Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Their Application in Partitioning of Phenol Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
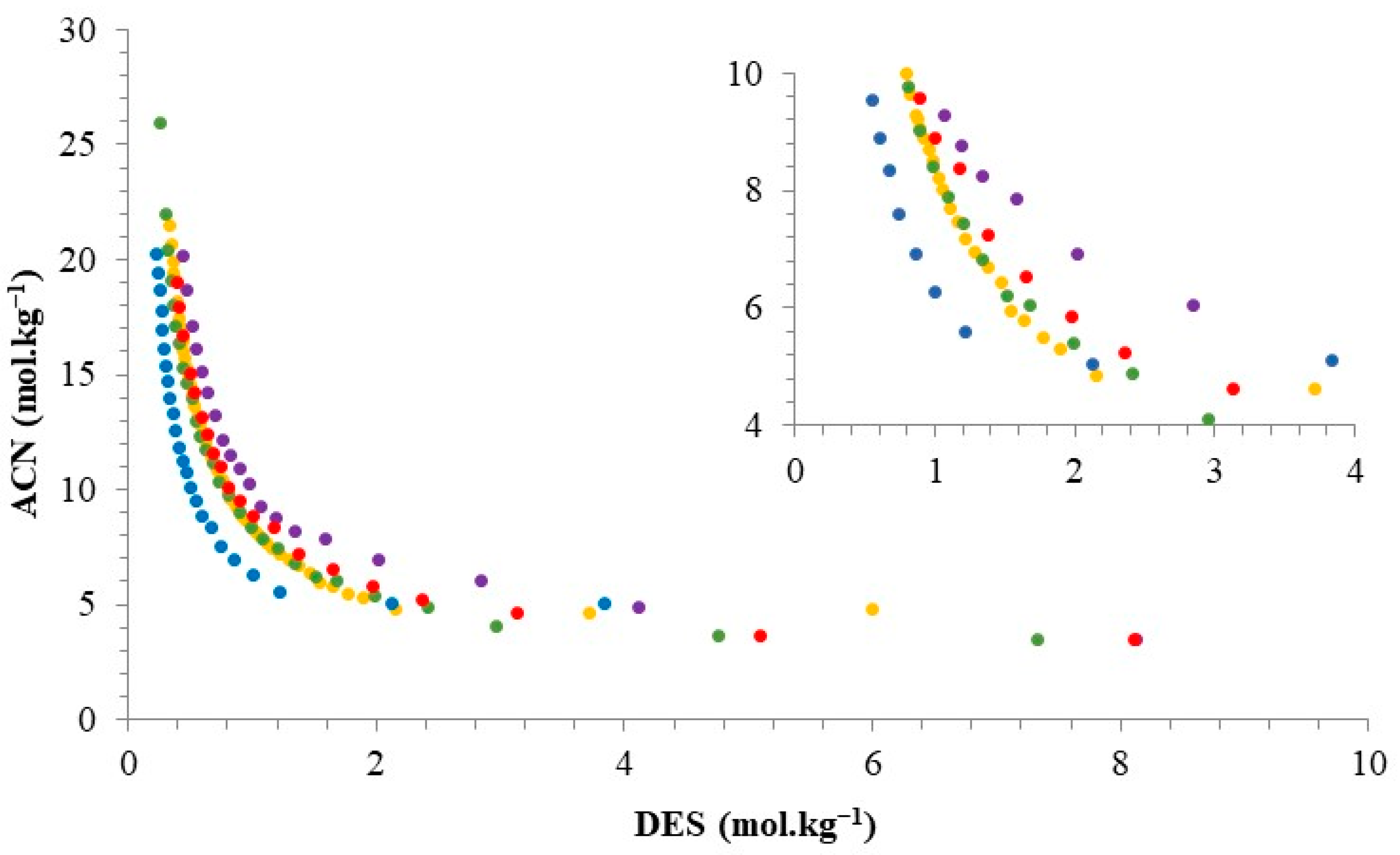
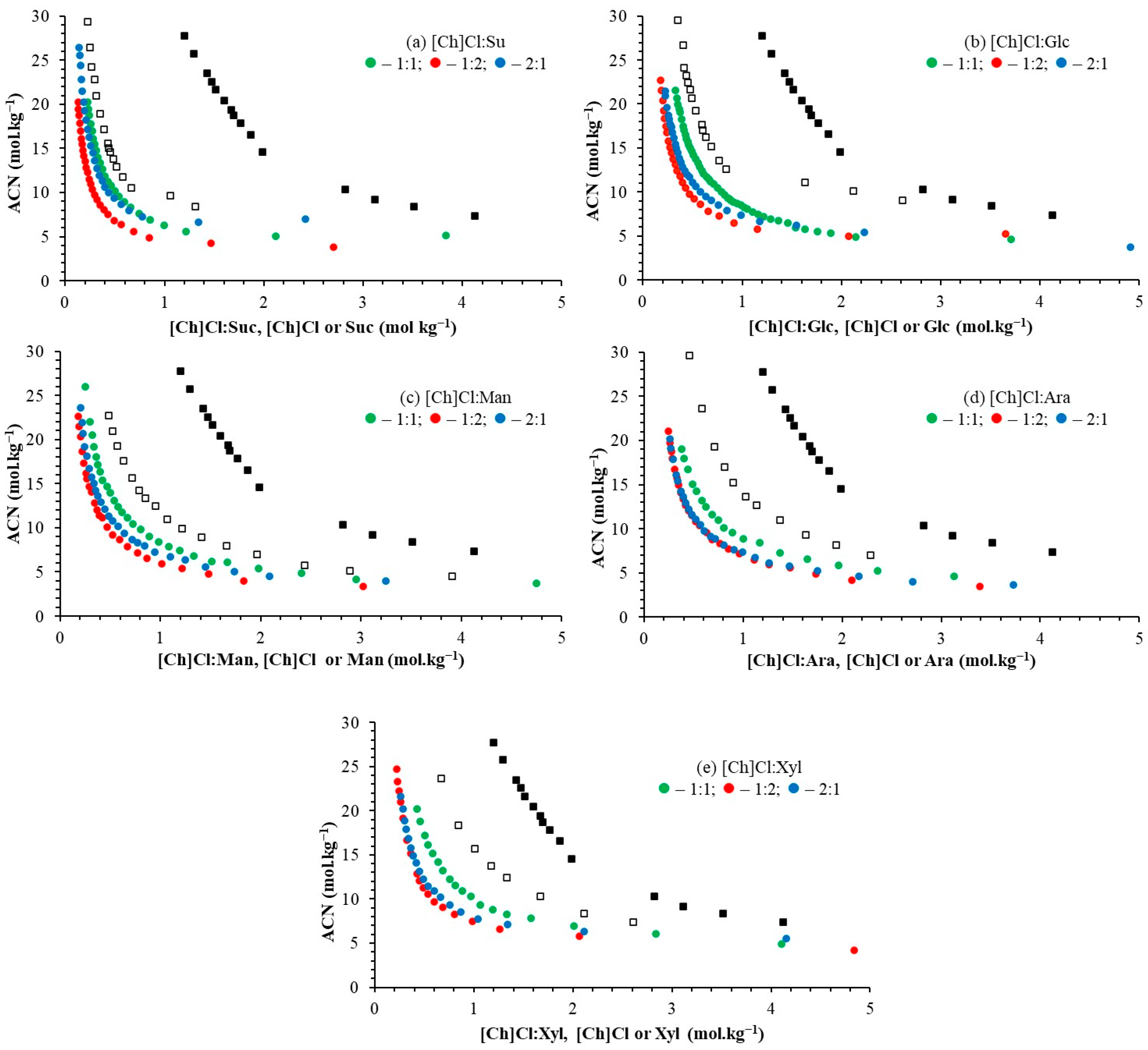
2.1. Binodal Curves
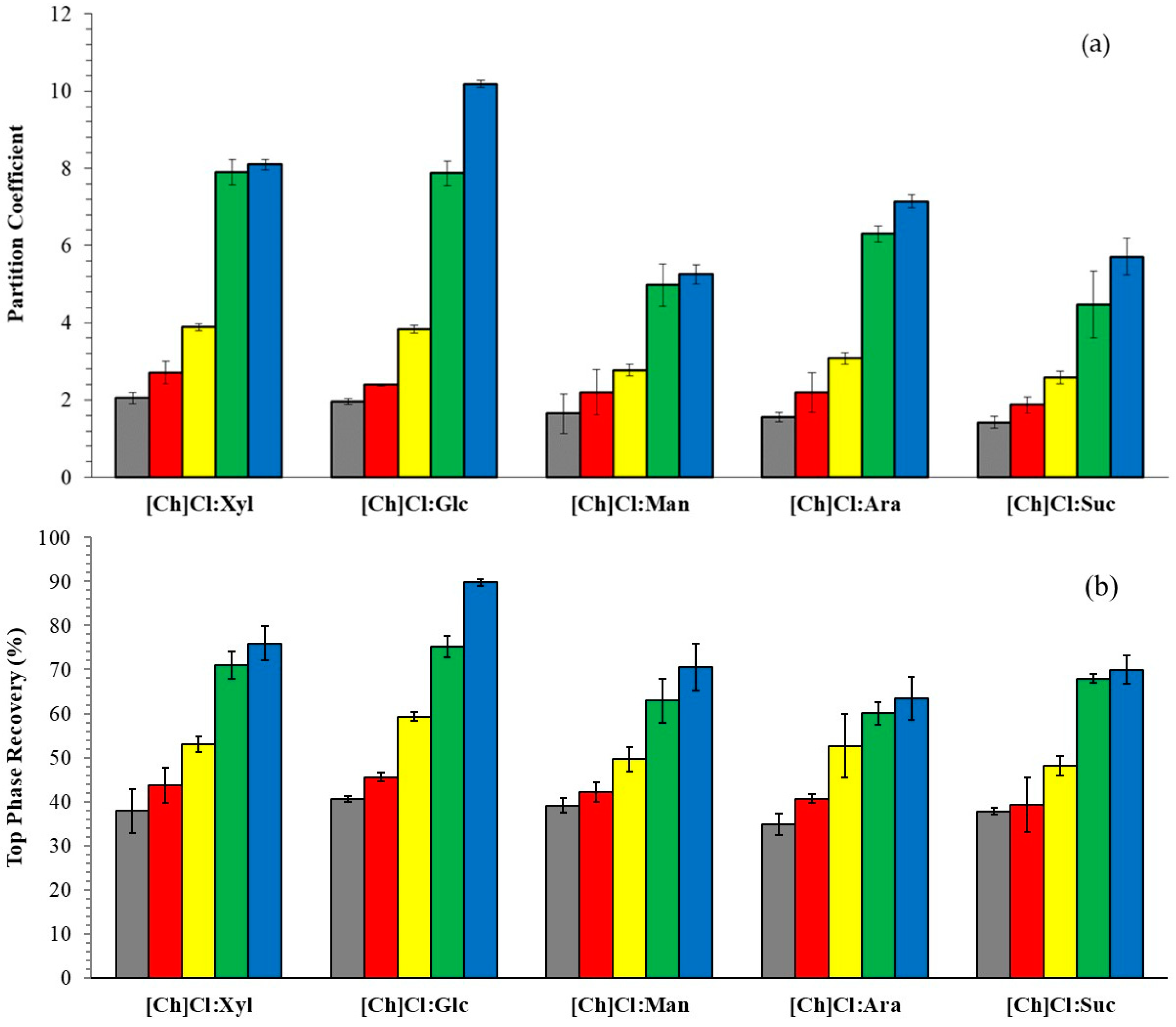
2.2. Partition of Phenolic Compounds
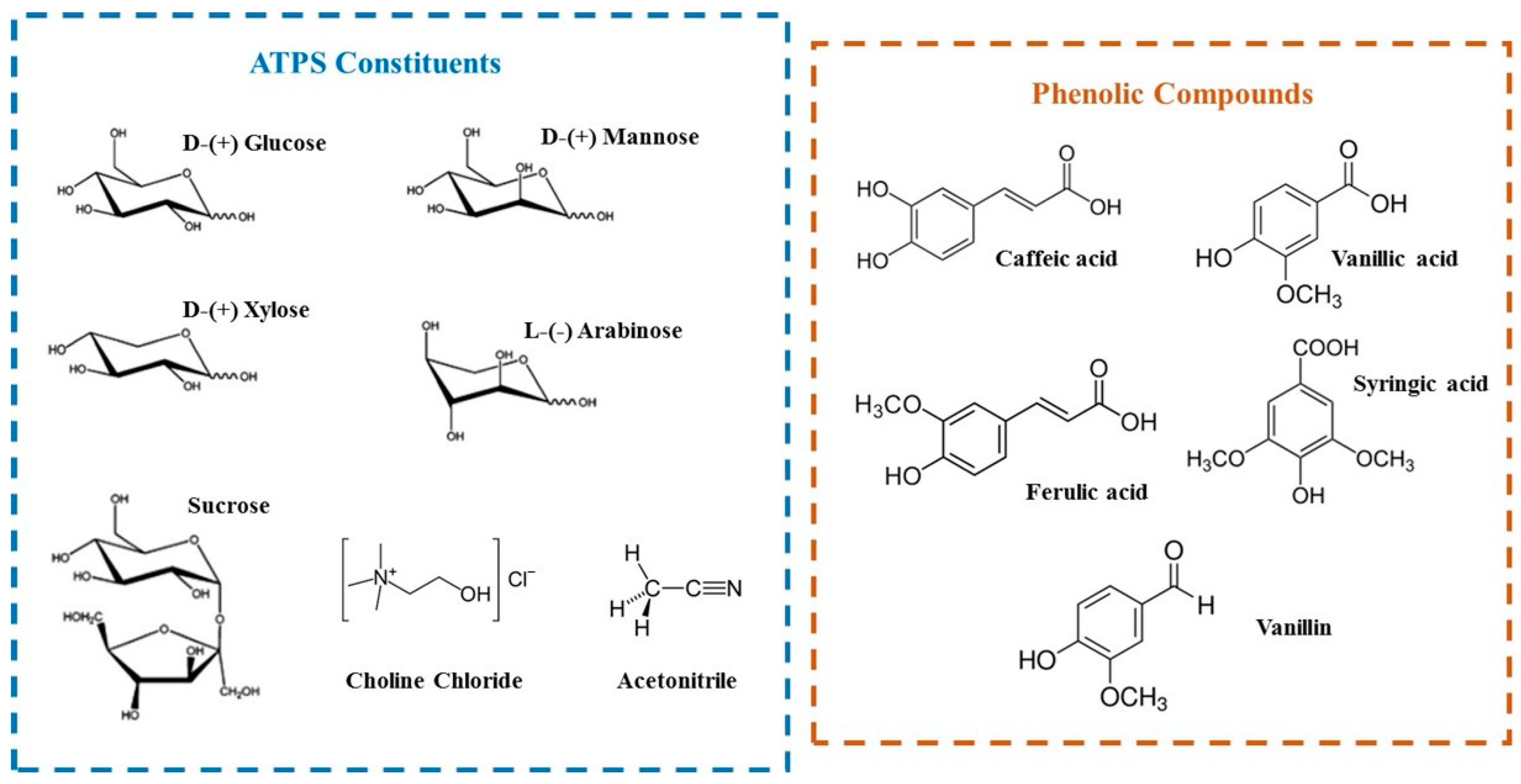
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Deep Eutectic Solvent
3.3. Binodal Curve
3.4. Partition of Phenolic Compounds on ATPS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, A.N.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, X.R.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, H.B. Resources and biological activities of natural polyphenols. Nutrients 2014, 6, 6020–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalikas, C.D. Extraction, separation, and detection methods for phenolic acids and flavonoids. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 3268–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Tsao, R.; Yang, R.; Cui, S.W. Phenolic acid profiles and antioxidant activities of wheat bran extracts and the effect of hydrolysis conditions. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Krawczyk, M.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. Determination of antioxidant activity, rutin, quercetin, phenolic acids and trace elements in tea infusions: Influence of citric acid addition on extraction of metals. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 40, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Thakali, K.M.; Jensen, G.S.; Wu, X. Phenolic acids of the two major blueberry species in the us market and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roleira, F.M.F.; Tavares-da-Silva, E.J.; Varela, C.L.; Costa, S.C.; Silva, T.; Garrido, J.; Borges, F. Plant derived and dietary phenolic antioxidants: Anticancer properties. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, B.R.; Heleno, S.A.; Oliveira, B.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phenolic compounds: Current industrial applications, limitations and future challenges. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.N. Chlorogenic acids and other cinnamates—Nature, occurrence and dietary burden. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milagros, A.L.; Argimiro, R.; Miguel, R.; Tangil, S. The effects of solvents on the phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of Stypocaulon scoparium algae extracts. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Redha, A.A. Review on extraction of phenolic compounds from natural sources using green deep eutectic solvents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 878–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyaningsih, W.; Saputro, I.E.; Palma, M.; Barroso, C.G. Pressurized liquid extraction of phenolic compounds from rice (Oryza sativa) grains. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.C.; Souza, M.C.; Sumere, B.R.; Silva, L.G.S.; Cunha, D.T.; Barbero, G.F.; Bezerra, R.M.N.; Rostagno, M.A. Simultaneous extraction and separation of bioactive compounds from apple pomace using pressurized liquids coupled on-line with solid-phase extraction. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, M.; Ribeiro, A.P.L.; Hosseinian, F.; Tsopmo, A. Phenolic acids, avenanthramides, and antioxidant activity of oats defatted with hexane or supercritical fluid. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelvas-Puello, L.M.; Franco-Arnedo, G.; Martínez-Correa, H.A.; Ballesteros-Vivas, D.; Sánchez-Camargo, A.D.P.; Miranda-Lasprilla, D.; Narváez-Cuenca, C.-E.; Parada-Alfonso, F. Supercritical fluid extraction of phenolic compounds from mango (Mangifera indica L.) seed kernels and their application as an antioxidant in an edible oil. Molecules 2021, 26, 7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmoune, F.; Spigno, G.; Moussi, K.; Remini, H.; Cherbal, A.; Madani, K. Pistacia lentiscus leaves as a source of phenolic compounds: Microwave-assisted extraction optimized and compared with ultrasound-assisted and conventional solvent extraction. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 61, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, M.; Taher, Z.M.; Rahmat, Z.; Chu, L.S. A review of ultrasound-assisted extraction for plant bioactive compounds: Phenolics, flavonoids, thymols, saponins and proteins. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinela, J.; Prieto, M.A.; Carvalho, A.M.; Barreiro, M.F.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic acids and flavonoids and production of antioxidant ingredients from tomato: A nutraceutical-oriented optimization study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 164, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, T.; Santos, S.C.R.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from chestnut processing waste using response surface methodology. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 395, 136452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalkiewicz, A.; Biesaga, M.; Pyrzynska, K. Solid-phase extraction procedure for determination of phenolic acids and some flavonols in honey. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1187, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Jia, L.; Xiang, H.; Peng, M.; Li, H.; Shi, S. Synthesis and characterization of hollow porous molecular imprinted polymers for the selective extraction and determination of caffeic acid in fruit samples. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Carniel, A.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Coelho, M.A.Z. Selective enzymes separation from the fermentation broth of Yarrowia lipolytica using aqueous two-phase system based on quaternary ammonium compounds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 324, 124539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, J.; Dang, K.K.; Ma, Q.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.Y.; Li, C.Q. Partition Behaviors of Different Polar Anthocyanins in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Extraction of Anthocyanins from Nitraria tangutorun Bobr. and Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Deng, M. Extraction and purification of quercitrin, hyperoside, rutin, and afzelin from Zanthoxylum Bungeanum maxim leaves using an aqueous two-phase system. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, C1593–C1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, A.M.; Athira, K.K.; Alves, M.B.; Gardas, R.L.; Pereira, J.F. Textile dyes effluents: A current scenario and the use of aqueous biphasic systems for the recovery of dyes. J. Water Proces. Eng. 2023, 55, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Pinto, I.; Espitia-Saloma, E.; Rosa, S.A.S.L.; Rito-Palomares, M.; Aguilar, O.; Arévalo-Rodríguez, M.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Azevedo, A.M. Integration of cell harvest with affinity-enhanced purification of monoclonal antibodies using aqueous two-phase systems with a dual tag ligand. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.C.L.; Nascimento, T.P.; Cunha, M.N.C.; Mehari, Y.; Berger, E.; Scheich, D.; Lingg, N.; Jungbauer, A. Purification of secretory IgA monoclonal antibodies enriched fraction directly from cell culture medium using aqueous two-phase systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.R.; Passos, H.; Pereira, M.M.; Lima, A.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Ionic liquids as additives to enhance the extraction of antioxidants in aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Gomes, P.G.C.; Buarque, F.S.; Soares, C.M.F.; Bjerk, T.R.; Lima, A.S. Novel strategy for extraction and partitioning of phenol compounds from industrial residue of seriguela (Spondia purpurea L.) using aqueous two-phase systems. Food Bioprod. Process 2023, 141, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rito-Palomares, M. Practical application of aqueous two-phase partition to process development for the recovery of biological products. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 807, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Madrid, M.; Rito-Palomares, M.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O.; Benavides, J. Potential of aqueous two-phase systems constructed on flexible devices: Human serum albumin as proof of concept. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, A.D.; Hsu, J.T. Protein partitioning in PEG/dextran aqueous two-phase systems. AIChE J. 1990, 36, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafarani-Moattar, M.T.; Sadeghi, R. Phase diagram data for several PPG + salt aquous biphasic system at 25 °C. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2001, 50, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, K.E.; Broker, G.A.; Willauer, H.D.; Huddleston, J.G.; Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Controlling the aqueous miscibility of ionic liquids: Aqueous biphasic systems of water-miscible ionic liquids and water-structuring salts for recycle, metathesis, and separations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6632–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, M.G.; Louros, C.L.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Aqueous biphasic systems composed of a water-stable ionic liquid + carbohydrates and their applications. Green. Chem. 2011, 13, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, J. Liquid-liquid equilibria of aqueous biphasic systems composed of 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium tetrafluoroborate + sucrose/maltose + water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 3612–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Freire, M.G.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Extraction of vanillin using ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S. Short-chain alcohol/salt-based aqueous two-phase system as a novel solvent for extraction of plant active ingredients: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, K.M.; Maciel, G.E.; Buarque, F.S.; Santos, A.J.; Marques, M.N.; Cavalcanti, E.B.; Lima, Á.S. Novel phase diagrams of aqueous two-phase systems based on tetrahydrofuran+ carbohydrates+ water: Equilibrium data and partitioning experiments. Fluid. Phase Equilibria 2017, 433, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Guimarães, D.E.; Soares, C.M.; Souza, R.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Lima, Á.S. Ethanolic two-phase system formed by polypropylene glycol, ethylene glycol and/or ionic liquid (phase-forming or adjuvant) as a platform to phase separation and partitioning study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Huang, Y.; Wen, Q.; Ding, X. Development of green betaine-based deep eutectic solvent aqueous two-phase system for the extraction of protein. Talanta 2016, 152, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.T.; Pei, D.; Yu, P.L.; Wei, J.T.; Wang, N.L.; Di, D.L.; Liu, Y.W. Aqueous two-phase systems based on deep eutectic solvents and their application in green separation processes. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, C.W.; Tey, B.T.; Hii, S.L.; Kamal, S.M.M.; Lan, J.C.W.; Ariff, A.; Ling, T.C. Purification of lipase derived from Burkholderia pseudomallei with alcohol/salt-based aqueous two-phase systems. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati-Kande, E.; Shekaari, H. Salting-out effect of sodium, potassium, carbonate, sulfite, tartrate and thiosulfate ions on aqueous mixtures of acetonitrile or 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone: A liquid-liquid equilibrium study. Fluid. Phase Equilibr 2013, 360, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, A.; Bahadori, E.; Cespi, D.; Passarini, F.; Cavani, F.; Tabanelli, T.; Rossetti, I. Acetonitrile from bioethanol ammoxidation: Process design from the grass-roots and life cycle analysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5441–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, N.; Wen, Q.; Yang, Q. Aqueous biphasic systems containing PEG-based deep eutectic solvents for high-performance partitioning of RNA. Talanta 2017, 170, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, P. Aqueous biphasic systems formed by deep eutectic solvent and new-type salts for the high-performance extraction of pigments. Talanta 2018, 181, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhong, H.R.; Wong, D.S.H.; Wan, C.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wei, T.C. A novel deep eutectic solvent-based ionic liquid used as electrolyte for dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.; Aparicio, S.; Ullah, R.; Atilhan, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Physicochemical Properties and Gas Separation Applications. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2616–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the synthesis and properties of deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride and carboxylic acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.L.; Santos, L.N.S.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Souza, R.L.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, A.S. Recovery of capsaicin from Capsicum frutescens by applying aqueous two-phase systems based on acetonitrile and cholinium-based ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 112, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, G.B.; Mourão, T.; Pereira, F.M.; Freire, M.G.; Fricks, A.T.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Aqueous two-phase systems based on acetonitrile and carbohydrates and their application to the extraction of vanillin. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural deep eutectic solvents − solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.O.; Sosa, F.H.B.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Mafra, M.R. Study of the pseudo-ternary aqueous two-phase systems of deep eutectic solvent (choline chloride:sugars)+ K2HPO4+ water. Fluid. Phase Equilibr 2017, 448, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Mohammadian, M.; Pazuki, G.; Shahriari, S. Partitioning of crocin in a novel aqueous two-phase system composed of a deep eutectic solvent and acetonitrile. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2022, 67, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Monteiro, S.S.A.; Ribeiro, B.D. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent as an inhibitor of metalloproteases (collagenase and elastase) in cosmetic formulation. 3 Biotech. 2023, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uedaira, H.; Ikura, M.; Uedaira, H. Natural-abundance oxygn-17 magnetic relaxation in aqueous solutions of carbohydrates. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1989, 62, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lii, C.Y.; Lai, M.F.; Liu, K.F. Factors influencing the retrogradation of two rice starches in low-molecular-weight saccharide solutions. J. Cereal Sci. 1998, 28, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uedaira, H.; Ishimura, M.; Tsuda, S.; Uedaira, H. Hydration of oligosaccharides. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1990, 63, 3376–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galema, S.A.; Blandamer, M.J.; Engberts, J.B.F.N. Stereochemical aspects of the hydration of carbohydrates, Kinetic medium effects of monosaccharides on a water catalyzed hydrolysis reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 9666–9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemspider. Available online: http://www.chemspider.com (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Le, P.H.; Ho, L.T.T.; Le, D.H.T.; Nguyen, V. Purification of coffee polyphenols extracted from coffee pulps (Coffee arabica L.) using aqueous two-phase system. Molecules 2023, 28, 5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosário, R.L.; Farias, F.O.; Mafra, M.R.; Soares, C.M.; Passos, H.; Coutinho, J.A.; Lima, Á.S. Acetonitrile as adjuvant to tune polyethylene glycol+ K3PO4 aqueous two-phase systems and its effect on phenolic compounds partition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 223, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Freire, C.S.; Silvestre, A.J.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A. Optimization of the gallic acid extraction using ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, Á.S.; Soares, C.M.F.; Paltram, R.; Halbwirth, H.; Bica, K. Extraction and consecutive purification of anthocyanins from grape pomace using ionic liquid solutions. Fluid. Phase Equilibria 2017, 451, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Nalatambi, S.; Mahaindran, A.; Tee, L.H.; Chua, B.L.; Oh, K.S.; Lam, W.H. Characterization of choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent for anthocyanin extraction via aqueous two-phase system: Physicochemical properties and liquid–liquid equilibrium phase diagram. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 18, e2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as a new extraction media for phenolic metabolites in Carthamus tinctorius L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6272–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsson, P.A.; Tjerneld, F. Aqueous two-phase separations. In Separation Processes in Biotechnology; Asenjo, J.A., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 287–317. [Google Scholar]
- Buarque, F.S.; Lima, T.S.P.; Carniel, A.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Coelho, M.A.; Souza, R.L.; Soares, C.M.; Pereira, M.M.; Lima, A.S. Hormones Concentration in an Aqueous Two-Phase System: Experimental and Computational Analysis. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2024, 47, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, I.N.; Rodrigues, L.C.V.; Soares, C.M.F.; Buarque, F.S.; Souza, R.L.; Lima, Á.S. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Their Application in Partitioning of Phenol Compounds. Molecules 2024, 29, 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184383
Souza IN, Rodrigues LCV, Soares CMF, Buarque FS, Souza RL, Lima ÁS. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Their Application in Partitioning of Phenol Compounds. Molecules. 2024; 29(18):4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184383
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Isabela N., Lucas C. V. Rodrigues, Cleide M. F. Soares, Filipe S. Buarque, Ranyere L. Souza, and Álvaro S. Lima. 2024. "Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Their Application in Partitioning of Phenol Compounds" Molecules 29, no. 18: 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184383
APA StyleSouza, I. N., Rodrigues, L. C. V., Soares, C. M. F., Buarque, F. S., Souza, R. L., & Lima, Á. S. (2024). Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Their Application in Partitioning of Phenol Compounds. Molecules, 29(18), 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184383







