Advances in Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Dermatological Applications: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation Method of Nanofiber Membrane
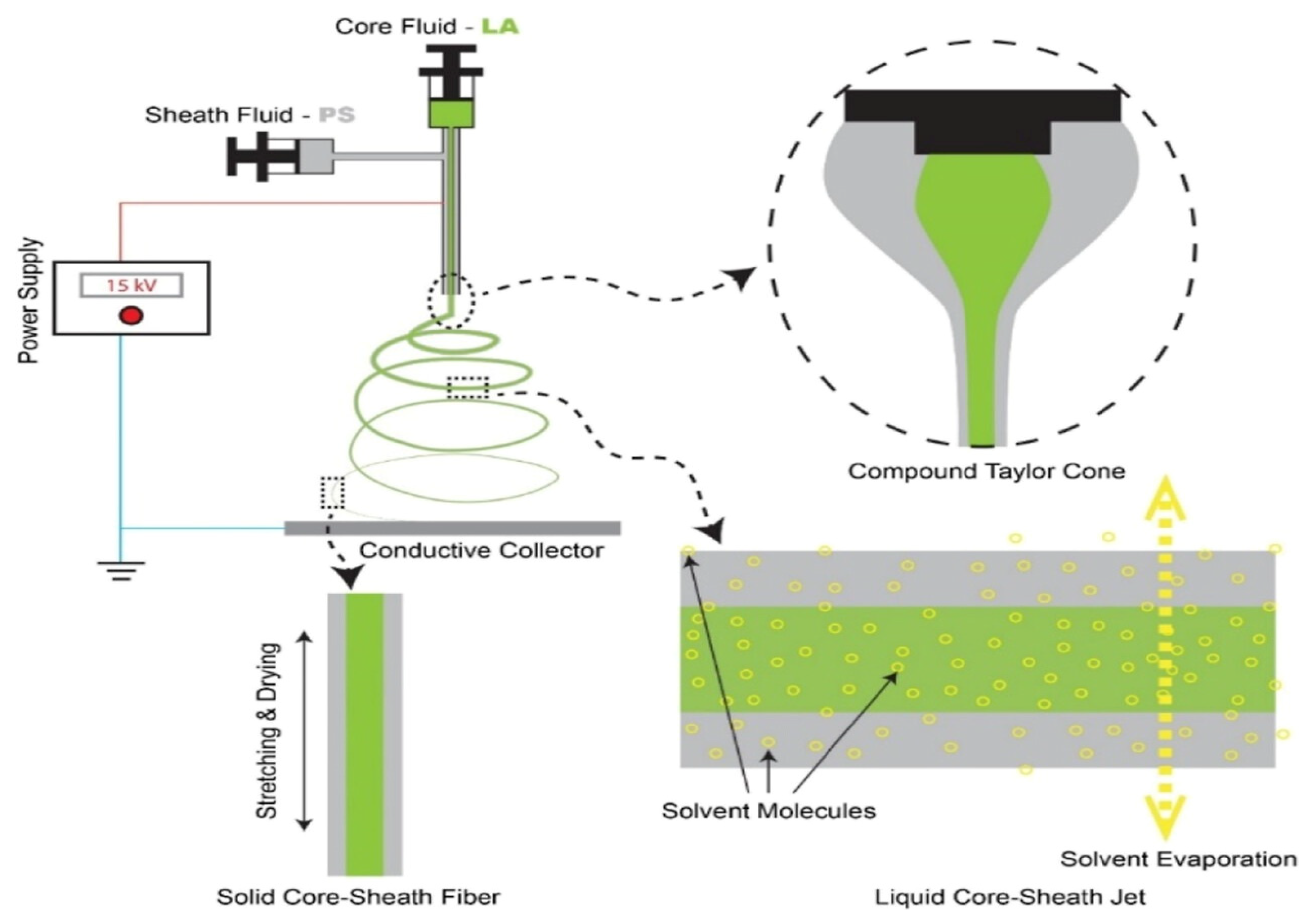
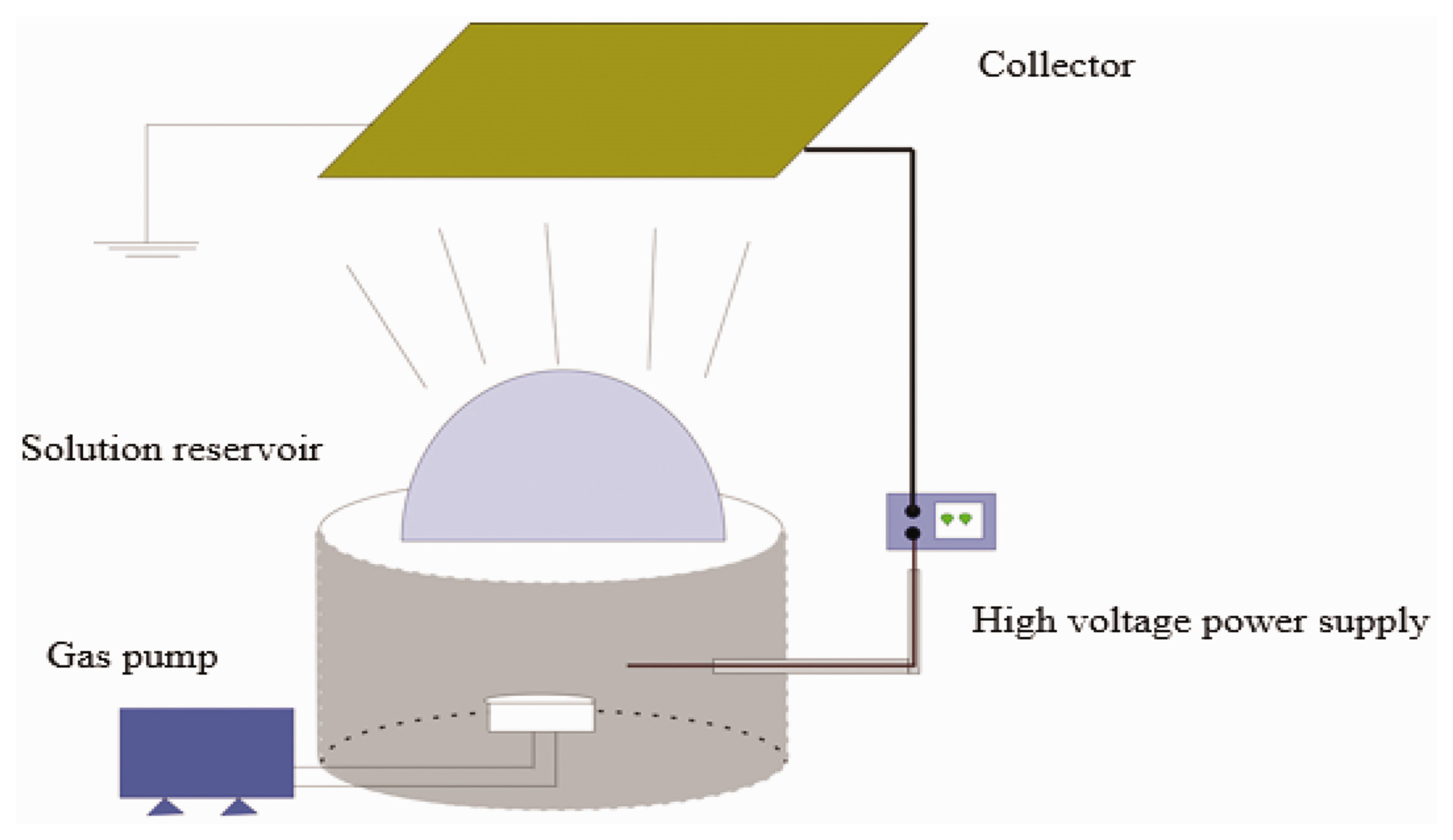
2.1. Electrospinning Principle
2.2. Electrospinning Classification
2.2.1. Coaxial Electrostatic Spinning
2.2.2. Side-by-Side Electrostatic Spinning
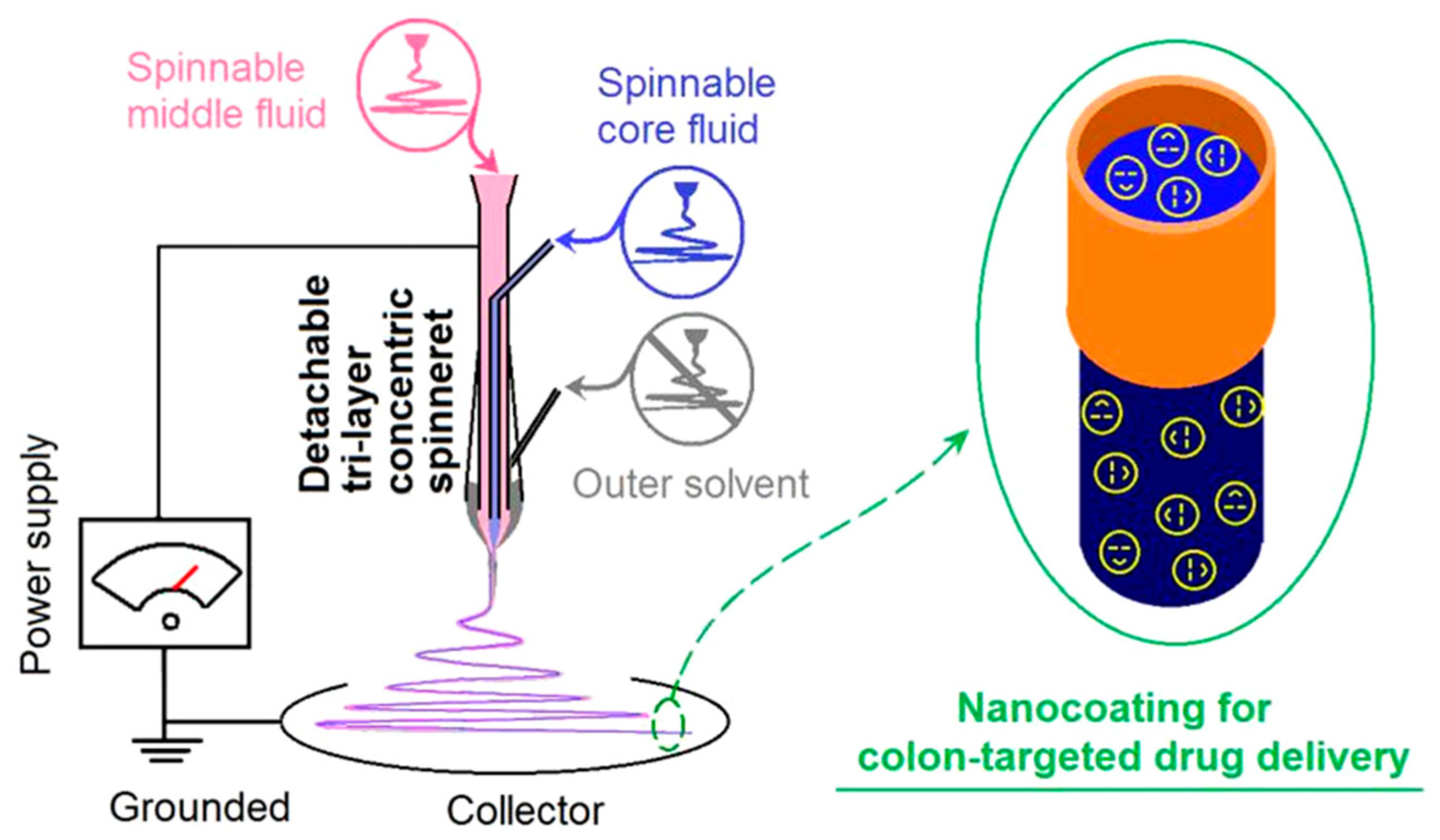
2.2.3. Triaxial Electrostatic Spinning
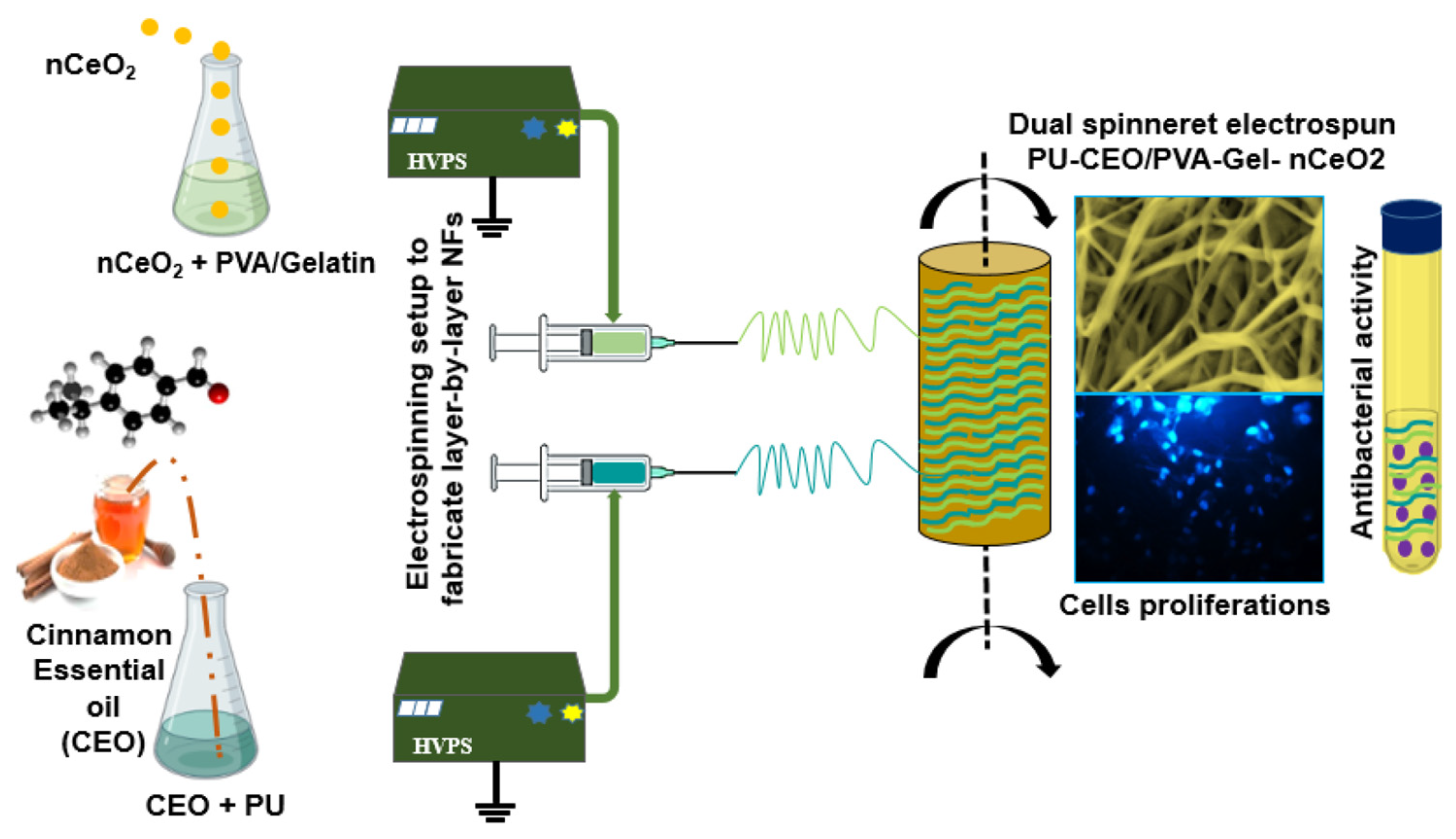
2.2.4. Multi-Nozzle Electrostatic Spinning
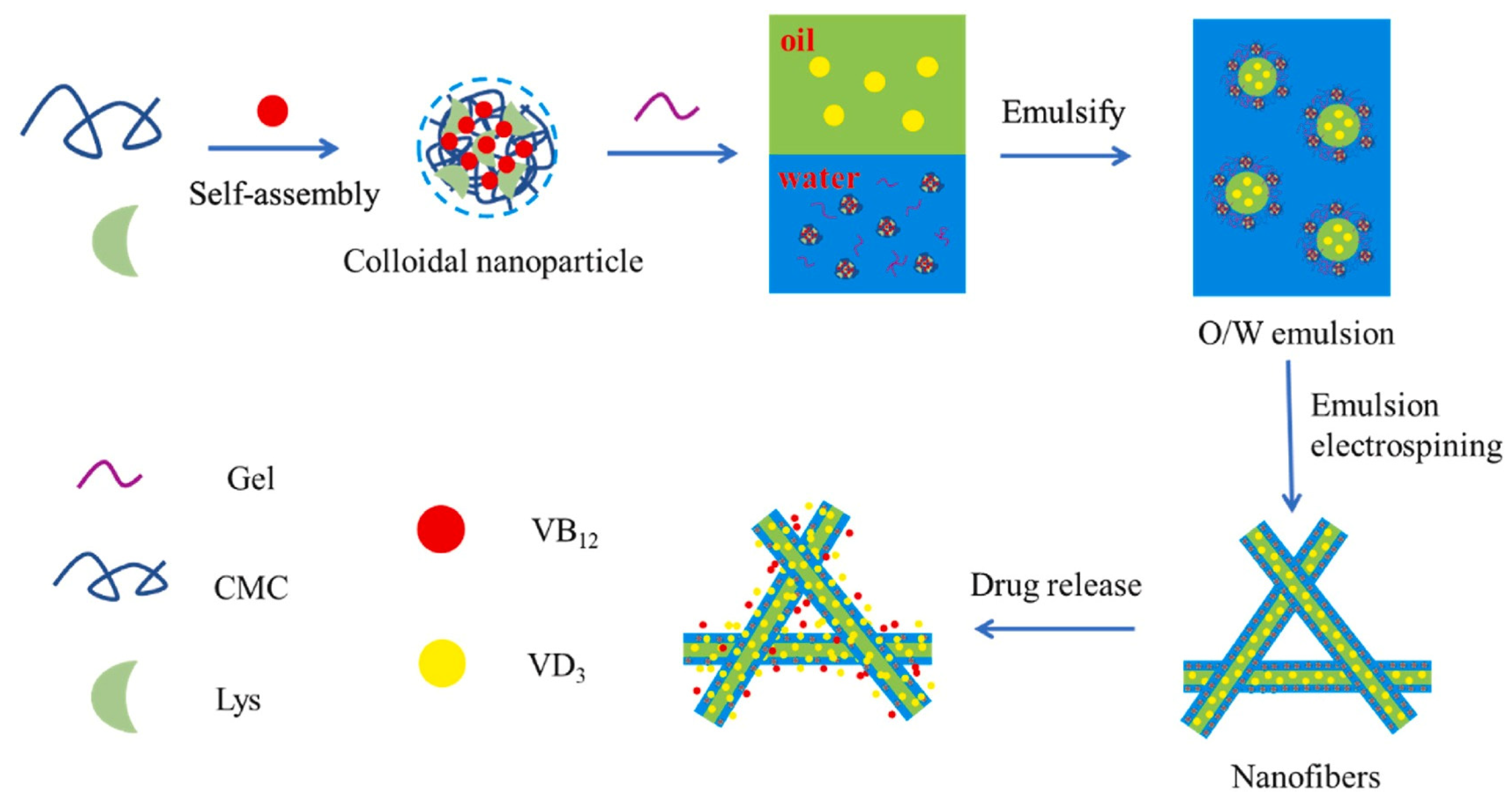
2.2.5. Emulsion Electrostatic Spinning
2.2.6. Bubble Electrospinning
3. Classification and Application of Nanofiber Membrane
4. Treatment of Dermatosis with Nanofiber Membrane
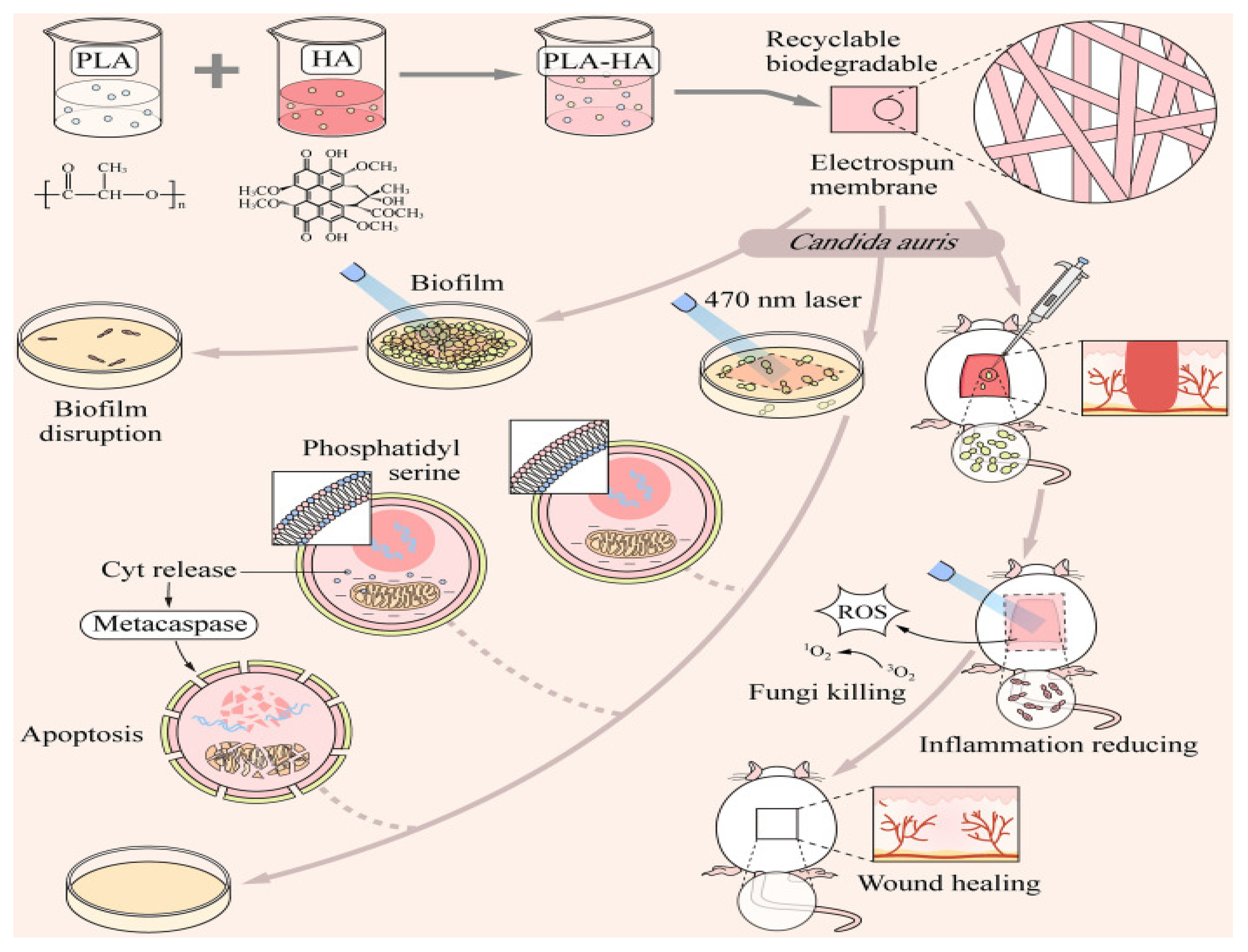
4.1. Mycosis
4.2. Skin Infection
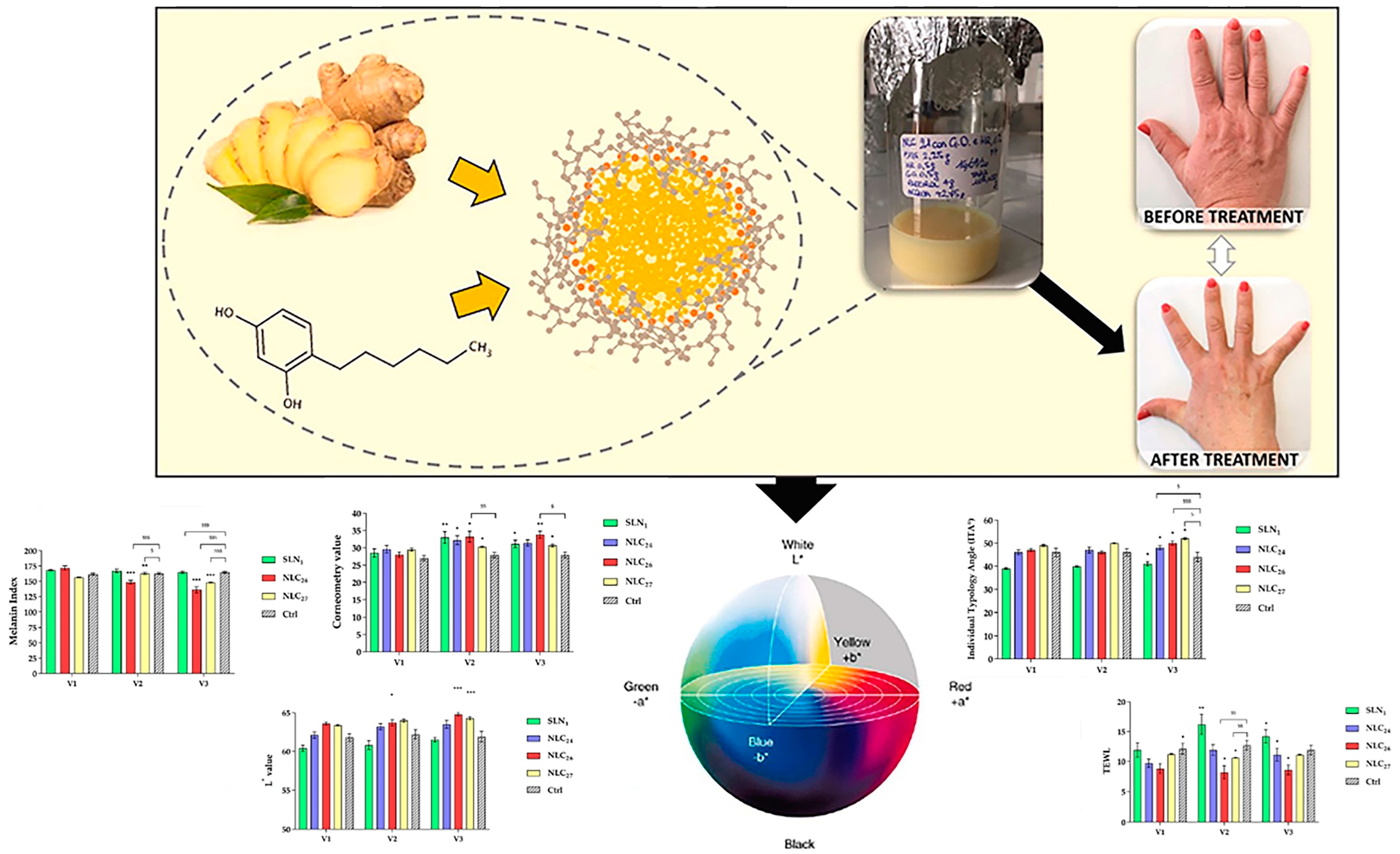
4.3. Cutaneous Pigmentation
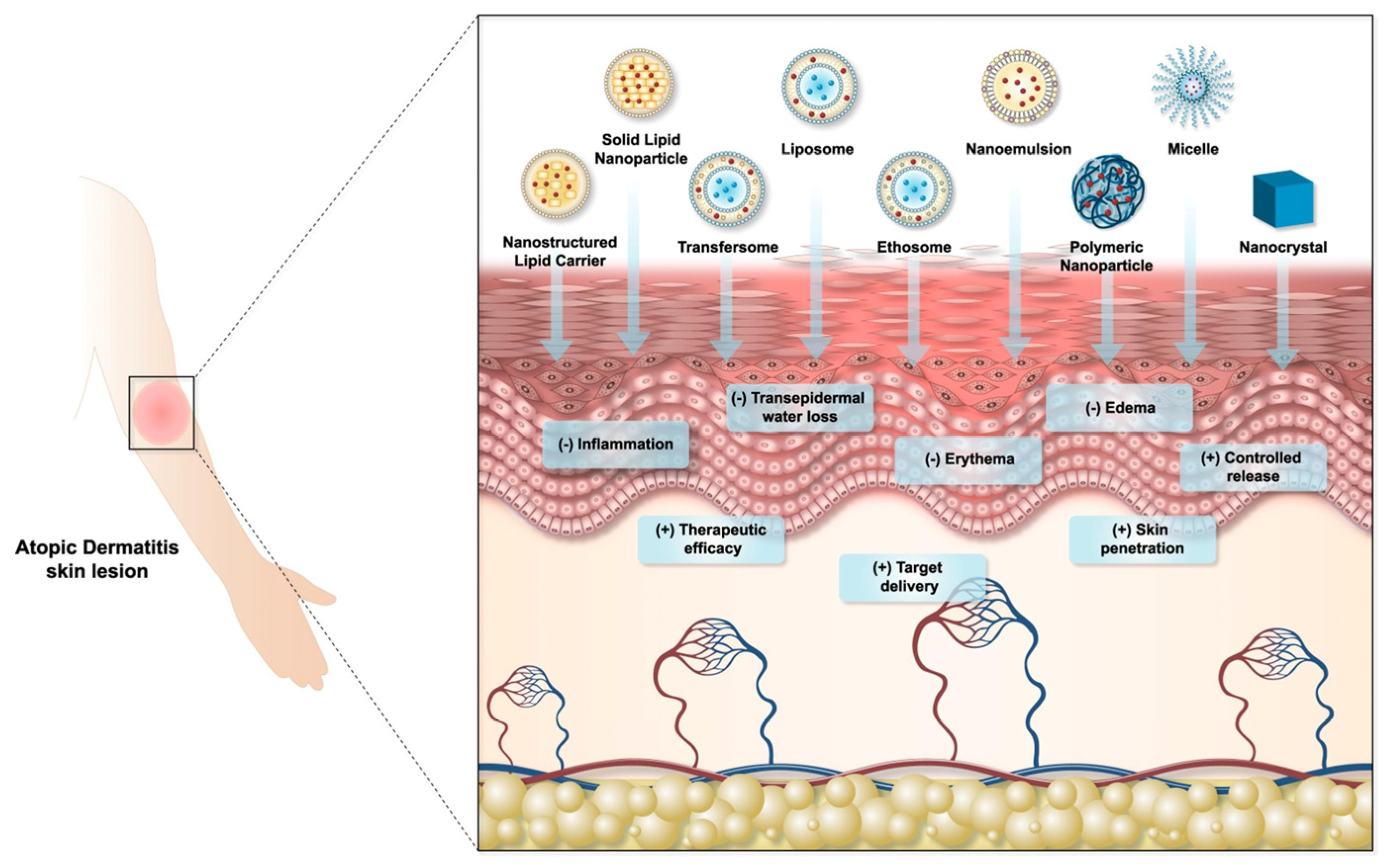
4.4. Atopic Dermatitis
4.5. Skin Cancer
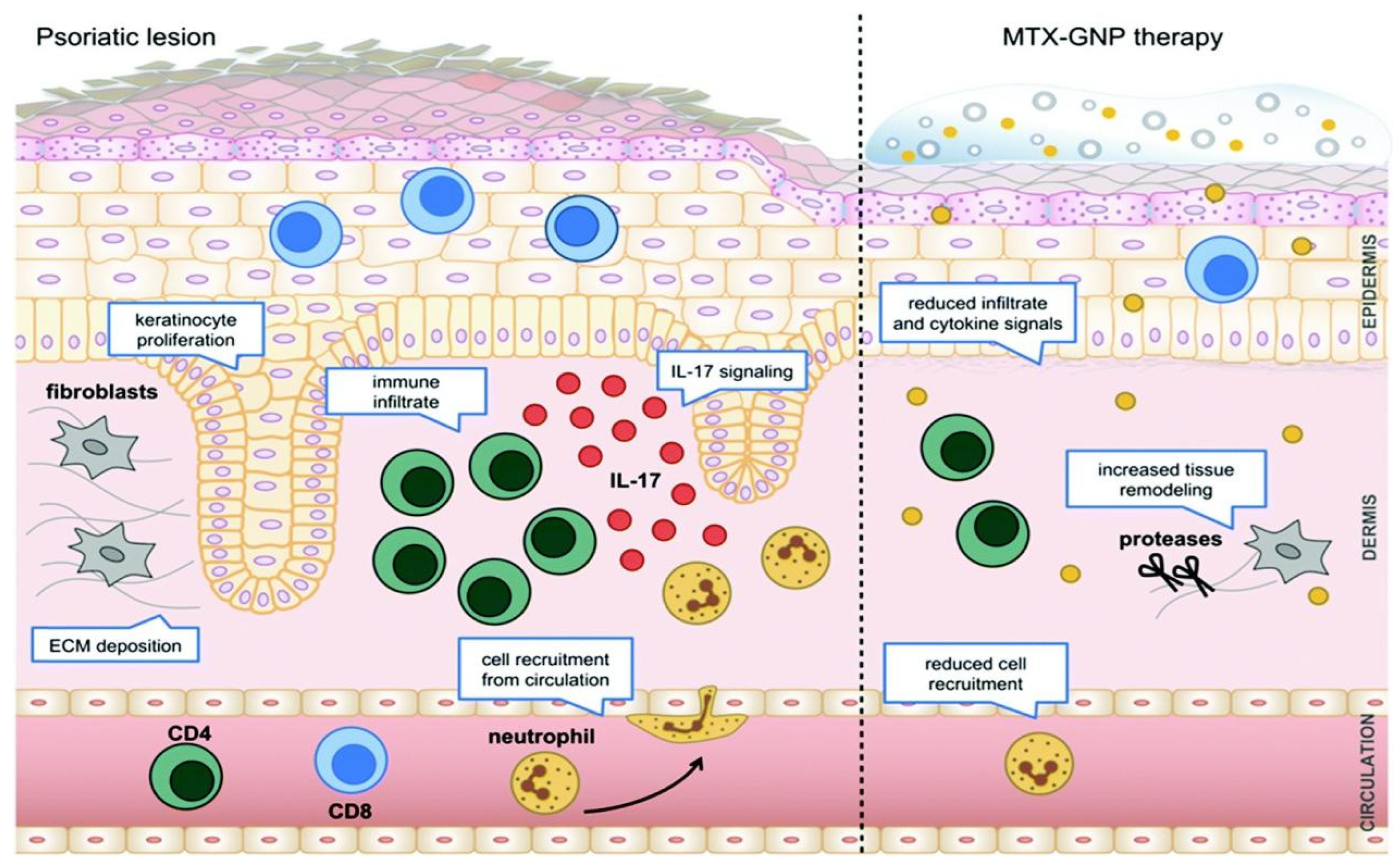
4.6. Psoriasis
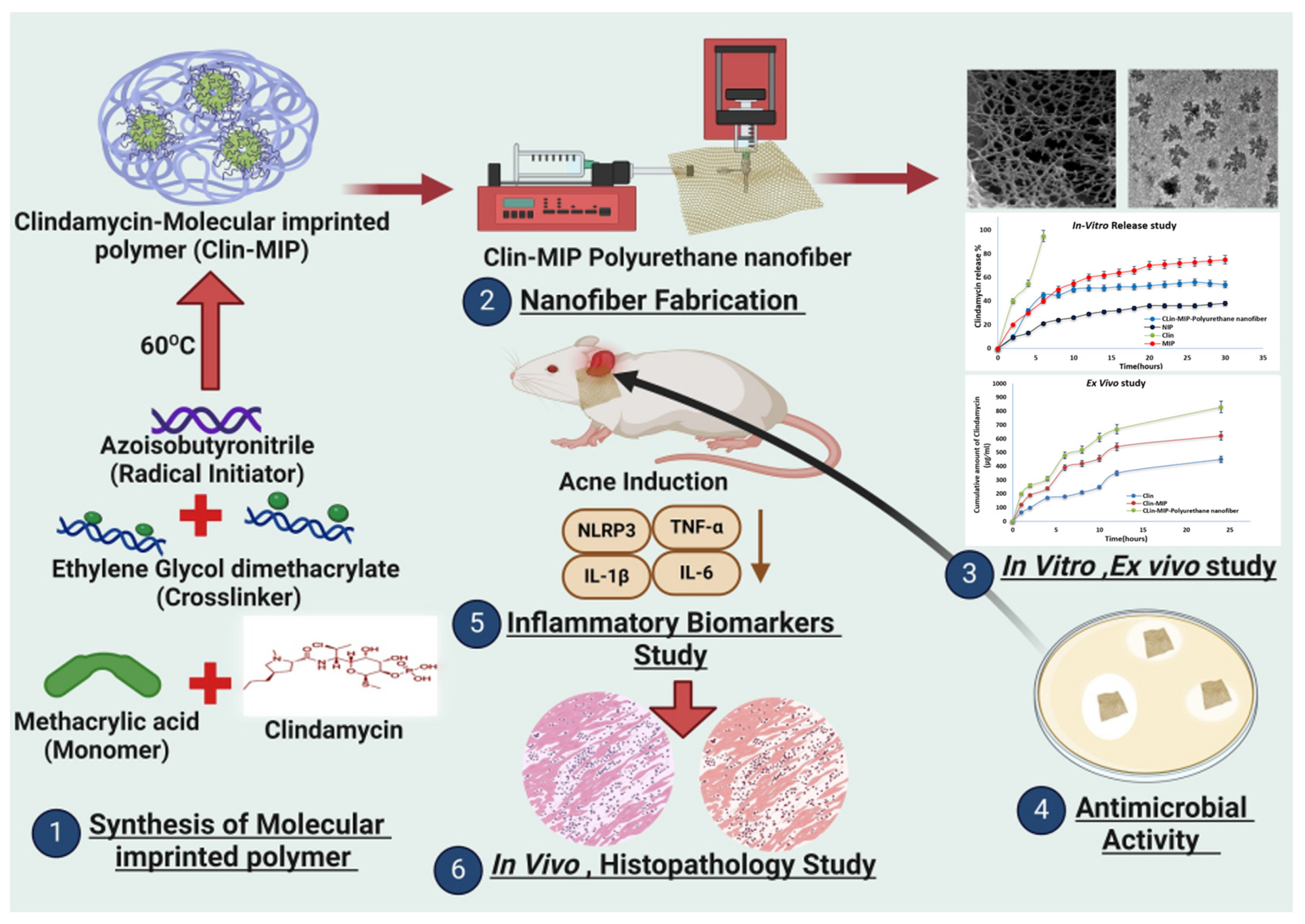
4.7. Acne
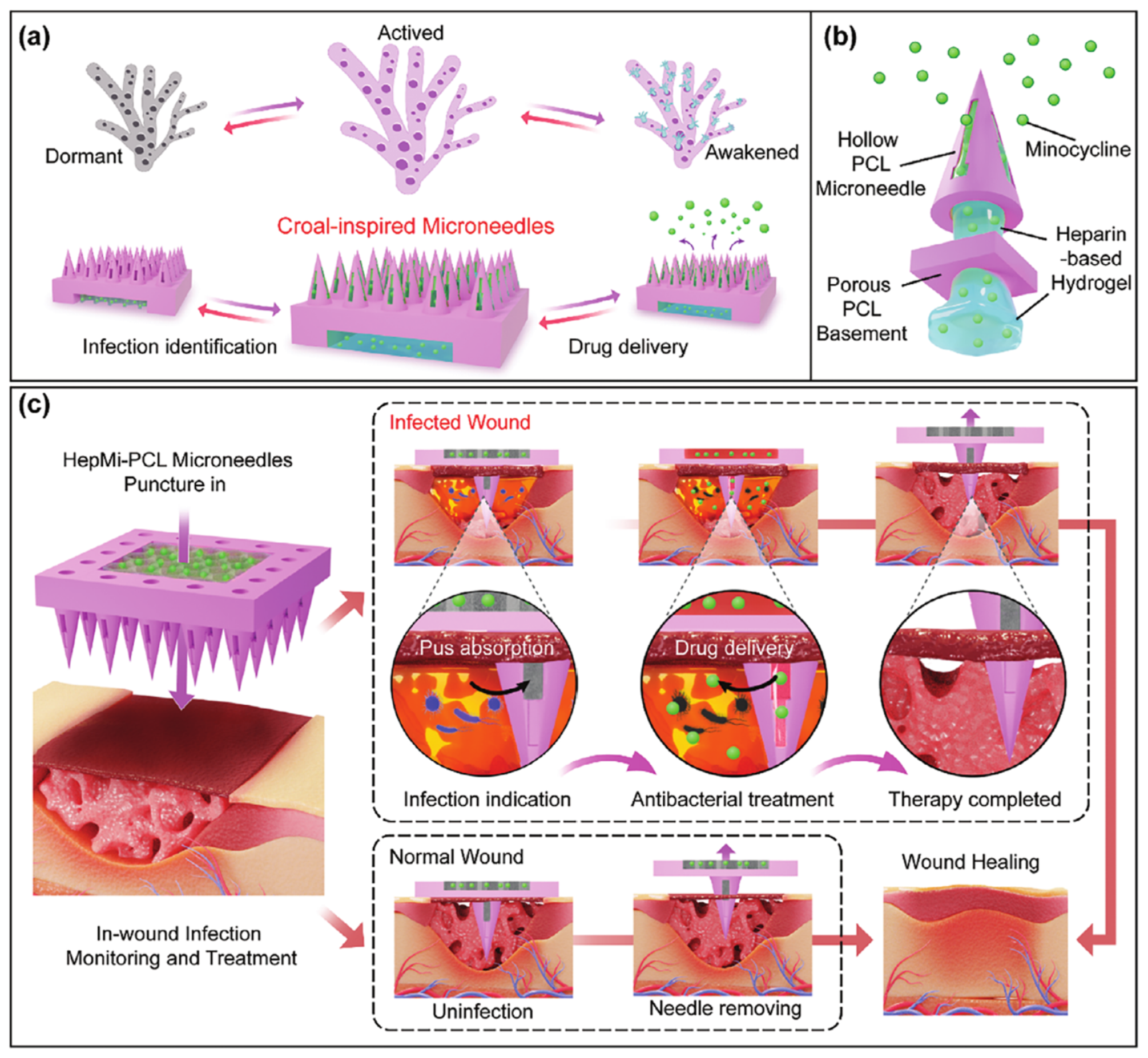
4.8. Wound
4.9. Other Diseases
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broughton, G.N.; Janis, J.E.; Attinger, C.E. The basic science of wound healing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 12S–34S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, I.; Alzahrani, A.R.; Alanazi, I.M.; Shahzad, N.; Shahid, I.; Falemban, A.H.; Azlina, M.; Arulselvan, P. Carbohydrate polymers-based surface modified nano delivery systems for enhanced target delivery to colon cancer—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, N.A.; Kumar, L. Treating colon cancers with a non-conventional yet strategic approach: An overview of various nanoparticulate systems. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 16–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latiyan, S.; Kumar, T.S.S.; Doble, M. Fabrication and evaluation of agarose-curdlan blend derived multifunctional nanofibrous mats for diabetic wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Wen, M.L.; Wei, Y.; Tang, T.T.; Yang, T.T.; Bai, H.T.; Guo, C.Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.C.; et al. Preparation of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan nanofibrous films incorporating graphene oxide and lanthanum chloride by electrospinning method for potential photothermal and chemical synergistic antibacterial applications in wound dressings. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 148, 106162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, C.; Hung, K.; Barveen, N.R.; Tseng, C.; Cheng, P.; Hardiansyah, A. Zwitterionic functional layer modified electrospun polyurethane nanofiber membrane incorporating silver nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial applications. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2024, 484, 130865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Huang, S.; Qin, X.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Ag nanoparticles-decorated pvdf nanofiber/net membranes with enhanced filtration and antibacterial efficiency for personal protective equipment. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 9252–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Du, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Incorporating nano-znco-zif particles in the electrospinning polylactide membranes to improve their filtration and antibacterial performances. Polym. Bull. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kalaaoui, K.; Boukhriss, A.; Bili, O.; Chaoui, M.A.; Majid, S.; El Hajaji, M.; Gmouh, S. Hybrid polyvinyl alcohol-silica antibacterial nanofiber fabricated by combined sol-gel and electrospinning techniques. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, N.; Sun, Y.; Shao, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Twebaze, C.B. Nanocellulose aerogels from banana pseudo-stem as a wound dressing. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 194, 116383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wei, Q.; Man, K.; Liang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Xin, H.; Yang, Y. Nanofibrous membrane promotes and sustains vascular endothelial barrier function. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 4988–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba Türk, E.; Demir, S.; Dan, Z.; Kahraman, M.V. Covalent immobilization of α-amylase onto thermally crosslinked electrospun pva/paa nanofibrous hybrid membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microfiber and multilayer nanofiber/microfiber scaffolds: Characterization of scaffolds and measurement of cellular infiltration. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2796–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliheidari, N.; Aliahmad, N.; Agarwal, M.; Dalir, H. Electrospun nanofibers for label-free sensor applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D. Preparing weathering-resistant superhydrophobic polymer/bentonite nano-composites for waterproof garment textiles via electrospinning. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 58, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, A.I.; Munir, M.M. Structure and morphology optimization of nanofiber membrane for the application of high-performance air filtration. Powder Technol. 2023, 430, 118978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosou, C.; Krokida, M.; Biliaderis, C.G. Encapsulation of β-carotene into food-grade nanofibers via coaxial electrospinning of hydrocolloids: Enhancement of oxidative stability and photoprotection. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant, antibacterial and antifungal electrospun nanofibers for food packaging applications. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsafi, S.R.; Rostamabadi, H.; Nishinari, K.; Amani, R.; Jafari, S.M. The role of emulsification strategy on the electrospinning of β-carotene-loaded emulsions stabilized by gum arabic and whey protein isolate. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Muthu Kumar, T.; Senthil Kumar, K.; Rajini, N.; Siengchin, S.; Ayrilmis, N.; Varada Rajulu, A. A comprehensive review of electrospun nanofibers: Food and packaging perspective. Composites Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senturk Parreidt, T.; Müller, K.; Schmid, M. Alginate-based edible films and coatings for food packaging applications. Foods 2018, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Chen, H.; Qi, C.; Lv, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. A novel electrospun nanofiber system with pegylated paclitaxel nanocrystals enhancing the transmucus permeability and in situ retention for an efficient cervicovaginal cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2024, 650, 123660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.; Liu, H. The applications of ferulic-acid-loaded fibrous films for fruit preservation. Polymers 2022, 14, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, F.; Yue, X.; Huang, C.; Zhao, S.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, C.; Qu, Y. Fabrication and characterization of PVA@PLA electrospinning nanofibers embedded with Bletilla striata polysaccharide and Rosmarinic acid to promote wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Yu, D.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z. Electrospun tri-layer nanodepots for sustained release of acyclovir. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 846, 156471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Zhou, J. How can electrospinning further service well for pharmaceutical researches? J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 2719–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yi, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, D.; Liu, P.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y. Electrospun janus core (ethyl cellulose//polyethylene oxide) @ shell (hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose acetate succinate) hybrids for an enhanced colon-targeted prolonged drug absorbance. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.; Liu, L. Tri-layer core–shell fibers from coaxial electrospinning for a modified release of metronidazole. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, D.M.; Chagas, P.A.M.; Leite, I.S.; Inada, N.M.; de Annunzio, S.R.; Fontana, C.R.; Campana-Filho, S.P.; Correa, D.S. Core-sheath nanostructured chitosan-based nonwovens as a potential drug delivery system for periodontitis treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Huang, C. Electrospun biomolecule-based drug delivery systems. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, Q.; Wan, J.; Yu, D.; Tan, F.; Yang, X. Improved synergistic anticancer action of quercetin and tamoxifen citrate supported by an electrospun complex nanostructure. Mater. Des. 2024, 238, 112657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liang, Z.; Guo, J.; Chen, B.; Zhou, S.; Yu, D. Application of electrospun drug-loaded nanofibers in cancer therapy. Polymers 2024, 16, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadisi, Z.; Farokhi, M.; Bakhsheshi Rad, H.R.; Jahanshahi, M.; Hasanpour, S.; Pagan, E.; Dolatshahi Pirouz, A.; Zhang, Y.S.; Kundu, S.C.; Akbari, M. Hyaluronic acid (HA)-based silk fibroin/zinc oxide core–shell electrospun dressing for burn wound management. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, e1900328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.A.M.; Gunduz, O.; Sahin, A.; Grinholc, M.; El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Megahed, M. Dual spinneret electrospun polyurethane/pva-gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds containing cinnamon essential oil and nanoceria for chronic diabetic wound healing: Preparation, physicochemical characterization and in-vitro evaluation. Molecules 2022, 27, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, M.A.; Nazeri, N.; Khoshnevisan, K.; Heshmat, R.; Omidfar, K. Three-layered pcl-collagen nanofibers containing melilotus officinalis extract for diabetic ulcer healing in a rat model. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Srivas, P.K.; Dadhich, P.; Das, B.; Maulik, D.; Dhara, S. Nano-/microfibrous cotton-wool-like 3d scaffold with core–shell architecture by emulsion electrospinning for skin tissue regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3563–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, F.; Rabiei Faradonbeh, D.; Malekshahi, Z.V.; Nekounam, H.; Ghaemi, B.; Yousefpoor, Y.; Ghanbari, H.; Faridi-Majidi, R. Hybrid pcl/chitosan-peo nanofibrous scaffolds incorporated with a. Euchroma extract for skin tissue engineering application. Carbohyd. Polym. 2022, 278, 118926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekren, N.; Karacan, C.E. Manufacturing of a portable electrospinning gun for biomedical applications. Rev. Romana De Mater. 2022, 52, 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.; Huang, J.; Luo, M.; Fang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wu, J.; Du, J. Near-field electrospun pcl fibers/gelma hydrogel composite dressing with controlled deferoxamine-release ability and retiform surface for diabetic wound healing. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, T.; Yan, Z.; Ji, D.; Li, J.; Pan, H. Preparation and evaluation of dual drug-loaded nanofiber membranes based on coaxial electrostatic spinning technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 629, 122410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.Y.; Boaretti, C.; Lorenzetti, A.; Martucci, A.; Roso, M.; Modesti, M. Effects of solvent and electrospinning parameters on the morphology and piezoelectric properties of pvdf nanofibrous membrane. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, B.S.; Yu, W.R. Recent progress in coaxial electrospinning: New parameters, various structures, and wide applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1704765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Wei, W.; Singh, H.; Xu, K.; Beck, C.; Wildy, M.; Schossig, J.; Hu, X.; Hyun, D.C.; Chen, W.; et al. Efficient and secure encapsulation of a natural phase change material in nanofibers using coaxial electrospinning for sustainable thermal energy storage. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 11570–11579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhao, H.; Muhammad, H.; Dong, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Chen, M. Dual-delivery of fgf-2/ctgf from silk fibroin/plcl-peo coaxial fibers enhances msc proliferation and fibrogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8509–8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaerkitcha, N.; Chuangchote, S.; Sagawa, T. Control of physical properties of carbon nanofibers obtained from coaxial electrospinning of pmma and pan with adjustable inner/outer nozzle-ends. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Wilkes, G.L. Some investigations on the fiber formation by utilizing a side-by-side bicomponent electrospinning approach. Polymer 2003, 44, 6353–6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J.Z. Electrospun janus zein–pvp nanofibers provide a two-stage controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs. Mater. Des. 2020, 196, 109075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Kang, S.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.; Wan, F.; Williams, G.R.; Bligh, S.A. Combination of structure-performance and shape-performance relationships for better biphasic release in electrospun janus fibers. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2021, 596, 120203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stie, M.B.; Gätke, J.R.; Chronakis, I.S.; Jacobsen, J.; Nielsen, H.M. Mucoadhesive electrospun nanofiber-based hybrid system with controlled and unidirectional release of desmopressin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Shen, H. Sheath-separate-core nanocomposites fabricated using a trifluid electrospinning. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagiah, N.; Murdock, C.J.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Nair, L.; Laurencin, C.T. Development of tripolymeric triaxial electrospun fibrous matrices for dual drug delivery applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Augustine, R.; Zaszczynska, A.; Barman, M.; Jain, A.; Hasan, A.; Kalarikkal, N.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Thomas, S. Novel drug delivery systems based on triaxial electrospinning based nanofibers. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 163, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Yu, D.; Liu, P. Elaborate design of shell component for manipulating the sustained release behavior from core-shell nanofibres. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Murugadoss, V.; Huang, M.; Yang, H.; Wan, F.; Yu, D.; Guo, Z. Electrospun structural nanohybrids combining three composites for fast helicide delivery. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Dou, C.; Chang, S.; Xie, Z.; Yu, D.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J. Core–shell eudragit s100 nanofibers prepared via triaxial electrospinning to provide a colon-targeted extended drug release. Polymers 2020, 12, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, P.; Kang, S.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D. Modified tri–axial electrospun functional core–shell nanofibrous membranes for natural photodegradation of antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Shi, J.; Xue, Y. Influence of electric field interference on double nozzles electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 3688–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehhudin, H.S.; Mohamad, E.N.; Mahadi, W.N.L.; Muhammad Afifi, A. Multiple-jet electrospinning methods for nanofiber processing: A review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.M.; Hohman, M.M.; Brenner, M.P.; Rutledge, G.C. Experimental characterization of electrospinning: The electrically forced jet and instabilities. Polymer 2001, 42, 9955–9967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, W.; Szadkowski, M. Investigation of electrospinning with the use of a multi-jet electrospinning head. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2005, 13, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, H.; Vineis, C.; Varesano, A.; Mowafi, S.; Taleb, M.A. A critique on multi-jet electrospinning: State of the art and future outlook. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2019, 8, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Bai, M.; Li, C.; Liu, R.; Lin, L. Fabrication of chitosan nanofibers containing tea tree oil liposomes against salmonella spp. In chicken. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 96, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J. Carrageenan/agar-based functional film integrated with zinc sulfide nanoparticles and pickering emulsion of tea tree essential oil for active packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Xu, B.; Xia, C.; Xu, M.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C. Dual drug-loaded core-shell nanofibers membranes via emulsion electrospinning and their controllable sustained release property. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2023, 88, 104909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanbakht, S.; Shaabani, A. Carboxymethyl cellulose-based oral delivery systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Tian, L.; Ding, X.; Ramakrishna, S. Drug-loaded emulsion electrospun nanofibers: Characterization, drug release and in vitro biocompatibility. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, A.O.; Castro, S.; Torres-Giner, S.; Lagaron, J.M.; Turkoglu Sasmazel, H. Novel poly(ε-caprolactone)/gelatin wound dressings prepared by emulsion electrospinning with controlled release capacity of ketoprofen anti-inflammatory drug. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 81, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, B.P.; Wei, M.X.; Shivashekaregowda, N.K.; Patnaik, S. Design, fabrication and characterization of pva/plga electrospun nanofibers carriers for improvement of drug delivery of gliclazide in type-2 diabetes. Proceedings 2020, 78, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Lee, S. Encapsulation of phytoncide in nanofibers by emulsion electrospinning and their antimicrobial assessment. Fiber. Polym. 2018, 19, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, J.; Xu, L.; Yu, J. Bubble-electrospinning for fabricating nanofibers. Polymer 2009, 50, 5846–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Dou, H. A modified yang-laplace equation for the bubble electrospinning considering the effect of humidity. Therm. Sci. 2013, 17, 629–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qian, M.; Li, Y. The maximal wrinkle angle during the bubble collapse and its application to the bubble electrospinning. Front. Mater. 2022, 8, 800567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Tian, D.; Zhou, B.Z.; Lu, Z.Q.; Wang, C.X. Last patents on bubble electrospinning. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 14, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; He, Z.; Han, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R. Structural design and environmental applications of electrospun nanofibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 137, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Zhu, J.; Long, Y. Preparation of arrayed helical micro/nanofibers by near-field electrospinning. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 25042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, Y. Control of bubble size and bubble number in bubble electrospinning. Comput. Math. Appl. 2012, 64, 1033–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Kong, H.; Yang, R.; Dou, H.; Faraz, N.; Wang, L.; Feng, C. Review on fiber morphology obtained by bubble electrospinning and blown bubble spinning. Therm. Sci. 2012, 16, 1263–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H. The smaller, the better: From the spider-spinning to bubble-electrospinning. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2012, 121, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; He, J.H. Bipolymer nanofibers: Engineering nanoscale interface via bubble electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e54878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, M. High-throughput preparation of silk fibroin nanofibers by modified bubble-electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.H.; Xu, L.; Yu, J.Y. The principle of bubble electrospinning and its experimental verification. J. Polym. Eng. 2008, 28, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Khan, T.; Basit, M.; Masood, R.; Raza, Z.A. Polyacrylonitrile-based electrospun nanofibers—A critical review. Materialwiss. Werkst. 2022, 53, 1575–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Li, Y.; He, J. Bubbfil spinning for mass-production of nanofibers. Therm. Sci. 2014, 18, 1718–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, J. Fabrication and characterization of zro2 nanofibers by critical bubble electrospinning for high-temperature-resistant adsorption and separation. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Kang, Z.; Che, X. Astragaloside/pvp/pla nanofiber functional dressing prepared by coaxial electrostatic spinning technology for promoting diabetic wound healing. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 210, 112950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monavari, M.; Sohrabi, R.; Motasadizadeh, H.; Monavari, M.; Fatahi, Y.; Ejarestaghi, N.M.; Fuentes-Chandia, M.; Leal-Egaña, A.; Akrami, M.; Homaeigohar, S. Levofloxacin loaded poly (ethylene oxide)-chitosan/quercetin loaded poly (d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) core-shell electrospun nanofibers for burn wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1352717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singaravelu, S.; Madhan, B.; Abrahamse, H.; Dhilip Kumar, S.S. Multifunctional embelin- poly (3-hydroxybutyric acid) and sodium alginate-based core-shell electrospun nanofibrous mat for wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 131128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, G.; Wang, C.; Yan, H. Sustained release of egf/bfgf growth factors achieved by mussel-inspired core–shell nanofibers with hemostatic and anti-inflammatory effects for promoting wound healing. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 190, 112003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Yusufu, R.; Guan, Z.; Chen, T.; Li, S.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lu, J.; Luo, M.; Wei, F. Multifunctional Bioactivity Electrospinning Nanofibers Encapsulating Emodin Provides a Potential Postoperative Management Strategy for Skin Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhaj, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Labbaf, S.; Emadi, R.; Marcus Seifalian, A.; Sharifianjazi, F. An antibacterial multi-layered scaffold fabricated by 3d printing and electrospinning methodologies for skin tissue regeneration. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2023, 645, 123357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Yu, D.; Bligh, S.A.; Lu, X. Electrospun multi-functional medicated tri-section janus nanofibers for an improved anti-adhesion tendon repair. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 492, 152359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zeng, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.; Wang, K. Preparation and investigation of cellulose acetate/gelatin janus nanofiber wound dressings loaded with zinc oxide or curcumin for enhanced antimicrobial activity. Membranes 2024, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Shen, J.; Tang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Yu, D. Engineered shellac beads-on-the-string fibers using triaxial electrospinning for improved colon-targeted drug delivery. Polymers 2023, 15, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Li, J.; Yu, D.; He, M.; Yang, J.; Williams, G.R. Nanosized sustained-release drug depots fabricated using modified tri-axial electrospinning. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, D.; Wang, G.; Williams, G.R.; Zhang, Z. Tunable drug release from nanofibers coated with blank cellulose acetate layers fabricated using tri-axial electrospinning. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 203, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram Rad, Z.; Mokhtari, J.; Abbasi, M. Preparation and characterization of calendula officinalis-loaded pcl/gum arabic nanocomposite scaffolds for wound healing applications. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadipour, M.; Karkhaneh, A.; Haghbin Nazarpak, M. An investigation into curcumin release from pla particles loaded in pcl-gelatin fibers for skin application. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2022, 71, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tören, E.; Mazari, A.A. Needless electrospun collagen/hyaluronic acid nanofibers for skin moisturization: Research. Polym. Advan. Technol. 2024, 35, e6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquer, A.; Kostakova, E.K.; Filova, E.; Lisnenko, M.; Broz, A.; Mullerova, J.; Novotny, V.; Havlickova, K.; Jakubkova, S.; Hauzerova, S.; et al. A novel bifunctional multilayered nanofibrous membrane combining polycaprolactone and poly (vinyl alcohol) enriched with platelet lysate for skin wound healing. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 1924–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouro, C.; Gomes, A.P.; Gouveia, I.C. Emulsion electrospinning of plla/pva/chitosan with hypericum perforatum l. As an antibacterial nanofibrous wound dressing. Gels 2023, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, F.; Ding, Z.; Zhu, B. Bletilla striata composite nanofibrous membranes prepared by emulsion electrospinning for enhanced healing of diabetic wounds. J. Biomater. Appl. 2023, 38, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Su, Z.; Zhang, S. Integration of Zn2+, atp, and bfgf to nanodressing with core–shell structure fabricated by emulsion electrospinning for wound healing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 3316–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Ren, G.; Li, B.; Li, D.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yue, W.; Yu, H.; Lu, D. Novel dry facial mask based on emulsion electrospinning. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 51, 104823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, C.; Zhuang, K.; Chen, W.; Zhang, M.; Dai, Y.; Tan, L.; Ran, Y.; Idnurm, A. A recyclable and light-triggered nanofibrous membrane against the emerging fungal pathogen candida auris. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ma, B.C.; Huang, W.; Kaltbeitzel, A.; Kizisavas, G.; Crespy, D.; Zhang, K.; Landfester, K. Visible light active nanofibrous membrane for antibacterial wound dressing. Nanoscale Horiz. 2018, 3, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Han, Y.; Tian, T.; Zhou, Q.; Yi, Z.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. Chinese sesame stick-inspired nano-fibrous scaffolds for tumor therapy and skin tissue reconstruction. Biomaterials 2019, 194, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severyukhina, A.N.; Petrova, N.V.; Yashchenok, A.M.; Bratashov, D.N.; Smuda, K.; Mamonova, I.A.; Yurasov, N.A.; Puchinyan, D.M.; Georgieva, R.; Baumler, H.; et al. Light-induced antibacterial activity of electrospun chitosan-based material containing photosensitizer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 70, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qin, S.; He, M.; Zhou, D.; Qin, Q.; Wang, H. Current applications of poly(lactic acid) composites in tissue engineering and drug delivery. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 199, 108238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore, L.; Inverardi, N.; Pandini, S.; Bignotti, F.; Chiellini, F. Pla/pcl-based foams as scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 7, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, Q.; Alishahi, M.; Davani, F.; Caravan, D.; Khorram, M.; Enjavi, Y.; Barzegar, S.; Esfandiari, F.; Zomorodian, K. Fabrication of amphotericin b-loaded electrospun core–shell nanofibers as a novel dressing for superficial mycoses and cutaneous leishmaniasis. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2021, 606, 120911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Fatease, A.; Alqahtani, A.; Khan, B.A.; Mohamed, J.M.M.; Farhana, S.A. Preparation and characterization of a curcumin nanoemulsion gel for the effective treatment of mycoses. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobus Berlitz, S.; Reginatto, P.; Machado, G.D.R.M.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Morisso, F.D.P.; Contri, R.V.; Külkamp-Guerreiro, I.C. Development of a clioquinol nanocarrier as a new, promising option for the treatment of dermatomycosis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-González, Y.; Prieto, C.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Lagarón, J.M. Development of antifungal electrospun nanofiber mats containing meyerozyma caribbica. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Steinkellner, S.; Feng, J. Deficiency of the melanin biosynthesis genes scd1 and thr1 affects sclerotial development and vegetative growth, but not pathogenicity, in sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.L.D.; Zilles, J.C.; Machado, A.U.; Marques, M.S.; Costa, B.S.D.; Guerreiro, I.C.K.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Contri, R.V. Polymeric nanocapsules containing ozonated oil and terbinafine hydrochloride as a potential treatment against dermatophytes. AAPS Pharmscitech. 2023, 24, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cela, E.M.; Urquiza, D.; Gómez, M.I.; Gonzalez, C.D. New weapons to fight against staphylococcus aureus skin infections. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Peng, S.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, R. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the bioactive nanofibers-encapsulated benzalkonium bromide for accelerating wound repair with mrsa skin infection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 4419–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, N.; Mehdipour, A.; Ghorbani, M.; Mesgari-Abbasi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Davaran, S. A novel multifunctional bilayer scaffold based on chitosan nanofiber/alginate-gelatin methacrylate hydrogel for full-thickness wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Wang, J. Selection of appropriate wound dressing for various wounds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heunis, T.D.J.; Smith, C.; Dicks, L.M.T. Evaluation of a nisin-eluting nanofiber scaffold to treat staphylococcus aureus-induced skin infections in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3928–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, K.S.; Jeong, L.; Lee, G.; Seo, B.; Park, Y.J.; Hong, S.; Roh, S.; Cho, J.J.; Park, W.H.; Min, B. Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers: Effects on the behavior of normal human keratinocytes and early-stage wound healing. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulker Turan, C.; Derviscemaloglu, M.; Guvenilir, Y. Enzymatically synthesized lactone-based copolymer and gelatin nanofibrous blends loaded with an olive leaf phenolic compound. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 108215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Shen, S.; Shi, H.; Yao, P.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Xu, R.X. Rational engineering of dual drug-formulated multifunctional microneedles to accelerate in vivo cutaneous infection treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.A. Diseases caused by arthropods and other noxious animals. In Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology; Burns, T., Breathnach, S., Cox, N., Griffiths, C., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bossche, K.; Naeyaert, J.M.; Lambert, J. The quest for the mechanism of melanin transfer. Traffic 2006, 7, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, S.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Chemical and instrumental approaches to treat hyperpigmentation. Pigment. Cell Res. 2003, 16, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzella, L.; Ebato, A.; Napolitano, A.; Koike, K. The late stages of melanogenesis: Exploring the chemical facets and the application opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.; Garcia-Carmona, F. 4-substituted resorcinols (sulfite alternatives) as slow-binding inhibitors of tyrosinase catecholase activity. J. Agr. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2061–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salea, R.; Veriansyah, B.; Tjandrawinata, R.R. Optimization and scale-up process for supercritical fluids extraction of ginger oil from zingiber officinale var. Amarum. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 120, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, G.; Di Muzio, L.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Laneri, S.; Cairone, F.; Cesa, S.; Petralito, S.; Paolicelli, P.; Casadei, M.A. Dual delivery of ginger oil and hexylresorcinol with lipid nanoparticles for the effective treatment of cutaneous hyperpigmentation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2023, 87, 104790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, K.; Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Akbari, J.; Hedayatizadeh-Omran, A. A promising and effective platform for delivering hydrophilic depigmenting agents in the treatment of cutaneous hyperpigmentation: Kojic acid nanostructured lipid carrier. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2021, 49, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, M.; Eslamifar, M.; Khezri, K. Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atapour-Mashhad, H.; Tayarani-Najaran, Z.; Golmohammadzadeh, S. Preparation and characterization of novel nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) and solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) containing coenzyme Q10 as potent antioxidants and antityrosinase agents. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Xing, M.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y. Clinical development and evaluation of a multi-component dissolving microneedle patch for skin pigmentation disorders. Polymers 2023, 15, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, Z.J.; Stachewicz, U. Electrospun fibers as carriers for topical drug delivery and release in skin bandages and patches for atopic dermatitis treatment. Wiley Interdiscip. Reviews. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2023, 15, e1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, G.; Rad, A.N.; Safdarian, M.; Rezaie, A.; Bavarsad, N.; Abbaspour, M. Self-microemulsification-assisted incorporation of tacrolimus into hydrophilic nanofibers for facilitated treatment of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene induced atopic dermatitis like lesions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2021, 62, 102326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroczyk, E.A.; Berniak, K.; Jaszczur, M.; Stachewicz, U. Topical electrospun patches loaded with oil for effective gamma linoleic acid transport and skin hydration towards atopic dermatitis skincare. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semnani, D.; Nasari, M.; Fakhrali, A. Pcl nanofibers loaded with beta-carotene: A novel treatment for eczema. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, R.; Shameh, A.A.; Aljarrah, M.; Hamed, R. Preparation and evaluation of polyvinylpyrrolidone electrospun nanofiber patches of pioglitazone for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Gama, M.; Peixoto, D.; Sousa-Oliveira, I.; Ferreira-Faria, I.; Zeinali, M.; Abbaspour-Ravasjani, S.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Hamishehkar, H.; Veiga, F. Nanocarrier-based dermopharmaceutical formulations for the topical management of atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 618, 121656, Erratum in Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2022, 627, 122146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Dubey, S.K.; Singhvi, G. The hedgehog pathway and its inhibitors: Emerging therapeutic approaches for basal cell carcinoma. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janani, I.; Lakra, R.; Kiran, M.S.; Korrapati, P.S. Selectivity and sensitivity of molybdenum oxide-polycaprolactone nanofiber composites on skin cancer: Preliminary in-vitro and in-vivo implications. J. Trace Elem. Med. Bio. 2018, 49, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengifo, A.F.C.; Stefanes, N.M.; Toigo, J.; Mendes, C.; Argenta, D.F.; Dotto, M.E.R.; Santos Da Silva, M.C.; Nunes, R.J.; Caon, T.; Parize, A.L.; et al. Peo-chitosan nanofibers containing carboxymethyl-hexanoyl chitosan/dodecyl sulfate nanoparticles loaded with pyrazoline for skin cancer treatment. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 119, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Yang, Z.; Shi, H.; Turki Jalil, A.; Mahmood Saleh, M.; Mi, W. Potentiation of curcumin-loaded zeolite y nanoparticles/pcl-gelatin electrospun nanofibers for postsurgical glioblastoma treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2023, 80, 104105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.F.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, J.; Yao, Y.; Ahmad, Z.; Chang, M.W. A novel core-shell nanofiber drug delivery system intended for the synergistic treatment of melanoma. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Self-heating multistage microneedle patch for topical therapy of skin cancer. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2308217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaj, S.M.; Kashem, T.B.; Ferdous, J.; Jahan, I.; Rawshan, H.; Prionty, N.J.; Rakib, R.; Sadman, M.A.; Faruk, H.B.; Reza, H.M.; et al. Skin cancer treatment with subcutaneous delivery of doxorubicin-loaded gelatin nanoparticles and nir activation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, Y.; Gorantla, S.; Singhvi, G. Insight into the pivotal role of signaling pathways in psoriasis pathogenesis, potential therapeutic molecules and drug delivery approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapalli, V.K.; Sharma, S.; Roy, A.; Singhvi, G. Design and dermatokinetic evaluation of apremilast loaded nanostructured lipid carriers embedded gel for topical delivery: A potential approach for improved permeation and prolong skin deposition. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 206, 111945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; See, L.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Tsou, T.C.; Lin, T.Y.; Lin, N.L. Efficacy and safety of indigo naturalis extract in oil (lindioil) in treating nail psoriasis: A randomized, observer-blind, vehicle-controlled trial. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Gao, J.; Guo, S.; Liu, H.; Cao, C.; Hong, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Xiao, W.; Song, P.; et al. Benefits of topical indigo naturalis nanofibrous patch on psoriatic skin: A transdermal strategy for botanicals. Mater Today Bio 2023, 22, 100756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ortega, L.; Mira, A.; Fernandez-Carvajal, A.; Mateo, C.R.; Mallavia, R.; Falco, A. Development of a new delivery system based on drug-loadable electrospun nanofibers for psoriasis treatment. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrýsková, N.; Sourivong, P.; Babincová, M.; Šimaljaková, M. Controlled release of tazarotene from magnetically responsive nanofiber patch: Towards more efficient topical therapy of psoriasis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, A.; Sahin, D.; Impellizzieri, D.; Nguyen, T.T.; Hafner, J.; Yawalkar, N.; Kurzbach, D.; Tan, G.; Akdis, C.A.; Nilsson, J.; et al. Nanoparticle-coupled topical methotrexate can normalize immune responses and induce tissue remodeling in psoriasis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, C.F.P.; Kilian, M. The natural history of cutaneous propionibacteria, and reclassification of selected species within the genus propionibacterium to the proposed novel genera acidipropionibacterium gen. Nov., Cutibacterium gen. Nov. And pseudopropionibacterium gen. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2016, 66, 4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrani, M.; Pourshamohammad, S.; Tabibiazar, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Mahmoudzadeh, M. Antimicrobial activity and stability of satureja khuzestanica essential oil pickering emulsions stabilized by starch nanocrystals and bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, S.; Gholizadeh, S.; Ebrahimi, A.; Almasi, H.; Hamishehkar, H.; Taheri, R.A. Development and characterization of the carvone-loaded zein/pullulan hybrid electrospun nanofibers for food and medical applications. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 183, 114964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Oh, S.; Huining, X.; Xiao, H. Antiacne effects of pva/zno composite nanofibers crosslinked by citric acid for facial sheet masks. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 2022, 4694921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama, S.; Movaffagh, J.; Shahroodi, A.; Jirofti, N.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S.; Beyraghdari, M.; Hashemi, M.; Kalalinia, F. Development and characterization of the electrospun melittin-loaded chitosan nanofibers for treatment of acne vulgaris in animal model. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 52, 15280837221112410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihova, M.; Cihalova, K.; Pouzar, M.; Kuthanova, M.; Jelinek, L.; Hromadko, L.; Cicmancova, V.; Heger, Z.; Macak, J.M. Biopolymeric fibers prepared by centrifugal spinning blended with zno nanoparticles for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 37, 102151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tören, E.; Mazari, A.A.; Buzgo, M. Exploring the efficacy of aha–bha infused nanofiber skin masks as a topical treatment for acne vulgaris. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhabal, S.F.; Abdelmonem, R.; El Nashar, R.M.; Elrefai, M.F.M.; Hamdan, A.M.E.; Safwat, N.A.; Shoela, M.S.; Hassan, F.E.; Rizk, A.; Kabil, S.L.; et al. Enhanced antibacterial activity of clindamycin using molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles loaded with polyurethane nanofibrous scaffolds for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Sun, X.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Fu, X.; Leong, K.W. Advanced drug delivery systems and artificial skin grafts for skin wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2019, 146, 209–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eming, S.A.; Martin, P.; Tomic-Canic, M. Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 265s–266s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Bai, X.; Yuan, Z.; Cao, X.; Jiao, X.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X. Layered nanofiber sponge with an improved capacity for promoting blood coagulation and wound healing. Biomaterials 2019, 204, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Tamayol, A.; Mostafalu, P.; Akbari, M.; Comotto, M.; Annabi, N.; Ghaderi, M.; Sonkusale, S.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Khademhosseini, A. Dermal patch with integrated flexible heater for on demand drug delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liang, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Two-pronged strategy of biomechanically active and biochemically multifunctional hydrogel wound dressing to accelerate wound closure and wound healing. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 9937–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Cheng, J.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y. Janus amphiphilic nanofiber membranes synergistically drive antibacterial and anti-inflammatory strategies for skin wound healing. Mater. Des. 2023, 227, 111778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Derayat, P.; Pourmanouchehri, Z.; Kahrarian, M.; Samimi, Z.; Hajialyani, M.; Bahrami, G.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Rashidi, K.; Tajehmiri, A.; et al. Characterization and evaluation of antibacterial and wound healing activity of naringenin-loaded polyethylene glycol/polycaprolactone electrospun nanofibers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2023, 81, 104182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Yao, G. Electrospinning/3d printing drug-loaded antibacterial polycaprolactone nanofiber/sodium alginate-gelatin hydrogel bilayer scaffold for skin wound repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 129705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, C.; Qiao, T.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Wan, Q.; Zhu, Z.; He, Y. Coral-inspired hollow microneedle patch with smart sensor therapy for wound infection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2314071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Jia, Y.; Qin, C.; Zhan, L.; Yan, X.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Long, Y. In situ deposition of a personalized nanofibrous dressing via a handy electrospinning device for skin wound care. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3482–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.R. Wound healing in older adults. Aging Health 2009, 5, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassiba, A.J.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Webster, T.J.; Luyt, A.S.; Abdullah, A.M.; Elzatahry, A.A. Review of recent research on biomedical applications of electrospun polymer nanofibers for improved wound healing. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 715–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haik, J.; Kornhaber, R.; Blal, B.; Harats, M. The feasibility of a handheld electrospinning device for the application of nanofibrous wound dressings. Adv. Wound Care 2017, 6, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, D.; Gupta, B. Dextran based herbal nanobiocomposite membranes for scar free wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J. Control Release 2014, 185, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, M.; Khorrami, M.; Yi, N.; Majd, S.; Abidian, M.R. Electrospinning of highly aligned fibers for drug delivery applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolsky-Papkov, M.; Agashi, K.; Olaye, A.; Shakesheff, K.; Domb, A.J. Polymer carriers for drug delivery in tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2007, 59, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwan, J.; Kumar, N.; Sharma, Y. Fabrication, characterization, and optimization of mn x o y nanofibers for improved supercapacitive properties. Nanomater. Synth. 2019, 13, 451–481. [Google Scholar]

| Types of Electrostatic Spinning Technology | Carbohydrate Types | Superiority | Treatment of Dermatosis Category | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coaxial electrostatic spinning | Specific protein polymer | Has higher cell proliferation efficiency; can change the surface characteristics; multi-system solution spinning; can easily manufacture nanofibers; easy to operate; excellent material handling ability; | Skin burning | [34] |
| Side-by-side electrostatic spinning | Synthetic polymer | The two solutions can be blended, and the release effect in vitro is remarkable; productivity can be improved. | Diabetic wound | [35] |
| Triaxial electrostatic spinning | Synthetic polymer | Able to build complex drug control system; promote the dissolution and penetration of drugs with poor water solubility in the model. | Diabetic ulcer | [36] |
| Emulsion electrostatic spinning | polysaccharide | Easy to process and control; suitable for delivering hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs. | Skin wound | [37] |
| Multi-nozzle electrostatic spinning | polysaccharide | Manufactures large nanofibers to increase yield and coverage. | Skin wound | [38] |
| Portable electrostatic spinning | Synthetic polymer | Flexible use; in situ spinning; higher voltage; accuracy of voltage and flow; safe use; precise deposition | Skin burning | [39] |
| Near-field electrostatic spinning | Synthetic polymer | Combining biological 3D printing with traditional disordered electrospinning technology, highly ordered ultrafine fibers can be prepared. | Diabetic wound | [40] |
| Classify | Type | Medicine Carrying | Main Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coaxial electrostatic spinning | PVP/PLA nanofibers | Astragaloside iv | Promote the healing of diabetic wounds | [86] |
| PEO-CS-LEV/PLGA-QS core–shell nanofibers | Levofloxacin | Used for burn wound healing | [87] | |
| PHB+SAL-PEO core–shell nanofiber mat | Embelin | Wound healing | [88] | |
| PCL shell and DOPA coating | Double growth factor (EGF/bFGF) | Wound healing | [89] | |
| PVP core layer combined with CS-PCL as shell layer. | rheum emodin | Skin cancer | [90] | |
| Side-by-side electrostatic spinning | Core–shell nanofibers of F127-Mup/Pec-Kr | Mupirocin | Wound dressing | [91] |
| Multifunctional medicinal three-segment Janus nanofiber | Beeswax, Quercetin and Ketoprofen | Anti-adhesion repair of tendon | [92] | |
| Janus nanofibers | Zinc oxide nanoparticles and curcumin | Wound dressing | [93] | |
| Triaxial electrostatic spinning | Beaded (BOTS) microfibers | CURcumin | Improve colon-targeted drug delivery | [94] |
| Cellulose acetate | Ferulic acid | Drug delivery | [95] | |
| Core–shell nanofibers (CSF) of Eudragit S100 (ES100) | Aspirin | Colon targeting prolongs drug release | [56] | |
| Protein nanocomposites-a drug coated with cellulose acetate | Ibuprofen | Regulating drug release | [96] | |
| Multi-nozzle electrostatic spinning | Poly ε-caprolactone (PCL), zein and gum Arabic (GA) | C. officinalis | Skin tissue engineering | [97] |
| PCL/gelatin nanofibers | CURcumin | Skin application | [98] | |
| Polycaprolactone/chitosan-polyethylene oxide (PCL/Cs-PEO) | A. euchroma | Application of skin tissue engineering | [38] | |
| Needle-free electrostatic spinning | Collagen/hyaluronic acid nanofibers | Collagen | Skin moisturizing | [99] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) and poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) nanofibers (PCL-PVA) | Platelet lysate | Chronic wound | [100] | |
| Emulsion electrostatic spinning | Poly (L-lactic acid) (PLLA)/poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA)/chitosan (CS) | Hypericum perforatum | Wound dressing | [101] |
| PLA nanofiber membrane | Bletilla tuber | Diabetic wound | [102] | |
| bFGF-ATP-Zn/PCL nano-dressing | Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) | Relieve wounds and scars | [103] | |
| PVA/RES/PR nano-materials | Resveratrol | Skin moisturizing mask | [104] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Wei, H.; Ding, Q.; Ding, C.; Zhang, S. Advances in Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Dermatological Applications: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 4271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174271
Han Y, Wei H, Ding Q, Ding C, Zhang S. Advances in Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Dermatological Applications: A Review. Molecules. 2024; 29(17):4271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174271
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yuanyuan, Hewei Wei, Qiteng Ding, Chuanbo Ding, and Shuai Zhang. 2024. "Advances in Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Dermatological Applications: A Review" Molecules 29, no. 17: 4271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174271
APA StyleHan, Y., Wei, H., Ding, Q., Ding, C., & Zhang, S. (2024). Advances in Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Dermatological Applications: A Review. Molecules, 29(17), 4271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174271







