Identification and Characterization of a Novel Prophage Lysin against Streptococcus dysgalactiae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Gene Lys1644 Encoding Lysin Exists in the Prophage pp6 Genome of S. dysgalactiae Lu24
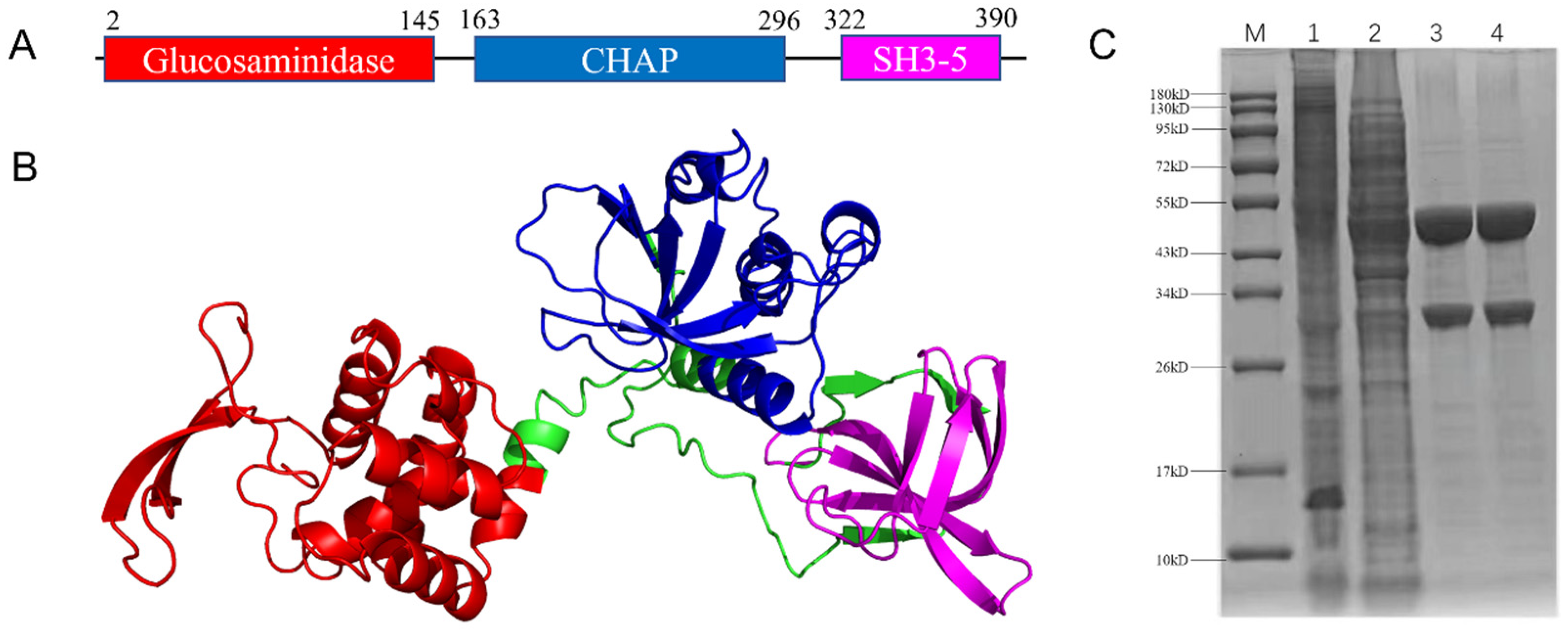
2.2. The Lysin Lys1644 Containing Two Lytic Domains Was Successfully Expressed and Purified
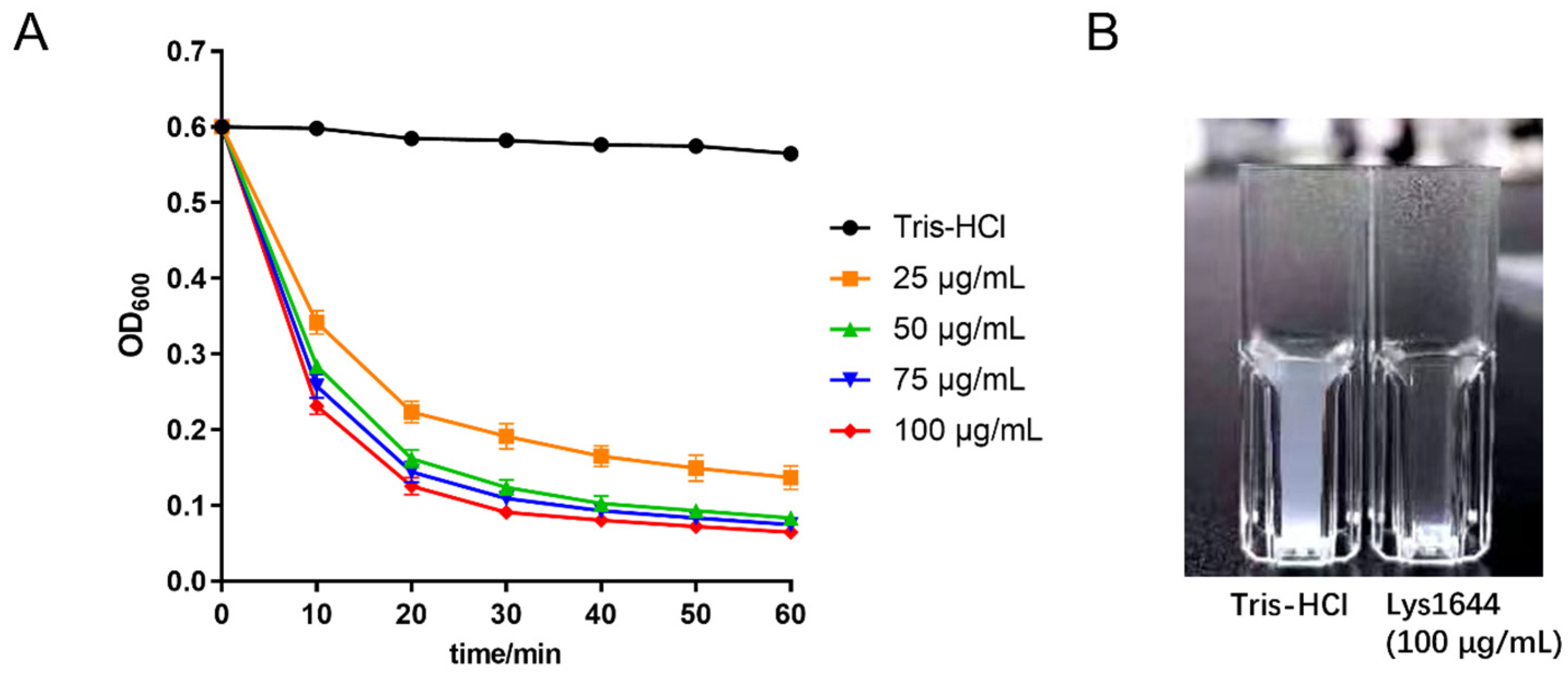
2.3. Lys1644 Is a Specific Lysin against S. dysgalactiae
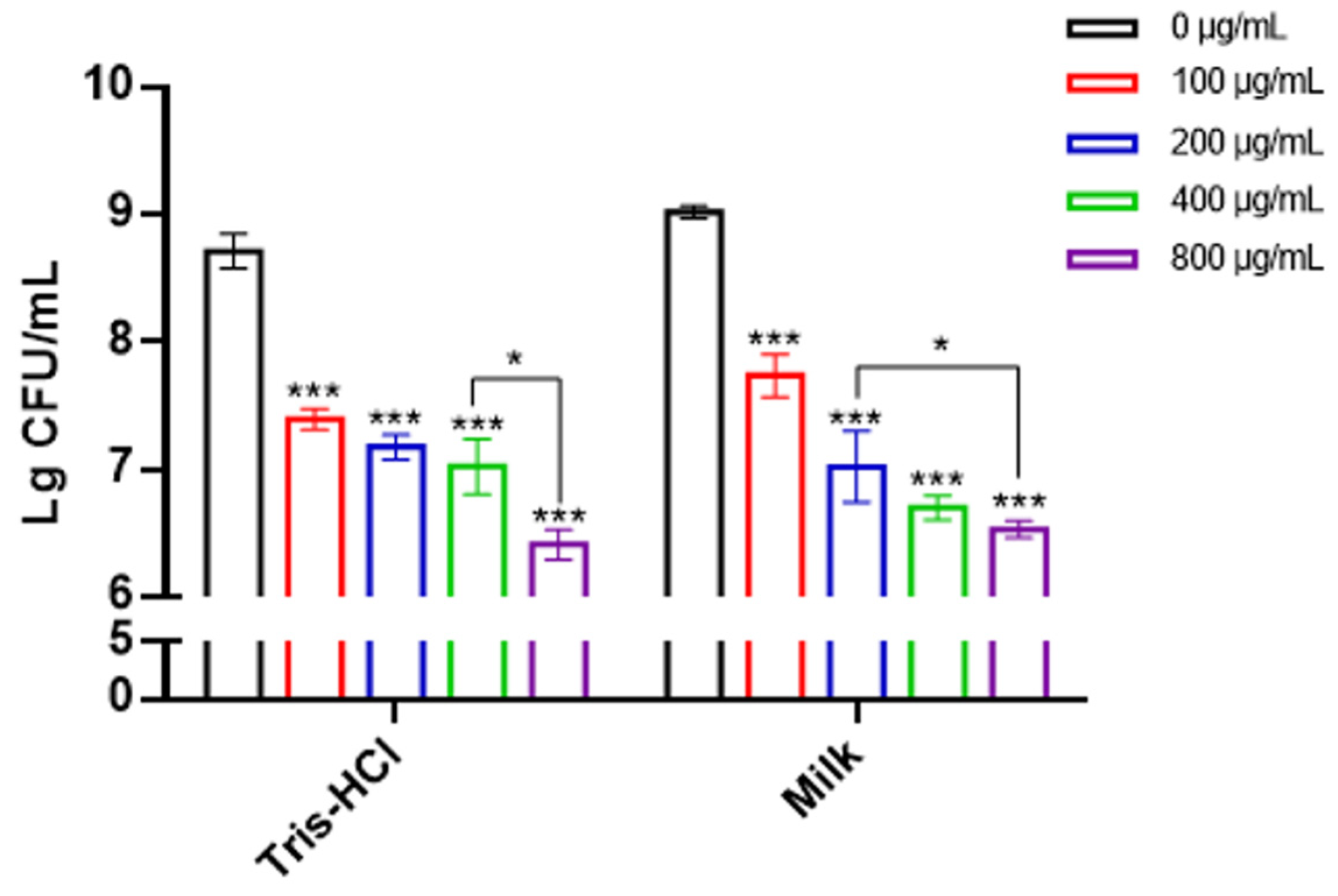
2.4. Lys1644 Has Fairly Strong Lytic Activity in Milk
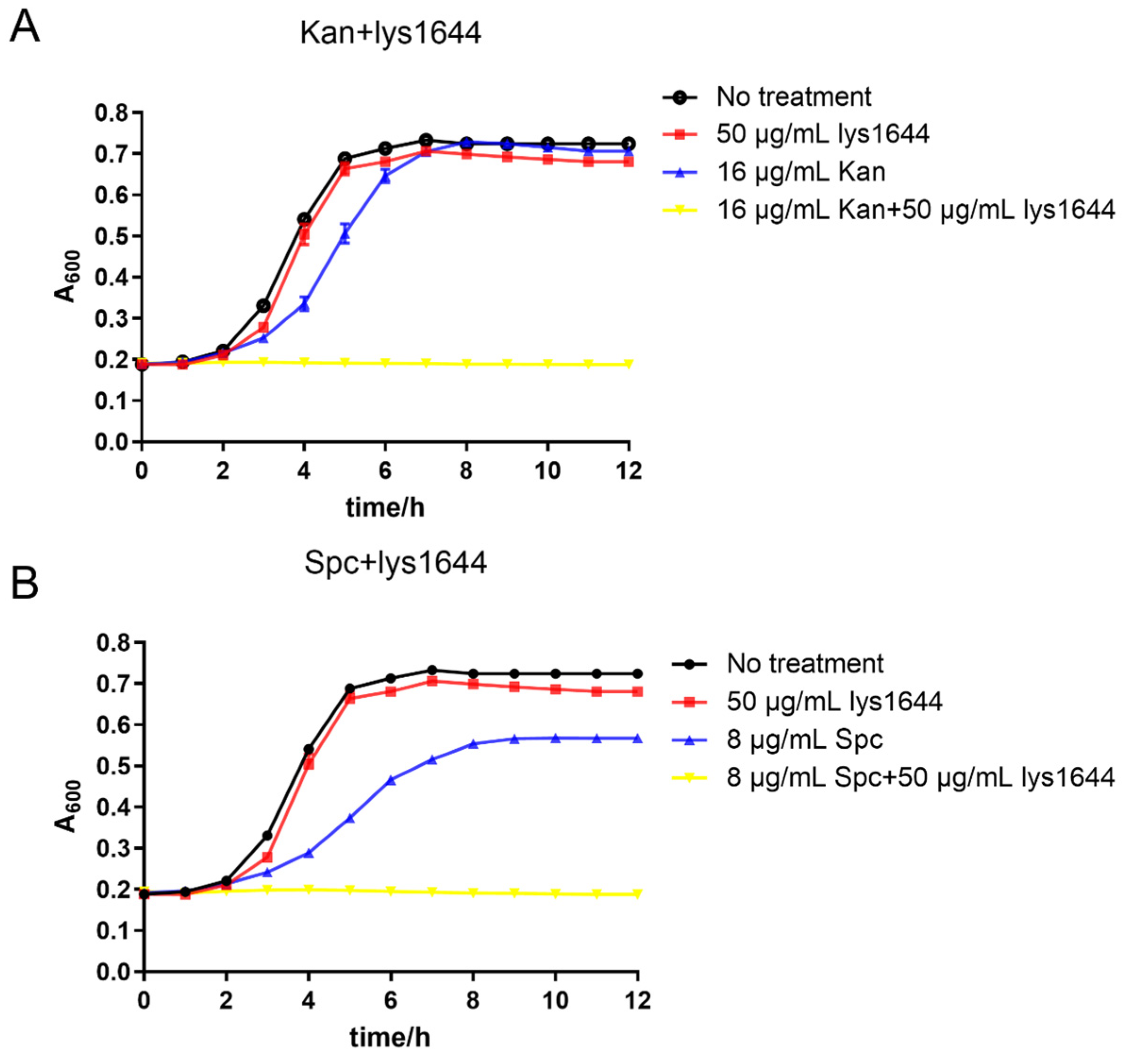
2.5. Lys1644 Has a Synergistic Effect with Antibiotics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacteria and Plasmids
4.2. Genome Sequencing and Prophage Analysis
4.3. Structural Analysis of Lys1644
4.4. Cloning of Lys1644
4.5. Recombinant Expression and Purification of Lys1644 Protein
4.6. Lytic Activity of Lys1644
4.7. Antibacterial Spectrum of Lysin Lys1644
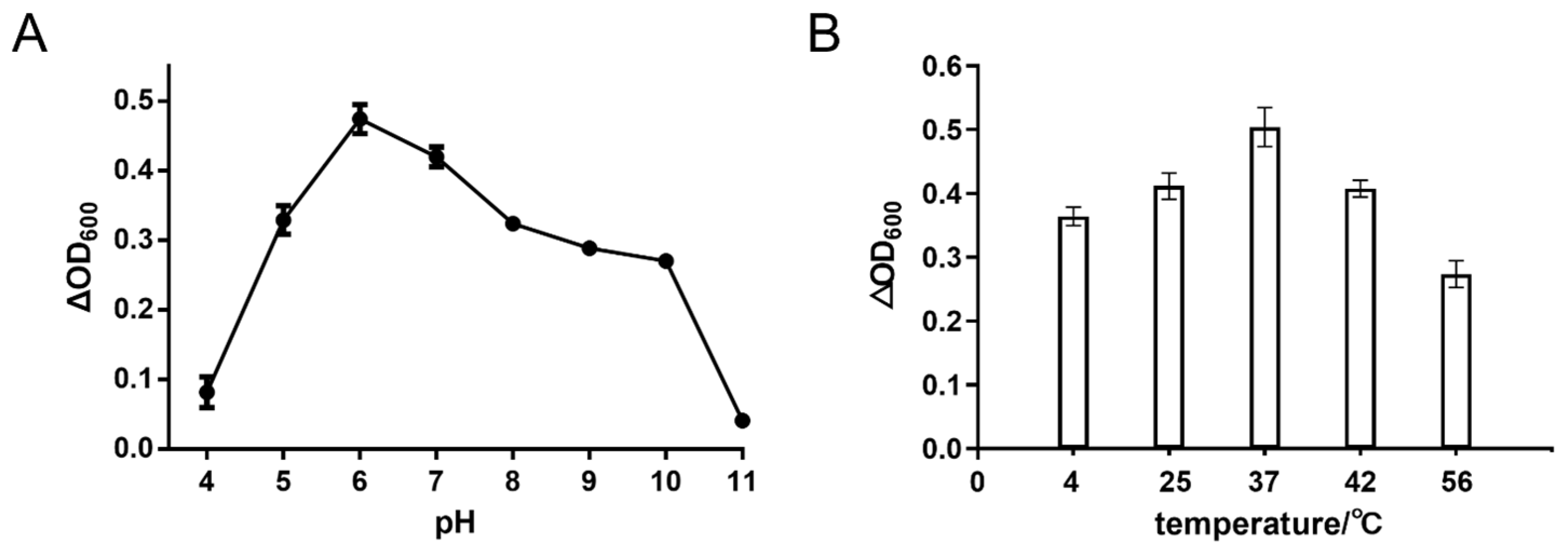
4.8. Optimal pH of Lys1644
4.9. Optimal Temperature of Lys1644
4.10. Lytic Activity of Lys1644 in Milk
4.11. Synergistic Bacteriostasis of Lys1644 and Antibiotics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashraf, A.; Imran, M. Causes. types, etiological agents, prevalence, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, effects on human health and future aspects of bovine mastitis. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2020, 21, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saintot, C.; André, J.; Hentgen, C.; Jacques, L.; Barrans, A. Meningitis and septic shock caused by Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp equisimilis. Med. Mal. Infect. 2018, 48, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crippa, B.L.; Rodrigues, M.X.; Tomazi, T.; Yang, Y.; de Oliveira Rocha, L.; Bicalho, R.C.; Silva, N.C.C. Virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance and phylogeny of bovine mastitis-associated Streptococcus dysgalactiae. J. Dairy Res. 2023, 90, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.; Henriques, M. Control of Bovine Mastitis: Old and Recent Therapeutic Approaches. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranjo-Lucena, A.; Slowey, R. Invited review: Antimicrobial resistance in bovine mastitis pathogens: A review of genetic determinants and prevalence of resistance in European countries. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Piepers, S.; Shan, R.X.; Cai, L.; Mao, S.; Zou, J.; Ali, T.; De Vliegher, S.; Han, B. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of antimicrobial resistance profiles in Streptococcus dysgalactiae isolated from bovine clinical mastitis in 5 provinces of China. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3344–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares-Pérez, J.; Kholif, A.E.; Rojas-Hernández, S.; Elghandour, M.M.M.Y.; Salem, A.Z.M.; Bastida, A.Z.; Velázquez-Reynoso, D.; Cipriano-Salazar, M.; Camacho-Díaz, L.M.; Alonso-Fresán, M.U.; et al. Prevalence of bovine subclinical mastitis, its etiology and diagnosis of antibiotic resistance of dairy farms in four municipalities of a tropical region of Mexico. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2015, 47, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, J.R.; Cameron, M.; Rodríguez-Lecompte, J.C.; Xia, F.; Heider, L.C.; Saab, M.; McClure, J.T.; Sánchez, J. Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Streptococcus uberis and Streptococcus dysgalactiae Isolates from Canadian Dairy Herds. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 22, 4–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikebe, T.; Okuno, R.; Sasaki, M.; Kanda, Y.; Otsuka, H.; Kawahara, R.; Ohya, H.; Suzuki, M.; Uchida, K.; Nihonmatsu, H.; et al. Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis isolated from patients with streptococcal toxic shock syndrome. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, E.; Draper, L.A.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. The Advantages and Challenges of Using Endolysins in a Clinical Setting. Viruses 2021, 13, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.; Kamel, M. Bovine mastitis prevention and control in the post-antibiotic era. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, S.B.; Alreja, A.B.; Nelson, D.C. Application of bacteriophage-derived endolysins to combat streptococcal disease: Current State and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 68, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.; Loomis, L.; Fischetti, V.A. Prevention and elimination of upper respiratory colonization of mice by group A streptococci by using a bacteriophage lytic enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4107–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lood, R.; Raz, A.; Molina, H.; Euler, C.W.; Fischetti, V.A. A highly active and negatively charged Streptococcus pyogenes lysin with a rare D-alanyl-L-alanine endopeptidase activity protects mice against streptococcal bacteremia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3073–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Nelson, D.; Zhu, S.; Fischetti, V.A. Removal of group B streptococci colonizing the vagina and oropharynx of mice with a bacteriophage lytic enzyme. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, D.G.; Dong, S.; Baker, J.R.; Engler, J.A. The bifunctional peptidoglycan lysin of Streptococcus agalactiae bacteriophage B30. Microbiol. 2004, 150, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, J.M.; Nelson, D.; Fischetti, V.A. Rapid killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae with a bacteriophage cell wall hydrolase. Science 2001, 294, 2170–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, J.M.; Djurkovic, S.; Fischetti, V.A. Phage lytic enzyme Cpl-1 as a novel antimicrobial for pneumococcal bacteremia. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 6199–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Linden, S.B.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.P.; Nelson, D.C.; Wei, H.P. A chimeolysin with extended-spectrum streptococcal host range found by an induced lysis-based rapid screening method. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.; Oh, J.T.; Sauve, K.; Bradford, P.A.; Cassino, C.; Schuch, R. Antimicrobial Activity of Exebacase (Lysin CF-301) against the Most Common Causes of Infective Endocarditis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.H.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Wei, C.H.; Yu, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.E.; Wei, H.P. Construction of a chimeric lysin Ply187N-V12C with extended lytic activity against staphylococci and streptococci. Microb Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmelcher, M.; Powell, A.M.; Camp, M.J.; Pohl, C.S.; Donovan, D.M. Synergistic streptococcal phage λSA2 and B30 endolysins kill streptococci in cow milk and in a mouse model of mastitis. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2015, 99, 8475–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oechslin, F.; Menzi, C.; Moreillon, P.; Resch, G. The multidomain architecture of a bacteriophage endolysin enables intramolecular synergism and regulation of bacterial lysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celia, L.K.; Nelson, D.; Kerr, D.E. Characterization of a bacteriophage lysin (Ply700) from Streptococcus uberis. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 130, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.L.; Yang, H.; Yu, J.P.; Wei, H.P. Molecular dissection of phage lysin PlySs2, Integrity of the catalytic and cell wall binding domains is essential for its broad lytic activity. Virol. Sin. 2015, 30, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awandkar, S.P.; Kulkarni, M.B.; Khode, N.V. Bacteria from bovine clinical mastitis showed multiple drug resistance. Vet. Res. Commun. 2022, 46, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, F.; Easwaran, M.; Daramola, O.I.; Ragab, S.; Lynch, S.; Oduselu, T.J.; Khan, F.M.; Ayobami, A.; Adnan, F.; Torrents, E.; et al. Phage-Encoded Endolysins. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, X. Bacteriophage Endolysin: A Powerful Weapon to Control Bacterial Biofilms. Protein J. 2023, 42, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.Y.; Megat Mazhar Khair, M.H.; Song, A.A.L.; Masarudin, M.J.; Chong, C.M.; In, L.L.A.; Teo, M.Y.M. Endolysins against Streptococci as an antibiotic alternative. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 935145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Lu, C. Lytic phages and prophages of Streptococcus suis--a review. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2015, 55, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McShan, W.M.; McCullor, K.A.; Nguyen, S.V. The Bacteriophages of Streptococcus pyogenes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forge, A.; Schacht, J. Aminoglycoside antibiotics. Audiol. Neurotol. 2000, 5, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, A.M.; Roach, D.R.; Strathdee, S.A. Stronger together? Perspectives on phage-antibiotic synergy in clinical applications of phage therapy. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferri, T.L.; Jansen, M.; Horz, H.P. Fighting Pathogenic Bacteria on Two Fronts: Phages and Antibiotics as Combined Strategy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Dutta, V.; Elhanafi, D.; Lee, S.; Osborne, J.A.; Kathariou, S. A Novel Restriction-Modification System Is Responsible for Temperature-Dependent Phage Resistance in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.; Chang, H.Y.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Kandasaamy, S.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Qureshi, M.; Raj, S.; et al. The InterPro protein families and domains database: 20 years on. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2021, 49, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Adler, J.; Wu, Z.; Green, T.; Zielinski, M.; Žídek, A.; Bridgland, A.; Cowie, A.; Meyer, C.; Laydon, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction for the human proteome. Nature 2021, 596, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Species | Strains | Lytic Effect |
|---|---|---|
| S. dysgalactiae | Lu24 | + |
| SD5-1 | + | |
| GS4-4 | + | |
| S. uberis | HB19-2 | − |
| SX5-2 | − | |
| S. agalactiae | H11-1 | − |
| S. infantarius | HB10-1 | − |
| S. suis | TA16 | − |
| S. pneumoniae | ATCC49619 | − |
| S. pneumoniae | CCUG1407 | − |
| S. pyogenes | ATCC12344 | − |
| L. monocytogenes | EGDe | − |
| S. aureus | SA2 | − |
| E. faecalis | V583 | − |
| E. faecium | SX4-1 | − |
| E. coli | ATCC25922 | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, J.; Jiang, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Prophage Lysin against Streptococcus dysgalactiae. Molecules 2024, 29, 3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143411
Xu L, Li X, Yang X, Zhao Y, Niu J, Jiang S, Ma J, Zhang X. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Prophage Lysin against Streptococcus dysgalactiae. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143411
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Linan, Xingshuai Li, Xiangpeng Yang, Yuzhong Zhao, Jianrui Niu, Shijin Jiang, Junfei Ma, and Xinglin Zhang. 2024. "Identification and Characterization of a Novel Prophage Lysin against Streptococcus dysgalactiae" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143411
APA StyleXu, L., Li, X., Yang, X., Zhao, Y., Niu, J., Jiang, S., Ma, J., & Zhang, X. (2024). Identification and Characterization of a Novel Prophage Lysin against Streptococcus dysgalactiae. Molecules, 29(14), 3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143411








