Combined Liposome–Gold Nanoparticles from Honey: The Catalytic Effect of Cassyopea® Gold on the Thermal Isomerization of a Resonance-Activated Azobenzene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Instruments
4.3. Preparation of the Cassyopea® Gold Samples
4.4. Kinetics Measurements
4.5. Preparation of the Sample for the Cryo-TEM Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Appenzeller, T. The man who dared to think small. Science 1991, 254, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamrungsap, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Fu, T.; Tan, W. Nanotechnology in therapeutics: A focus on nanoparticles as a drug delivery system. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Nanotechnology: A Revolution in Modern Industry. Molecules 2023, 28, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saritha, G.N.G.; Anju, T.; Kumar, A. Nanotechnology—Big impact: How nanotechnology is changing the future of agriculture? J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 10, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Zare, M.; Thomas, V.; Kumar, T.S.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nano-based drug delivery systems: Conventional drug delivery routes, recent developments and future prospects. Med. Drug Discov. 2022, 15, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, S.B.; Adnan, R.; Rameez Khan, R.M.; Rashid, M. Gold, Silver, and Palladium Nanoparticles: A Chemical Tool for Biomedical Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhilkar, P.R.; Bodhne, A.S.; Yerpude, S.T.; Madankar, R.S.; Somkuwar, S.R.; Daddemal-Chaudhary, A.R.; Lambat, A.P.; Desimone, M.; Sharma, R.; Chaudhary, R.G. Phyto-derived metal nanoparticles: Prominent tool for biomedical applications. OpenNano 2023, 14, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, A.; Asila, V.; Boitel-Aullen, G.; Lam, M.; Salmain, M.; Boujday, S. Silver-Based Plasmonic Nanoparticles for and Their Use in Biosensing. Biosensors 2019, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păduraru, D.N.; Ion, D.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Mușat, F.; Andronic, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Bolocan, A. Recent Developments in Metallic Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy, Diagnosing and Imaging Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlec, A.F.; Corciova, A.; Boev, M.; Batir-Marin, D.; Mircea, C.; Cioanca, O.; Danila, G.; Danila, M.; Bucur, A.F.; Hancianu, M. Current Overview of Metal Nanoparticles’ Synthesis, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications, with a Focus on Silver and Gold Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisar, P.; Ali, N.; Rahman, L.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K. Antimicrobial activities of biologically synthesized metal nanoparticles: An insight into the mechanism of action. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skóra, B.; Szychowski, K.A.; Gmiński, J. A concise review of metallic nanoparticles encapsulation methods and their potential use in anticancer therapy and medicine. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 154, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.; Guan, Z.; Ofoegbu, P.C.; Clubb, P.; Rico, C.; He, F.; Hong, J. Green synthesis of nanoparticles: Current developments and limitations. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Shariq, M.; Asif, M.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Malan, P.; Ahmad, F. Green nanotechnology: Plant-mediated nanoparticle synthesis and application. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Briffa, S.M.; Swingler, S.; Gibson, H.; Kannappan, V.; Adamus, G.; Kowalczuk, M.; Martin, C.; Radecka, I. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Curcumin-Cyclodextrins Loaded into Bacterial Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Wound Dressing Applications. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasbarri, C.; Angelini, G. An overview on the role of cyclodextrins in the synthesis of silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction. Arkivoc 2022, 2022, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, D. Honey mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2010, 75, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldeiu, A.; Simion, M.; Mihalache, I.; Radoi, A.; Banu, M.; Varasteanu, P.; Nadejde, P.; Vasile, E.; Acasandrei, A.; Popescu, R.C.; et al. Comparative analysis of honey and citrate stabilized gold nanoparticles: In vitro interaction with proteins and toxicity studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2019, 197, 111519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, G.H.; Akyuz, G.; Kaymazlar, E.; Andac, M. An Investigation of Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Turkish Honey Against Pathogenic Bacterial Strains. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2023, 13, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasbarri, C.; Angelini, G. Honey-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles in aqueous solution and inside supramolecular aggregates. The Cassyopea® effect. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 691, 133852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenzl, C.; Hirsch, T.; Baeumner, A.J. Liposomes with high refractive index encapsulants as tunable signal amplification tools in surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11157–11163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, F.; Bally, M.; Städler, B.; Chandrawati, R. Liposomes and lipid bilayers in biosensors. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musielak, M.; Potoczny, J.; Bos-Liedke, A.; Kozak, M. The combination of liposomes and metallic nanoparticles as multifunctional nanostructures in the therapy and medical imaging-a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Malinick, A.S.; Yang, T.; Cheng, W.; Cheng, Q. Gold nanoparticle-coupled liposomes for enhanced plasmonic biosensing. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2020, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Sun, W.; Lin, X.; Wang, R.; Li, C.; Zong, L.; Fu, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, S. Robust emission in near-infrared II of lanthanide nanoprobes conjugated with Au (LNPs-Au) for temperature sensing and controlled photothermal therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wei, J.; Li, X.; Tian, M.; Wang, Z.; Shen, C.; Sun, W.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Lv, E.; et al. Near-Infrared-Responded High Sensitivity Nanoprobe for Steady and Visualized Detection of Albumin in Hepatic Organoids and Mouse Liver. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2202505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold Nanoparticles in Nanomedicine: Preparations, Imaging, Diagnostics, Therapies and Toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, A.G.; Jiang, H.; Hochwald, S.N.; Delano, M.; Cance, W.G.; Grobmyer, S.R. Emerging Implications of Nanotechnology on Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Cancer 2006, 107, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Buchman, J.; Rodriguez, R.S.; Ring, H.L.; He, J.; Bantz, K.C.; Haynes, C.L. Stabilization of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: Preservation and Improvement of Plasmonic Functionalities. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 664–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, S.; Bricout, H.; Addad, A.; Sonnendecker, C.; Zimmermann, W.; Monflier, E.; Léger, B. Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol with gold nanoparticles stabilized by large-ring cyclodextrins. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 21007–21011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idoudi, S.; Ismail, R.; Rachid, O.; Elhissi, A.; Alkilany, A.M. The Golden Liposomes: Preparation and Biomedical Applications of Gold-Liposome Nanocomposites. J. Nanotheranostics 2023, 4, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.; Dawood, A.; Rida; Saira, F.; Malik, A.; Alkholief, M.; Ahmad, H.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Bazighifan, O. Enhancing catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles in a standard redox reaction by investigating the impact of AuNPs size, temperature and reductant concentrations. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M. Analyses of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles produced from strawberry fruit pomace extracts in terms of biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, antioxidant ability, photodegradation, and in-silico studies. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 102327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolwas, K.; Derkachova, A.; Shopa, M. Size characteristics of surface plasmons and their manifestation in scattering properties of metal particles. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Szcześ, A. Zeta potential and surface charge of DPPC and DOPC liposomes in the presence of PLC enzyme. Adsorption 2016, 22, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruso, J.M.; Besada, L.; Martínez-Landeira, P.; Seoane, L.; Prieto, G.; Sarmiento, F. Interactions Between Liposomes and Cations in Aqueous Solution. J. Liposome Res. 2003, 13, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comotti, M.; Della Pina, C.; Matarrese, R.; Rossi, M. The Catalytic Activity of “Naked” Gold Particles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5812–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett-Tapley, G.L.; D’Alfonso, C.; Pacioni, N.L.; McTiernan, C.D.; González-Béjar, M.; Lanzalunga, O.; Alarcon, E.I.; Scaiano, J.C. Gold nanoparticle catalysis of the cis–trans isomerization of azobenzene. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10073–10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, C.; Ruoko, T.-P.; Kuntze, K.; Virkki, M.; Priimagi, A. New tricks and emerging applications from contemporary azobenzene research. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2022, 21, 1719–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprell, L.; Hüll, K.; Stawski, P.; Schön, C.; Michalakis, S.; Biel, M.; Sumser, M.P.; Trauner, D. Restoring light sensitivity in blind retinae using a photochromic AMPA receptor agonist. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzl, J.; Mehlhorn, M.; Gawronski, H.; Rieder, K.H.; Morgenstern, K. Reversible cis-trans isomerization of a single azobenzene molecule. Angew. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasbarri, C.; Angelini, G. Polarizability over dipolarity for the spectroscopic behavior of azobenzenes in room-temperature ionic liquids and organic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, G.; Canilho, N.; Emo, M.; Kingsley, M.; Gasbarri, C. Role of solvent and effect of substituent on azobenzene isomerization by using room-temperature ionic liquids as reaction media. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 7430–7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, G.; Campestre, C.; Scotti, L.; Gasbarri, C. Kinetics and energetics of thermal cis-trans isomerization of a resonance-activated azobenzene in BMIM-based ionic liquids for PF6-/Tf2N- comparison. Molecules 2017, 22, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokić, J.; Gothe, M.; Wirth, J.; Peters, M.V.; Schwarz, J.; Hecht, S.; Saalfrank, P. Quantum chemical investigation of thermal cis-to-trans isomerization of azobenzene derivatives: Substituent effects, solvent effects, and comparison to experimental data. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 6763–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blevins, A.A.; Blanchard, G.J. Effect of positional substitution on the optical response of symmetrically disubstituted azobenzene derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 4962–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maria, P.; Fontana, A.; Gasbarri, C.; Siani, G.; Zanirato, P. Kinetics of the Z-E isomerization of monosubstituted azobenzenes in polar organic and aqueous micellar solvents. Arkivoc 2009, 2009, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, G.; Scotti, L.; Aceto, A.; Gasbarri, C. Silver nanoparticles as interactive media for the azobenzenes isomerization in aqueous solution: From linear to stretched kinetics. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 284, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L.; Fausto, R.; Reva, I. Structural and spectroscopic characterization of E- and Z-isomers of azobenzene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 16919–16930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yager, K.G.; Barrett, C.J. Novel photo-switching using azobenzene functional materials. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 2006, 182, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, T.J.; Dennison, S.R.; Baker, M.J.; Snape, T.J. Functionalizing the azobenzene motif delivers a light-responsive membrane-interactive compound with the potential for photodynamic therapy applications. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 8067–8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contini, C.; Hindley, J.W.; Macdonald, T.J.; Barritt, J.D.; Ces, O.; Quirke, N. Size dependency of gold nanoparticles interacting with model membranes. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witzigmann, D.; Sieber, S.; Porta, F.; Grossen, P.; Bieri, A.; Strelnikova, N.; Pfohl, T.; Prescianotto-Baschong, C.; Huwyler, J. Formation of lipid and polymer based gold nanohybrids using a nanoreactor approach. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74320–74328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
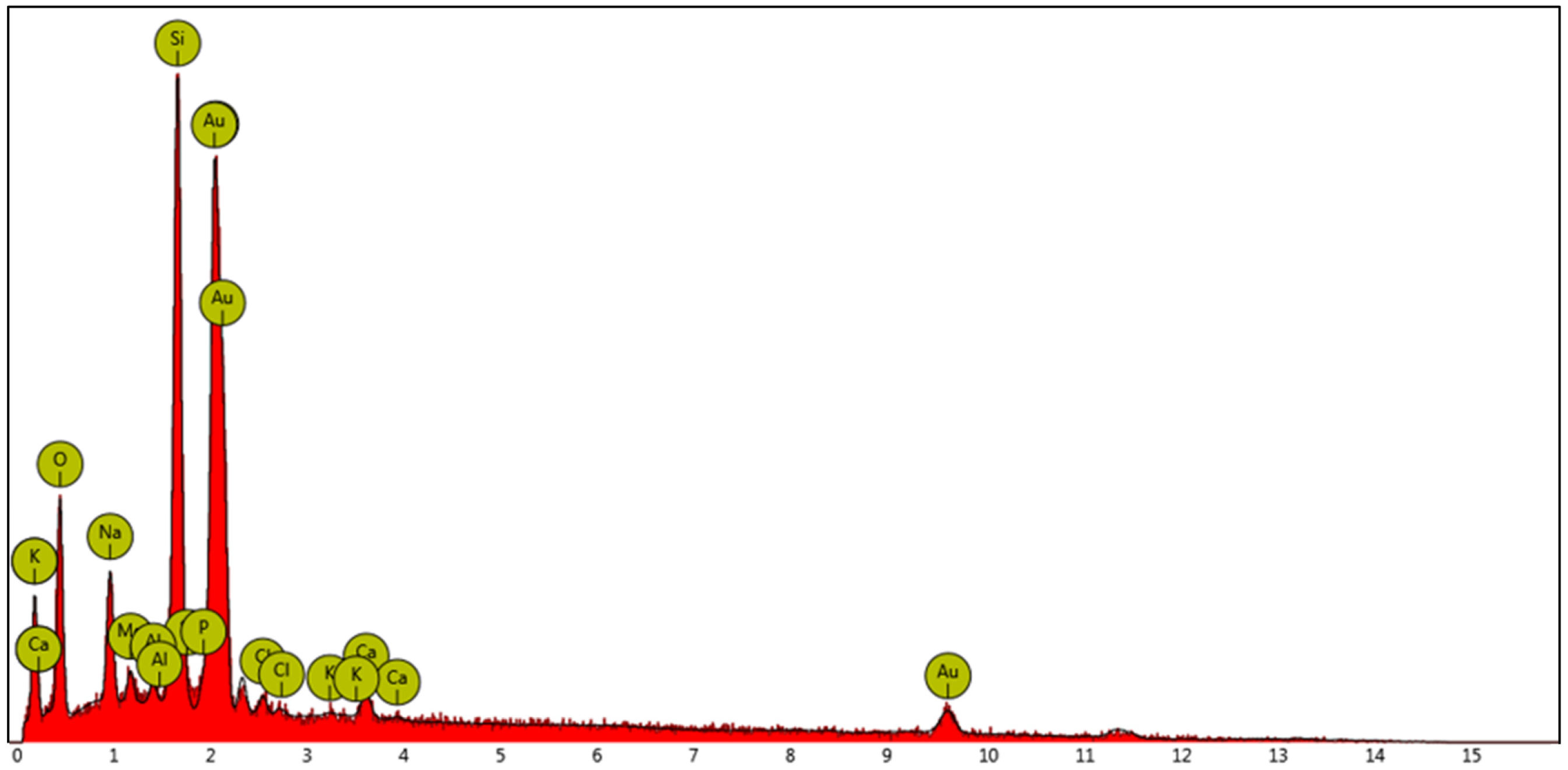
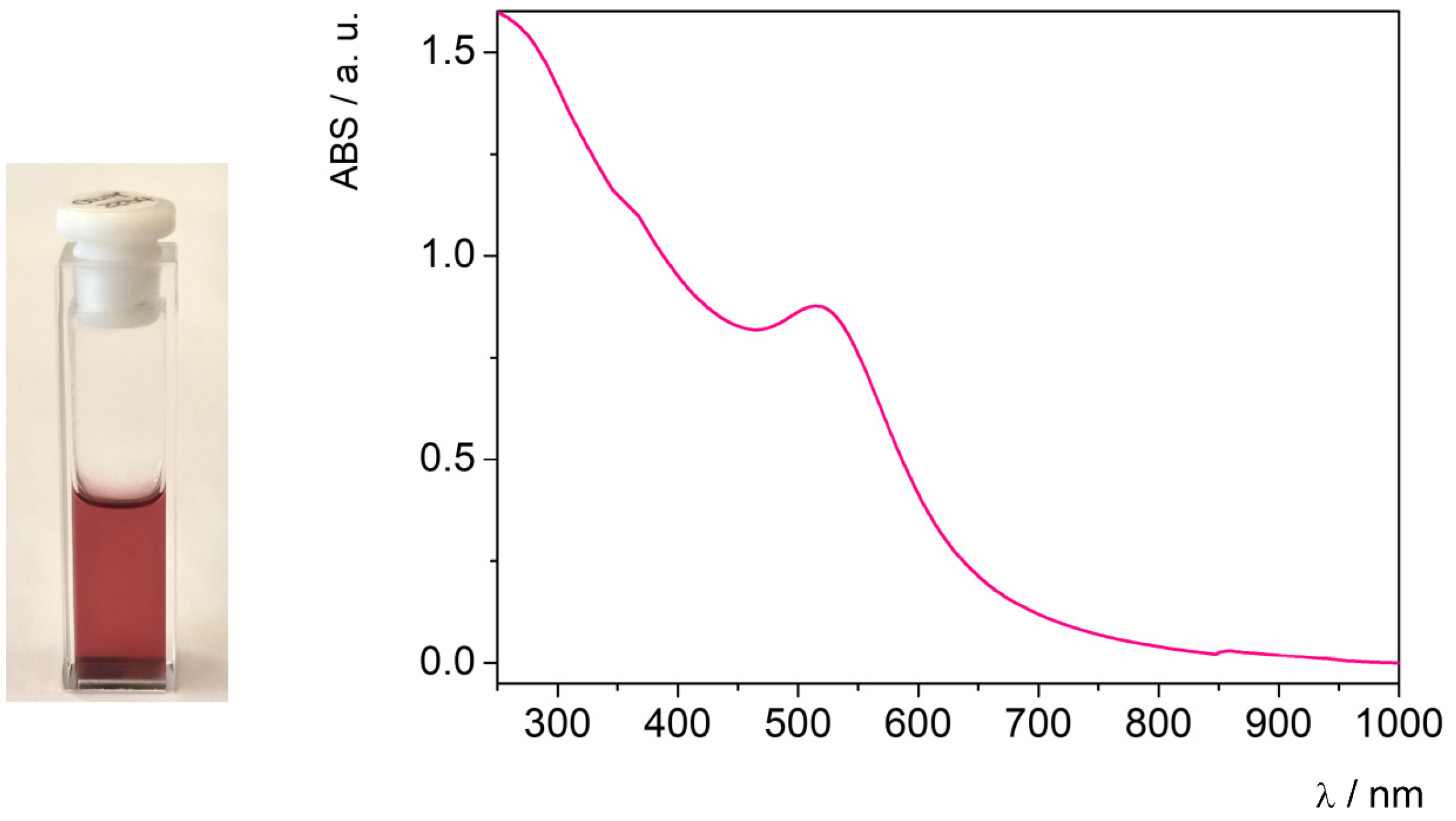
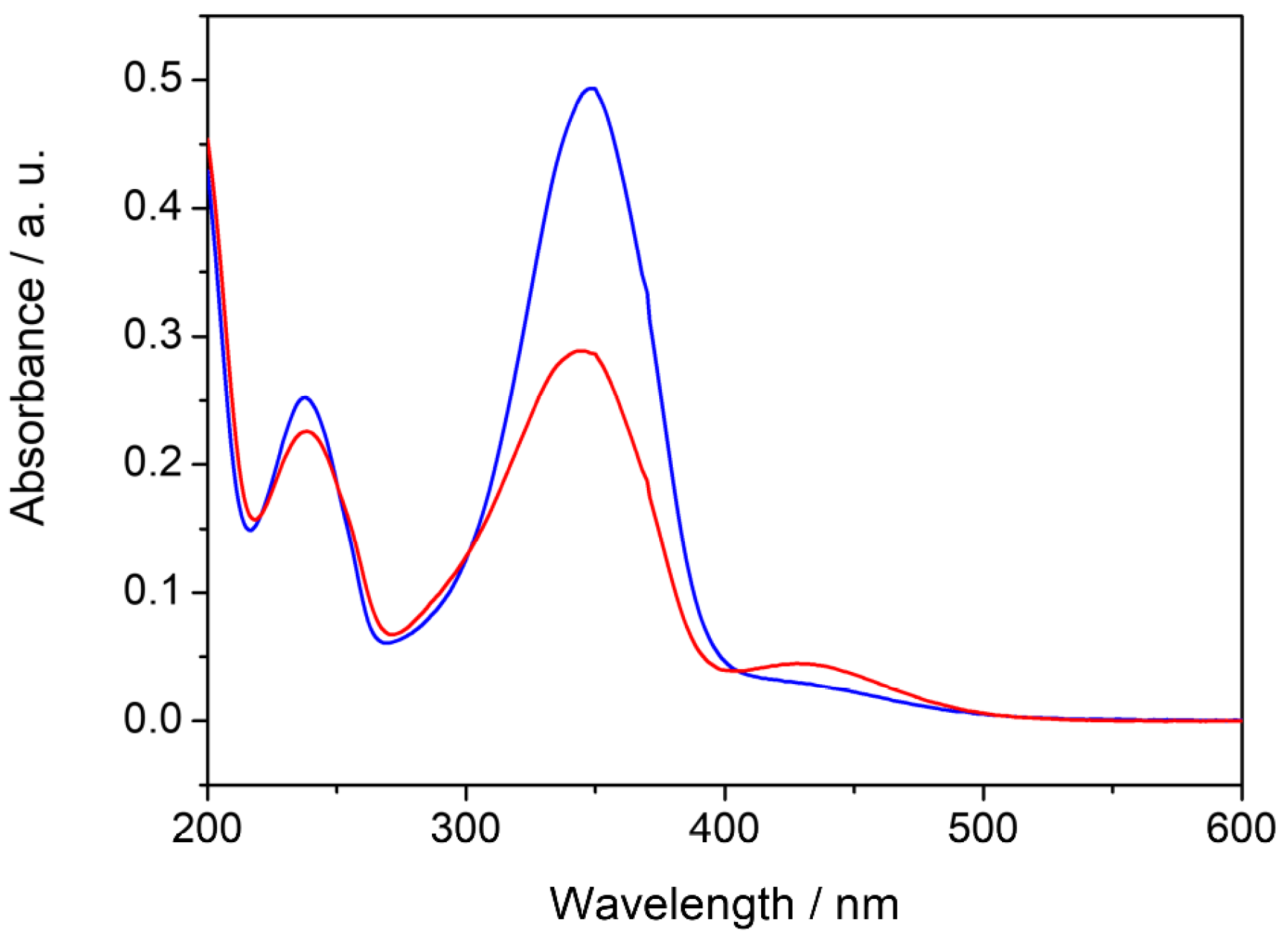

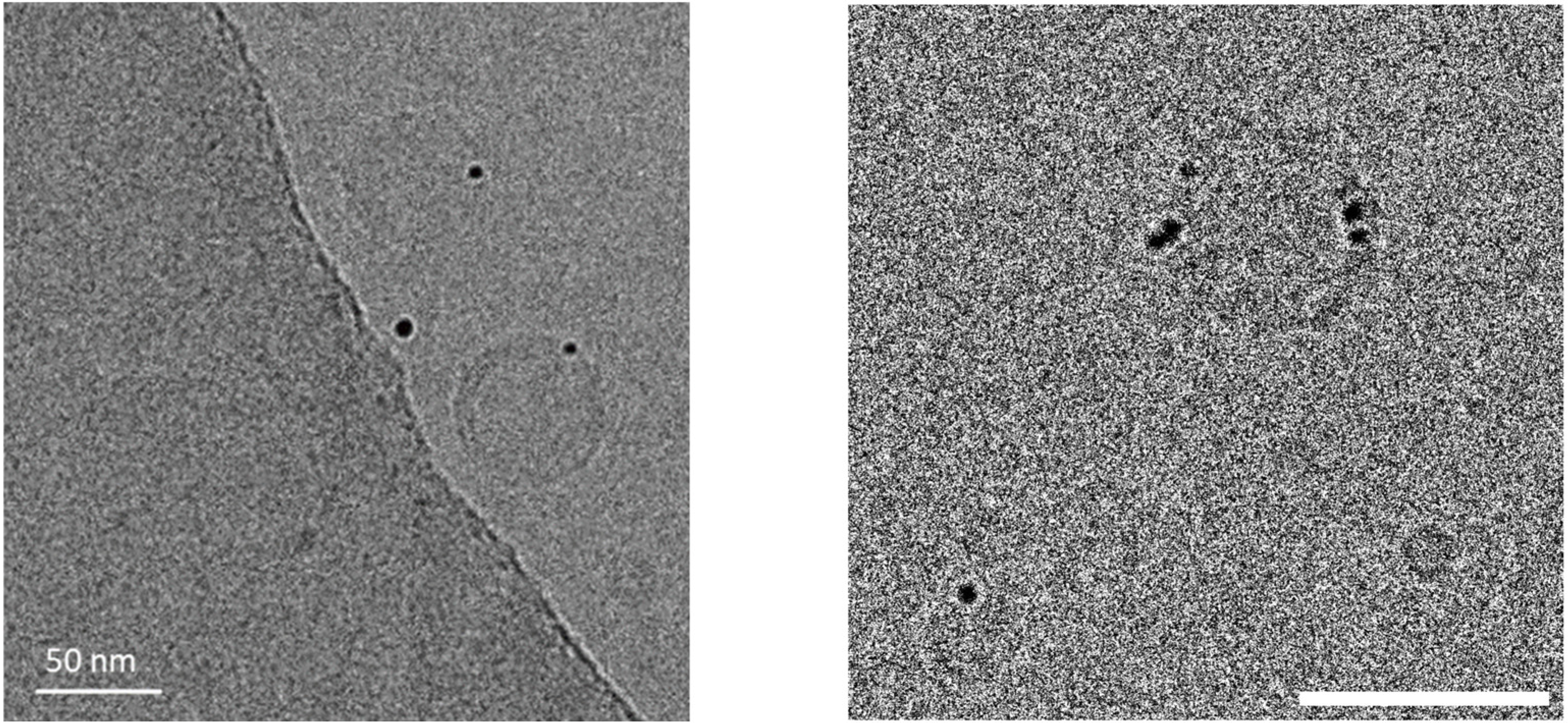
| Mean Size (nm) | Polydispersion Index (PDI) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| 151.4 ± 1.1 | 0.282 ± 0.005 | −46.5 ± 1.9 |
| Sample | kobs/s−1 |
|---|---|
| Cassyopea® Gold | 1.80 (±0.1) × 10−3 |
| AuNPs | 69.3 (±0.1) × 10−3 |
| Pure Cassyopea® | 8.15 (±0.2) × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelini, G.; Gasbarri, C. Combined Liposome–Gold Nanoparticles from Honey: The Catalytic Effect of Cassyopea® Gold on the Thermal Isomerization of a Resonance-Activated Azobenzene. Molecules 2024, 29, 3998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173998
Angelini G, Gasbarri C. Combined Liposome–Gold Nanoparticles from Honey: The Catalytic Effect of Cassyopea® Gold on the Thermal Isomerization of a Resonance-Activated Azobenzene. Molecules. 2024; 29(17):3998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173998
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelini, Guido, and Carla Gasbarri. 2024. "Combined Liposome–Gold Nanoparticles from Honey: The Catalytic Effect of Cassyopea® Gold on the Thermal Isomerization of a Resonance-Activated Azobenzene" Molecules 29, no. 17: 3998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173998
APA StyleAngelini, G., & Gasbarri, C. (2024). Combined Liposome–Gold Nanoparticles from Honey: The Catalytic Effect of Cassyopea® Gold on the Thermal Isomerization of a Resonance-Activated Azobenzene. Molecules, 29(17), 3998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173998







