β,β-Dimethylacrylalkannin, a Natural Naphthoquinone, Inhibits the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Modulating Tumor-Associated Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
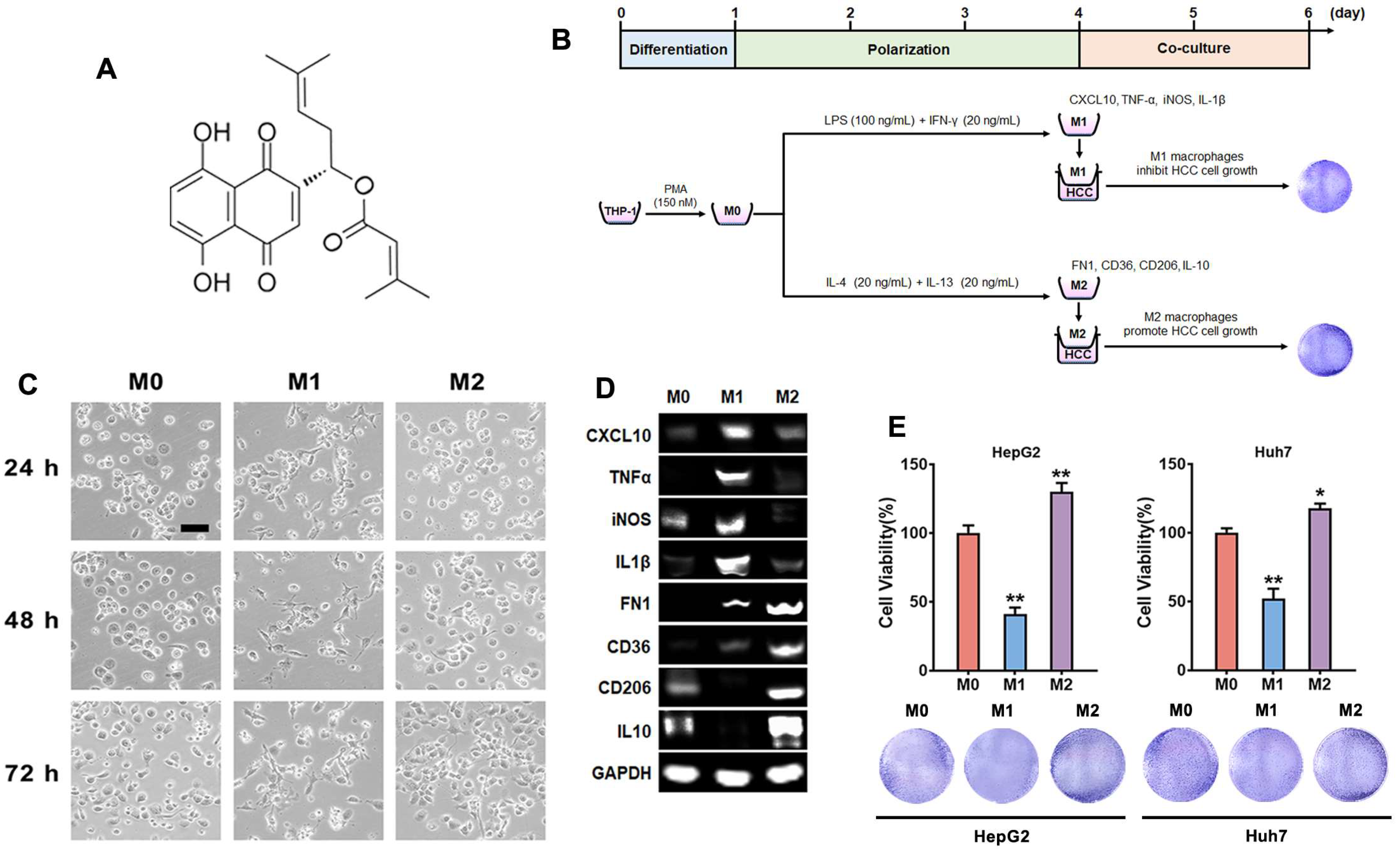
2.1. Polarizing THP-1 Macrophages and Their Effects on HCC Cells
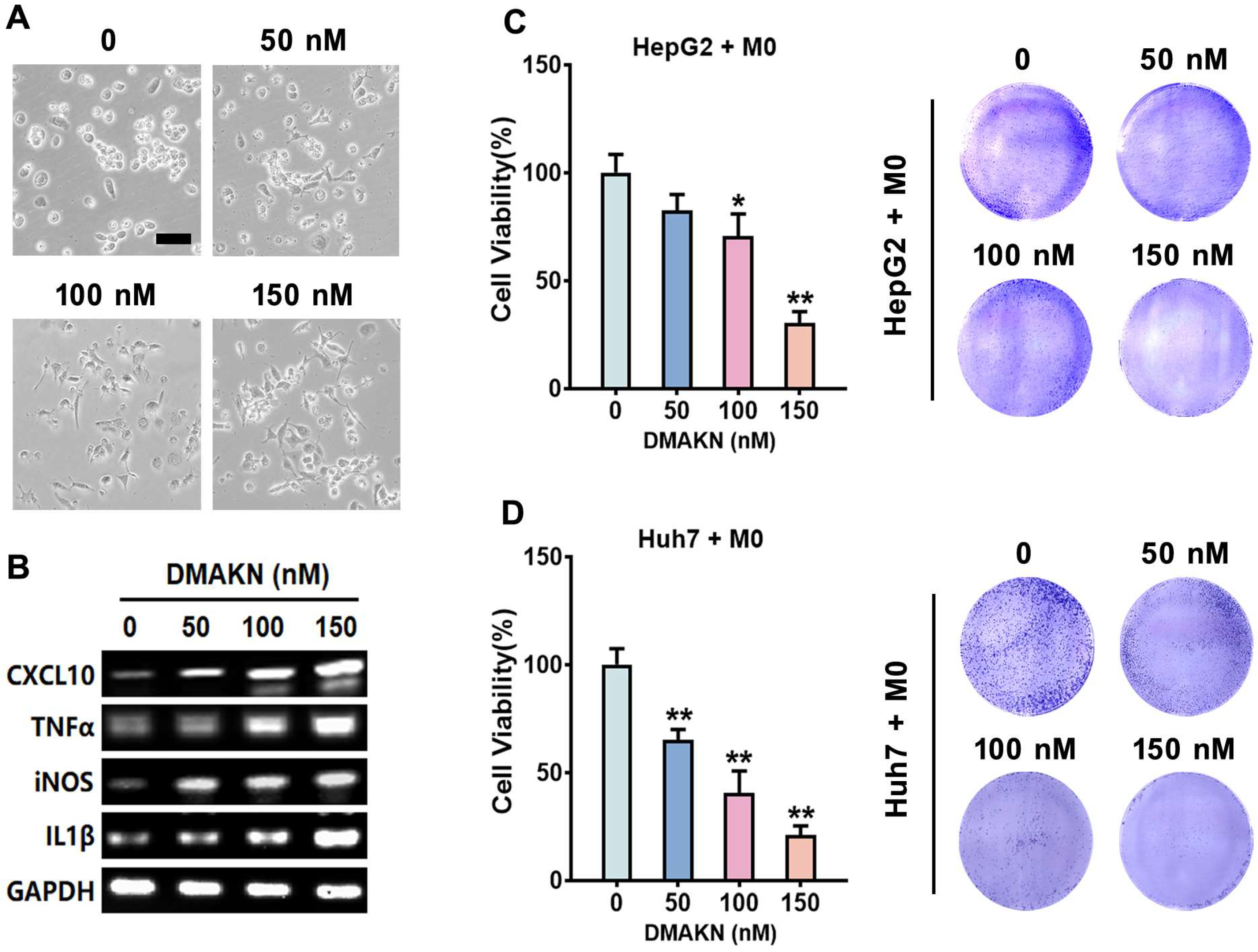
2.2. Screening DMAKN Concentrations Used in Macrophages
2.3. DMAKN-Induced M1 Macrophage Polarization Exhibits Anti-HCC Effects
2.4. DMAKN Enhances Anti-HCC Activity by Sensitizing M1 Macrophage Polarization
2.5. DMAKN Inhibits HCC Cell Viability by Suppressing M2 Macrophage Polarization
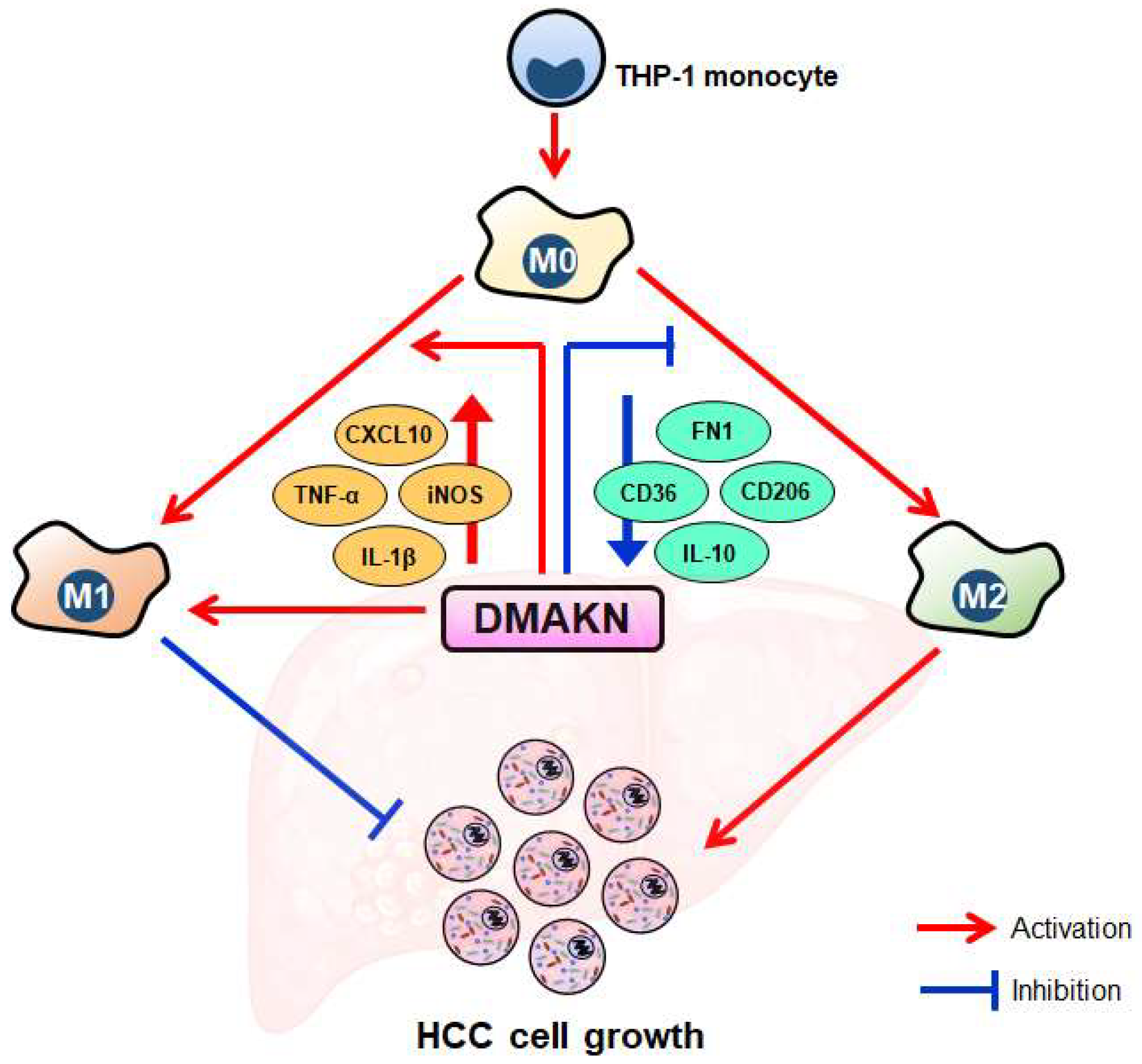
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. The Differentiation, Polarization, and Co-Culture of THP-1 Macrophages with HCC Cells
4.4. MTT Assay for Screening DMAKN Concentrations
4.5. Analysis of the Impact of Macrophages on HCC Cells
4.6. Reverse Transcriptase (RT)—Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganesan, P.; Kulik, L.M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: New developments. Clin. Liver Dis. 2023, 27, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alawyia, B.; Constantinou, C. Hepatocellular carcinoma: A narrative review on current knowledge and future prospects. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, Z.J.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Ruff, S.M.; Mohseni, A.; Kamel, I.R.; Cloyd, J.M.; Pawlik, T.M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. JAMA Surg. 2023, 158, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi Birgani, M.; Carloni, V. Tumor microenvironment, a paradigm in hepatocellular carcinoma progression and therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muppala, S. Significance of the tumor microenvironment in liver cancer progression. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2020, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000prime Rep. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasingam, S.D.; Citartan, M.; Thang, T.H.; Mat Zin, A.A.; Ang, K.C.; Ch’ng, E.S. Evaluating the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages into M1 and M2 phenotypes in human cancer tissue: Technicalities and challenges in routine clinical practice. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Hou, X.; Liu, W.; Han, Z.; Wei, L. Macrophages and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitakis, K.; Koletsa, T.; Mitroulis, I.; Germanidis, G. Tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis, prognosis and therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, T.; Zheng, B.; Chen, L. Individualized precision treatment: Targeting TAM in HCC. Cancer Lett. 2019, 458, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-W.; Chen, S.; Chen, G.-Q. Recent advances in natural compounds inducing non-apoptotic cell death for anticancer drug resistance. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023, 6, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.-J.; Qi, M.; Li, N.; Lei, Y.-H.; Zhang, D.-M.; Chen, J.-X. Natural products and their derivatives: Promising modulators of tumor immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogurcu, N.; Sevimli-Gur, C.; Ozmen, B.; Bedir, E.; Korkmaz, K.S. ALCAPs induce mitochondrial apoptosis and activate DNA damage response by generating ROS and inhibiting topoisomerase I enzyme activity in K562 leukemia cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-P.; Yan, X.-D.; Fan, X.-Y.; Ling, Y.-H.; Li, C.; Lin, L.; Qin, D.; Liu, T.-T.; Li, Y.; Li, H. Oral acute and chronic toxicity studies of β, β-dimethylacrylalkannin in mice and rats. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 4, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chanput, W.; Mes, J.J.; Wichers, H.J. THP-1 cell line: An in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donne, R.; Lujambio, A. The liver cancer immune microenvironment: Therapeutic implications for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1773–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Peng, X.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Huang, M.; Wei, S.; Zhang, S.; He, G.; Liu, J.; Fan, Q. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma: Biology, strategy, and immunotherapy. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunna, C.; Mengru, H.; Lei, W.; Weidong, C. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 877, 173090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sha, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Reprogramming tumor associated macrophages toward M1 phenotypes with nanomedicine for anticancer immunotherapy. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 1900181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, E.; Johnston, T.P.; Ghaneifar, Z.; Vahedi, P.; Goleij, P.; Azhdari, S.; Moghaddam, A.S. Immunomodulatory therapeutic effects of curcumin on M1/M2 macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Cur. Mol. Pharmacol. 2023, 16, 2–14. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Teng, Y. Resveratrol attenuates TNBC lung metastasis by down-regulating PD-1 expression on pulmonary T cells and converting macrophages to M1 phenotype in a murine tumor model. Cell. Immunol. 2021, 368, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Liu, X.-K.; Kang, Z.-P.; Wang, M.-X.; Zhao, H.-M.; Huang, J.-Q.; Xiao, Q.-P.; Liu, D.-Y.; Zhong, Y.-B. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorated experimental colitis by regulating the balance of M1/M2 macrophage polarization and the homeostasis of intestinal flora. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 917, 174742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. ALCAP2 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion via the ubiquitination of beta-catenin by upregulating the E3 ligase NEDD4L. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Yin, F.; Fredimoses, M.; Zhao, J.; Fu, X.; Xu, B.; Liang, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, K.; Lei, M. Targeting FGFR1 by β, β-dimethylacrylalkannin suppresses the proliferation of colorectal cancer in cellular and xenograft models. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liang, H.; Zen, K. Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage M1–M2 polarization balance. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freshney, R.I. Basic Principles of Cell Culture; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhao, M.-m.; Sun, S.; Guo, X.-L.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.-A.; Lee, W.-H.; Zhang, Y. A high concentration of DMSO activates caspase-1 by increasing the cell membrane permeability of potassium. Cytotechnology 2018, 70, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazan, A.; Marusiak, A.A. Protocols for Co-Culture Phenotypic Assays with Breast Cancer Cells and THP-1-Derived Macrophages. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2024, 29, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C. Curcumin modulates macrophage polarization through the inhibition of the toll-like receptor 4 expression and its signaling pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyiramana, M.M.; Cho, S.B.; Kim, E.-J.; Kim, M.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Nam, H.J.; Kim, N.-G.; Park, S.-H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kang, S.S. Sea hare hydrolysate-induced reduction of human non-small cell lung cancer cell growth through regulation of macrophage polarization and non-apoptotic regulated cell death pathways. Cancers 2020, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name | GenBank Acc. No. | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Expected Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CXCL10 | NM_001565.4 | Sense: CCACGTGTTGAGATCATTGCT | 152 |
| Antisense: TGCATCGATTTTGCTCCCCT | |||
| TNF-α | NM_000594.4 | Sense: AGCCCATGTTGTAGCAAACC | 260 |
| Antisense: GGCTCTTGATGGCAGAGAGG | |||
| iNOS | NM_000625.4 | Sense: GGCAAGCCCAAGGTCTATGT | 187 |
| Antisense: CCTCGACCTGCTCCTCATTC | |||
| IL-1β | NM_000576.3 | Sense: AACCTCTTCGAGGCACAAGG | 197 |
| Antisense: GTCCTGGAAGGAGCACTTCAT | |||
| FN1 | NM_001306129.2 | Sense: CCGCCGAATGTAGGACAAGA | 261 |
| Antisense: GACAGAGTTGCCCACGGTAA | |||
| CD36 | NM_000072.3 | Sense: GGTCCTTATACGTACAGAGTTCG | 164 |
| Antisense: GCCACAGCCAGATTGAGAAC | |||
| CD206 | NM_002438.4 | Sense: GTGATGGGACCCCTGTAACG | 111 |
| Antisense: CTGCCCAGTACCCATCCTTG | |||
| IL-10 | NM_000572.3 | Sense: AAGAAGGCATGCACAGCTCA | 249 |
| Antisense: GGCAACCCAGGTAACCCTTA | |||
| GAPDH | NM_014364.5 | Sense: TGTGGGCATCAATGGATTTGG | 116 |
| Antisense: ACACCATGTATTCCGGGTCAAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, L.-S.; Lin, Z.; Gong, R.-H.; Lin, Y.-S.; Qiao, X.-F.; Hu, Q.-M.; Qin, W.-H.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.-Q. β,β-Dimethylacrylalkannin, a Natural Naphthoquinone, Inhibits the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Modulating Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Molecules 2024, 29, 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163919
Shen L-S, Lin Z, Gong R-H, Lin Y-S, Qiao X-F, Hu Q-M, Qin W-H, Chen S, Yang Y, Chen G-Q. β,β-Dimethylacrylalkannin, a Natural Naphthoquinone, Inhibits the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Modulating Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163919
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Li-Sha, Zesi Lin, Rui-Hong Gong, Yu-Shan Lin, Xing-Fang Qiao, Qian-Mei Hu, Wei-Han Qin, Sibao Chen, Yong Yang, and Guo-Qing Chen. 2024. "β,β-Dimethylacrylalkannin, a Natural Naphthoquinone, Inhibits the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Modulating Tumor-Associated Macrophages" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163919
APA StyleShen, L.-S., Lin, Z., Gong, R.-H., Lin, Y.-S., Qiao, X.-F., Hu, Q.-M., Qin, W.-H., Chen, S., Yang, Y., & Chen, G.-Q. (2024). β,β-Dimethylacrylalkannin, a Natural Naphthoquinone, Inhibits the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Modulating Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Molecules, 29(16), 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163919







