Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis to Reveal Metabolite of Morus alba L. in Different Medicinal Parts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
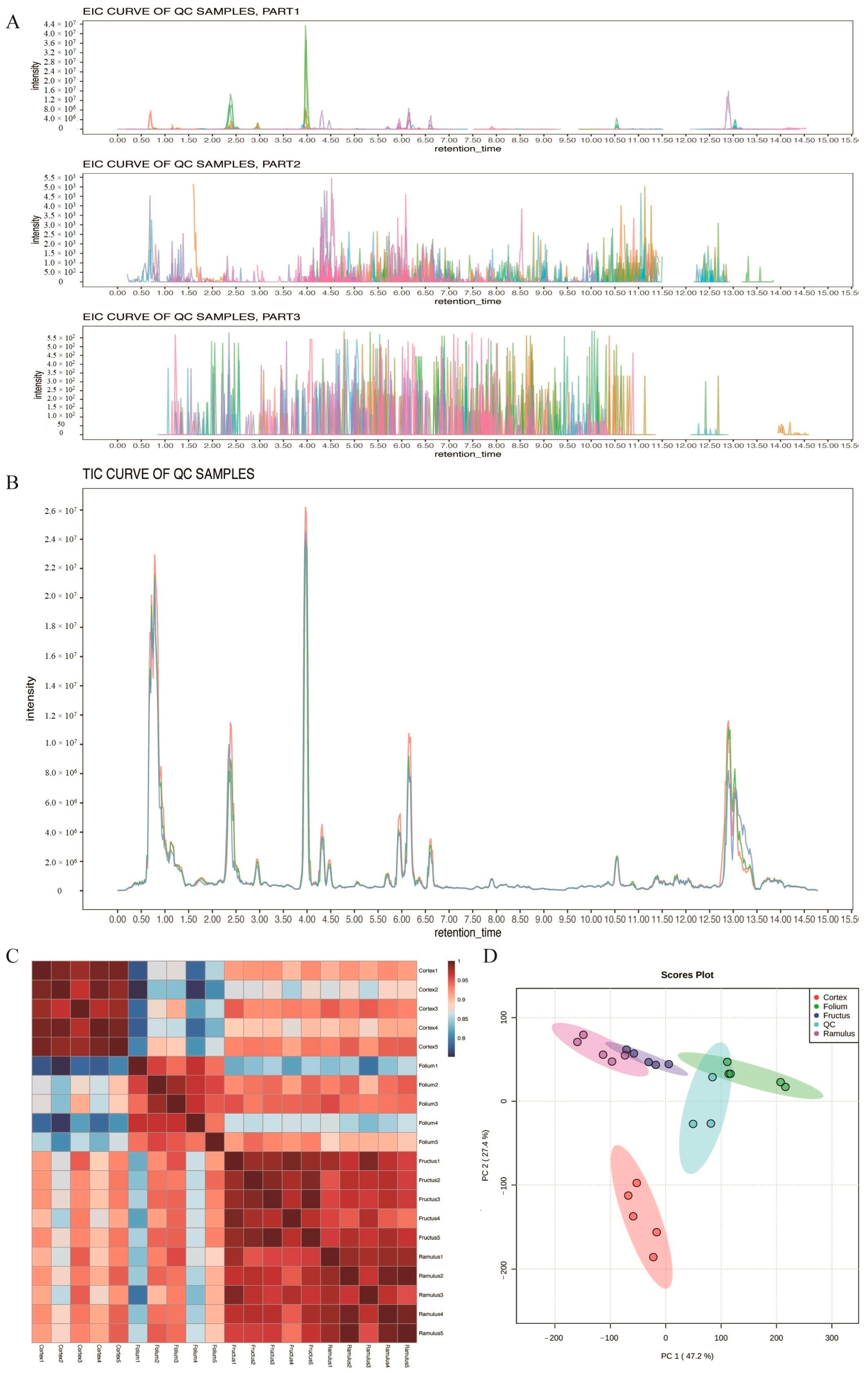
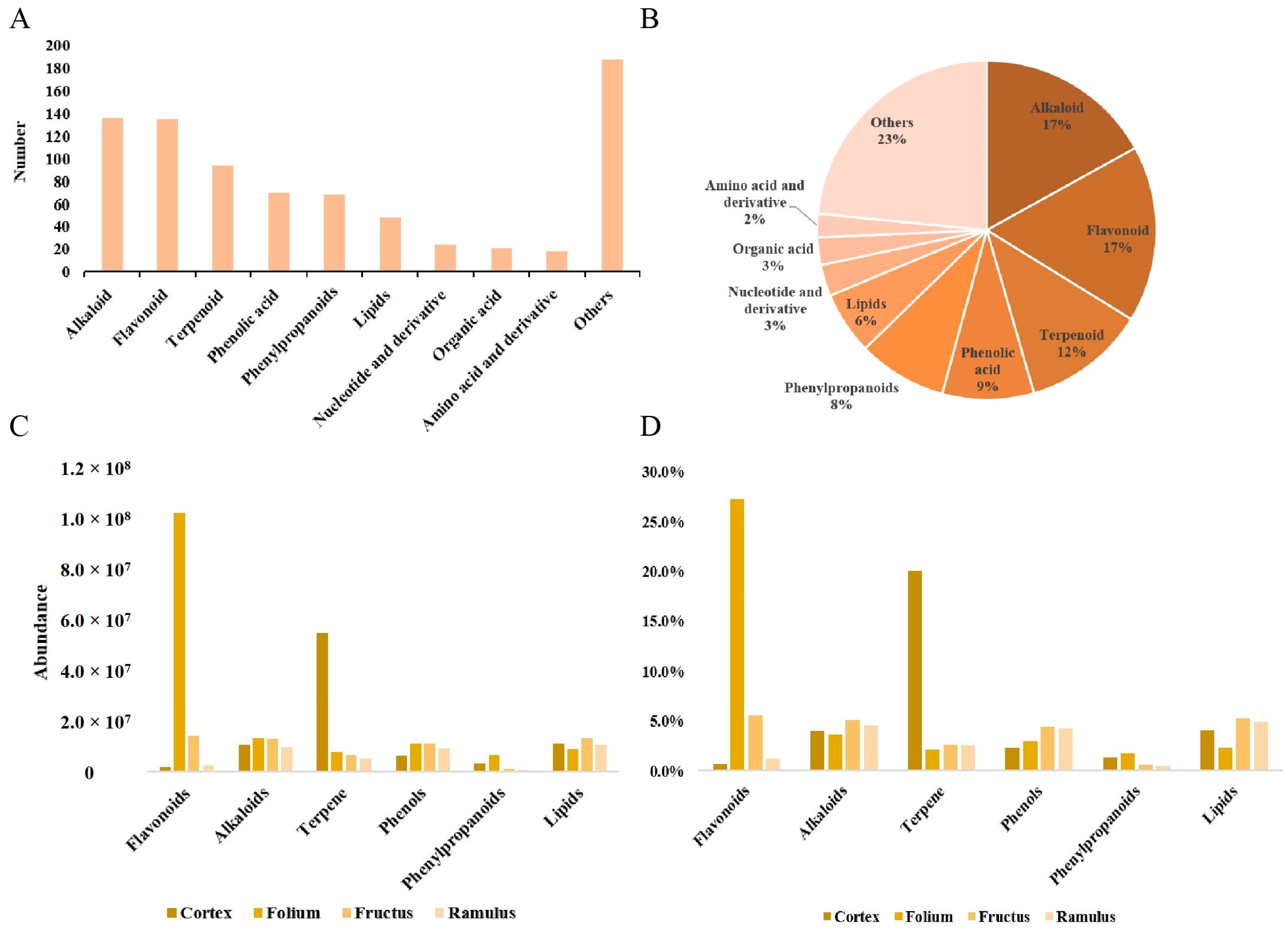
2.1. Metabolic Profiling Based on UHPLC–MS Analysis
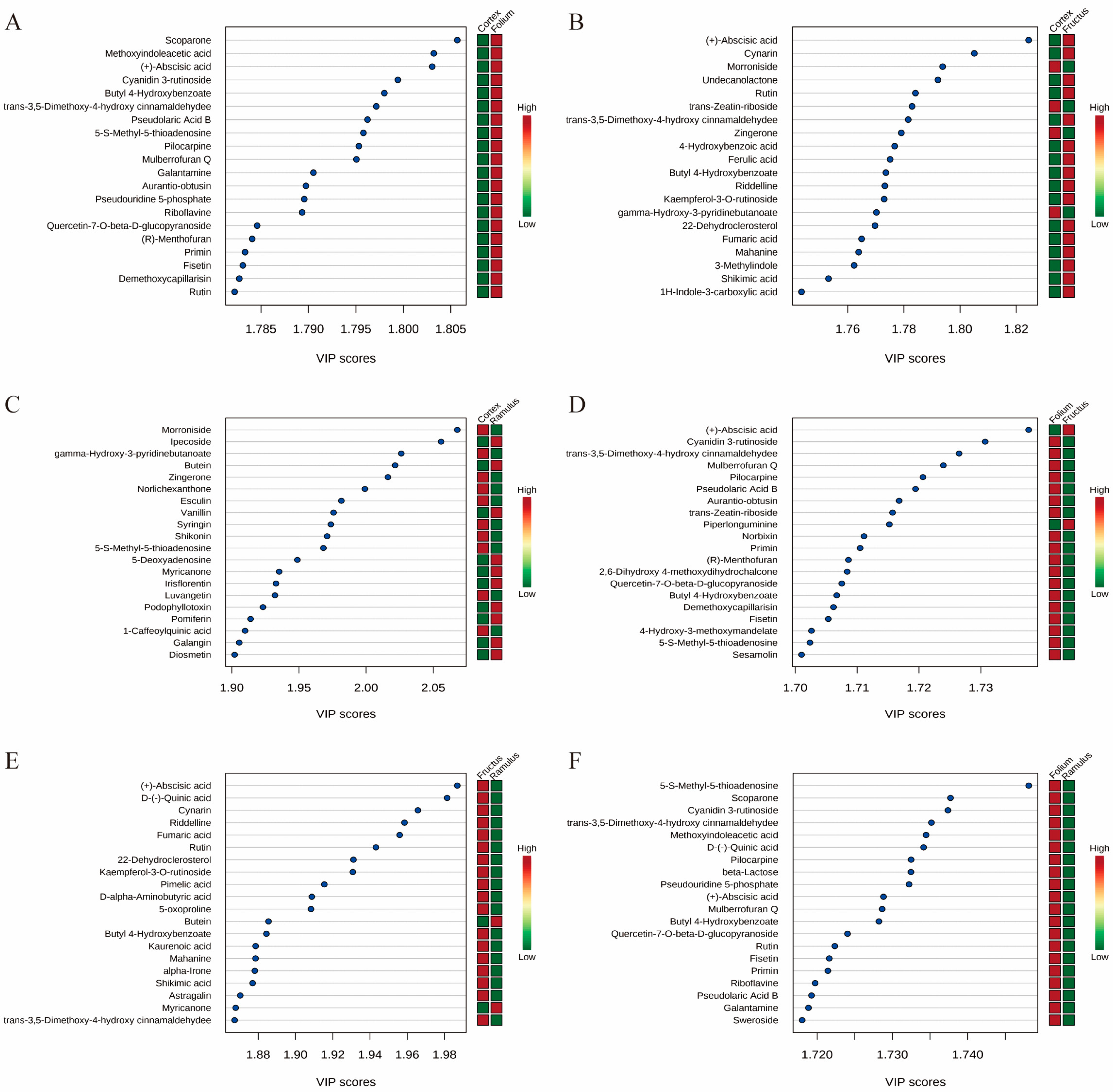
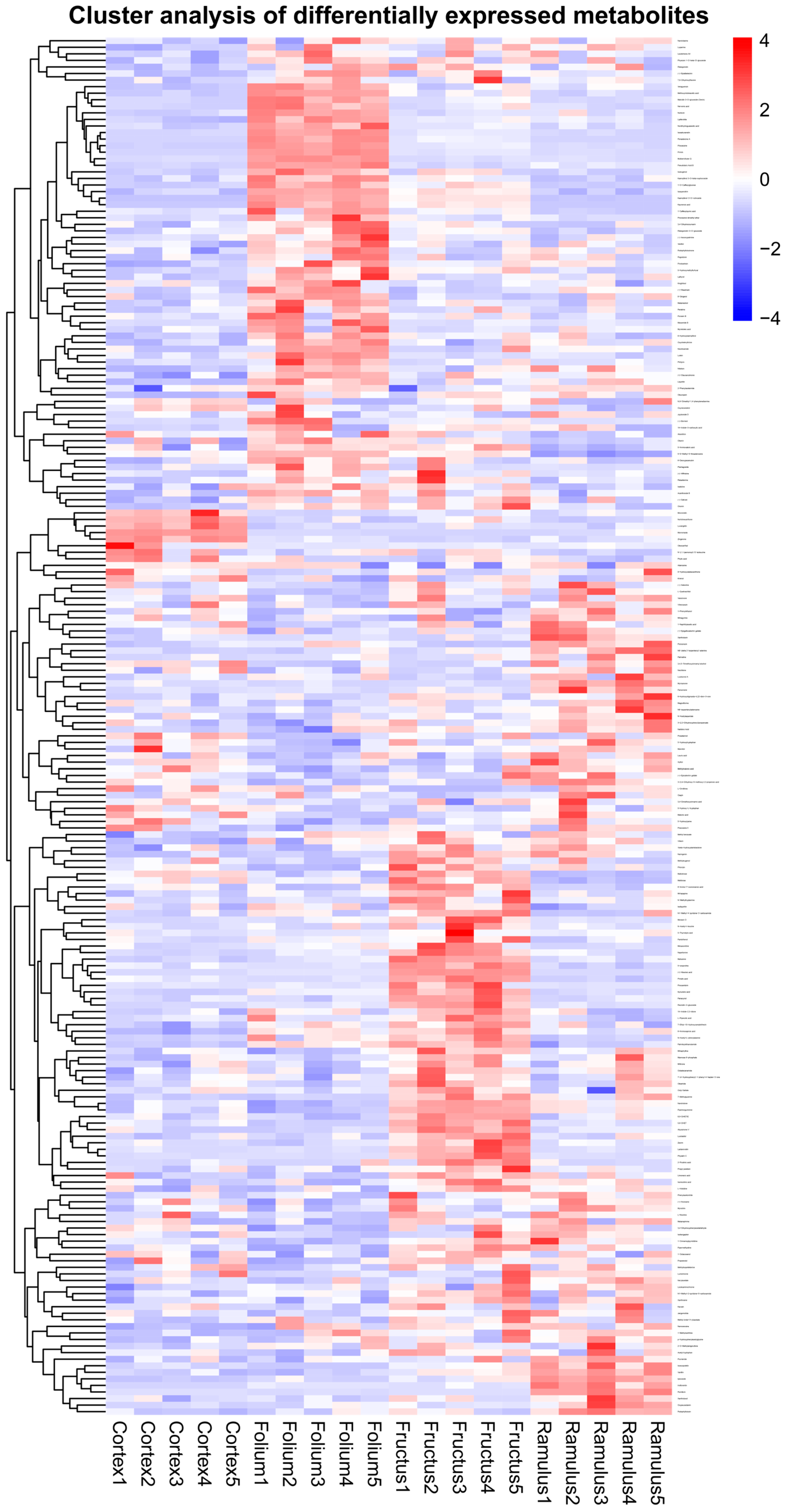
2.2. Differential Metabolites Analysis
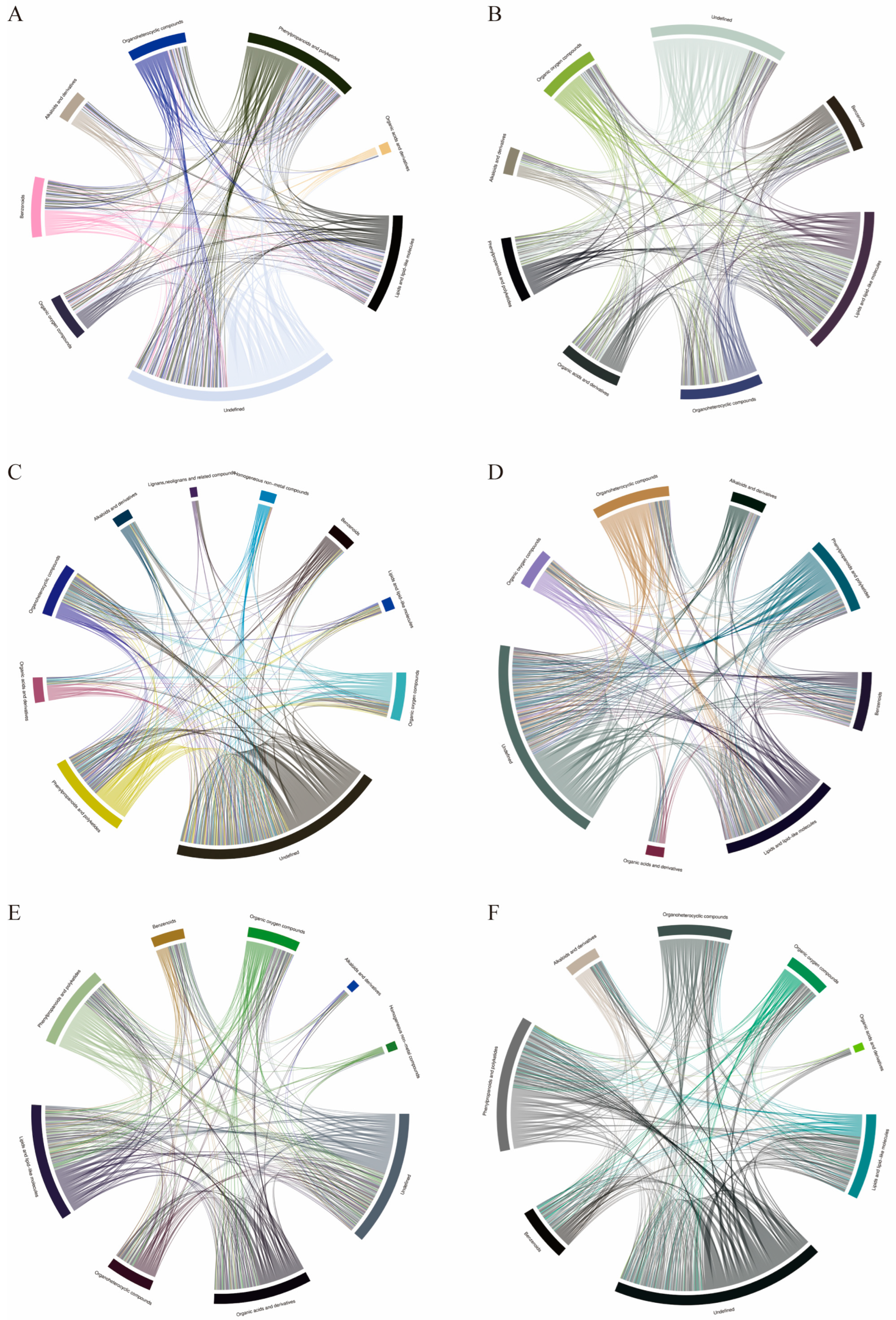
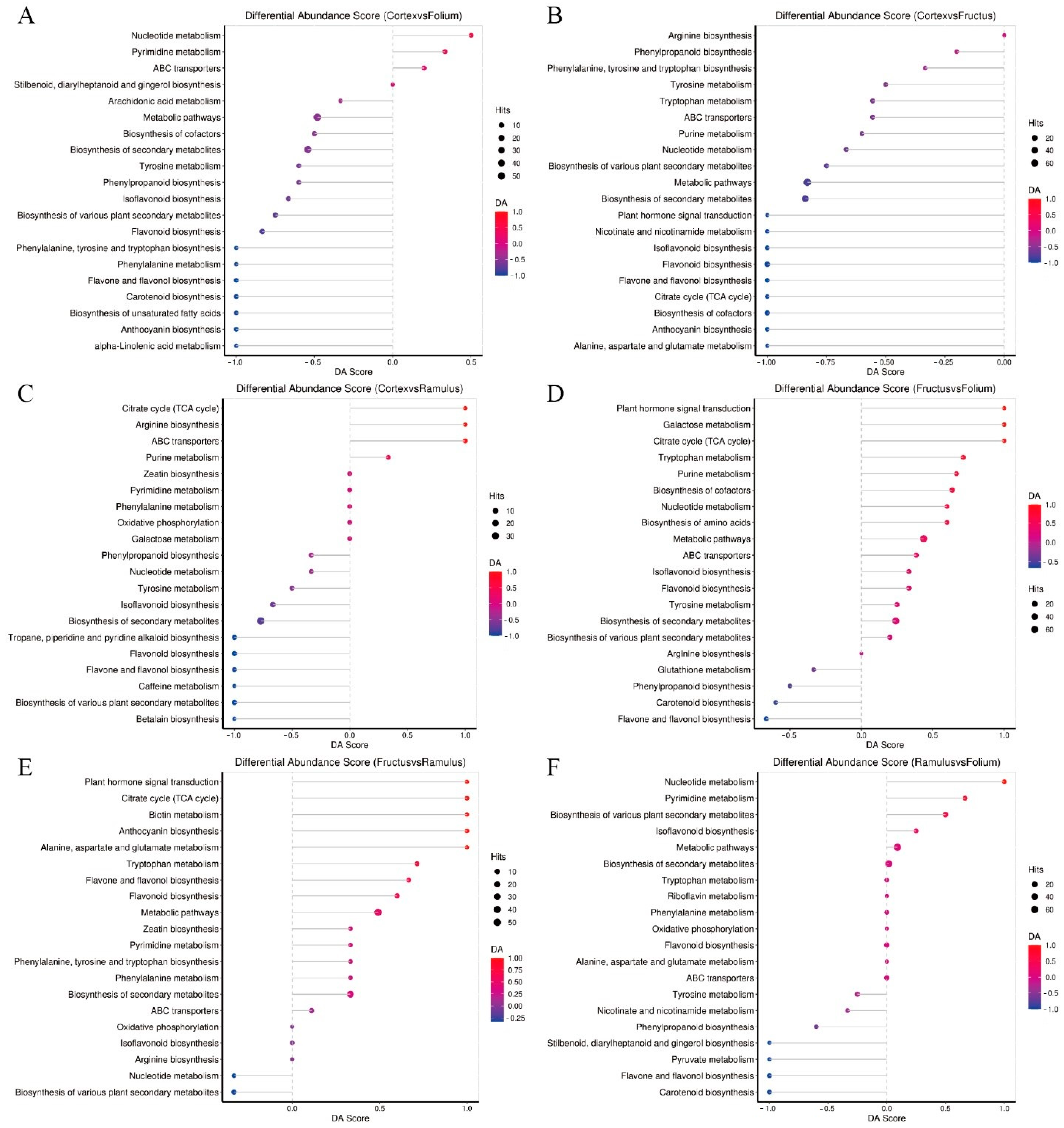
2.3. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Sample Preparation and Extraction
4.3. UHPLC–MS Conditions
4.4. Metabolite Identification and Quantification
4.5. Systematic Correlativity Analysis and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, T.; Shuang, F.F.; Fu, Q.Y.; Ju, Y.X.; Zong, C.M.; Zhao, W.G.; Zhang, D.Y.; Yao, X.H.; Cao, F.L. Evaluation of the Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) Fruits from Different Varieties in China. Molecules 2022, 27, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattil, A.; Hamid; Dash, K.K.; Shams, R.; Sharma, S. Nutritional composition, phytochemical extraction, and pharmacological potential of mulberry: A comprehensive review. Future Foods 2024, 9, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, B.; Parveen, R.; Zahiruddin, S.; Khan, M.U.; Mohapatra, S.; Ahmad, S. Nutritional constituents of mulberry and their potential applications in food and pharmaceuticals: A review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3909–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Chai, X.; Hou, G.; Zhao, F.; Meng, Q. Phytochemistry, bioactivities and future prospects of mulberry leaves: A review. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, D.M.; van den Berg, M.A.; Hall, R.D. Towards superior plant-based foods using metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhan, C.; Yang, C.; Fernie, A.R.; Luo, J. Metabolomics-centered mining of plant metabolic diversity and function: Past decade and future perspectives. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Lou, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, H.P.; Ma, F.W.; Pan, W.D.; Chen, Z. Profiling alkaloids in Aconitum pendulum N. Busch collected from different elevations of Qinghai province using widely targeted metabolomics. Phytochemistry 2022, 195, 113047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-H.; Liu, F.; Xiong, L. Medicinal parts of mulberry (leaf, twig, root bark, and fruit) and compounds thereof are excellent traditional Chinese medicines and foods for diabetes mellitus. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 106, 105619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shao, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Duan, H. Comparative analysis of tuberous root metabolites between cultivated and wild varieties of Rehmannia glutinosa by widely targeted metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, D.; Duan, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, M. Metabolite accumulation and metabolic network in developing roots of Rehmannia glutinosa reveals its root developmental mechanism and quality. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Zhao, R.; Xu, J.; Ge, Y.; Li, R.; Li, R. Accumulation Pattern of Flavonoids during Fruit Development of Lonicera maackii Determined by Metabolomics. Molecules 2021, 26, 6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, A.; Qin, X.; Du, G. Characterization of multiple chemical components of GuiLingJi by UHPLC-MS and 1H NMR analysis. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Razali, U.H.M.; Saikim, F.H.; Mahyudin, A.; Mohd Noor, N.Q.I. Morus alba L. Plant: Bioactive Compounds and Potential as a Functional Food Ingredient. Foods 2021, 10, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yang, L.; Xue, Q.; Yao, F.; Sun, J.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y. Antioxidant evaluation-guided chemical profiling and structure-activity analysis of leaf extracts from five trees in Broussonetia and Morus (Moraceae). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Urso, G.; Mes, J.J.; Montoro, P.; Hall, R.D.; de Vos, R.C.H. Identification of Bioactive Phytochemicals in Mulberries. Metabolites 2020, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Fang, J.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Chang, Y.; Ning, N.; Guo, H.; et al. Structures, bioactivities and future prospective of polysaccharides from Morus alba (white mulberry): A review. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Jiménez, F.J.; Ruiz-Malagón, A.J.; Molina-Tijeras, J.A.; Diez-Echave, P.; Vezza, T.; Hidalgo-García, L.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Arráez-Román, D.; Cenis, J.L.; Lozano-Pérez, A.A.; et al. Comparative Study of the Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Leaf Extracts from Four Different Morus alba Genotypes in High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Yang, H.; Ke, X.X.; Cui, H.J. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Morus alba L. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2022, 47, 2373–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Patel, M.; Snoussi, M. (Eds.) Ethnobotany and Ethnopharmacology of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants: Steps Towards Drug Discovery; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; Volume 7, pp. 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Song, P.; Chao, Z. Untargeted Metabolomics Coupled with Chemometrics for Leaves and Stem Barks of Dioecious Morus alba L. Metabolites 2022, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Liao, X.; Kuang, H.M.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, S.H. LC-MS Metabolite Profiling and the Hypoglycemic Activity of Morus alba L. Extracts. Molecules 2022, 27, 5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Fan, S.; Liao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Effect of Frost on the Different Metabolites of Two Mulberry (Morus nigra L. and Morus alba L.) Leaves. Molecules 2023, 28, 4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, B.; Zahiruddin, S.; Basist, P.; Irfan, M.; Abass, S.; Ahmad, S. Metabolomic Profiling and Identification of Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Compounds from Leaves of Different Varieties of Morus alba Linn Grown in Kashmir. ACS omega 2022, 7, 24317–24328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Park, G.H.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.R.; Koo, J.S.; Jeong, J.B. Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activity of mulberry (Morus alba L.) root bark. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.R.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, S.J.; Shin, S.; Lee, G.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Song, G.Y.; Oh, S. Root Bark of Morus alba L. and Its Bioactive Ingredient, Ursolic Acid, Suppress the Proliferation of Multiple Myeloma Cells by Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Zhang, Y.Q. Metabolic effects of mulberry branch bark powder on diabetic mice based on GC-MS metabolomics approach. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X. Analysis of Traditional Chinese Medicine’s Theory of Meridian Distribution (Lung Meridian) and the Compatibility Rules of Lung-Related Formulas and Its Application in the Development of Marine Traditional Chinese Medicine. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S.; Xie, X.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Liu, E. Andrographolide Attenuates RSV-induced Inflammation by Suppressing Apoptosis and Promoting Pyroptosis after Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection In Vitro. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2024, 27, 1776–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.F.; Yuan, S.T.; Yuan, F.L.; Jiang, C.X. Research progress on chemical components, pharmacological effects and clinical application of Zedoary Turmeric Oil Injection. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2023, 54, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.D.; Hou, B.L.; Yang, Y.G.; Tang, Z.S.; Xu, H.B. Diterpenoids from Acanthopanacis cortex and their anti-inflammatory activity studies. Fitoterapia 2024, 176, 106021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Tao, J.; Qian, Y.; Feng, F.; Hu, X.; Xu, T.; Jin, H.; Ruan, H.; Zheng, H.F.; Tong, P. Morroniside ameliorates inflammatory skeletal muscle atrophy via inhibiting canonical and non-canonical NF-κB and regulating protein synthesis/degradation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1056460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yu, S.; Liu, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, J.; Ji, P.; Zhang, P.; Fu, Y.; Le, Y.; et al. Morroniside promotes skin wound re-epithelialization by facilitating epidermal stem cell proliferation through GLP-1R-mediated upregulation of β-catenin expression. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2024, 56, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, K.; Pan, G.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Peng, C.; Deng, L.; Cui, H. Cortex mori extracts induce apoptosis and inhibit tumor invasion via blockage of the PI3K/AKT signaling in melanoma cells. Frontiers in pharmacology 2022, 13, 1007279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ye, J.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Feng, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Ramulus mori (Sangzhi) alkaloids regulates gut microbiota disorder and its metabolism profiles in obese mice induced by a high-fat diet. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1166635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; An, M.; Kim, J.K.; Lim, Y.H. Antiobesity effect of ethanolic extract of Ramulus mori in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes and high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 251, 112542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, H.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Lin, W.; Ma, X.; Yang, C.; Hao, M.; Zhao, K.; et al. Effects of mulberry twig alkaloids (Sangzhi alkaloids) and metformin on blood glucose fluctuations in combination with premixed insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1272112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Lian, C.F.; Sun, Q.W.; Wang, T.T.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ye, J.; Gao, L.L.; Yang, Y.F.; Liu, S.N.; Shen, Z.F.; et al. Ramulus mori (Sangzhi) Alkaloids Alleviate High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Yang, X.; Ding, X.; Ju, S.; Zhang, B.; Lin, Z. Ramulus mori (Sangzhi) alkaloids tablets for diabetes mellitus: A regulatory perspective. Fitoterapia 2023, 166, 105444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Long, X.; Zou, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Q. Mulberry leaf phenolics and fiber exert anti-obesity through the gut microbiota-host metabolism pathway. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 1432–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, R.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, X.; Wei, J.; Yin, R.; Zhao, J.; Tian, J. Effects and Mechanistic Role of Mulberry Leaves in Treating Diabetes and its Complications. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2023, 51, 1711–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xi, M.; Gao, F.; Li, M.; Dong, T.; Geng, Z.; Liu, C.; Huang, F.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; et al. Evaluation of mulberry leaves’ hypoglycemic properties and hypoglycemic mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1045309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurudome, N.; Minami, Y.; Kajiya, K. Fisetin, a major component derived from mulberry (Morus australis Poir.) leaves, prevents vascular abnormal contraction. BioFactors 2022, 48, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Ji, X.; Shan, C.; Song, J.; Zhao, J. Exploring the pharmacological components and effective mechanism of Mori folium against periodontitis using network pharmacology and molecular docking. Arch. Oral Biol. 2022, 139, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Lin, Q.; Xie, H.; Lu, W.; Chi, Y.; Chen, D. Lyophilized aqueous extracts of Mori fructus and Mori ramulus protect Mesenchymal stem cells from OH-treated damage: Bioassay and antioxidant mechanism. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.S.; Ji, T.; Su, S.L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.L.; Shang, E.X.; Guo, S.; Qian, D.W.; Duan, J.A. Mulberry leaves ameliorate diabetes via regulating metabolic profiling and AGEs/RAGE and p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, W.; Liang, G.; Qi, J. Mulberry leaves attenuate D-galactose-induced aging in vivo and in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 311, 116286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Shin, K.C.; Yoou, S.K.; Park, H.J.; Eun, S.H.; Bae, Y.M.; Lee, H.M.; Chae, H.J.; Chae, S.W.; Choi, B.H. Effects of an ethanolic extract of mulberry fruit on blood pressure and vascular remodeling in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2019, 41, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, W.; Bai, S.; Ye, L.; Du, J.; Zhong, M.; Liu, J.; Zhao, R.; Shen, B. White mulberry fruit polysaccharides enhance endothelial nitric oxide production to relax arteries in vitro and reduce blood pressure in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 109022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriyaprom, S.; Kaewkod, T.; Promputtha, I.; Desvaux, M.; Tragoolpua, Y. Evaluation of Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of White Mulberry (Morus alba L.) Fruit Extracts. Plants 2021, 10, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Pan, X.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Bahetjan, Y.; Lu, B.; Pang, K.; Yang, X.; et al. Black mulberry extract inhibits hepatic adipogenesis through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in T2DM mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; An, N.; Ni, W.; Gao, Q.; Yu, Y. Capsaicin affects macrophage anti-inflammatory activity via the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2023, 93, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.; Alqahtani, A.; Ojo, O.A.; Shaheen, H.M.; Wasef, L.; Elzeiny, M.; Ismail, M.; Shalaby, M.; Murata, T.; Zaragoza-Bastida, A.; et al. Biological Properties, Bioactive Constituents, and Pharmacokinetics of Some Capsicum spp. and Capsaicinoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambhani, S.; Kondhare, K.R.; Giri, A.P. Diversity in Chemical Structures and Biological Properties of Plant Alkaloids. Molecules 2021, 26, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Huang, G. Extraction, purification, structural modification, activities and application of polysaccharides from different parts of mulberry. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3939–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Gao, Y.; Xue, J.; Yang, Y.; Yin, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, M. Phytochemicals, Pharmacological Effects and Molecular Mechanisms of Mulberry. Foods 2022, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Time | Flow Rate | A% | B% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 400 | 98 | 2 |
| 0.5 | 400 | 98 | 2 |
| 10 | 400 | 50 | 50 |
| 11 | 400 | 5 | 95 |
| 13 | 400 | 5 | 95 |
| 13.1 | 400 | 98 | 2 |
| 15 | 400 | 98 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Qian, Y.; Wei, M. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis to Reveal Metabolite of Morus alba L. in Different Medicinal Parts. Molecules 2024, 29, 3981. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173981
Wang X, Qian Y, Wei M. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis to Reveal Metabolite of Morus alba L. in Different Medicinal Parts. Molecules. 2024; 29(17):3981. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173981
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinwei, Yiyun Qian, and Min Wei. 2024. "Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis to Reveal Metabolite of Morus alba L. in Different Medicinal Parts" Molecules 29, no. 17: 3981. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173981
APA StyleWang, X., Qian, Y., & Wei, M. (2024). Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis to Reveal Metabolite of Morus alba L. in Different Medicinal Parts. Molecules, 29(17), 3981. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29173981






