Synergistic Therapeutic Effects of D-Mannitol–Cerium–Quercetin (Rutin) Coordination Polymer Nanoparticles on Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Size, Zeta Potential, and Encapsulation Efficiency Distribution of MCQ/R NPs
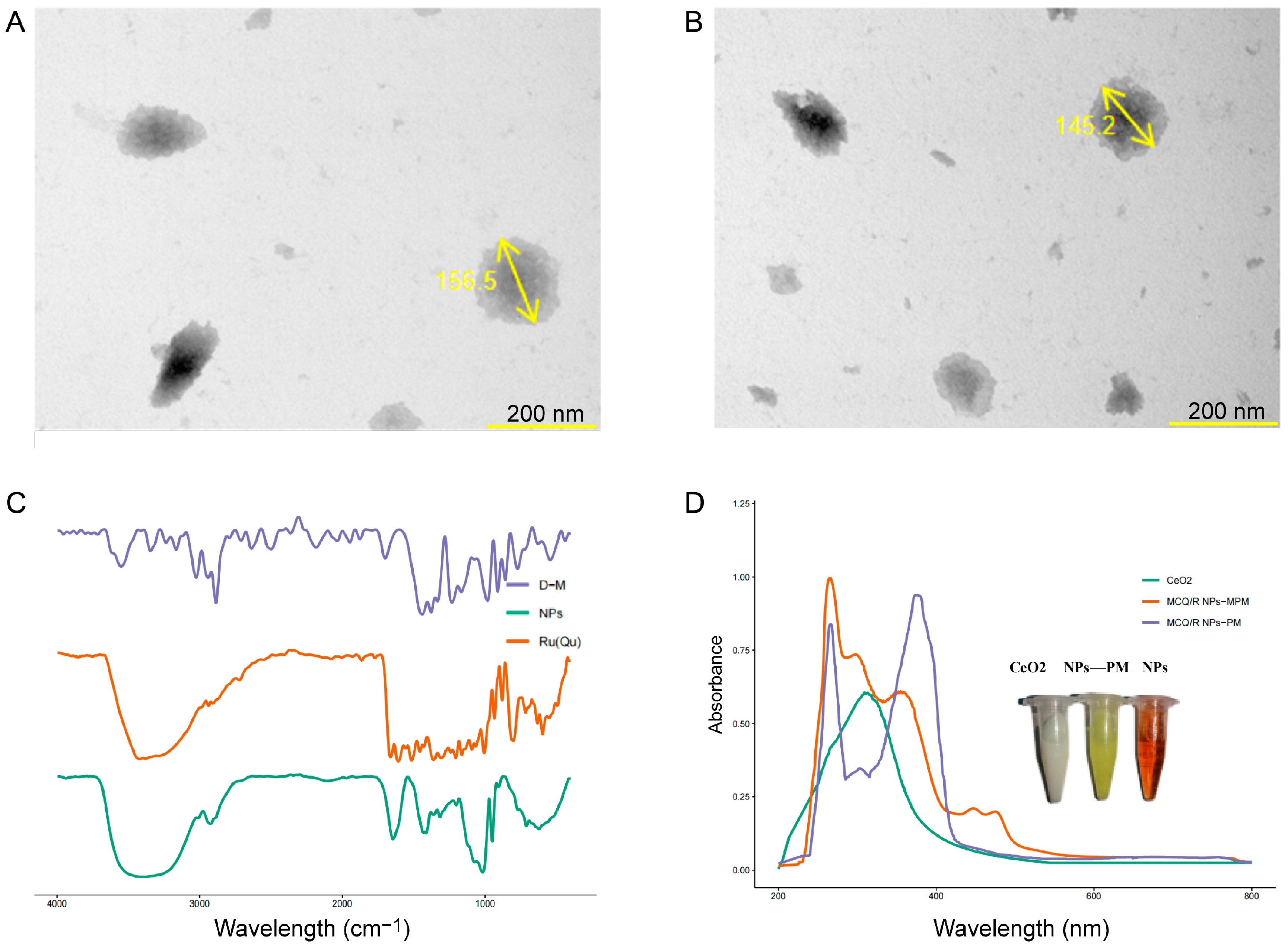
2.2. TEM and ICP-MS Analysis of Coordination Polymers
2.3. UV–Vis Spectra of MCQ/R NPs
2.4. Infrared Spectra of MCQ/R NPs
2.5. Stability Assessment of MCQ/R NPs
2.6. Hemolysis Assay
2.7. Antioxidant Activities of MCQ/R NPs
2.8. Changes in Lung Wet-to-Dry Weight Ratio
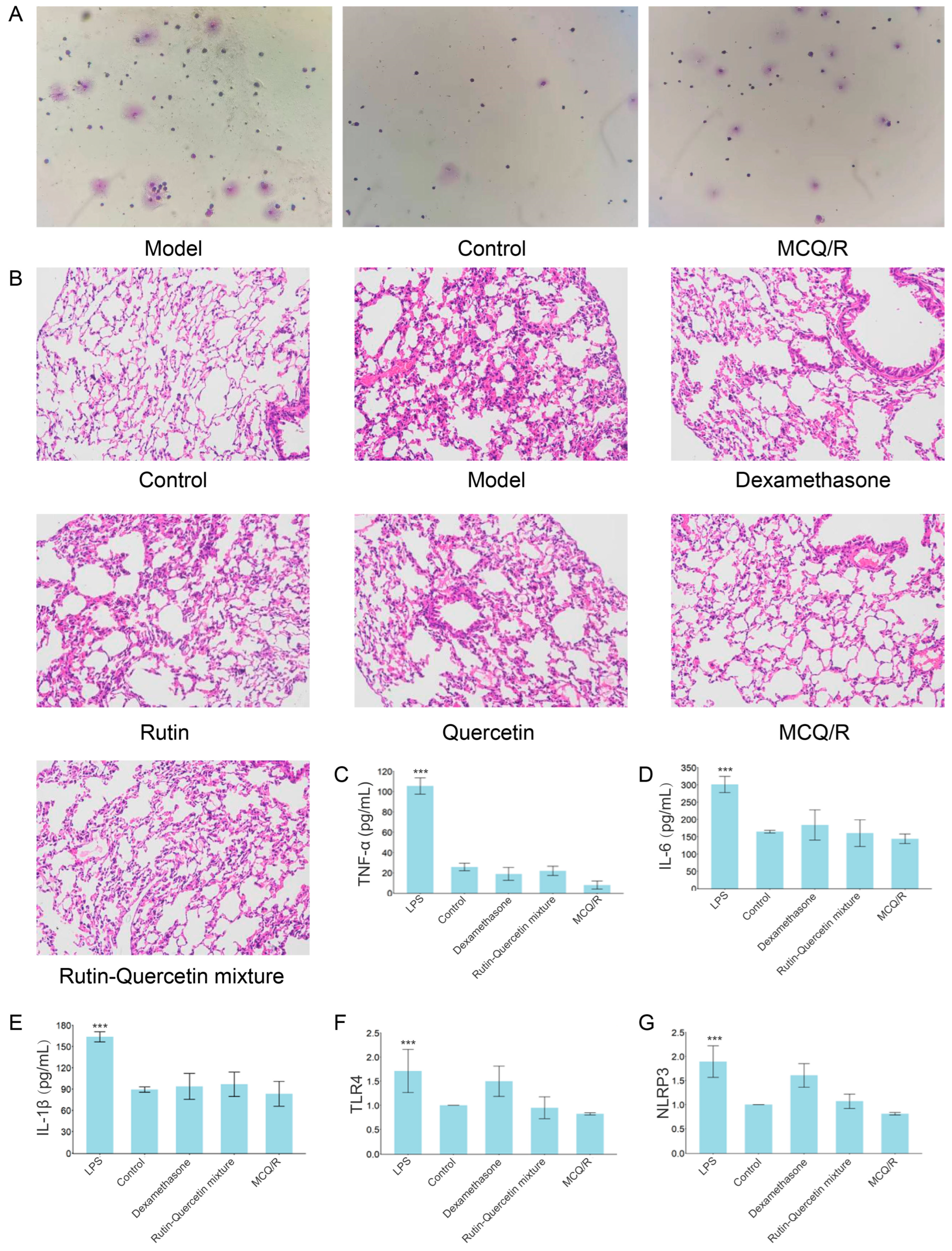
2.9. Inflammatory Cell Differential Count
2.10. Histopathological Examination of Mouse Lung Tissue via Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) Staining
2.11. Serum Inflammatory Cytokine Levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α
2.12. Expression of TLR4 and NLRP3 mRNA in Lung Tissue
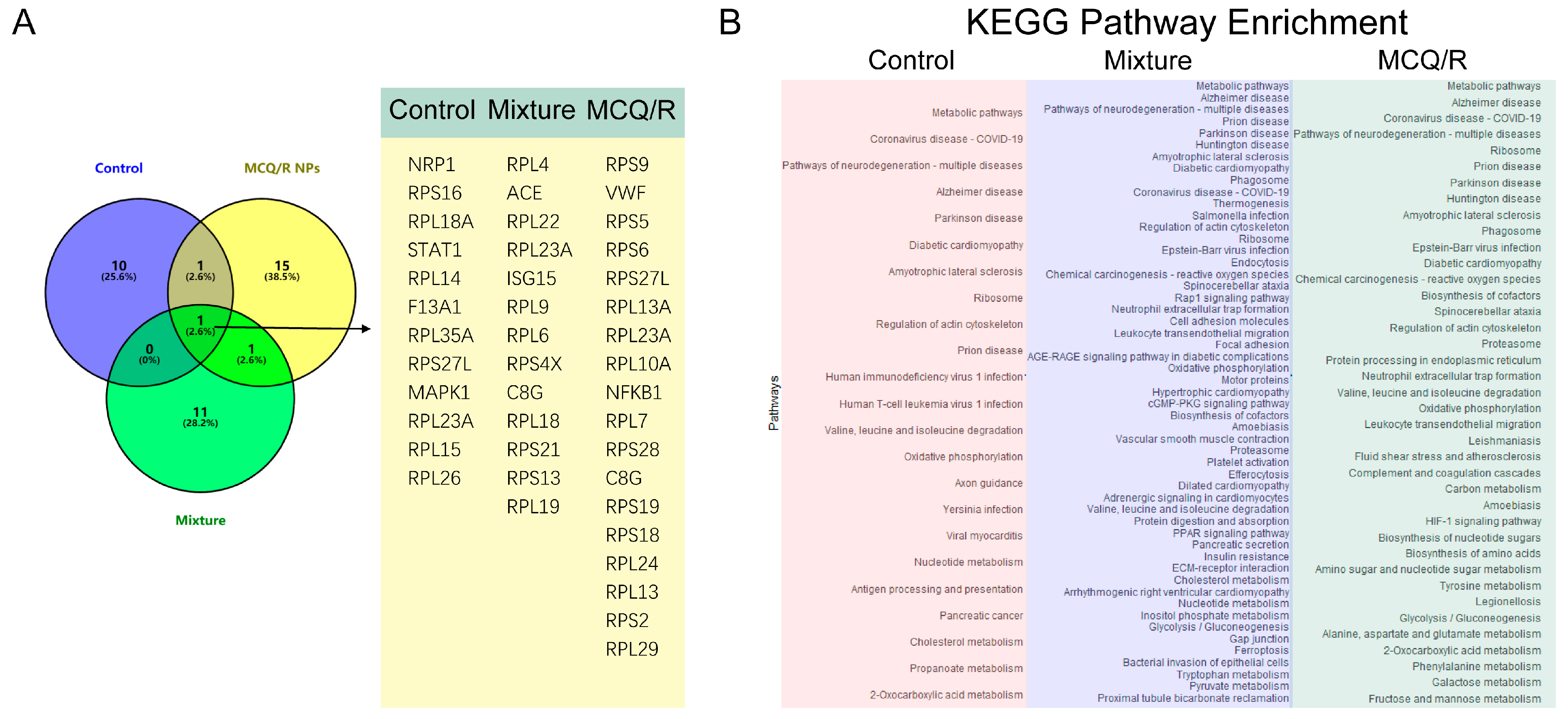
2.13. Proteomics Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Methods, Materials, and Animals
4.1. Materials and Animals
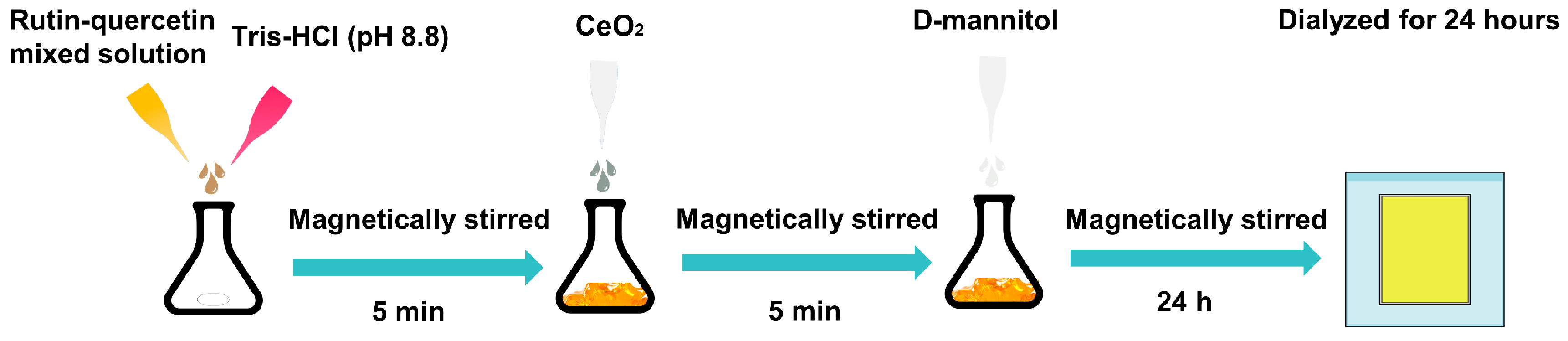
4.2. Synthesis and Characterization of MCQ/R NPs
4.3. Characterization of Coordination Polymers
4.3.1. TEM and ICP-MS Analysis
4.3.2. UV–vis Spectrophotometry
4.3.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
4.4. Stability Test of MCQ/R NPs
4.5. Radical Scavenging Ability Experiment
4.6. Hemolysis Test
4.7. Animal Grouping, Administration, Modeling, and Sample Collection
4.8. Pulmonary Tissue Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.9. Serum Levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 Were Measured in Mice
4.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Was Employed to Assess mRNA Expression Levels
4.11. Proteomics Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Renia, L.; MacAry, P.A.; Ng, L. The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, C.R.; Ye, Q.Y.; Hou, W.J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Xiao, G.P.; Li, X.N.; Li, Y.H.; et al. Pathogenic role of leukotriene b4 in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell hyper- permeability induced by one lung ventilation in rabbits. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2017, 37, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Mokra, D. Acute lung injury—From pathophysiology to treatment. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69 (Suppl. 3), S353–S366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Wu, L.; Sun, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, C.; Ren, X.; Shao, Q.; York, P.; Tong, J.; Zhu, J.; et al. Antioxidant biodegradable covalent cyclodextrin frameworks as particulate carriers for inhalation therapy against acute lung injury. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 38421–38435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tongyoo, S.; Permpikul, C.; Mongkolpun, W.; Vattanavanit, V.; Udompanturak, S.; Kocak, M.; Meduri, G.U. Hydrocortisone treatment in early sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavendran, K.; Willson, D.; Notter, R.H. Surfactant therapy for acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care Clin. 2011, 27, 525–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Rho, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Song, S.H.; Yoo, J.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.H. Protective effects of diphenyleneiodonium, an nadph oxidase inhibitor, on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, J.E.; Matthay, M.A. Clinical review: Early treatment of acute lung injury--paradigm shift toward prevention and treatment prior to respiratory failure. Crit. Care 2012, 16, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xiang, D.; Ju, L.; Shen, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Friend or foe? The roles of antioxidants in acute lung injury. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; James, J.; Dhatariya, K. Management of hyperglycaemia and steroid (glucocorticoid) therapy: A guideline from the joint british diabetes societies (jbds) for inpatient care group. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Jin, D.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; An, X.; Duan, L.; Yang, C.; Zhou, R.; Duan, Y.; et al. Efficacy and mechanisms of traditional chinese medicine for covid-19: A systematic review. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.H.; Yang, J.J.; Yang, M.L.; Li, Y.C.; Kuan, Y.H. Rutin decreases lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and the mapk-nf-kappab pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 69, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-B.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Wang, Y.-L.; Kaur, P.; Yang, B.-G.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, L.; Cui, Y.-L. A novel inhalable quercetin-alginate nanogel as a promising therapy for acute lung injury. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-L.; Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Lin, F.-Y.; Han, D.-D.; Dai, M.-H.; Li, W.; Pan, P.-H. Quercetin protects against lps-induced lung injury in mice via sirt1-mediated suppression of pkm2 nuclear accumulation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 936, 175352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satari, A.; Ghasemi, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Asgharian, S.; Lorigooini, Z. Rutin: A flavonoid as an effective sensitizer for anticancer therapy; Insights into multifaceted mechanisms and applicability for combination therapy. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 9913179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basaran, E.; Ozturk, A.A.; Senel, B.; Demirel, M.; Sarica, S. Quercetin, rutin, and quercetin-rutin incorporated hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 172, 106153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Shao, Y.; Jin, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, C.; Qu, C.; Sun, S.; Cui, C.; Liu, M. The protective effect of rutin against lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice based on the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic combination model. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Yang, M.-L.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-J.; Yeh, C.-H.; Pan, P.-H.; Horng, C.-T.; Kuo, W.-H.; Kuan, Y.-H. Protective effect of rutin on lps-induced acute lung injury via down-regulation of mip-2 expression and mmp-9 activation through inhibition of akt phosphorylation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, F.U.; Aman, W.; Ullah, I.; Qureshi, O.S.; Mustapha, O.; Shafique, S.; Zeb, A. Effective use of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for the treatment of selected tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7291–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Potential of nanoparticles as permeation enhancers and targeted delivery options for skin: Advantages and disadvantages. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3271–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Shi, X.; Zhong, S.; Peng, Y.; Qi, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhou, W. Metal-phenolic networks for cancer theranostics. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 2825–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, S.C.; Zhu, M.H.; Zhu, X.D.; Luan, X.; Liu, X.L.; Lai, X.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, Q.; Sun, P.; et al. Metal phenolic network-integrated multistage nanosystem for enhanced drug delivery to solid tumors. Small 2021, 17, e2100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Zeng, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, X.; Ke, Y.; He, X.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, Q. A step-by-step multiple stimuli-responsive metal-phenolic network prodrug nanoparticles for chemotherapy. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Applications of metal-phenolic networks in nanomedicine: A review. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 5786–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, L.; Ju, Y.; Dai, Y. Recent advances in metal-phenolic networks for cancer theranostics. Small 2021, 17, e2100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, R.; Khorsandi, K.; Esfahani, H.S.; Habibi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, G. Preparation of cerium-curcumin and cerium-quercetin complexes and their leds irradiation assisted anticancer effects on mda-mb-231 and a375 cancer cell lines. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 34, 102326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopoldini, M.; Russo, N.; Chiodo, S.; Toscano, M. Iron chelation by the powerful antioxidant flavonoid quercetin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6343–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolatabadi, J.E. Molecular aspects on the interaction of quercetin and its metal complexes with dna. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemiec, S.M.; Hilton, S.A.; Wallbank, A.; Louiselle, A.E.; Elajaili, H.; Hu, J.; Singh, S.; Seal, S.; Nozik, E.; Smith, B.; et al. Lung function improves after delayed treatment with cnp-mir146a following acute lung injury. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 40, 102498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, S.M.; Hilton, S.A.; Wallbank, A.; Azeltine, M.; Louiselle, A.E.; Elajaili, H.; Allawzi, A.; Xu, J.; Mattson, C.; Dewberry, L.C.; et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticle delivery of microrna-146a for local treatment of acute lung injury. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2021, 34, 102388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemirkan, A.; Kucuk, A.; Gunes, I.; Arslan, M.; Tuncay, A.; Sivgin, V.; Sezen, S.C.; Boyunaga, H. The effect of cerium oxide on lung injury following lower extremity ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats under desflurane anesthesia. Saudi Med. J. 2021, 42, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuncay, A.; Sivgin, V.; Ozdemirkan, A.; Sezen, S.C.; Boyunaga, H.; Kucuk, A.; Gunes, I.; Arslan, M. The effect of cerium oxide on lung tissue in lower extremity ischemia reperfusion injury in sevoflurane administered rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 7481–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Li, S.; Chen, H. Macrophages in lung injury, repair, and fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, R.; Ito, T.; Tagami, T.; Takii, T.; Ozeki, T. Development of dried emulsion/mannitol composite microparticles through a unique spray nozzle for efficient delivery of hydrophilic anti-tuberculosis drug against alveolar macrophages. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.H.; Chen, H.I.; Jen, C.J. Exercise enhances surfactant-mediated phagocytosis in bronchoalveolar macrophages. Chin. J. Physiol. 2005, 48, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Voci, S.; Gagliardi, A.; Salvatici, M.C.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Influence of the dispersion medium and cryoprotectants on the physico-chemical features of gliadin- and zein-based nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Yi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. A green and highly efficient method to deliver hydrophilic polyphenols of salvia miltiorrhiza and carthamus tinctorius for enhanced anti-atherosclerotic effect via metal-phenolic network. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 215, 112511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S/N | Volume of CeO2 (μL) | Volume of Medicines (μL) | Volume of Tris-Hcl 8.8 (μL) | Volume of D-Mannitol (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 21 | 110 | 200 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F2 | 31 | 110 | 200 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F3 | 41 | 110 | 200 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F4 | 31 | 65 | 200 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F5 | 31 | 110 | 200 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F6 | 31 | 175 | 200 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F7 | 31 | 110 | 150 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F8 | 31 | 110 | 200 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F9 | 31 | 110 | 250 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F10 | 31 | 110 | 250 | 4 (10 mg/mL) |
| F11 | 31 | 110 | 250 | 4 (20 mg/mL) |
| F12 | 31 | 110 | 250 | 4 (40 mg/mL) |
| F13 | 31 | 110 | 250 | 4 (10 mg/mL) |
| S/N | Diameter (nm) | Polydispersity Index | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 259.3 ± 3.13 | 0.273 ± 0.02 | −16.5 ± 1.31 |
| F2 | 187.4 ± 4.93 | 0.170 ± 0.07 | −13.9 ± 0.80 |
| F3 | 321.2 ± 18.47 | 0.260 ± 0.03 | −30.8 ± 2.65 |
| F4 | 141.9 ± 1.17 | 0.175 ± 0.03 | −24.7 ± 2.50 |
| F5 | 163.9 ± 1.66 | 0.210 ± 0.02 | −24.8 ± 1.54 |
| F6 | 288.6 ± 4.29 | 0.302 ± 0.05 | −25.6 ± 0.85 |
| F7 | 156.2 ± 1.25 | 0.198 ± 0.81 | −17.9 ± 3.41 |
| F8 | 170.3 ± 3.68 | 0.265 ± 0.94 | −22.6 ± 2.11 |
| F9 | 138.5 ± 4.51 | 0.147 ± 0.65 | −23.5 ± 1.60 |
| F10 | 138.5 ± 4.51 | 0.147 ± 0.65 | −17.9 ± 3.41 |
| F11 | 170.3 ± 3.68 | 0.265 ± 0.94 | −22.6 ± 2.10 |
| F12 | 156.2 ± 1.25 | 0.198 ± 0.81 | −23.5 ± 1.61 |
| F13 | 156.5 ± 2.875 | 0.147 ± 0.043 | −23.5 ± 2.28 |
| Group | W/D |
|---|---|
| Control | 5.647 * |
| LPS | 6.659 |
| Dexamethasone | 5.716 * |
| MCQ/R | 5.591 * |
| Rutin | 5.847 * |
| Quercetin | 5.601 * |
| Rutin–Quercetin mixture | 5.767 * |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG | ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG |
| TLR4 | AGCTTCTCCAATTTTTCAGAACTTC | TGAGAGGTGGTGTAAGCCATGC |
| NLRP3 | ACCTCAACAGTCGCTACACG | ATGGTTTTCCCGATGCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, C.; Li, X. Synergistic Therapeutic Effects of D-Mannitol–Cerium–Quercetin (Rutin) Coordination Polymer Nanoparticles on Acute Lung Injury. Molecules 2024, 29, 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122819
Zhang Y, Wang H, Yang R, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Jiang C, Li X. Synergistic Therapeutic Effects of D-Mannitol–Cerium–Quercetin (Rutin) Coordination Polymer Nanoparticles on Acute Lung Injury. Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122819
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yusheng, Hong Wang, Ruiying Yang, Ying Zhang, Yao Chen, Cuiping Jiang, and Xianyu Li. 2024. "Synergistic Therapeutic Effects of D-Mannitol–Cerium–Quercetin (Rutin) Coordination Polymer Nanoparticles on Acute Lung Injury" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122819
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, H., Yang, R., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Jiang, C., & Li, X. (2024). Synergistic Therapeutic Effects of D-Mannitol–Cerium–Quercetin (Rutin) Coordination Polymer Nanoparticles on Acute Lung Injury. Molecules, 29(12), 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122819






