Acidity Constants of Boronic Acids as Simply as Possible: Experimental, Correlations, and Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Collecting acidity constant data for monosubstituted phenylboronic acids with simple substituents;
- -
- Checking correlations with corresponding compounds (carboxylic acids);
- -
- Checking correlations with data for solvents other than water;
- -
- Selection of the simplest methods for determining pKa;
- -
- Performing measurements for a series of missing compounds and assessing their accuracy;
- -
- Correlation checking using the above results as a uniform database.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Correlation of Acidity: Boronic vs. Benzoic Acids
- The substituent does not form intramolecular hydrogen bonds with the B-OH group. In this case, the steric hindrance makes it difficult to form a tetrahedral form, and the acidity of the compound is lower than that of the corresponding para isomer. This can be observed for such substituents as CH3, NO2, and OCF3, and the reduction in acidity is approximately by one pKa unit. A much stronger reduction occurs in the case of the bulk CF3 group—here, the change in pKa is over 2 pKa units. It is worth noting that the steric effect is opposite to that observed for carboxylic acids, where the acidity of the ortho isomer is higher than that of the para isomer.
- The substituent forms intramolecular bonds with the B-OH group. This occurs in the case of such substituents as F, CHO, and OR [54], and the acidity of the ortho isomer is higher than that of the para isomer by from 0.3 to 0.9 units. The increase in acidity can be explained by the stabilization of the tetrahedral form B(OH)3−, which has a more favorable hydrogen bond geometry than in the case of the planar B(OH)2 group.
2.2. Hammett Equation
2.3. Other Solvents
2.4. Determination of pKa Values of New Compounds: Comparison of Experimental Methods
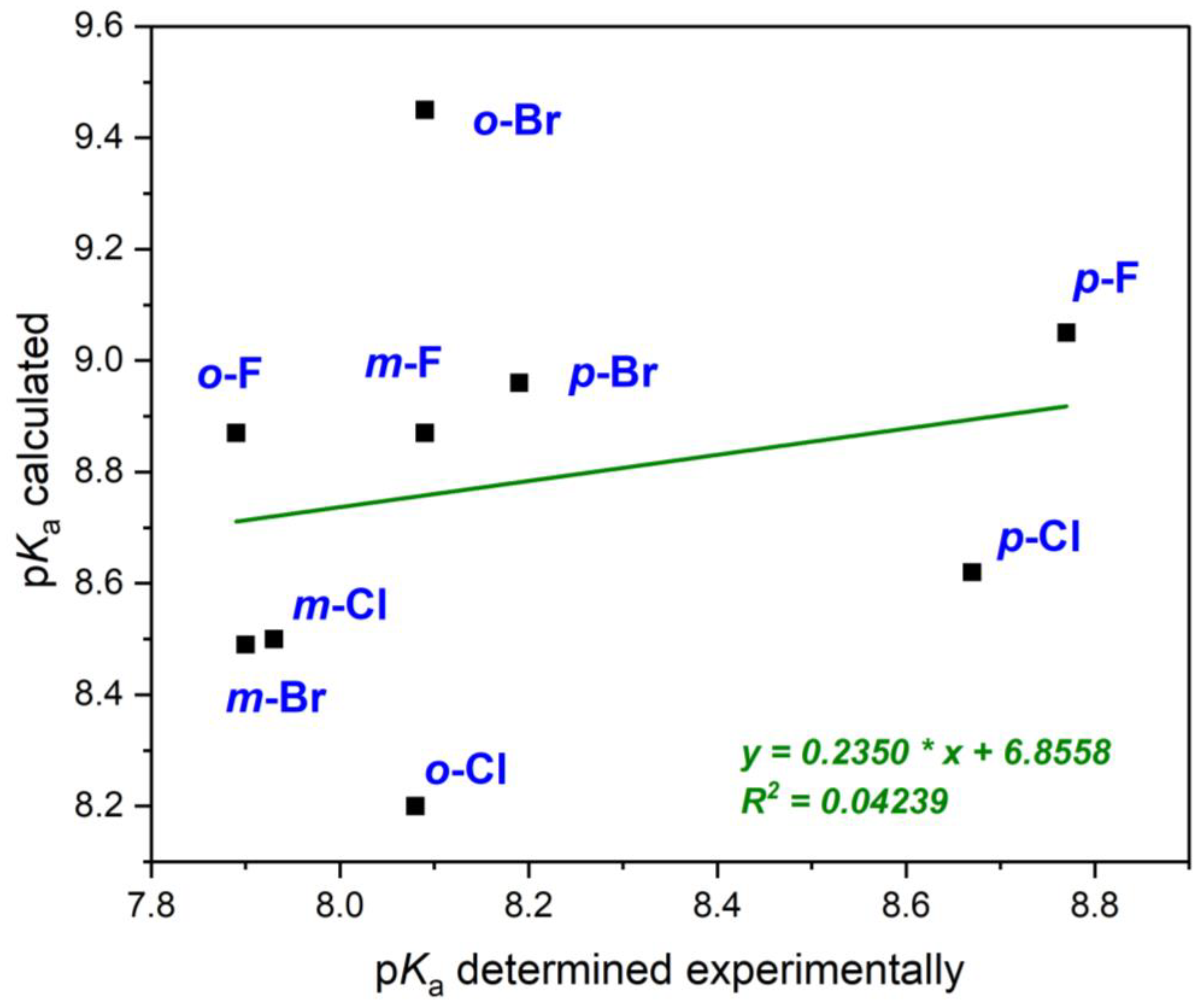
2.5. Determination of pKa by Calculations
3. Experimental
3.1. pKa Determination
3.2. Potentiometric Method P1
3.3. Potentiometric Method P2
3.4. Spectrophotometric Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, D.G. Boronic Acids: Preparation and Applications in Organic Synthesis, Medicine and Materials, 2nd ed.; Hall, D.G., Ed.; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; ISBN 9783527606542. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyabu, R.; Kubo, Y.; James, T.D.; Fossey, J.S. Boronic acid building blocks: Tools for sensing and separation. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk-Woźniak, A.; Borys, K.M.; Sporzyński, A. Recent Developments in the Chemistry and Biological Applications of Benzoxaboroles. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 5224–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk-Woźniak, A.; Sporzyński, A. Diboronic Acids and Their Derivatives: New Perspectives in Sensing and Materials’ Chemistry. In Advances in Materials Science Research; Wythers, M.C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 32, pp. 201–233. ISBN 978-1-53613-329-5. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, A. Cross-Coupling Reactions of Organoboranes: An Easy Way to Construct C-C Bonds (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6722–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, G.F.; Vilar, R.; Woscholski, R. Molecular recognition with boronic acids-applications in chemical biology. J. Chem. Biol. 2013, 6, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.-Y.; Wang, W. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs): From design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 548–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- António, J.P.M.; Russo, R.; Carvalho, C.P.; Cal, P.M.S.D.; Gois, P.M.P. Boronic acids as building blocks for the construction of therapeutically useful bioconjugates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3513–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, B.; Akhter, G.; Hamid, H.; Kesharwani, P.; Alam, M.S. Benzoxaboroles: New emerging and versatile scaffold with a plethora of pharmacological activities. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1252, 132057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.D.; Phillips, M.D.; Shinkai, S. Boronic Acids in Saccharide Recognition; James, T.D., Phillips, M.D., Shinkai, S., Eds.; RSC Publishing: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shmakov, M.M.; Prikhod’ko, S.A.; Panchenko, V.N.; Timofeeva, M.N.; Bardin, V.V.; Parmon, V.N.; Adonin, N.Y. The organoboron compounds: Their Lewis acidity and catalytic activity. Catal. Rev. 2024, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lebœuf, D.; Moran, J. Brønsted Acid and H-Bond Activation in Boronic Acid Catalysis. Chem.–Eur. J. 2020, 26, 9883–9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, P.; Greb, L. What Distinguishes the Strength and the Effect of a Lewis Acid: Analysis of the Gutmann–Beckett Method. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, X.-X.; Song, B.-N.; Huang, Y.-J.; Ouyang, W.-J.; Li, Z.; James, T.D.; Jiang, Y.-B. Direct sensing of fluoride in aqueous solutions using a boronic acid based sensor. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13987–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuchi, A.; Sakurai, J.; Tatebe, A.; Hattori, H.; Wada, H. Performance of arylboronic acids as ionophore for inorganic anions studied by fluorometry and potentiometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 387, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jańczyk, M.; Adamczyk-Woźniak, A.; Sporzyński, A.; Wróblewski, W. Organoboron compounds as Lewis acid receptors of fluoride ions in polymeric membranes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 733, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, U.; Gutmann, V.; Gerger, W. The acceptor number—A quantitative empirical parameter for the electrophilic properties of solvents. Monatshefte Chem./Chem. Mon. 1975, 106, 1235–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, V. Empirical parameters for donor and acceptor properties of solvents. Electrochim. Acta 1976, 21, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, M.A.; Strickland, G.C.; Holland, J.R.; Sukumar Varma, K. A convenient n.m.r. method for the measurement of Lewis acidity at boron centres: Correlation of reaction rates of Lewis acid initiated epoxide polymerizations with Lewis acidity. Polymer 1996, 37, 4629–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk-Woźniak, A.; Jakubczyk, M.; Sporzyński, A.; Żukowska, G. Quantitative determination of the Lewis acidity of phenylboronic catechol esters—Promising anion receptors for polymer electrolytes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2011, 14, 1753–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabroff, D.L.; Branch, G.E.K. Addition Compounds of Phenylboric Acid with Bases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933, 55, 1663–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporzyński, A.; Lewandowski, M.; Zarychta, B.; Zaleski, J. Complexes of Benzeneboronic Acid and Triphenylboroxin with Amines. Pol. J. Chem. 2005, 79, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Iovine, P.M.; Fletcher, M.N.; Lin, S. Condensation of Arylboroxine Structures on Lewis Basic Copolymers as a Noncovalent Strategy toward Polymer Functionalization. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6324–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemoz, K.M.; Franz, A.K. NMR Quantification of Hydrogen-Bond-Activating Effects for Organocatalysts including Boronic Acids. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 1126–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, M.; Baron, V.; Kalfus, K.; Pytela, O.; Vecera, M. Dissociation constants of substituted benzoic acids in water and in organic solvents. Collect. Czecholslovak Chem. Commun. 1986, 51, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortüm, G.; Vogel, W.; Andrussow, K. Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids in Aqueous Solutions; William Clowes and Sons Limited, Ed.; Butterworths: London, UK, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.; Taft, W. A survey of Hammett substituent constants and resonance and field parameters. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbelt, J.M.; Henrich, C.; Vanden Berg, S.G. Comparison of pKá Values Determined by Electrometric Titration and Ultraviolet Absorption Methods. Anal. Chem. 1954, 26, 726–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yue, D.; Lv, E.; Wu, L.; Qin, W. Reporter-Free Potentiometric Sensing of Boronic Acids and Their Reactions by Using Quaternary Ammonium Salt-Functionalized Polymeric Liquid Membranes. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, L.I.; Fyles, T.M.; James, T.D. Binary and ternary phenylboronic acid complexes with saccharides and Lewis bases. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11175–11190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torssell, K. Zur Kenntnis der Arylborsauren. 7. Komplexbildung Zwischen Phenylborsaure und Fruktose. Ark. Kemi 1957, 10, 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Branch, G.E.K.; Yabroff, D.L.; Bettman, B. The Dissociation Constants of the Chlorophenyl and Phenetyl Boric Acids1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektenova, G.A. Ionization constants of boronic acids and their complexation with diols. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 84, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, O.; Saeki, T.; Nagaoka, Y.; Fueno, T. Temperature-jump rate studies of the association reactions of boric and benzeneboronic acids with hydroxide ion. J. Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 1712–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clear, C.G.; Branch, G.E.K. The dissociation of hydrogen ions from the sulfates of aminophenylboronic acids. J. Org. Chem. 1938, 2, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahem, I.; Hammar, P.; Vesely, J.; Rios, R.; Eriksson, L.; Córdova, A. Organocatalytic asymmetric hydrophosphination of alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes: Development, mechanism and DFT calculations. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Matsumura, T.; Takao, N.; Yamagishi, H.; Takahashi, M.; Iwatsuki, S.; Ishihara, K. Fast trigonal/tetragonal interconversion followed by slow chelate-ring closure in the complexation of boronic acids. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2005, 358, 3355–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzeczańska, D.; Adamczyk-Woźniak, A.; Kulpa, A.; Ossowski, T.; Sporzyński, A. Fluorinated Boronic Acids: Acidity and Hydrolytic Stability of Fluorinated Phenylboronic Acids. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 4493–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkkilä, A.; Saario, S.M.; Käsnänen, H.; Leppänen, J.; Poso, A.; Nevalainen, T. Discovery of Boronic Acids as Novel and Potent Inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7057–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Springsteen, G.; Deeter, S.; Wang, B. The relationship among pKa, pH, and binding constants in the interactions between boronic acids and diols—It is not as simple as it appears. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11205–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westmark, P.R.; Gardiner, S.J.; Smith, B.D. Selective Monosaccharide Transport through Lipid Bilayers Using Boronic Acid Carriers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11093–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshikawa, T.; Pochamroen, S.; Takai, N.; Ida, N.; Takemoto, T.; Yamashita, M. Molecular Recognition and Resolution of Geometrical Isomers of Benzoic Acids by Brucine. Heterocycl. Commun. 2002, 8, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zoubi, R.M.; Marion, O.; Hall, D.G. Direct and Waste-Free Amidations and Cycloadditions by Organocatalytic Activation of Carboxylic Acids at Room Temperature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2876–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widequist, S. On the stability of the cyanobenzoic acids in aqueous solution. Ark. Kemi 1951, 383–387. [Google Scholar]
- Kilinc, E. Resistance of Acetyl-, Formyl-, and Methoxy-Phenylboronic Acids to Boroxine Formation and Their Employment in Fluoride Determination of Dental Formulations and Beverages by Fluorescence Quenching. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2024, 90, 1358–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torssell, K.; McClendon, J.H.; Somers, G.F. Chemistry of Arylboric Acids VIII. The Relationship between Physico-chemical Properties and Activity in Plants. Acta Chem. Scand. 1958, 12, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirouflet, J. Cinetique de louverture et de la fermeture des cycles lactoniques—Influences structurales. 3. Lactonisation des acides ortho-methylolbenzoiques. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1954, 21, 769–770. [Google Scholar]
- Mock, W.L.; Morsch, L.A. Low barrier hydrogen bonds within salicylate mono-anions. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytela, O.; Kulhánek, J. Ortho Effect in Dissociation of Benzoic Acids with Electron-Accceptor Substituents Using the AISE Theory; Relation to para Substitution and Solvent. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 2002, 67, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiadjiev, S.E.; Lightner, D.A. Carboxylic acid ionization constants by 19F NMR spectroscopy. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 1999, 12, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yu, Z.; Wen, S.; Ni, H.; Ullah, N.; Lan, Y.; Lu, Y. Chiral phosphine-mediated intramolecular [3 + 2] annulation: Enhanced enantioselectivity by achiral Brønsted acid. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 5196–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozdalik, J.T.; Marek, P.H.; Madura, I.D.; Gierczyk, B.; Popenda, Ł.; Schroeder, G.; Adamczyk-Woźniak, A.; Sporzyński, A. Structures and properties of trifluoromethylphenylboronic acids. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1180, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk-Woźniak, A.; Gozdalik, J.T.; Kaczorowska, E.; Durka, K.; Wieczorek, D.; Zarzeczańska, D.; Sporzyński, A. (Trifluoromethoxy)Phenylboronic Acids: Structures, Properties, and Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, a2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk-Woźniak, A.; Sporzyński, A. The influence of ortho-substituents on the properties of phenylboronic acids. J. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 913, a121202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffé, H.H. A Reëxamination of the Hammett Equation. Chem. Rev. 1953, 53, 191–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.B.; March, J. March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sporzyński, A.; Leszczyński, P. Solubility of phenylboronic compounds in water. Mediterr. J. Chem. 2017, 6, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomsho, J.W.; Benkovic, S.J. Examination of the reactivity of benzoxaboroles and related compounds with a cis-diol. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 11200–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fini, A.; De Maria, P.; Guarnieri, A.; Varoli, L. Acidity Constants of Sparingly Water-Soluble Drugs from Potentiometric Determinations in Aqueous Dimethyl Sulfoxide. J. Pharm. Sci. 1987, 76, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, P.A.; Reid, M.; Leach, A.G.; Campbell, A.D.; King, E.J.; Lloyd-Jones, G.C. Base-Catalyzed Aryl-B(OH)2 Protodeboronation Revisited: From Concerted Proton Transfer to Liberation of a Transient Aryl Anion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13156–13165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrowicki, J.; Liwo, A. Determination of equilibrium parameters by minimization of an extended sum of squares. Talanta 1990, 37, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrowicki, J.; Liwo, A. DECFAM—A new computer oriented algorithm for the determination of equilibrium constants from potentionmetric and/or spectrophotometric measurements—I: Basic principles of the method and calculations of equilibrium concentrations. Comput. Chem. 1984, 8, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrowicki, J.; Liwo, A. DECFAM—A new computer oriented algorithm for the determination of equilibrium constants from potentiometric and/or spectrophotometric measurements—II: Methods based on analytical expressions. Comput. Chem. 1984, 8, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.A.; Dhar, D.; Elgrishi, N.; Kandemir, B.; McWilliams, S.F.; Howland, W.C.; Chen, C.-H.; Dempsey, J.L. Redox-Induced Structural Reorganization Dictates Kinetics of Cobalt(III) Hydride Formation via Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 3393–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.K.; Hall, D.G.; Hooper, T.N.; Ingleson, M.J.; Ishid, N.; Ishihara, K.; Jakle, F.; Johnson, H.C.; Lee, S.; Leonori, D.; et al. Topic in Organometallic Chemistry 49—Synthesis and Applications of Organoboron Compounds; Whiting, E., Fernández, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kheirjou, S.; Abedin, A.; Fattahi, A. Theoretical descriptors response to the calculations of the relative pKa values of some boronic acids in aqueous solution: A DFT study. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2012, 1000, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylewska, A.; Jacewicz, D.; Zarzeczańska, D.; Chmurzyński, L. Determination of dissociation constants for coordination compounds of Cr(III) and Co(III) using potentiometric and spectrophotometric methods. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2008, 40, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| X | 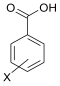 Benzoic Benzoic |  Boronic Boronic | Hammett Const. [27] | |||||
| H | 4.21 [25], 4.16 [28] | 8.9 [29], 8.7 [30], 8.64 [31], 8.86 [32], | ||||||
| 8.72 [21], 8.90 [33], 8.70 [34] | ||||||||
| ortho | meta | para | ortho | meta | para | meta | para | |
| OH | 2.85 [28] | 4.09 [25] | 4.59 [25] | 8.55 [35] | 0.12 | −0.37 | ||
| 3.94 [28] | 4.48 [28] | |||||||
| F | 3.27 [36] | 3.88 [25] | 4.16 [25] | 7.83 [37] | 7.50 [37] | 8.66 [37] | 0.34 | 0.06 |
| 7.89 [38] | 8.09 [38] | 8.77 [38] | ||||||
| 7.85 [38] | 8.15 [38] | 8.71 [38] | ||||||
| 8.7 [39] | 8.6 [40] | |||||||
| 9.1 [41] | ||||||||
| 9.0 [39] | ||||||||
| Cl | 2.94 [42] | 3.82 [42] | 3.98 [42] | 8.3 [29] | 0.37 | 0.23 | ||
| 3.01 [28] | 3.70 [28] | 4.00 [28] | ||||||
| 3.84 [25] | 4.00 [25] | |||||||
| Br | 2.85 [42] | 3.81 [42] | 4.00 [25] | 8.8 [40] | 0.39 | 0.23 | ||
| 2.81 [28] | 3.78 [28] | 3.93 [28] | ||||||
| 3.99 [25] | ||||||||
| I | 2.84 [28] | 3.79 [28] | 3.98 [28] | 8.9 [43] | 0.35 | 0.18 | ||
| 3.88 [25] | 4.00 [25] | |||||||
| CN | 3.14 [44] | 3.59 [25] | 3.5 [25] | 7.5 [39] | 7.7 [39] | 0.56 | 0.66 | |
| CH3 | 3.81 [28] | 4.24 [28] | 4.36 [28] | 9.7 [29] | 9.0 [29] | 9.3 [29] | −0.07 | −0.17 |
| 4.27 [25] | 4.35 [25] | 9.00 [33] | 9.26 [33] | |||||
| 8.74 [34] | 8.95 [34] | |||||||
| OCH3 | 4.02 [28] | 3.92 [28] | 4.41 [28] | 9.0 [45] | 8.7 [45] | 9.3 [45] | 0.12 | −0.27 |
| 4.12 [25] | 4.49 [25] | 9.0 [40] | 8.5 [40] | 9.3 [29] | ||||
| 9.0 [39] | 8.7 [41] | 9.32 [46] | ||||||
| 9.7 [29] | 8.4 [39] | |||||||
| CHO | 4.56 [47] | 3.77 [48] | 7.3 [45] | 7.5 [45] | 7.7 [45] | 0.35 | 0.42 | |
| 4.5 [49] | 7.31 [46] | 7.8 [40] | 7.6 [40] | |||||
| 7.80 [46] | 7.80 [46] | |||||||
| COCH3 | 3.86 [25] | 3.74 [25] | 8.0 [45] | 7.7 [45] | 0.38 | 0.50 | ||
| 8.0 [40] | 7.7 [40] | |||||||
| NO2 | 2.17 [42] | 3.45 [42] | 3.44 [42] | ca. 8.5 [46] | 7.1 [40] | 7.4 [39] | 0.71 | 0.78 |
| 2.14 [28] | 3.50 [25] | 3.40 [25] | 7.3 [46] | 7.15 [46] | ||||
| CF3 | 2.73 [50] | 3.75 [25] | 3.77 [51] | 9.58 [52] | 7.88 [52] | 7.39 [37] | 0.43 | 0.54 |
| 3.90 [50] | 3.77 [50] | 9.45 [52] | 7.85 [52] | 8.1 [39] | ||||
| 8.5 [39] | 7.87 [37] | 7.82 [52] | ||||||
| 7.9 [39] | 7.90 [52] | |||||||
| OCF3 | 9.53 [53] | 7.79 [53] | 8.11 [53] | 0.38 | 0.35 | |||
| 9.49 [53] | 7.96 [53] | 8.03 [53] | ||||||
| Substituent | pKa H2O (Spectr) | pKa H2O (Pot) | pKa H2O/Dioxane |
|---|---|---|---|
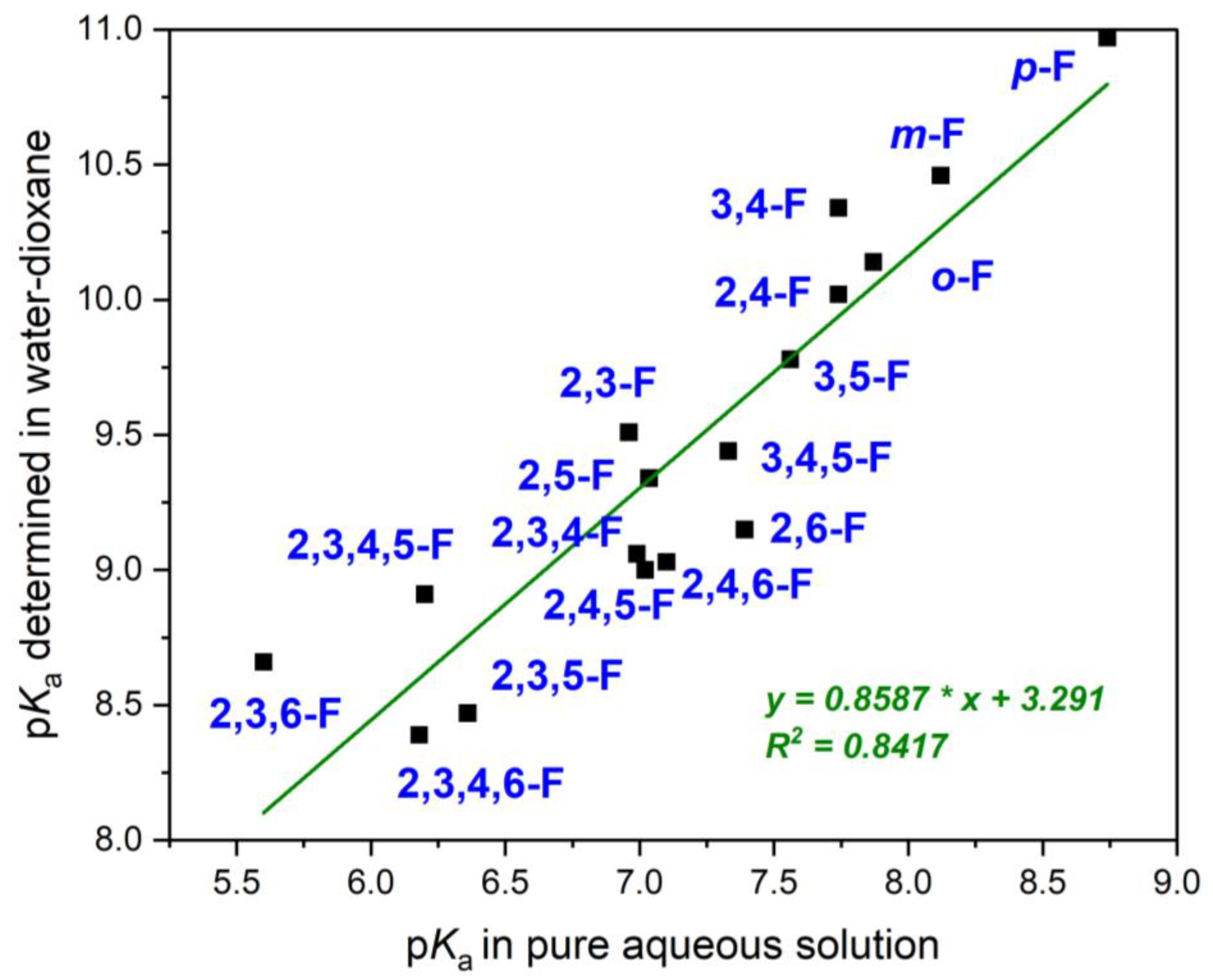
| 2F | 7.89 | 7.85 | 10.14 |
| 3F | 8.09 | 8.15 | 10.46 |
| 4F | 8.77 | 8.71 | 10.97 |
| 2,3F | 6.99 | 6.93 | 9.51 |
| 2,4F | 7.75 | 7.73 | 10.02 |
| 2,5F | 7.06 | 7.01 | 9.34 |
| 2,6F | 7.37 | 7.41 | 9.15 |
| 3,4F | 7.74 | - | 10.34 |
| 3,5F | 7.60 | 7.52 | 9.78 |
| 2,3,4F | 6.97 | 7.01 | 9.06 |
| 2,3,5F | 6.34 | 6.38 | 8.47 |
| 2,3,6F | 5.60 | - | 8.66 |
| 2,4,5F | 7.06 | 6.98 | 9.00 |
| 2,4,6F | 7.10 | - | 9.03 |
| 3,4,5F | 7.34 | 7.32 | 9.44 |
| 2,3,4,5F | 6.23 | 6.17 | 8.91 |
| 2,3,4,6F | 6.17 | 6.19 | 8.39 |
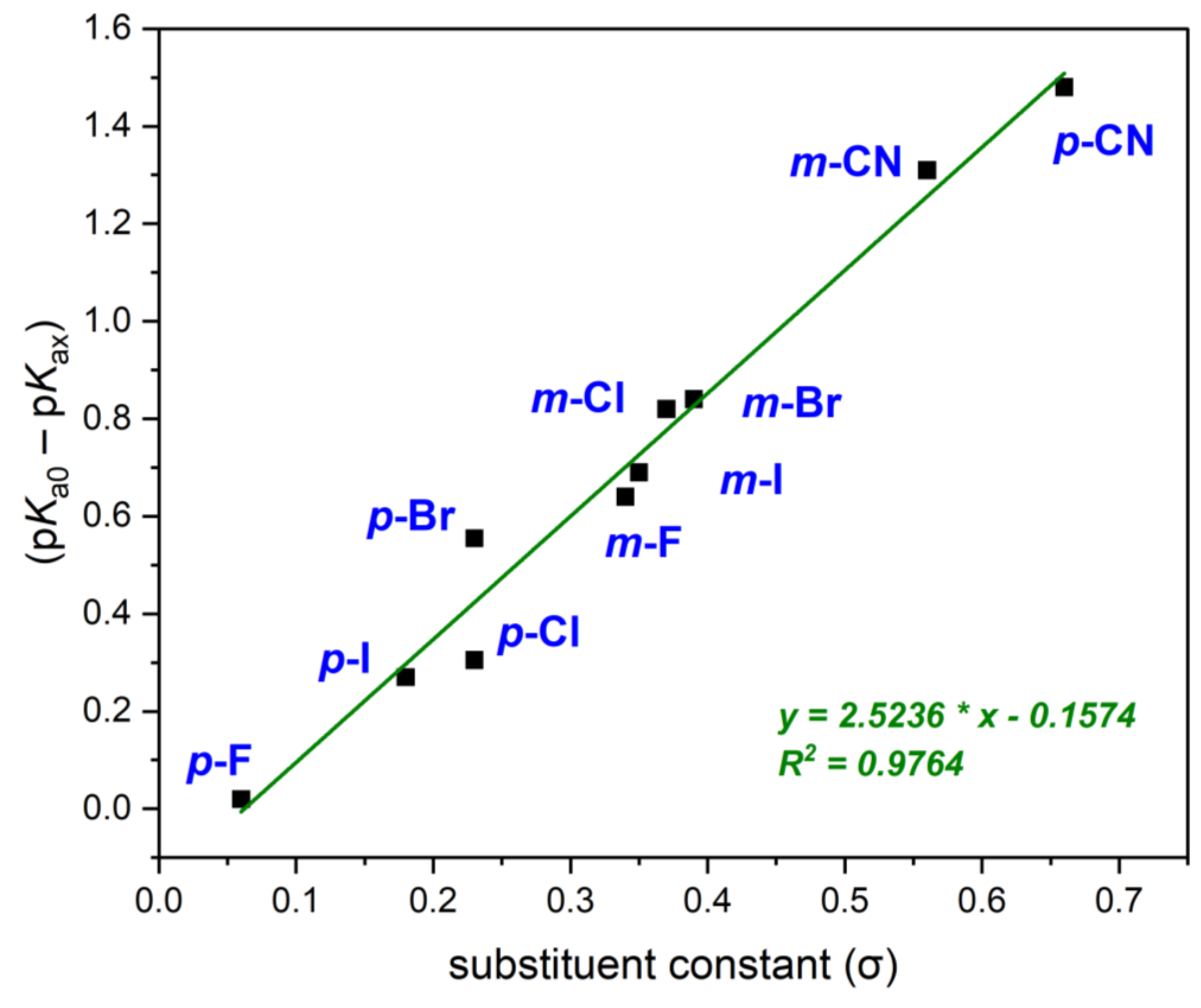
| Substituent | Position | pKa | Hammett Constant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrophotometric S | Potentiometric P1 | Potentiometric P2 | |||
| F * | ortho | 7.89 ± 0.01 | 7.85 ± 0.07 | - | - |
| meta | 8.09 ± 0.01 | 8.15 ± 0.11 | - | 0.34 | |
| para | 8.77 ± 0.01 | 8.71 ± 0.10 | - | 0.06 | |
| Cl | ortho | 8.08 ± 0.01 | 8.07 ± 0.02 | 7.96 ± 0.02 | - |
| meta | 7.93 ± 0.02 | 7.95 ± 0.03 | 7.81 ± 0.01 | 0.37 | |
| para | 8.67 ± 0.04 | 8.24 ± 0.04 | 8.17 ± 0.02 | 0.23 | |
| Br | ortho | 8.09 ± 0.03 | 8.18 ± 0.03 | 8.04 ± 0.03 | - |
| meta | 7.90 ± 0.04 | 7.94 ± 0.03 | 7.77 ± 0.01 | 0.39 | |
| para | 8.19 ± 0.01 | 8.22 ± 0.05 | 8.19 ± 0.03 | 0.23 | |
| I | ortho | 8.63 ± 0.03 | 8.51 ± 0.04 | 7.92 ± 0.02 | - |
| meta | 8.13 ± 0.05 | 8.01 ± 0.03 | 7.79 ± 003 | 0.35 | |
| para | 8.56 ± 0.01 | 8.42 ± 0.05 | 8.06 ± 0.01 | 0.18 | |
| CN | ortho | 7.01 ± 0.10 | 6.89 ± 0.08 | - | - |
| meta | 7.50 ± 0.02 | 7.40 ± 0.04 | 0.56 | ||
| para | 7.32 ± 0.04 | 7.24 ± 0.04 | 0.66 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sporzyński, A.; Adamczyk-Woźniak, A.; Zarzeczańska, D.; Gozdalik, J.T.; Ramotowska, P.; Abramczyk, W. Acidity Constants of Boronic Acids as Simply as Possible: Experimental, Correlations, and Prediction. Molecules 2024, 29, 2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112713
Sporzyński A, Adamczyk-Woźniak A, Zarzeczańska D, Gozdalik JT, Ramotowska P, Abramczyk W. Acidity Constants of Boronic Acids as Simply as Possible: Experimental, Correlations, and Prediction. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112713
Chicago/Turabian StyleSporzyński, Andrzej, Agnieszka Adamczyk-Woźniak, Dorota Zarzeczańska, Jan T. Gozdalik, Paulina Ramotowska, and Wiktoria Abramczyk. 2024. "Acidity Constants of Boronic Acids as Simply as Possible: Experimental, Correlations, and Prediction" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112713
APA StyleSporzyński, A., Adamczyk-Woźniak, A., Zarzeczańska, D., Gozdalik, J. T., Ramotowska, P., & Abramczyk, W. (2024). Acidity Constants of Boronic Acids as Simply as Possible: Experimental, Correlations, and Prediction. Molecules, 29(11), 2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112713







