Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Media Using Facilely Synthesized Magnesium Borate/Magnesium Oxide Nanostructures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Mg₃B₂O₆/MgO Nanostructures
2.2. Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Solutions
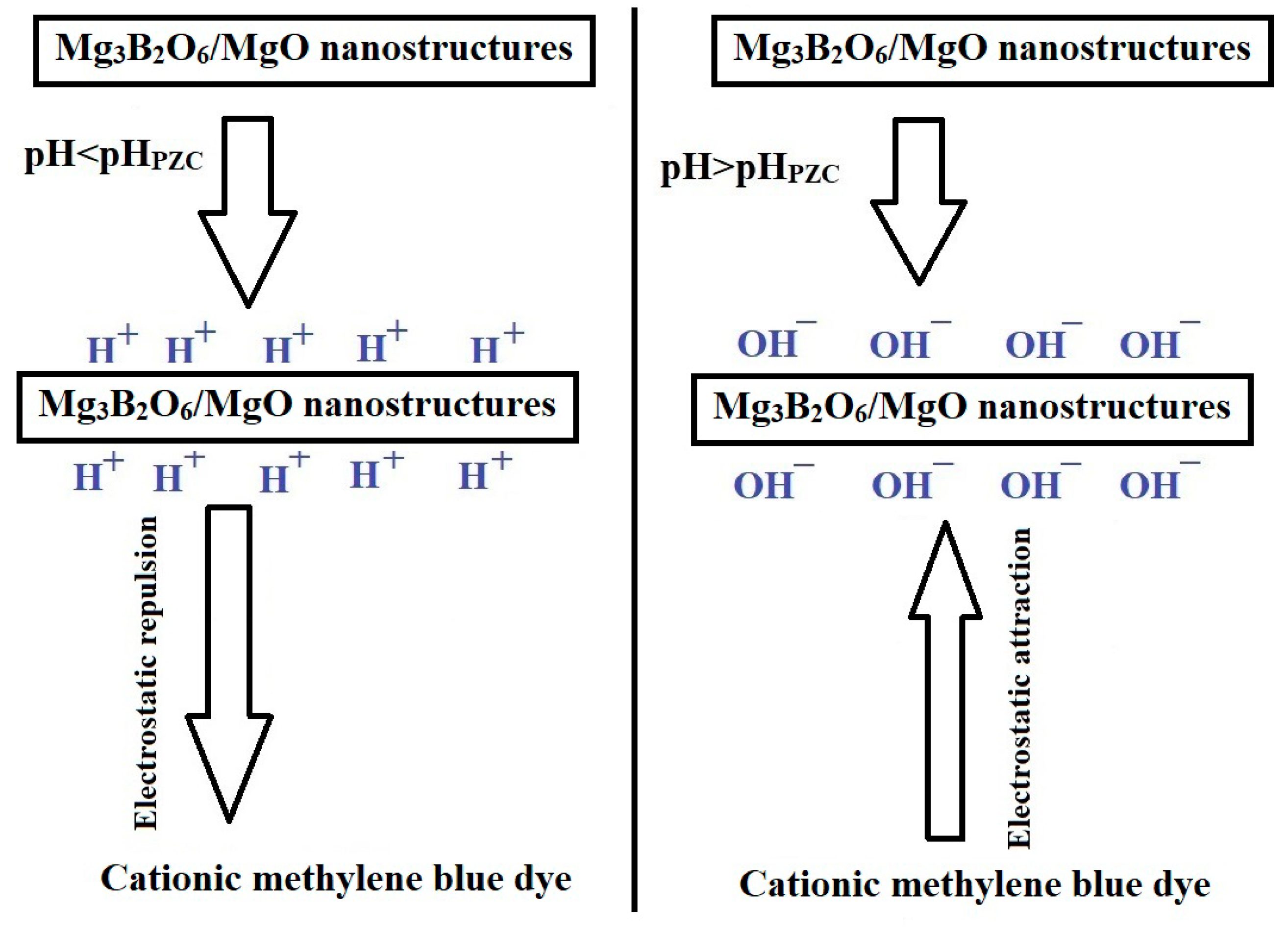
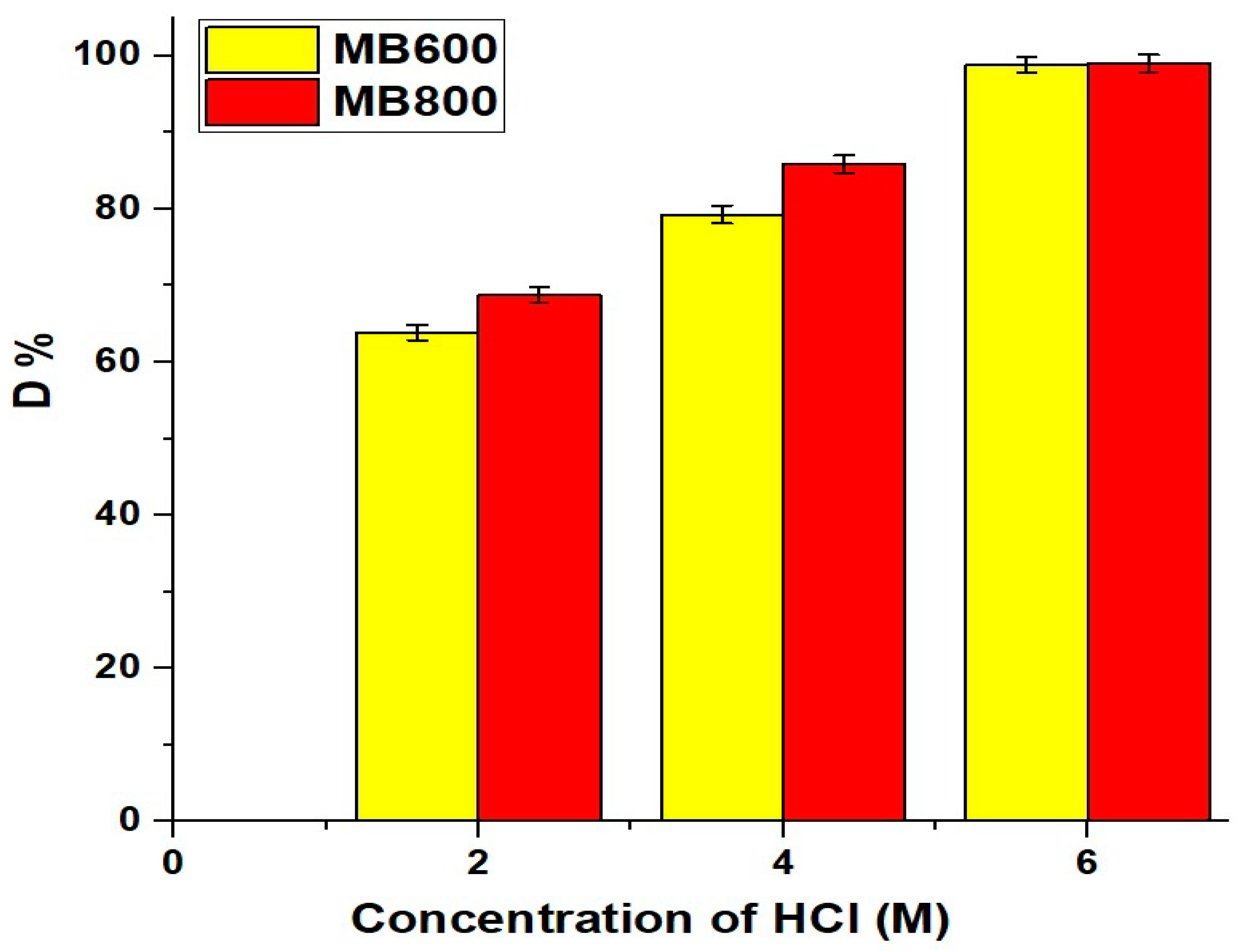
2.2.1. Influence of pH
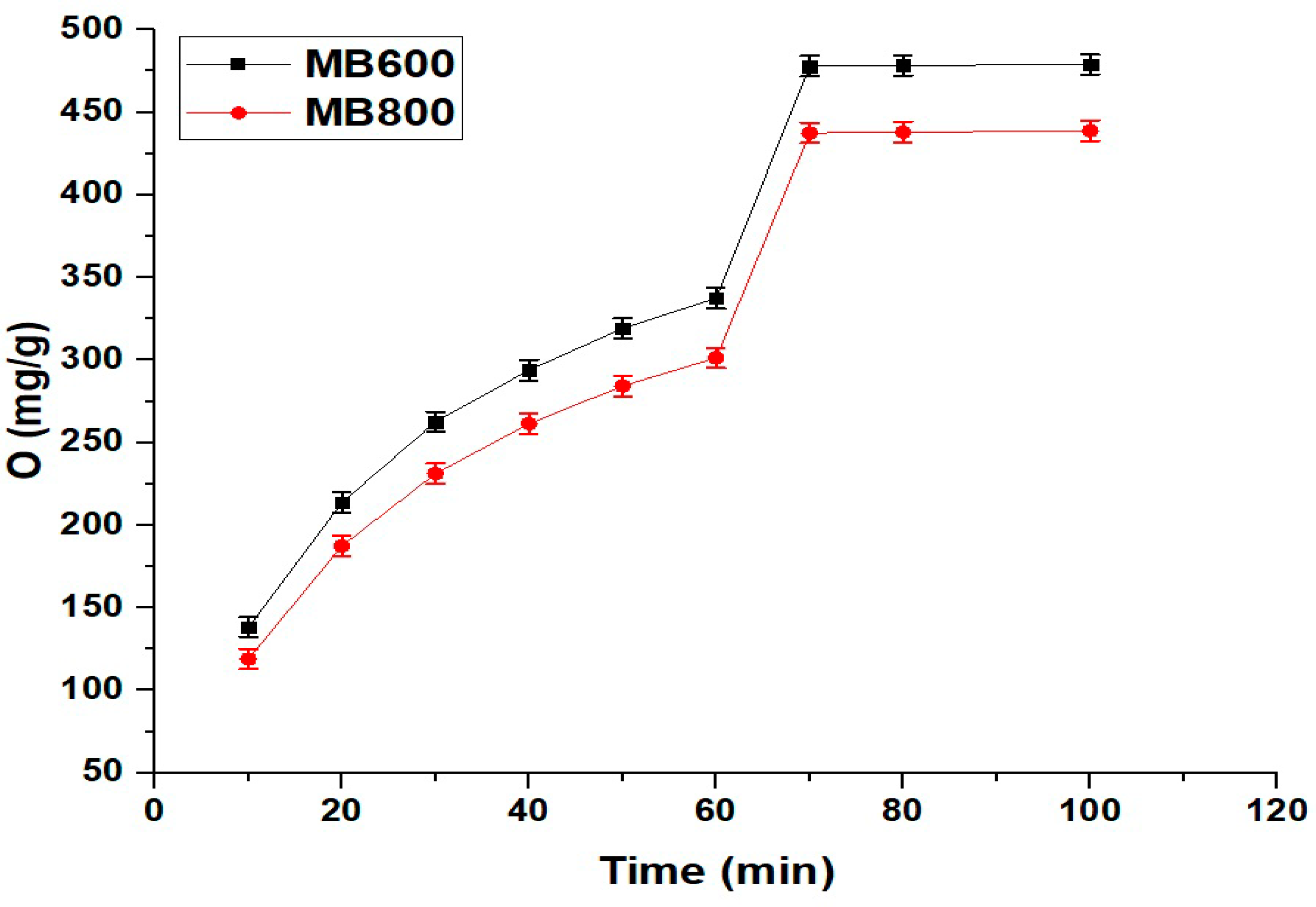
2.2.2. Influence of Contact Time
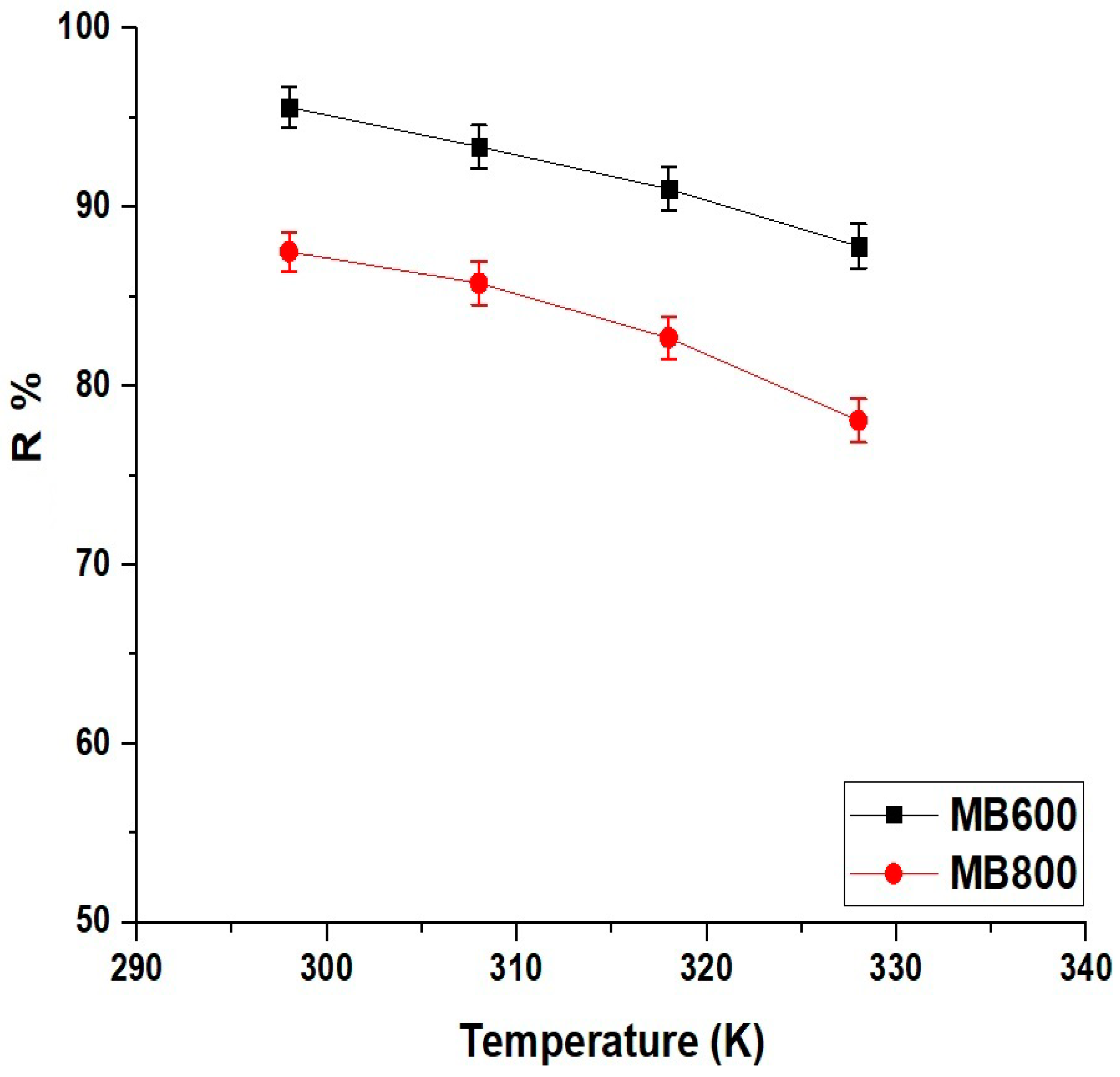
2.2.3. Influence of Temperature
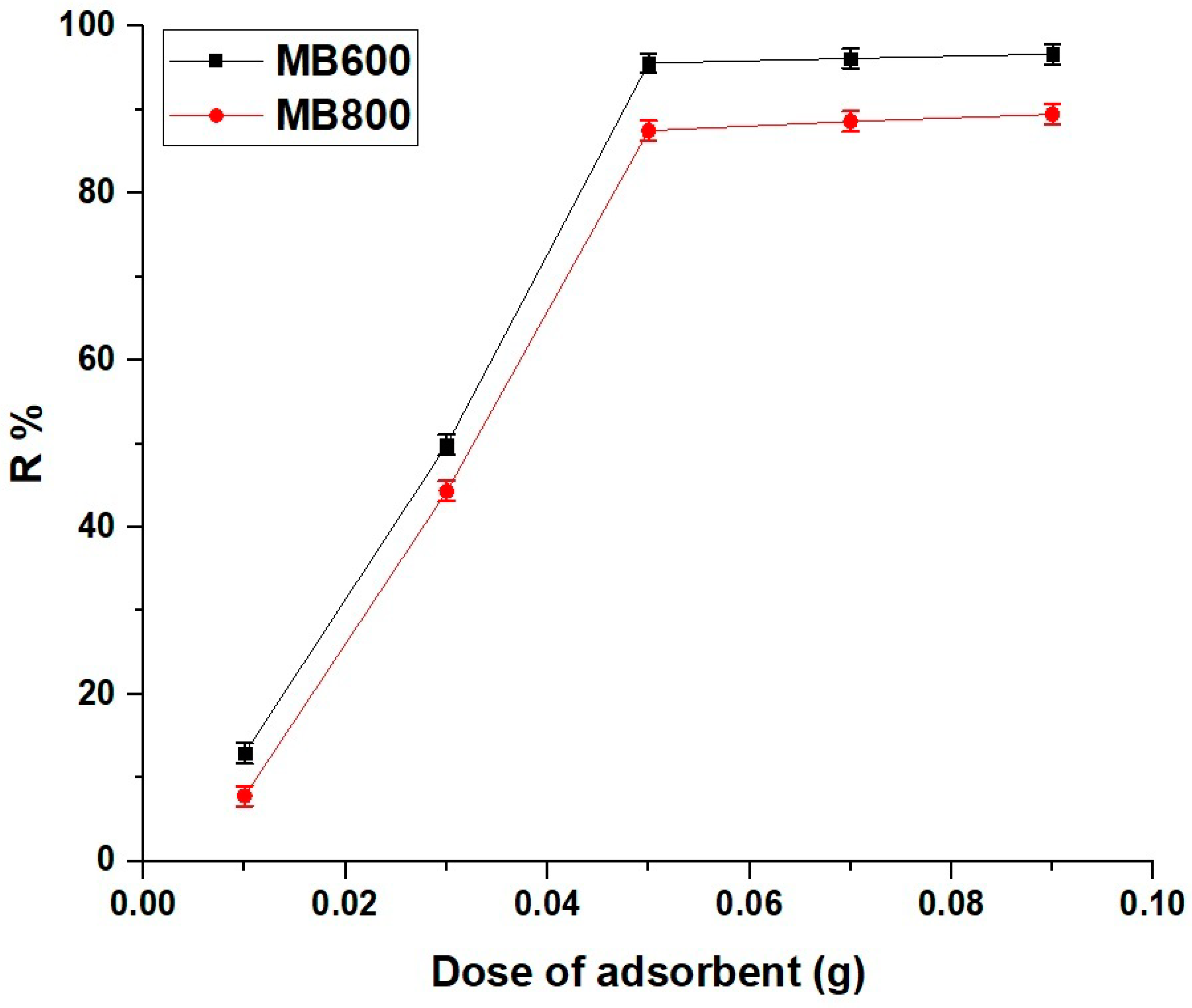
2.2.4. Influence of Adsorbent Dose
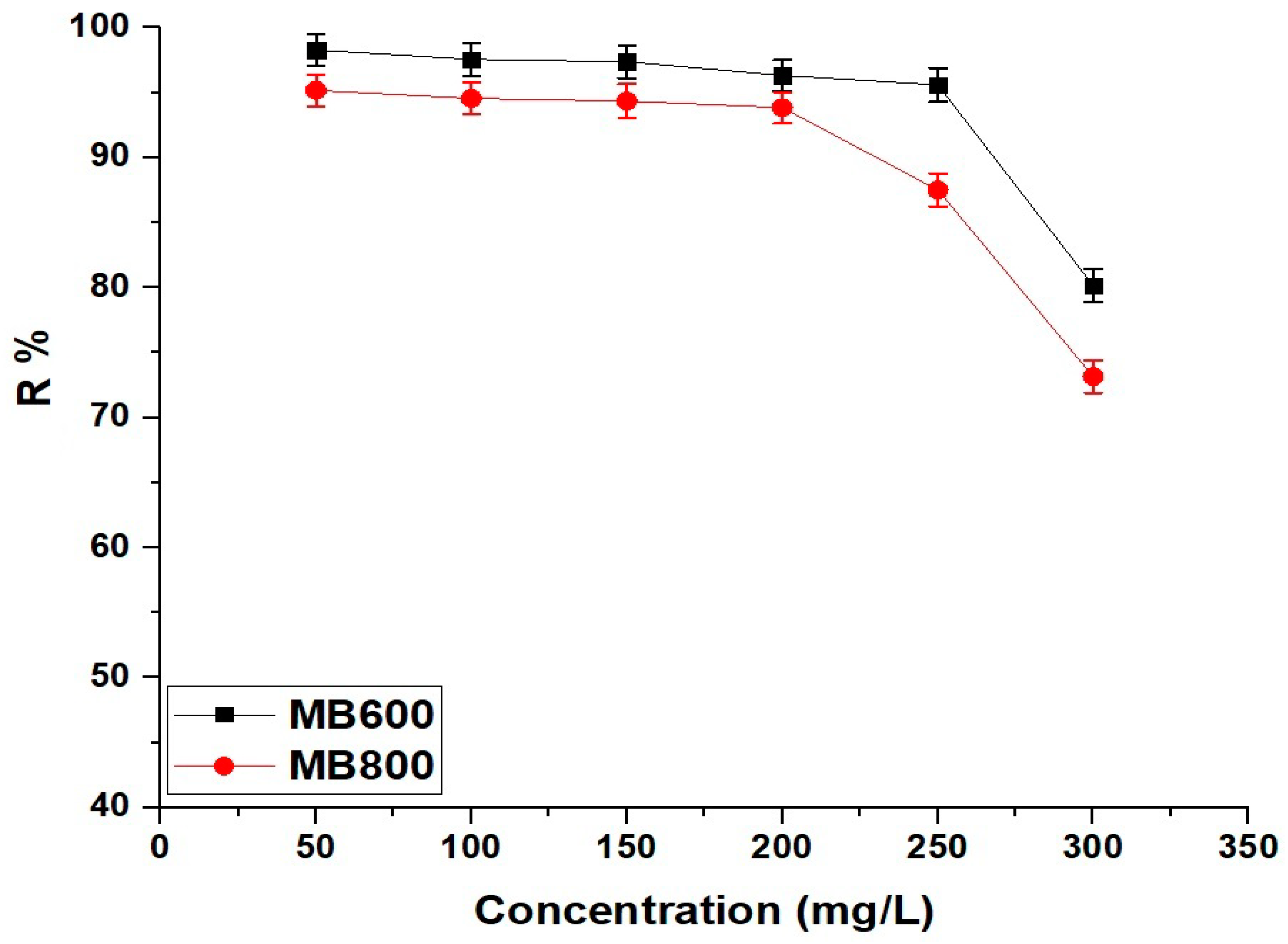
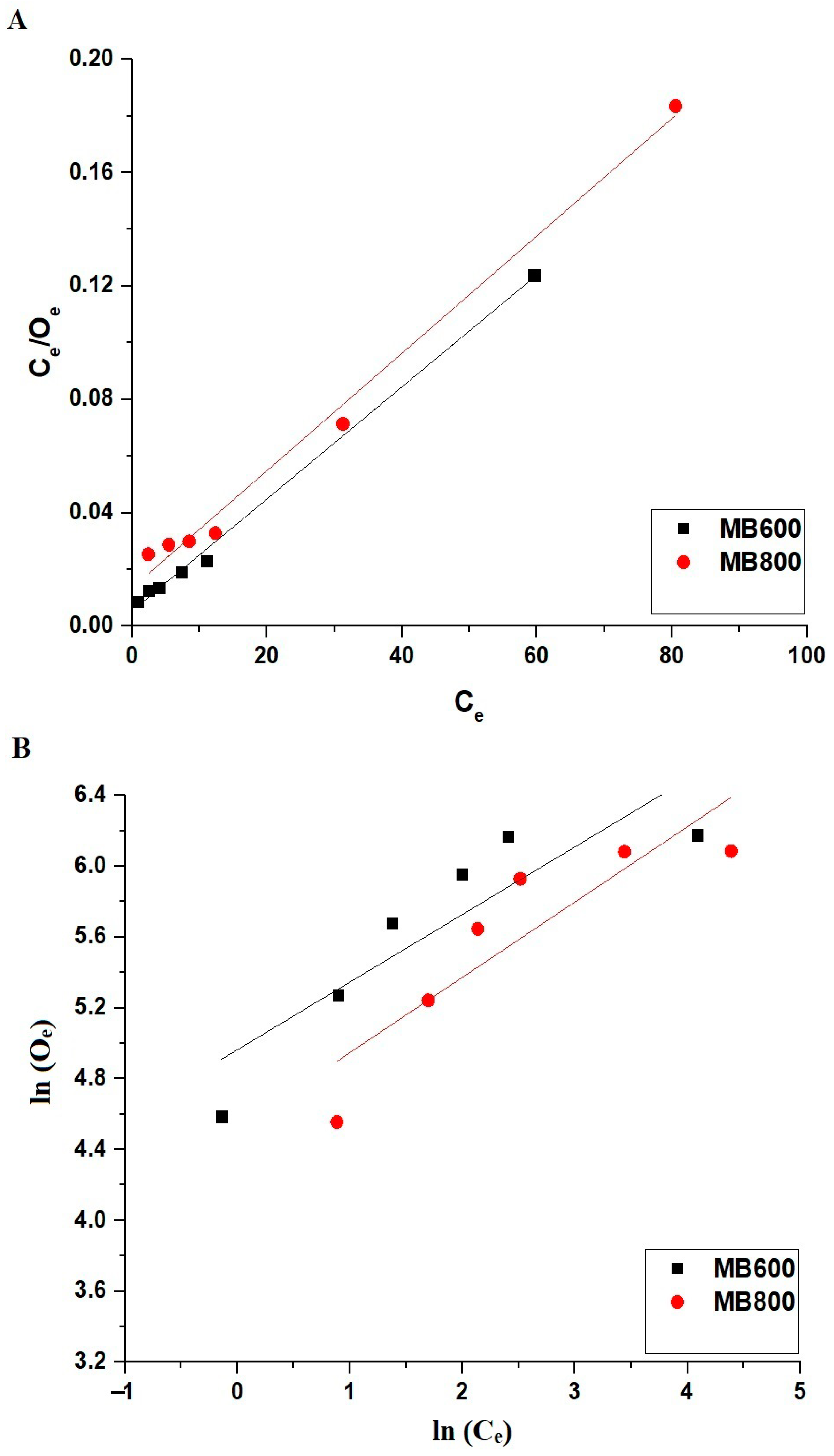
2.2.5. Influence of Concentration
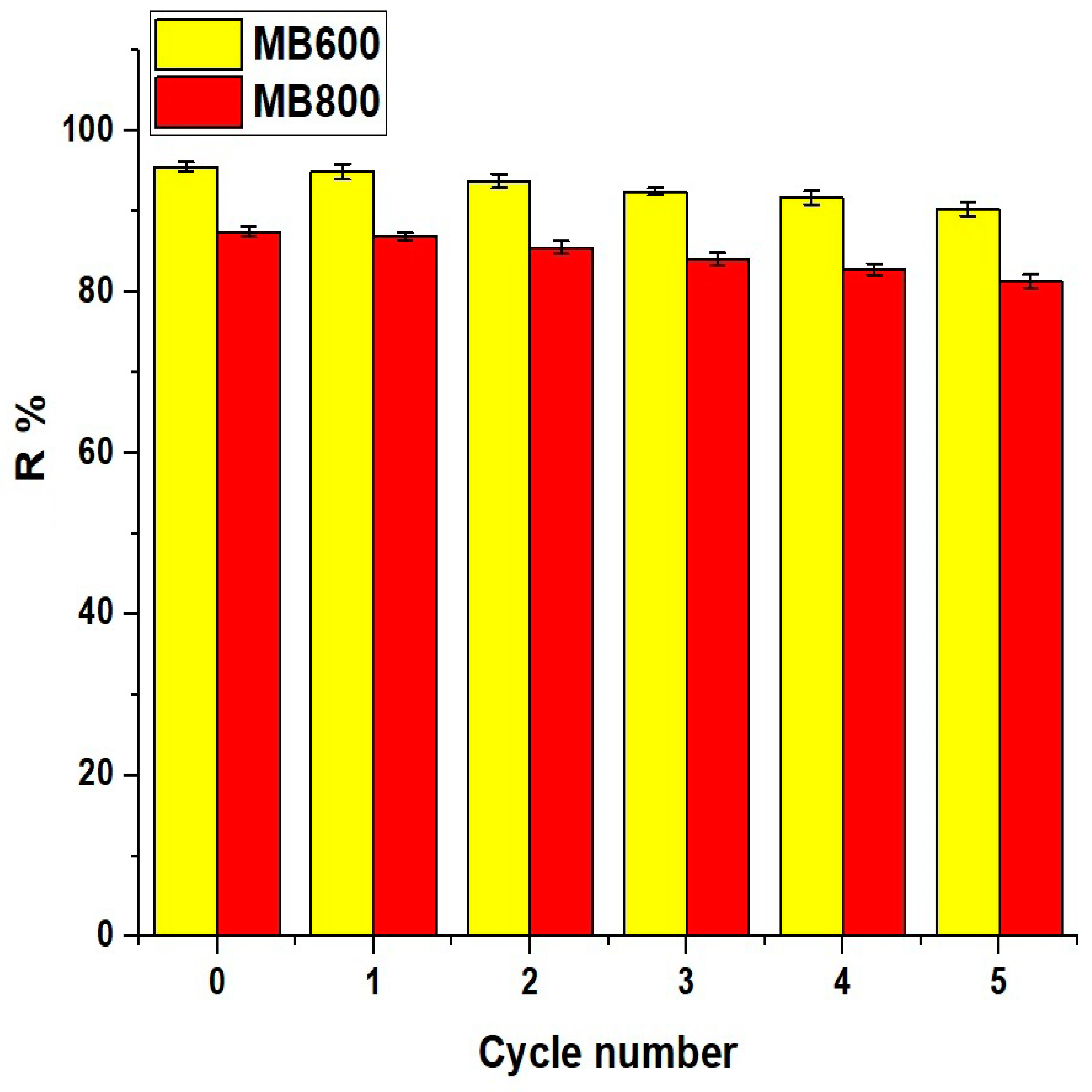
2.2.6. Effect of Regeneration and Reusability
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
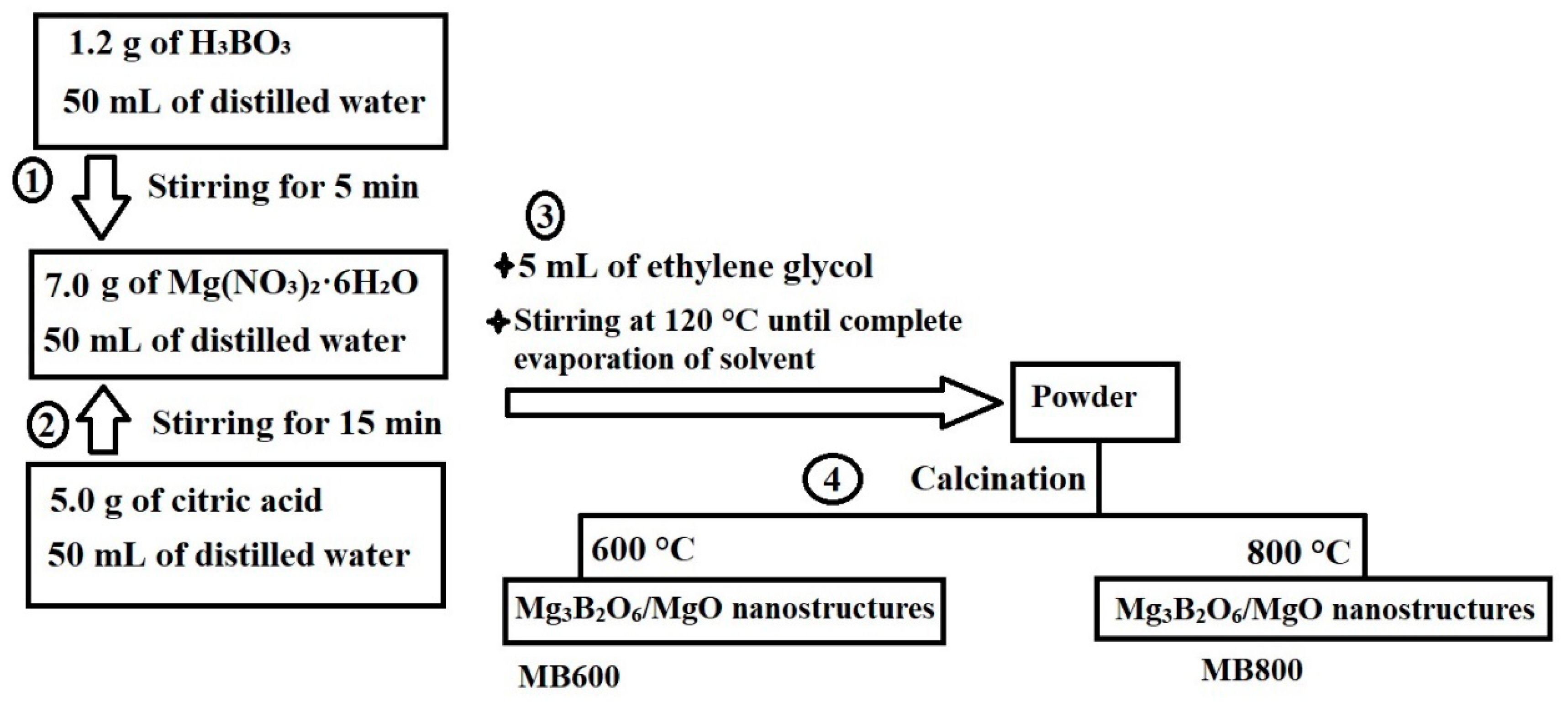
3.2. Synthesis of Mg3B2O6/MgO Nanostructures
3.3. Instrumentation
3.4. Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Media
3.5. Point of Zero Charge (pHPZC) of the MB600 and MB800 Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, D.; Nam, S.N.; Jung, B.; Soo Choi, J.; Min Park, C.; Earn Choong, C.; Jang, M.; Cho, K.S.; Jun, B.M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of Selected Contaminants of Dyes and Pharmaceuticals Using MXene-Based Nanoadsorbents: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 341, 126864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenol, Z.M.; El Messaoudi, N.; Ciğeroglu, Z.; Miyah, Y.; Arslanoğlu, H.; Bağlam, N.; Kazan-Kaya, E.S.; Kaur, P.; Georgin, J. Removal of Food Dyes Using Biological Materials via Adsorption: A Review. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Pandey, A.; Rosy; Sharma, Y.C. A Review on Sustainable Mesoporous Activated Carbon as Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Hazardous Dyes from Industrial Wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Jaymand, M. Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels for Removal of Synthetic Dyes: A Comprehensive Review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 486, 215152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Zohra, S.T.; Ijaz, S.; Iqbal, M.; Iqbal, J.; Bibi, I.; Nouren, S.; El Messaoudi, N.; Nazir, A. Cellulose-Based Materials and Their Adsorptive Removal Efficiency for Dyes: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 1337–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goscianska, J.; Ciesielczyk, F. Lanthanum Enriched Aminosilane-Grafted Mesoporous Carbon Material for Efficient Adsorption of Tartrazine Azo Dye. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 280, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffan, S.; Bardi, L.; Marzona, M. Azo Dye Biodegradation by Microbial Cultures Immobilized in Alginate Beads. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre Meskel, A.; Kwikima, M.M.; Meshesha, B.T.; Habtu, N.G.; Naik, S.V.C.S.; Vellanki, B.P. Malachite Green and Methylene Blue Dye Removal Using Modified Bagasse Fly Ash: Adsorption Optimization Studies. Environ. Challenges 2024, 14, 100829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Magsorbents: Potential Candidates in Wastewater Treatment Technology—A Review on the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 500, 166408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladoye, P.O.; Ajiboye, T.O.; Omotola, E.O.; Oyewola, O.J. Methylene Blue Dye: Toxicity and Potential Elimination Technology from Wastewater. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, L.; Yan, A.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Qu, R. Facile Fabrication of UiO-66-NH2 Modified with Dodecyl and Polyethyleneimine by Post-Synthesis Functionalization Strategy and Simultaneous Adsorption Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 692, 134019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, A.K.; Shadangi, K.P.; Sarangi, P.K. Efficient Removal of Rhodamine B Dye Using Biochar as an Adsorbent: Study the Performance, Kinetics, Thermodynamics, Adsorption Isotherms and Its Reusability. Chemosphere 2024, 354, 141702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabizadeh Chianeh, F.; Valikhan Anaraki, M.; Mahmoudian, F.; Farzin, S. A New Methodology for the Prediction of Optimal Conditions for Dyes’ Electrochemical Removal; Application of Copula Function, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Multi-Objective Optimization. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 182, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intisar, A.; Ramzan, A.; Hafeez, S.; Hussain, N.; Irfan, M.; Shakeel, N.; Gill, K.A.; Iqbal, A.; Janczarek, M.; Jesionowski, T. Adsorptive and Photocatalytic Degradation Potential of Porous Polymeric Materials for Removal of Pesticides, Pharmaceuticals, and Dyes-Based Emerging Contaminants from Water. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustos-Terrones, Y.A.; Hermosillo-Nevárez, J.J.; Ramírez-Pereda, B.; Vaca, M.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G.; Bustos-Terrones, V.; Rojas-Valencia, M.N. Removal of BB9 Textile Dye by Biological, Physical, Chemical, and Electrochemical Treatments. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 121, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakairu, G.W.A.; Kapanga, P.M.; Ntale, M.; Lusamba, S.N.; Tshimanga, R.M.; Ammari, A.; Shehu, Z. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Zeolite/Bi2O3 Nanocomposite in Removal of Rhodamine B Dye from Wastewater. Clean. Water 2024, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.L.; Kieu, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Truong, T.T.T.; Hoang, D.T.; Vu, T.L.C.; Nguyen, T.M.T.; Le, T.S.; Doan, T.H.Y.; Pham, T.D. Surface Modification of Zeolite by Cationic Surfactant and the Application on Adsorptive Removal of Azo Dye Ponceau 4R. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1304, 137619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektar, M.; Ali Rasekh, H.; Jaafar Soltanianfard, M. Synthesis and Characterization of CoFe2O4@SiO2-Polyethyleneimine Magnetic Nanoparticle and Its Application for Ultrasonic-Assisted Removal of Disulfine Blue Dye from Aqueous Solution. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5430–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasbaji, M.; Ibrahim, I.; Mennani, M.; Abdelatty Abuelalla, O.; Fekry, S.S.; Mohamed, M.M.; Salama, T.M.; Moneam, I.A.; Mbarki, M.; Moubarik, A.; et al. Future Trends in Dye Removal by Metal Oxides and Their Nano/Composites: A Comprehensive Review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 158, 111546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichave, M.S.; Kature, A.Y.; Koranne, S.V.; Shinde, R.S.; Gongle, A.S.; Choudhari, V.P.; Topare, N.S.; Raut-Jadhav, S.; Bokil, S.A. Nano-Metal Oxides-Activated Carbons for Dyes Removal: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 77, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kadhi, N.S.; Al-Senani, G.M.; Algethami, F.K.; Shah, R.K.; Saad, F.A.; Munshi, A.M.; Rehman, K.; Khezami, L.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Calcium Ferrite Nanoparticles: A Simple Synthesis Approach for the Effective Disposal of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Environments. Inorganics 2024, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalili, Z.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Successful Removal of Safranine T Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Inorganics 2024, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Wang, S.; Gao, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, G.; Yang, H. CTAB-Assisted Synthesis of Bi2MoO6 Hierarchical Microsphere and Its Application as a Novel Efficient and Recyclable Adsorbent in Removing Organic Pollutants. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 656, 130441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, J.; Yi, Z.; Wang, S.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Highly-Efficient and Recyclable Bi2O2CO3 Adsorbent Achieved by Surfactant Modification and Its Application in Pollutant Removal. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 159, 112091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Almehizia, A.A.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Obaidullah, A.J.; Naglah, A.M.; Al-Farraj, E.S.; Khairy, M.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Fe0.5Mn0.5Co2O4/Fe2O3 as a Novel Nanocomposite for the Effective Photocatalytic Decomposition of Safranin Dye. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2023, 33, 2354–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Parmar, L.K.; Dager, H.S.; Bhardwaj, P.; Yadav, A. Structural and Dielectric Analysis of Cu-Doped NiCo2O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Green Synthesis Approach. Chem. Phys. Impact 2024, 8, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Khairy, M.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Efficient Disposal of Basic Fuchsin Dye from Aqueous Media Using ZrO2/MgMn2O4/Mg(Mg0.333Mn1.333)O4 as a Novel and Facilely Synthesized Nanocomposite. Inorganics 2023, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Pandey, V.; Singh, V.K.; Majhi, M.R. Synthesis and Characterization of Single-Phase Magnesium Borate Nanorod via Solution Reaction Cum Sintering Process. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 27086–27093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, D.; Zhu, B.; Cheng, B.; Jiang, C. Adsorptive Removal of an Anionic Dye Congo Red by Flower-like Hierarchical Magnesium Oxide (MgO)-Graphene Oxide Composite Microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghanmi, R.M.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Simple Production and Characterization of ZnO/MgO Nanocomposite as a Highly Effective Adsorbent for Eliminating Congo Red Dye from Water-Based Solutions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 161, 112137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangor, F.I.M.S.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Waste-to-Value: Synthesis of Nano-Aluminum Oxide (Nano-γ-Al2O3) from Waste Aluminum Foils for Efficient Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, X. Amine Functionalized Sodium Alginate Hydrogel for Efficient and Rapid Removal of Methyl Blue in Water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jia, S.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Li, N.; Qiao, J.; Li, C.Z. A Novel-Green Adsorbent Based on Betaine-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles for Removal of Methyl Blue. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Qiu, H.; Sun, M. Fabrication of Novel Magnetic Chitosan Grafted with Graphene Oxide to Enhance Adsorption Properties for Methyl Blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Wu, Y.; Liu, N.; Wu, Y. Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide Modified Diatomite Waste as a Novel Adsorbent for Organic Dye Removal: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism Studies. Polyhedron 2020, 175, 114227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naushad, M.; Alqadami, A.A.; AlOthman, Z.A.; Alsohaimi, I.H.; Algamdi, M.S.; Aldawsari, A.M. Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherm and Reusability Studies for the Removal of Cationic Dye from Aqueous Medium Using Arginine Modified Activated Carbon. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Reghioua, A.; Yaseen, Z.M. Zwitterion Composite Chitosan-Epichlorohydrin/Zeolite for Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Reactive Red 120 Dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtar, A.; Abdelkrim, S.; Djelad, A.; Sardi, A.; Boukoussa, B.; Sassi, M.; Bengueddach, A. Adsorption Behavior of Cationic and Anionic Dyes on Magadiite-Chitosan Composite Beads. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, D.S.; Islam, M.N.; Othman, M.H.D.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Quayum, M.E.; Islam, M.A.; Ismail, I.M.I.; Habib, A. Nano-Zinc Oxide Fibers: Synthesis, Characterization, Adsorption of Acid Blue 92 Dye, Isotherms, Thermodynamics and Kinetics. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Tsoutsa, E.K.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Simultaneous Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes on Quaternary Mixtures by Adsorption onto Banana, Orange and Pomegranate Peels. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 685, 133176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, W.I.; Kenawy, I.M.M.; Abou El-Reash, Y.G.; Mousa, A.A. Microwave Assisted Modification of Cellulose by Gallic Acid and Its Application for Removal of Aluminium from Real Samples. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
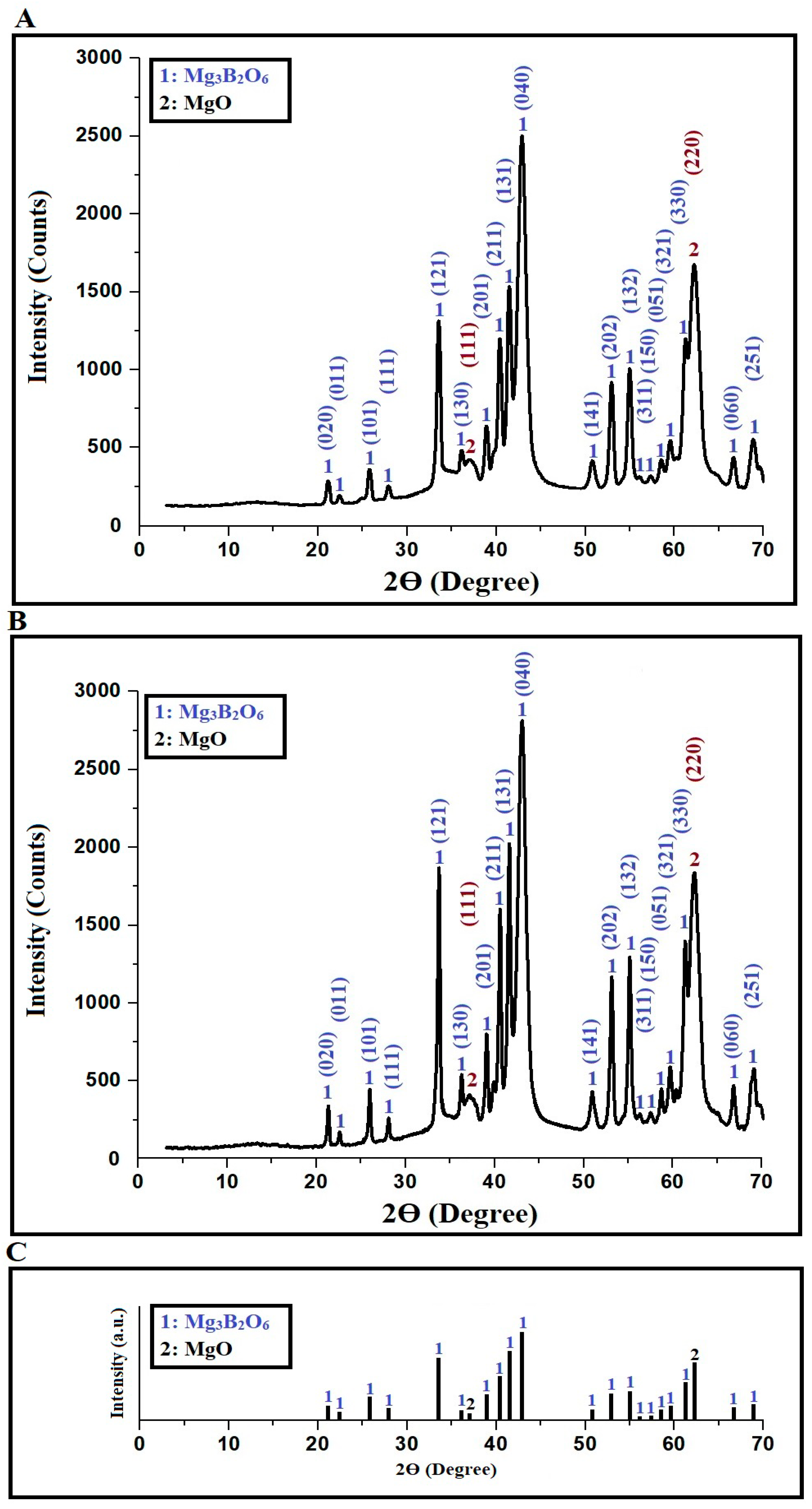
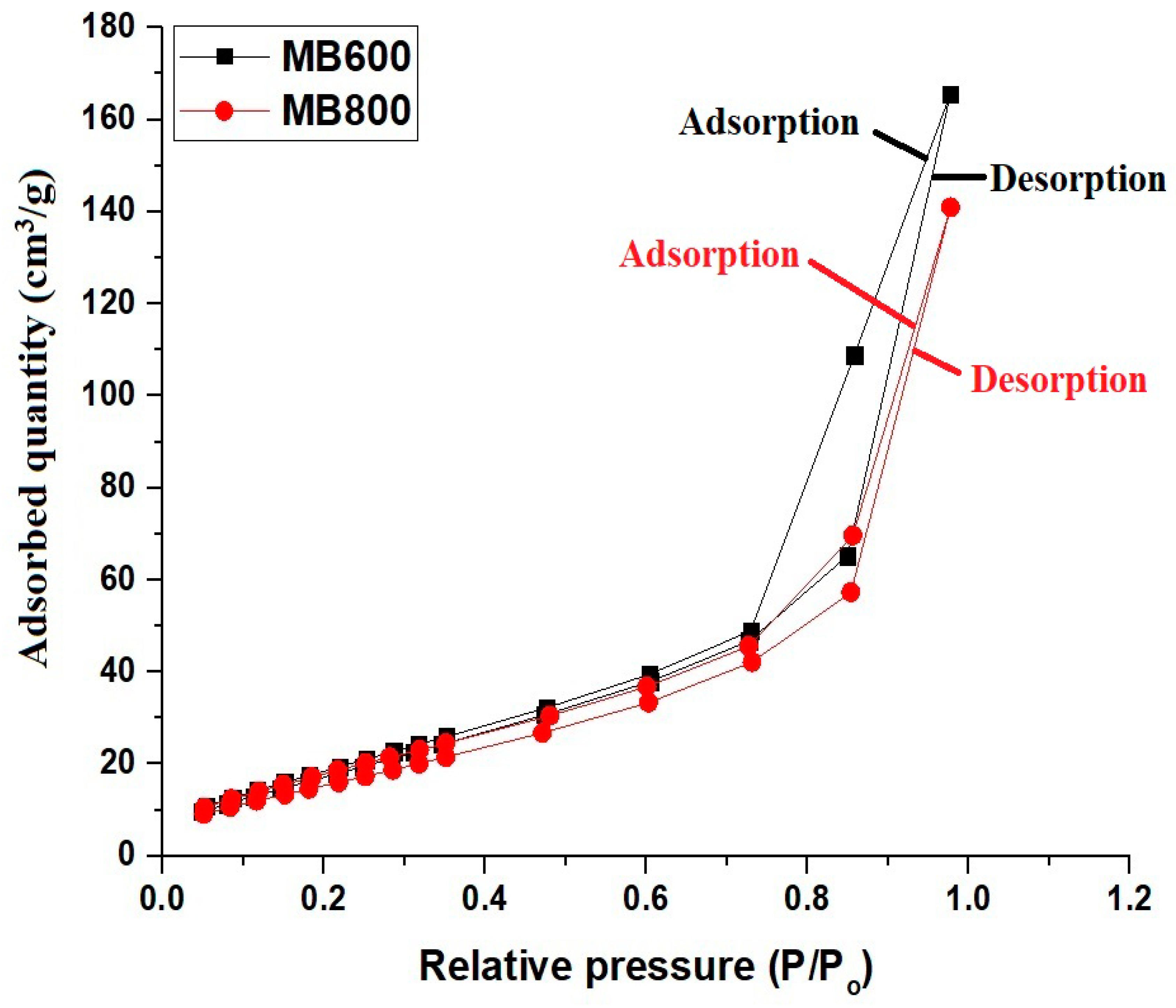

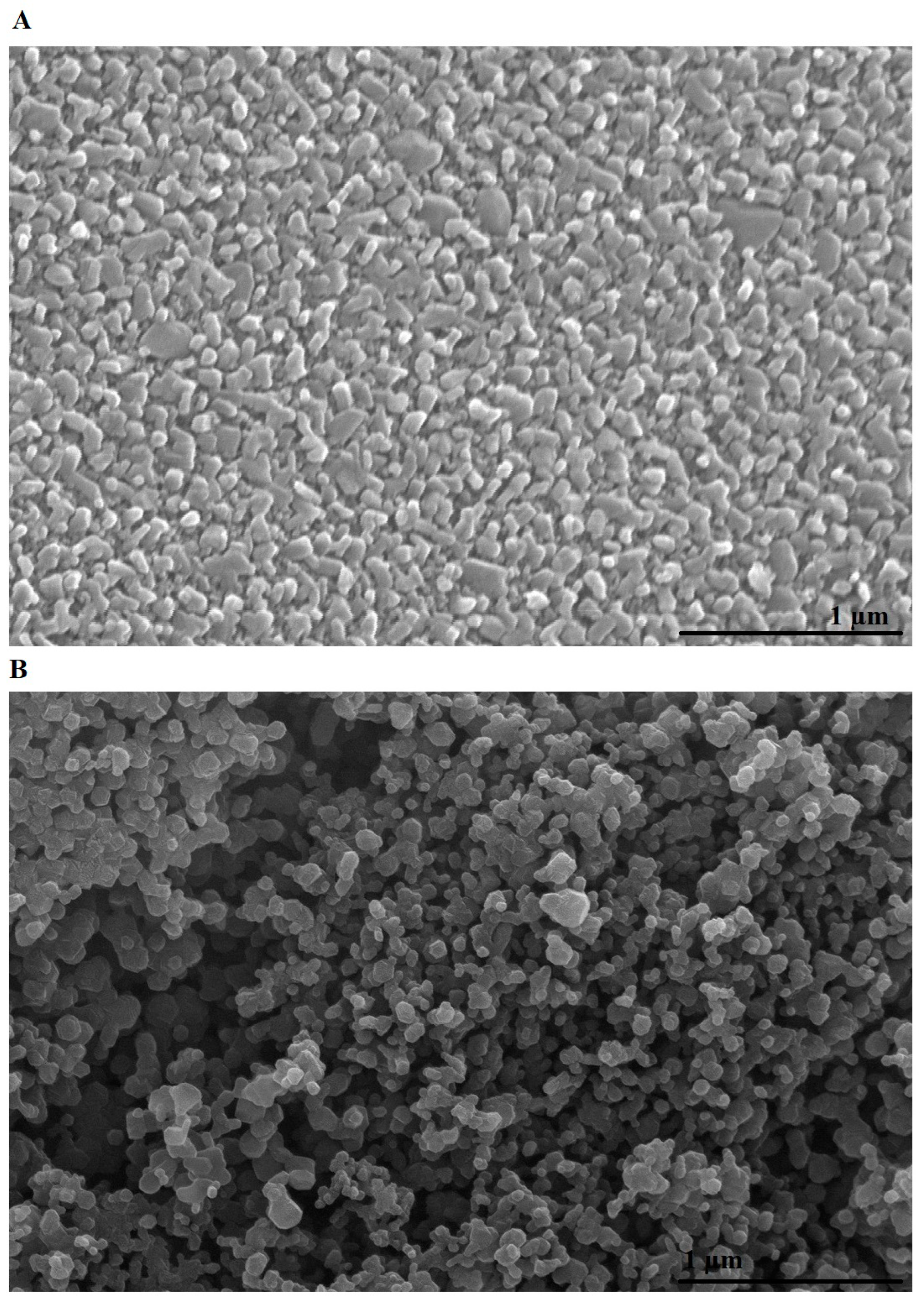
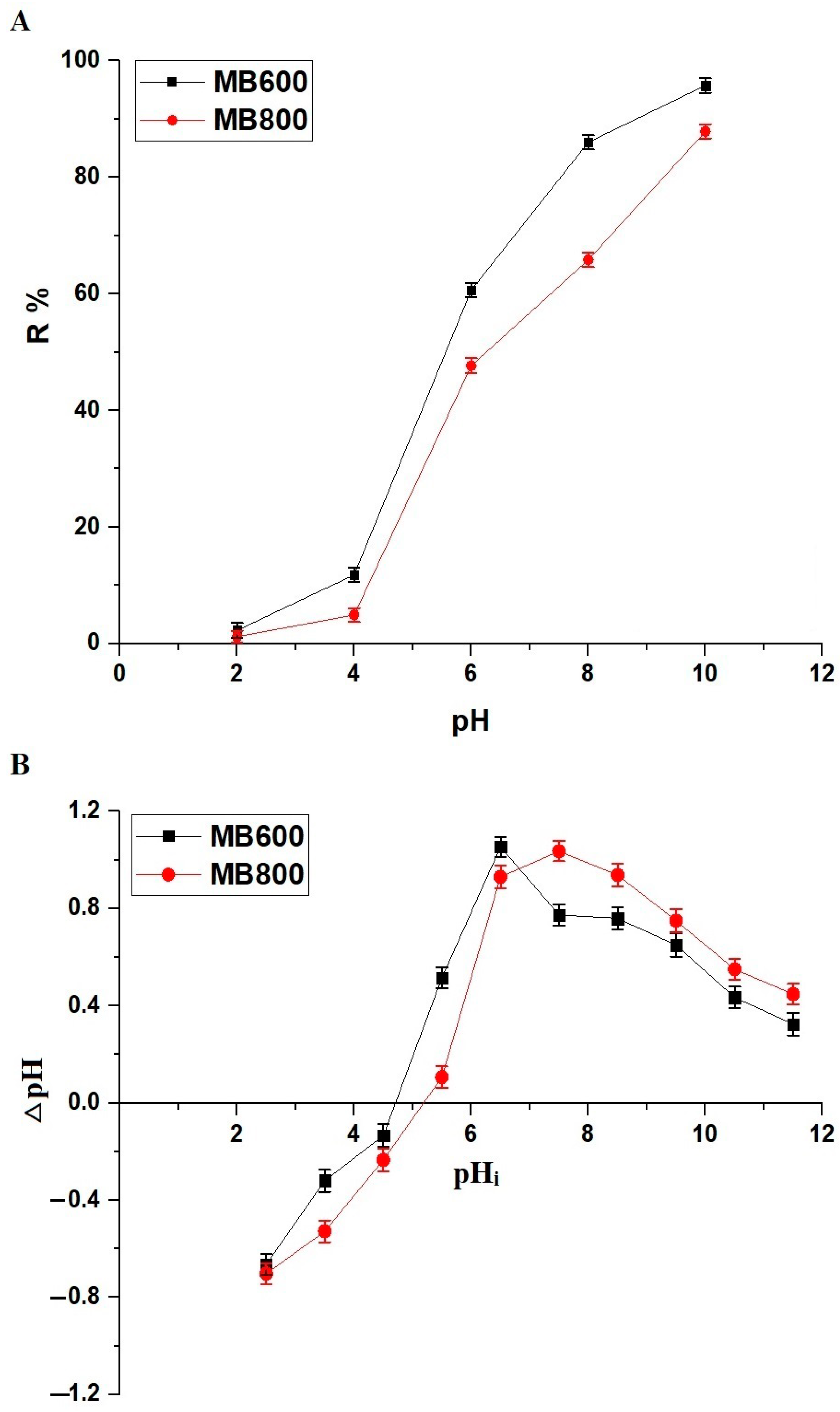


| Surface Textures | MB600 | MB800 |
|---|---|---|
| BET surface area (m2/g) | 74.63 | 64.82 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.2568 | 0.2186 |
| Mean pore size (nm) | 6.88 | 6.75 |
| Adsorbent | OExp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (1/min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | F2 (g/mg·min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| MB600 | 477.90 | 0.01743 | 381.38 | 0.9783 | 8.6870 × 10−5 | 473.93 | 0.9999 |
| MB800 | 437.52 | 0.01679 | 356.30 | 0.9787 | 8.7107 × 10−5 | 434.78 | 0.9999 |
| Adsorbent | ΔS° (kJ/molK) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 308 | 318 | 328 | |||
| MB600 | 0.06812 | −29.65 | −49.95 | −50.63 | −51.31 | −51.99 |
| MB800 | 0.03926 | −18.38 | −30.08 | −30.47 | −30.86 | −31.26 |
| Adsorbent | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omax (mg/g) | F4 (L/mg) | R2 | Omax (mg/g) | F3 (mg/g) (L/mg)1/n | 1/Y | R2 | |
| MB600 | 505.05 | 0.3646 | 0.9966 | 1177.25 | 143.21 | 0.3815 | 0.7398 |
| MB800 | 483.09 | 0.1529 | 0.9896 | 961.68 | 92.15 | 0.4248 | 0.7362 |
| Adsorbent | Omax (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| γ-Al2O3 | 175.40 | [31] |
| Amine-functionalized sodium alginate hydrogel | 400.00 | [32] |
| Betaine-modified magnetic nanoparticles | 136.00 | [33] |
| Chitosan/graphene oxide composite | 81.50 | [34] |
| Hydrolyzed-polyacrylamide-modified diatomite waste | 37.12 | [35] |
| Activated carbon | 219.90 | [36] |
| Chitosan/epichlorohydrin/zeolite composite | 156.10 | [37] |
| Magadiite–chitosan composite beads | 45.25 | [38] |
| MB600 | 505.05 | This study |
| MB800 | 483.09 | This study |
| Influence | Concentration of Methylene Blue Dye (mg/L) | Volume of Methylene Blue Dye Solution (mL) | Quantity of Adsorbent (g) | Contact Time (min) | Temperature (K) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 250 | 100 | 0.05 | 180 | 298 | 2–10 |
| Time | 250 | 100 | 0.05 | 10–100 | 298 | 10 |
| Temperature | 250 | 100 | 0.05 | 70 | 298–328 | 10 |
| Dose of adsorbent | 250 | 100 | 0.01–0.09 | 70 | 298 | 10 |
| Concentration of dye | 50–300 | 100 | 0.05 | 70 | 298 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Hegazey, R.M.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Media Using Facilely Synthesized Magnesium Borate/Magnesium Oxide Nanostructures. Molecules 2024, 29, 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143392
Al-Wasidi AS, Hegazey RM, Abdelrahman EA. Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Media Using Facilely Synthesized Magnesium Borate/Magnesium Oxide Nanostructures. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143392
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Wasidi, Asma S., Raed M. Hegazey, and Ehab A. Abdelrahman. 2024. "Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Media Using Facilely Synthesized Magnesium Borate/Magnesium Oxide Nanostructures" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143392
APA StyleAl-Wasidi, A. S., Hegazey, R. M., & Abdelrahman, E. A. (2024). Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Media Using Facilely Synthesized Magnesium Borate/Magnesium Oxide Nanostructures. Molecules, 29(14), 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143392







