Efficacy of Agricultural Residue-Derived Biochar for Tackling Cadmium Contamination in an Aqueous Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Biochar
2.1.1. Agricultural Residues Composition
2.1.2. SEM Analysis
2.1.3. Elemental Analysis and BET Surface Area
2.1.4. FTIR Analysis
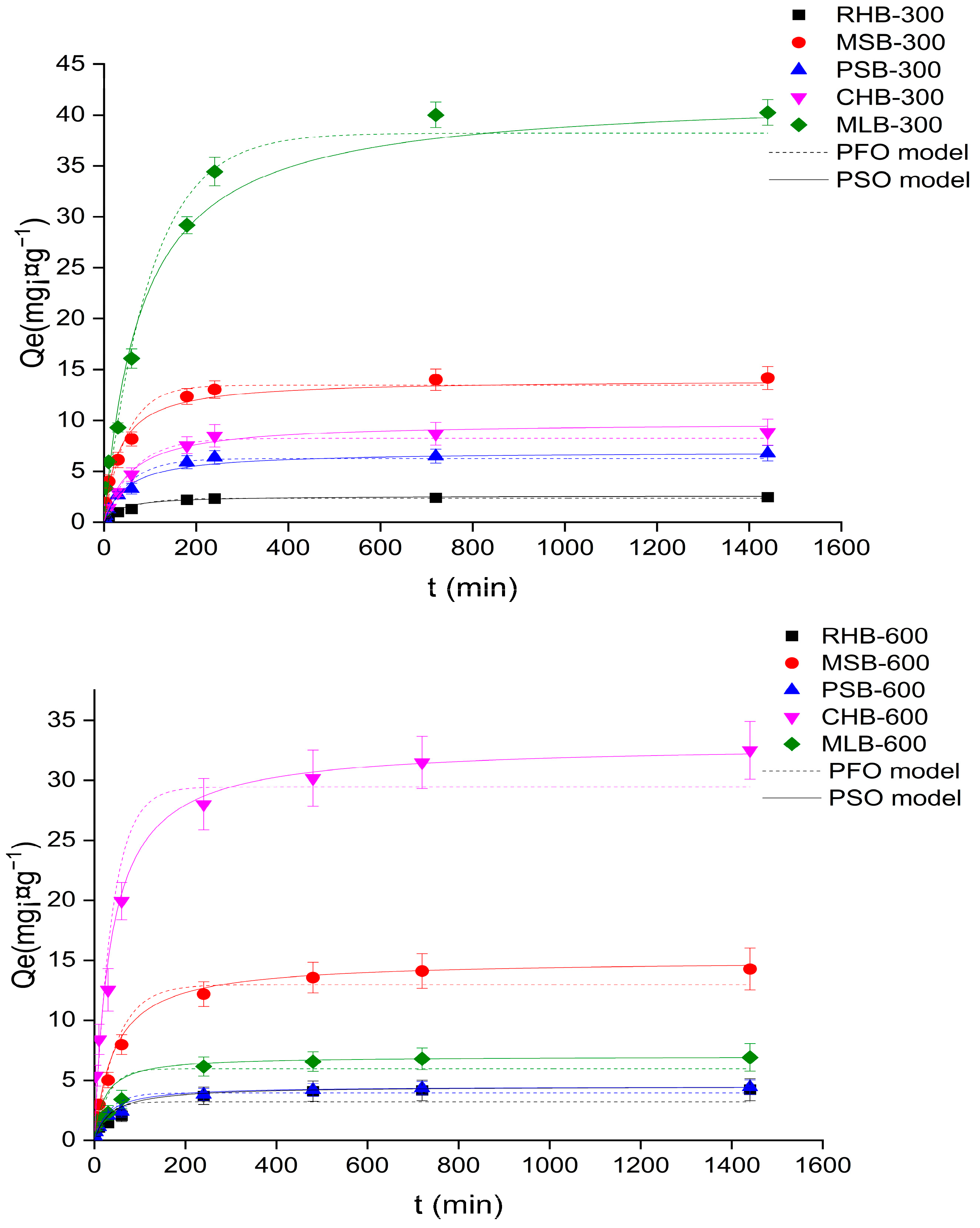
2.2. Adsorption Characteristics
2.2.1. Adsorption Kinetics
2.2.2. Sorption Isotherms
2.2.3. Effect of the pH on Cd(II) Adsorption
2.2.4. Effect of Ionic Strength on Cd(II) Adsorption
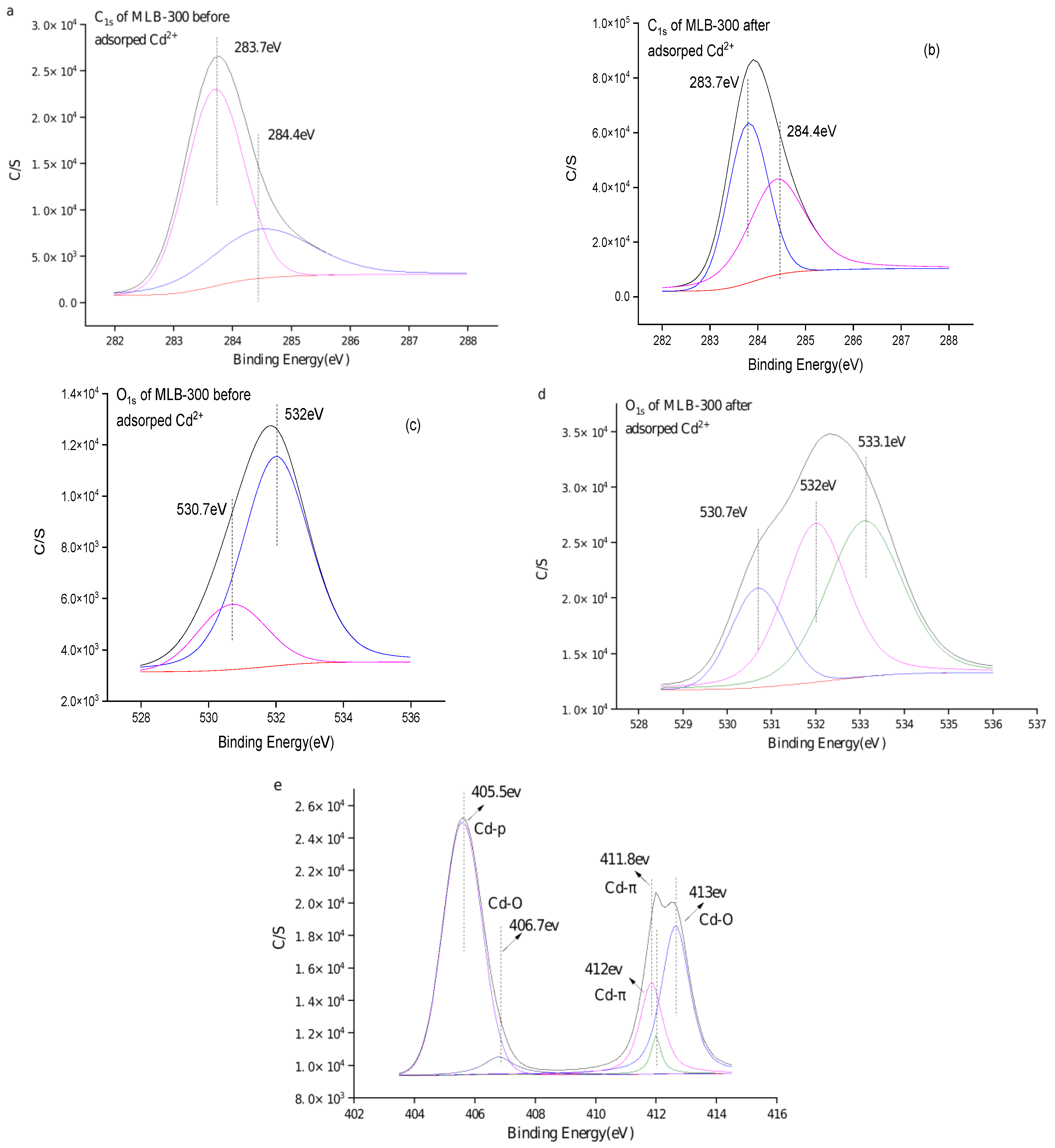
2.2.5. FTIR Spectra Prior- and Post-Cd(II) Adsorption
2.2.6. XPS Spectra Prior- and Post-Cd(II) Adsorption
2.2.7. Correlation Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical and Materials
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
3.3. Characterization and Analysis
3.4. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thornton, I. Geochemistry of cadmium. In Cadmium in the Environment; Mislin, H., Ravera, O., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Satarug, S.; Baker, J.R.; Urbenjapol, S.; Haswell-Elkins, M.; Reilly, P.E.B.; Williams, D.J.; Moore, M.R. A global perspective on cadmium pollution and toxicity in non-occupationally exposed population. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 137, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chary, N.S.; Kamala, C.T.; Raj, D.S.S. Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 69, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peternele, W.S.; Winkler-Hechenleitner, A.A.; Pineda, E.A.G. Adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) onto functionalized formic lignin from sugar cane bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 68, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.W.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Cao, X.D. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by biochars derived from anaerobically digested biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.S.; Piskorz, J. The continuous flash pyrolysis of biomass. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1984, 62, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Dara, S. Binding heavy metal ions with polymerized onion skin. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1981, 19, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, S.; Konishi, Y.; Tomisaki, H.; Nakanishi, M. Separation of mercury from aqueous mercuric chloride solutions by onion skins. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1986, 21, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, J.M.; Reuter, F.W.; Waiss, A.C., Jr. Removal of cupric ion from solution by contact with peanut skins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1975, 19, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati Matin, N.; Jalali, M.; Antoniadis, V.; Shaheen, S.M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Rinklebe, J. Almond and walnut shell-derived biochars affect sorption-desorption, fractionation, and release of phosphorus in two different soils. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 124888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne Costa, E.T.; Winkler-Hechenleitner, A.A.; Gómez-Pineda, E.A. Removal of cupric ions from aqueous solutions by contact with corncobs. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1995, 30, 2593–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, H.; Horigoshi, S.; Saka, S. Effects of side-chain hydroxyl groups on pyrolytic β-ether cleavage of phenolic lignin model dimer. J. Wood Sci. 2007, 53, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, Y.W.; Wu, H.; Yu, Y. Effect of cellulose–lignin interactions on char structural changes during fast pyrolysis at 100–350 °C. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2021, 38, 3977–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, P.; Garcia Moscoso, J.L.; Kumar, S.; Cao, X.; Mao, J.; Schafran, G. Removal of copper and cadmium from aqueous solution using switchgrass biochar produced via hydrothermal carbonization process. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 109, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Solomon, D.; Sohi, S.; Thies, J.E.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Luizão, F.J.; Engelhard, M.H.; Neves, E.G.; Wirick, S. Stability of biomass-derived black carbon in soils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 6069–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandylis, K.; Hadjigeorgiou, I.; Harizanis, P. The nutritive value of mulberry leaves (Morus alba) as a feed supplement for sheep. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Insight into biochar properties and its cost analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 84, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Johnson, M.G.; Kleber, M. Dynamic Molecular Structure of Plant Biomass-Derived Black Carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chunhui, L.; Jin, T.; Puli, Z.; Bin, Z.; Duo, B.; Xuebin, L. Simultaneous removal of fluoride and arsenic in geothermal water in Tibet using modified yak dung biochar as an adsorbent. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 181266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimiya, M.; Lima, I.; Klasson, K.; Chang, S.; Wartelle, L.; Rodgers, J. Immobilization of heavy metal ions (CuII, CdII, NiII, and PbII) by broiler litter-derived biochars in water and soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5538–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Chen, W.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, D. Adsorption of sulfonamides to demineralized pine wood biochars prepared under different thermochemical conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Lian, F.; Cui, G.; Liu, Z. N-doping effectively enhances the adsorption capacity of biochar for heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2017, 193, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Tu, R.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Gao, T.; Yang, M.; Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Goto, T. Synthesis of large size uniform single-crystalline trilayer graphene on premelting copper. Carbon 2017, 122, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, T.; Dong, T.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Z.; Feng, W.; Wang, T. Structural interplay and macroscopic aggregation of rice albumins after binding with heavy metal ions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; Chronology; WHO (World Health Organ): Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 38, pp. 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; He, C.; Shen, C.; Guo, J.; Mubeen, S.; Yuan, J.; Yang, Z. Toxicity of cadmium and its health risks from leafy vegetable consumption. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1373–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.H.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Messele, S.A.; Naeth, M.A.; El-Din, M.G.; Chang, S.X. Biochar properties and lead (II) adsorption capacity depend on feedstock type, pyrolysis temperature, and steam activation. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Bulk Element Composition (%) | Ash Content (%) | SBET (m2g−1) | VTPV (cm3g−1) | Pore Width (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | |||||
| RHB-300 | 54.51 | 3.79 | 40.14 | 1.56 | 23.55 | 19.37 | 0.009 | 1.84 |
| RHB-600 | 59.00 | 1.79 | 38.02 | 1.19 | 32.58 | 268.81 | 0.134 | 2.00 |
| MSB-300 | 61.96 | 4.19 | 31.14 | 2.71 | 13.55 | 13.50 | 0.007 | 2.10 |
| MSB-600 | 70.79 | 2.04 | 24.95 | 2.22 | 17.59 | 229.09 | 0.126 | 2.20 |
| PSB-300 | 64.29 | 4.11 | 30.48 | 1.12 | 7.7 | 1.59 | 0.004 | 10.85 |
| PSB-600 | 76.97 | 2.28 | 19.76 | 0.99 | 12.05 | 292.31 | 0.142 | 1.94 |
| CHB-300 | 57.97 | 3.84 | 36.57 | 1.62 | 17.44 | 3.26 | 0.008 | 10.01 |
| CHB-600 | 71.01 | 1.97 | 25.95 | 1.07 | 21.03 | 141.92 | 0.070 | 1.97 |
| MLB-300 | 54.64 | 4.84 | 35.25 | 5.27 | 19.05 | 39.93 | 0.022 | 2.17 |
| MLB-600 | 53.26 | 1.83 | 47.27 | 4.16 | 32.35 | 26.46 | 0.029 | 4.43 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg g−1) | K1 | R2 | Kf | 1/n | R2 | |
| RHB-300 | 19.79 ± 3.500 | 0.05 | 0.921 | 1.305 | 0.586 | 0.986 |
| RHB-600 | 19.43 ± 2.144 | 0.08 | 0.899 | 1.835 | 0.531 | 0.975 |
| MSB-300 | 25.87 ± 0.564 | 0.1 | 0.971 | 3.315 | 0.457 | 0.964 |
| MSB-600 | 23.82 ± 0.562 | 0.08 | 0.954 | 2.482 | 0.504 | 0.971 |
| PSB-300 | 20.05 ± 1.209 | 0.1 | 0.961 | 2.838 | 0.436 | 0.946 |
| PSB-600 | 17.73 ± 1.249 | 0.03 | 0.887 | 0.537 | 0.732 | 0.972 |
| CHB-300 | 21.64 ± 2.268 | 0.1 | 0.967 | 3.124 | 0.432 | 0.953 |
| CHB-600 | 31.26 ± 0.903 | 0.08 | 0.936 | 2.727 | 0.557 | 0.955 |
| MLB-300 | 33.86 ± 5.238 | 0.19 | 0.979 | 4.543 | 0.526 | 0.932 |
| MLB-600 | 29.04 ± 0.729 | 0.1 | 0.956 | 3.891 | 0.457 | 0.970 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Song, Z.; Li, J.; Pan, C.; Qiu, W. Efficacy of Agricultural Residue-Derived Biochar for Tackling Cadmium Contamination in an Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2024, 29, 3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153545
Liu Q, Song Z, Li J, Pan C, Qiu W. Efficacy of Agricultural Residue-Derived Biochar for Tackling Cadmium Contamination in an Aqueous Solution. Molecules. 2024; 29(15):3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153545
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qinghai, Zhengguo Song, Jingwen Li, Chongshuang Pan, and Weiwen Qiu. 2024. "Efficacy of Agricultural Residue-Derived Biochar for Tackling Cadmium Contamination in an Aqueous Solution" Molecules 29, no. 15: 3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153545
APA StyleLiu, Q., Song, Z., Li, J., Pan, C., & Qiu, W. (2024). Efficacy of Agricultural Residue-Derived Biochar for Tackling Cadmium Contamination in an Aqueous Solution. Molecules, 29(15), 3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153545





