Facile Fabrication of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8@Regenerated Cellulose Nanofibrous Membranes for Effective Adsorption of Tetracycline Hydrochloride
Abstract
1. Introduction
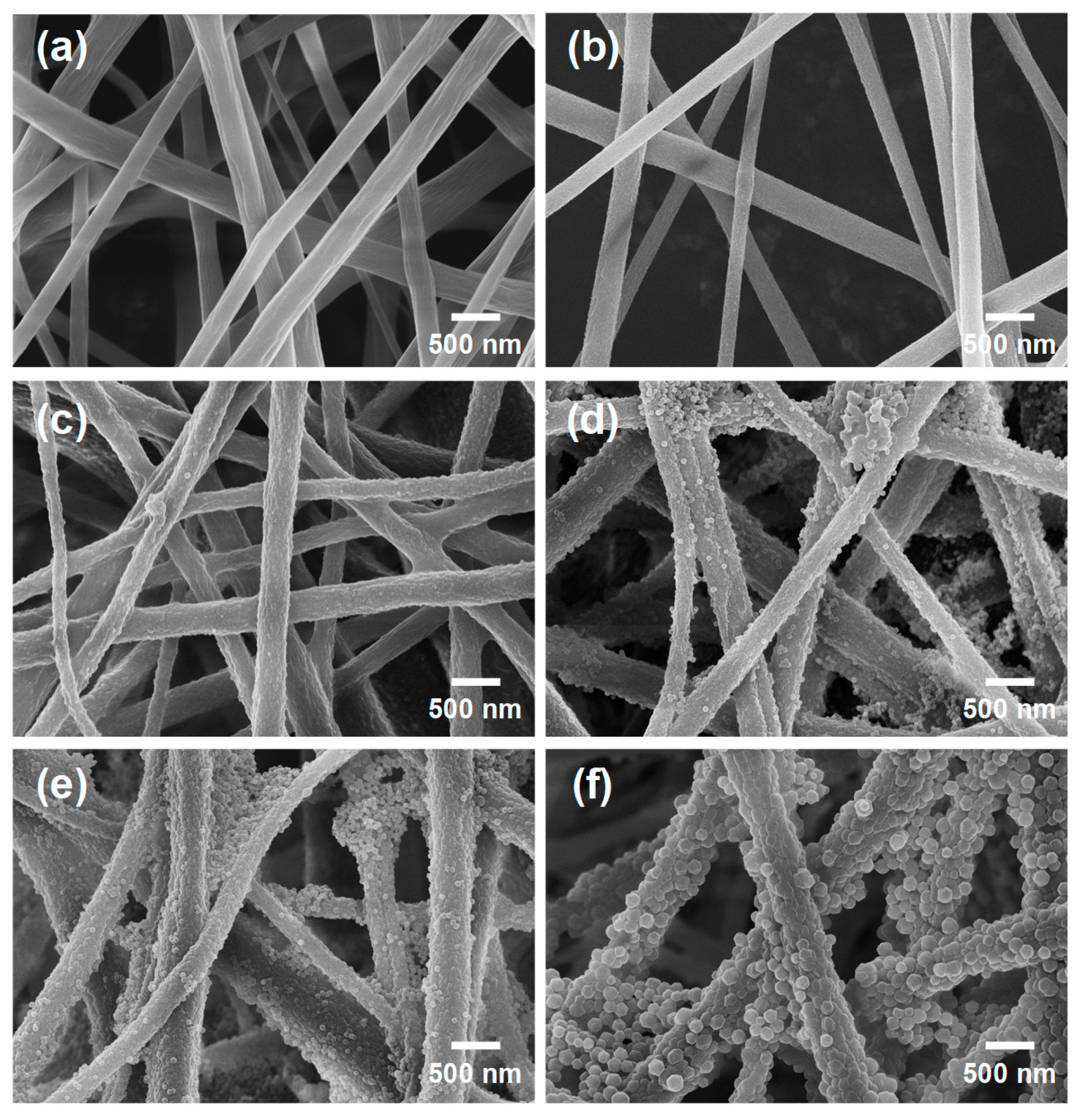
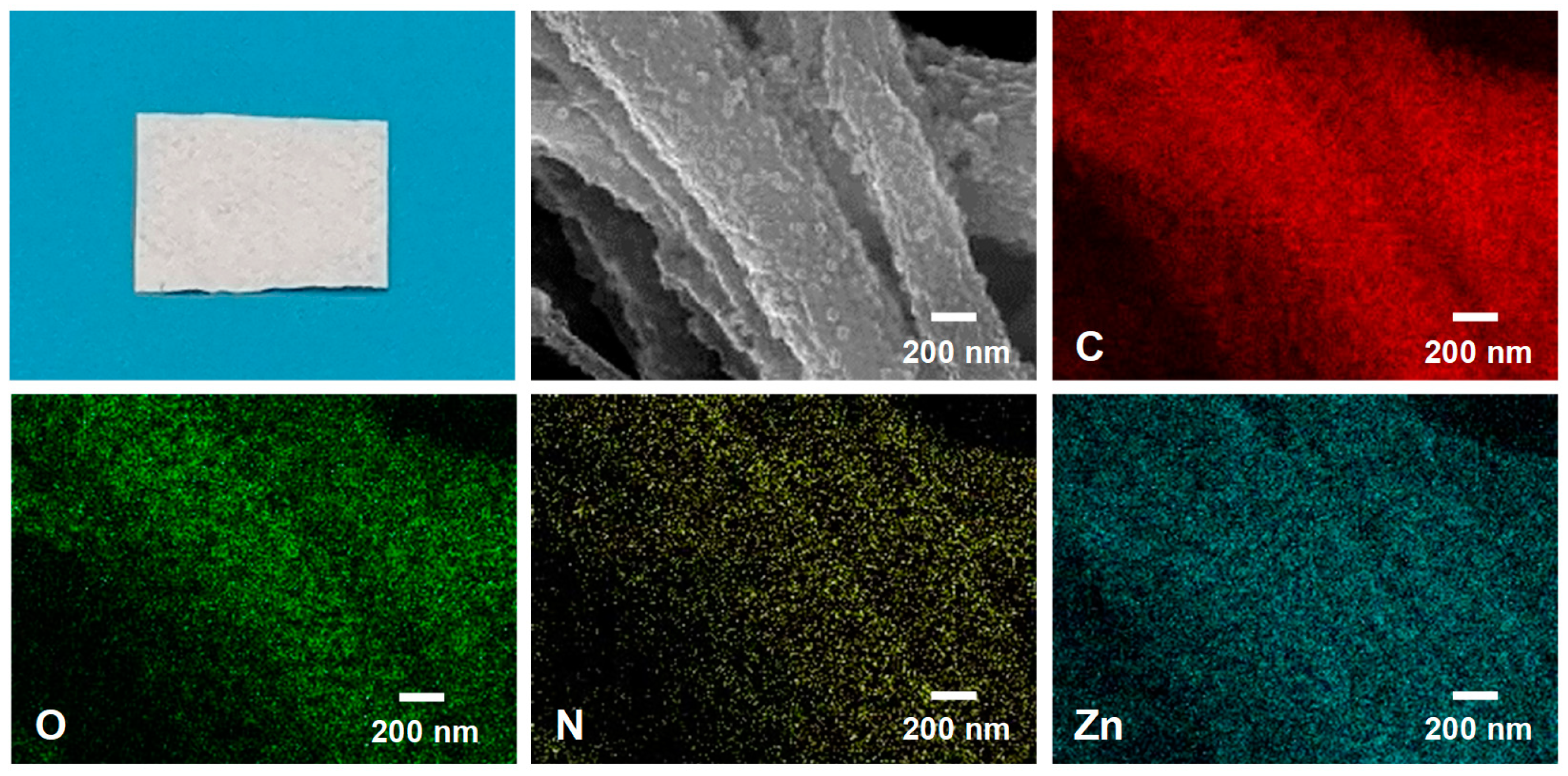
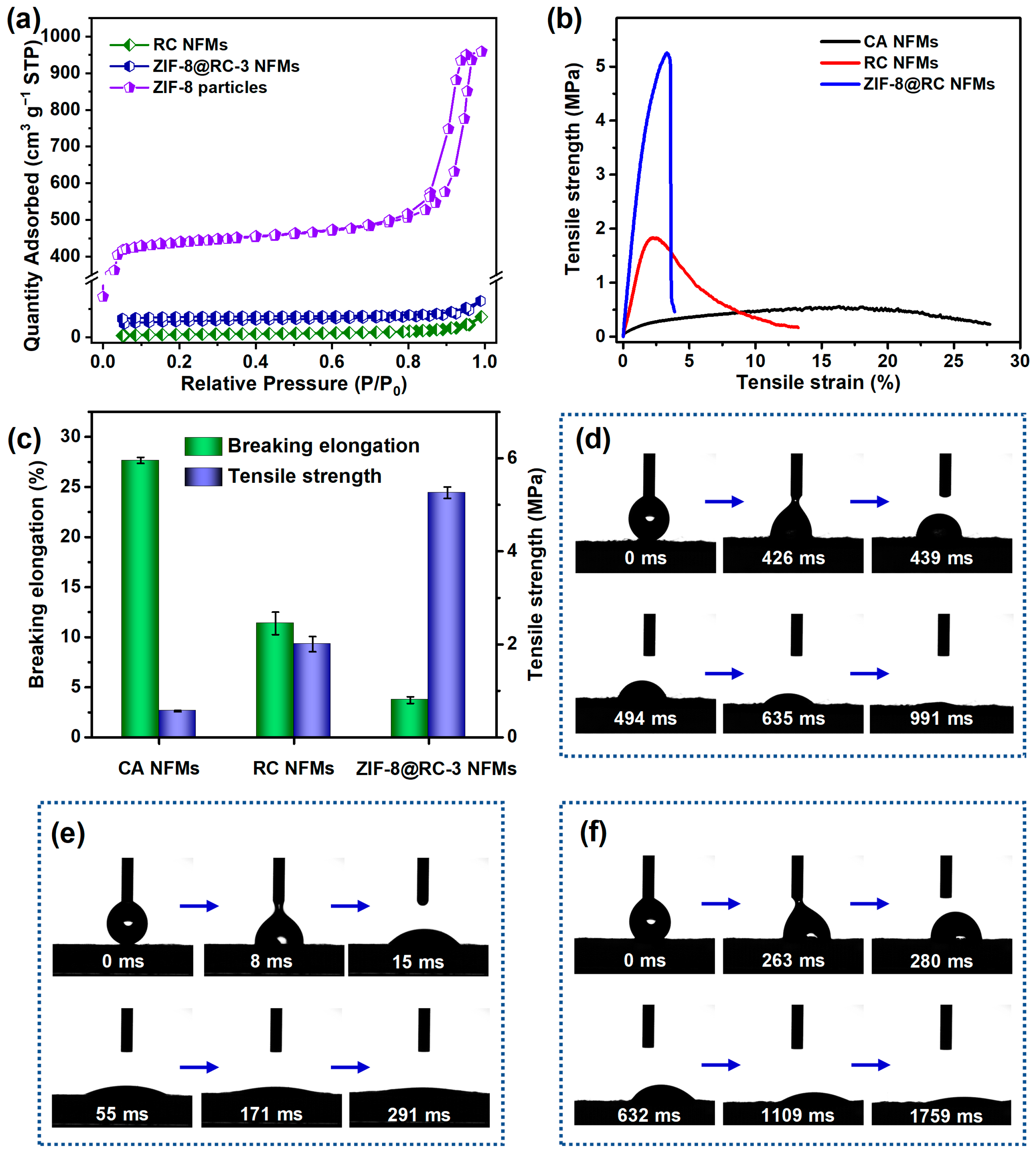
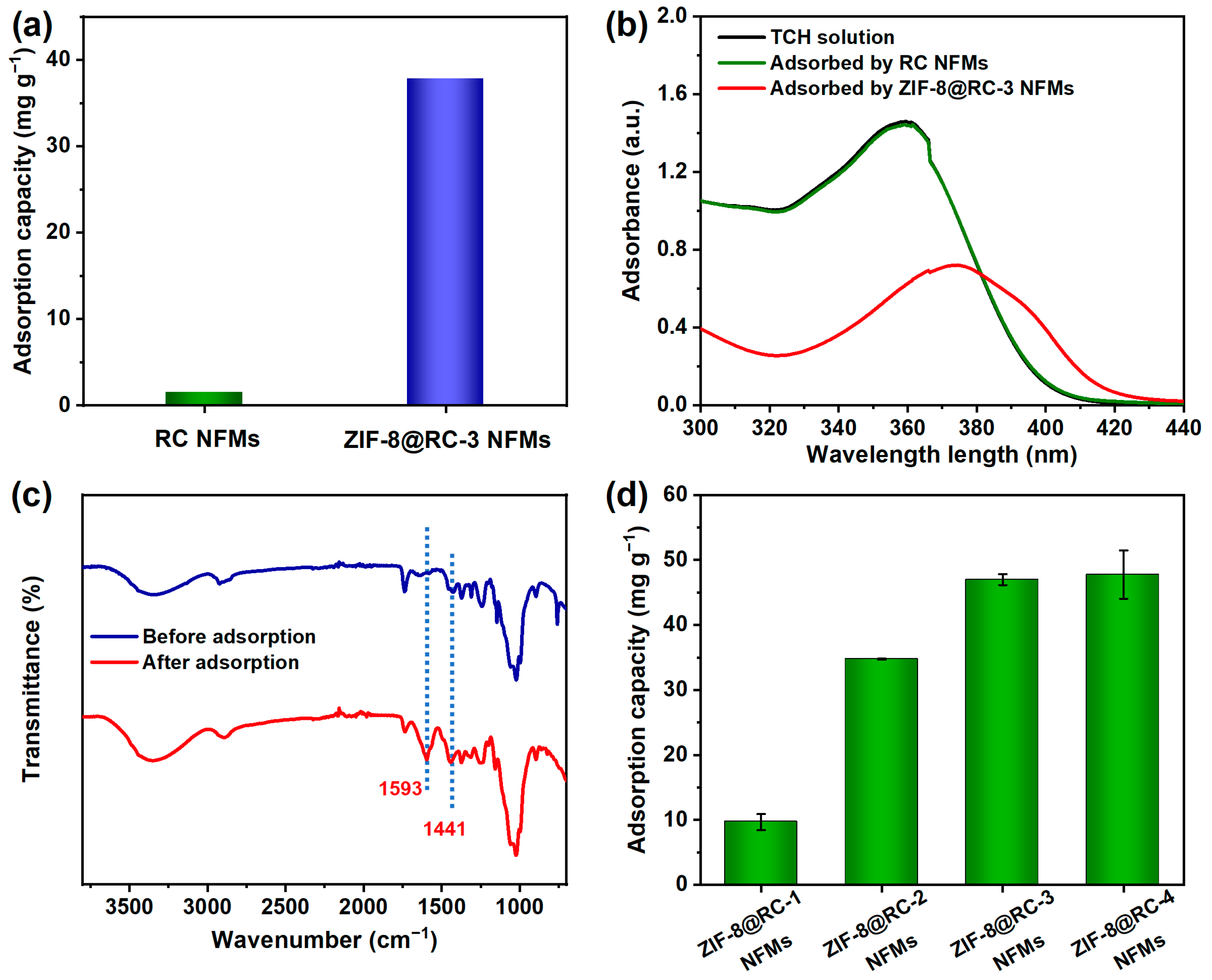
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of the ZIF-8@RC NFMs
3.3. Measurement of the TCH Adsorption Performance
3.4. Instruments and Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Bian, Z.; Peng, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, H. Dual-function oxygen vacancy of BiOBr intensifies pollutant adsorption and molecular oxygen activation to remove tetracycline hydrochloride. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, S. Enhanced Adsorption of Aqueous Tetracycline Hydrochloride on Renewable Porous Clay-Carbon Adsorbent Derived from Spent Bleaching Earth via Pyrolysis. Langmuir 2019, 35, 3925–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S. A novel MIL-125(Ti)-based nanocomposite for enhanced adsorption and catalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride: Synergetic mechanism of calcination and the nitrogen-containing reticulated surface layer. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2023, 645, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wong, N.; Sunarso, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiong, X.; Wang, F. Characterization of BiOBr/g-C3N4 heterostructures immobilized on flexible electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers for photocatalytic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 569, 151011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, C.; Ma, D.; Chen, W.; Ao, T. Effective and structure-controlled adsorption of tetracycline hydrochloride from aqueous solution by using Fe-based metal-organic frameworks. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 542, 148662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, A.; Kumar, S.; Giri, B.; Kim, K. Antibiotic resistance in major rivers in the world: A systematic review on occurrence, emergence, and management strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 1484–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, T.; Peng, H.; Zheng, X. Efficient adsorption-photocatalytic removal of tetracycline hydrochloride over octahedral MnS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Y.; Qin, T.; Li, D.; Dong, X.; Muddassir, M.; Zhong, A. A new type Co(II)-based photocatalyst for the nitrofurantoin antibiotic degradation. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1312, 138501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dang, Z.; Muddassir, M.; Raza, S.; Zhong, A.; Wang, X.; Jin, J. A new Cd(II)-based coordination polymer for efficient photocatalytic removal of organic dyes. Molecules 2023, 28, 6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, C.; Xue, Y. Enhanced adsorption for the removal of tetracycline hydrochloride (TC) using ball-milled biochar derived from crayfish shell. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 615, 126254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Yang, M.; Zhai, J.; Bai, W.; Dai, L.; Liu, L.; Jiang, S.; Wang, W.; Ren, E.; Cheng, C.; et al. Bamboo cellulose-derived activated carbon aerogel with controllable mesoporous structure as an effective adsorbent for tetracycline hydrochloride. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 12558–12570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.; Wang, B.; Wu, P.; Lee, X.; Xing, Y.; Chen, M.; Gao, B. Adsorption of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater by modified biochar: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Bolan, N.; Shaheen, S.M.; Xu, S.; Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Hu, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, F.; et al. Conversion of biological solid waste to graphene-containing biochar for water remediation: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Huang, H.; Liang, D.; Xie, Y.; Kong, F.; Yang, Q.; Fu, J.; Dou, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Z. Adsorption of tetracycline hydrochloride on layered double hydroxide loaded carbon nanotubes and site energy distribution analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, R.; Yang, Q.; Huang, B.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, W.; Zou, J.; Chen, Q. Adsorption characteristics of tetracycline hydrochloride and oxytetracycline by a MOF-525(Co) metal organic framework. Colloid. Surf. A 2023, 677, 132443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Liang, Z.; Chen, D. Removal of tetracycline hydrochloride from wastewater by Zr/Fe-MOFs/GO composites. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 9977–9984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gascon, J.; Li, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Metal-organic frameworks based membranes for liquid separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7124–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, J.; Chew, J. Metal-organic framework membranes for wastewater treatment and water regeneration. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 404, 213116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, P.; Yang, G.; Hou, L.; Zhang, W.; Han, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y. Supramolecular control of MOF pore properties for the tailored guest adsorption/separation applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 434, 213709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, D.; Ammar, M.; Rammal, M.; Al-Ghoul, M.; Hmadeh, M. Crystal growth of ZIF-8, ZIF-67, and their mixed-metal derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shi, W.; Cui, L.; Xu, C. Enhancing contaminant rejection efficiency with ZIF-8 molecular sieving in sustainable mixed matrix membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Chen, W.; Ao, T. Hierarchically porous ZIF-8 for tetracycline hydrochloride elimination. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2021, 99, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, T. Recent advances on ZIF-8 composites for adsorption and photocatalytic wastewater pollutant removal: Fabrication, applications and perspective. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2021, 441, 213985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhou, L.; Jin, X.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Simultaneous removal of tetracycline and oxytetracycline antibiotics from wastewater using a ZIF-8 metal organic-framework. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tong, J.; Zhu, L.; Pan, D. In situ growth of ZIF-8 on carboxymethyl chitosan beads for improved adsorption of lead ion from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, B.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, H. Polyamide thin-film nanocomposite membrane containing star-shaped ZIF-8 with enhanced water permeance and PPCPs removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 120886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Shi, S.; Hu, J. Applications of electrospinning in human health: From detection, protection, regulation to reconstruction. Nano Today 2023, 48, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Ge, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Fu, Q. General synthesis of flexible CuO nanoparticles-anchored ZrO2 nanofibrous membranes for catalytic oxidation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Kang, S.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D. Electrospun Functional Nanofiber Membrane for Antibiotic Removal in Water: Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, T.; Luo, R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Wang, L. In situ growth of ZIF-8 on PAN fibrous filters for highly efficient U(VI) removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24164–24171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shao, H.; Ma, Q.; Yu, W.; Dong, X. Self-supporting flexible metal-organic framework-based electrospun nanofibers membrane for efficient removal of tetracycline from aqueous solutions. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 312, 123233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Preparation of polydopamine-modified zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 functionalized electrospun fibers for efficient removal of tetracycline. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Tang, X.; Feng, S.; Zhong, Z.; Yao, J.; Yao, Z. ZIF-8@SiO2 composite nanofiber membrane with bioinspired spider web-like structure for efficient air pollution control. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 581, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Hou, D.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, T.; Menkhaus, T.J.; Fong, H. Electrospun regenerated cellulose nanofibrous membranes surface-grafted with polymer chains/brushes via the atom transfer radical polymerization method for catalase immobilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20958–20967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Han, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, L.; Shi, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Yue, T.; Li, Z. Shapeable three-dimensional CMC aerogels decorated with Ni/Co-MOF for rapid and highly efficient tetracycline hydrochloride removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Highly Carbonylated Cellulose Nanofibrous Membranes Utilizing Maleic Anhydride Grafting for Efficient Lysozyme Adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15658–15666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fu, Q.; Yu, J.; Liu, L.; Ding, B. Cellulose Nanofibrous Membranes Modified with Phenyl Glycidyl Ether for Efficient Adsorption of Bovine Serum Albumin. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2019, 1, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, A.; Jiang, Z.; Kasher, R. Hydrostable ZIF-8 layer on polyacrylonitrile membrane for efficient treatment of oilfield produced water. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 133513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Yuksekdag, A.; Ağtaş, M.; Mehrabi, M.; Salehi, E.; Castro-Muňoz, R.; Koyuncu, I. Zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) modified cellulose acetate NF membranes for potential water treatment application. Carbohyd. Polym. 2023, 299, 120230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, N.; Jin, X.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. A new nFe@ZIF-8 for the removal of Pb(II) from wastewater by selective adsorption and reduction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, J.; Cui, H.; Yuan, B.; Fu, M. Magnetic responsive Fe3O4-ZIF-8 core-shell composites for efficient removal of As(III) from water. Colloid. Surf. A 2018, 539, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; You, T.; Wang, K.; Xu, F. Effects of polymorphs on dissolution of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Seo, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Beak, K. Structural control of cellulose nanofibrous composite membrane with metal organic framework (ZIF-8) for highly selective removal of cationic dye. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Jeong, H.; Lee, A.; An, H.; Lee, J. Heteroepitaxially grown zeolitic imidazolate framework membranes with unprecedented propylene/ propane separation performances. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12304–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, M.; Cohen, S. In situ modification of metal-organic frameworks in mixed-matrix membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2015, 54, 9029–9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Jang, M.; Cho, B.; Kwon, H.; Kim, S.; Ahn, W. ZIF-8: A comparison of synthesis methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 271, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Wang, Y.; Andrews, C.; Zheng, C. One-step construction of hierarchical porous channels on electrospun MOF/polymer/graphene oxide composite nanofibers for effective arsenate removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhou, M.; Luo, P.; Shang, J.; Wang, P.; Lyu, L. Deposition of MOFs on polydopamine-modified electrospun polyvinyl alcohol/silica nanofibers mats for chloramphenicol adsorption in water. Nano 2020, 15, 2050046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Liu, L.; Yin, X.; Ji, F.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun regenerated cellulose nanofiber based metal-chelating affinity membranes for protein adsorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sann, E.; Pan, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhan, S.; Xia, F. Highly hydrophobic ZIF-8 particles and application for oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Guo, X.; Chen, R.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Lin, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M. Enhanced anti-biofouling ability of polyurethane anti-cavitation coating with ZIF-8: A comparative study of various sizes of ZIF-8 on coating. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 144, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, M.; Olivier, P.; Garcia, J. Effect of Cassie-Baxter versus Wenzel states on ice adhesion: A fracture toughness approach. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2022, 194, 103440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Wan, D.; Shi, Y.; He, Q.; Chen, J. Synergetic adsorption and Fenton-like degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by magnetic spent bleaching earth carbon: Insights into performance and reaction mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Zuo, C.; Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Ao, T. Efficient removal of tetracycline by a hierarchically porous ZIF-8 metal organic framework. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 111254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Ding, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Ke, F.; Liu, J. Self-adjusted bimetallic zeolitic-imidazolate framework-derived hierarchical magnetic carbon composites as efficient adsorbent for optimizing drug contaminant removal. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, B.; An, H.; Chen, Z.; Cui, H. Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride using a palygorskite-supported Cu2O-TiO2 composite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, C.; Chen, W.; Ao, T. Facile fabrication of N-doped hierarchical porous carbons derived from soft-templated ZIF-8 for enhanced adsorptive removal of tetracycline hydrochloride from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xiong, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, J. Zeolitic imidazolate metal organicfamework ZIF-8 with ultra-high adsorption capacity bound tetracycline in aqueoussolution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82127–82137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, Z.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, W. Copper-doped ZIF-8 with highadsorption performance for removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 285, 121219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Jhung, S. Adsorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products over metal-organic frameworks functionalized with hydroxyl groups: Quantitative analyses of H-bonding in adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, N.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qi, F.; Li, S.; Wu, Y. Preparation of polydopamine nanofibers mat as a recyclable and efficient adsorbent for simultaneous adsorption of multiple tetracyclines in water. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Xie, D.; Ge, J.; Zhang, W.; Shan, H. Negatively Charged Composite Nanofibrous Hydrogel Membranes for High-Performance Protein Adsorption. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premarathna, K.; Rajapaksha, A.; Adassoriya, N.; Sarkar, B.; Sirimuthu, N.; Cooray, A.; Ok, Y.; Vithanage, M. Clay-biochar composites for sorptive removal of tetracycline antibiotic in aqueous media. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kori, A.; Ramavandi, B.; Mahmoodi, S.; Javanmardi, F. Magnetization and ZIF-67 modification of Aspergillus flavus biomass for tetracycline removal from aqueous solutions: A stable and efficient composite. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, F.; Cen, Q. Efficient adsorption of tetracycline hydrochloride on biochar-ceramsite composite: Optimization of response surface methodology and investigation of adsorption mechanism. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 24, 100525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Facile access to highly flexible and mesoporous structured silica fibrous membranes for tetracyclines removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qin, Y.; Sun, K.; Ahmed, J.; Tian, W.; Ma, Z. Round-the-Clock Adsorption–Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride by Ag/Ni-TiO2. Materials 2024, 17, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sathiyaseelan, A.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Jin, T.; Wang, M. Zirconium and cerium dioxide fabricated activated carbon-based nanocomposites for enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic removal of methylene blue and tetracycline hydrochloride. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

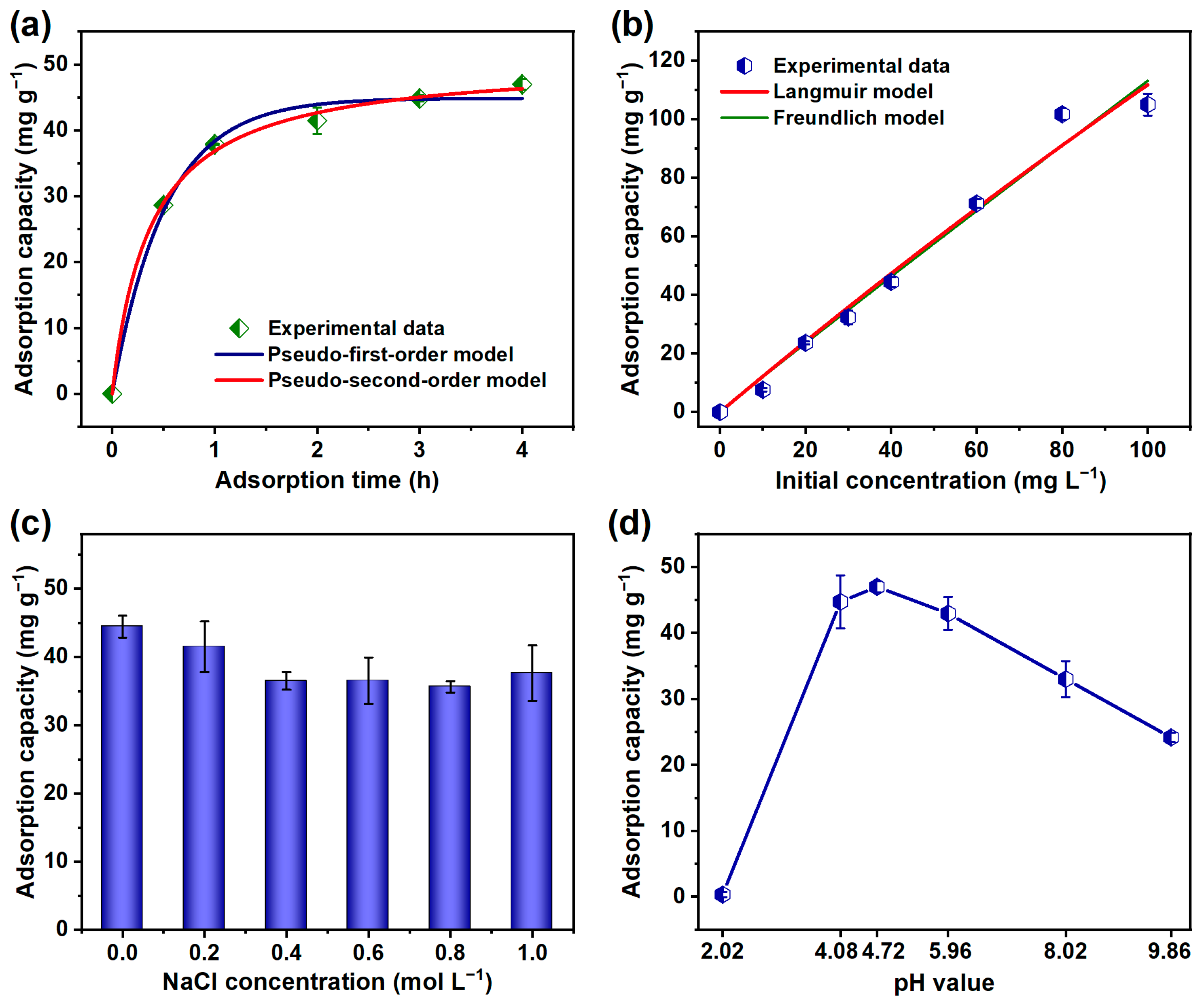
| Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg g−1) | k1 (h−1) | R2 | qe (mg g−1) | k2 (g mg−1 h−1) | R2 |
| 44.87 | 1.928 | 0.991 | 50.66 | 0.053 | 0.998 |
| Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg g−1) | KL (L mg−1) | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 |
| 1230.18 | 0.001 | 0.979 | 16.11 | 1.408 | 0.978 |
| Sample Name | Concentration of Zn(NO3)2 (mol L−1) | Concentration of 2-Methylimidazole (mol L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8@RC-1 NFMs | 0.009 | 0.23 |
| ZIF-8@RC-2 NFMs | 0.018 | 0.45 |
| ZIF-8@RC-3 NFMs | 0.036 | 0.91 |
| ZIF-8@RC-4 NFMs | 0.071 | 1.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Xie, D.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Shan, H. Facile Fabrication of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8@Regenerated Cellulose Nanofibrous Membranes for Effective Adsorption of Tetracycline Hydrochloride. Molecules 2024, 29, 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174146
Wang Z, Fu Q, Xie D, Wang F, Zhang G, Shan H. Facile Fabrication of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8@Regenerated Cellulose Nanofibrous Membranes for Effective Adsorption of Tetracycline Hydrochloride. Molecules. 2024; 29(17):4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174146
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhirong, Qiuxia Fu, Dandan Xie, Fujie Wang, Guangyu Zhang, and Haoru Shan. 2024. "Facile Fabrication of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8@Regenerated Cellulose Nanofibrous Membranes for Effective Adsorption of Tetracycline Hydrochloride" Molecules 29, no. 17: 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174146
APA StyleWang, Z., Fu, Q., Xie, D., Wang, F., Zhang, G., & Shan, H. (2024). Facile Fabrication of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8@Regenerated Cellulose Nanofibrous Membranes for Effective Adsorption of Tetracycline Hydrochloride. Molecules, 29(17), 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174146







