, D.; Lu, L.; et al. Fe-doped carbon dots: A novel biocompatible nanoplatform for multi-level cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshenawy, E.A.; El-Malla, S.F.; Hammad, S.F.; Mansour, F.R. Green microwave-prepared N and S Co-doped carbon dots as a new fluorescent nano-probe for tilmicosin detection. Talanta 2023, 265, 124853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.V.; Maharjan, R.-S.; Kanase, A.; Siewert, K.; Rosenkranz, D.; Singh, R.; Laux, P.; Luch, A. Machine-Learning-Based Approach to Decode the Influence of Nanomaterial Properties on Their Interaction with Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 13, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
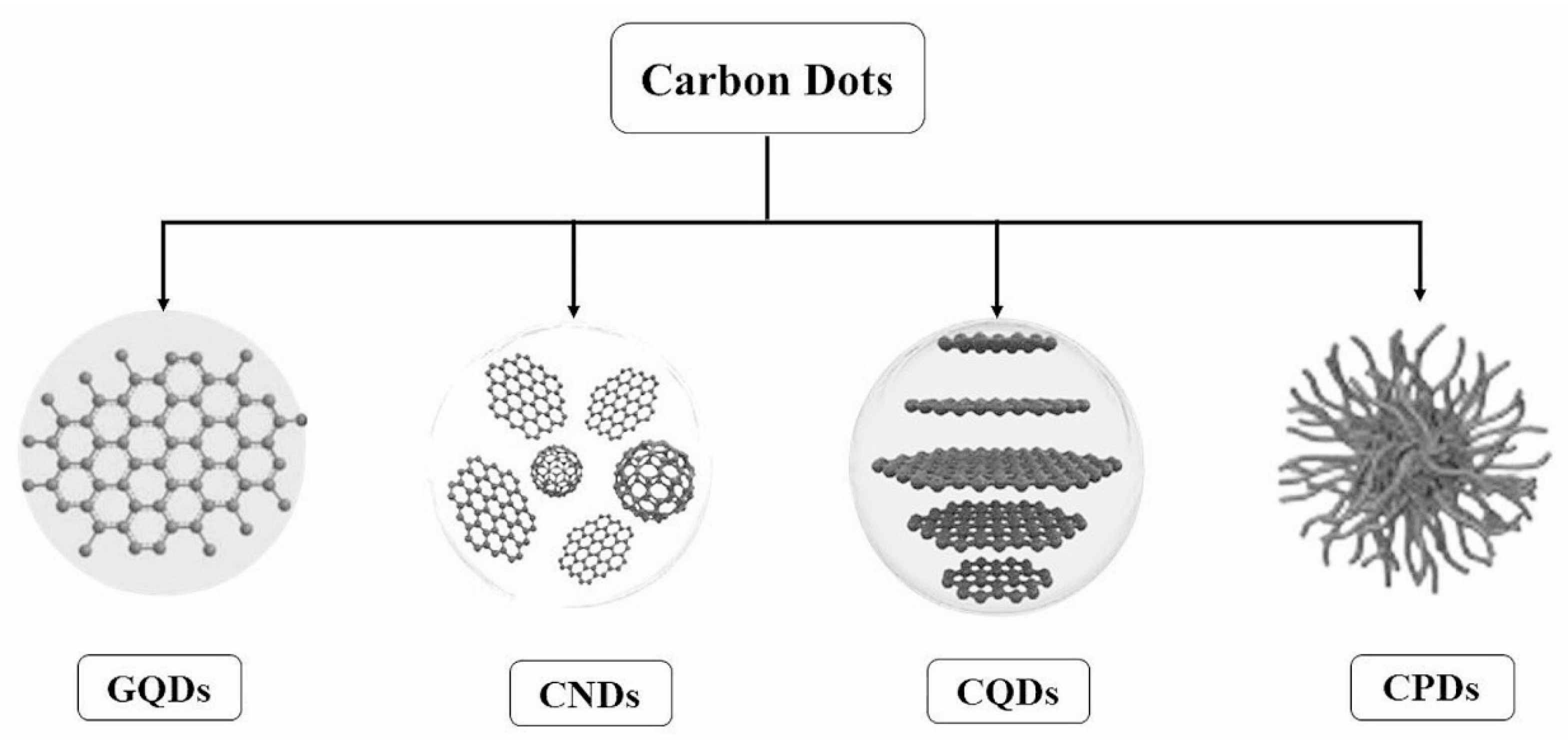




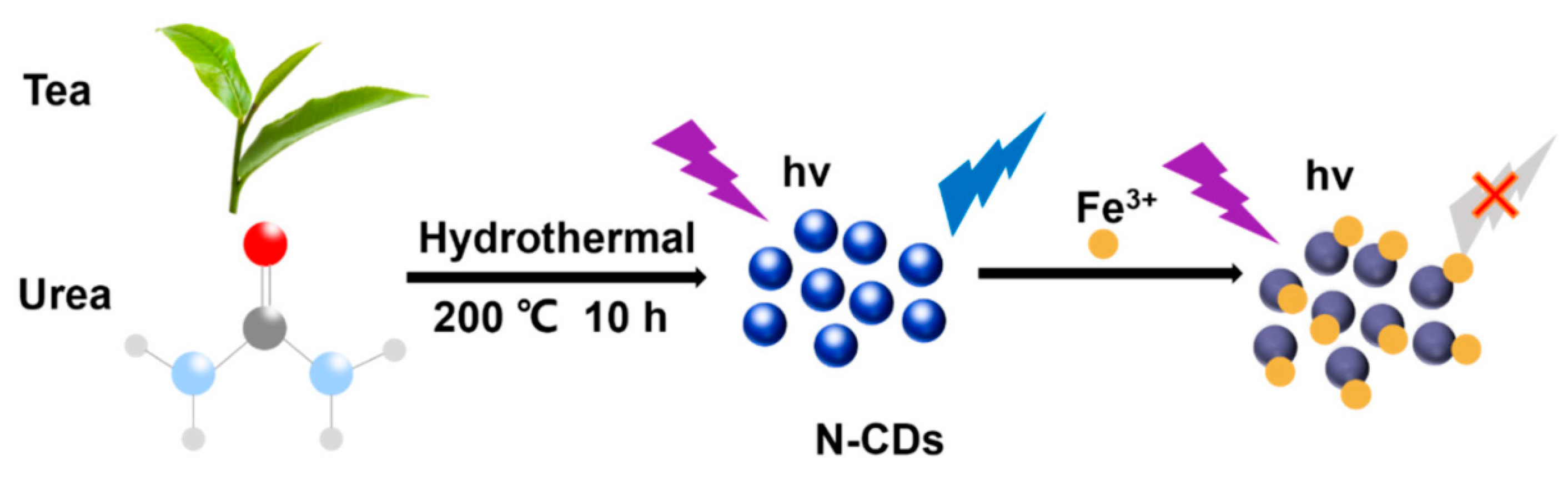



| Method | Size Distribution/nm | Maximum QY |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrothermal treatment | 0.4–18.6 | 90% [60] |
| Microwave irradiation | 1.7–10 | 40.38% [79] |
| Heating | 1.4–7 | 48% [92] |
| Extraction | 2.5–17.73 | 40% [87] |
| Pyrolysis | 2.26–9.35 | 20% [93] |
| Carbonization | 1–17 | 33.7% [94] |
| Source | Method | Quantum Yield | Size (nm) | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Carbonization | nil | ~2–10 | Cryoprotectants | [101] |
| Apple seeds | Pyrolysis | 20% | <10 | Detection of 4-nitrophenol bioimaging | [93] |
| Chickpea peel | Pyrolysis | 10% | 7 | Bioimaging | [102] |
| Gynostemma | Calcination | 5.7% | 2.5 | Bioimaging and antioxidants | [103] |
| Papaya leaf juice | Extraction | 12.34% | 5–9 | Fluorescent antibacterial gel | [104] |
| Tea leaf residue | Oxidative pyrolysis | 14.8% | <10 | Sensors for gefitinib | [105] |
| Amino acids | Hydrothermal | 90% | <10 | Bioimaging and photocatalysis | [60] |
| Camel milk | Hydrothermal | 24.6% | <10 | Mn7+ sensing and anti-amyloid and anticancer activities | [42] |
| Sugarcane bagasse pulp | Hydrothermal | 17.98% | 0.75–2.75 | Nonlinear optical devices, bioimaging, and pharmaceutical applications | [51] |
| Rice husk | Hydrothermal | 3% | 4–5 | Detection of alcohol vapors | [106] |
| Mint leaf | Extraction | 7.64% | <10 | Biosensors, green reductants, and biomarkers | [107] |
| Chicken eggshell membrane | Hydrothermal | 8% | 3.35 ± 0.5 | Probe for selective DNA recognition | [108] |
| Citric acid and branched PEI25000 | Hydrothermal | nil | 18.6 | Enhanced antibacterial activity | [109] |
| Passion fruit shells | Hydrothermal | 1.8% | <5 | Fluorescent probe | [110] |
| Coriander leaves | Hydrothermal carbonization | 6.48% | 1.5–3 | Detecting Fe3+ | [36] |
| Dopamine hydrochloride and o-phenylenediamine | Hydrothermal | 1.27% | 2.3 | Fluorescence probe | [111] |
| Linseed | Hydrothermal carbonization | 14.2% | 4–8 | Biosensors and bioimaging | [112] |
| Bacillus cereus | Hydrothermal | 18.3% | 3.3 | Detection of p-nitrophenol and bioimaging | [47] |
| Coffee beans | Hydrothermal | 9.8% | 3.1–6.0 | Fe3+ detection and cell imaging | [99] |
| Carrot juice | Hydrothermal carbonization | 5.16% | 3–8 | Bioimaging | [113] |
| Date kernels | Hydrothermal | 12.5% | 1–5 | Fluorescence probe and cellular imaging | [114] |
| Corn flour | Hydrothermal carbonization | 7.7% | 2–6 | Bioimaging and detecting Cu2+ | [115] |
| Citric acid | Microwave irradiation | 19.2% | 10 | Detection of Hg2+ and I− | [116] |
| ASDA-Na4 and m-phenylenediamine | Hydrothermal | 77.68% | 0.4–2.6 | Detecting Hg2+ and MnO4− | [100] |
| Milk | Microwave irradiation | 18.7% | <10 | Fluorescent labeling, bioimaging, and biosensors | [117] |
| Camphor leaves | Hydrothermal | nil | 1–4 | Detecting Fe3+ and isoniazid | [118] |
| Lignocellulose | Microwave irradiation | nil | 2–3 | Bioimaging | [119] |
| Plum juice | Microwave irradiation | 35.44% | 3.1 ± 0.27 | Fluorescent nanoprobe | [120] |
| Gelatin | Microwave irradiation | 34% | <10 | Biomedical applications | [121] |
| Mulberry silkworm cocoon | Pyrolysis | 6.32% | 2.26–9.35 | Anti-inflammatory properties | [122] |
| Gadodiamide | Hydrothermal | 48.2% | 3.35 | Liver cancer-targeted imaging and therapy | [123] |
| Mangosteen pulp | Heating | nil | 5 | Cell imaging | [124] |
| Tryptophan and formic acid | Hydrothermal | 58.4% | 1.7 | Fluorescence imaging | [125] |
| Honey | Heating | 19.8% | 2 | Imaging and sensing | [82] |
| Plectranthus amboinicus leaves | Microwave irradiation | 17% | 2.43 ± 0.02 | Fe3+ detection and bioimaging | [73] |
| Coffee beans | Heating | 48% | 5 ± 2 | Nano-sensors and bioimaging agents | [92] |
| Aloe barbadensis miller | Microwave irradiation | 31% | <5 | Bioimaging, anticancer, and photocatalytic applications | [77] |
| Manilkara zapota | Carbonization | 7.9% | 2.9 ± 0.7 | Bioimaging of bacterial and fungal cells | [126] |
| Microalgae | Carbonization | nil | 5 | Decoration of TiO2 nanoparticles | [74] |
| Date palm leaf fronds | Carbonization | 33.7% | <10 | Bioimaging and drug delivery | [94] |
| Black tea | Carbonization | 26% | ~17 | Drug delivery | [127] |
| Waste frying oil | Carbonization | 3.66% | ~2.6 | Bioimaging | [128] |
| Aloe vera leaf gel | Carbonization | 16.4% | 1.5–3.7 | Drug delivery | [129] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, K.; Wei, Y. Engineering of Green Carbon Dots for Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184508
Shang J, Zhou Q, Wang K, Wei Y. Engineering of Green Carbon Dots for Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications. Molecules. 2024; 29(18):4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184508
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Junjie, Qian Zhou, Kehan Wang, and Yunlin Wei. 2024. "Engineering of Green Carbon Dots for Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications" Molecules 29, no. 18: 4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184508
APA StyleShang, J., Zhou, Q., Wang, K., & Wei, Y. (2024). Engineering of Green Carbon Dots for Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications. Molecules, 29(18), 4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184508








