Synthesis and Anti-Trypanosoma cruzi Activity of New Pyrazole-Thiadiazole Scaffolds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
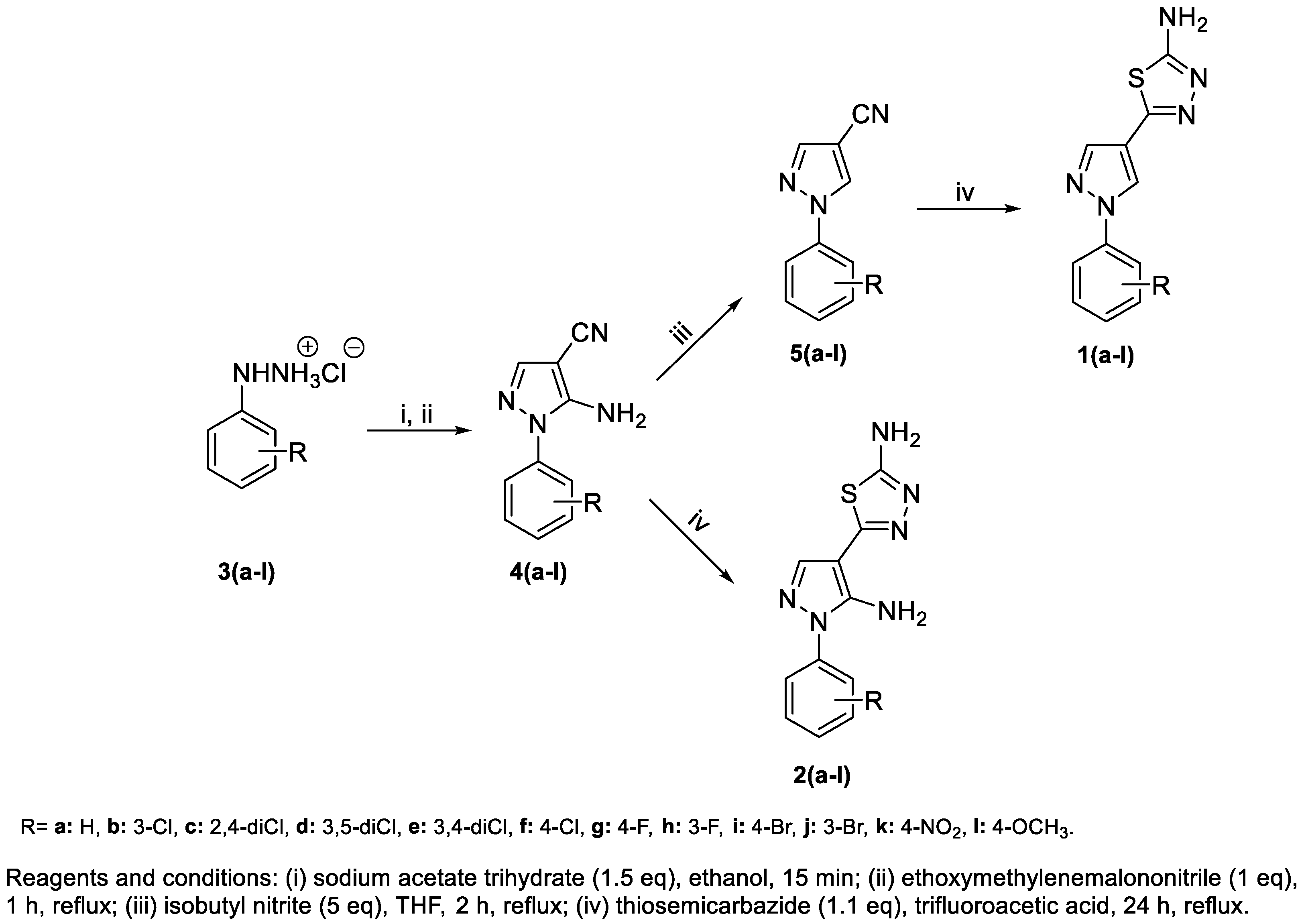
2.1. Chemistry
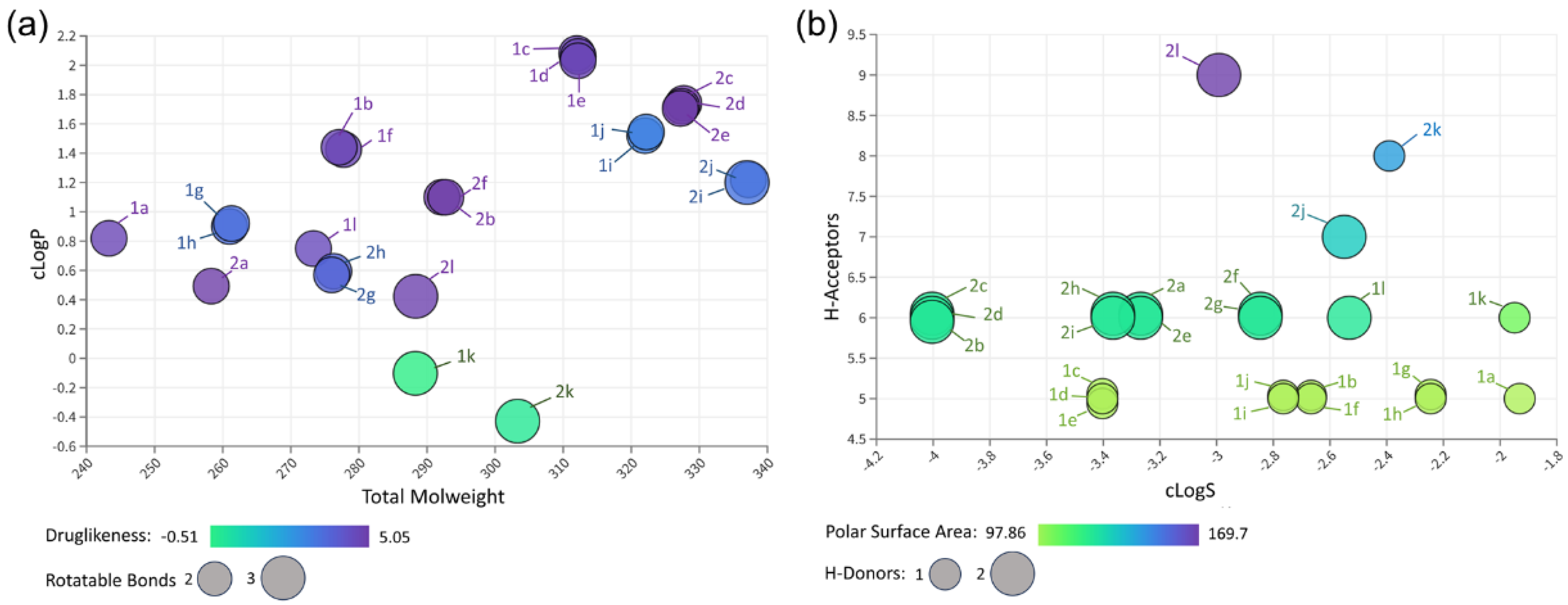
2.2. Prediction of Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Cytotoxicity and Antiparasitic Effect of Pyrazole-Thiadiazole Derivatives
2.4. Structure–Activity Relationship by Similarity
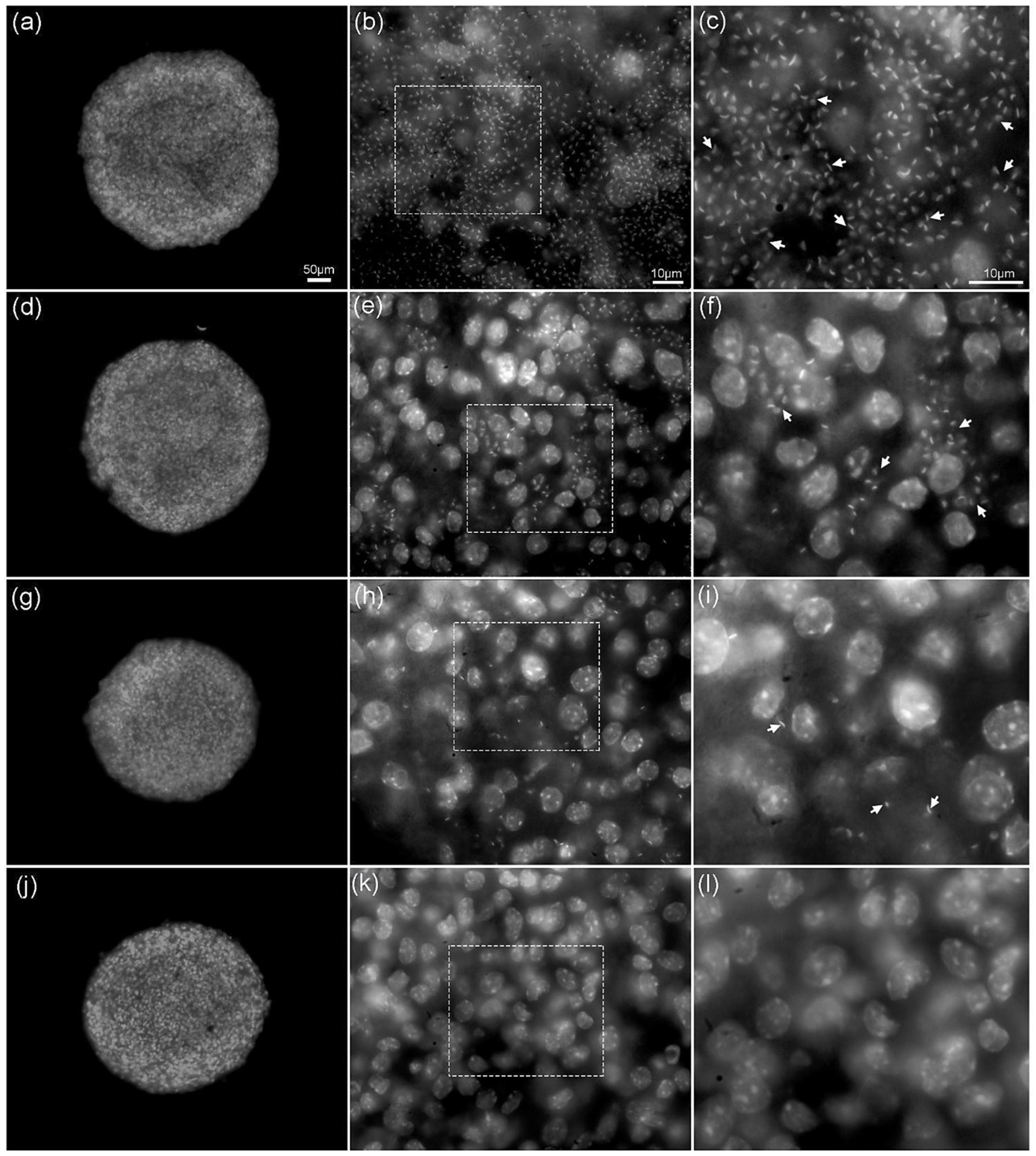
2.5. Ultrastructural Analysis
2.6. The Toxicity of Pyrazole-Thiadiazole Selected Candidates on Cardiac Muscle Cells
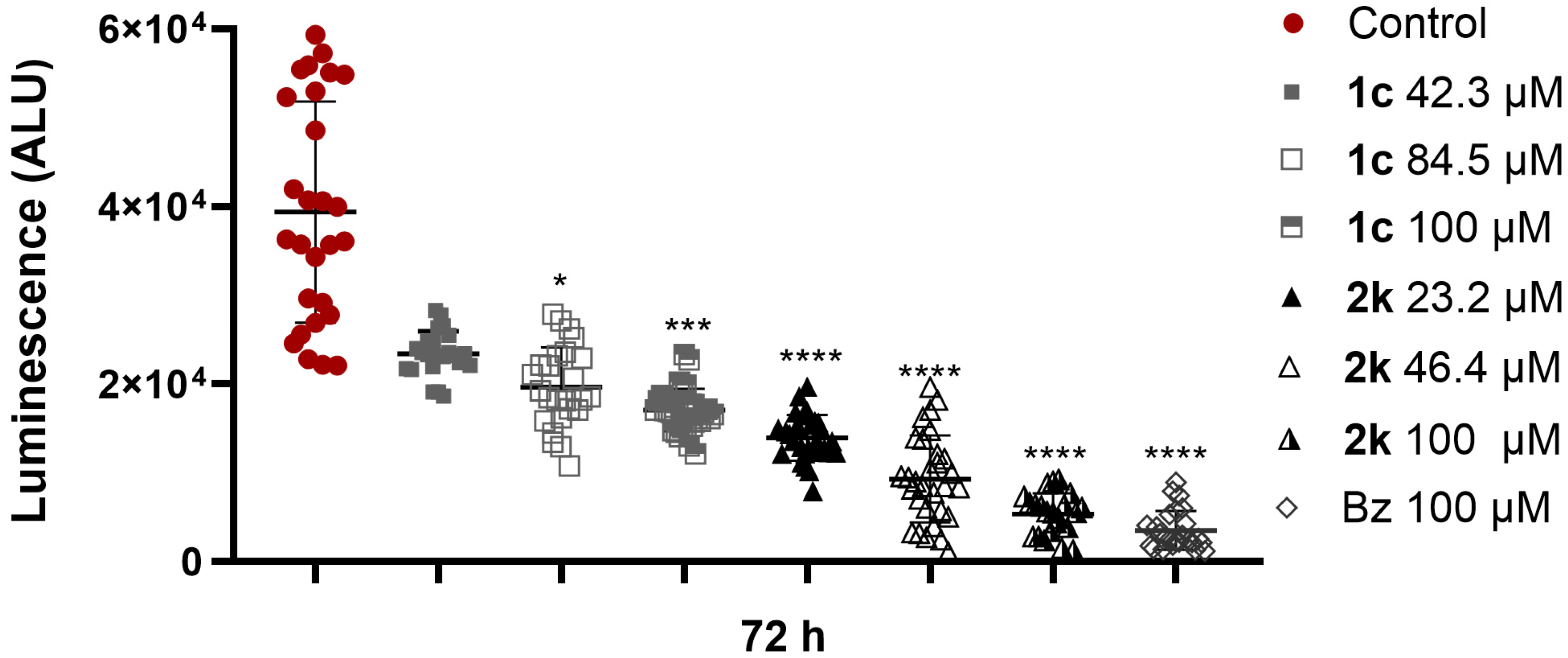
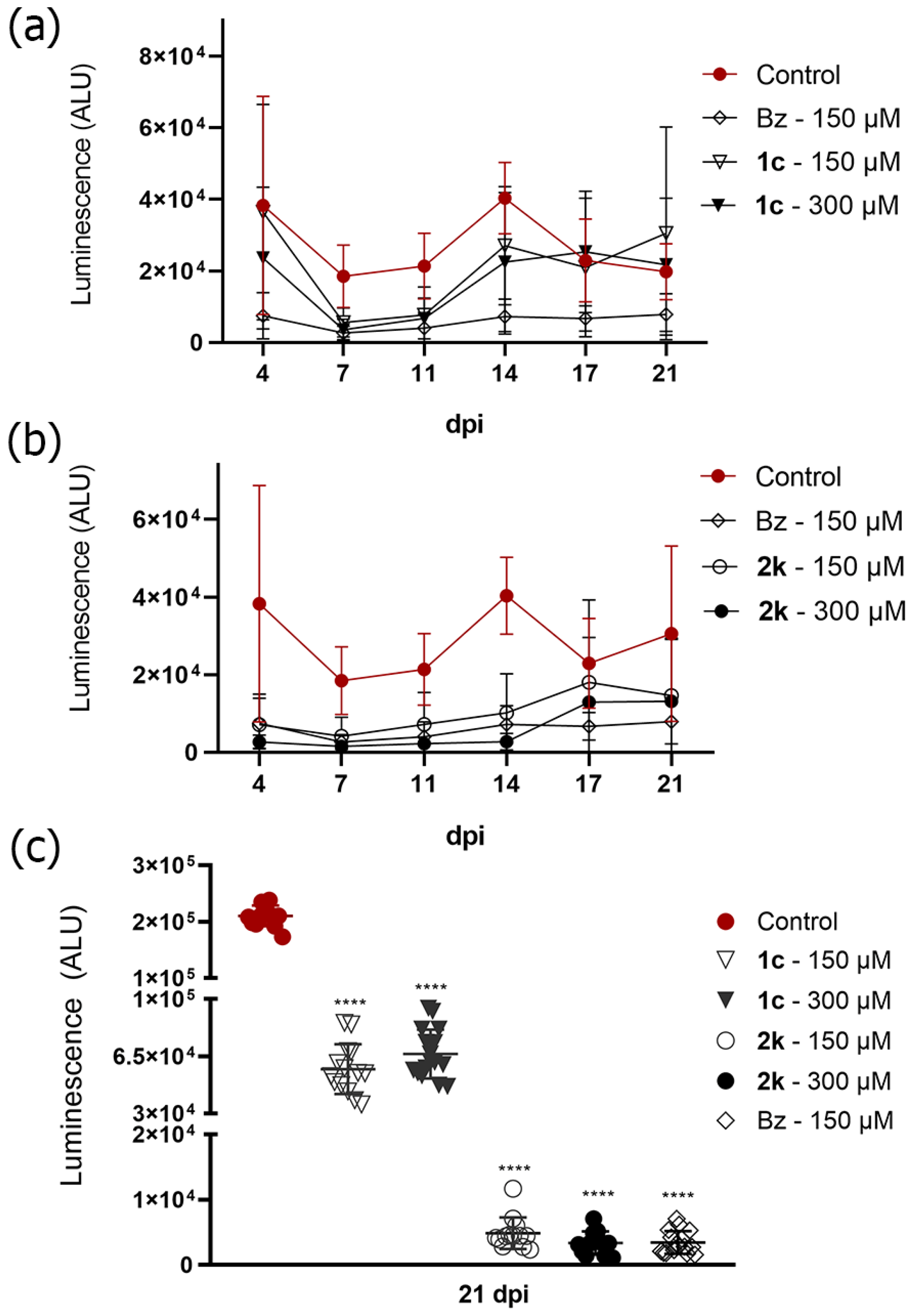
2.7. Pyrazole-Thiadiazole Efficacy in T. cruzi-Infected 3D Cardiac Microtissue
2.8. Ability of Pyrazole-Thiadiazole to Prevent Reactivation of Infection
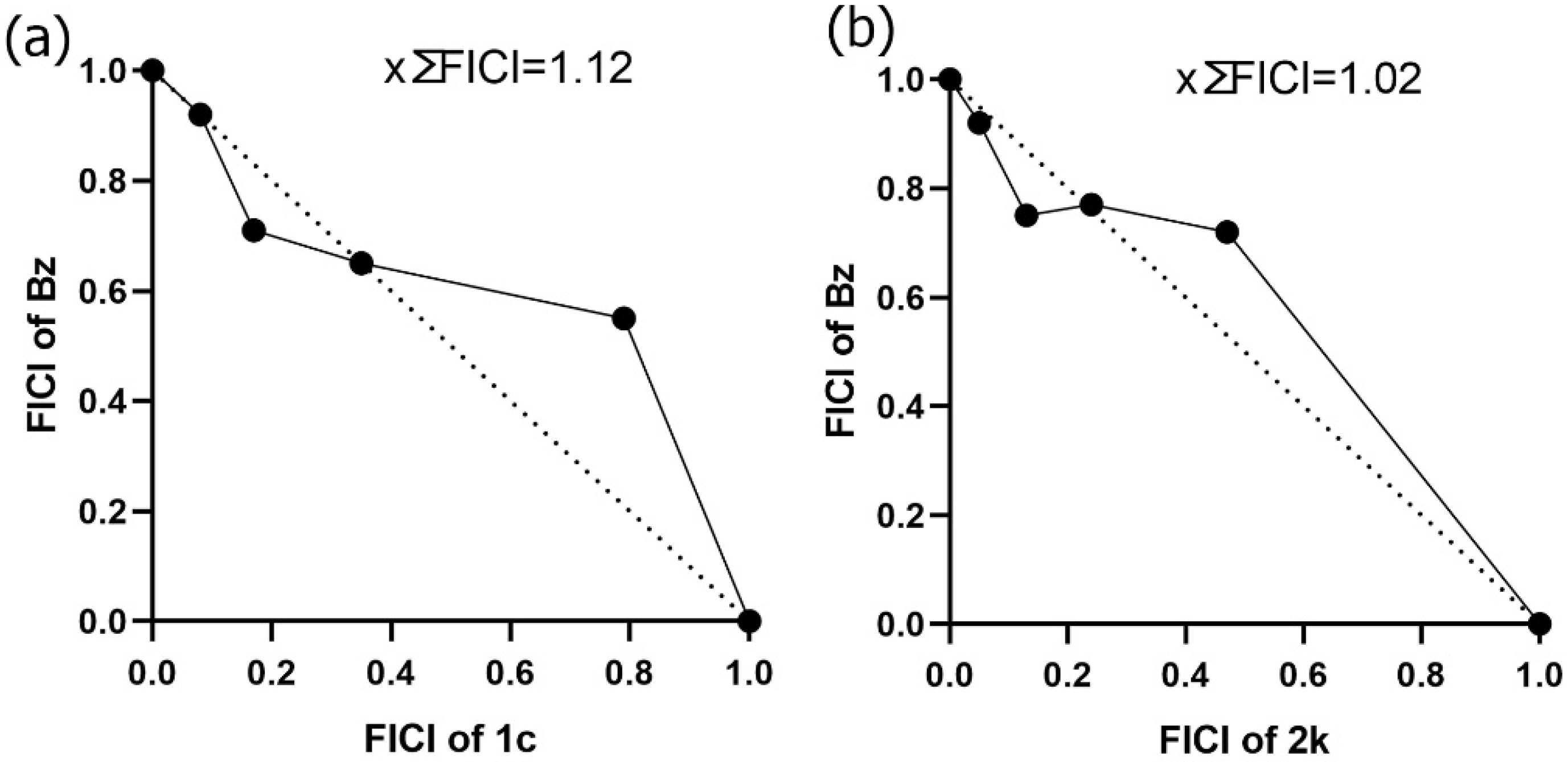
2.9. Drug Combination Effect
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1(a-l) and 2(a-l)
3.2. In Silico Analysis
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Trypanosoma cruzi
3.5. Toxicity in Mammalian Cells
3.6. Anti-T. cruzi Activity In Vitro
3.7. Antiparasitic Activity in 3D Cardiac Microtissues
3.8. Washout Assay
3.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.10. In Vitro Drug Combination
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alevi, K.C.C.; de Oliveira, J.; Rocha, D.S.R.; Galvão, C. Trends in taxonomy of Chagas disease vectors (Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae): From Linnaean to integrative taxonomy. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.B.; Praça, Y.R.; Bentes, K.L.D.S.; Santiago, P.B.; Silva, S.M.M.; Silva, G.D.S.; Motta, F.N.; Bastos, I.M.D.; de Santana, J.M.; de Araújo, C.N. Triatomines: Trypanosomatids, bacteria, and viruses potential vectors? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Paredes, C.; Villamil-Gómez, W.E.; Schultz, J.; Henao-Martínez, F.; Parra-Henao, G.; Rassi, A., Jr.; Rodríguez-Morales, A.J.; Suarez, J.A. A deadly feast: Elucidating the burden of orally acquired acute Chagas disease in Latin America—Public health and travel medicine importance. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 36, 101565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Chagas Disease (also Known as American Trypanosomiasis). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chagas-disease-(American-trypanosomiasis) (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- World Health Organization. Ending the Neglect to Attain the Sustainable Development Goals: A Road Map for Neglected Tropical Diseases 2021–2030. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/338565 (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Pan American Health Organization. Less than 10% of People with Chagas Receive a Diagnosis. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/news/13-4-2023-less-10-people-chagas-receive-diagnosis (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Pérez-Molina, J.A.; Molina, I. Chagas disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 6, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassi, A.; Marin-Neto, J.A. Chagas disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 375, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keegan, R.; Yeung, C.; Baranchuk, A. Sudden cardiac death risk stratification and prevention in Chagas disease: A non-systematic review of the literature. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 9, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, A.S.; Vermeij, D.; Ramos, A.N., Jr.; Luquetti, A.O. Chagas disease. Lancet 2024, 403, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillo, C.A.; Marin-Neto, J.A.; Avezum, A.; Sosa-Estani, S.; Rassi, A., Jr.; Rosas, F.; Villena, E.; Quiroz, R.; Bonilla, R.; Britto, C. Randomized trial of benznidazole for chronic Chagas’ cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Neto, J.A.; Rassi, A., Jr. The challenge of risk assessment in the riddle of Chagas heart disease. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2022, 6, 210172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Nicolau, P.; Fernández, M.L.; Sulleiro, E.; Villar, J.C.; Perez-Molina, J.A.; Correa-Oliveira, R.; Sosa-Estani, S.; Sánchez-Montalvá, A.; Del Carmen Bangher, M.; Moreira, O.C.; et al. Efficacy of three benznidazole dosing strategies for adults living with chronic Chagas disease (MULTIBENZ): An international, randomised, double-blind, phase 2b trial. Lancet 2024, 24, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, I.; Prat, J.G.; Salvador, F.; Treviño, B.; Sulleiro, E.; Serre, N.; Pou, D.; Roure, S.; Cabezos, J.; Valerio, L. Randomized trial of posaconazole and benznidazole for chronic Chagas’ disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, C.A.; Waskin, H.; Sosa-Estani, S.; Del Carmen Bangher, M.; Cuneo, C.; Milesi, R.; Mallagray, M.; Apt, W.; Beloscar, J.; Gascon, J.; et al. Benznidazole and posaconazole in eliminating parasites in asymptomatic T. cruzi carriers: The STOP-CHAGAS Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinazo, M.-J.; Forsyth, C.; Losada, I.; Esteban, E.T.; García-Rodríguez, M.; Villegas, M.L.; Molina, I.; Crespillo-Andújar, C.; Gállego, M.; Ballart, C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of fexinidazole for treatment of chronic indeterminate Chagas disease (FEXI-12): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrico, F.; Gascón, J.; Barreira, F.; Blum, B.; Almeida, I.C.; Alonso-Vega, C.; Barboza, T.; Bilbe, G.; Correia, E.; Garcia, W.; et al. New regimens of benznidazole monotherapy and in combination with fosravuconazole for treatment of Chagas disease (BENDITA): A phase 2, double-blind, randomised trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrico, F.; Gascón, J.; Ortiz, L.; Pinto, J.; Rojas, G.; Palacios, A.; Barreira, F.; Blum, B.; Schijman, A.G.; Vaillant, M.; et al. A phase-2, randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept trial of oral fexinidazole in adults with chronic indeterminate Chagas disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 4, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabaldón-Figueira, J.C.; Martinez-Peinado, N.; Escabia, E.; Ros-Lucas, A.; Chatelain, E.; Scandale, I.; Gascon, J.; Pinazo, M.J.; Alonso-Padilla, J. State-of-the-art in the drug discovery pathway for Chagas disease: A framework for drug development and target validation. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2023, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfarr, K.M.; Krome, A.K.; Al-Obaidi, I.; Batchelor, H.; Vaillant, M.; Hoerauf, A.; Opoku, N.O.; Kuesel, A.C. The pipeline for drugs for control and elimination of neglected tropical diseases: 1. Anti-infective drugs for regulatory registration. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi Shiran, J.; Ghanbari, M.; Mohammadnejadi, E.; Razzaghi-Asl, N. Structural insight into privileged heterocycles as anti-Trypanosoma cruzi and brucei agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthwal, T.; Paliwal, S.; Nain, S. Diverse biological activities of 1,3,4-thiadiazole scaffold. Chemistry 2022, 4, 1654–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Arora, V. Pyrazole as an anti-microbial scaffold: A comprehensive review. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2023, 20, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reviriego, F.; Olmo, F.; Navarro, P.; Marín, C.; Ramírez-Macías, I.; García-España, E.; Albelda, M.T.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, R.; Sánchez-Moreno, M.; Arán, V.J. Simple dialkyl pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylates show in vitro and in vivo activity against disease-causing trypanosomatids. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadeh, F.; Jafari, E.; Saeedi, M.; Saberi, S. Synthesis and evaluation of thiadiazole-based antileishmanial agents. J. Rep. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 9, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennani, F.E.; Doudach, L.; Cherrah, Y.; Ramli, Y.; Karrouchi, K.; Faouzi, M.E.A. Overview of recent developments of pyrazole derivatives as an anticancer agent in different cell line. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 97, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, P.J.; Bari, S.B.; Surana, S.J.; Shirkhedkar, A.A.; Bonde, A.G.; Khadse, S.C.; Ugale, V.G.; Nagar, A.A.; Cheke, R.S. discovery and anticancer activity of novel 1,3,4-thiadiazole- and aziridine-based indolin-2-ones via in silico design followed by supramolecular green synthesis. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 17270–17294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzanidou, M.; Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Pyrazoles and pyrazolines as anti-inflammatory agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, A.; Lozynskyi, A.; Shtrygol, S.; Lesyk, R. An overview on 1,2,4-triazole and 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives as potential anesthesic and anti-inflammatory agents. ScienceRise Pharm. Sci. 2022, 2, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Rahmani, R.; Russell, S.; Deora, G.S.; Ferrins, L.; Toynton, A.; Jones, A.; Sykes, M.; Kessler, A.; Eufrasio, A.; et al. Discovery of potent N-ethylurea pyrazole derivatives as dual inhibitors of Trypanosoma brucei and Trypanosoma cruzi. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 11, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, R.R.S.; Bello, M.L.; Barreto, I.R.L.; Vera, M.A.F.; Muri, E.M.F.; Albuquerque, S.; Dias, L.R.S. New carbohydrazide derivatives of 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine and trypanocidal activity. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2016, 88, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linciano, P.; Dawson, A.; Pöhner, I.; Costa, D.M.; Sá, M.S.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A.; Luciani, R.; Gul, S.; Witt, G.; Ellinger, B.; et al. Exploiting the 2-Amino-1,3,4-Thiadiazole Scaffold To Inhibit Trypanosoma brucei Pteridine Reductase in Support of Early-Stage Drug Discovery. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 5666–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.H.; Barbosa, J.M.; Bernardino, P.; Sueth-Santiago, V.; Wardell, S.M.; Wardell, J.L.; Decoté-Ricardo, D.; Melo, T.G.; da Silva, E.F.; Salomão, K.; et al. Synthesis and trypanocidal activity of novel pyridinyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.C.; Lazarin-Bidóia, D.; Desoti, V.C.; Falzirolli, H.; da Silva, C.C.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Silva, S.O.; Nakamura, C.V. 1,3,4-Thiadiazole derivatives of R–(+)–limonene benzaldehyde-thiosemicarbazones cause death in Trypanosoma cruzi through oxidative stress. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.d.N.A.; Pianoski, K.E.; dos Santos, M.G.; Lazarin-Bidóia, D.; Volpato, H.; Moura, S.; Nakamura, C.V.; Rosa, F.A. Antiparasitic Behavior of Trifluoromethylated Pyrazole 2-Amino-1,3, 4-thiadiazole Hybridsand Their Analogues: Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationship. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 591570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, M.E.; Lechuga, G.; Lara, L.S.; Souto, B.A.; Viganó, M.G.; Bourguignon, S.C.; Calvet, C.M.; Oliveira, F.O.R., Jr.; Alves, C.R.; Souza-Silva, F.; et al. Synthesis, structure-activity relationship and trypanocidal activity of pyrazole-imidazoline and new pyrazole-tetrahydropyrimidine hybrids as promising chemotherapeutic agents for Chagas disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, L.M.R.; Lechuga, G.C.; Lara, L.d.S.; Ferreira, B.S.; Pereira, C.N.; Silva, R.C.; Dos Santos, M.S.; Pereira, M.C.S. Structural optimization and biological activity of pyrazole derivatives: Virtual computational analysis, recovery assay and 3d culture model as potential predictive tools of effectiveness against Trypanosoma cruzi. Molecules 2021, 26, 6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, L.d.S.; Lechuga, G.C.; Orlando, L.M.R.; Ferreira, B.S.; Souto, B.A.; dos Santos, M.S.; Pereira, M.C.S. Bioactivity of novel pyrazole-thiazolines scaffolds against Trypanosoma cruzi: Computational approaches and 3d spheroid model on drug discovery for Chagas disease. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, G.S.; Souto, B.A.; Pereira, C.N.; Teixeira, B.C.; Dos Santos, M.S. A convenient synthesis of pyrazole-imidazoline derivatives by microwave irradiation. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2019, 56, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, A.L.P.G.; Vegi, P.F.; Faria, J.V.; Pinto, G.S.P.; Dos Santos, M.S.; Sathler, P.C.; Saito, M.S.; Santana, M.; Dutra, T.P.P.; Rodrigues, C.R.; et al. Pyrazolyl-tetrazoles and imidazolyl-pyrazoles as potential anticoagulants and their integrated multiplex analysis virtual screening. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishankhodzhaeva, M.M.; Kadyrova, S.A.; Surazhskaya, M.D.; Parpiev, N.A.; Koz, P.A. Crystalline and Molecular Structure of 2-amino-5-phenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 37, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S. Why 90% of clinical drug development fails and how to improve it? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3049–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, R.; Ioset, J.R. Screening strategies to identify new chemical diversity for drug development to treat kinetoplastid infections. Parasitology 2014, 141, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuno, K.; Burrows, J.N.; Duncan, K.; Hooft van Huijsduijnen, R.; Kaneko, T.; Kita, K.; Mowbray, C.E.; Schmatz, D.; Warner, P.; Slingsby, B.T. Hit and lead criteria in drug discovery for infectious diseases of the developing world. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiodi, D.; Ishihara, Y. “Magic Chloro”: Profound effects of the chlorine atom in drug discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 5305–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, T.J.; Hunter, R.; Kaschula, C.H.; Marques, H.M.; Misplon, A.; Walden, J. Structure−function relationships in aminoquinolines: Effect of amino and chloro groups on quinoline−hematin complex formation, inhibition of β-hematin formation, and antiplasmodial activity. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz-Garcia, J.L.; Borges, B.S.; Souza-Melo, N.; Machado, L.V.; Miranda, J.S.; Pacheco-Lugo, L.A.; Moretti, N.S.; Wheleer, R.; Soares Medeiros, L.C.; DaRocha, W.D. Trypanin disruption affects the motility and infectivity of the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 807236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralston, K.S.; Hill, K.L. Trypanin, a component of the flagellar dynein regulatory complex, is essential in the bloodstream form African trypanosomes. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabututu, Z.P.; Thayer, M.; Melehani, J.H.; Hill, K.L. CMF70 Is a subunit of the dynein regulatory complex. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 3587–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralston, K.S.; Lerner, A.G.; Diener, D.R.; Hill, K.L. Flagellar motility contributes to cytokinesis in Trypanosoma brucei and is modulated by an evolutionarily conserved dynein regulatory system. Eukaryot. Cell 2006, 5, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.; de Jesus, A.R.; Cross, G.A. Deletion of an immunodominant Trypanosoma cruzi surface glycoprotein disrupts flagel-lum-cell adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, A.R.; Cooper, R.; Espinosa, M.; Gomes, J.E.; Garcia, E.S.; Paul, S.; Cross, G.A. Gene deletion suggests a role for Trypanosoma cruzi surface glycoprotein GP72 in the insect and mammalian stages of the life cycle. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 106, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, L.; Robinson, D.; Bastin, P. Novel roles for the flagellum in cell morphogenesis and cytokinesis of trypanosomes. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5336–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, S.; Kohl, L.; Ngai, I.; Wheeler, R.J.; Gull, K. A repetitive protein essential for the flagellum attachment zone filament structure and function in Trypanosoma brucei. Protist 2008, 159, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, F.D.; Sanchez, M.A.; Landfear, S.M. Touching the surface: Diverse roles for the flagellar membrane in kinetoplastid parasites. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, 00079-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetovic, A.; Souza, R.T.; Santos, M.R.M.; Cordero, E.M.; Bastos, I.M.D.; Santana, J.M.; Ruiz, J.C.; Lima, F.M.; Marini, M.M.; Mortara, R.A.; et al. The repetitive cytoskeletal protein H49 of Trypanosoma cruzi is a calpain-like protein located at the flagellum attachment zone. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 27634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairlamb, A.H.; Bowman, I.B.R. Uptake of trypanocidal drug suramin by bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei and its effects on respiration and growth rate in vivo. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1980, 1, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voogd, T.E.; Vansterkenburg, E.L.; Wilting, J.; Janssen, L.H. Recent research on the biological activity of suramin. Pharmacol. Rev. 1993, 45, 177–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bisaggio, D.F.; Campanati, L.; Pinto, R.C.; Souto-Padron, T. Effect of suramin on trypomastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi: Changes on cell motility and on the ultrastructure of the flagellum-cell body attachment region. Acta Trop. 2006, 98, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoshina, P.; Rodriguez, B.; Bueno-Orovio, A. Toward a broader view of mechanisms of drug cardiotoxicity. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Xiao, X. Effects of Different doses of doxorubicin on H9C2 cells. J. Biosci. Med. 2022, 10, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiuza, L.F.d.A.; Batista, D.G.J.; Girão, R.D.; Hulpia, F.; Finamore-Araújo, P.; Aldfer, M.M.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; De Koning, H.P.; Moreira, O.; Van Calenbergh, S.; et al. Phenotypic evaluation of nucleoside analogs against Trypanosoma cruzi infection: In vitro and in vivo approaches. Molecules 2022, 27, 8087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltantabar, P.; Calubaquib, E.L.; Mostafavi, E.; Ghazavi, A.; Stefan, M.C. Heart/liver-on-a-chip as a model for the evaluation of cardiotoxicity induced by chemotherapies. Organs-on-a-Chip 2021, 3, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuppinger, C. 3D cardiac cell culture: A critical review of current technologies and applications. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadano, K.; Miyagawa, S.; Takeda, M.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Kazusa, K.; Takamatsu, K.; Akashi, M.; Sawa, Y. Cardiotoxicity assessment using 3D vascularized cardiac tissue consisting of human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 22, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.; Kitsuka, T.; Nakayama, K. Scaffold-based and scaffold-free cardiac constructs for drug testing. Biofabrication 2021, 22, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrouet, C.; Dorilas, N.; Rejniak, K.A.; Tuncer, N. Comparison of drug inhibitory effects (IC50) in monolayer and spheroid cultures. Bull. Math. Biol. 2020, 82, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melissaridou, S.; Wiechec, E.; Magan, M.; Jain, M.V.; Chung, M.K.; Farnebo, L.; Roberg, K. The effect of 2D and 3D cell cultures on treatment response, EMT profile, and stem cell features in head and neck cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeffe, A.O.; Hale, C.; Cotton, J.A.; Yardley, V.; Gupta, K.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Murdan, S.; Croft, S.L. Novel 2D and 3D assays to determine the activity of anti-leishmanial drugs. Microorganisms. 2020, 8, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.; Arez, F.; Alves, P.M.; Badolo, L.; Brito, C.; Fischli, C.; Fontinha, D.; Oeuvray, C.; Prudêncio, M.; Rottmann, M.; et al. Translation of liver stage activity of M5717, a Plasmodium elongation factor 2 inhibitor: From bench to bedside. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.E.; Tekiel, V.; Campo, V.A. In vitro evaluation of Resveratrol as a potential pre-exposure prophylactic drug against Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 20, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Fiuza, L.F.; Batista, D.D.G.J.; Nunes, D.F.; Moreira, O.C.; Cascabulho, C.; Soeiro, M.N.C. Benznidazole modulates the release of inflammatory mediators by cardiac spheroids infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Exp. Parasitol. 2021, 221, 108061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, M.L.; Kennedy, E.K.; Read, K.D.; Kaiser, M.; Avery, V.M. Temporal and wash-out studies identify medicines for malaria venture pathogen box compound with fast-acting activity against both Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, L.M.; Thomas, J.; Lewis, M.D.; Cotillo, I.; Gray, D.W.; De Rycker, M. Development of Trypanosoma cruzi in vitro assays to identify compounds suitable for progression in Chagas’ disease drug discovery. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, 0006612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso-Santos, C.; Ferreira de Almeida Fiuza, L.; França da Silva, C.; Mazzeti, A.L.; Donola Girão, R.; Melo de Oliveira, G.; da Gama, J.B.D.; Cruz, M.O.; Lins, S.G.N.; Maes, L.; et al. 7-Aryl-7-deazapurine 30-deoxyribonucleoside derivative as a novel lead for Chagas’ disease therapy: In vitro and in vivo pharmacology. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeti, A.L.; Capelari-Oliveira, P.; Bahia, M.T.; Mosqueira, V.C.F. Review on experimental treatment strategies against Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 31, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, E.O.J.; Kalesh, K.; Steel, P.G. Navigating drug repurposing for Chagas disease: Advances, challenges, and opportunities. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 27, 1233253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.P.; Nascimento, M.S.; Franco, C.H.; Bortoluci, K.; Silva, M.N.; Zingales, B.; Gibaldi, D.; Castaño Barrios, L.; Lannes-Vieira, J.; Cariste, L.M.; et al. Drug repurposing in Chagas disease: Chloroquine potentiates benznidazole activity against Trypanosoma cruzi in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 15, 0028422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, Y.A.; Bahia, M.T.; Caldas, I.S.; Mazzeti, A.L.; Novaes, R.D.; Boas, R.V.B.; Santos, L.J.S.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Marques, M.J.; Diniz, L.F. Amlodipine increases the therapeutic potential of ravuconazole upon Trypanosoma cruzi infection, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e02497–e2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeti, A.; Gonçalves, K.; Mota, S.; Pereira, D.; Diniz, L.; Bahia, M. Combination therapy using nitro compounds improves the efficacy of experimental Chagas disease treatment. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, J.S.; França, S.C.; Batista, D.D.G.J.; Nefertiti, A.; Fiuza, L.F.D.A.; Fonseca-Berzal, C.R.; Bernardino, S.P.; Batista, M.M.; Sijm, M.; Kalejaiye, T.D.; et al. Efficacy of novel pyrazolone phosphodiesterase inhibitors in experimental mouse models of Trypanosoma cruzi. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, 00414–00420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammerman, N.C.; Beier-Sexton, M.; Azad, A.F. Growth and maintenance of Vero cell lines. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirelles, M.N.; de Araujo-Jorge, T.C.; Miranda, C.F.; de Souza, W.; Barbosa, H.S. Interaction of Trypanosoma cruzi with heart muscle cells: Ultrastructural and cytochemical analysis of endocytic vacuole formation and effect upon myogenesis in vitro. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1986, 41, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Garzoni, L.R.; Adesse, D.; Soares, M.J.; Rossi, M.I.; Borojevic, R.; de Meirelles, M.d.N. Fibrosis and hypertrophy induced by Trypanosoma cruzi in a three-dimensional cardiomyocyte-culture system. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, C.; Henriques-Pons, A.; Meuser-Batista, M.; Ribeiro, A.S.; de Souza, W. In vivo imaging of mice infected with bioluminescent Trypanosoma cruzi unveils novel sites of infection. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, L.M.R.; Lara, L.d.S.; Lechuga, G.C.; Rodrigues, G.C.; Pandoli, O.G.; de Sá, D.S.; Pereira, M.C.S. Antitrypanosomal activity of 1,2,3-triazole-based hybrids evaluated using in vitro preclinical translational models. Biology 2023, 12, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fivelman, Q.L.; Adagu, I.S.; Warhurst, D.C. Modified fixed-ratio isobologram method for studying in vitro interactions between atovaquone and proguanil or dihydroartemisinin against drug-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob. Agents. Chem. 2004, 48, 4097–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odds, F.C. Synergy, antagonism, and what the chequerboard puts between them. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Anti-T. cruzi Activity (mean ± SD µM) | Cytotoxicity (Mean ± SD µM) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trypomastigotes | Intracellular Amastigotes | Vero Cells | ||||||
| Compounds | IC50 | IC90 | SI | IC50 | IC90 | SI | pIC50 | CC50 |
| 1a | >100 | >100 | >5 | 68.63 ± 1.03 | >70 | >7.49 | 4.16 | >500 |
| 1b | >100 | >100 | >5 | 68.11 ± 2.99 | >70 | >7.73 | 4.17 | >500 |
| 1c | 21.71 ± 2.94 | >100 | >23.03 | 13.54 ± 4.47 | 42.27 ± 3.47 | >32.96 | 4.87 | >500 |
| 1d | >100 | >100 | >5 | 58.66 ± 12.29 | >70 | >8.29 | 4.23 | >500 |
| 1e | >100 | >100 | >5 | 18.75 ± 2.28 | 40.37 ± 13.31 | >25.64 | 4.73 | >500 |
| 1f | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 1g | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 1h | >100 | >100 | >5 | 66.85 ± 3.37 | >70 | >7.86 | 4.17 | >500 |
| 1i | >100 | >100 | >5 | 28.41 ± 1.77 | >70 | >17.53 | 4.55 | >500 |
| 1j | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 1k | >100 | >100 | >5 | 58.33 ± 12.83 | >70 | >8.16 | 4.23 | >500 |
| 1l | 53.03 ± 4.44 | >100 | >9.43 | 24.46 ± 4.21 | >70 | >19.08 | 4.61 | >500 |
| 2a | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 2b | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 2c | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 2d | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 2e | 72.62 ± 6.76 | >100 | >6.88 | 33.64 ± 2.16 | 58.83 ± 8.26 | >13.73 | 4.47 | >500 |
| 2f | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 2g | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 2h | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 2i | >100 | >100 | >5 | 68.73 ± 0.05 | >70 | >7.58 | 4.16 | >500 |
| 2j | >100 | >100 | >5 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| 2k | >100 | >100 | >5 | 10.37 ± 1.21 | 23.19 ± 4.23 | >33.87 | 4.98 | >500 |
| 2l | >100 | >100 | >100 | >70 | >70 | >7.14 | <4.15 | >500 |
| Bz | 12.82 ± 2.66 | >100 | >38.88 | 3.61 ± 1.25 | 11.53 ± 4.17 | >158.23 | 5.44 | >500 |
| Compounds | Toxicity CC50 (Mean ± SD µM) | |
|---|---|---|
| 2D Culture | 3D Culture | |
| 1c | >500 | >500 |
| 2k | 191.20 ± 21.0 | >500 |
| Bz | >500 | >500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, T.P.d.; Orlando, L.M.R.; Lara, L.d.S.; Paes, V.B.; Dutra, L.P.; dos Santos, M.S.; Pereira, M.C.d.S. Synthesis and Anti-Trypanosoma cruzi Activity of New Pyrazole-Thiadiazole Scaffolds. Molecules 2024, 29, 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153544
Souza TPd, Orlando LMR, Lara LdS, Paes VB, Dutra LP, dos Santos MS, Pereira MCdS. Synthesis and Anti-Trypanosoma cruzi Activity of New Pyrazole-Thiadiazole Scaffolds. Molecules. 2024; 29(15):3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153544
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Thamyris Perez de, Lorraine Martins Rocha Orlando, Leonardo da Silva Lara, Vitoria Barbosa Paes, Lucas Penha Dutra, Mauricio Silva dos Santos, and Mirian Claudia de Souza Pereira. 2024. "Synthesis and Anti-Trypanosoma cruzi Activity of New Pyrazole-Thiadiazole Scaffolds" Molecules 29, no. 15: 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153544
APA StyleSouza, T. P. d., Orlando, L. M. R., Lara, L. d. S., Paes, V. B., Dutra, L. P., dos Santos, M. S., & Pereira, M. C. d. S. (2024). Synthesis and Anti-Trypanosoma cruzi Activity of New Pyrazole-Thiadiazole Scaffolds. Molecules, 29(15), 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153544








