Abstract
The main varieties of Echinopsis Radix recorded in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia are the roots of Echinops latifolius Tausch or Echinops grijsii Hance. However, the chemical constituents and biological activities of this herb have not been reviewed. In order to clarify the chemical constituents of the main varieties of this herb and improve the quality of Chinese medicinal material resources, this paper systematically reviewed their chemical constituents and related biological activities. Phytochemical investigations reveal eighty-five compounds including fort y-nine thiophenes (1–49), eight flavonoids (50–57), seven caffeic acids and its derivatives (58–64), eight sesquiterpenoids (65–72), and thirteen triterpenoids and other compounds (73–85) were reported from Echinopsis Radix. The review of biological activities suggests that thiophenes are the main secondary metabolites of the medicinal material which exert antitumor, insecticidal and antifungal activities. In addition, caffeic acid and its derivatives and sesquiterpenes are potential active ingredients worthy of further study. This review provides an important scientific basis for the development of active ingredients and resource quality evaluation of Echinopsis Radix.
1. Introduction
As is known to all, the Asteraceae family is one of the biggest families in the world. And the related reports have revealed that it comprises 1000 genera and 25,000–30,000 species, which are widely distributed around the world [1]. Among them, there are over 200 genera and 2000 species in China, and widely distributed throughout the country. It is worth noting that the Asteraceae plant “Loulu”, as a traditional Chinese medicine, has a long history of application in classic prescriptions. As reported, it is commonly used in clinical practice for breast abscess swelling and pain, carbuncle and back pain, scrofula toxin, milk obstruction, and dampness and numbness [2,3]. However, for many years, there has been controversy over the textual research of “Loulu”, especially “Qizhou Loulu” and “Yuzhou Loulu”. Modern researches have shown that “Qizhou Loulu” and “Yuzhou Loulu” are plants of the same family but different genera, and their active ingredients and pharmacological effects are different. Therefore, the two mentioned plants above are recorded separately in the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, namely, “Loulu” refers to the dry roots of Rhaponticum uniflorum (L.) DC., which is the genus Rhaponticum, and “Yuzhou Loulu” also named Echinopsis Radix refers to the dry roots of Echinops latifolius Tausch or Echinops grijsii Hance, which is the genus Echinops [4,5,6]. As is well known, the chemical composition and biological activity of traditional Chinese medicine are important indicators for identifying and evaluating the quality of medicinal materials. However, there is currently no systematic review on the chemical composition and biological activity of Echinopsis Radix (“Yuzhou Loulu”).
As a famous folk medicine, Echinopsis Radix is a perennial herbaceous plant. And it is widely distributed in Gansu, Hebei, Henan, and Liaoning provinces of China. It can exert functions such as clearing heat and detoxifying, expelling pus and stopping bleeding, and eliminating carbuncle and lower breast. It is mainly used for the treatment of ulcers, abscesses, skin heat toxicity, and milk obstruction. According to the description of Echinopsis Radix (“Yuzhou Loulu”) in the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the plants also include Echinops latifolius Tausch and Echinops grijsii Hance [7,8]. Furthermore, it is worth mentioning that in the Flora of China, the Latin name for “Echinops latifolius Tausch” has now been revised to Echinops davuricus Fisch. ex Hornem [9]. In recent years, there have been increasing reports on the chemical composition and biological activity of Echinopsis Radix, but there is no review report on this medicinal herb. In summary, this paper provides a review of the chemical components and biological activities reported in the key varieties of Echinopsis Radix, with the aim of providing reference for resource quality evaluation and further development of novel natural lead compounds in Echinopsis Radix.
2. Methodology
The relevant studies were searched through PubMed, Web of science, Scienfinder, Google Scholar, Wanfang, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure databases. Firstly, Echinopsis Radix (“Yuzhou Loulu”), chemical composition, and biological activity were used as key words for retrieval, and the search time was set to within 10 years. The results showed that there were no comprehensive reports on the chemical composition and biological activity of Echinopsis Radix (“Yuzhou Loulu”). Subsequently, papers from the past 20 years have been indexed with Echinopsis Radix (“Yuzhou Loulu”), Echinops latifolius Tausch, Echinops grijsii Hance, and Echinops davuricus Fisch. ex Hornem as key words. Moreover, chemical composition and biological activity were further screened as keywords. Then, the chemical composition is classified and summarized according to types thiophenes, flavonoids, caffeoyl quinic acids, sesquiterpenoids, and other compounds, including compound names and structural diagrams. And, the corresponding biological activities of compounds have also been searched and summarized, including anti-tumor, insecticidal, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, hepatoprotective activity and AKR1B10 inhibitory, as well as anti-viral activity. Finally, we systematically reviewed the chemical composition of Echinopsis Radix included in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and discussed the corresponding biological activities of the monomer compounds. The literature retrieval process is as shown in the following Figure 1.
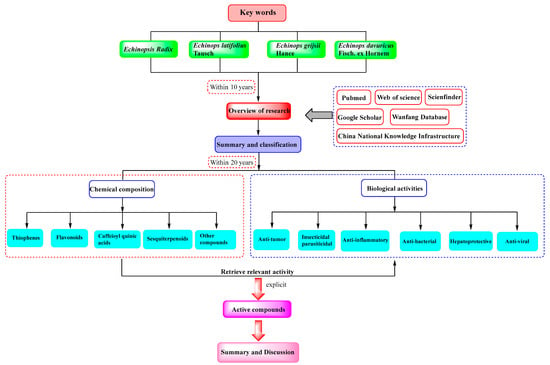
Figure 1.
Literature retrieval process.
3. Phytochemicals
So far, thiophene sesquiterpenes, flavonoids, caffeic acids and their derivatives have been reported from Echinopsis Radix. Specially, various types of thiophene have been reported like monothiophene, dithiophene, triphenylthiophene, and tetrathiophene. As presented in Table 1, eighty-five compounds were isolated and identified through various chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques. It is widely known that thiophene compounds are typical secondary metabolites of Echinopsis Radix. The root of the plant is the main source of the thiophenes, while most of the sesquiterpenes, caffeic acid, and flavonoids have also been reported from the aerial part of the plant.

Table 1.
The names of compounds 1–85 isolated from Echinopsis Radix.
3.1. Thiophenes
Thiophenes are the most common chemical constituents in the genus Echinops. So far, a total of forty-nine thiophenes have been reported from Echinopsis Radix. They are classified as eleven monothiophenes (1–11), twenty-seven dithiophenes (12–38), six trithiophenes (39–44), and five dithiophene dimers (45–49).
Eleven monothiophenes were isolated from Echinopsis Radix. As shown in Figure 2, the C-2 and C-5 positions of these compounds are usually substituted by fatty hydrocarbon or ester groups. It is worth noting that most aliphatic hydrocarbon substituents typically contain alkyne functional groups. Among them, compounds 7 and 8 are a pair of cis trans isomers of olefins isolated from the roots of E. latifolius [10]. In addition, compounds 9–11 were three polyacetylene monothiophenes isolated from the roots of E. grijsii [11]. And compounds 9 and 10 are two chlorinated halogenated monothiophenes.
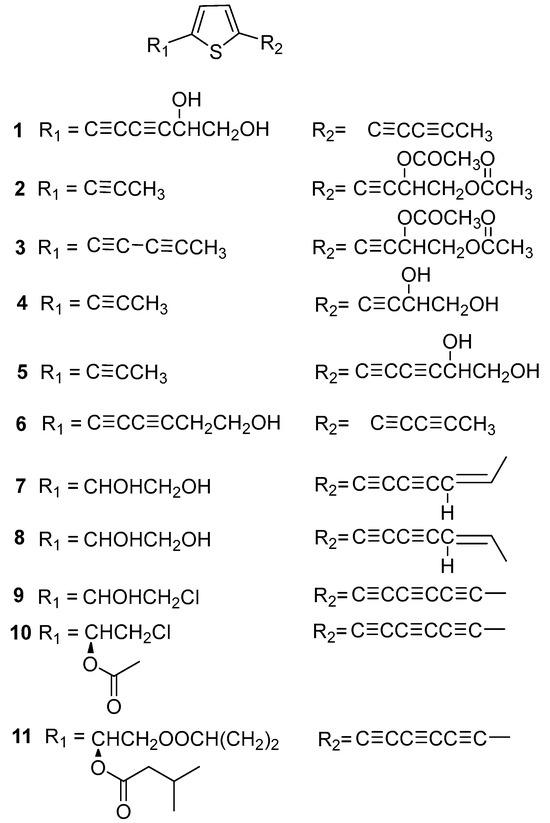
Figure 2.
Monothiophenes reported from Echinopsis Radix.
As we all know, thiophenes are biosynthetically derived from fatty acids and reduced sulphur. Most of the thiophenes comprised two thiophene rings in their structure and connected through C-2 and C-2′, namely bithiophene. As presented in Figure 3, a total twenty-seven dithiophenes were reported from Echinopsis Radix. Among them, they are eighteen mono substituted with C-5 position (12–29) and nine double substituted with C-5 and C-5′ positions (30–38). Most of these compounds are lipophilic, with ester, acyl, and hydroxyl groups mainly present in the side chains. Compounds 15, 21, and 24 were firstly isolated from the roots of E. latifolius by Wang Yi’s research team [12,13]. And compound 25 with the 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-1-butyny side chain was firstly isolated from the roots of E. grijsii [14]. Compounds 32–34 are three new disubstituted thiophenes reported for the first time from the roots of E. grijsii [11]. In addition, compounds 33 and 35 are two chlorine containing disubstituted thiophenes.
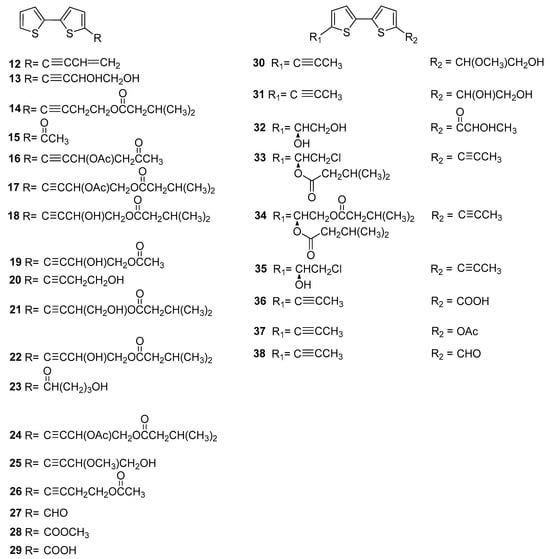
Figure 3.
Dithiophenes reported from Echinopsis Radix.
Furthermore, some thiophene compounds with more than two thiophene rings have also been reported from Echinopsis Radix. Among them, the triphenylthiophene compound α-terthienyl (39) was firstly isolated from E. grijsii [15]. Triphenylthiophenes are not commonly found in the genus Echinops, and only five have been isolated from Echinopsis Radix [16]. Among them (Figure 4), four compounds (40–43) with C-5 or C-5′ positions substituted by chlorine, acetyl, or hydroxyl groups, and all were isolated from E. grijsii. Interestingly, a trithiophene compound containing three thiophene rings (44) has been firstly reported from E. latifolius, although it is a derivative of the polymerization of monothiophene and bithiophene [17]. Additionally, five dithiophene dimers have been reported (45–49), which are connected by carbon-carbon bond or carbon-oxygen bond [18,19,20]. Among them, cardopatine (45) and isocardopatine (46) are a pair of epimers, while echinbithiophenedimers A (47) and B (48) are a pair of epimers. And compounds 47–49 possessed new carbon skeletons are the first examples of bithiophene dimers furnished by different cyclic diethers. Importantly, compounds 47 and 48 feature an unprecedented 1,3-dioxolane ring system and compound 49 features an unusual 1,4-dioxane ring. The structural types of thiophene compounds of Echinopsis Radix are enriched via these compounds, which make good examples of novel thiophene polymers in natural products.
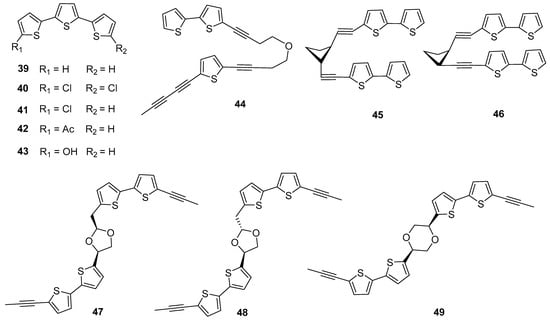
Figure 4.
Tricyclic and tetracyclic thiophenes reported from Echinopsis Radix.
3.2. Flavonoids
Although flavonoids are relatively common in most plants, only eight flavonoids (50–57) have been reported from Echinopsis Radix (Figure 5). And all these flavonoids and their glycosides were isolated from the aboveground portion of the plant. For example, compounds 50–55 were reported from the aerial part of E. grijsii [21], while the glycoside derivatives of flavonoids 56 and 57 were first reported from the flowers of E. grijsii [22].
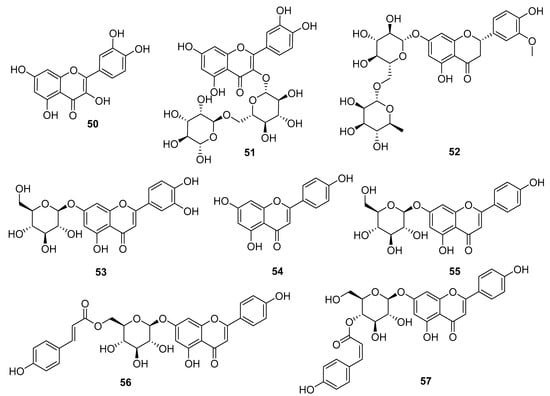
Figure 5.
Flavonoids reported from Echinopsis Radix.
3.3. Caffeoyl Quinic Acids
Caffeic acid and its derivatives are very rare in the entire genus Echinops. So far, seven caffeic acid compounds (58–64) have been obtained by Xue Pei-feng et al. from the flowers of E. latifolius [22]. These compounds are not only the first to be obtained from this plant, but also the first to be discovered from the genus Echinops. As shown in Figure 6, compounds 59–64 are both obtained by esterification of one quinic acid with two caffeic acids.
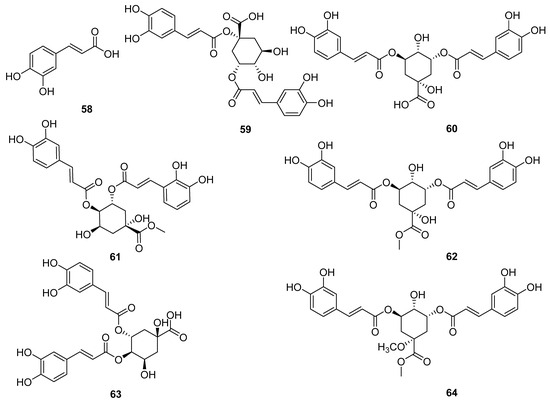
Figure 6.
Caffeoyl quinic acids reported from Echinopsis Radix.
3.4. Sesquiterpenoids
Eight sesquiterpenoid compounds were obtained from Echinopsis Radix and classified as two sesquiterpene dimers (65 and 66) and six eudesmane-type sesquiterpenes (67–72) (Figure 7). Compounds 65 and 67 were isolated for the first time from the methanol extract of the root of E. latifolius [10]. And compound 65 is an unprecedented new carbon skeleton dimer sesquiterpene formed by the cyclization of two eudesmane-type sesquiterpenes. Compounds 66 and 68–72 were isolated from the ethyl acetate extraction portion of the root of E. grijsii [23]. And compound 66 represented a totally new carbon skeleton of the disesquiterpenoid, featuring a unique 6/6/5/6/6 ring system with an oxaspiro unit. Additionally, the biogenetically possible precursors of 66 suggested that it could be produced by incorporating two analogues of oxygenated eudesmanes. Especially, sesquiterpenes and sesquiterpene dimers of Echinopsis Radix are a class of components that deserve attention.
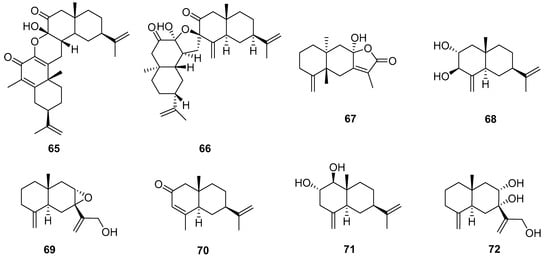
Figure 7.
Sesquiterpenoids reported from Echinopsis Radix.
3.5. Other Compounds
In addition to the chemical components reported above, Echinopsis Radix is also rich in many other components, such as triterpenes, steroids, benzothiophenes, and fatty acids [24,25,26]. The structures of other compounds (73–82) are presented in Figure 8. Compounds 73, 76–78 are four pentacyclic triterpenoid compounds, of which 73 and 78 belong to the oleanolane type, while 76 and 77 belong to the ursulane type. Steroids 74 and 75, as well as fatty acids 81 and 82 are widely present in various plants and have been reported in the roots or flowers of E. latifolius. Compounds 79 and 80 are the only two benzothiophene glycosides and aglycones discovered from the roots of E. grijsii. Furthermore, in our previous study on the aboveground part of E. davuricus, compounds 83–85 were isolated for the first time.
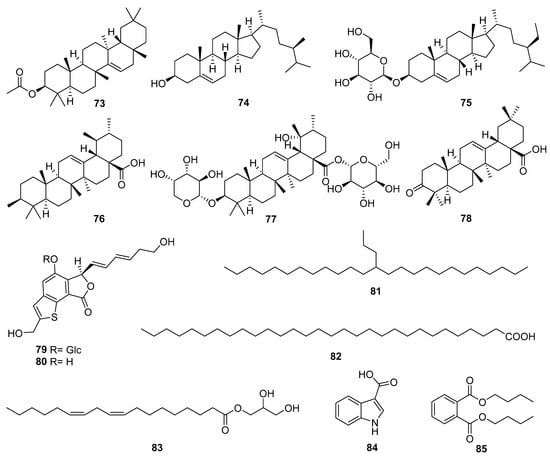
Figure 8.
Other compounds reported from Echinopsis Radix.
4. Biological Activities
As a traditional Chinese medicine, Echinopsis Radix exhibits various pharmacological activities, such as anti-tumor, antiviral, anti-HIV, anti-bacterial, insecticidal and parasiticidal effects, liver protection, immune regulation, and anti-inflammatory effects [24]. However, due to its complex chemical composition, most of the reported pharmacological effects are crude extracts or mixtures, and the chemical structure is not yet clear. In recent years, with the continuous deepening of research on the chemical composition of Echinopsis Radix, the biological activity of monomer compounds has also been reported. Therefore, it is necessary to summarize the biological activity of monomeric compounds from Echinopsis Radix.
4.1. Anti-Tumor Activity
Early studies have shown that the crude extract of Echinopsis Radix exhibits excellent anti-tumor activity. In recent years, the main anti-tumor active ingredients have also been reported. Wang et al. reported the important cytotoxic activities of compounds 23 and 45 on human melanoma cells (A375-S2) and cervical cancer cells (Hela), with IC50 values from 3.1 to 13.5 µmol/L. And the phototoxicity of two thiophene compounds is lower than that of α-terthienyl with stronger activity [17]. The study results of Zhang et al. revealed that compounds 1, 5, 6, 12, 19, 31, and 80 exhibit good cytotoxic activity against leukemia cell lines HL60 and K562, with IC50 values from 0.23 to 30.6 µg/mL. Among them, the cytotoxicity of monothiophenes 1 (with IC50 values 0.23 and 0.47 µg/mL) and 6 (with IC50 values 0.27 and 0.45 µg/mL) are much higher than that of other thiophenes, [24]. And the substituted alkyne groups on both sides of a single thiophene may be a key factor in enhancing cytotoxic activity. Jin et al. reported the cytotoxicity of compounds 2, 3, 12, 14, 16, 17, and 39 on four types of tumor cells (hepatocellular carcinoma cells HepG2, leukemia cells K562 and HL60, breast cancer cells MCF-7) based on tracking the active components of dichloromethane. Among them, compounds 2, 14, and 16 showed high cell inhibitory rate against HL60 (with IC50 values 10, 8 and 12 µg/mL, respectively), compounds 17 and 39 showed major inhibitory activity against K562 (with IC50 values 12 and 7 µg/mL), and compounds 16 and 17 are two main inhibitory influences on cytotoxicity against HepG2 (with IC50 values 10 and 1.8 µg/mL) [27]. In summary, the cytotoxicity of thiophene is related to thiophene polymerization and side chain substitution, and acyl substituted dithiophenes exhibit stronger anti-tumor activity than α-trithiophene and monothiophene.
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Although there are many reports on the anti-inflammatory activity of Echinopsis Radix, they all focus on the crude extract [28,29]. However, there are relatively few reports on monomeric compounds that exhibit anti-inflammatory activity in the plants. At present, only five anti-inflammatory active compounds have been reported from Echinopsis Radix. In 2015, The research results of Chang Fangpin et al. revealed that compounds 1, 13, and 20 exhibited significant inhibitory activity against nitrite of LPS-stimulated production in the RAW 264.7 cell line. And the IC50 values were 2.5, 20.0 and 6.7 μg/mL, respectively [14]. Subsequently, Jin Qinghao et al. discovered the important anti-inflammatory activities of compounds 7, 8, 30, and 31, with IC50 values of 12.8–48.7 μM. [10]. The structure-activity relationship analysis suggested that the anti-inflammatory activity of monothiophene is stronger than that of dithiophene, while the activity of double substituted dithiophene is better than that of single substituted dithiophene. In addition, the presence of cis double bonds in monothiophene enhances anti-inflammatory activity.
4.3. Hepatoprotective Activity
In early pharmacological studies, Lin et al. reported that Echinopsis Radix has a significant hepatoprotective effect, which can improve CCl4 induced liver necrosis and dysfunction in rats [30]. Subsequently, Li Xifeng et al. demonstrated that the hepatoprotective effect of the ethanol extract may be related to its ability to scavenge free radicals and resist oxidation in the body [31]. Until 2010, Shi jing et al. first reported that compound 1 possessed potent NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase1 (NQO1) inducing activity and could activate Keap1-Nrf2 pathway effectively in murine hepatoma Hepa 1c1c7 cells [32]. In addition, our previous chemical and biological activity studies revealed that the important anti-cancer targets of Echinopsis Radix, especially the anti-liver cancer AKR1B10, by network pharmacology strategies. And for the first time, compounds 83 and 85 have been reported to have significant AKR1B10 inhibitory activity, which provides new ideas for later research on the hepatoprotective effect of Echinopsis Radix [26].
4.4. Insecticidal and Parasiticidal Activity
Natural thiophene compounds show obvious insecticidal effects, such as phototoxic activity against bacteria, yeasts, insects and various experimental microorganisms. The mosquito-killing effect of α-T (compound 39) was firstly reported by Nivsarkar et al. [33], and then the insecticidal effects of other thiophenes have also been reported. In 2017, Zhao Meiping et al. obtained three compounds 12, 14, and 39 insecticidal activities against mosquito larvae based on activity directed separation. Among them, 12 and 14 possessed sound larvicidal activity against the fourth instar larvae of Ae. albopictus with LC50 values of 0.34 g/mL and 0.45 g/mL, respectively. And 12 and 14 had LC50 values against the fourth instar larvae of An. sinensis of 1.36 g/mL and 5.36 g/mL, respectively. In addition, 12 and 14 also possessed LC50 values against the fourth instar larvae of C. pipiens pallens of 0.12 g/mL and 0.33 g/mL, respectively [34]. In 2019, Liu Tingting et al.’s research revealed that compounds 9, 10, 30, 32, 33, 35, 37, and 38 showed stronger nematicidal activity against Meloidogyne incognita than commercial nematicide abamectin. And 30, 32, 33, and 35 have been proven to be non phototoxic. Specially, compounds 32 and 35 were the most potent thiophenes against M. incognita with LC50 values 2.57 and 0.91 μg/mL in light, 1.80 and 0.86 μg/mL in dark, respectively [11]. Subsequently, Liu Tingting et al. also reported that the new framework of sesquiterpene dimers 66 exhibited stronger insecticidal activity than sesquiterpene compounds 68–72, and even stronger insecticidal activity against aphids than the commercially available aphid fungicide pyrimethadone [23]. Additionally, Wu Haibo et al. demonstrated for the first time that compounds 47–49 of dithiophene dimer had better nematicidal activity against Meloidogyne incognita than commercial nematicides ethoxyphosphorus, and had no phototoxicity [20]. The above research results indicate that thiophene backbone is essential for nematicidal activity, while disubstituted groups were helpful for nonphototoxicity. And acyl groups can inhibit the effect of light on activity, while chlorine plays an important role in promoting activity. Furthermore, sesquiterpene dimers and dithiophene dimers could be served as novel potential biological insecticides.
4.5. Anti-Bacterial Activity
The inhibitory activities of the total extract and each extract of Echinopsis Radix against fungi such as Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Salmonella typhi and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were first reported by Li Xifeng. et al. The results showed that the ethyl acetate and n-butanol extracts were effective parts with antibacterial activity [32]. In the study of plant comprehensive disease complexes, Liu Tingting et al. revealed the excellent antifungal activity of thiophene compounds against six fungi (F. solani, F. oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum, F. oxysporum f. sp. niveum, P. infestans, C. gloeosporioides, and A. alternate). Among them, compared with the commercial fungicide carbendazim, compounds 9, 10, 31–33, 35, and 36 exhibited equal or better antifungal activity against six plant pathogenic fungi [23]. Importantly, the antifungal activities of dimeric dithiophene 47–49 were first reported by Wu Haibo et al. The results showed that they had good antifungal activity against five plant pathogenic fungi. And compound 49 had antibacterial activity similar to carbendazim against Fusarium oxysporum and rice blast fungus, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 8 μg/mL [20]. The structure-activity relationship analysis suggests that thiophene substituted with chlorine has the strongest antibacterial activity, and dimeric dithiophene is an important potential antifungal agent.
4.6. Anti-Viral Activity
So far, there are few reports on the antiviral activity of Echinopsis Radix. Only triple-thiophene compound 39 has been shown to have significant anti-HIV activity. Although the activity of a decreased in the presence of bovine serum, it could inactivate 104 or 105 viral vectors at a mass concentration of 0.1 mg/mL [35]. Therefore, the antiviral activities of triple-thiophene compounds and their derivatives are worthy of further study.
5. Conclusions
Echinopsis Radix (“Yuzhou Loulu”) as well as E. latifolius, E. grijsii, and E. davuricu is are important resource of traditional Chinese medicine. This review not only shows their rich chemical composition and diverse biological activities, but also demonstrates their common chemical composition and similar biological activities. And thiophene compounds with various types including monothiophene, dithiophene, trithiophene, and dimeric dithiophene, are typical secondary metabolites. Biological activity survey reveals that the most abundant bioactive secondary metabolites in this medicinal herb are thiophene compounds, which are mentioned as responsible for the anti-tumor, insecticidal, and anti-fungal effects observed. Significantly, the discussion of structure-activity relationships lays the foundation for the development of active compounds. In addition, it has been observed that the potential uses of Echinopsis Radix in the hepatoprotective effect and antiviral activity have not been scientifically addressed yet. This review not only clarifies the main chemical components of Echinopsis Radix for the quality evaluation, but also provides scientific ideas for further exploration of its active ingredients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S. and Y.W.; methodology, N.S.; software, S.M.; validation, H.K., C.Z. and L.J.; formal analysis, X.Z.; investigation, Y.Z.; resources, P.S.; data curation, Y.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.; writing—review and editing, N.S.; visualization, Y.W.; supervision, P.S.; project administration, N.S.; funding acquisition, P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21702178), Project of Science and Technology Department of Henan Province (242102310503), Postgraduate Education Reform and Quality (YJS2023AL082), Graduate Education Reform Project of Henan Province (2023SJGLX294Y), the Training Plan of Young Backbone Teachers in Universities of Henan Province (2021GGJS144), the Key Scientific Research Program in Universities of Henan Province (23A350012), the National Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (202310480020), Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Henan Province (202310480023) Scientific Research Innovation Team of Xuchang University (2023ZYTD03), the Horizontal Cooperation Project (2023HX181).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the logistical support provided by Zhaoxue Sun and Lixiang Li for this review.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rolnik, A.; Beata, O. The plants of the Asteraceae family as agents in the protection of human health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China: Volume I; China Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, N.; Liu, J.; Fang, K.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, W.; Shu, P. Research progress on pharmacological activity and clinical application of Loulu (Rhapontici Radix). Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 40, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, M.; Zhang, M.; Huo, C.; Shi, Q.; Gu, Y. Chemical constituents of plants from the genus Rhaponticum. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 594–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitew, H.; Ariaya, H. The genus Echinops: Phytochemistry and biological activities: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 437397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Yi, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Chen, S. Research on revision of origins to Chinese medicinal materials in 2020 edition of Chinese pharmacopoeia. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2021, 46, 2617–2622. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Fang, Y.; Chang, H.; Yang, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhan, Z. Herbal textual research on Rhapontici Radix in famous classical formulas. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2023, 29, 72–87. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, L.; Lao, S. Study on mechanism of Loulu (Rhapontici radix) treating gastric cancer based on network pharmacology. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 38, 65–68, 283–284. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Board of Flora of China. Chinese Academy of Sciences, Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987; Volume 78, p. 710. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Lee, J.W.; Jang, H.; Choi, J.E.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.; Hong, J.T.; Lee, M.K.; Hwang, B.Y. Dimeric sesquiterpene and thiophenes from the roots of Echinops latifolius. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5995–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wu, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H. Thiophenes from Echinops grijsii as a preliminary approach to control disease complex of root-knot nematodes and soil-borne fungi: Isolation, activities, and structure-nonphototoxic activity relationship analysis. J. Agri. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 6160–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, D.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y. Chemical constituents of thiophenes from Echinops latifolius Tausch. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2008, 3, 194–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, L.; Xue, P.; Gao, J. Research progress in medicinal plant Echinops Latifolius Tausch. China Pharm. 2015, 18, 1968–1971. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, F.; Chen, C.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Qu, C.; Wu, J.; Huang, G.; Kuo, Y. A new bithiophene from the root of Echinops grijsii. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 2147–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, K.; Jia, Z.; Nikaido, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, D. Echinothiophene, a novel benzothiophene glycoside from the roots of Echinops grijissii. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, M.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, D. New thiophenes from Echinops grijisii. J. Asian Nat. Prod. 2002, 4, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Meng, D.; Li, Z.; Li, N. Two new thiophenes from Echinops latiflius and their phototoxic activities. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, T. Studies on the chemical constituents of Radix Echinopsis. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 1989, 20, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Cui, Y.; Lou, Z.; Gao, C.; Huang, L. Studies on the chemical constituents of Echinops grijisii (I). Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 1992, 23, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wu, H.; Kuang, M.; Lan, H.; Wen, Y.; Liu, T. Novel bithiophene dimers from Echinops latifolius as potential antifungal and nematicidal agents. J. Agri. Food. Chem. 2020, 68, 11939–11945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, G.; Cui, Y. Studies on the chemical constituents of up-terra parts of Echinops grijisii. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2002, 33, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, P.; Bolati, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, N.; Wang, J.; Gao, J. Study on chemical constituents from inflorescence of Echinops latifolius. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2017, 19, 3921–3926. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Wu, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, L. Echingridimer A, an oxaspiro dimeric sesquiterpenoid with a 6/6/5/6/6 fused ring system from Echinops grijsii and aphicidal activity evaluation. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 10757–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liang, D.; Jin, W.; Qua, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, Z. Cytotoxic thiophenes from the root of Echinops grijisii Hance. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 2009, 64, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Lou, Z.; Gao, C.; Wang, D. Studies on the chemical constituents of Echinops grijisii (II). Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 1992, 23, 512–514. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, N.; Ma, S.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Kang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; et al. Unveiling the anticancer mechanism of Echinops davuricus: Isolation and evaluation of AKR1B10 inhibitors. Chem. Biodiversity 2024, 21, e202302053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Shi, Q.; Hong, C.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Qu, H. Cytotoxic properties of thiophenes from Echinops grijissi Hance. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, X.; Wang, Y.; An, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y. Spectrum-effect relationship on anti-inflammatory effective fraction of Echinopsis Radix. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2014, 20, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; An, S.; Zhu, Y. Screening effective part of Echinopsis Radix via bacteriostasis and anti-inflammatory activities. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2015, 21, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Yen, M.; Chiu, H.; Chang, C. The pharmacological and pathological studies on Tawan folk medicine (IV): The effects of Echinops grijsii and E. latifolius. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1990, 18, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, C.; Hu, L.; Fang, X.; Tang, L.; Zhang, W.; An, S.; Wang, Y. Effect of alcohol extract of Radix Echinopsis on acute liver injury mice induced by carbon tetrachloride. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2014, 26, 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H. 2-(penta-1, 3-diynyl)-5-(3, 4-dihydroxybut-1-ynyl) thiophene, a novel NQO1 inducing agent from Echinops grijsii Hance. Molecules 2010, 15, 5273–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivsarkar, M.G.; Pradeep, K.; Malini, L.; Manmohan, M.L. Superoxide dismutase in the anal gills of the mosquito larvae of Aedes aegypti: Its inhibition by α-terthienyl. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1991, 16, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z. Identification of larvicidal constituents of the essential Oil of Echinops grijsii roots against the three species of mosquitoes. Molecules 2017, 22, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.B.; Harris, L.; Teeple, A.; Towers, G.H. The anti-HIV activity of the phytochemical α-terthienyl. Antivir. Res. 1993, 20, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).