The Role of Ascorbic Acid in the Process of Azo Dye Degradation in Aqueous Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Experimental Conditions
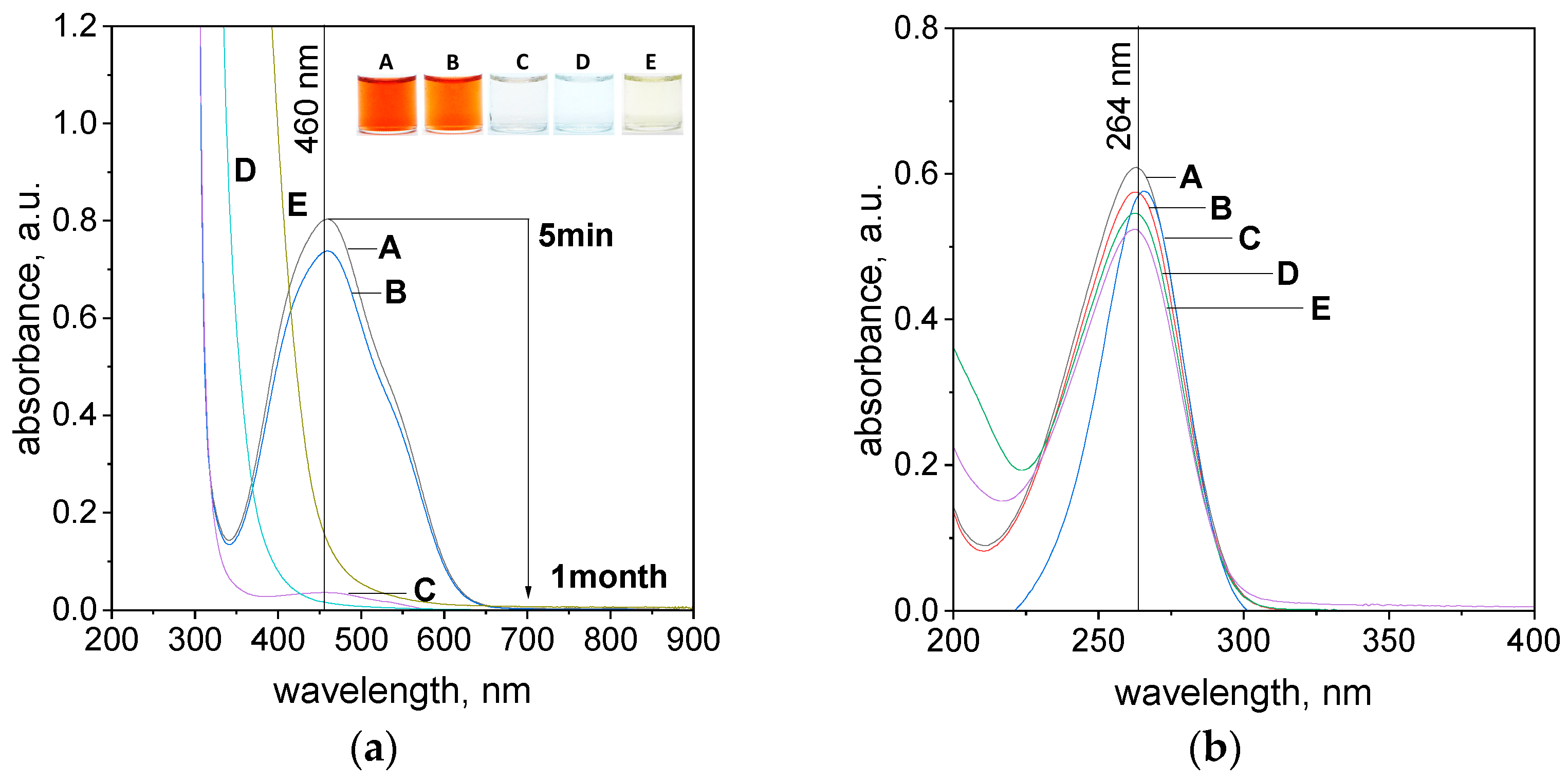
2.2. Spectra of Reagents and Molar Coefficients Determination
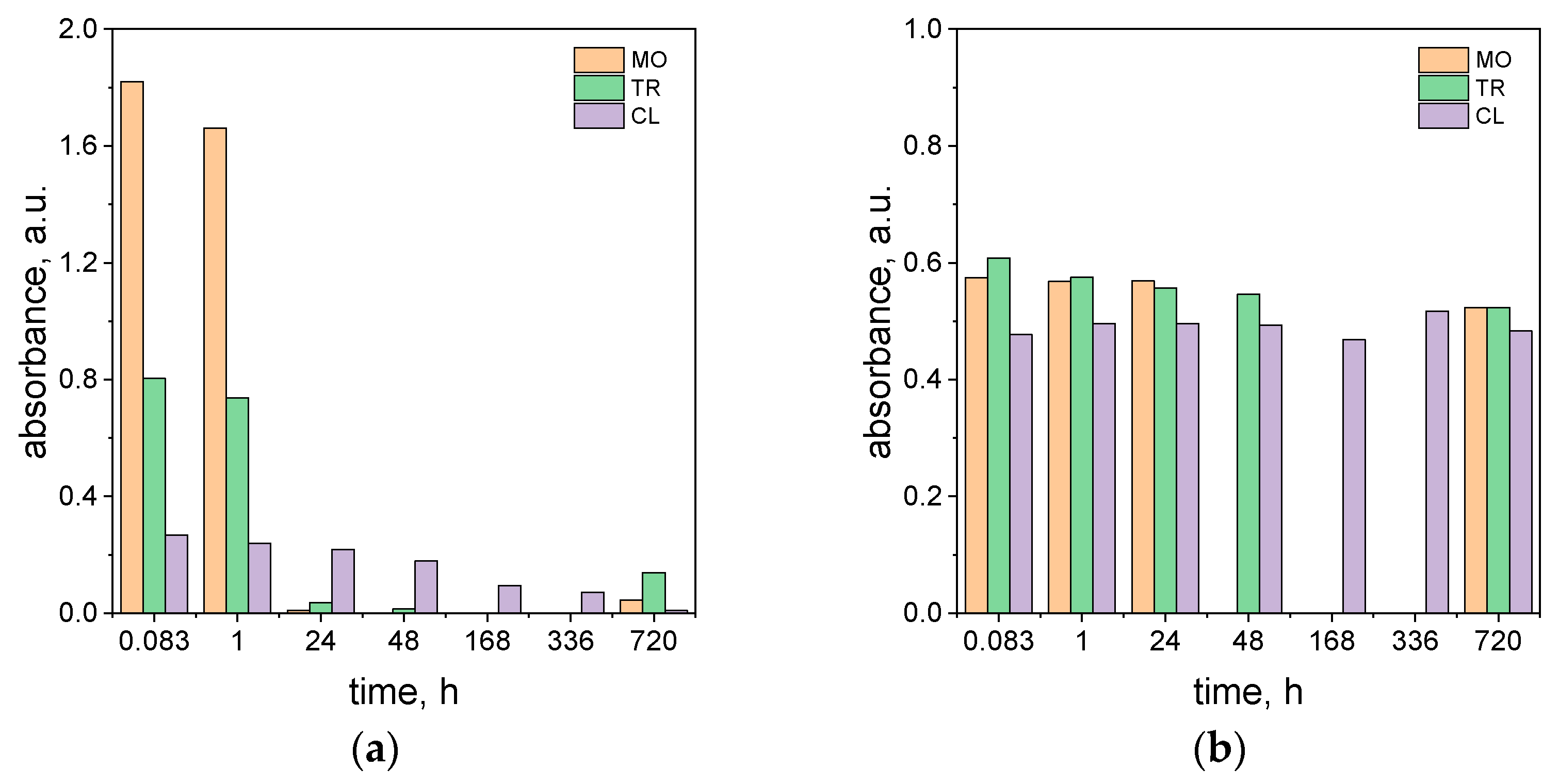
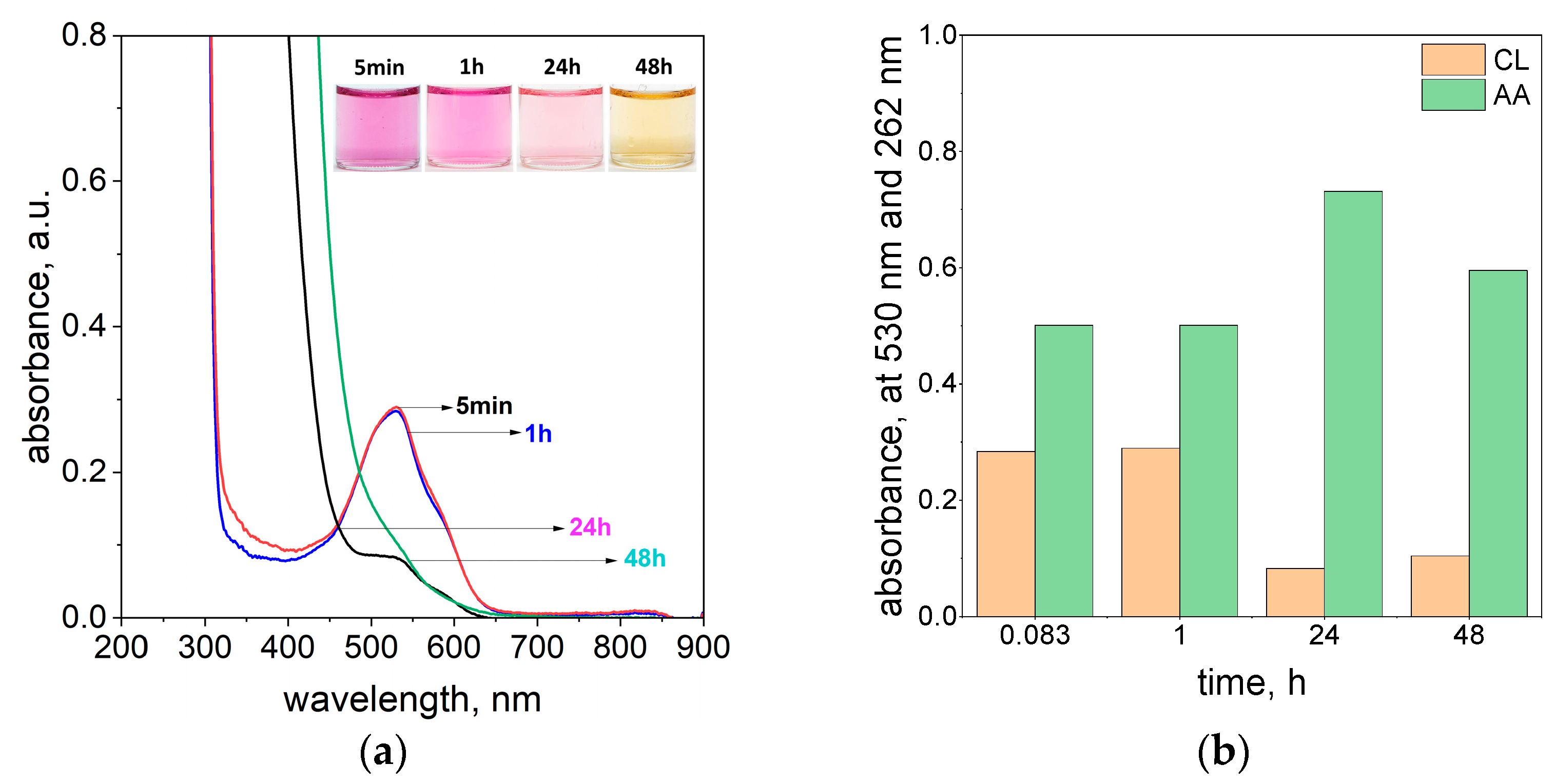
2.3. The Process of Azo Dye Degradation
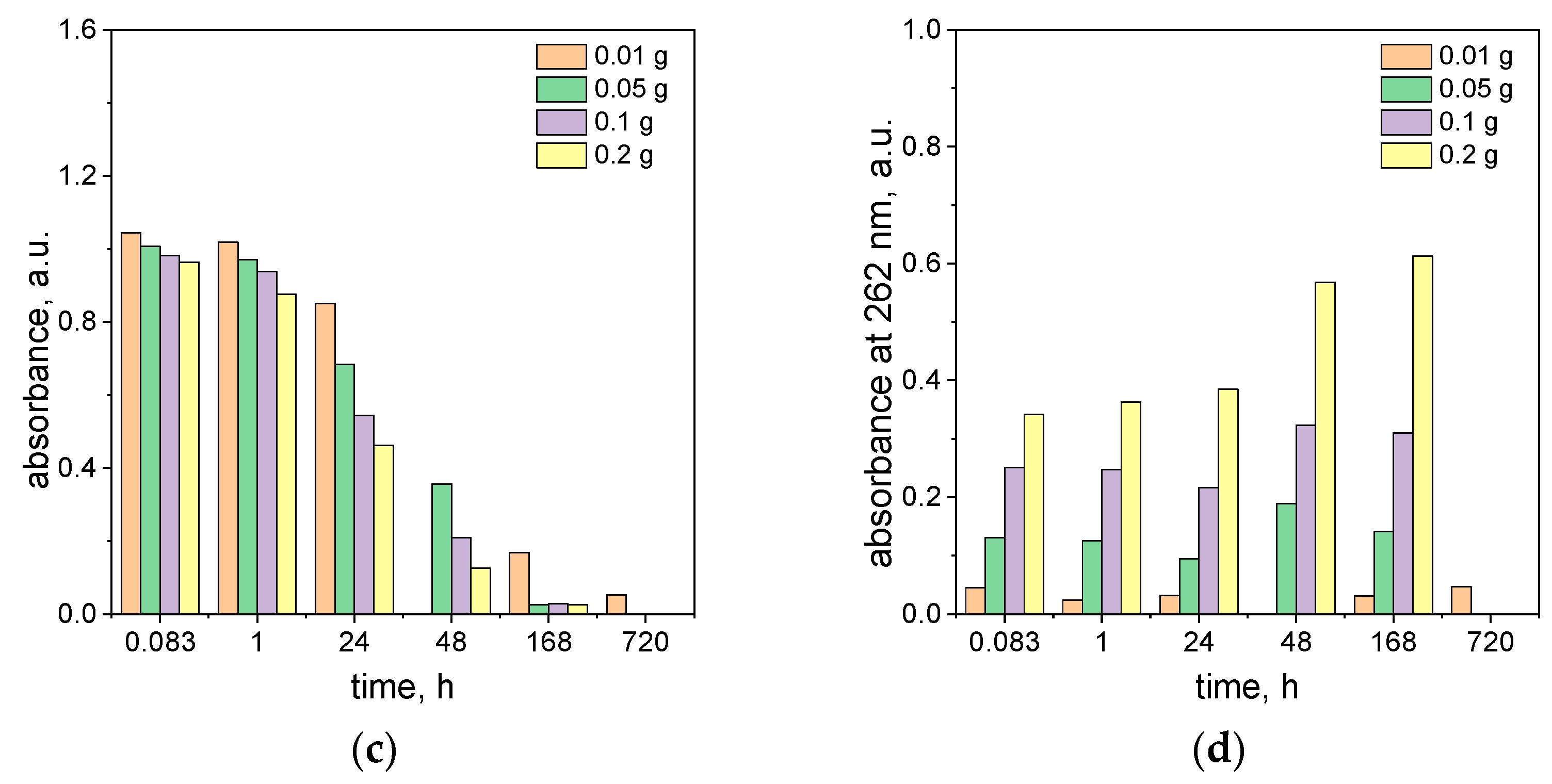
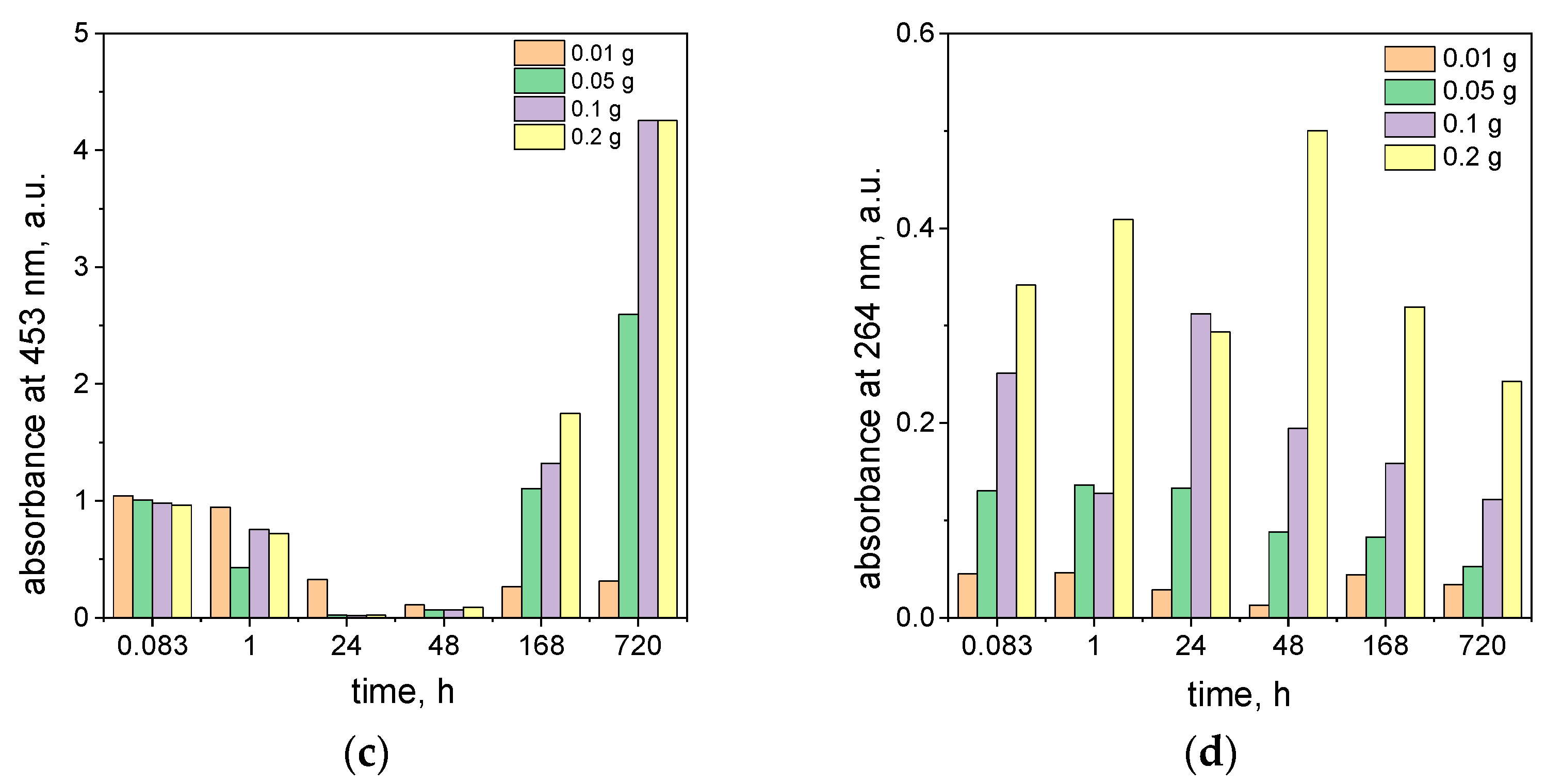
2.4. The Influence of the Ascorbic Acid Concentration on the Process of Azo Dye Degradation
2.5. The Influence of Temperature on the Process of Dye Removal
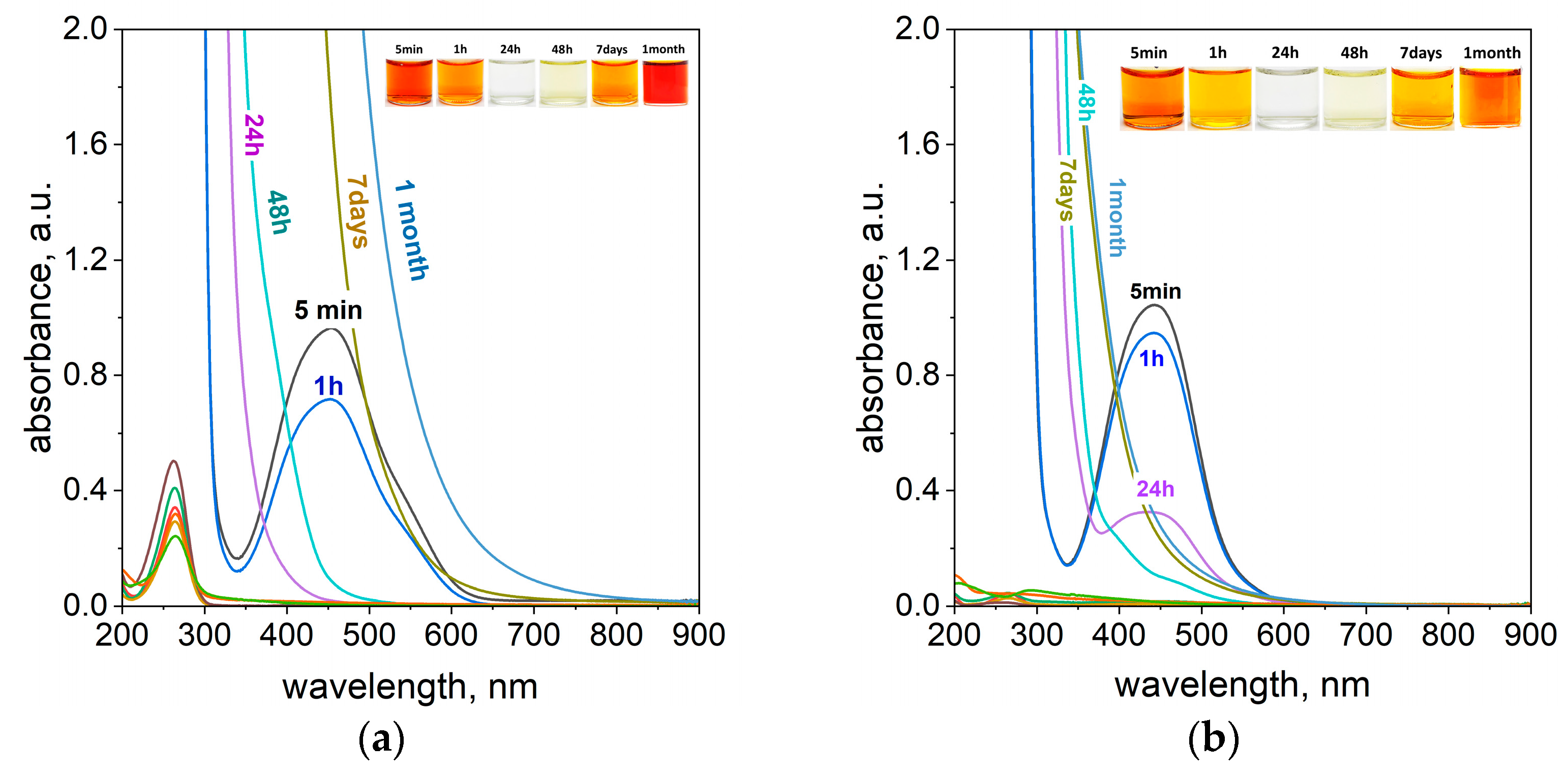
2.6. The Influence of Daylight Exposition on the Process of Dye Degradation
2.7. The Mechanism of Azo Dye Degradation Using Ascorbic Acid
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
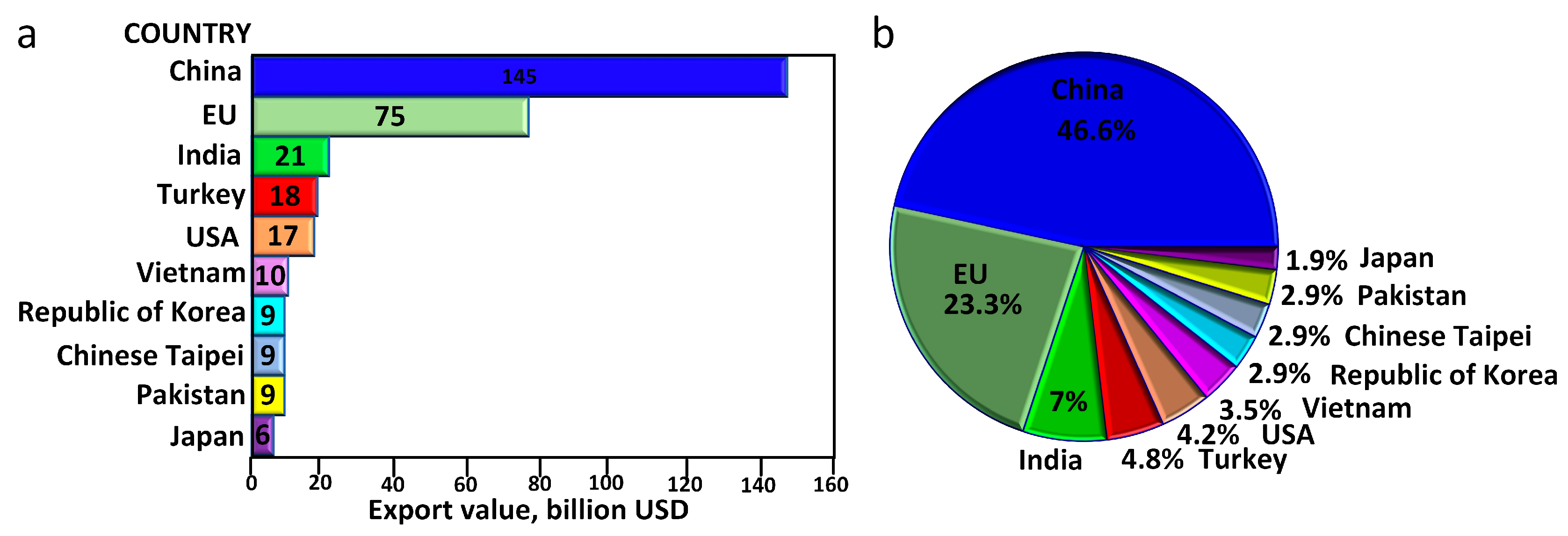
- Benkhaya, S.; M’Rabet, S.; El Harfi, A. Classifications, properties, recent synthesis and applications of azo dyes. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipskikh, O.; Korotkova, E.; Khristunova, Y.; Barek, J.; Kratochvil, B. Sensors for voltammetric determination of food azo dyes—A critical review. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 260, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Gubitosa, J.; Fini, P.; Nuzzo, S.; Cosma, P. Amino-grafted mesoporous MCM-41 and SBA-15 recyclable adsorbents: Desert-rose-petals-like SBA-15 type as the most efficient to remove azo textile dyes and their mixture from water. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 26, e00231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtfouse, E.; Schwarzbauer, J.; Robert, D. Environmental Chemistry: Green Chemistry and Pollutants in Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sayyed, M.K.; Hashemi, H. Chapter 15—Azo dyes: Sources, occurrence, toxicity, sampling, analysis, and their removal methods. In Emerging Freshwater Pollutants: Analysis, Fate and Regulations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Azo Compound. 31 October 2018. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/azo-compound (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Top Textile Exporting Countries Worldwide 2021. November 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/236397/value-of-the-leading-global-textile-exporters-by-country/ (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Thangaraj, S.; Bankole, P.O.; Sadasivam, S.K. Microbial degradation of azo dyes by textile effluent adapted, Enterobacter hormaechei under microaerophilic condition. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 250, 126805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Singh, P.; Iyengar, L. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 59, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Baldrian, P.; Nerud, F. Decolorization of structurally different synthetic dyes using cobalt(II)/ascorbic acid/hydrogen peroxide system. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyetade, J.A.; Machunda, R.L.; Hilonga, A. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in textile wastewater by Polyaniline composite catalyst-a review. Sci. Afr. 2022, 17, e01305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Yuan, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, L. Ultra-thin carbon nitride activated periodate for efficient tetracycline degradation with the assistance of visible light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 338, 126505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale-Júnior, E.D.; da Silva, D.R.; Fajardo, A.S.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. Treatment of an azo dye effluent by peroxi-coagulation and its comparison to traditional electrochemical advanced processes. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaff, A.R.; Venkatesh, S.; Venkatesh, K. Degradation of Azo Dye by Ozone Oxidation: Cost Analysis and Buffering Effects on Dye Decomposition. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2021, 44, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, E.; Rapf, M.; Di Michele, A.; Rossetti, I. Photochemical vs. photocatalytic azo-dye removal in a pilot free-surface reactor: Is the catalyst effective? Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Tang, N.; Jiang, L.; Yang, J.; Guo, J.; Yuan, X.; Liang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, H. Bimetallic nanoparticles meet polymeric carbon nitride: Fabrications, catalytic applications and perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 462, 214500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, W.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Yuan, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Accelerated Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycle for ultrafast removal of acetaminophen by a novel W18O49 co-catalytic Fe3+/H2O2 fenton-like system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 342, 127056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, D.; Jiang, H.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, L. MoO2 co-catalytic Fe3+/periodate for tetracycline degradation: Key role of Fe/Mo cycling and high-valent iron (Fe(IV)) generation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 346, 127509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.; Yasid, N.A.; Othman, A.R.; Shukor, M.Y. Biosorption of Azo Dyes by Bacterial Biomass: A review. J. Environ. Microbiol. Toxicol. 2023, 11, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauernfeind, J.C. Ascorbic Acid Technology in Agricultural, Pharmaceutical, Food, and Industrial Applications. In Ascorbic Acid: Chemistry, Metabolism, and Uses; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; pp. 395–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luty-Błocho, M.; Pacławski, K.; Wojnicki, M.; Fitzner, K. The kinetics of redox reaction of gold(III) chloride complex ions with l-ascorbic acid. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2013, 395, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnicki, M.; Fitzner, K.; Luty-Błocho, M. Kinetic studies of nucleation and growth of palladium nanoparticles. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 465, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Lin, J.-D.; Zou, H.-M.; Liao, D.-W. Effects of surface modification of TiO2 with ascorbic acid on photocatalytic decolorization of an azo dye reactions and mechanisms. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 241, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, P.; Huang, D.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Qin, L.; Li, B.; He, J.; Yi, H.; Cheng, M.; et al. Au nanoparticles decorated on activated coke via a facile preparation for efficient catalytic reduction of nitrophenols and azo dyes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Huang, X.; Ai, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. Ascorbic acid/Fe@Fe2O3: A highly efficient combined Fenton reagent to remove organic contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Sharma, A.K.; Sanghi, R. Poly(acrylamide) functionalized chitosan: An efficient adsorbent for azo dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakimoto, R.; Kitamura, T.; Ito, F.; Usami, H.; Moriwaki, H. Decomposition of methyl orange using C60 fullerene adsorbed on silica gel as a photocatalyst via visible-light induced electron transfer. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 166–167, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yussif, N.M. Vitamin C; LeBlanc, J.G., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszko, D.; Celiński-Mysław, D.; Klimatologii, Z.; Geografii, I.; Przestrzennej, G. Warunki Solarne Krakowa I Możliwości Ich Wykorzystania W Helioenergetyce. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2016, 15, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witmer, J.R.; Wetherell, B.J.; Wagner, B.A.; Du, J.; Cullen, J.J.; Buettner, G.R. Direct spectrophotometric measurement of supra-physiological levels of ascorbate in plasma. Redox Biol. 2016, 8, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pach, A.; Podborska, A.; Csapo, E.; Luty-Błocho, M. Tropaeolin OO as a Chemical Sensor for a Trace Amount of Pd(II) Ions Determination. Molecules 2022, 27, 4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luty-Błocho, M.; Podborska, A.; Musielak, B.; Hessel, V. The specialized twin-solution method for selective Pd(II) ions determination and methyl orange removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 340, 116884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podborska, A.; Luty-Błocho, M. Molecular structure of methyl orange and its role in the process of [Pd(Azo)] compound and MOF formation. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1273, 134312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.A.; Hisaindee, S.; Saleh, N. Spectroscopic studies of keto–enol tautomeric equilibrium of azo dyes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 18097–18110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, J.C. Dehydroascorbic acid. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 881, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoh, K.B.; Hahn, F.; Métayer, A.; Lamy, C. FTIR spectroelectrochemical investigation of the electrocatalytic ox-idation of ascorbic acid at platinum electrodes in acid medium. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 3965–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boatright, W.L. Oxygen dependency of one-electron reactions generating ascorbate radicals and hydrogen peroxide from ascorbic acid. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, R.L.; Espinoza, A.G.; Litter, M.I. Photodegradation of an azo dye of the textile industry. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, J.; Kuruppu, S.; Pradeep, U. The promoting effect of MgO layer in sensitized photodegradation of colorants on TiO2/MgO composite oxide. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 276, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldegebrieal, G.K. Synthesis method, antibacterial and photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles for azo dyes in wastewater treatment: A review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 120, 108140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes Da Silva, C.; Luís Faria, J. Photochemical and photocatalytic degradation of an azo dye in aqueous solution by UV irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 155, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, N.; Salari, D.; Khataee, A. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dye acid red 14 in water: Investigation of the effect of operational parameters. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 157, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, B.; Pant, H.R.; Barakat, N.A.; Park, M.; Jeon, K.; Choi, Y.; Kim, H.-Y. Carbon nanofibers decorated with binary semiconductor (TiO2/ZnO) nanocomposites for the effective removal of organic pollutants and the enhancement of antibacterial activities. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 7029–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajchakit, U.; Limpanuparb, T. Greening the Traffic Light: Air Oxidation of Vitamin C Catalyzed by Indicators. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luty-Błocho, M.; Wojnicki, M.; Grzonka, J.; Kurzydłowski, K. The synthesis of stable platinum nanoparticles in the microreactor. Arch. Met. Mater. 2014, 59, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabelli, D.E.; Bielski, B.H.J. Kinetics and Mechanism for the Oxidation of Ascorbic Acid/Ascorbate by HO2/O2− Radicals. A Pulse Radiolysis and Stopped-Flow Photolysis Study. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 1809–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Yagnik, G.B.; Zhou, F. Reaction rates and mechanism of the ascorbic acid oxidation by molecular oxygen facilitated by Cu(II)-containing amyloid-β complexes and aggregates. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 4896–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielski, B.H.J. Reevaluation of the Spectral and Kinetic Properties of HO2 AND O2− Free Radicals. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 28, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zee, F.P.; Villaverde, S. Combined anaerobic–aerobic treatment of azo dyes—A short review of bioreactor studies. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1425–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickhoff, J.; Arndt, N.B.; Böckmann, M.; Doltsinis, N.L.; Ravoo, B.J.; Kortekaas, L. Reversible, Red-Shifted Photoisomerization in Protonated Azobenzenes. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 10605–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qian, Y.; Feng, R.; Ding, Y.; Zu, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Yu, G. Reversible redox chemistry in azobenzene-based organic molecules for high-capacity and long-life nonaqueous redox flow batteries. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 31222, 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/1_2-Diphenylhydrazine (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 23668839, Tropaeolin OO. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Tropaeolin-OO (accessed on 24 June 2024).

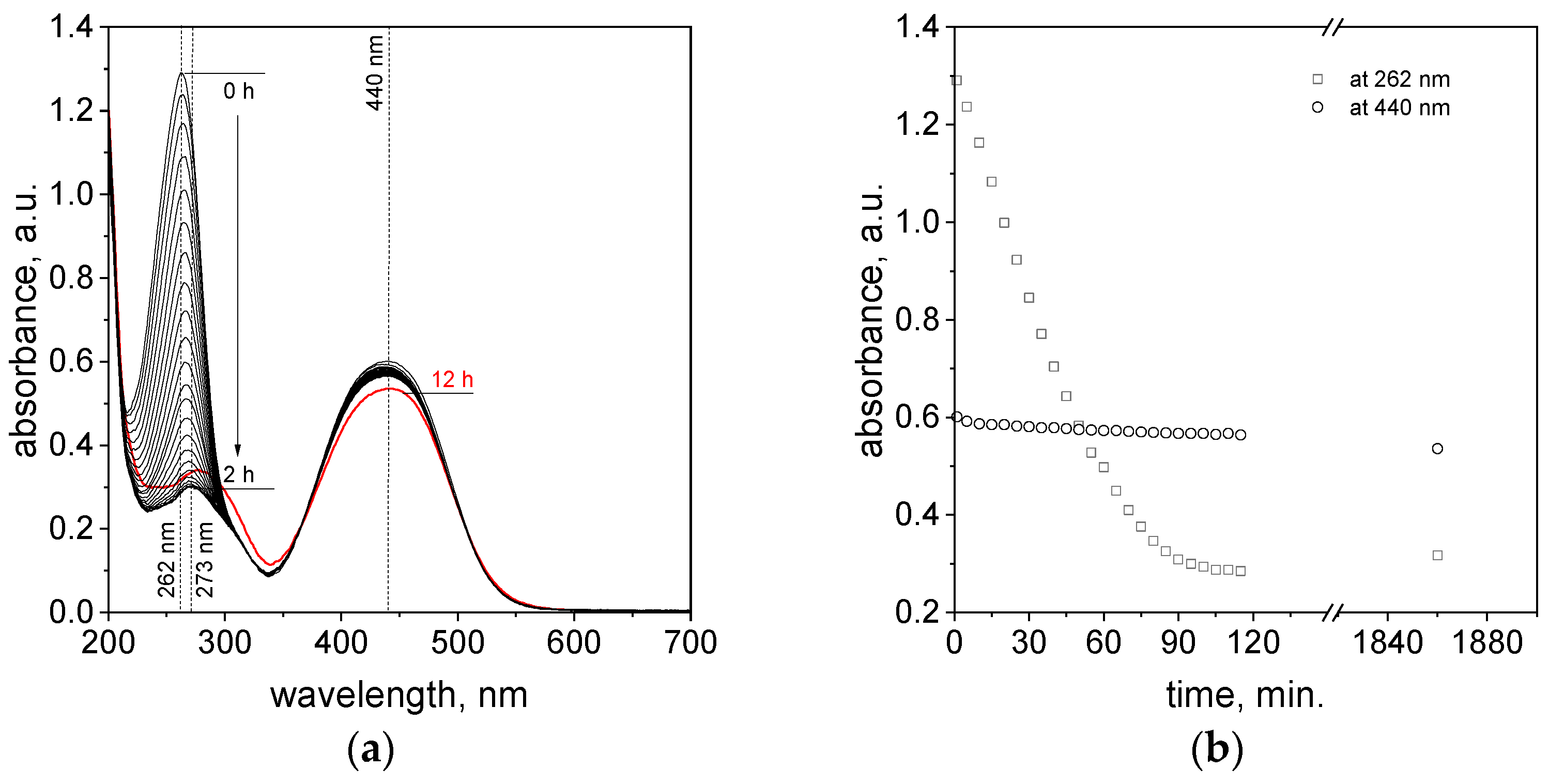
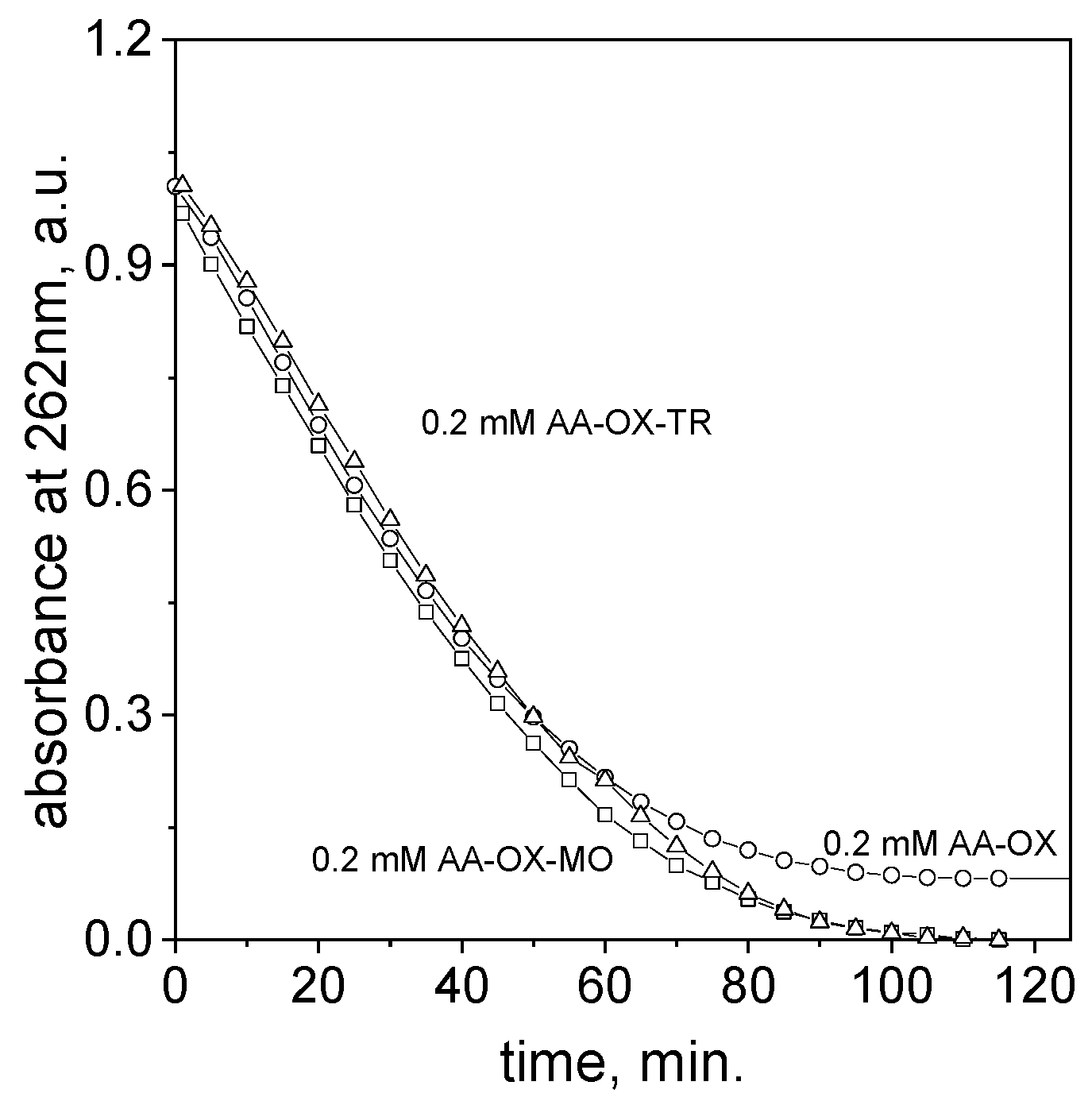
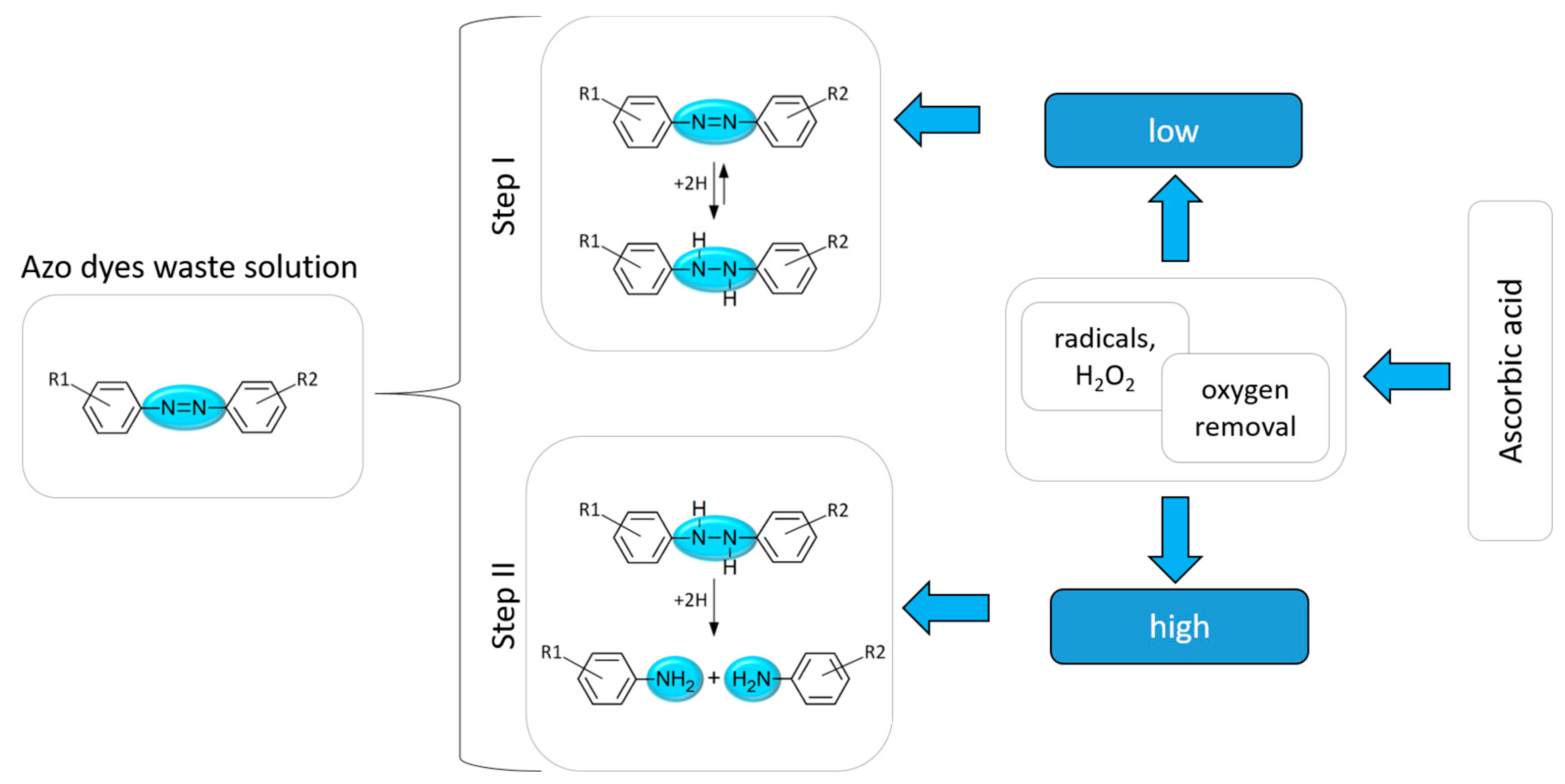
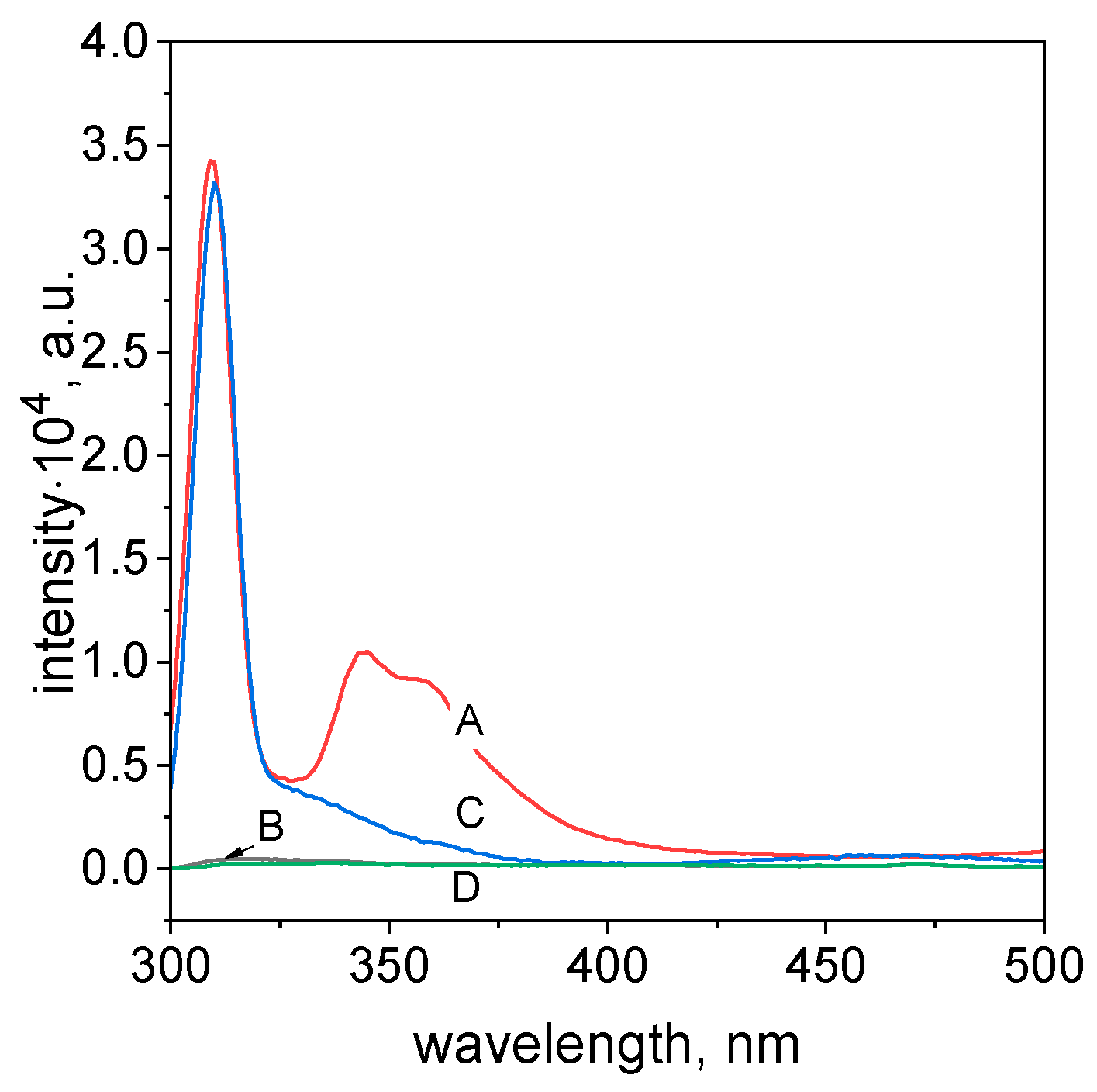
| Initial Concentration of Azo Dye Solutions | The Initial Content of Ascorbic Acid | The Volume of Azo Dye Solution (MO, TR, CL) | T | Exposition to Daylight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0, TR, MO, CL, mol/dm3 | m0, AA, g | VTR, MO, CL, mL | °C | |
| The molar coefficient determination | ||||
| 5 × 10−6 | 4 | 20 | ||
| 1 × 10−5 | ||||
| 5 × 10−5 | ||||
| 1 × 10−4 | ||||
| 2 × 10−4 | ||||
| The influence of ascorbic acid concentration and temperature on the process of dye degradation | ||||
| 5 × 10−5 | 0.01 | 4 | 20 | DLE |
| 0.05 | 50 | |||
| 0.10 | ||||
| 0.20 | ||||
| The influence of daylight exposition/protection on the process of dye degradation | ||||
| 5 × 10−5 | 0.4 | 4 | 20 | |
| 50 | ||||
| Solution | ɛ1 (λ1) | ɛ2 (λ2) | ɛ3 (λ3) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M−1cm−1 | M−1cm−1 | M−1cm−1 | ||
| Ascorbic acid | 17,232 ± 243 (246 nm) | This work | ||
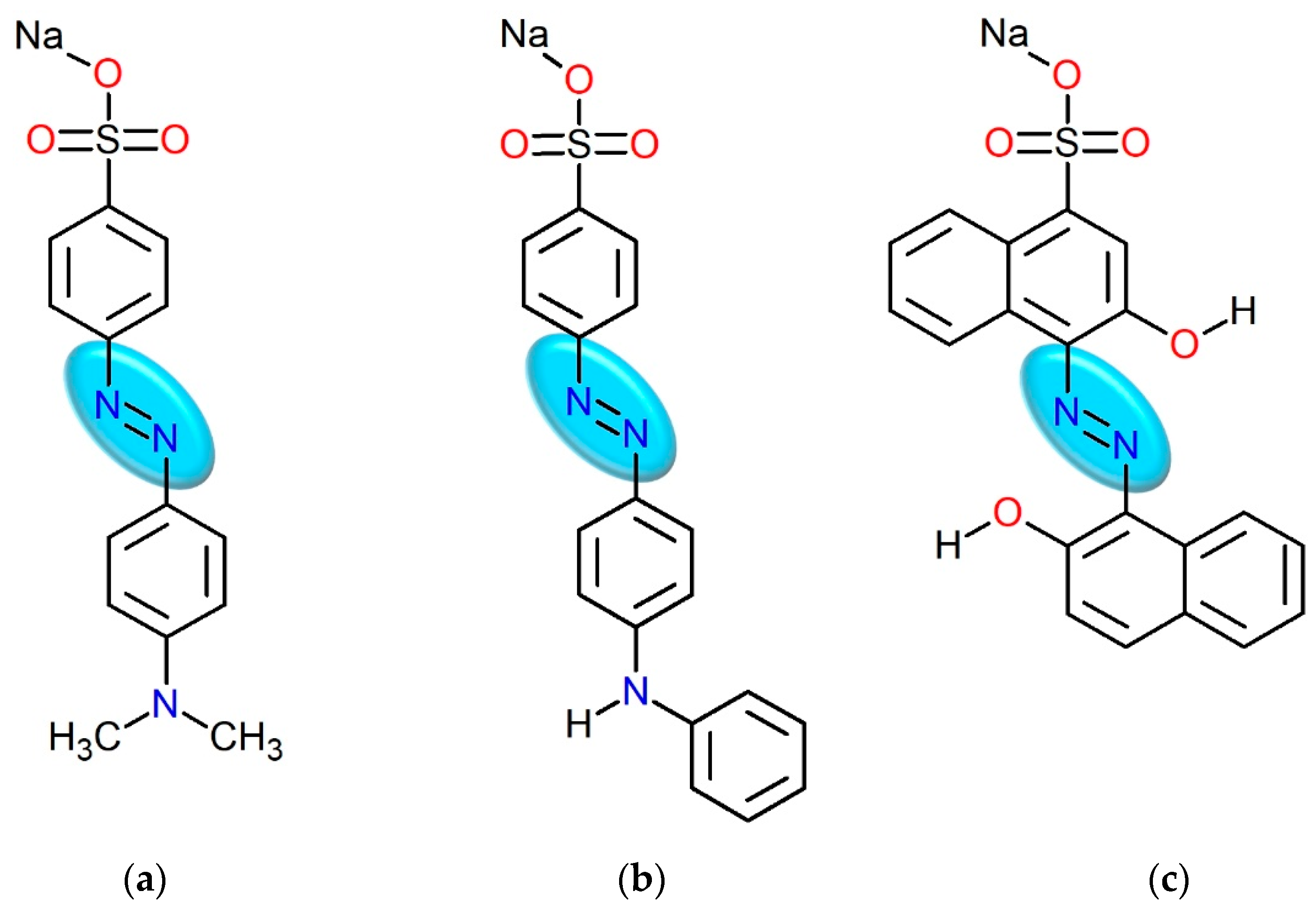
| Tropaeolin OO | 12,452 ± 2 (272 nm) | 25,160 ± 58 (445 nm) | [32] | |
| Methyl Orange | 14,353 ± 59 (274 nm) | 39,226 ± 59 (465 nm) | [33] | |
| Calcon | 18,709 ± 20 (218 nm) | 2327 ± 4 (340 nm) | 6432 ± 21 (544 nm) | This work |
| The Concentration of Ascorbic Acid (CAA), M | Observed First-Order Rate Constant (kobs), h−1 | |
|---|---|---|
| TR | MO | |
| 0.014 | 0.020 | 0.080 |
| 0.071 | 0.023 | 0.094 |
| 0.14 | 0.029 | 0.127 |
| 0.28 | 0.036 | 0.164 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pach, A.; Zaryczny, A.; Podborska, A.; Luty-Błocho, M. The Role of Ascorbic Acid in the Process of Azo Dye Degradation in Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2024, 29, 3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153659
Pach A, Zaryczny A, Podborska A, Luty-Błocho M. The Role of Ascorbic Acid in the Process of Azo Dye Degradation in Aqueous Solution. Molecules. 2024; 29(15):3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153659
Chicago/Turabian StylePach, Adrianna, Aleksandra Zaryczny, Agnieszka Podborska, and Magdalena Luty-Błocho. 2024. "The Role of Ascorbic Acid in the Process of Azo Dye Degradation in Aqueous Solution" Molecules 29, no. 15: 3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153659
APA StylePach, A., Zaryczny, A., Podborska, A., & Luty-Błocho, M. (2024). The Role of Ascorbic Acid in the Process of Azo Dye Degradation in Aqueous Solution. Molecules, 29(15), 3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153659









