Phytochemical Characterization of Two New Olive Oil Genotypes Growing in Southern Tunisia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of the Pomological Characterization of Fruits
2.1.1. Fruit Weight
2.1.2. Maturity Index (MI)
2.1.3. Fat Content Relative to Dry Weight
2.2. Quality Criteria
2.3. Pigment Contents
2.4. Tocopherol Content
2.5. Fatty Acid Composition
2.6. Sterolic Content
2.7. Phenolic Composition
2.8. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Characterization
2.9. Correlation Analyses
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Area of Study and Plant Material
3.2. Pomological Characterization of Fruits
3.3. Preparation of Virgin Olive Oil Samples
3.4. Calculation of Quality Criteria
3.5. Determination of Chlorophyll and Carotenoid Contents
3.6. Screening of Lipid Profile
3.6.1. Determination of α-tocopherol Content
3.6.2. Evaluation of the Fatty Acid Profile
3.6.3. Determination of Total Sterols
3.7. Determination of Phenolic Compounds
3.7.1. Extraction Step
3.7.2. LC/MS Analysis
3.8. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bendini, A.; Cerretani, L.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Gomez-Caravaca, A.M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernandez-Gutiérrez, A.; Lercker, G. Phenolic Molecules in Virgin Olive Oils: A Survey of Their Sensory Properties, Health Effects, Antioxidant Activity and Analytical Methods. An Overview of the Last Decade. Molecules 2007, 12, 1679–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtourou, F.; Jabeur, H.; Lazzez, A.; Bouaziz, M. Characterization and discrimination of Oueslati VOOs from adult and young trees in different ripening stages using sterols, pigments and alcohols in tandem with chemometrics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3512–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabeur, H.; Zribi, A.; Abdelhedi, R.; Bouaziz, M. Effect of olive storage conditions on Chemlali olive oil quality and the effective role of fatty acids alkyl esters in checking olive oils authenticity. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, S.; Omri, A.; Grati, K.N.; Marra, F.P. Molecular characterization and genetic relationships of cultivated Tunisian olive varieties (Olea europaea L.) using SSR markers. J. New Sci. Agric. Biotech. 2017, 40, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar]
- IOC. Available online: https://www.internationaloliveoil.org/1105-olivae-124-tutta-la-tunisa-olivicola-in-un-click/?lang=it (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Loubiri, A.; Taamalli, A.; Talhaoui, N.; NaitMohamed, S.; Carretero, A.S.; Zarrouk, M. Usefulness of phenolic profile in the classification of extra virgin olive oils from autochthonous and introduced cultivars in Tunisia. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, A.; Abdelhamid, S.; Ayadi, M.; Araouki, A.; Gharsallaoui, M.; Gouiaa, M.; Benincasa, C. The investigation of minor and rare Tunisian olive cultivars to enrich and diversify the olive genetic resources of the country. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 95, 103657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccouri, B.; Rajhi, I.; Zarrouk, M. Bioactive compounds and oxidative stability of feral olive oils from Tunisian Amazigh Mountains using LC-ESI-QTOF-MS approach for the development of innovative food products. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 2843–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mohamed, M.; Zelasco, S.; Ben Ali, S.; Guasmi, F.; Triki, T.; Conforti, F.L.; Grati Kamoun, N. Exploring olive trees genetic variability in the South East of Tunisia. Genet. Mol. Res. 2017, 16, gmr16039850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GratiKamoun, N.; Khlif, M.; Amdoun, L.; Arous, M.N.; Rekik, H.; Hamdi, M.T.; Rebik, B.; Abichou, M.; Maliane, A.; Labiadh, L. Ezzaitouna Caractérisation des Variétés D’olivier en Tunisie; Institut de l’olivier: Sfax, Tunisia, 2001; pp. 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jaouadi, R.; Mtaoua, H.; Ben Salah, M.; Ferchichi, A. Pomological Characterization and Mineral Study of Fruit of Some Local and Introduced Varieties of Olive-tree (Olea europaea L.) Cultivated in South of Tunisia. J. Arid. Land Stud. 2009, 19, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Rosati, A.; Paoletti, A.; Al Hariri, R.; Morelli, A.; Famiani, F. Partitioning of dry matter into fruit explains cultivar differences in vigor in young olive (Olea europaea L.) trees. Hortic. Sci. 2018, 53, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, G.; Macaluso, L.; Grilo, F.; Marra, F.P.; Caruso, T. Toward the valorization of olive (Olea europaea var. europaea L.) biodiversity: Horticultural performance of seven Sicilian cultivars in a hedgerow planting system. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumrah, M.A.; Jan, M.; Hussain, A.; Akhtar, S.; Nawaz, H.; Afzal, M.; Humara, U. Evaluation of Some Promising Varieties of Olive (Olea europaea L.) for Growth and Yield under Pothwar Regions of Punjab. Pak. J. Agric. Res. 2021, 34, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ali, S.; Guasmi, F.; Ben Mohamed, M.; Benhaj, K.; Boussora, F.; Triki, T.; Grati Kammoun, N. Identification of internal control genes for gene expression studies in olive mesocarp tissue during fruit ripening. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2018, 117, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi-Mezghani, S.; Le Dréau, Y.; Molinet, J.; Hammami, M.; Grati Kammoun, N.; Artaud, J. Biodiversity of Tunisian virgin olive oils: Varietal origin classification according to their minor compounds. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondi, A.; Bertazza, G.; Magli, M. Effect of olive fruits quality on the natural antioxidant compounds in extra virgin olive oil of Emilia-Romagna region. Progress. Nutr. 2004, 6, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Essiari, M.; Rachid, Z.; Chimi, H. Contribution à l’étude de la typicité des huiles d’olives vierges produites dans la région de Sais (Maroc). Olivae 2014, 119, 8–22. [Google Scholar]
- Oteros, J.; Orlandi, F.; García-Mozo, H.; Aguilera, F.; Ben Dhiab, A.; Tommaso, B.; Galán, C. Better prediction of Mediterranean olive production using pollen-based models. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, S.B.; Manrique, T.; Rapoport, H.F. Cultivar-based fruit size in olive depends on different tissue and cellular processes throughout growth. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 130, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannachi, H.; Marzouk, S. Flowering in the wild olive (Olea europaea L.) tree (oleaster): Phenology, flower abnormalities and fruit set traits for breeding the olive. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 8142–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOC. International Trade Standard Applying to Olive Oils and Olive-Pomace Oils. 2019. Available online: https://www.internationaloliveoil.org/wp (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Ben-Hassine, K.; Yangui, I.; Mnif, W.; Taamalli, A.; Benincasa, C.; Kamoun, N.; Malouche, D. Chemometric Analysis and Physicochemical Composition of Foreign and Tunisian Olive Oil: Consumer Preferences. Hindawi J. Food Qual. 2022, 2020, 3981028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosi, S.; Kosma, I.S.; Badeka, A.V. Quality characteristics of Koroneiki olive oil from Zakynthos island (Greece) and differentiation depending on the altitude level. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, T.H.; Pereira, J.A.; Cabrera-Vique, C.; Lara, L.; Oliveira, A.F.; Seiquer, I. Characterization of Arbequina virgin olive oils produced in different regions of Brazil and Spain: Physicochemical properties, oxidative stability and fatty acid profile. J. Food Chem. 2016, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargouri, B.; Ben Hmida, R.; Koseoglu, O.; Bouaziz, M. Physico-chemical analysis of virgin olive oils from fresh and fallen fruits for assessing the quality and shelf life: Characterization by chemometrics. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 2705–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diraman, H.; Dibeklioğlu, H. Characterization of Turkish virgin olive oils produced from early harvest olives. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 86, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargouri, B.; Ammar, S.; Zribi, A.; Ben Mansour, A.; Bouaziz, M. Effect of growing region on quality characteristics and phenolic compounds of Chemlali extra-virgin olive oils. Acta Physiol. Plant 2013, 35, 2801–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzerini, C.; Domenici, V. Pigments in extra-virgin olive oils produced in Tuscany (Italy) in different years. Foods 2017, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, S.; Machado, B.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Santos, C.; Silva, A.M.S.; CelesteDias, M. Modulation of phenolic and lipophilic compounds of olive fruits in response to combined drought and heat. J. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, D.; Karabekir, Y.; Schreiner, M. Variations of phenolic compounds, fatty acids and some qualitative characteristics of Sarıulak olive oil as induced by growing area. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtourou, F.; Valli, E.; Ben Mansour, A.; Bendini, A.; Gallina Toschi, T.; Bouaziz, M. Characterization of virgin olive oils obtained from minor Tunisian varieties for their valorization. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccouri, B.; Baccouri, O.; Zarrouk, W. Evaluation de la Composition des Huiles de Quelques Oléastres Sélectionnés: Les Antioxydants Naturels. Revue des Régions Arides—Numéro spécial—Actes du Séminaire International: Gestion des Ressources et Applications Biotechnologiques en Aridoculture et Cultures Oasiennes: Perspectives pour la Valorisation des Potentialités du Sahara. 2006, pp. 244–249. Available online: https://biblio.univ-annaba.dz/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Gherib-Asma-.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Debbabi, M.; Nury, T.; Zarrouk, A.; Mekahli, N.; Bezine, M.; Sghaier, R.; Grégoire, S.; Martine, L.; Durand, P.; Camus, E.; et al. Protective effects of α-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol and oleic acid, three compounds of olive oils, and no effect of trolox, on 7-ketocholesterol-induced mitochondrial and peroxisomal dysfunction in microglial BV-2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manai-Djebali, H.; Krichène, D.; Ouni, Y.; Gallardo, L. Chemical profiles of five minor olive oil varieties grown in central Tunisia. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 27, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakouhi, F.; Harrabi, S.; Absalon, C.; Sbei, K.; Boukhchina, S.; Kallel, H. α-Tocopherol and fatty acids contents of someTunisian table olives (Olea europea L.): Changes in their composition during ripening and processing. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motilva, M.J.; Ramo, T.; Paz Romero, M. Caracterizacióngeográfica de los aceites de oliva vírgenes de la denominación de origenprotegida ‘‘Les Garrigues’’ por su perfil de ácidos grasos. Grasas Aceites 2001, 52, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Mansour, A.; Gargouri, B.; Flamini, G.; Bouaziz, M. Effect of Agricultural Sites on Differentiation between Chemlali and Neb Jmel Olive Oils. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivier, D.; Artaud, J.; Pinatel, C.; Durbec, J.P.; Guérère, M. Differentiation of French virgin olive oil RDOs by sensory characteristics, fatty acid and triacylglycerol compositions and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivier, D.; Artaud, J.; Pinatel, C.; Durbec, J.P.; Guérère, M. Triacylglycerol and fatty acid compositions of French virgin olive oils. Characterization by chemometrics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5723–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, L.C.; Cunha, S.C.; Amaral, J.S.; Pereira, J.A.; Andrade, P.B.; Seabra, R.M. Chemometric characterization of three varietal olive oils (Cvs. Cobrancosa, Madural and Verdeal Transmontana) extracted from olives with different maturation indices. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerma-García, M.J.; Simó-Alfonso, E.F.; Méndez, A.; Lliberia, J.L.; Herrero-Martínez, J.M. Classification of extra virgin olive oils according to their genetic variety using linear discriminant analysis of sterol profiles established by ultra-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry detection. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Temime, S.; Manai, H.; Methenni, K.; Baccouri, B.; Abaza, L.; Daoud, D.; Zarrouk, M. Sterolic composition of Chétoui virgin olive oil: Influence of geographical origin. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 1018/2013 of 23 October 2013 Amending Regulation (EU) No 432/2012 Establishing a List of Permitted Health Claims Made on Foods other than those Referring to the Reduction of Disease Risk and to Children’s Development and Heal. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32013R1018&from=EN (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Haddada, F.M.; Krichene, D.; Manai, H.; Oueslati, I.; Daoud, D.; Zarrouk, M. Analytical evaluation of six monovarietal virgin olive oils from northern Tunisia. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiti, N.; Msallem, M.; Triki, S.; Cherif, A. Etude de la fraction insaponifiable de l’huile d’olive de différentes variétés Tunisiennes. Riv. Ital. Delle Sostanze Grasse 2002, 79, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Rigane, G.; Ayadi, M.; Boukhris, M.; Sayadi, S.; Bouaziz, M. Characterisation and phenolic profiles of two rare olive oils from southern Tunisia: Dhokar and Gemri-Dhokar cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsaftakis, A.; Kotsifaki, F.; Stefanoudaki, E. Effect of extraction system, stage of ripeness, and kneading temperature on the sterol composition of virgin olive oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 1477–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghim, J.; Ben Mohamed, M.; Bagues, M.; Guasmi, F.; Triki, T.; Nagaz, K. Irrigation effects on phenolic profile and extra virgin olive oil quality of “Chemlali” variety grown in South Tunisia. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 141, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Herrera, M.; Velez-Martın, A.; Ramos-Merchante, A.; Richter, P.; Beltran, R.; Sayago, A. Characterization and evaluation of phenolic profiles and color as potential discriminating features among Spanish extra virgin olive oils with protected designation of origin. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorini, A.; Aranha, B.C.; Antunes, B.D.F.; Otero, D.M.; Jacques, A.C.; Zambiazi, R.C. Metabolic profile of olive leaves of different cultivars and collection times. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uylaşer, V. Changes in phenolic compounds during ripening in Gemlik variety olive fruits obtained from different locations. CyTA J. Food 2015, 2, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, O.; Mazzaglia, G.; Sánchez-Ortiz, A.; Ocaña-Peinado, F.M.; Rivas, A. Phenolic content of Sicilian virgin olive oils and their effect on MG-63 human osteoblastic cell proliferation. Grasas Aceites 2014, 65, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Brahim, S.; Kelebek, H.; Ammar, S.; Abichou, M.; Bouazi, M. LC-MS phenolic profiling combined with multivariate analysis as an approach for the characterization of extra virgin olive oils of four rare Tunisian cultivars during ripening. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachicha Hbaieb, R.; Kotti, F.; Valli, E.; Bendini, A.; Gallina Toschi, T.; Gargouri, M. Effect of Tunisian olive ripeness on endogenous enzymes and virgin olive oil phenolic composition. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2017, 62, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilo, F.; Liberto, E.; Reichenbach, S.E. Untargeted and targeted fngerprinting of extra virgin olive oil volatiles by com- prehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with mass spec- trometry: Challenges in long-term studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5289–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimidou, M.; Lytridou, M.; Boskou, D.; Paooa-Lousi, A.; Kotsifaki, F.; Petrakis, C. On the determination of minor phenolic acids of virgin olive oil by RP-HPLC. Grasas Aceites 1996, 47, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajoub, A.; Pacchiarotta, T.; Hurtado-Fernández, E.; Olmo-García, L.; García-Villalba, R.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Mayboroda, O.A.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A. Comparing two metabolic profiling approaches (liquid chromatography and gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry) for extra-virgin olive oil phenolic compounds analysis: A botanical classification perspective. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1428, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Mohamed, M.; Rocchetti, G.; Montesano, D.; Ben Ali, S.; Guasmi, F.; Grati-Kamoun, N.; Lucini, L. Discrimination of Tunisian and Italian extra-virgin olive oils according to their phenolic and sterolic fingerprints. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulak, M.; Cetinkaya, H. A systematic review: Polyphenol contents in stressed-olive trees and its fruit oil. Polyphenols 2018, 1, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Papachatzis, A.; Gougoulias, N.; Ntalla, M.N.; Papachatzis, A. Comparative study on polyphenols content and antioxidant effect from some olive fruit varieties grown in central Greece. Anal. Univ. Din. Craiova-Biol. Hortic. Technol. Prelucr. Prod. Agric. Ing. Med. 2019, 29, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano-García, I.; Olmo-García, L.; Polo-Megías, D.; Serrano, A.; León, L.; De la Rosa, R.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A. Fruit phenolic and triterpenic composition of progenies of Olea europaea subspp. cuspidata, an interesting phytochemical source to be Included in olive breeding programs. Plants 2022, 11, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechhab, T.; Lechhab, W.; Cacciola, F.; Salmoun, F. Sets of internal and external factors influencing olive oil (Olea europaea L.) composition: A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 1069–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.; Mulinacci, N.; Pinelli, P.; Vincieri, F.F.; Cimato, A. Polyphenolic content in five tuscany cultivars of Olea europaea L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Measurement of antioxidant activity. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 757–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, E.; Farina, A.; Leone, A.; Mazzara, E.; Urbani, S.; Selvaggini, R.; Servili, M.; Ninfali, P. Phenolic compounds and quality parameters of family farming versus protected designation of origin (PDO) extra-virgin olive oils. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 43, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laincer, F.; Laribi, R.; Tamendjari, A.; Arrar, L.; Rovellini, P.; Venturini, S. Olive oils from Algeria: Phenolic compounds, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Grasas-y-Aceites 2014, 65, e001. [Google Scholar]
- Merouane, A.; Noui, A.; Medjahed, H.; Nedjari Benhadj Ali, K.; Saadi, A. Activité antioxydante des composés phénoliques d’huile d’olive extraite par méthode traditionnelle. Int. J. Bio. Chem. Sci. 2015, 8, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannachi, H.; Elfalleh, W.; Laajel, M.; Ennajeh, I.; Mechlouch, R.F.; Nagaz, K. Chemical Profiles and Antioxidant Activities of Leaf, Pulp, and Stone of Cultivated and Wild Olive Trees (Olea europaea L.). Int. J. Fruit. Sci. 2020, 20, 350–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlif, I.; Jellali, K.; Michel, T.; Halabalaki, M.; LeandrosSkaltsounis, A.; Allouche, N. Characteristics, Phytochemical Analysis and Biological Activities of Extracts from Tunisian Chetoui Olea europaea Variety. J. Chem. 2015, 15, 418731. [Google Scholar]
- Saoudi, B.; Lachraf, A.; Laib, F.; Touarfia, M.; Haberra, S. Quality Characteristics of Some Algerian Olive Oils with Antioxidant Activity. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelló, J.R.; Motilva, M.J.; Tovar, M.J.; Romero, M.P. Changes in commercial virgin olive oil (cv Arbequina) during storage, with special emphasis on the phenolic fraction. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib Al, M.; Mawiya, J.; Nass, H.; Ali Abd El, N.; Aly Shehat, W.; Salim Bani, N.; Sohail Akh, M. Comparative Phytochemical Investigations and in vitro Pharmacological Activities of Different Brands of Olive Oil. J. Appl. Sci. 2022, 22, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, G.; Kelebek, H.; Selli, S. Antioxidant Activity in Olive Oils. Olives and Olive Oil in Health and Disease Prevention, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021; pp. 313–325, Chapter 26. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Hmida, R.; Frikha, N.; BouguerraNeji, S.; Kit, G.; Medina, F.; Bouaziz, M. Synthesis of high added value compounds through catalytic oxidation of 2-phenylethanol: A kinetic study. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2020, 52, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis Al Hashemi, M.; Al Maktoumi, H.; Jawaid Akhtar, M.; Khan, S.A. Antioxidant activity and in silico anticholinesterase studies of major phenolic constituents of three commercial olive oils: A comparative study. Pharmacol. Res.-Nat. Prod. 2024, 2, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, K.; Oztop, M.H.; Lia, F. The Effect of Hydrolysis on the Antioxidant Activity of Olive Mill Waste. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.; Ahmadi, F.; Cottrell, J.J.; Dunshea, F.R. Comprehensive metabolite fingerprinting of Australian black and green olives and their antioxidant and pharmaco kinetics properties. Separations 2023, 10, 354. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 8292-1; Corps Gras D’origines Animale et Végétale—Détermination de la Teneur en Corps Gras Solides par RMN Pulsée. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Uceda, M.; Frıas, L. Harvest dates. Evolution of the fruit ofcontent, oil composition and oil quality. In Proceedings of the II Seminario Oleıcola Internacional; International Olive-oilCouncil, Cordoba, Spain, 6–17 October 1975. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 3960; Corps Gras D’origines Animale et Végétale-Determination de L’indice de Peroxyde; Détermination Avec Point D’arrêt Iodométrique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- European Union Commission Regulation (EEC). On the characteristics of olive and olive pomace oils and their analytical methods. Off. J. Eur. Community L 1991, 248, 2568. [Google Scholar]
- Conseil Oléicole International (14 October 2013). Conseil. 2013. Available online: http://www.internationaloliveoil.org/web/aafrances/corp/AreasActivitie/economics/Areas (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Wolff, J.P. Manuel D’analyse Des Corps Gras; Edition Azoulay: Paris, France, 1968; p. 245. [Google Scholar]
- Minguez-Mosquera, M.I.; Rejano-Navarro, L.; Gandul-Rojas, B.; SanchezGomez, A.H.; Garrido-Fernandez, J. Color pigment, correlation in virgin olive oil. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 1991, 68, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOCS: Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemist 1989. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=1131143 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Lucini, L.; Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Canaguier, R.; Kumar, P.; Colla, G. The effect of a plant-derived biostimulant on metabolic profiling and crop performance of lettuce grown under saline conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 182, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICO. Règlement D’exécution (ue) n o 29/2012 de la Commission du 13 Janvier 2012 Relatif Aux Normes de Commercialisation de L’huile D’olive 2012. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2012:012:0014:0021:FR:PDF (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Rocchetti, G.; Lucini, L.; Chiodelli, G.; Giuberti, G.; Montesano, D.; Masoero, F.; Trevisan, M. Impact of boiling on free and bound phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of commercial gluten-free–pasta. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100 Pt 2, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
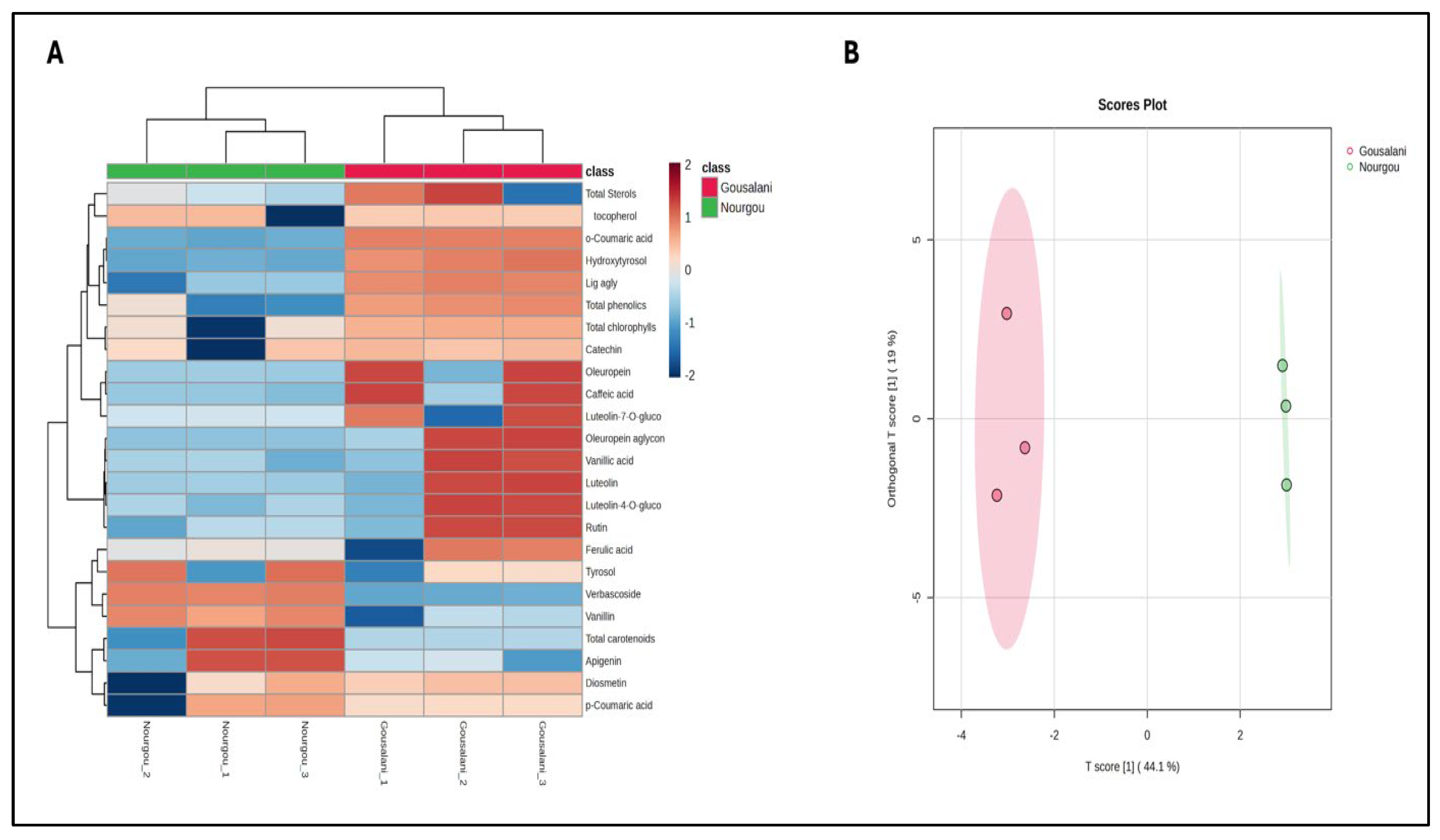
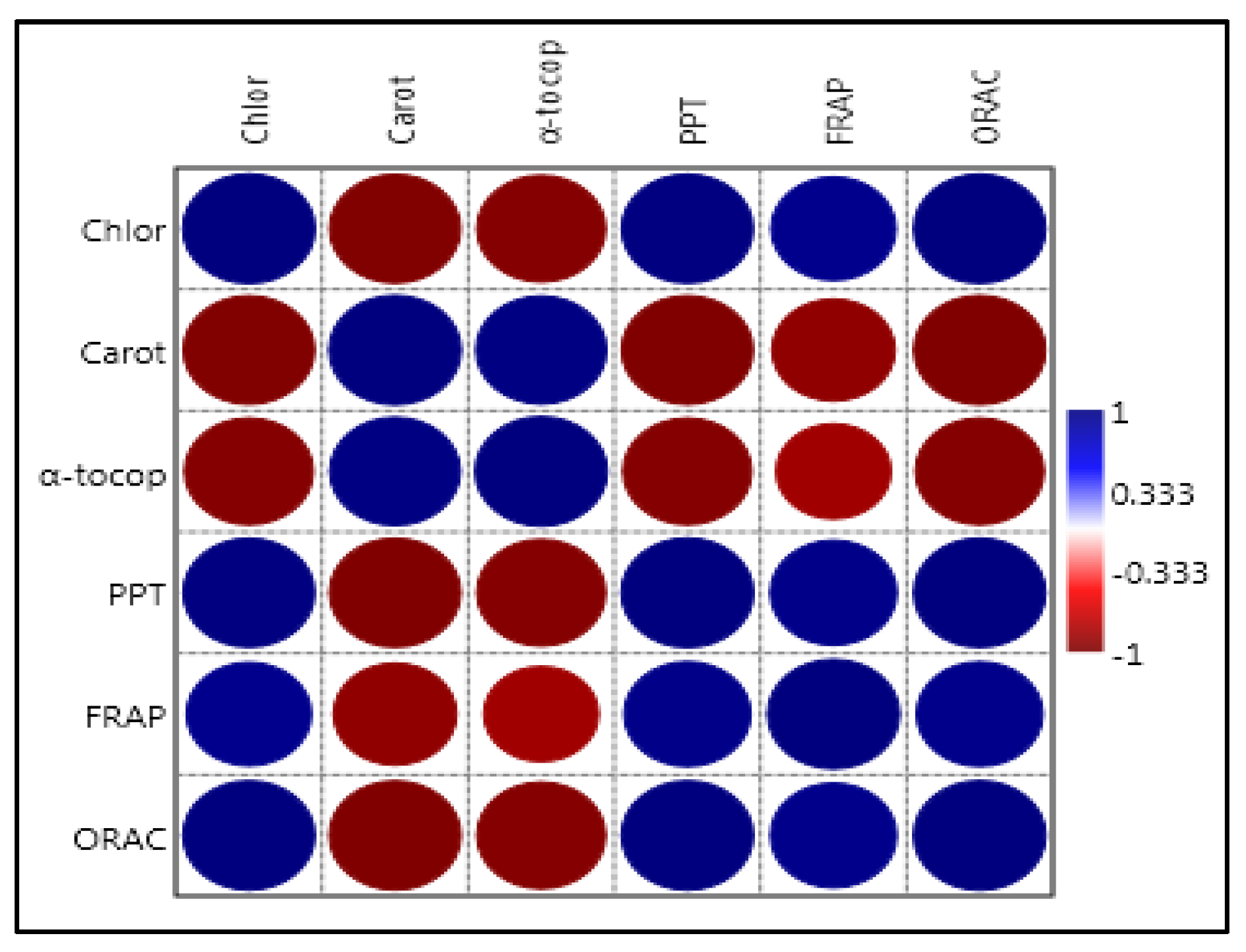
| Cultivars | Fruit Weight (PMF) (g) | Maturity Index (MI) | Fat Content Relative to Dry Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nourgou | 1.28 ± 0.02 a | 3.50 ± 0.556 a | 38.41 ± 0.078 b |
| Gousalani | 1.31 ± 0.03 a | 2.19 ± 0.111 b | 47.00 ± 0.158 a |
| Cultivar | Acidity | K232 | K270 | Peroxide Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nourgou | 0.39 ± 0.026 b | 2.29 ± 0.036 a | 0.17 ± 0.013 a | 1.09 ± 0.017 a |
| Gousalani | 0.49 ± 0.045 a | 2.22 ± 0.036 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 a | 1.12 ± 0.017 a |
| Cultivar | Chlorophyll | Carotenoids | Alpha-Tocopherol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nourgou | 1.37 ± 0.026 b | 10.86 ± 0.155 a | 186.866 ± 1.093 a |
| Gousalani | 1.64 ± 0.017 a | 3.97 ± 0.045 b | 175.593 ± 1.011 b |
| Fatty Acid/Cultivars | Gousalani | Nourgou | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Myristic acid (C14:0) | 0.01 ± 0.006 | 0.01 ± 0.001 | ns |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 13.32 ± 0.29 b | 17.48 ± 0.50 a | *** |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1) | 0.65 ± 0.045 b | 1.23 ± 0.026 a | *** |
| Margaric acid (C17:0) | 0.025 ± 0.002 b | 0.03 ± 0.002 a | ns |
| Margaroleic acid (C17:1) | 0.04 ± 0.001 b | 0.05 ± 0.012 a | ns |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 2.65 ± 0.045 b | 3.52 ± 0.545 a | * |
| Oleic acid (C18:1) | 68.73 ± 0.651 a | 65.33 ± 0.588 b | ** |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2) | 13.47 ± 0.113 a | 11.06 ± 0.149 b | *** |
| Linolenic acid (C18:3) | 0.55 ± 0.045 b | 0.73 ± 0.052 a | ** |
| Arachidic acid (C20:0) | 0.30 ± 0.017 b | 0.40 ± 0.017 a | *** |
| Gadoleic acid (C20:1) | 0.20 ± 0.017 a | 0.11 ± 0.010 b | *** |
| Cultivars | Total Sterols | Total Phenolic Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Nourgou | 1036.4 ± 147.8 b | 348.03 ± 2.670 b |
| Gousalani | 1931.4 ± 251.4 a | 516.16 ± 10.793 a |
| Phenolic Class | Compound | Gousalani | Nourgou | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secoiridoids | Oleuropein | 78.60 ± 0.544 a | 9.51 ± 0.482 b | *** |
| Oleuropeinaglycone | 164.99 ± 0.121 a | 1.01 ± 0.052 b | *** | |
| Ligstroside aglycone | 62.040 ± 1.027 a | 22.46 ± 0.134 b | *** | |
| Verbascoside | 4.63 ± 0.045 b | 7.00 ± 0.026 a | *** | |
| Phenolic alcohols | Hydroxytyrosol | 6.19 ± 0.190 a | 2.56 ± 0.088 b | *** |
| Tyrosol | 4.77 ± 0.220 b | 7.14 ± 0.079 a | *** | |
| Phenolic acids | Caffeic | 0.96 ± 0.018 a | 0.59 ± 0.026 b | *** |
| Vanillic | 0.74 ± 0.015 b | 1.46 ± 0.036 a | *** | |
| p-cumaric | 2.10 ± 0.017 b | 2.53 ± 0.062 a | *** | |
| Ferulic | 1.46 ± 0.036 a | 0.99 ± 0.020 b | *** | |
| o-cumaric | 12.60 ± 0.017 a | 0.55 ± 0.045 b | *** | |
| Flavonoids | Catechin | 0.7367 ± 0.015 | 0.73 ± 0.065 | ns |
| Luteolin-7-O-glucoside | 0.31 ± 0.019 b | 1.59 ± 0.017 a | *** | |
| Rutin | 1.28 ± 0.017 a | 0.33 ± 0.026 b | *** | |
| Luteolin-4-O-glucoside | 26.83 ± 0.221 a | 4.53 ± 0.062 b | *** | |
| Luteolin | 3.66 ± 0.040 a | 0.78 ± 0.036 b | *** | |
| Apigenin | 0.66 ± 0.045 b | 1.71 ± 0.078 a | *** | |
| Diosmetin | 1.29 ± 0.034 | 1.29 ± 0.105 | ns | |
| Phenolic aldehydes | Vanillin | 0.47 ± 0.030 b | 0.83 ± 0.034 a | *** |
| Total phenolic content | 516.16 ± 14.562 a | 348.03 ± 2.670 b | *** | |
| VIP Features | VIP [t] | VIP [ortho-t] |
|---|---|---|
| o-coumari acid | 1.502 | 0.025 |
| Verbascoside | 1.5015 | 0.048 |
| Hydroxytyrosol | 1.5013 | 0.083 |
| Ligstroside aglycone | 1.443 | 0.289 |
| Vanillin | 1.335 | 0.921 |
| Total phenolic content | 1.305 | 0.660 |
| Caffeic acid | 1.167 | 0.348 |
| Oleuropein aglycone | 1.127 | 1.220 |
| Oleuropein | 1.025 | 0.384 |
| Vanillic acid | 1.007 | 1.368 |
| Antioxidant Activity/Cultivar | Nourgou | Gousalani | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method 1: FRAP mg GAE/100 g | 15.66 ± 6.506 b | 50.00 ± 9.165 a | ** |
| Method 2: ORAC mM TEAC | 2024.5 ± 349.500 b | 8796.00 ± 343.000 a | *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Mohamed, M.; Ben Ali, S.; Rocchetti, G.; Tlahig, S.; Bennani, L.; Guasmi, F. Phytochemical Characterization of Two New Olive Oil Genotypes Growing in Southern Tunisia. Molecules 2024, 29, 3997. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173997
Ben Mohamed M, Ben Ali S, Rocchetti G, Tlahig S, Bennani L, Guasmi F. Phytochemical Characterization of Two New Olive Oil Genotypes Growing in Southern Tunisia. Molecules. 2024; 29(17):3997. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173997
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Mohamed, Mbarka, Sihem Ben Ali, Gabriele Rocchetti, Samir Tlahig, Leila Bennani, and Ferdaous Guasmi. 2024. "Phytochemical Characterization of Two New Olive Oil Genotypes Growing in Southern Tunisia" Molecules 29, no. 17: 3997. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173997
APA StyleBen Mohamed, M., Ben Ali, S., Rocchetti, G., Tlahig, S., Bennani, L., & Guasmi, F. (2024). Phytochemical Characterization of Two New Olive Oil Genotypes Growing in Southern Tunisia. Molecules, 29(17), 3997. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173997









