Low-Molecular-Weight Peptides Prepared from Hypsizygus marmoreus Exhibit Strong Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Extraction Results of H. marmoreus Protein
2.2. Preparation of H. marmoreus Peptides
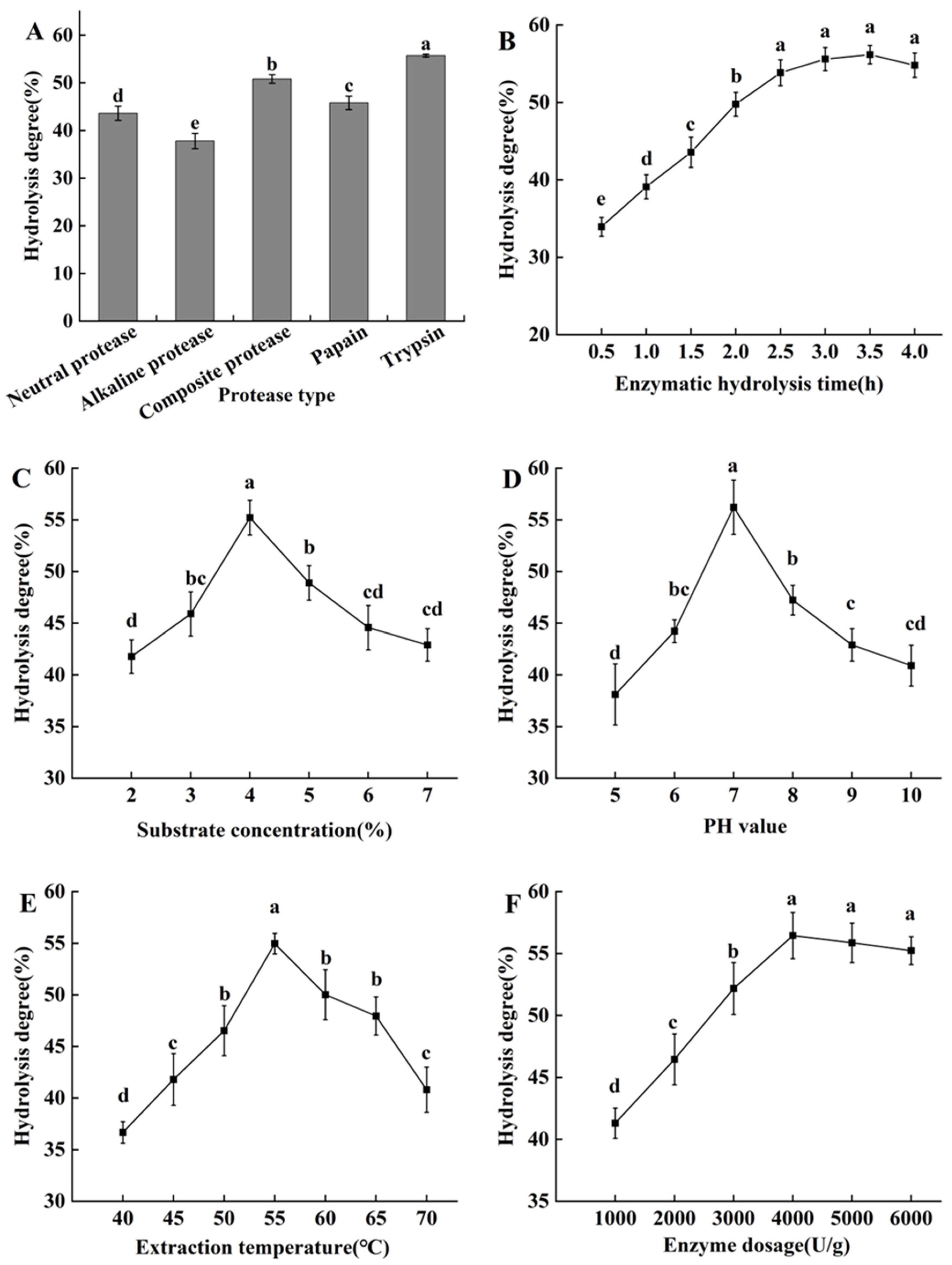
2.2.1. Screening of Proteases
2.2.2. The Effects of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Duration Time
2.2.3. The Effects of Substrate Concentration
2.2.4. The Effect of Different pH
2.2.5. The Effect of Extraction Temperature
2.2.6. The Effect of Enzyme Dosages
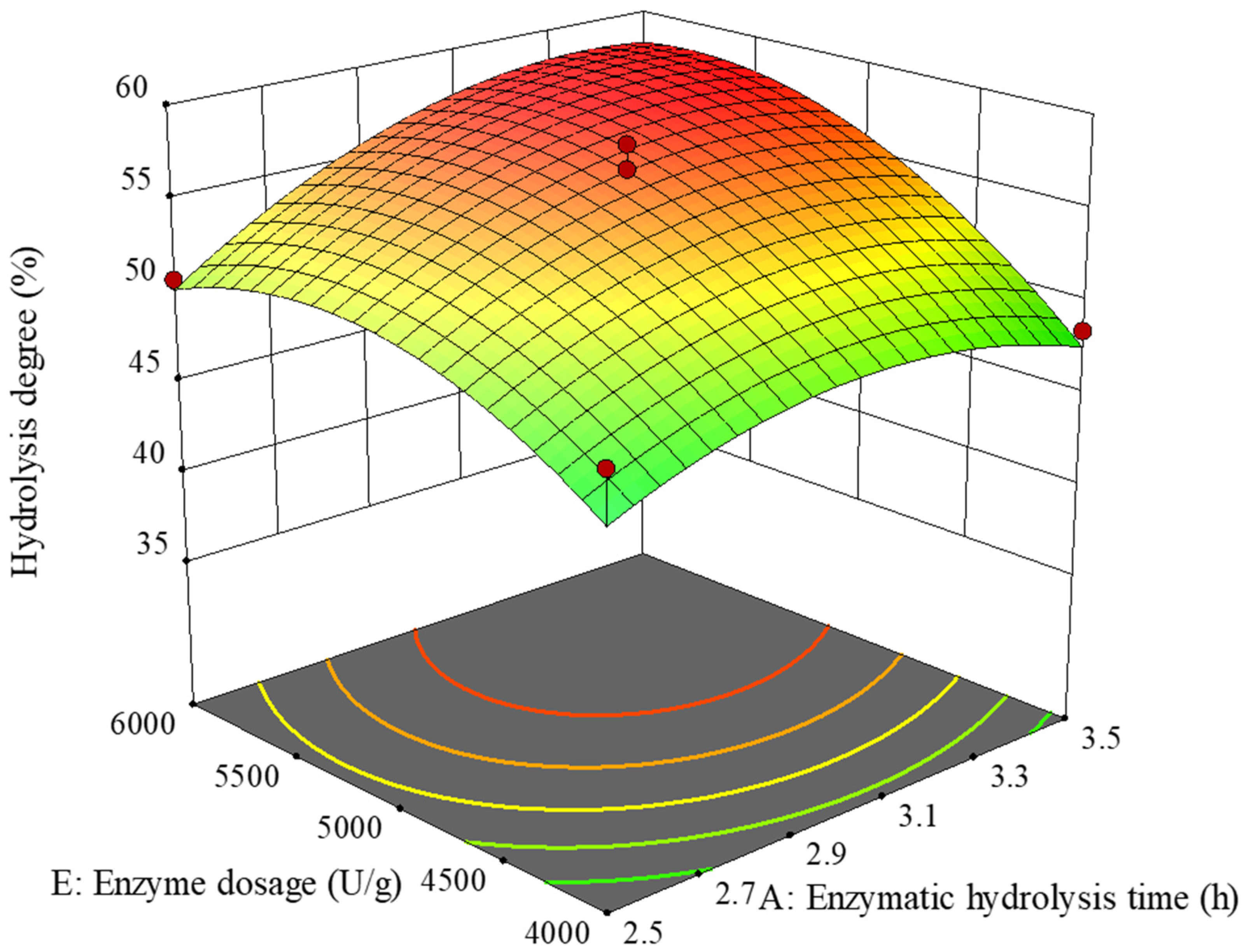
2.2.7. Response Surface Analysis Scheme and Regression Model
2.3. In Vitro Antioxidant Test
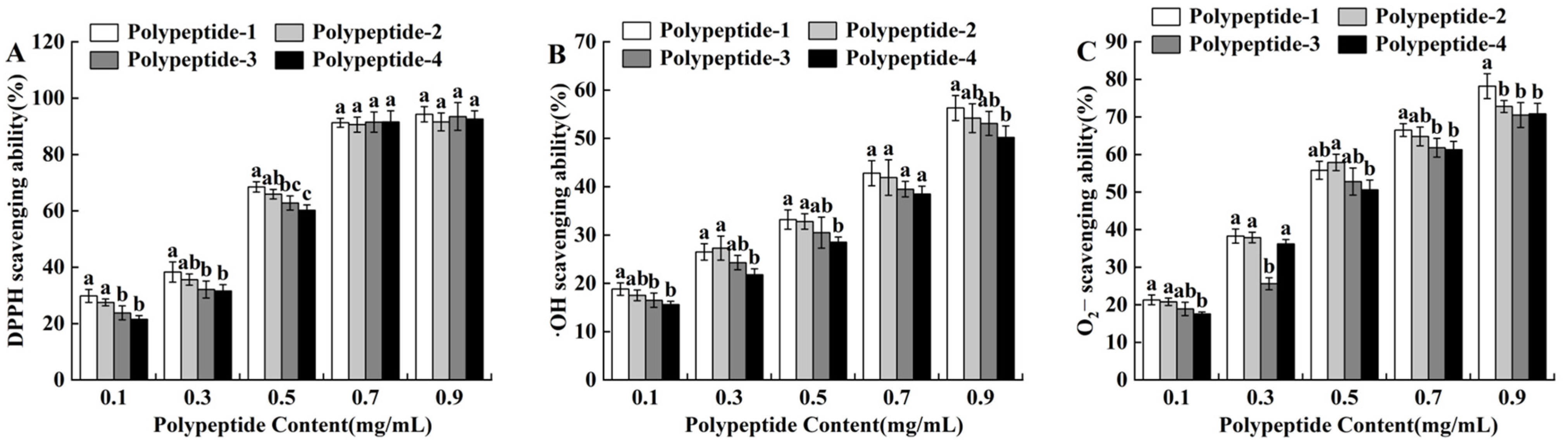
2.3.1. 1,1-Diphenyl-2-Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Free Radical Scavenging Ability
2.3.2. Determination of •OH Radical Scavenging Ability
2.3.3. Determination of ·O2− Radical Scavenging Ability
2.4. Antibacterial Activity of H. marmoreus Peptides
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Extraction of H. marmoreus Protein
3.3. Preparation of H. marmoreus Peptides
3.3.1. Hydrolysis Process
3.3.2. Screening of Proteases
3.3.3. Single-Factor Experiment
3.3.4. Response Surface Test
3.3.5. Determination of Hydrolysis Degree
3.4. Peptides’ Grading
3.5. In Vitro Antioxidant Test
3.5.1. Determination of DPPH Scavenging Ability
3.5.2. Determination of •OH Scavenging Ability
3.5.3. Determination of ·O2− Scavenging Ability
3.6. Determination of Antibacterial Activity
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Hai, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Feng, Z.; Ye, M.; Zhang, J. Hydrogen-rich water mediates redox regulation of the antioxidant system, mycelial regeneration and fruiting body development in Hypsizygus marmoreus. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Wu, H.; Guo, L.; Dou, M.; et al. Identifying a melanogenesis-related candidate gene by a high-quality genome assembly and population diversity analysis in Hypsizygus marmoreus. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 48, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yin, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Nie, S. Structural characterization and rheological properties of an alkali-extracted β-glucan from Hypsizygus marmoreus. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lei, Y.; Qin, Z.; Liu, J.; Rensing, C.; Lin, Z.; Lin, D. Effects of Seafood Mushroom Spent Substrate Solid-State Fermentation combined with PGPR as a microbial fertilizer on the soil environment and growth promotion of Cenchrus fungigraminus. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, P.; He, X.; Ayyash, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D.; Geng, F.; Li, H.; Ng, S.B.; Liu, H.; Gan, R. Untargeted metabolomics analysis of non-volatile metabolites and dynamic changes of antioxidant capacity in Douchi with edible mushroom by-products. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Feng, T.; Sun, M.; Song, S.; Yao, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, F. Novel umami peptide from Hypsizygus marmoreus hydrolysate and molecular docking to the taste receptor T1R1/T1R3. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kido, S.; Tanaka, R. Umami-enhancing effect of mushroom stocks on Japanese fish stock based on the equivalent umami concentration (EUC) value. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2023, 34, 100832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Y.; Tang, B.; Wu, L.; Weng, M.; Sun, J.; Chen, J. Grey correlation analysis of drying characteristics and quality of Hypsizygus marmoreus (crab-flavoured mushroom) by-products. Molecules 2023, 28, 7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketemepi, H.K.; Awang, M.A.B.; Seelan, J.S.S.; Noor, N.Q.I.M. Extraction process and applications of mushroom-derived protein hydrolysate: A comprehensive review. Future Foods 2024, 9, 100359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, D.K.; Maity, P.; Nandi, A.K.; Pattanayak, M.; Panda, B.C.; Mandal, A.K.; Tripathy, S.; Acharya, K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Gupta, N.; et al. Structural elucidation and immunostimulating property of a novel polysaccharide extracted from an edible mushroom Lentinus fusipes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, D.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.; Wan, J.; Tang, L.; Mao, W.; Wang, Y.; Gong, M.; et al. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of arthroconidia obtained from the edible mushroom Hypsizygus marmoreus. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 171, 105878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Antibacterial mechanism of rose essential oil against Pseudomonas putida isolated from white Hypsizygus marmoreus at cellular and metabolic levels. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 196, 116523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleczek, M.; Siwulski, M.; Rzymski, P.; Budka, A.; Kalač, P.; Jasińska, A.; Gąsecka, M.; Budzyńska, S.; Niedzielski, P. Comparison of elemental composition of mushroom Hypsizygus marmoreus originating from commercial production and experimental cultivation. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 236, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, T.; Gan, B. Evaluation of the nutritional value, umami taste, and volatile organic compounds of Hypsizygus marmoreus by simulated salivary digestion in vitro. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, P.V.; Islam, J.; Narzary, P.; Sharma, D.; Sultana, F. Bioactive compounds, nutraceutical values and its application in food product development of oyster mushroom. J. Future Foods 2024, 4, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Chen, P.; Chen, X. Bioactive peptides derived from fermented foods: Preparation and biological activities. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 101, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Pino, F.; Millan-Linares, M.C.; Montserrat-de-la-Paz, S. Strengths and limitations of in silico tools to assess physicochemical properties, bioactivity, and bioavailability of food-derived peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, S.; Hosseini, S.E.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Taheri, S. Extraction of bioactive peptides produced in probiotic yoghurt and determination of their biological activities. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 139, 105544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Monem, N.M.; El-Saadani, M.A.; Daba, A.S.; Saleh, S.R.; Aleem, E. Exopolysaccharide-peptide complex from oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) protects against hepatotoxicity in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 24, 100852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, R.W.; Macharia, J.M.; Wagara, I.N.; Bence, R.L. The antioxidant potential of different edible and medicinal mushrooms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y. Anti-osteoporosis effects and underpinning mechanisms of food-derived bioactive peptides: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhuang, M.; Ding, Y. A review on mushroom-derived bioactive peptides: Preparation and biological activities. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekoohi, N.; Harnedy-Rothwell, P.; Sharkey, S.; Lafferty, R.; Khatib, N.; O’ Harte, F.; FitzGerald, R.J. Purification and characterization of multifunctional peptides with in situ insulinotropic and antioxidative activity from a blue whiting (Micromesistius poutassou) protein hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 116, 106173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.T.; Pandey, I.; Hachenberger, Y.; Krause, B.C.; Haidar, R.; Laux, P.; Luch, A.; Singh, M.P.; Singh, A.V. Emerging paradigm against global antimicrobial resistance via bioprospecting of mushroom into novel nanotherapeutics development. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, K.; Sasidharan, S.P.; Yang, X. A concise review of mushrooms antiviral and immunomodulatory properties that may combat against COVID-19. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Guha, S.; Majumder, K. Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides in Human Health: Challenges and Opportunities. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aursuwanna, T.; Noitang, S.; Sangtanoo, P.; Srimongkoi, T.; Puthong, S.; Reamtong, O.; Karnchanatat, A. Investigating the cellular antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of the novel peptides in lingzhi mushrooms. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, W. Antioxidant, antitumor and immunostimulatory activities of the polypeptide from Pleurotus eryngii mycelium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolormaa, Z.; Kang, M.G.; Seo, G.S.; Lee, Y.W.; Lee, J.S. Analysis of nutritional characteristics and physiological functionality of Hypsizygus marmoreus (Brown cultivar). Korean J. Mycol. 2012, 40, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Jia, L. Characterization, anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation of polysaccharides by Hypsizygus marmoreus against LPS-induced toxicity on lung. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, C.; Zhang, M.; Mayo, K.V.; Sun, L.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, Y. Structure and antioxidant activity of six mushroom-derived heterogalactans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Zhu, L.; Qu, Y.; Qu, X.; Mu, M.; Zhang, M.; Muneer, G.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, L. Analyses of active antioxidant polysaccharides from four edible mushrooms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; Zheng, B.; Liu, R. Comparison of phenolics, antioxidant, and antiproliferative activities of two Hypsizygus marmoreus varieties. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, K.; Pajak, W.; Sulkowska-Ziaja, K.; Krakowska, A.; Lazur, J.; Fidurski, M.; Marzec, K.; Zieba, P.; Fijalkowska, A.; Szewczyk, A.; et al. Hypsizygus marmoreus as a Source of Indole Compounds and Other Bioactive Substances with Health-Promoting Activities. Molecules 2022, 27, 8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jia, X.; Zheng, X.; Mo, Y.; Teng, J.; Huang, L.; Xia, N. Physicochemical and functional properties of Pleurotus eryngii proteins with different molecular weight. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 184, 115102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, J.; Su, A.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Mariga, A.F.; Yang, W. Isolation, purification and identification of immunologically active peptides from Hericium erinaceus. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girjal, V.U.; Neelagund, S.; Krishnappa, M. Antioxidant properties of the peptides isolated from Ganoderma lucidum fruiting body. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2012, 18, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ruan, G.; Jin, F.; Xu, J.; Wang, F. Purification, identification, and synthesis of five novel antioxidant peptides from Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume) protein hydrolysates. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 92, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.; Majumdar, S.; Das, A.; Barui, A.; Bhowal, J. Evaluation of bioactive properties of Pleurotus ostreatus mushroom protein hydrolysate of different degree of hydrolysis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 149, 111768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, Z.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Hesari, J.; Akbari-Adergani, B.; Andreu, D. Antioxidant, anticancer and ACE-inhibitory activities of bioactive peptides from wheat germ protein hydrolysates. Food Biosci. 2019, 32, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Jin, X.; Lai, F.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, J. Chemical analysis and antioxidant activities in vitro of polysaccharide extracted from Opuntia ficus indica Mill. cultivated in China. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandi, R.; Willmore, W.G.; Tsopmo, A. Structural characterization of peroxyl radical oxidative products of antioxidant peptides from hydrolyzed proteins. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palencia, E.R.; Hinton, D.M.; Bacon, C.W. The Black Aspergillus Species of Maize and Peanuts and Their Potential for Mycotoxin Production. Toxins 2010, 2, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournas, V.S.; Niazi, N.S.; Kohn, J.S. Fungal Presence in Selected Tree Nuts and Dried Fruits. Microbiol. Insights 2015, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.J.; Bertoldo, R.; Fungaro, M.H.P.; Boulders, F.P.; Taniwaki, M.H.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Iamanaka, B.T. Black aspergilli in Brazilian onions: From field to market. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 337, 108958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Zou, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Guo, L.; Lin, J. Study on the physicochemical and emulsifying property of proteins extracted from Pleurotus tuoliensis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Song, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Yan, W.; Deng, M.; Xiao, C. Low-Molecular-Weight Polylysines with Excellent Antibacterial Properties and Low Hemolysis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gao, J.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Ma, B. Bioactive Peptides from Edible Mushrooms-The Preparation, Mechanisms, Structure-Activity Relationships and Prospects. Foods 2023, 12, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Das, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Pal, N.; Das, N. Fungi’s treasure in cosmeceuticals-a comprehensive chemical approach. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 166, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test Number | Solid–Liquid Ratio (A) | pH (B) | Ultrasonic Power (C) | Ultrasonic Time (D) | Empty Column (E) | Percent Extraction Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 37.2 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 39.6 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 47.8 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 41.3 |
| 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 49.8 |
| 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 46.6 |
| 7 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 42.1 |
| 8 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 46.9 |
| 9 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 48.3 |
| 10 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 52.6 |
| 11 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 45.3 |
| 12 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 41.7 |
| 13 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 37.5 |
| 14 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 38.5 |
| 15 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 39.2 |
| 16 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 48.9 |
| K1 | 165.9 | 172.8 | 178 | 159.5 | 175.9 | |
| K2 | 185.4 | 177.3 | 170.3 | 169.3 | 178.9 | |
| K3 | 187.9 | 174.4 | 181.5 | 199.1 | 173.6 | |
| K4 | 164.1 | 178.8 | 173.5 | 175.4 | 174.9 | |
| k1 | 41.48 | 43.20 | 44.50 | 39.88 | 43.98 | |
| k2 | 46.35 | 44.33 | 42.58 | 42.33 | 44.73 | |
| k3 | 46.98 | 43.60 | 45.38 | 49.78 | 43.73 | |
| k4 | 41.03 | 44.70 | 43.38 | 43.85 | 43.73 | |
| R | 5.95 | 1.5 | 2.8 | 9.9 | 1 | |
| Excellent level | A3 | B4 | C3 | D3 |
| Source of Differences | SS | df | MS | F | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 118.3669 | 3 | 39.4556 | 31.0115 | ** |
| B | 5.5519 | 3 | 1.8506 | 1.4546 | |
| C | 18.2169 | 3 | 6.0723 | 4.7727 | |
| D | 212.7469 | 3 | 70.9156 | 55.7385 | ** |
| E | 3.8169 | 3 | 1.2723 | ||
| Total | 358.6994 | 15 |
| Number | Enzymatic Hydrolysis Time X1 (h) | Substrate Concentration X2 (%) | pH Value X3 | Extraction Temperature X4 (°C) | Enzyme Dosage X5 (U/g) | Hydrolysis Degree (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47.19 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 51.59 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 38.06 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 39.38 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 48.12 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 49.06 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 46.31 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 48.01 |
| 9 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 43.61 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 36.13 |
| 11 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 52.03 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 41.91 |
| 13 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 44.62 |
| 14 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 50.71 |
| 15 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 45.73 |
| 16 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 52.69 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 44.88 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 43.78 |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 52.41 |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 51.97 |
| 21 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 47.93 |
| 22 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 36.85 |
| 23 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 48.62 |
| 24 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 38.28 |
| 25 | −1 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 46.97 |
| 26 | 1 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 53.53 |
| 27 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 47.41 |
| 28 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 54.06 |
| 29 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 43.56 |
| 30 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 46.03 |
| 31 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 54.34 |
| 32 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 53.29 |
| 33 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 49.06 |
| 34 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 48.45 |
| 35 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 50.65 |
| 36 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 56.76 |
| 37 | 0 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 47.35 |
| 38 | 0 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 39.82 |
| 39 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 47.35 |
| 40 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 39.71 |
| 41 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 56.81 |
| 42 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 55.88 |
| 43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 58.13 |
| 44 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 56.81 |
| 45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 56.21 |
| 46 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 56.59 |
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 87.80 | 1 | 87.80 | 44.14 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X2 | 356.55 | 1 | 356.55 | 179.26 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X3 | 5.37 | 1 | 5.37 | 2.70 | 0.1129 | |
| X4 | 0.78 | 1 | 0.78 | 0.39 | 0.536 | |
| X5 | 209.24 | 1 | 209.24 | 105.20 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X1X2 | 2.37 | 1 | 2.37 | 1.19 | 0.2853 | |
| X1X3 | 0.19 | 1 | 0.19 | 0.095 | 0.7603 | |
| X1X4 | 0.00203 | 1 | 0.00203 | 0.00102 | 0.9748 | |
| X1X5 | 11.29 | 1 | 11.29 | 5.68 | 0.0251 | * |
| X2X3 | 0.14 | 1 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.7952 | |
| X2X4 | 0.00303 | 1 | 0.00303 | 0.00152 | 0.9692 | |
| X2X5 | 1.74 | 1 | 1.74 | 0.88 | 0.3583 | |
| X3X4 | 0.14 | 1 | 0.14 | 0.073 | 0.7898 | |
| X3X5 | 3.10 | 1 | 3.10 | 1.56 | 0.2236 | |
| X4X5 | 0.11 | 1 | 0.11 | 0.055 | 0.8169 | |
| X12 | 66.49 | 1 | 66.49 | 33.43 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X22 | 790.02 | 1 | 790.02 | 397.19 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X32 | 188.93 | 1 | 188.93 | 94.98 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X42 | 146.96 | 1 | 146.96 | 73.88 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X52 | 102.49 | 1 | 102.49 | 51.53 | <0.0001 | ** |
| Model | 1523.01 | 20 | 76.15 | 38.29 | <0.0001 | ** |
| Residual | 49.73 | 25 | 1.99 | |||
| Misfit term | 46.74 | 20 | 2.34 | 3.91 | 0.068 | |
| Pure error | 2.98 | 5 | 0.60 | |||
| Total variation | 1572.73 | 45 |
| Sample | Staphylococcus aureus | Salmonella typhimurium | Escherichia coli | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Aspergillus niger |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypeptides-1 | 11.37 ± 0.48 a | 12.03 ± 0.22 a | 13.51 ± 0.42 a | 12.72 ± 0.68 a | 7.13 ± 0.25 b |
| Polypeptides-2 | 7.08 ± 0.35 b | 4.62 ± 0.16 d | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 9.17 ± 0.43 c | 6.98 ± 0.36 b |
| Polypeptides-3 | 10.11 ± 0.67 a | 9.71 ± 0.56 b | 6.77 ± 0.39 b | 10.58 ± 0.39 ab | 0.00 ± 0.00 c |
| Polypeptides-4 | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 7.92 ± 0.28 c | 5.99 ± 0.32 b | 8.76 ± 0.19 c | 8.95 ± 0.32 a |
| No. | Solid–Liquid Ratio (g:mL) | pH | Ultrasonic Power (W) | Ultrasonic Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:25 | 10 | 200 | 25 |
| 2 | 1:30 | 11 | 250 | 30 |
| 3 | 1:35 | 12 | 300 | 35 |
| 4 | 1:40 | 13 | 350 | 40 |
| No. | Enzymatic Hydrolysis Time X1 (h) | Substrate Concentration X2 (%) | pH Value X3 | Extraction Temperature X4 (°C) | Enzyme Dosage X5 (U/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 2.5 | 3 | 6 | 50 | 4000 |
| 0 | 3.0 | 4 | 7 | 55 | 5000 |
| +1 | 3.5 | 5 | 8 | 60 | 6000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; Wei, Y.; Yang, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Lai, P. Low-Molecular-Weight Peptides Prepared from Hypsizygus marmoreus Exhibit Strong Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities. Molecules 2024, 29, 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143393
Zhou S, Xiao Z, Sun J, Li L, Wei Y, Yang M, Yang Y, Chen J, Lai P. Low-Molecular-Weight Peptides Prepared from Hypsizygus marmoreus Exhibit Strong Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143393
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shaoxiong, Zheng Xiao, Junzheng Sun, Longxiang Li, Yingying Wei, Mengjie Yang, Yanrong Yang, Junchen Chen, and Pufu Lai. 2024. "Low-Molecular-Weight Peptides Prepared from Hypsizygus marmoreus Exhibit Strong Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143393
APA StyleZhou, S., Xiao, Z., Sun, J., Li, L., Wei, Y., Yang, M., Yang, Y., Chen, J., & Lai, P. (2024). Low-Molecular-Weight Peptides Prepared from Hypsizygus marmoreus Exhibit Strong Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities. Molecules, 29(14), 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143393




