In Vitro Investigations into the Potential Drug Interactions of Pseudoginsenoside DQ Mediated by Cytochrome P450 and Human Drug Transporters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inhibitory Effects of PDQ on CYP450 Enzymes
2.1.1. Inhibition of Positive Control Inhibitors against CYP450
2.1.2. Inhibition Effects of PDQ on CYP450 Enzymes
2.2. Inhibitory Effects of PDQ on Drug Transporters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Inhibition of CYP450 Enzymes
4.2. Inhibition of Human Drug Transporters
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, L.; Wang, C.; Yuan, C. Ginsenosides from American ginseng: Chemical and pharmacological diversity. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, L.; Peng, W.; Ma, S.; Zhu, C.; Fu, F.; Heinbockel, T. Ginseng derivative ocotillol enhances neuronal activity through increased glutamate release: A possible mechanism underlying increased spontaneous locomotor activity of mice. Neuroscience 2011, 195, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, W.; Ye, Q. Anti-inflammatory and anti-gouty-arthritic effect of free Ginsenoside Rb1 and nano Ginsenoside Rb1 against MSU induced gouty arthritis in experimental animals. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 332, 109285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jung, Y.; Kim, K.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, H.; Wang, B.; Quan, F.; Kang, S. Antiviral activity of fermented ginseng extracts against a broad range of influenza viruses. Viruses 2018, 10, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Guan, X.; Guo, S.; Li, C.; Niu, R.; Gao, J.; Jiang, M.; Bai, L.; Leung, E.L.; et al. 20(S)-protopanaxatriol promotes the binding of P53 and DNA to regulate the antitumor network via multiomic analysis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 1020–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, J. The Semisynthesis Method and Drug Use of Pseudo-Ginsengenin DQ. China Patent CN200510016774.4, 6 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y. Pseudo-ginsengenin DQ ameliorated aconitine-induced arrhythmias by influencing Ca2+ and K+ currents in ventricular myocytes. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 25999–26005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Lin, M.; Han, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, J. Determination of Pseudoginsengenin DQ in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and application of the method in a pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2013, 933, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Bi, Y.; Jiang, N. Study on the structure-function relationship of 20(S)-panaxadiol and its epimeric derivatives in myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Yang, G.; Guo, M.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Yang, Q.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.; Fang, X.; et al. Design, synthesis, and discovery of ocotillol-type amide derivatives as orally available modulators of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Liu, J.; Li, P. Pseudoginsengenin DQ exhibits therapeutic effects in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via Sirt1/NF-kappaB and caspase signaling pathway without compromising its antitumor activity in mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H. The Pharmacokinetic Study of PPD1 Guttate Pills. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration. In Vitro Drug Interaction Studies—Cytochrome P450 Enzyme- and Transporter-Mediated Drug Interactions; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; O’Barr, S.A.; Wong, R.A.; Yeung, S.; Chow, M.S. Ginseng and anticancer drug combination to improve cancer chemotherapy: A critical review. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014, 168940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Jin, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, H.; Xu, X.; He, S.; Chen, S.; Hou, W.; Guo, Q.; Hua, B. Ginsenoside Rg3 serves as an adjuvant chemotherapeutic agent and VEGF inhibitor in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 7826753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.W. Inhibitory effect of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 on human platelet aggregation and intracellular Ca2+ levels via cyclic adenosine monophosphate dependent manner. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2018, 23, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Pang, H.; Du, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Q. Effect of Panax notoginseng saponins on the pharmacokinetics of aspirin in rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1040, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Ma, J.; Li, T.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, N.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Shao, J.; Jia, L. Global deregulation of ginseng products may be a safety hazard to warfarin takers: Solid evidence of ginseng-warfarin interaction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5813–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.S.; Wei, G.; Dey, L.; Karrison, T.; Nahlik, L.; Maleckar, S.; Kasza, K.; Ang-Lee, M.; Moss, J. Brief communication: American ginseng reduces warfarin’s effect in healthy patients: A randomized, controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Dong, J.; Li, X.; Du, F.; Jia, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Niu, W.; Li, C. Molecular mechanisms governing different pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides and potential for ginsenoside-perpetrated herb-drug interactions on OATP1B3. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, S.J.; Kang, W.Y.; Heo, J.K.; Jo, J.; Choi, W.G.; Liu, K.H.; Lee, S.; Choi, M.K.; Han, Y.H.; Lee, H.S.; et al. A comprehensive in vivo and in vitro assessment of the drug interaction potential of red ginseng. Clin. Ther. 2018, 40, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogacz, A.; Karasiewicz, M.; Dziekan, K.; Procyk, D.; Górska-puakszta, M.; Kowalska, A.; Mikolajczak, P.; Ozarowski, M.; Czerny, B. Impact of Panax ginseng and ginkgo biloba extracts on expression level of transcriptional factors and xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome p450 enzymes. Herba. Pol. 2016, 62, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H. Gut microbiota-mediated pharmacokinetics of ginseng saponins. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. Cytochrome P450-mediated cardiovascular drug interactions. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2011, 7, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sossalla, S.; Vollmann, D. Arrhythmia-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2018, 115, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deodhar, M.; Rihani, S.B.A.; Arwood, M.J.; Darakjian, L.; Dow, P.; Turgeon, J.; Michaud, V. Mechanisms of CYP450 inhibition: Understanding drug-drug interactions due to mechanism-based inhibition in clinical practice. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, D.A.; Balimane, P.V. Application of in vitro CYP and transporter assays to predict clinical drug–drug interactions. Bioanalysis 2018, 10, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Ding, S.; Liang, S.; Wu, X.; Lie, Z.; Zhou, G. Effects of atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, and pravastatin on antiplatelet activity of clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndrome and different CYP2C19 genotypes. Chin. Pharm. J. 2019, 54, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar]
- Dansette, P.M.; Rosi, J.; Bertho, G.; Mansuy, D. Cytochromes P450 catalyze both steps of the major pathway of clopidogrel bioactivation, whereas paraoxonase catalyzes the formation of a minor thiol metabolite isomer. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornio, A.; Backman, J.T. Cytochrome P450 in pharmacogenetics: An update. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018, 83, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Braun, M.M.; Stevens, W.A.; Barstow, C.H. Stable coronary artery disease: Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2018, 97, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, W. Inhibitory effects of Dansette cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4 by extracts and alkaloids of Gelsemium elegans roots. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 166, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.R.; Wang, Y.; Cai, R.Z.; Lin, R.; Sun, H.; Liu, J. Association of cytochrome P450 2C19 polymorphisms with coronary heart disease risk: A protocol for systematic review and meta analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e23652–e23657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.E.; Halpert, J.R. Structures of cytochrome P450 3A4. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrychova, T.; Anzenbacherova, E.; Hudecek, J.; Skopalik, J.; Lange, R.; Hildebrandt, P.; Otyepka, M.; Anzenbacher, P. Flexibility of human cytochrome P450 enzymes: Molecular dynamics and spectroscopy reveal important function-related variations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1814, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirghani, R.A.; Yasar, U.; Zheng, T.; Cook, J.M.; Gustafsson, L.L.; Tybring, G.; Ericsson, O. Enzyme kinetics for the formation of 3-hydroxyquinine and three new metabolites of quinine in vitro; 3-hydroxylation by CYP3A4 is indeed the major metabolic pathway. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 1368–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, T. The Correlation Analysis of mRNA, Protein and the Rate of Nifedipine Metabolism by Cytochrome P450 3A4 in Chinese Human Liver Microsomes. Master Thesis, Northeast University, Xi’an, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sohns, C.; Zabel, M. Current role of amiodarone in antiarrhythmic therapy. Herzschrittmacherther. Elektrophysiol. 2010, 21, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.T.; Liu, D.; Song, C.L.; Zhu, Y.L. Study on Transport Mechanism of Amiodarone and Effect of Atorvastatin on Transport of Amiodarone by Caco-2 Cell Monolayer Model. Eval. Anal. Medicat. Chin. Hosp. 2016, 16, 1472–1474. [Google Scholar]

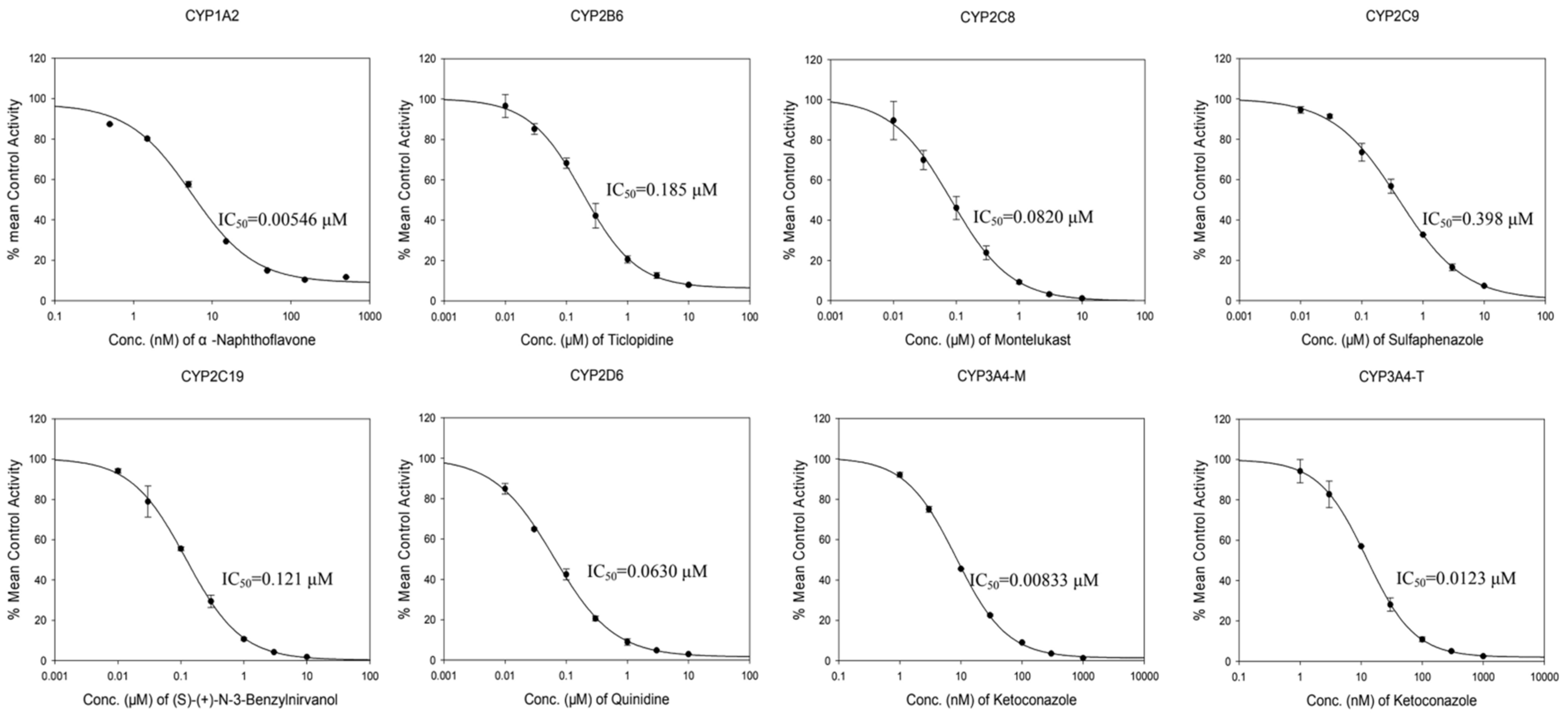


| CYP Isoform | Positive Control Inhibitor | Positive Control Inhibitor IC50/μM | PDQ IC50/µM |
|---|---|---|---|
| CYP1A2 | α-naphthoflavone | 0.00546 | >100.0 |
| CYP2B6 | ticlopidine | 0.185 | 45.3 |
| CYP2C8 | montelukast | 0.082 | 16.4 |
| CYP2C9 | sulfaphenazole | 0.398 | 11.7 |
| CYP2C19 | (S)-(+)-N-3-benzylnirvanol | 0.121 | 0.698 |
| CYP2D6 | quinidine | 0.063 | 52.0 |
| CYP3A4 (Midazolam) | ketoconazole | 0.00833 | 2.02 |
| CYP3A4 (Testosterone) | ketoconazole | 0.0123 | 6.79 |
| Transporter | Positive Control Inhibitor (PCI) | PCI Conc./µM | Percentage Inhibition of PCI | PDQ IC50/μM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hBCRP | Ko143 | 10 | 14.1 | 1.08 |
| hOAT1 | Probenecid | 100 | 18.0 | >30 |
| hOAT3 | Probenecid | 100 | 21.5 | >30 |
| hOATP1B1 | Rifampicin | 60 | 18.5 | 13.06 |
| hOATP1B3 | Rifampicin | 60 | 20.2 | >30 |
| hOCT2 | Cimetidine | 600 | 42.7 | >30 |
| hMDR1(P-gp) | Verapamil | 10 | 26.9 | 0.41 |
| CYP Isoform | Probe Substrate (conc./µM) | Positive Control Inhibitor | Metabolic Analyte |
|---|---|---|---|
| CYP1A2 | phenacetin (75) | α-naphthoflavone | acetaminophen |
| CYP2B6 | bupropion (80) | ticlopidine | hydroxybupropion |
| CYP2C8 | amodiaquine (2) | montelukast | N-desethylamodiaquine |
| CYP2C9 | diclofenac (10) | sulfaphenazole | 4′-hydroxydiclofenac |
| CYP2C19 | S-mephenytoin (20) | (S)-(+)-N-3-benzylnirvanol | (±)4′-hydroxymephenytoin |
| CYP2D6 | dextromethorphan (10) | quinidine | dextrorphan |
| CYP3A4 | midazolam (2) | ketoconazole | 1′-hydroxymidazolam |
| CYP3A4 | testosterone (40) | ketoconazole | 6β-hydroxytestosterone |
| CYP Isoform | Incubation Time/min | Internal Standard (conc./µM) | Supernatant: Water (v/v) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CYP1A2 | 10 | acetaminophen-d4 (0.6) | 1:3 |
| CYP2B6 | 10 | hydroxybupropion-d6 (0.32) | 1:10 |
| CYP2C8 | 10 | N-desethylamodiaquine-d5 (1.8) | 1:29 |
| CYP2C9 | 10 | 4′-hydroxydiclofenac-d4 (0.8) | 1:7 |
| CYP2C19 | 20 | (±)4′-hydroxymephenytoin-d3 (0.08) | 2:1 |
| CYP2D6 | 20 | dextrorphan-d3 (0.16) | 1:9 |
| CYP3A4 | 3 | 1′-hydroxymidazolam-13C3 (0.4) | 1:3 |
| CYP3A4 | 10 | 6β-hydroxytestosterone-d7 (6.4) | 1:3 |
| Transporter | Radiolabeled Substrate | Substrate conc./µM | Positive Control Inhibitor | Inhibitor conc./µM | Incubation Time/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hBCRP | 3H-ES | 1 | Ko143 | 10 | 5 |
| hOAT1 | 14C-PAH | 5 | Probenecid | 100 | 2 |
| hOAT3 | 3H-ES | 0.05 | Probenecid | 100 | 2 |
| hOATP1B1 | 3H-ES | 0.1 | Rifampicin | 60 | 2 |
| hOATP1B3 | 3H-EG | 1 | Rifampicin | 60 | 2 |
| hOCT2 | 14C-TEA | 5 | Cimetidine | 600 | 5 |
| hMDR1(P-gp) | 3H-Digoxin | 25 | Verapamil | 10 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Feng, H. In Vitro Investigations into the Potential Drug Interactions of Pseudoginsenoside DQ Mediated by Cytochrome P450 and Human Drug Transporters. Molecules 2024, 29, 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112482
Li Z, Wang C, Liu J, Li P, Feng H. In Vitro Investigations into the Potential Drug Interactions of Pseudoginsenoside DQ Mediated by Cytochrome P450 and Human Drug Transporters. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112482
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhuo, Cuizhu Wang, Jinping Liu, Pingya Li, and Hao Feng. 2024. "In Vitro Investigations into the Potential Drug Interactions of Pseudoginsenoside DQ Mediated by Cytochrome P450 and Human Drug Transporters" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112482
APA StyleLi, Z., Wang, C., Liu, J., Li, P., & Feng, H. (2024). In Vitro Investigations into the Potential Drug Interactions of Pseudoginsenoside DQ Mediated by Cytochrome P450 and Human Drug Transporters. Molecules, 29(11), 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112482







