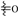Abstract
With the increasing global incidence and mortality rates of cancer, the development of novel anti-tumor drugs has become particularly urgent. Scutellaria barbata D. Don, a perennial herb belonging to the genus Scutellaria in the family Lamiaceae, has aroused extensive attention for its medicinal value in recent years. This article presents an exhaustive review of the flavonoid, diterpene, and other chemical constituents harbored within Scutellaria barbata, delving into the intricate mechanisms by which these compounds orchestrate their anti-tumor effects via diverse biological pathways. Remarkably, these compounds distinguish themselves through their capability to regulate cellular signaling, inhibit cancer cell proliferation, trigger apoptosis, disrupt angiogenesis, and bolster immune responses. These anti-tumor effects are achieved through strategic modulation of pivotal signaling cascades, particularly the PI3K/Akt/mTOR, MAPK, and NFκB pathways. In addition, this article also summarizes the clinical applications of Scutellaria barbata in tumor treatment, especially its potential in alleviating the side effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy and improving patients’ quality of life. In conclusion, this review comprehensively summarizes and analyzes the chemical constituents, anti-tumor mechanisms, and clinical applications of Scutellaria barbata, with the aim of systematically reviewing the existing research results and exploring potential future research directions.
1. Introduction
Cancer poses a significant threat to human health due to its difficulty in early diagnosis, high recurrence rates, and poor treatment outcomes. According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), the incidence and mortality rates of cancer are increasing globally, with millions of people dying from various types of cancer each year. To date, the available cancer treatments include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Although surgical resection is considered as the only effective treatment, many advanced cancer patients still require chemotherapy to reduce tumor growth or inhibit metastasis. However, due to the limited tumor-specific cytotoxic effects of existing drugs and the presence of resistance mechanisms in tumor cells, few advanced cancer patients benefit from chemotherapy, resulting in low long-term survival rates [1]. Traditional Chinese herbal medicine has a history of thousands of years of clinical application in China, accumulating rich experience and knowledge. Additionally, Chinese medicine contains numerous unknown components with potential pharmacological activity and therapeutic potential. Using modern technology to discover new drug molecules from Chinese medicine and develop them into new medications has shown great potential in the field of cancer treatment [2].
Scutellaria barbata D. Don (also known as Ban Zhi Lian) is a perennial herb of the Lamiaceae family, widely distributed in East Asia, including China, Japan, and Korea, and has been widely used in traditional medical systems in these countries. According to the literature, Scutellaria barbata has been used medicinally for hundreds of years, firstly documented in “Authentic Surgery” by the Ming Dynasty physician Chen Shigong, where it was noted for its efficacy in treating snake bites [3]. In the traditional Chinese medicine system, Scutellaria barbata is known for its effects of clearing heat and detoxifying, promoting diuresis to reduce swelling, and activating the blood circulation to resolve stasis. Additionally, it is often used alone or in combination with other herbs, such as Hedyotis diffusa (Bai Hua She She Cao), to treat tumors [4]. In the modern Chinese medicine system, Scutellaria barbata is included in the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, indicated for conditions like sores and abscesses, sore throat, traumatic injuries, edema, jaundice, and snake bites. Currently, there are proprietary Chinese medicines like Scutellaria barbata capsules and tablets for treating sore throat caused by acute pharyngitis. Moreover, many compound preparations contain Scutellaria barbata, such as Kang Gu Sui Yan Pian, Re Yan Ning He Ji, and Compound Banmao Capsule. With the advancement of modern medical research, the efficacy of Scutellaria barbata in cancer treatment has gained widespread attention from the scientific community.
Modern research on Chinese medicine has identified nearly 300 compounds from Scutellaria barbata through various extractions and separation methods, with the main ones being flavonoids and diterpenoids, along with polysaccharides, volatile compounds, trace elements, and steroids [5]. Flavonoids, the primary active components of Scutellaria barbata, include quercetin, luteolin, scutellarein, scutellarin, wogonin, and baicalein [6]. The terpenoids are mainly neo-clerodane diterpenoids, which have potential applications in immunomodulation and anti-tumor activities, and also show some antibacterial and antiviral activity [5].
Scutellaria barbata has demonstrated good hepatoprotective effects in clinical settings and was initially used as an adjuvant treatment for liver cancer. With deeper research into its components, Scutellaria barbata’s active ingredients have shown efficacy against malignant tumors such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, and leukemia [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Scutellaria barbata extracts, rich in flavonoids, can exert anti-tumor effects by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis, inhibiting cell migration and invasion, suppressing angiogenesis, and modulating immunity [15]. Combining traditional Chinese medicine with chemotherapy is a distinctive feature of cancer treatment in China. Scutellaria barbata can enhance the efficacy of anti-tumor drugs and exhibit significant potential in overcoming drug resistance by inhibiting drug efflux pumps and regulating apoptosis [16,17]. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties can improve the tumor microenvironment and inhibit tumor progression. Scutellaria barbata exerts its anti-tumor effects by regulating multiple signaling pathways. It can inhibit the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, reducing tumor cell growth and survival. The active components of Scutellaria barbata can inhibit the MAPK signaling pathway, including ERK, JNK, and p38, suppressing tumor cell proliferation and survival. Furthermore, it can inhibit the NFκB pathway, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, alleviating inflammation, and thereby inhibiting tumor cell growth [4,18].
Currently, research on Scutellaria barbata has made some progress, though most studies remain at the laboratory stage, with relatively few clinical application studies. This review summarizes the clinical application of Scutellaria barbata in cancer treatment, providing an intuitive assessment of its therapeutic effects. Presently, the clinical application of Scutellaria barbata is mainly focused on adjuvant cancer therapy, particularly in alleviating side effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy and improving patients’ quality of life.
This review aims to comprehensively summarize and analyze the chemical constituents, anti-tumor mechanisms, and clinical applications of Scutellaria barbata, systematically organizing the existing research outcomes and exploring future research directions. By summarizing the progress in the chemical composition and anti-tumor mechanisms of Scutellaria barbata, this review not only helps evaluate its potential application value in various cancers but also provides scientific evidence for its application in modern medicine, serving as a reference for future research and application. Despite the promising anti-tumor potential demonstrated by Scutellaria barbata in laboratory studies, further research is needed to verify its safety and efficacy in clinical applications.
2. Chemical Constituents
Numerous studies have reported on the chemical constituents of Scutellaria barbata, primarily including flavonoids, terpenoids, polysaccharides, volatile compounds, and trace elements. As research into Scutellaria barbata deepens, an increasing number of components are being isolated and identified. This section reviewed the research progress on the chemical constituents of Scutellaria barbata over the past decade, providing a reference for further research and the development of new therapeutic agents derived from Scutellaria barbata.
2.1. Flavanoids
Flavonoids are viewed as a significant chemical component of Scutellaria barbata, and modern pharmacological studies have demonstrated their relevant anti-tumor activity. Numerous extraction methods for flavonoids have been reported, including solvent extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and acid–alcohol precipitation [19]. As shown in Figure 1, flavonoids can be classified into flavones, flavonols, flavanones, flavanonols, and chalcones, based on their core structures. According to Table 1 and Figure 2, over seventy flavonoids have been isolated and identified from Scutellaria barbata, including forty-seven flavones, three flavonols, fourteen flavanones, seven flavanonols, and one chalcone. Many active flavonoid components exist in glycoside form. Experiments have shown that the main flavonoid components of Scutellaria barbata include scutellarin, scutellarein, quercetin, luteolin, apigenin, and wogonin. Additionally, the extraction and exploration of flavonoid components are ongoing. Zhou et al. reported full-scan (FS)–parent ions list (PIL)–higher energy collision-induced dissociation (HCD)–MS/MS (FS-PIL-HCD-MS/MS) was used to discover potential flavonoid components. Further separation and identification are expected to reveal new flavonoid structures [20].
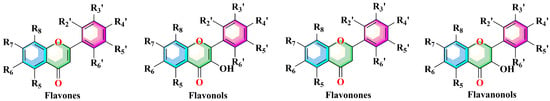
Figure 1.
Core structure of flavones, flavonols, flavonones, and flavanonols in Scutellaria barbata.

Table 1.
Flavonoids in Scutellaria barbata.
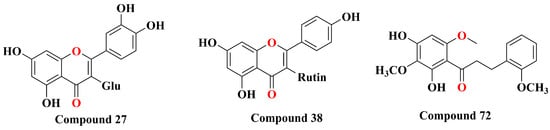
Figure 2.
Structure of compound 27, 38, and 72.
2.2. Terpenoids
Terpenoids are the most abundant chemical constituents in Scutellaria barbata, exhibiting significant pharmacological activity. The primary components are diterpenoids, with over 160 identified compounds. Additionally, triterpenoids such as ursolic acid and oleanolic acid have also been isolated and identified.
2.2.1. Diterpenoids
The main diterpenoids in Scutellaria barbata are primarily diterpenes and diterpene alkaloids, with their structures mainly classified as neo-clerodane diterpenoid. As Figure 3 shows, based on the variations in the side chain from C11 to C16, these diterpenoids can be categorized into three main classes. Class I features an unsaturated lactone ring formed between C13 and C16. Class II consists of compounds where C11–C16 and C8 form a spiro ring, usually existing in lactone form. Class III compounds feature a hexahydrofurano-furan ring type bicyclic structure formed between C11 and C16.
Figure 3.
Three main core structure types of diterpenoids in Scutellaria barbata.
With further variations in the chemical structure of the side chains, these classes can be refined into seven structural types, as shown in Figure 4. The diversity in structural types and different substituent groups contributes to the large number of diterpenoid compounds. This section summarizes the diterpenoid compounds based on their structural types (Table 2 and Figure 5). Type A compounds are characterized by the cyclization of C13 to C16, forming an α-β unsaturated five-membered lactone. This type features a conjugated double bond between C11–C12 and C13–C14, and a double bond between C3–C4. Currently, 36 compounds of this type have been identified. When the C3–C4 double bond in Type A compounds was substituted with a single bond, the resulting compounds were classified as Type B. So far, 11 such Type B compounds have been systematically cataloged and definitively characterized. If the C11–C12 bond in Type A is a single bond, it is classified as a Type C compound, with 32 such compounds identified till now. Together, Type A, B, and C compounds constitute Class I, totaling 79 compounds. Type D compounds are characterized by a spirocyclic structure where C13 is linked to C8, forming a five-membered lactone structure with C13 as the spiro atom, and a double bond between C3–C4. To date, 14 compounds of this type have been identified. Type E compounds differ from Type D compounds in that the C3–C4 bond is a single bond. There are 54 such compounds. Combined with Type D, they form Class II, totaling 68 compounds. Type F compounds feature a bicyclic structure formed by a tetrahydrofuran and a furan ring, cyclizing from C11 to C16. Seven compounds of this type have been identified. Type G compounds are characterized by a spirocyclic lactone formed between C11–C16 and C8. This type is relatively rare, with only three compounds identified. Types F and G together constitute Class III, with a total of 10 compounds. In addition, there are 10 other types of compounds identified.
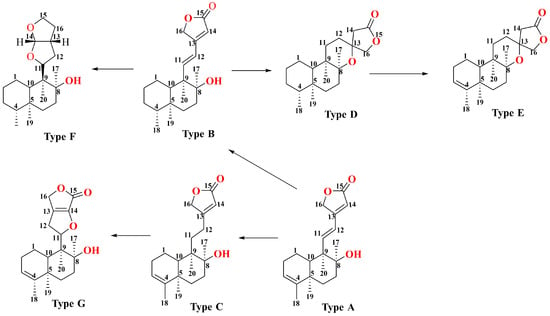
Figure 4.
Side chain changes of the core structure of diterpenoids in Scutellaria barbata.

Table 2.
The neo-clerodane-type diterpenoids isolated from Scutellaria barbata.
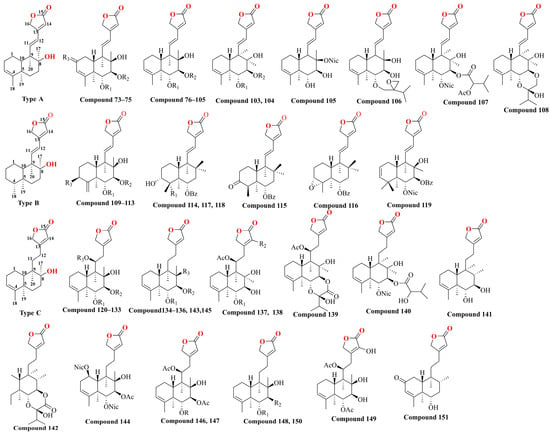
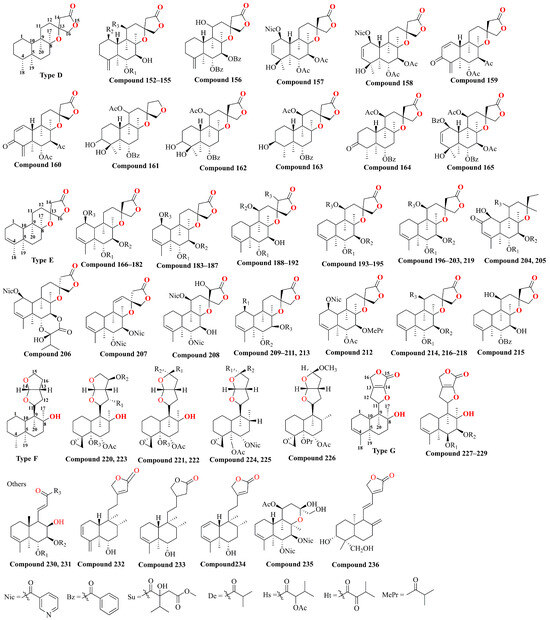
Figure 5.
The chemical structure of diterpenoids isolated from Scutellaria barbata.
2.2.2. Triterpenoids
Reports on triterpenoids in Scutellaria barbata are relatively limited. In 1988, Kuo et al. firstly isolated scutellarie acid from Scutellaria barbata. Subsequently, other triterpenoids such as stigmasterol, eleutheroside A, β-sitosterol, oleanolic acid, and ursolic acid have been identified [83,84,85].
2.3. Polysaccharides
In addition to flavonoids and terpenoids, Scutellaria barbata contains abundant polysaccharides distributed across different medicinal parts of the plant (whole plant, roots, stems, leaves, and flowers), with the highest concentration found in the roots. Xu et al. reported that the polysaccharide (PSB) has an average molecular weight of 13,000 Da and consists of six monosaccharides: rhamnose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, galactose, and glucose [86]. Meng et al. isolated and purified the SPS4 component, which comprises rhamnose, fucose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, glucose, and galactose, with a molar ratio of 0.22:0.26:1.0:0.09:0.51:1.82:2.09 [87]. Kong et al. extracted and identified acidic polysaccharide SPS II, and gas chromatography analysis of its hydrolysates revealed the presence of arabinose, mannose, fructose, and galactose [88]. Wu et al. obtained a homogeneous polysaccharide component, B3-PS2, with a molecular weight of 1100 kDa, primarily composed of glucose, galactose, and arabinose in a molar ratio of 2.7:2.7:1.0, along with small amounts of mannose, rhamnose, fucose, and xylose [89]. Wang et al. indicated that the monosaccharide composition of Scutellaria barbata polysaccharides includes rhamnose, fucose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, glucose, and galactose, with a molar ratio of 1.00:0.13:0.80:0.10:0.34:0.56:2.04 [90]. Sun et al. identified a polysaccharide, SPS2p, with monosaccharide composition of galactose, glucose, mannose, and arabinose, in a ratio of 1.59:2.59:1.00:1.31 [91]. Lin et al. discovered that the polysaccharide SBPW3 consists of glucose, arabinose, rhamnose, mannose, xylose, and galactose in a molar ratio of 20.59:25.68:2.51:12.56:10.94:27.72 [92]. Su et al. isolated two water-soluble polysaccharides, SBP-1A and SBP-2A, with monosaccharide compositions of galactosamine hydrochloride, rhamnose, arabinose, glucosamine hydrochloride, galactose, glucose, xylose, and mannose. The molar ratios of these components in SBP-1A were 0.6:0.3:0.6:30.6:2.3:38.4:16.1:8:1.4 and in SBP-2A were 0.6:0.5:0.8:36.3:4.4:42.7:9.2:2.6:0.7 [7]. Wu et al. isolated polysaccharides with an average molecular weight of 1.25 × 104 Da, primarily composed of arabinose, galacturonic acid, galactose, glucose, and glucuronic acid in a molar ratio of 1.00:2.09:4.52:4.73:4.90 [93].
2.4. Volatile Compounds
Scutellaria barbata contains a rich variety of volatile oils with notable antimicrobial activity. Recent studies, primarily using GC-MS, have identified over 70 volatile components. Yu et al. isolated 41 volatile oil components, with the main compounds being hexahydrofarnesylacetone (11.0%), 3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-ol (7.8%), menthol (7.7%), and 1-octen-3-ol (7.1%) [94]. Zhang et al. identified 35 volatile oil components, with high relative contents of furfural (20.53%), thymol (24.10%), and palmitic acid (16.56%) [95]. Wang et al. identified 54 volatile oil components, with 11 compounds having contents above 1%, with the most abundant being palmitic acid (34.07%), linoleic acid (12.21%), and phytol (5.90%) [96]. Yang et al. identified 43 volatile oil components, with 10 compounds having contents above 1%, with the most abundant being n-palmitic acid (21.03%), (Z,Z)-9,12-linoleic acid (17.07%), trans-13-octadecenoic acid (14.10%), and stearic acid (2.52%) [97]. Differences in the volatile components can be attributed to factors such as the origin of Scutellaria barbata, harvest time, storage conditions, sample preparation, and analytical methods [97].
2.5. Trace Elements
Scutellaria barbata contains various trace elements such as Fe, Zn, Mn, Se, Ca, Mg, K, and Cu, with higher concentrations than many other traditional Chinese medicines [98,99]. Studies have shown significant positive correlations between the total flavonoid content and Zn content, and a very significant positive correlation with Mn content; polysaccharides also showed significant positive correlations with Zn and Mn contents [98]. These trace elements work synergistically in Scutellaria barbata, providing significant positive effects on human physiological functions.
2.6. Steroids
Steroids are a class of naturally occurring organic compounds widely distributed in nature. Using supercritical CO2 fluid extraction, steroidal components can be selectively extracted from Scutellaria barbata, with steroidal compounds accounting for 60% of the total components. The identified steroidal compounds include β-sitosterol, stigmasterol, campesterol, stigmast-4-en-3-one [100], Cholest-5-ene-3-thiol (3β)-Stigmastan-3,5,22-trien [97], and Daucosterol [101].
2.7. Phenylpropanoid and Lignan
Relatively fewer phenylpropanoids and lignans have been isolated from Scutellaria barbata. Currently, E−1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-but-1-en-3-one [102], 4-(3,4-dihydroxy-phenyl)-but-3-en-2-one [37], Chlorogenic acid [36], [(E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-acrylic acid ethyl] ester [31], pinoresinol, medioresinol [103], and d-syringaresinol [83] have been isolated.
2.8. Phenolic Acids
Various phenolic acids have been isolated from Scutellaria barbata, including benzoic acid, cinnamic acid [104], vanillic acid, isovanillic acid [105], 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid [35], and (S)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-pyran-4-one [31].
2.9. Others
In addition to the aforementioned types of compounds, there are a few other types of compounds reported in Scutellaria barbata, such as coumarins and amides [106,107]. Due to their limited quantity, the pharmacological effects of these compounds in Scutellaria barbata are relatively less studied.
3. Anti-Tumor Mechanism
In traditional Chinese medicine theory, Scutellaria barbata is renowned for its efficacy in clearing heat, detoxification, diuresis, resolving swelling, promoting blood circulation, and removing blood stasis. Its therapeutic effects on liver diseases have also been widely reported. In recent years, Scutellaria barbata has attracted significant attention in oncology. With the advancement of modern medical technology, the mechanisms of its anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral effects have been gradually elucidated [6,48,59].
Research has shown that Scutellaria barbata and its extracts exert inhibitory effects on various cancer cells, including liver cancer [7,8,9,10,11,108], breast cancer [12,13,14], ovarian cancer [109], and prostate cancer [110]. The active components in Scutellaria barbata achieve anti-tumor effects through pathways such as the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation [111], induction of cancer cell apoptosis [9], suppression of tumor cell migration and invasion [12], and inhibition of tumor angiogenesis [8]. Among the identified chemical constituents of Scutellaria barbata extracts, flavonoids such as quercetin, luteolin, scutellarin, and wogonin have been extensively studied for their anti-tumor properties [8,112]. In clinical practice, in addition to being used independently for adjunctive cancer therapy, Scutellaria barbata is often combined with Hedyotis diffusa due to the latter’s effects in clearing heat, detoxification, promoting diuresis, resolving swelling, and dispersing masses. This combination exhibits synergistic effects and is widely applied in the adjuvant treatment of cancer.
3.1. Inhibition of Tumor Cell Proliferation
Tumor cells can evade normal cellular regulatory mechanisms, proliferating uncontrollably and invading adjacent tissues. They often produce their own growth factors and activate intracellular signaling pathways such as RAS/Erk and PI3K/Akt/mTOR, which sustain continuous cell proliferation. Therefore, the classical strategy of anti-tumor drugs focuses on inhibiting tumor cell proliferation. As shown in Figure 6, SBD inhibited the proliferation of tumor cells and induced apoptosis of the tumor cells by multiple signaling pathways.
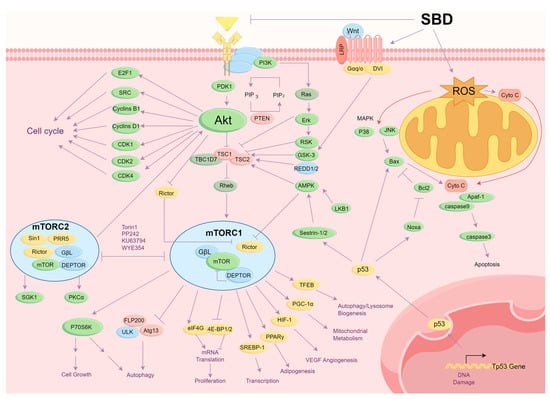
Figure 6.
SBD inhibited the proliferation of tumor cells and induced the apoptosis of tumor cells by multiple signaling pathways.
Studies have demonstrated that wogonin and scutellarin in Scutellaria barbata can influence the expression of cell-cycle-related proteins by downregulating Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), thereby blocking the transition of cells from the G1 to S phase and inhibiting cell proliferation. Hnit et al. found that the combination of Scutellaria barbata and Hedyotis diffusa extract reduces DNA content accumulation in G2/M phase prostate cancer cells, suggesting inhibition of mitotic regulators and transcriptional suppression, thereby preventing prostate tumor cells from transitioning from the G2 to M phase and inhibiting tumor cell growth. Importantly, this cell cycle arrest is not due to DNA damage but involves the decreased expression of Cyclin B1, CDK1, PLK1, and Aurora A [110]. TP53 is a crucial tumor suppressor gene that inhibits tumor formation by inducing cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. Active ingredients such as quercetin and baicalein in Hedyotis diffusa–Scutellaria barbata (HD-SB) upregulate TP53 and P21, promoting cell cycle arrest in HepG2 cells. CDK2, a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) family, phosphorylates numerous transcription factors and participates in various cancer signaling pathways, thereby promoting cancer development. TP53 regulates the mRNA and protein expression levels of CDK2 [113]. Li et al. reported that quercetin and luteolin inhibit the activity of CDK2, thereby blocking the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells through the cell cycle [114]. Furthermore, TP53 enhances the expression of Bcl-2, P21, and P14 while inhibiting BAX expression, promoting apoptosis in liver cancer cells [115]. Sheng et al. treated prostate cancer cells (PCa) with ethanol extracts of Scutellaria barbata D. Don (SBD) and found that SBD induces apoptosis and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in PCa by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [18]. Su et al. optimized the extraction process of acidic polysaccharides from Scutellaria barbata using response surface methodology (RSM), obtaining two highly pure homogeneous acidic polysaccharides SBP-1a and SBP-1b. Both polysaccharides were shown to inhibit the proliferation of HepG2 cells. Additionally, SBP-2A altered the morphology of HepG2 cells, significantly inducing apoptosis by upregulating p53, increasing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, and downregulating Cyclin D1 and CDK4, thereby arresting HepG2 cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle [7].
With the rapid development of interdisciplinary fields such as computer science, life sciences, and medicine, network pharmacology has accelerated drug discovery and development using big data and computational biology techniques. Qi et al. identified quercetin, luteolin, wogonin, and apigenin as the main active flavonoids in Scutellaria barbata. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis indicated that these active ingredients target key pathways such as the glucocorticoid receptor (NR3C1), phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA), tumor antigen p53 (TP53), transcription factor AP-1 (JUN), mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1), Myc proto-oncogene protein (Myc), cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), and ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2 (ABCG2) in the treatment of colorectal cancer. GO analysis demonstrated that active ingredients from Scutellaria barbata regulate cell cycle arrest to inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells [116]. Yang et al. used the Traditional Chinese Medicines for Systems Pharmacology Database (TCMSP), screened the effective ingredients of Scutellaria barbata, and analyzed KEGG and GO to study potential targets for treating liver cancer. The study identified flavonoids such as wogonin, Rhamnazin, quercetin, baicalein, and luteolin, which may act on targets such as CDK1, CDK4, SRC, and E2F1 through pathways including PI3K-Akt signaling, IL-17 signaling, and TNF signaling, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of liver cancer cells [9]. Shi et al. identified some active ingredients including baicalein, wogonin, luteolin, and quercetin from Scutellaria barbata, and employed network pharmacology to establish their relationship with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Experimental results showed that baicalein and baicalin downregulate key proteins in the PI3K/AKT and p53 signaling pathways in CNE2 cells, inhibiting the proliferation of NPC cells [112].
3.2. Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells
Tumor cells typically evade programmed cell death by upregulating anti-apoptotic proteins and downregulating pro-apoptotic proteins. Therefore, inducing apoptosis is a crucial biological mechanism to inhibit cancer progression. Numerous studies have shown that the active components of Scutellaria barbata can exert anticancer effects by inducing apoptosis. Research by Bao et al. demonstrated that the active components of Scutellaria barbata induce cell apoptosis to inhibit tumor cell growth. As shown in Figure 6, extracts of Scutellaria barbata activate the mitochondrial pathway, increasing the Bax/Bcl2 ratio, promoting cytochrome c release, activating downstream Caspase-9 and Caspase-3, and triggering autophagic responses to induce cell apoptosis. Additionally, active components in Scutellaria barbata can activate the death receptor pathway, such as the Fas receptor, subsequently activating Caspase-8 and inducing cell apoptosis [16]. Liu et al. found that Scutellaria barbata and Hedyotis diffusa extracts significantly reduce cell viability in colorectal cancer cells (HCT116) by downregulating Bcl-2, upregulating cleaved-caspase-3 and Bax, promoting ROS generation, and inducing apoptosis. The study also demonstrated significant inhibition of colon cell migration in a dose-dependent manner [17].
Network pharmacology methods have also revealed that the active ingredients of Scutellaria barbata can significantly induce cancer cell apoptosis. Zhang et al.’s network pharmacology study suggested that flavonoids such as quercetin, luteolin, and wogonin in SBD downregulate mRNA expression of ovarian-cancer-related genes including AKT1, VEGFA, JUN, TNF, and Caspase-3, inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting cancer cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis [111].
Lu et al. constructed a “herb-composition-target-disease” network and predicted that the Scutellaria barbata and Hedyotis diffusa combination contains 29 flavonoid active components with anti-tumor effects. In vivo and in vitro experiments revealed that these active components significantly induced apoptosis in cancer cells, markedly reduced the expression of p-EGFR, HSP90, p-AKT, p-PI3K, and bcl-2, and increased the expression of ppar, bax, cleaved caspase 3, and cleaved PARP. The results of this study suggest that HD-SB may induce apoptosis by inhibiting the EGFR/ppar/PI3K/AKT pathway [4]. Ma et al. identified 75 components from Scutellaria barbata extract using high-performance liquid chromatography and predicted through a “drug-component-target-pathway” model that the Scutellaria barbata and Hedyotis diffusa combination exerts anti-tumor effects by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway. This was further confirmed by flow cytometry and caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 activity assays, demonstrating that the Scutellaria barbata extract inhibits tumors by inducing apoptosis in cancer cells [117]. Yang et al. isolated the ethyl acetate fraction (EA11) of Scutellaria barbata and Hedyotis diffusa extract, demonstrating through in vivo and in vitro studies that EA11 reduces the protein expression of PDE7B, PD-L1, β-catenin, and cyclin D1 in 4T1 cells, while increasing cellular cAMP concentration and miR-200c expression. Moreover, EA11 partially exerts its anticancer effects by inactivating the MAPK and AKT signaling pathways. These findings suggest that the ethyl acetate fraction of Scutellaria barbata and Hedyotis diffusa extract disrupts the miR-200c-PDE7B/PD-L1-AKT/MAPK axis to prevent breast tumor development [14].
Collectively, these studies demonstrate that flavonoid compounds in Scutellaria barbata extract induce cancer cell apoptosis, thereby exerting anticancer effects.
3.3. Inhibition of Cell Migration and Invasion
Cancer cells can metastasize from primary sites through the blood or lymphatic systems, invading healthy tissues to form new tumors, which is a major cause of cancer-related mortality. As shown in Figure 7, studies have shown that the active components of Scutellaria barbata can inhibit tumor cell migration and invasion by suppressing the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and inhibiting matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), thereby reducing tumor metastasis.
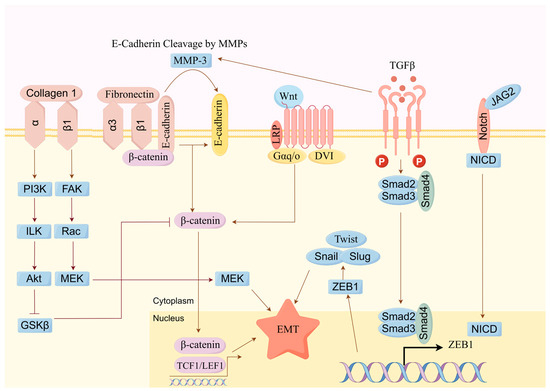
Figure 7.
SBD inhibits the invasion and migration of tumor cells through multiple mechanisms.
Zheng et al. evaluated the impact of total flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata on breast cancer bone metastasis using in vitro cell experiments and animal models. The results suggested that total flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata may reduce the expression of bone-resorbing factor PTHrP and inhibit downstream molecule RANKL/OPG secretion, thereby inhibiting the metastasis of breast cancer cells [12]. Xu et al. found that combined treatment with HD-SB significantly inhibits the proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells. Network pharmacology analysis indicated that quercetin, luteolin, and baicalein may be important anticancer components in HD-SB, potentially acting on targets such as EGFR, MAPK1, VEGFA, and PIK3CG to inhibit ovarian cancer growth and migration via focal adhesion pathways [110]. Liu et al. reported that flavonoid components can downregulate the expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), such as MMP2 and MMP9, thereby inhibiting the invasion and migration ability of tumor cells [118]. Huang et al. discovered that active components of Scutellaria barbata can inhibit the phosphorylation of Smad2, Smad3, JNK, p38, and ERK in HepG2 liver cancer cells, blocking TGF-β/Smad/MAPK signaling activation. Concurrently, they observed the downregulation of IntegrinαV, Integrinβ3, MMP2, and MMP9 protein expression, reversing EMT and thereby inhibiting the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells [119].
These studies collectively demonstrate that active components of Scutellaria barbata enhance cell adhesion, reduce cancer cell migration and invasion by inhibiting EMT, and suppress MMPs. These processes are mediated by key signaling pathways including TGF-β/Smad/MAPK, EGFR, PI3K/Akt, and RANKL/OPG.
3.4. Inhibition of Angiogenesis
Tumor angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to tumors, is crucial for tumor growth and metastasis. Anti-angiogenesis therapy is a key strategy in treating prostate cancer and other cancers. Research conducted by Sheng et al. indicates that Scutellaria barbata treatment can inhibit the interaction between PCa cells and HUVECs, thereby suppressing angiogenesis. Additionally, SBD alone or conditioned media from SBD-treated PCa cells reduced HUVEC tube formation on Matrigel without affecting HUVEC viability. Through multiple mechanisms such as inhibiting angiogenesis, inactivating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, inducing apoptosis, and arresting the cell cycle at the G2/M phase, Scutellaria barbata exhibits strong anti-prostate-cancer activity [18].
Yang et al. found that polysaccharides from Scutellaria barbata (PSB) effectively inhibit cell proliferation in vitro and the phosphorylation of human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) 2. The vivo studies using the Calu-3 subcutaneous xenograft model demonstrated the significant anti-tumor activity of PSB. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis showed PSB dose-dependently reduced microvessel density, indicating its anti-tumor effect is primarily linked to its anti-angiogenesis properties [120]. Shiau et al. investigated how Scutellaria barbata regulates the molecular mechanism of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1)-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression. The results showed that Scutellaria barbata inhibits HIF-1α expression, phosphorylates its upstream signaling mediator AKT, and reduces VEGF expression in tumor cells. Additionally, it inhibits endothelial cell migration and proliferation under hypoxic conditions and significantly inhibits tumor growth in vivo, as evidenced by reducing microvessel density in tumor immunohistochemistry studies [121]. Wei et al. reported that the ethanol extract of Scutellaria barbata (EESB) was shown to inhibit tumor growth in colorectal cancer mouse models without affecting body weight gain. Further research revealed that EESB inhibits Sonic Hedgehog (SHH)-mediated tumor angiogenesis, contributing to its anticancer effects [122]. Zhang et al. demonstrated that the active compound luteolin in Scutellaria barbata exerts anti-tumor effects through multiple synergistic pathways, including the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis [111]. Similarly, studies by Gong et al. indicate that Scutellaria barbata exhibits anti-tumor effects both in vitro and in vivo. The mechanisms through which SBD exerts its anti-tumor effects may include improving the tumor inflammatory microenvironment, blocking the cell cycle, promoting apoptosis, and inhibiting angiogenesis [8]. Additionally, Wang et al. have shown that the primary active components of Scutellaria barbata, luteolin, and quercetin, act on core targets such as AKT1, MAPK1, IL6, EGFR, SRC, VEGFA, and TP53. These interactions affect drug resistance, apoptosis, immune regulation, and angiogenesis, contributing to its efficacy against adverse-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML) [123].
In conclusion, these studies collectively demonstrate that extracts from Scutellaria barbata can downregulate vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) expression, inhibit the VEGF signaling pathway, suppress angiogenesis, and thereby exert anticancer effects. These mechanisms contribute significantly to the therapeutic potential of Scutellaria barbata in cancer treatment strategies.
3.5. Reduction of Cancer Cell Drug Resistance
Drug resistance in cancer cells poses a significant challenge in cancer treatment, often leading to decreased efficacy or even treatment failure with many anticancer drugs such as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and multidrug resistance (MDR) mechanisms. Combining traditional Chinese medicine with chemotherapy has been shown to mitigate cancer cell resistance and enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Research by Lin et al. demonstrated that EESB reduces the expression of CyclinD1, Bcl-2, and ATP binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (ABCG2), while upregulating p21 and Bax expression in HCT-8/5-FU colorectal cancer cells. This modulation suppresses the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway, thereby inhibiting chemotherapy resistance in these cells [124]. Shao et al. found that salvigenin, an active compound from Scutellaria barbata, enhances the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells to 5-FU and attenuates the resistance of HCC 5-FU-resistant cells to the drug. Salvigenin achieves its anticancer effects by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway, thereby impeding aerobic glycolysis and 5-FU chemotherapy resistance in HCC cells [10]. Li et al., using modern isolation and purification techniques, isolated and identified novel clerodane-type diterpenoid compounds from Scutellaria barbata. The vitro evaluation of these compounds revealed their ability to reverse multidrug resistance in HepG2/Adr cells when combined with doxorubicin (Adr). Experimental evidence suggested that these diterpenoid compounds may reverse tumor cell multidrug resistance by inhibiting the P-glycoprotein efflux function [125]. Zhang et al. reported that the anticancer effects of Scutellaria barbata may involve multiple compounds acting on various targets and pathways in ovarian cancer. For instance, wogonin enhances apoptosis in ovarian cancer CAOV3/DDP cells resistant to cisplatin by reducing Bcl-2 expression, thereby augmenting cisplatin’s anti-tumor effects. Additionally, wogonin treatment increases tumor cell apoptosis and enhances the cytotoxicity of TNF-α and TRAIL to tumor cells, blocks the tumor cell cycle, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and synergizes with chemotherapy drugs through ROS and Ca2+-mediated signaling pathways [111]. Wang et al. showed that luteolin and quercetin were the main active components of Scutellaria barbata against adverse-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML) through the network pharmacology research. These compounds were found to affect drug resistance, cellular behaviors, apoptosis, immune regulation, cell metabolism, angiogenesis, and other signaling pathways through core targets such as AKT1, MAPK1, IL6, EGFR, SRC, VEGFA, and TP53 [123].
Scutellaria barbata exerts its potential in overcoming cancer drug resistance by mechanisms such as inhibiting drug efflux pumps and controlling apoptosis, thereby enhancing the efficacy of anticancer drugs. Future research aims to elucidate its precise mechanisms of action and explore its clinical application value in anticancer therapy.
3.6. Improvement of Tumor Microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment (TME) refers to the surroundings in which tumor cells exist, comprising blood vessels, immune cells, fibroblasts, bone-marrow-derived inflammatory cells, various signaling molecules, and extracellular matrix. This microenvironment plays a crucial role in the initiation, growth, and metastasis of tumors through continuous interactions. Tumors can influence their microenvironment by releasing signaling molecules to promote angiogenesis and induce immune tolerance. Conversely, immune cells within the microenvironment can also affect the growth and development of cancer cells.
Gong et al. reported that Scutellaria barbata inhibits the proliferation of HepG2 cells in vitro in a dose-dependent manner and significantly suppresses tumor growth in mice. Scutellaria barbata can modulate the infiltration of Treg and Th17 cells in the tumor microenvironment, reducing the number of CD4+,CD25+,Foxp3+,Treg cells and Th17 cells in tumor tissues. This modulation decreases IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-17A levels in the serum of liver cancer mice (p < 0.01), while increasing IL-2 and IFN-γ levels (p < 0.01) [8]. Li et al. showed that a 1:1 mixture of Scutellaria barbata and Scutellaria barbata ethyl acetate extracts significantly downregulates LMO1 expression. LMO1 overexpression weakens the inhibitory effects of Scutellaria barbata on cell proliferation and invasion, inducing an inflammatory tumor microenvironment. Additionally, downregulating LMO1 expression can suppress cell proliferation and migration by reducing AKT/mTOR pathway activation [13]. Zhang et al. showed that AKT1, VEGFA, JUN, TNF, and Caspase-3 are central among all target genes through protein–protein interaction network analysis. VEGFA is often overexpressed in solid tumors and malignant diseases, significantly promoting tumor angiogenesis. Cell experiments demonstrated that active compounds such as baicalein and wogonin from Scutellaria barbata inhibit VEGFA expression. This targeted regulation affects other cell types within the tumor microenvironment and influences tumor function [111].
4. Clinical Application
In the clinical practice of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), several compound formulas containing Scutellaria barbata are utilized for the treatment or adjunctive therapy of tumors. For instance, “Intestine Formula” is used for advanced metastatic colorectal cancer, Compound Banmao Capsules combined with cisplatin and paclitaxel injection (DP) are employed for advanced ovarian cancer, Yipi Fuzheng Recipe effectively reduces the incidence of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in esophageal cancer patients, Yangzheng Xiaojie Capsules improve the quality of life and prolong life expectancy in patients with advanced gastrointestinal cancers, Ankangxin Capsules are applicable for the treatment of lung cancer, cervical cancer, liver cancer, and gastric cancer, Anticancer Pills are used for HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer, Ban zhi Qin lian decoction is prescribed for non-small-cell lung cancer, and Hedyotis diffusa–Scutellaria barbata is used for maintenance therapy in malignant tumors. This section reviews the clinical studies on Scutellaria barbata, providing a straightforward assessment of its therapeutic effects [126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133].
A clinical study targeting advanced refractory colorectal cancer patients who had progressed after multiple chemotherapy regimens randomized them into treatment and control groups, each comprising 30 cases. The treatment group received Intestine Formula (containing Scutellaria barbata) along with optimal supportive care, while the control group received only optimal supportive care until patient loss to follow-up or death. The results showed that after 2 months, the treatment group demonstrated an improvement rate in TCM symptom scores of 76.7%, a total effective rate by Karnofsky Performance Score of 86.7%, and a tumor control rate of 60.0%, all significantly higher than the control group’s rates of 43.3%, 53.3%, and 33.3%, respectively (p < 0.05). Immunologically, the treatment group showed a significant increase in NK cell count and CD4/CD8 ratio compared to before treatment (p < 0.05), effectively improving patient symptoms and modulating immunity. The treatment group’s half-year survival rate, one-year survival rate, and two-year survival rate were 92.8%, 57.1%, and 14.2%, respectively, with a median survival period of 13 months, all significantly higher than those of the control group (p < 0.05) [126].
A clinical study investigating the clinical efficacy of Compound Banmao Capsules combined with the DP regimen (cisplatin plus paclitaxel injection) in treating advanced ovarian cancer included 114 patients receiving treatment. Using randomization, patients were divided into treatment and control groups, with 57 cases in each. The control group received the DP chemotherapy regimen, while the treatment group received oral Compound Banmao Capsules (containing Scutellaria barbata) in addition to the control group’s treatment. The results indicated that post-treatment, the disease control rates were 45.6% and 68.4% for the control and treatment groups, respectively, and the objective response rates were 63.2% and 77.2%, respectively, with statistically significant differences (p < 0.05). One-year survival rate, three-year survival rate, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were significantly higher in the treatment group compared to the control group, with statistically significant differences observed between the two groups (p < 0.05) [127].
An observational clinical study assessing the clinical efficacy of Yipi Fuzheng Formula combined with chemotherapy in treating advanced esophageal cancer included 41 patients. Using random numerical methods, the patients were allocated into a treatment group (n = 20) and a control group (n = 21). The control group received paclitaxel plus nedaplatin chemotherapy regimen, while the treatment group received Yipi Fuzheng Formula (containing Scutellaria barbata) in addition to the control group’s treatment. The results demonstrated statistically significant differences between the treatment and control groups in terms of improvement in TCM syndrome scores, TCM syndrome effectiveness, Karnofsky Performance Score (KPS), and immune indicators (p < 0.05). The treatment group showed improvements in nausea and vomiting symptoms (p < 0.05) and reduced the incidence of side effects [128] to some extent.
An observational clinical study on the combined use of Endu (Enzalutamide) and Yangzheng Xiaoji Capsules in treating advanced gastrointestinal malignant tumors included 80 patients. They were randomly divided into a control group of 38 cases and an observation group of 42 cases. The control group received Endu combined with capecitabine maintenance therapy, while the observation group received Endu combined with Yangzheng Xiaoji Capsules. The results showed that after treatment, both groups exhibited significant improvements in serum inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6, and CRP compared to before treatment (p < 0.05). CD4+ and CD4+/CD8+ ratios increased significantly post-treatment (p < 0.05), with more pronounced changes in the observation group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). Changes in KPS scores were more significant in the observation group than the control group (p < 0.05). The observation group showed significantly better scores in functional domains, symptom domains, and overall survival quality compared to the control group (p < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in one-year PFS rates and OS rates between the two groups (p > 0.05), and adverse reactions were significantly fewer in the observation group (p > 0.05) [129].
A clinical study exploring the application effectiveness of Ankangxin Capsules combined with cisplatin in adjuvant chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) involved 90 patients. They were randomly divided into a control group and an observation group, each comprising 45 cases. The control group received a gemcitabine plus cisplatin (GP) regimen, while the observation group received Ankangxin Capsules in addition to the control group’s treatment. The results showed that the clinical benefit rate in the observation group was 66.67%, significantly higher than the control group’s 46.67%, with statistically significant differences (p < 0.05). CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD4+/CD8+, and NK levels were significantly higher in the observation group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). The observation group had significantly lower rates of nausea, vomiting, rash, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, hepatic dysfunction, and toxic side effects compared to the control group (p < 0.05) [130].
A clinical study investigating the short-term and long-term efficacy of Anticancer Pills combined with trastuzumab and chemotherapy in HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer patients included 98 subjects. They were randomly divided into an observation group and a control group, each comprising 49 cases. The control group received a trastuzumab and mFOLFOX6 chemotherapy regimen, while the observation group additionally received Anticancer Pills orally. After treatment, the observation group showed significantly higher effective rates and control rates compared to the control group (p < 0.05). PFS, OS, one-year survival rate, and three-year survival rate were all significantly higher in the observation group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). During treatment, the observation group had significantly lower incidence rates of cardiac toxicity, gastrointestinal reactions, hepatic toxicity, renal toxicity, bone marrow suppression, and neurological toxicity compared to the control group (p < 0.05) [131].
A clinical efficacy analysis study on the combination of Ban zhi Qin lian decoction and gefitinib in treating elderly patients with NSCLC included 63 elderly NSCLC patients. According to the treatment nature, they were randomly divided into a gefitinib treatment group (control group) with 31 cases and a Ban zhi Qin lian decoction combined with gefitinib treatment group (study group) with 32 cases. The results showed that the study group achieved a 100% probability of disease remission and stabilization, significantly higher than the control group’s 81.3% (p < 0.05), effectively alleviating clinical discomfort symptoms and improving patient comfort comprehensively [132].
A clinical study on the maintenance treatment effectiveness of Hedyotis diffusa–Scutellaria barbata in malignant tumor maintenance treatment selected 80 gastric cancer patients who completed first-line effective chemotherapy. Using a double-blind principle, the patients were divided into a control group and a maintenance treatment group, each with 40 cases. The control group received routine maintenance treatment, while the maintenance treatment group received Hedyotis diffusa–Scutellaria barbata for maintenance treatment in addition to the control group’s treatment. The results indicated that the maintenance treatment group had a significantly higher effective rate (RR) than the control group, with statistically significant differences (p < 0.05). The maintenance treatment group also showed significantly higher improvement rates in overall quality of life compared to the control group (p < 0.05), and the incidence of adverse reactions in the maintenance treatment group was significantly lower than that in the control group (p < 0.05) [133].
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Scutellaria barbata, a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, has a medicinal history spanning over four centuries. This plant contains a wealth of chemical constituents, primarily including flavonoids, diterpenoids, polysaccharides, and essential oils. These components bestow Scutellaria barbata with broad pharmacological activities, particularly demonstrating significant potential in the field of anti-tumor therapy.
This paper comprehensively summarized the research findings on Scutellaria barbata from the past decade, identifying 72 flavonoids and 164 diterpenoids. The main active flavonoid constituents include quercetin, luteolin, scutellarein, scutellarin, wogonin, and baicalein, which are pivotal to the anti-tumor effects of Scutellaria barbata. Diterpenoids are more numerous compared to other components due to their diverse core structures and abundant substituents. Studies indicate that diterpenoids possess certain cytotoxic and anti-tumor activities.
Modern pharmacological studies have gradually elucidated the anti-tumor mechanisms of Scutellaria barbata, including the inhibition of tumor cell proliferation, promotion of tumor cell apoptosis, inhibition of cell invasion and migration, regulation of the immune system, and anti-angiogenesis. The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is abnormally activated in tumor cells. The activation promotes cancer cell proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion while inhibiting apoptosis. According to the literature, Scutellaria barbata extract can inhibit the phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt. On one hand, the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway can suppress proto-oncogenes and reduce the expression of Src Family Kinases and TNF genes, thereby inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and migration and promoting apoptosis. On the other hand, it can reduce the expression of cell cycle proteins such as Cyclins B1, Cyclins D1, CDK1, CDK2, and CDK4, preventing the transition of tumor cells from the G2 phase to the M phase and inhibiting cell proliferation. SBD can inhibit the expression of NFκB in tumor cells, thereby activating the tumor suppressor gene TP53 and promoting the expression of tumor necrosis factor Fas. The overexpression of TP53 also affects cell cycle proteins like CDK2, causing cell cycle arrest. Meanwhile, TP53 and Fas induce the downregulation of the anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2 and the upregulation of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax. The increasing Bax/Bcl-2 ratio also enhances the expression of cytochrome C. Cytochrome C can not only directly disrupt the mitochondrial membrane, inducing cancer cell apoptosis, but also can form apoptosomes with Caspase9 and Apaf-1, activating the expression of Caspase3 and inducing cancer cell apoptosis. Research has also reported that SBD can induce the production of ROS, mediated by the MAPK pathway, leading to the expression of pro-apoptotic factors such as JNK and P38, thereby triggering cancer cell apoptosis. Scutellaria barbata can also inhibit EMT through the TGF-β and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, preventing cancer cell invasion and migration. SBD inhibits tumor angiogenesis by suppressing the VEGF pathway, exerting an anticancer effect. Extracts of Scutellaria barbata inhibit the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, reducing the expression level of the ABC transporter ABCG2, suppressing the efflux function of ABC transporters, and increasing drug accumulation in cancer cells, thereby exhibiting anti-tumor activity. In terms of the anti-tumor mechanisms of Scutellaria barbata extracts, although sufficient evidence exists, a considerable portion of research has been conducted through network pharmacology combined with simple in vitro experiments, failing to validate related mechanisms in vivo. Future studies on the anti-tumor mechanisms of Scutellaria barbata extract require further in-depth investigations to support its clinical anti-tumor applications.
Clinically, Scutellaria barbata has been widely used in the treatment of various tumors such as prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, and lung cancer. In adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy, Scutellaria barbata has been shown to improve patient symptoms, reduce adverse reactions to chemotherapy, enhance quality of life, and increase therapeutic efficacy. However, the clinical application of Scutellaria barbata still faces challenges such as the standardization of components, determination of dosage, and long-term safety assessment.
Despite some progress in this research, there remain many unknown aspects of the chemical constituents and anti-tumor mechanisms. Firstly, identifying, isolating, and elucidating the specific molecular structures for the observed anti-tumor effects is a meticulous and time-consuming process. Moreover, the anti-tumor mechanisms of these compounds are often multifaceted. The intricacies of these interactions, often involving intricate networks of proteins, genes, and metabolic pathways, render them difficult to fully comprehend and harness for therapeutic purposes. Furthermore, the variability in tumor biology across different cancer types and even within individual patients presents another layer of complexity. This underscores the need for a more personalized approach to cancer treatment, where the specific chemical constituents and mechanisms of action are tailored to the unique characteristics of each patient’s tumor. In conclusion, despite the progress made in recent years, the chemical constituents and anti-tumor mechanisms of many potential cancer therapeutics remain largely unknown. Advances in technology and ongoing research efforts are critical to unraveling these mysteries and developing more effective and targeted cancer treatments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S. and C.L.; methodology, J.S. and C.L.; software, J.S.; validation, J.S., C.L. and Q.L.; formal analysis, J.S.; investigation, J.S.; resources, J.S.; data curation, J.S. and Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S.; writing—review and editing, J.S.; visualization, J.S., Y.X. and Z.Z.; supervision, C.L.; project administration, C.L.; funding acquisition, C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No data was used for the research described in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol3-kinase |
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ERK | Extracellular-regulated protein kinases |
| JNK | C-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| NFκB | Nuclear factor kappa-B |
| SBP | Scutellaria barbata polysaccharide |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| PLK1 | Polo-like kinase 1 |
| TP53 | Tumor protein p53 |
| BAX | BCL2-associated X |
| P21 | Protein 21 |
| HepG2 | Human hepatocellular carcinomas |
| Bax | BCL2-associated X |
| Bcl | B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| CNE | Human nasopharyngeal cancer cell |
| SBD | Scutellaria barbata D. Don |
| VEGFA | Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| p-EGFR | p-Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| PDE7B | cAMP-specific 3′,5′-cyclic phosphodiesterase 7B |
| PTHrP | Parathyroid-hormone-related protein |
| HD-SB | Hedyotis diffusa–Scutellaria barbata |
| Smad | Drosophila mothers against decapentaplegic protein |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| LMO1 | LIM domain only 1 |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| OS | Overall survival |
References
- Banerjee, J.; Tiwari, A.K.; Banerjee, S. Drug repurposing for cancer. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2024, 207, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Xu, C.; Song, J.; Jin, Y.; Gao, X. Mechanisms of Traditional Chinese medicine/natural medicine in HR-positive Breast Cancer: A comprehensive Literature Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J. Textual research on herbs of Scutellaria barbata. TCM Res. 2006, 19, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Zhan, S.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Lin, X.; Xu, H. Antitumor Effects and the Compatibility Mechanisms of Herb Pair Scleromitrion diffusum (Willd.) R. J. Wang-Sculellaria barbata D. Don. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, F.; Chen, W. A review of the ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and quality control of Scutellaria barbata D. Don. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 254, 112260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.T.; Li, S.M.; Pan, B.W.; Xiao, J.W.; Pang, Y.X.; Xie, S.X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Wei, Y. Identification of Flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don as Inhibitors of HIV-1 and Cathepsin L Proteases and Their Structure-Activity Relationships. Molecules 2023, 28, 4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Wu, L.; Liang, Q.; Lin, X.; Xu, X.; Yu, S.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Fu, Y.; Gao, X.; et al. Extraction Optimization, Structural Characterization, and Anti-Hepatoma Activity of Acidic Polysaccharides from Scutellaria barbata D. Don. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 827782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Kao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, F.; Zhao, H. Systematic Investigation of Scutellariae barbatae Herba for Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Network Pharmacology. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 4365739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y. Study on the mechanism of action of Scutellaria barbata on hepatocellular carcinoma based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1072547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Chen, J.; Li, A.; Ma, L.; Tang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Salvigenin Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glycolysis and Chemoresistance Through Inactivating the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β Pathway. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 5217–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Luo, H.; Huang, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhao, L.; Li, P.; Zhong, C.; Liu, F. AURKB, CHEK1 and NEK2 as the Potential Target Proteins of Scutellaria barbata on Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 3295–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Kang, W.; Liu, H.; Guo, S. Inhibition effects of total flavonoids from Sculellaria barbata D. Don on human breast carcinoma bone metastasis via downregulating PTHrP pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3137–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Z.; Sun, X. Ethyl Acetate Fraction from Hedyotis Diffusa Plus Scutellaria barbata Inhibits the Progression of Breast Cancer via Targeting LMO1 and AKT/Mtor Signaling Pathway. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2024, 27, 27–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, T.; Cao, Y.L.; Lv, Y.X.; Chang, Q.Q.; Zhang, D.D. Ethyl Acetate Fraction from Hedyotis diffusa plus Scutellaria barbata Exerts Anti-Breast Cancer Effect via miR-200c-PDE7B/PD-L1-AKT/MAPK Axis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 3587095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wu, Y.; Lv, D.L.; Feng, L. Scutellarein selectively targets multiple myeloma cells by increasing mitochondrial superoxide production and activating intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Li, L.; Xue, X. Flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata inhibit activation of tumor-associated macrophages by blocking the Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 39, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, T.; Tao, W.; Liao, N.; Yan, Q.; Li, L.; Tan, J.; Shen, W.; Cheng, H.; Sun, D. Flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don exert antitumor activity in colorectal cancer through inhibited autophagy and promoted apoptosis via ATF4/sestrin2 pathway. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022, 99, 154007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, W.; Wang, T.; Peng, Y. Scutellaria barbata D.Don (SBD) extracts suppressed tumor growth, metastasis and angiogenesis in Prostate cancer via PI3K/Akt pathway. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-S.; Wei, M.-C. Kinetics and mass transfer considerations for an ultrasound-assisted supercritical CO2 procedure to produce extracts enriched in flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 32, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Yin, X.; Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Ren, Y. A strategy integrating parent ions list-modified mass defect filtering-diagnostic product ions for rapid screening and systematic characterization of flavonoids in Scutellaria barbata using hybrid quadrupole-orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1674, 463149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I.; Lee, T.K.; Lim, I.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, C.H. Regulation of IGF-I production and proliferation of human leiomyomal smooth muscle cells by Scutellaria barbata D. Don in vitro: Isolation of flavonoids of apigenin and luteolin as acting compounds. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 205, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Suzaki, S.; Nishikawa, T.; Kihara, M.; Shibata, H.; Higuti, T. Phytochemical flavones isolated from Scutellaria barbata and antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 72, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.C.; Wei, M.C. Development and characterization of a green procedure for apigenin extraction from Scutellaria barbata D. Don. Food Chem. 2018, 252, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.Q.; Han, L.W.; Wang, X.M.; Hou, H.R.; Liu, K.C. Study on Anti-Angiogenic Activity of the Chemical Constituents from Scutellaria barbata. Chin. Pharm. J. 2012, 47, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.R.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.; Hwang, K.W.; Park, S.Y. Constituents from Scutellaria barbata Inhibiting Nitric Oxide Production in LPS-Stimulated Microglial Cells. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, P.; Sun, T.F.; Han, L.; Hu, Y.N.; Du, H.T.; Liu, H. Research Progress on Chemical Constituents of Scutellaria barbata. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2020, 45, 5117–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Duan, X.C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.Z. Studies on chemical constituents of flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata. Anhui Med. J. 2019, 40, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.Y.; Liu, G.Q. Isolation and identification of the diterpenold and flavone in Scutellaria barbata D. Don. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 1993, 2, 63–64. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Lin, J.; Li, G.; Lin, X. Chromatographic fingerprint and quantitative analysis of seven bioactive compounds of Scutellaria barbata. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Chemical Constituents of Scutellaria barbata. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2014, 20, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.Y.; Zhang, D.W.; Dai, S.J. Isolation and Identification of Chemical Consistents from the Whole herb of Scutellaria Barbata. Mod. Chin. Med. 2011, 13, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ren, F.C.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, J.K. Scutebarbatines W-Z, new neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata and structure revision of a series of 13-spiro neo-clerodanes. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Yang, G.C.; Li, D.H.; Hu, X.X.; Sun, L.X. Chemical constituents from Scutellaria barbata. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Herbal. Drugs 2016, 47, 4322–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Tong, C.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Shi, F.; Shi, S.; Xiao, Y. Flavonoid aglycone–oriented data-mining in high-performance liquid chromatography–quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry: Efficient and targeted profiling of flavonoids in Scutellaria barbata. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.K. Two New Phenols from Scutellaria barbata. Molecules 2011, 16, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Xue, X.X.; Yao, Q.Q. Research of chemical constituents of Scutellaria barbata. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Herbal. Drugs 2008, 39, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.S.; Zhou, Y.W.; Ye, Y.H.; Du, N. Studies on the flavonoids in herb from Scutellaria barbata. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2004, 29, 957–959. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Li, X. Chemical constituents of Scutellaria barbata D. Don. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2006, 23, 637–640. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Q.; Wei, L.; Zhan, Y.; Shen, A.; Sferra, T.J.; Peng, J. Scutellaria barbata D Don Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth via Suppression of Multiple Signaling Pathways. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Li, Z. Studies on the Flavonoids in Scutellaria barbata with LC-MS. J. Cap. Capital Norm. Univ. 2009, 30, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, D.; Wang, T.; Hu, L.; Gao, X. Isolation and identification of flavonoids of whole plant of Scutellaria barbata D.Don. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2011, 28, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Wei, W.J.; Ma, K.L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, K. Phytotoxic neo-clerodane diterpenoids from the aerial parts of Scutellaria barbata. Phytochemistry 2020, 171, 112230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.C.; Hu, J.H.; Li, B.L.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.Y.; Sun, L.X. Six New neo-Clerodane Diterpenoids from Aerial Parts of Scutellaria barbata and Their Cytotoxic Activities. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Thao, T.; Phuong, D.T.; Hanh, T.T.; Thao, N.P.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Two new neoclerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don growing in Vietnam. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 16, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.J.; Sun, J.Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, L. Bioactive ent-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. J. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.C.; Liang, C.; Li, S.G.; Liu, M.; Jia, M.J.; Xu, X.N.; Wang, X.B.; Hua, H.M.; Sun, L.X. Neoclerodane diterpenoids from aerial parts of Scutellaria barbata. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Di, Y.T.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, L.L.; He, H.P. Neoclerodane Diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, C.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xu, J.; Lee, K.H.; Gu, Q. Neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata with activity against Epstein-Barr virus lytic replication. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ma, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, J. Cytotoxic Neo-Clerodane Diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata D.Don. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1800499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.J.; Tao, J.Y.; Liu, K.; Jiang, Y.T.; Shen, L. neo-Clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata with cytotoxic activities. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.J.; Shen, L.; Ren, Y. Two new neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 50, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Hu, P.; Ji, J.; Li, X.; Chen, J. Neoclerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata with cytotoxic activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.J.; Peng, W.B.; Zhang, D.W.; Shen, L.; Wang, W.Y.; Ren, Y. Cytotoxic neo-clerodane diterpenoid alkaloids from Scutellaria barbata. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1793–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon, E.T.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, C.; Jin, Q.; Jang, H.; Lee, D.; Ahn, J.S.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.K. neo-Clerodane Diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata and Their Inhibitory Effects on LPS-Induced Nitric Oxide Production. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2292–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, G.M.; Xia, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, L.N.; Luo, J.G.; Kong, L.Y. neo-Clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata mediated inhibition of P-glycoprotein in MCF-7/ADR cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Xu, F.M.; Yan, X.Z.; Zhu, Y. Scutebarsatine a, a new neoclerodane-type diterpenoid alkaloid from Scutellaria barbata. Chin. Chem. Lett. 1996, 56, 333–334. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.J.; Liang, D.D.; Ren, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, L. New neo-clerodane diterpenoid alkaloids from Scutellaria barbata with cytotoxic activities. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.P.; Qu, G.W.; Yue, X.D.; Li, G.S.; Dai, S.J. Scutelinquanines A–C, three new cytotoxic neo-clerodane diterpenoid from Scutellaria barbata. Phytochem. Lett. 2010, 3, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, D.; Jia, J.; Zou, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, X.; Ma, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Structure and anti-inflammatory activity of neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. Phytochemistry 2023, 213, 113771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; Quang, T.H.; Trung, N.Q.; Cuong, N.T.; An, N.T.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Van Kiem, P.; Van Minh, C. Scutebarbatolides A-C, new neo -clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don with cytotoxic activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 29, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.J.; Qu, G.W.; Yu, Q.Y.; Zhang, D.W.; Li, G.S. New neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata with cytotoxic activities. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.J.; Chen, M.; Liu, K.; Jiang, Y.T.; Shen, L. Four new neo-clerodane diterpenoid alkaloids from Scutellaria barbata with cytotoxic activities. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.J.; Peng, W.B.; Shen, L.; Zhang, D.W.; Ren, Y. Two new neo-clerodane diterpenoid alkaloids from Scutellaria barbata with cytotoxic activities. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 11, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizu, H.; Imoto, Y.; Tomimori, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Kadota, S.; Tsubono, K. Studies on the Constituents of Scutellaria Species. XVIII. Structures of Neoclerodane-Type Diterpenoids from the Whole Herb of Scutellaria rivularis WALL. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Tsubono, K.; Kadota, S.; Kizu, H.; Imoto, Y.; Tomimori, T. Structures of scuterivulactone C1 and C2 by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. New clerodane type diterpenoids from Scutellaria rivularis Wall. Chem. Lett. 1987, 16, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Kuo, Y.H.; Cheng, M.C.; Wang, Y. Structures of Scutellones D and E Determined from X-Ray Diffraction, Spectral and Chemical Evidence. Neoclerodane-Type Diterpenoids from Scutellaria rivularis WALL. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 2642–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Kuo, Y.H.S.C. Two New Neoclerodane Type Diterpenoids from Scutellaria rivularis. Heterocycles 1988, 27, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; He, X.; He, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, R.; Fan, P.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, Z. The genus Scutellaria an ethnopharmacological and phytochemical review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 279–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Kuo, Y.H. Four New Neoclerodane-Type Diterpenoids, Scutellones B, G, H, and I, from Aerial Part of Scutellaria Rivularis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.Q.; Song, W.B.; Wang, W.Q.; Xuan, L.J. Scubatines A-F, new cytotoxic neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don. Fitoterapia 2017, 119, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Di, Y.T.; Liu, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; He, H.P. Cytotoxic neoclerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, Y.; Choi, I.; Min, B.S.; Shim, S.H. Two novel neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, G.W.; Yue, X.D.; Li, G.S.; Yu, Q.Y.; Dai, S.J. Two new cytotoxic ent-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.S.; Yan, W.; Bai, L.H.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.Q. neo-Clerodane Diterpenoids from the Aerial Parts of Scutellaria barbata with Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Tang, X.L.; Jiang, T.; Li, P.F.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Bioassay-guided isolation of neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.H. A New Diterpenoid from Aerial Parts of Scutellaria barbata. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2014, 50, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Pham, V.C.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Tran, V.H.; Doan, T.M.H. Novel Antioxidant neo-Clerodane Diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 2009, 5810–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.J.; Wang, G.F.; Chen, M.; Liu, K.; Shen, L. Five new neo-clerodane diterpenoid alkaloids from Scutellaria barbata with cytotoxic activities. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.X.; Cao, Y.X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L. A new neoclerodane diterpenoid from Scutellaria barbata. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Herbal. Drugs 2015, 46, 2843–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Ling-Li, L.; Ying-Tong, D.I.; Xiao-Jiang, H.; Hong-Ping, H.E. Scutellin A, a New Neoclerodane Diterpenoid from Scutellaria barbata (Labiatae). Plant Divers. 2009, 31, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizu, H.; Imoto, Y.; Tomimori, T.; Tsubono, K.; Kadota, S.; Kikuchi, T.J.C.; Bulletin, P. Structure of scuterivulactone d determined by two-dimensional nmr spectroscopy. a new diterpenoid from a chinese crude drug “ban zhi lian” (scutellaria rivularis wall). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.J.; Peng, W.B.; Shen, L.; Zhang, D.W.; Ren, Y. New norditerpenoid alkaloids from Scutellaria barbata with cytotoxic activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zuo, T.T.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhu, L.X.; Zhang, G.G. Chemical constituents of Scutellaria barbata D. Don (II). Chin. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 18, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Shu-Heng, H.E.; Dan-Dan, G.E.; Peng, Z.; Xiu-Mei, G.; Tao, W. Isolation and identification of chemical constituents from whole plant of Scutellaria barbata D.Don (II). J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2011, 28, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.G.; Gu, Z.L. Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Effects of Scutellaria barbata. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 2004, 23, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.M.; Guo, L.W.; Chen, J.W. Isolation and physico-chemical properties of polysaccharide from the herb of Scutellaria barbata D. Don. Nat. Prod. Product. Res. Dev. 1992, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.F.; Li, Z.X.; Wang, B.F.; Meng, X.Q.; Chen, Y.Z. Study on Polysaccharide from Scutellaria Barbata. J. Lanzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 1992, 28, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.L.; Zhang, J. Extraction, separation and preliminary structure research of polysaccharide from Scutellaria barbata. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2008, 30, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wei, H.P.; Wang, J.B. Anti-complement activity of polysaccharide B3-PS2 purified from Herba Scutellariae barbatae. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2009, 44, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Dai, L.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Liao, H.M.; Zhang, K. Purification, properties and antioxidant activity of acidic polysaccharide SBPs from Scutellaria barbata. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Herbal. Drugs 2009, 40, 728–731. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Sun, D.; Wang, X. Effects of Scutellaria barbata polysaccharide on the proliferation, apoptosis and EMT of human colon cancer HT29 Cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Ming, Y.L. Advances on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Scutellaria barbata. Subtrop. Plant Sci. 2015, 44, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, N.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Wu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W.; et al. Polysaccharide from Scutellaria barbata D. Don attenuates inflammatory response and microbial dysbiosis in ulcerative colitis mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Lei, J.; Yu, H.; Cai, X.; Zou, G. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil Scutellaria barbata. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.W.; Hui, R.H.; Hou, D.Y. Analysis of Volatile Components in Scutellaria barbata D. Don. J. Chin. Mass. Spectrom. Soc. 2009, 30, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, T.S.; Chen, F.L.; Lin, J.M. GC-MS analysis of volatile oil from Scutellaria barbata. J. South. Med. Univ. 2009, 29, 1482–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.W.; Hu, J.F.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yin, W.J.; Lv, Q.T.; Rong, R. Optimization of the supercritical carbon dioxide extraction conditions for Scutellaria barbata D. Don by orthogonal test and GC-MS analysis. Mod. Instrum. 2012, 18, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qin, R. Quantitative changes analysis between contents of active ingredients and trace elements in Scutellaria barbata D. Don. Chem. Res. Appl. 2017, 29, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Bei, Z.Y.; Luo, X.B.; Li, Y.B. Determination of Microelements in Herba Scutellariae Barbatae by Microwave-assisted Sample Digestion-flame Atom ic Absorption Spectrametric. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2008, 19, 709–710. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.L. Studies on extraction of Scutellaria barbata D. Don by supercritical fluid of CO2. Pharm. J. Chin. PLA 2004, 20, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Xiao, H.T.; Meng, D.L.; Wang, J.H. Chemical constituents of Scutellaria barbata. Mod. Chin. Med. 2009, 11, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducki, S.; Hadfield, J.A.; Lawrence, N.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, X. Isolation of E-1-(4′-Hydroxyphenyl)-but-1-en-3-one from Scutellaria barbata. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, G.; Zuo, T.; Wang, S. Chemical constituents of the whole plant of Scutellaria barbata D. Don. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2008, 27, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, M.; Nishiyama, T.; Matsukawa, Y.; Moriyasu, M. Cytotoxic activities of flavonoids from two Scutellaria plants in Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 91, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimori, T.; Miyaichi, Y.; Imoto, Y.; Kizu, H. Studies on the constitutents of Scutellaria species (VIII). On the flavonoid constituents of “Ban Zhi Lian”, the whole herb of Scutellaria rivularis. J. Pharmacogn. 1986, 40, 432–433. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Guo-Gang, Z.; De-Shuang, M.; Ying-Na, L.I. Chemical constituents of Scutellaria barbata D.Don (I). Chin. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 18, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, P.; Li, G. Studies on Chemical Consisutents of Scutellaria barbata D. Don. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2013, 43, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Wen, X.; Yan, S.; Gu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X. Network-based pharmacology-based research on the effect and mechanism of the Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata pair in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W. Exploring the mechanisms of anti-ovarian cancer of Hedyotis diffusa Willd and Scutellaria barbata D. Don through focal adhesion pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnit, S.S.T.; Yao, M.; Xie, C.; Ge, G.; Bi, L.; Jin, S.; Jiao, L.; Xu, L.; Long, L.; Nie, H.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of G(2)/M regulatory proteins and perturbation of G(2)/M Cell cycle transition by a traditional Chinese medicine recipe. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 251, 112526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, C.; Li, H.; Ding, C.; Wang, L.; Wu, H.; Dai, W.; Wang, C. Exploration of the effect and mechanism of Scutellaria barbata D. Don in the treatment of ovarian cancer based on network pharmacology and in vitro experimental verification. Medicine 2023, 102, e36656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Tang, F.; Tian, D.; He, Y. Molecular Assessment of Scutellaria barbata D. Don in the Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 1988378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, B.; Sun, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Baicalein: A review of its anti-cancer effects and mechanisms in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, S.; Jia, H.; Bai, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Flavonoids from tartary buckwheat induce G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravina, G.L.; Senapedis, W.; McCauley, D.; Baloglu, E.; Shacham, S.; Festuccia, C. Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport as a therapeutic target of cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, P.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Fang, C.; Lin, L. Investigating the Mechanism of Scutellariae barbata Herba in the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer by Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 3905367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.T.; Zhang, G.L.; Dai, C.F.; Zhang, B.R.; Cao, K.X.; Wang, C.G.; Yang, G.W.; Wang, X.M. Scutellaria barbata and Hedyotis diffusa herb pair for breast cancer treatment: Potential mechanism based on network pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Mastriani, E.; Li, Q.H.; Bao, H.X.; Zhou, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Main components of pomegranate, ellagic acid and luteolin, inhibit metastasis of ovarian cancer by down-regulating MMP2 and MMP9. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, K. Study on Inhibition of Reversal of Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition by Extracts from Scutellaria Barbata for Cell Migration and Invasion of Hepatoma Cells. J. New Chin. Med. 2019, 51, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, G.; Hou, G.; Liu, Q.; Hu, W.; Zhao, P.; He, Y. Scutellaria barbata D. Don polysaccharides inhibit the growth of Calu-3 xenograft tumors via suppression of the HER2 pathway and angiogenesis. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 2721–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, A.L.; Shen, Y.T.; Hsieh, J.L.; Wu, C.L.; Lee, C.H. Scutellaria barbata inhibits angiogenesis through downregulation of HIF-1α in lung tumor. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Lin, J.; Xu, W.; Cai, Q.; Shen, A.; Hong, Z.; Peng, J. Scutellaria barbata D. Don Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis via Suppression of Hedgehog Pathway in a Mouse Model of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 9419–9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lyu, C.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Dong, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, J.X.; Xu, R.R. A drug-biomarker interaction model to predict the key targets of Scutellaria barbata D. Don in adverse-risk acute myeloid leukaemia. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 2351–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Feng, J.; Yang, H.; Yan, Z.; Li, Q.; Wei, L.; Lai, Z.; Jin, Y.; Peng, J. Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer by regulating PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Yan, W.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Liu, D. Reversal of multi-drug resistance in HepG2/ADR cells by neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2020, 32, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Xie, S.; Wei, Z.; Wei, L.; Xiaoping, L.; Jiao, S.; Chun, Y. Clinical study on the treatment of 30 cases of advanced refractory colorectal cancer with “Intestinal Compound”. Jiangsu J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 49, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L. Clinical observation of Compound Banmao Capsules combined with DP regiment in treatment of advanced ovarian cancer. Drugs Clin. 2018, 33, 2050–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Jiao, J.; Ye, Z.; Wang, K. Clinical Analysis of Yipi Fuzheng Recipe combined with Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Advanced Esophageal Cancer. J. Shaanxi Univ. Chin. Med. 2019, 42, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cao, L.; Gao, S.; Li, R.; Wang, A.; Li, L.; Wang, G. Clinical Effect of Yangzheng Xiaoji Capsule Combined with Endostar in Treatment of Advanced Malignant Tumor of Digestive Tract. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 36, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, T. Application effect of Ankangxin Capsule combined with Cisplatin in the adjuvant chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. China Pr. Prac. Med. 2018, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Luo, J.; Du, M.; Zhang, X. Effect of Anti-cancer Pill Combined with Trastuzumab and Chemotherapy on Short Term Efficacy and Long-term Efficacy of HER2 Positive Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer. Pract. J. Cancer 2019, 34, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Clinical analysis of Ban zhi Qin lian decoction joint with gefitinib in the treatment of elderly non-small cell lung cancer. Captial Food Med. 2020, 27, 186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.; Guo, Y. Clinical study of oldenlandia diffusa-scutellaria barbata for the maintenance treatment of malignant tumors. J. Gannan Med. Univ. 2022, 42, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).