Use of Euphorbia balsamifera Extract in Precursor Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Bromocresol Green and Bromophenol Blue Toxic Dyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
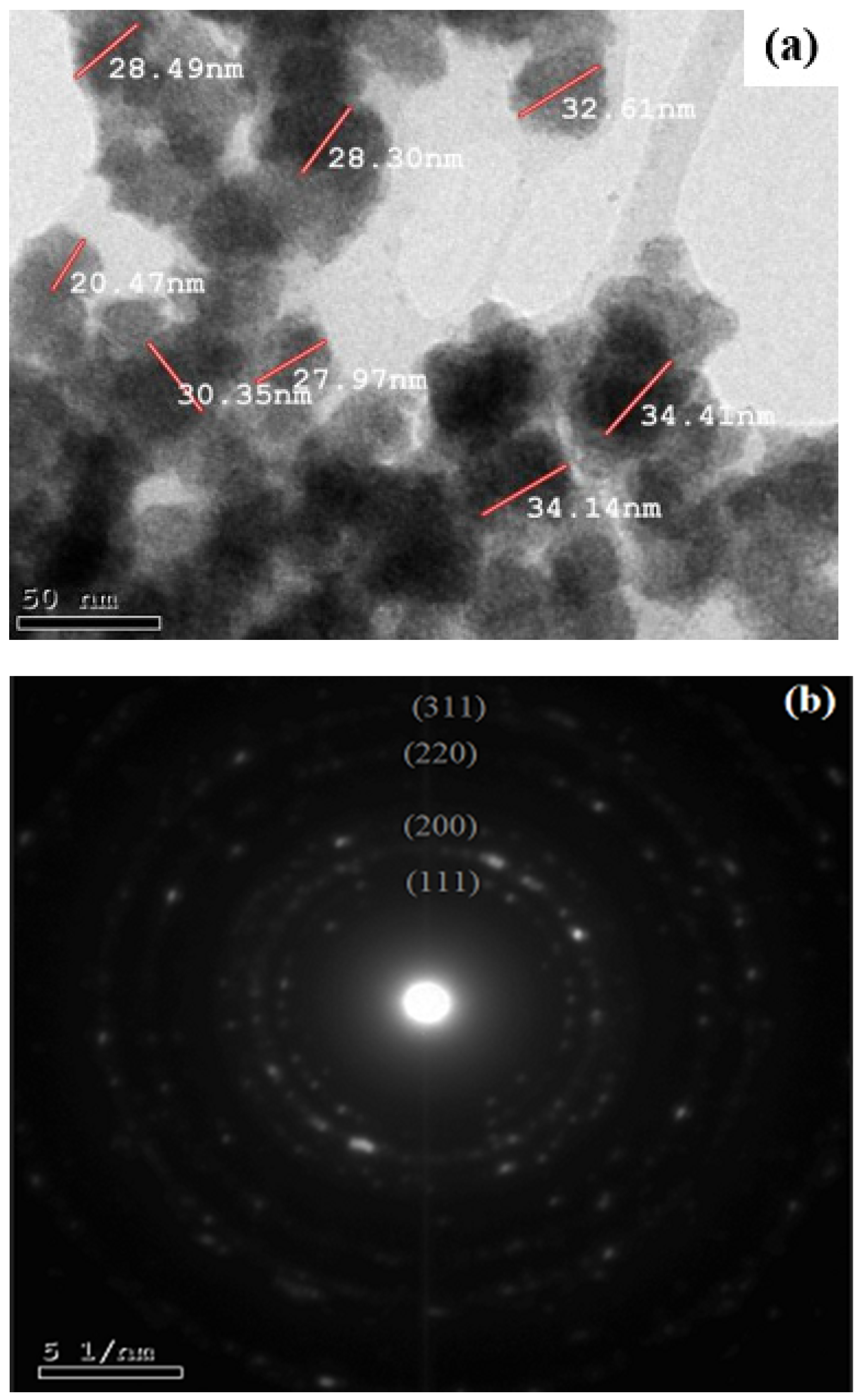
2.1. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
2.1.1. Powder X-ray Diffraction Studies (XRD)
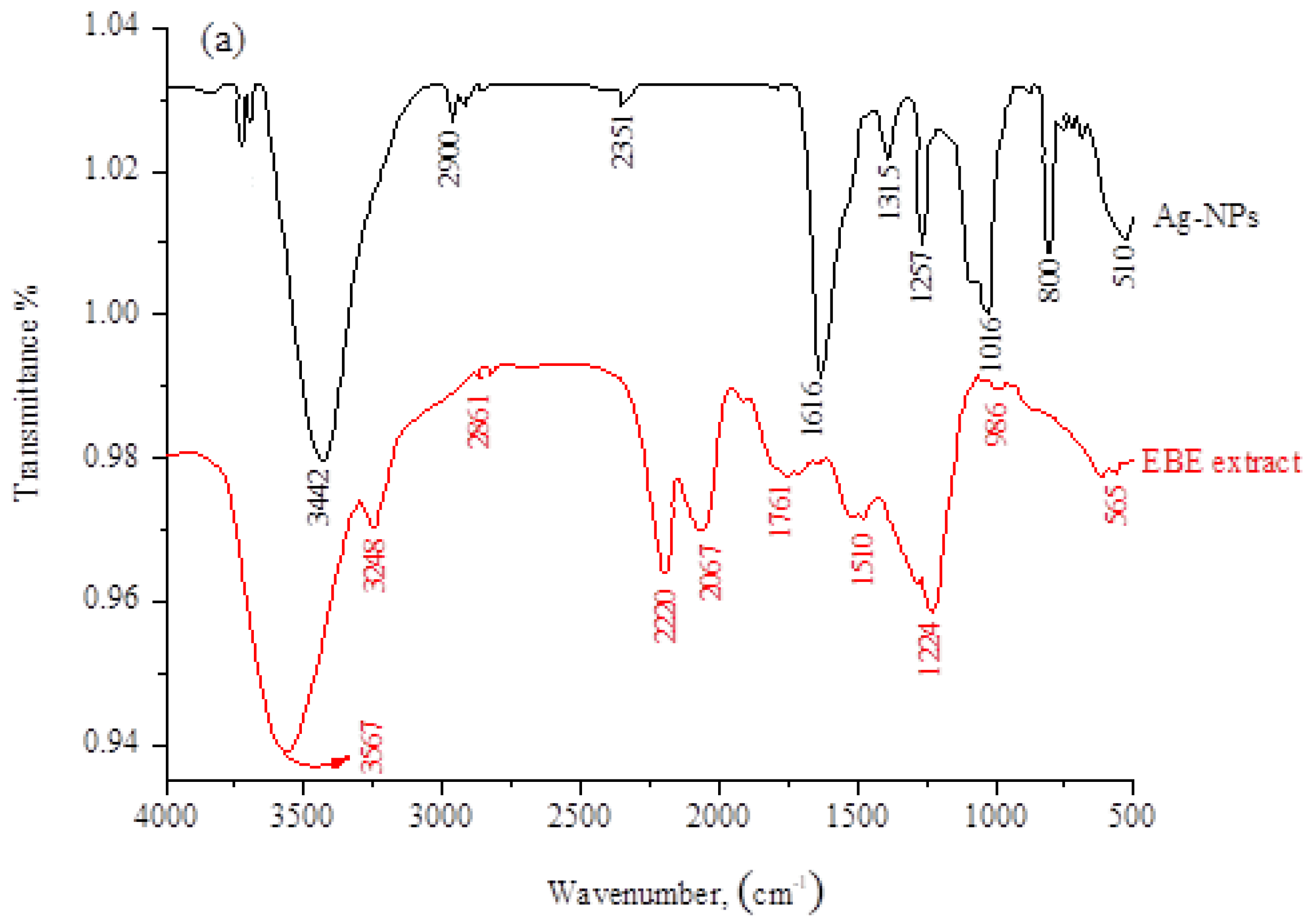
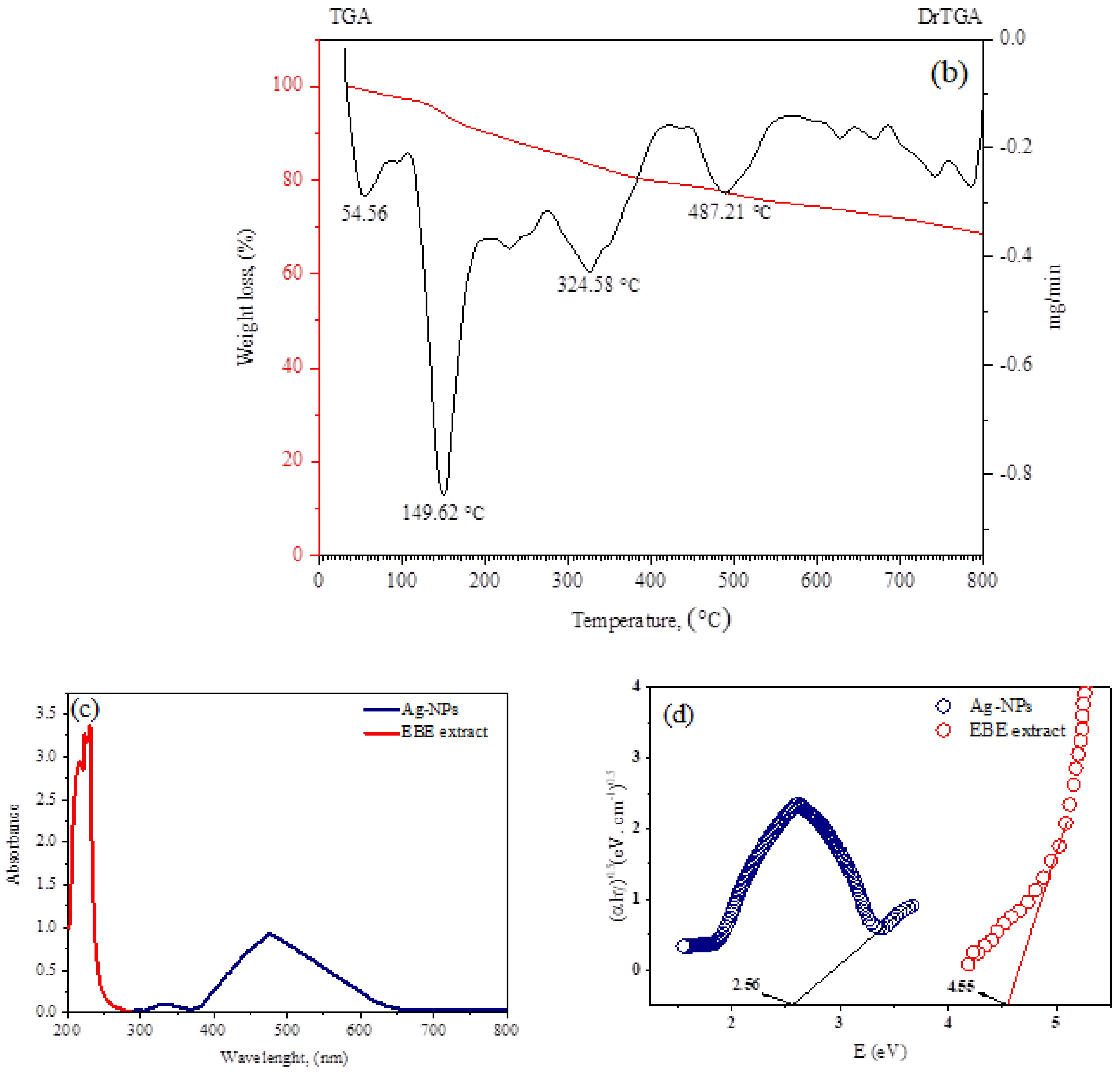
2.1.2. IR, TGA, and Ultraviolet/Visible Absorption Spectra
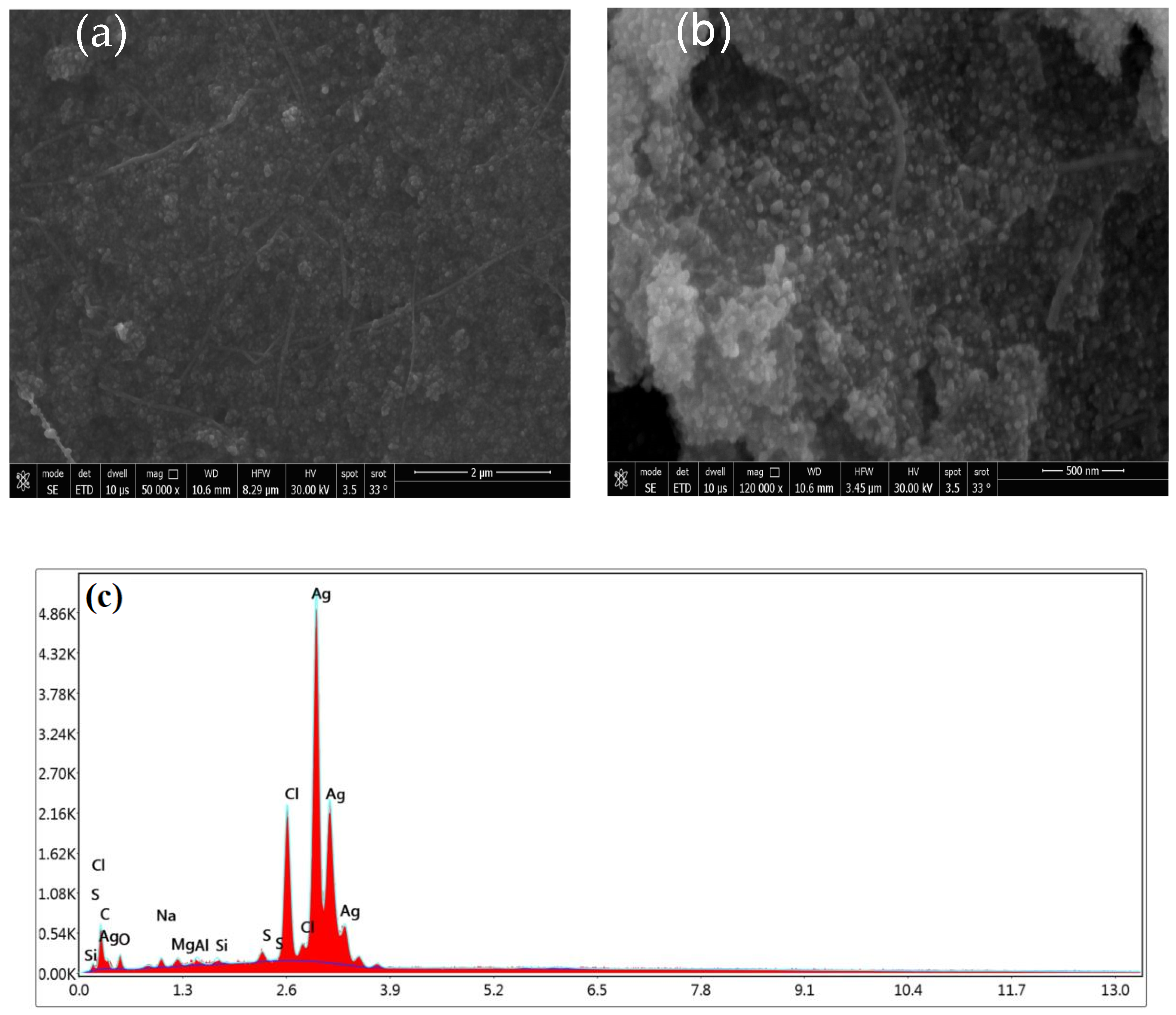
2.1.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy, EDAX, and BET Analyses
2.2. Features of Silver Nanoparticle Adsorption
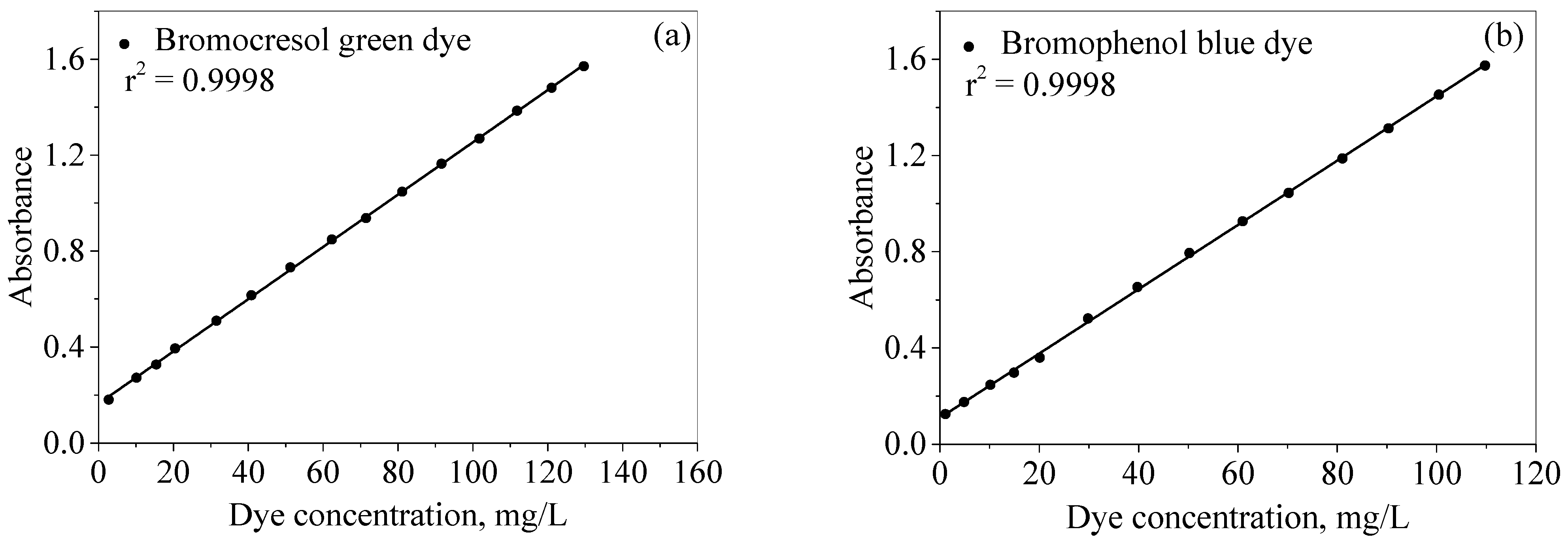
2.2.1. Calibration Curves of Dyes
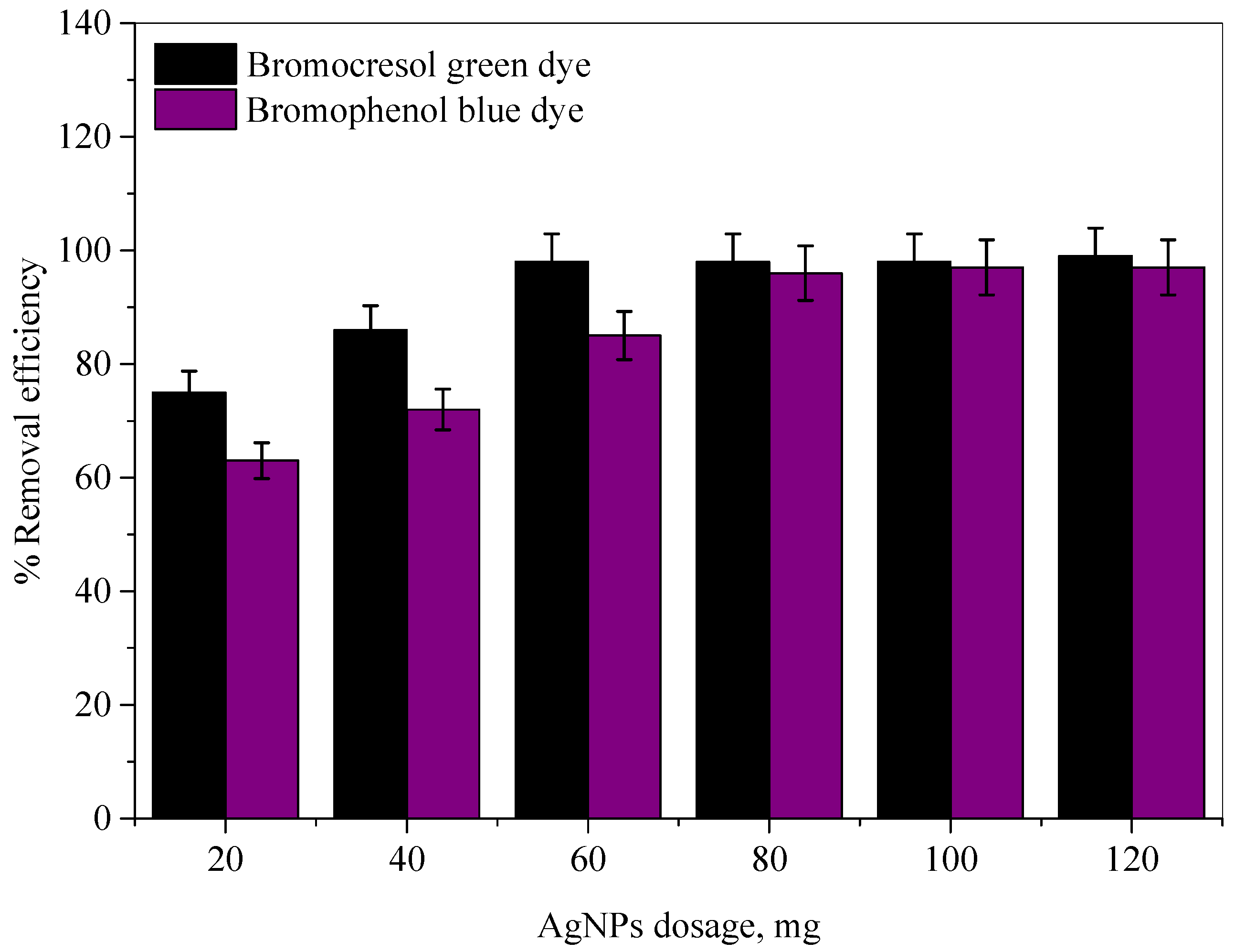
2.2.2. Effect of Ag-NP Dosage
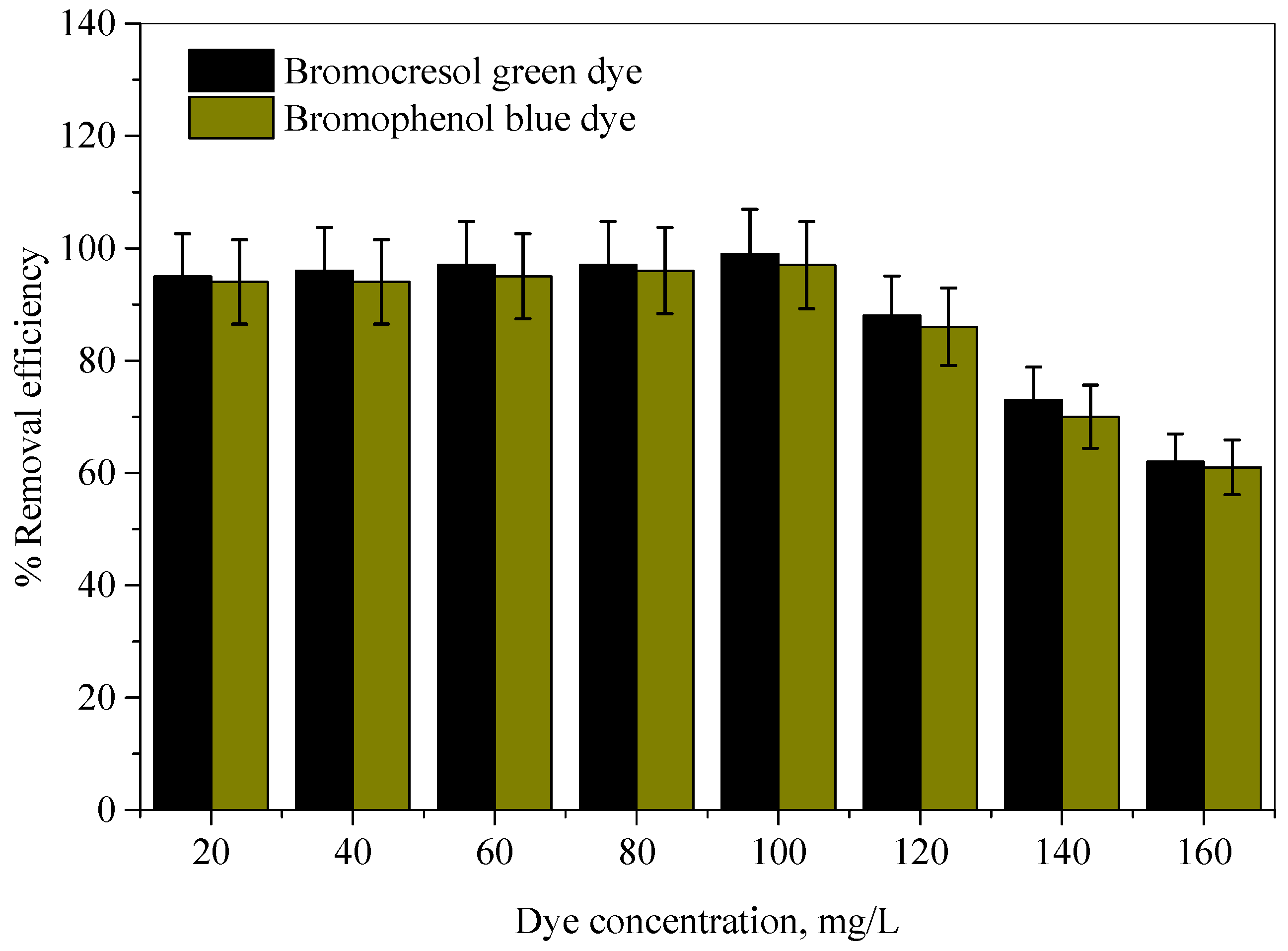
2.2.3. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
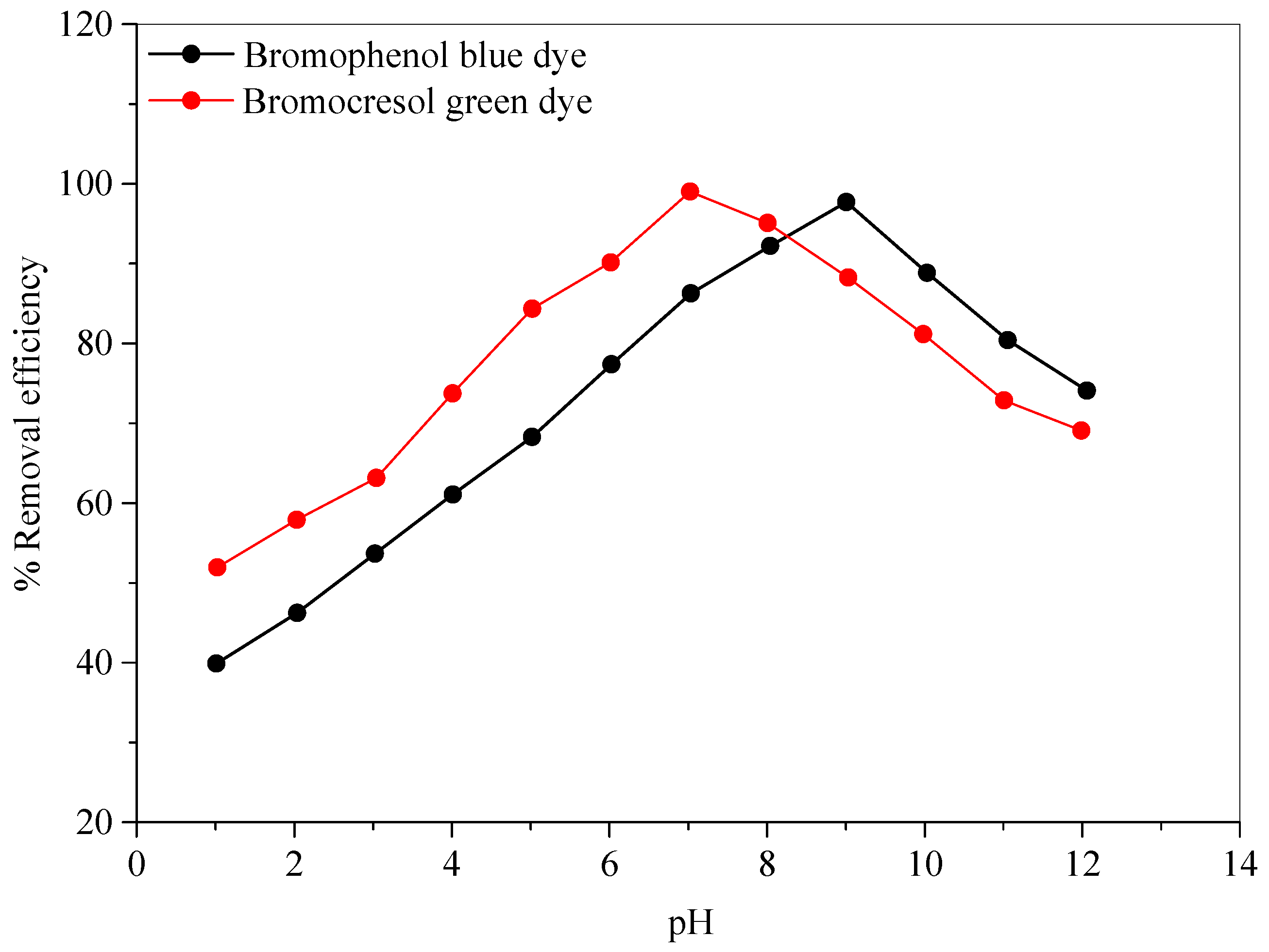
2.2.4. Effect of pH
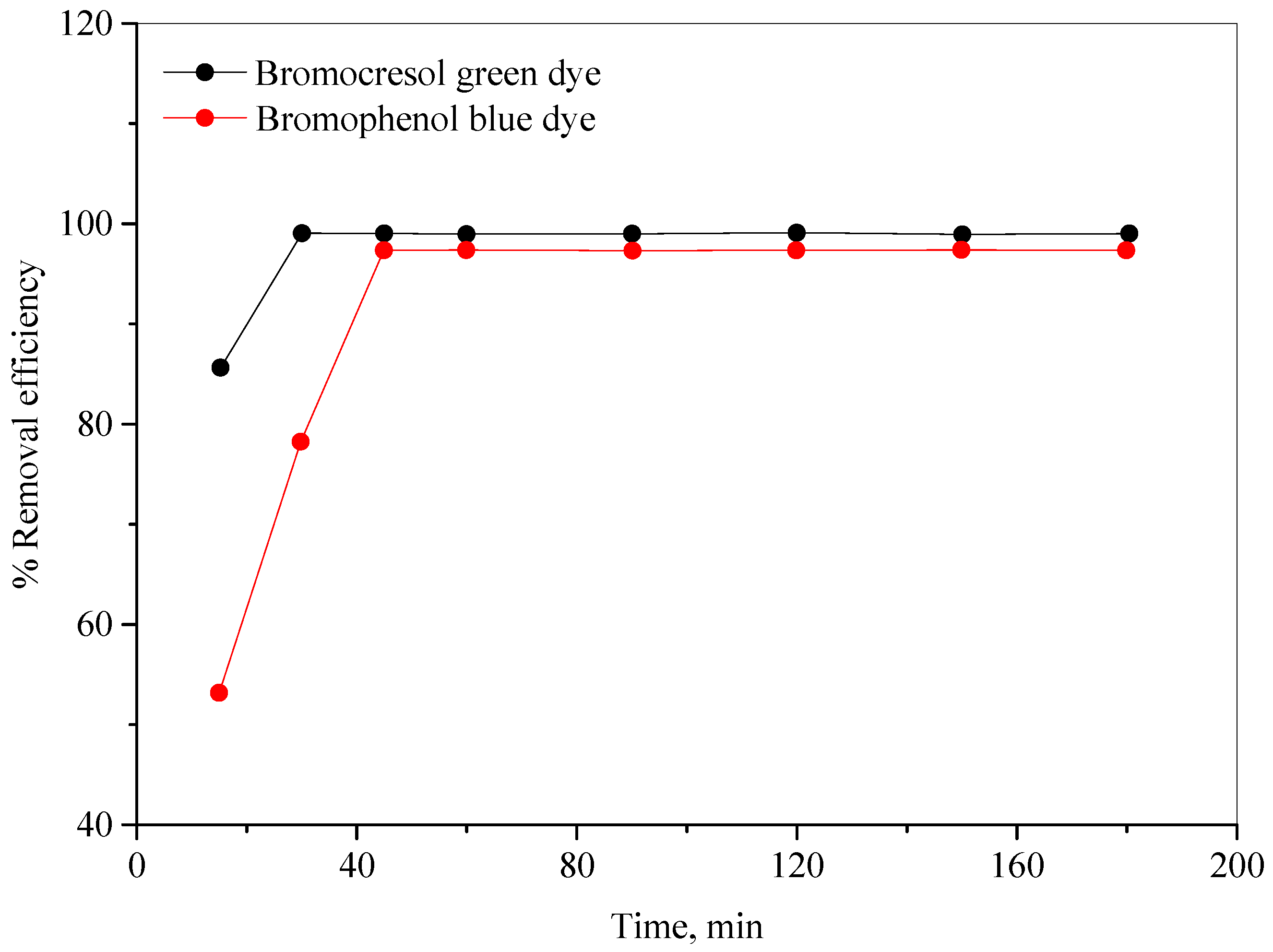
2.2.5. Effect of Stirring Time
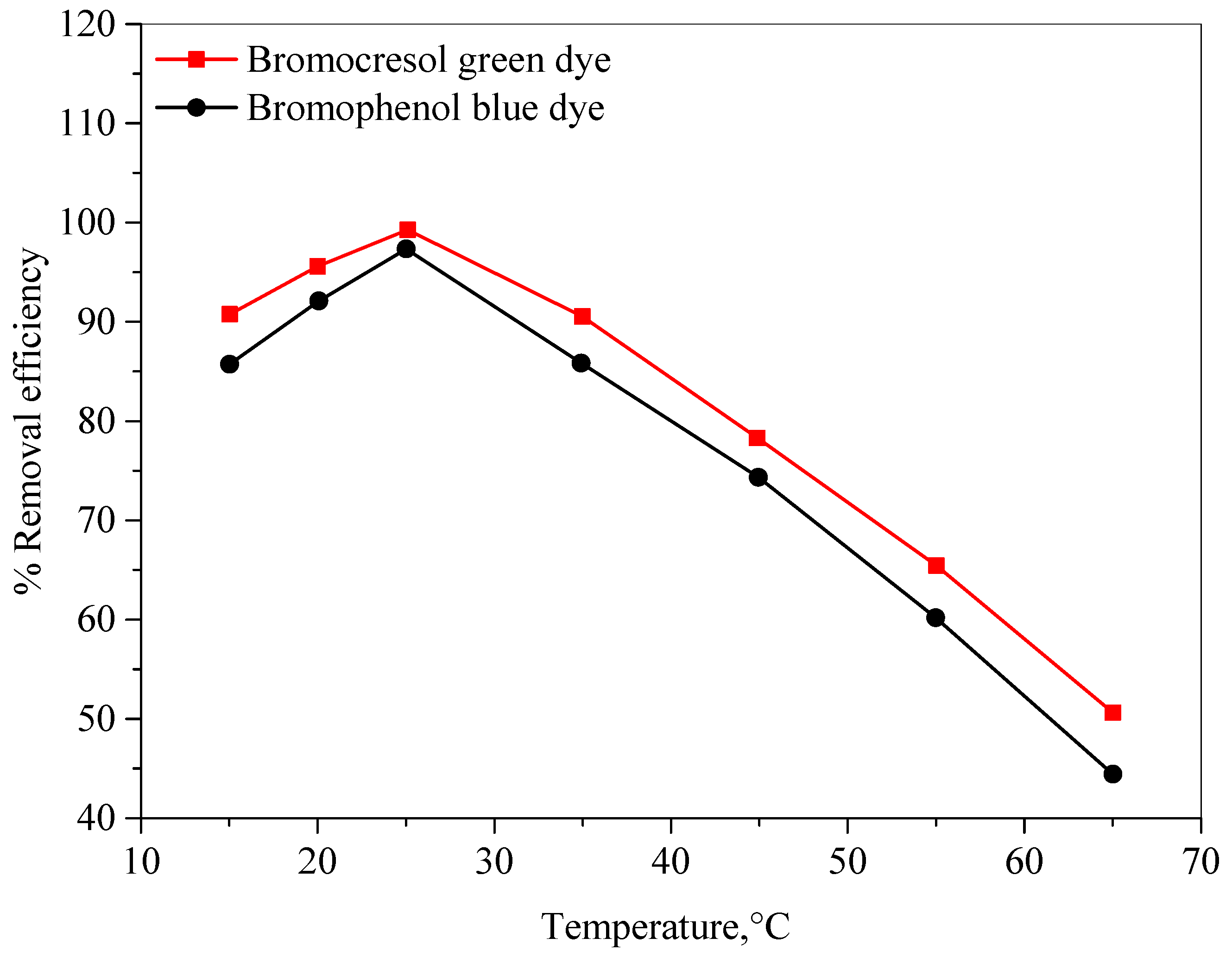
2.2.6. Effect of Temperature
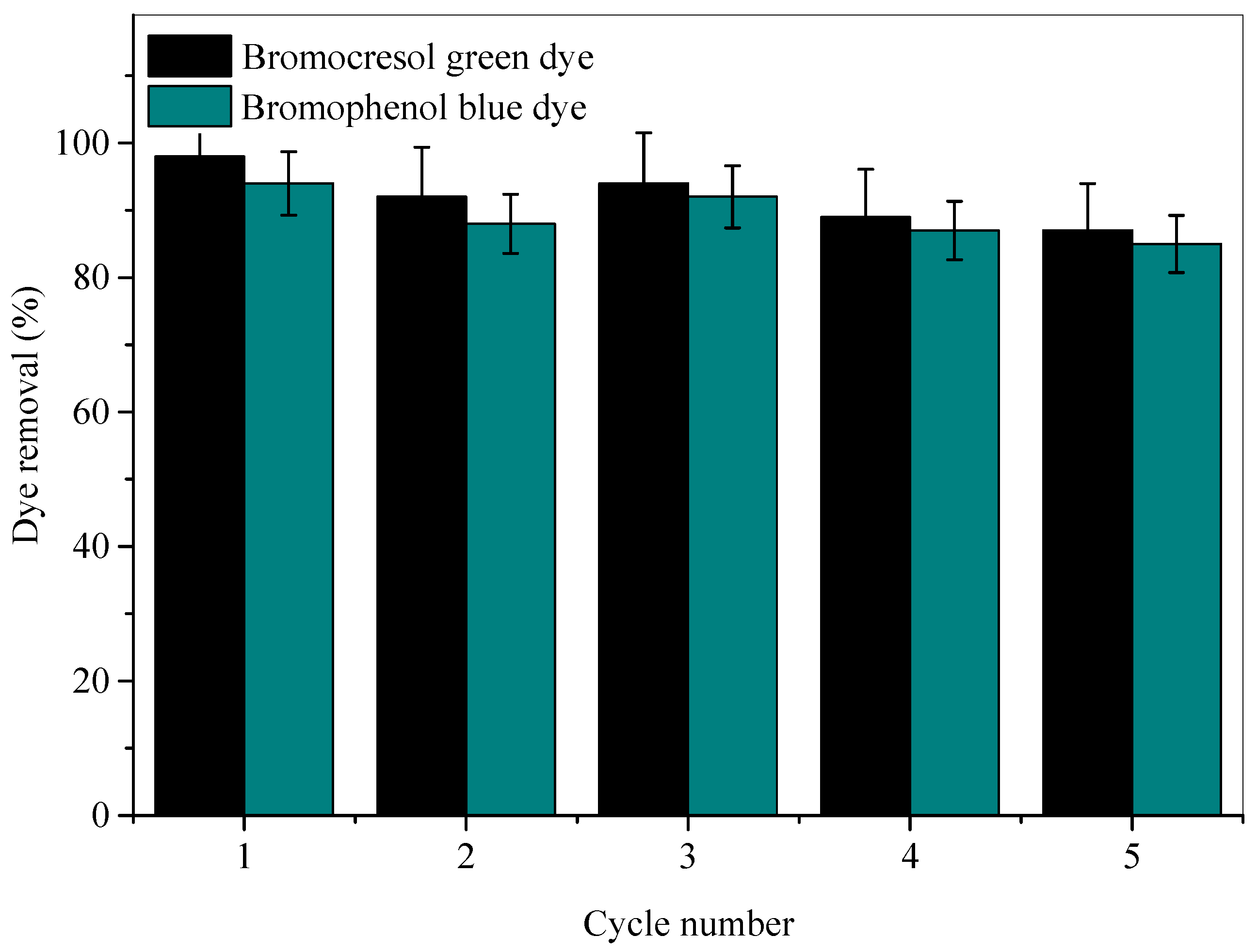
2.3. Reusability and Regeneration of Ag-NPs
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Adsorption Kinetics
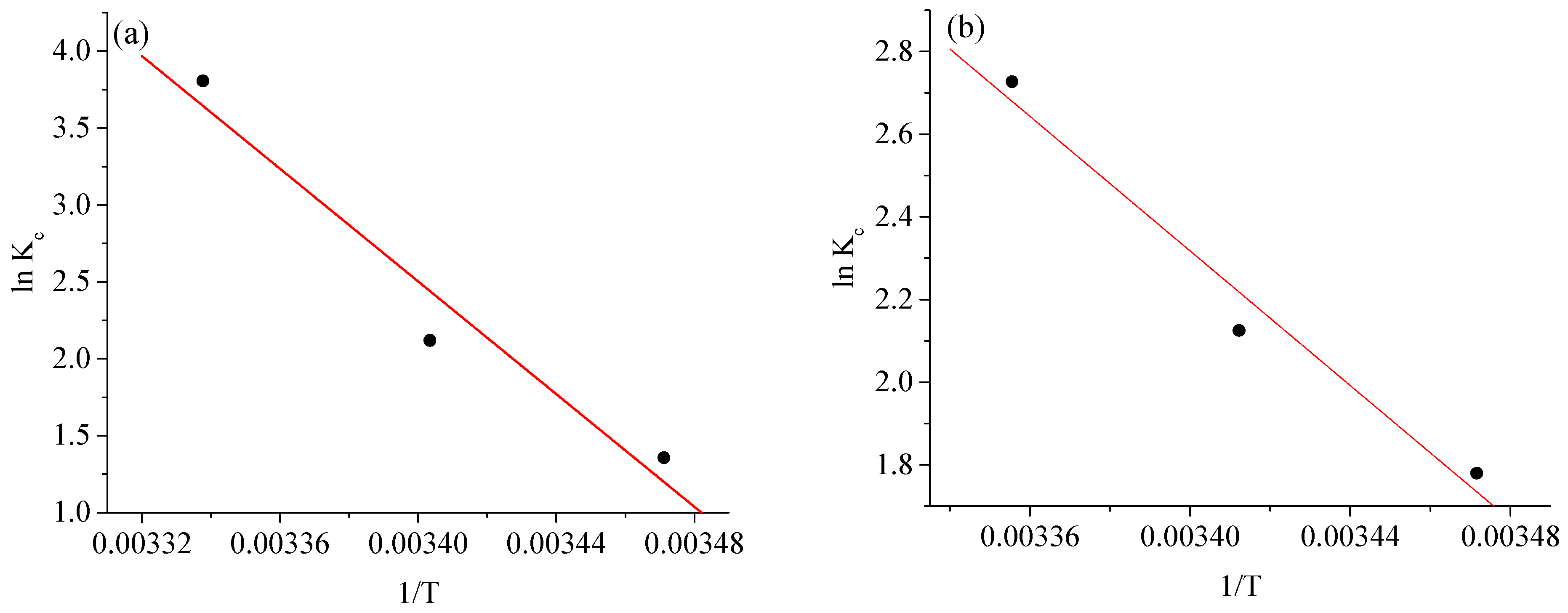
2.6. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Preparation of Plant Extracts
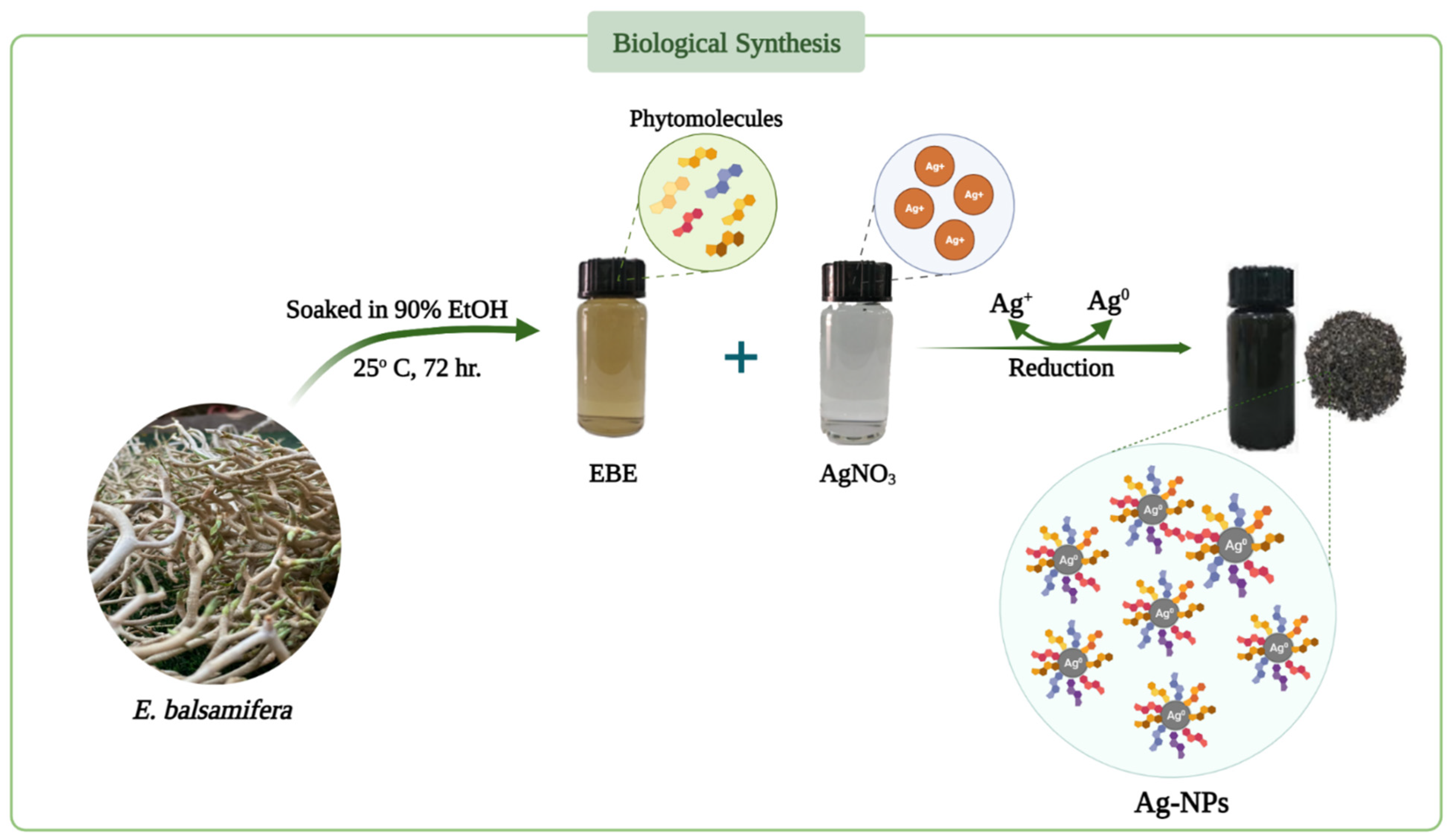
3.3. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs)
3.4. Characterization
3.5. Reagents
3.6. Preparation of Dye Solutions
3.7. General Procedure for Decolorization of Dyes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabłocka-Godlewska, E.; Przystaś, W.; Grabińska-Sota, E. Possibilities of obtaining from highly polluted environments: New bacterial strains with a significant decolorization potential of different synthetic dyes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachiyar, C.V.; Rakshi, A.; Sandhya, S.; Jebasta, N.B.D.; Nellore, J. Developments in treatment technologies of dye-containing effluent: A review. In Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; p. 100339. [Google Scholar]
- Niculescu, V.-C.; Raboaca, M.S. Efficient rice-husk-derived silica nanocatalysts for organic dye removal from water. Catalysts 2021, 11, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, M.; Gutiérrez-Bouzán, M.C. Electrochemical techniques in textile processes and wastewater treatment. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 629103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcher, S.; Kornmüller, A.; Jekel, M. Anion exchange resins for removal of reactive dyes from textile wastewaters. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4717–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, R.D.; Kane, P.B. Colour removal using nanoparticles. Text. Cloth. Sustain. 2017, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alswieleh, A.M. Efficient Removal of Dyes from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption on L-Arginine-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Processes 2022, 10, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, N.S.; Amari, A.; Katubi, K.M.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Harharah, H.N.; Rebah, F.B.; Tahoon, M.A. The biocatalytic degradation of organic dyes using laccase immobilized magnetic nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahmatkesh, S.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Bokhari, A.; Sundaramurthy, S.; Panneerselvam, B.; Rezakhani, Y. Wastewater treatment with nanomaterials for the future: A state-of-the-art review. In Environmental Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; p. 114652. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, A.; Hussain, S.; Mushtaq, W.; Zubair, M.; Siddique, K.; Attia, K.; Khan, N.; Fiaz, S.; Azeem, F.; Chen, Y. Application of silver nanoparticles synthesized through varying biogenic and chemical methods for wastewater treatment and health aspects. In Environmental Science and Pollution Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Palani, G.; Trilaksana, H.; Sujatha, R.M.; Kannan, K.; Rajendran, S.; Korniejenko, K.; Nykiel, M.; Uthayakumar, M. Silver Nanoparticles for Waste Water Management. Molecules 2023, 28, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaram, S.; Razafindralambo, H.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Vasantharaj, S.; Ghafarifarsani, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Raeeszadeh, M. Applications of Green Synthesized Metal Nanoparticles—A Review. In Biological Trace Element Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Abdussalam-Mohammed, W.; Mohamed, L.; Abraheem, M.S.; Mansour, M.M.; Sherif, A.M. Biofabrication of Silver Nanoparticles Using Teucrium Apollinis Extract: Characterization, Stability, and Their Antibacterial Activities. Chemistry 2023, 5, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.; Rauf, A.; Khan, S.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Alshammari, A.; Alharbi, M.; Alam, A.; Suleria, H.A.R. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Rhazya stricta Decne Extracts and Their Anti-Microbial and Anti-Oxidant Activities. Crystals 2023, 13, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.-H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. ‘Green’ synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications—An updated report. Saudi. Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, M.; Khan, R.; Afridi, K.; Nadhman, A.; Ullah, S.; Faisal, S.; Mabood, Z.U.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Green Synthesis of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles (CeO(2) NPs) and Their Antimicrobial Applications: A Review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5951–5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlalveni, C.; Lallianrawna, S.; Biswas, A.; Selvaraj, M.; Changmai, B.; Rokhum, S.L. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts and their antimicrobial activities: A review of recent literature. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 2804–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Lee, C.-S. Green Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Clerodendrum inerme; Characterization, Antimicrobial, and Antioxidant Activities. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.F.; Xiaoyi, L.; Shaoqin, Z.; Horváth, P.G.; Bak, M.; Bejó, L.; Sipos, G.; Alpár, T. Functional silver nanoparticles synthesis from sustainable point of view: 2000 to 2023—A review on game changing materials. In Heliyon; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; p. 12322. [Google Scholar]
- Masum, M.M.I.; Siddiqa, M.M.; Ali, K.A.; Zhang, Y.; Abdallah, Y.; Ibrahim, E.; Qiu, W.; Yan, C.; Li, B. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Phyllanthus emblica Fruit Extract and Its Inhibitory Action Against the Pathogen Acidovorax oryzae Strain RS-2 of Rice Bacterial Brown Stripe. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsareii, S.A.; Manaa Alamri, A.; AlAsmari, M.Y.; Bawahab, M.A.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Shaikh, I.A.; Shettar, A.K.; Hoskeri, J.H.; Kumbar, V. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles from Rhizophora apiculata and Studies on Their Wound Healing, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Cytotoxic Activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettadili, F.E.; Aghris, S.; Laghrib, F.; Farahi, A.; Saqrane, S.; Bakasse, M.; Lahrich, S.; El Mhammedi, M.A. Recent advances in the nanoparticles synthesis using plant extract: Applications and future recommendations. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1248, 131538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkamu, W.W.; Bitew, L.T. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Hagenia abyssinica (Bruce) J.F. Gmel plant leaf extract and their antibacterial and anti-oxidant activities. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salayová, A.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Daneu, N.; Baláž, M.; Lukáčová Bujňáková, Z.; Balážová, Ľ.; Tkáčiková, Ľ. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Activity Using Various Medicinal Plant Extracts: Morphology and Antibacterial Efficacy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.; Grace, O.M.; Saslis-Lagoudakis, C.H.; Nilsson, N.; Simonsen, H.T.; Rønsted, N. Global medicinal uses of Euphorbia L. (Euphorbiaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 176, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Jannet, S.; Hymery, N.; Bourgou, S.; Jdey, A.; Lachaal, M.; Magné, C.; Ksouri, R. Antioxidant and selective anticancer activities of two Euphorbia species in human acute myeloid leukemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riina, R.; Villaverde, T.; Rincón-Barrado, M.; Molero, J.; Sanmartín, I. More than one sweet tabaiba: Disentangling the systematics of the succulent dendroid shrub Euphorbia balsamifera. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 59, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljubiri, S.M.; Mahgoub, S.A.; Almansour, A.I.; Shaaban, M.; Shaker, K.H. Isolation of diverse bioactive compounds from Euphorbia balsamifera: Cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity studies. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamba, A.; Hassan, L. Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial activities of Euphorbia balsamifera leaves, stems and root against some pathogenic microorganisms. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 4, 645–652. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.B.; Shameli, K.; Darroudi, M.; Yunus, W.M.Z.W.; Ibrahim, N.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver/Clay Nanocomposites by Chemical Reduction Method. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 6, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, S.; Oves, M.; Khan, A.U. Obliteration of bacterial growth and biofilm through ROS generation by facilely synthesized green silver nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, J.; Wang, D.; Kim, Y.-J.; Ahn, S.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Wang, C.; Yang, D.C. Biosynthesis, characterization, and bioactivities evaluation of silver and gold nanoparticles mediated by the roots of Chinese herbal Angelica pubescens Maxim. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Perumalsamy, H.; Lee, S.; Hwang, E.; Yi, T.-H. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Euphrasia officinalisleaf extract to inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraj, M.; Rajesh, M.; Arun, R.; MubarakAli, D.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sivanandhan, G.; Dev, G.K.; Manickavasagam, M.; Premkumar, K.; Thajuddin, N. An investigation on the cytotoxicity and caspase-mediated apoptotic effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Podophyllum hexandrum on human cervical carcinoma cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya Tahir, M.; Ahmad, A.; Alothman, A.; Mushab, M.S.S.; Ali, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Thespesia populnea Bark Extract for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue (MB) Degradation via Photocatalysis with Antimicrobial Activity and for Anticancer Activity. In Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications; NIH: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2022; Volume 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Naghizade Asl, M.; Mahmodi, N.M.; Teymouri, P.; Shahmoradi, B.; Rezaee, R.; Maleki, A. Adsorption of organic dyes using copper oxide nanoparticles: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 25278–25287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Tiwari, K.N.; Saini, R.; Kumar, P.; Mishra, S.K.; Yadav, V.B.; Nath, G. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis L. and assessment of its antioxidant, antimicrobial response. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 2266–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvith, V.; Philip, D. Catalytic degradation of methylene blue using biosynthesized gold and silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalakshmi, K.; Venugobal, J.; Ramasamy, V. Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Das, M.P.; Velusamy, P. Sesbania grandiflora leaf extract mediated green synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles against selected human pathogens. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 104, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, M.; Umadevi, M. Silver and gold nanoparticles for sensor and antibacterial applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 128, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasiuk, R.; Frackowiak, J.E.; Krychowiak, M.; Matuszewska, M.; Kawiak, A.; Ziabka, M.; Lendzion-Bielun, Z.; Narajczyk, M.; Krolicka, A. Synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles through a photomediated reaction in an aqueous environment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 315. [Google Scholar]
- Parvathiraja, C.; Shailajha, S.; Shanavas, S.; Mubina, K. Photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of bio-treated Ag nanoparticles synthesized using Tinospora cordifolia leaf extract. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 8515–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Badot, P.-M. Starch-based biosorbents for dyes in textile wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2010, 12, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, Y.N.; de Paula Filho, F.J.; Bacurau, V.P.; Menezes, J.M.C.; Fan, A.Z.; Melo, R.P.F. Removal of Methylene Blue from a synthetic effluent by ionic flocculation. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, M.Y.; Ahmed, I.S.; Mohamed, T.Y.; Khatab, M. A controlled, template-free, and hydrothermal synthesis route to sphere-like α-Fe2O3 nanostructures for textile dye removal. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 20001–20013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Shi, Q.; Feng, J.; Yao, J.; Huang, H.; Xie, X. Adsorption Behaviors of Cationic Methylene Blue and Anionic Reactive Blue 19 Dyes onto Nano-Carbon Adsorbent Carbonized from Small Precursors. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Kinetic modeling of liquid-phase adsorption of reactive dyes and metal ions on chitosan. Water Res. 2001, 35, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

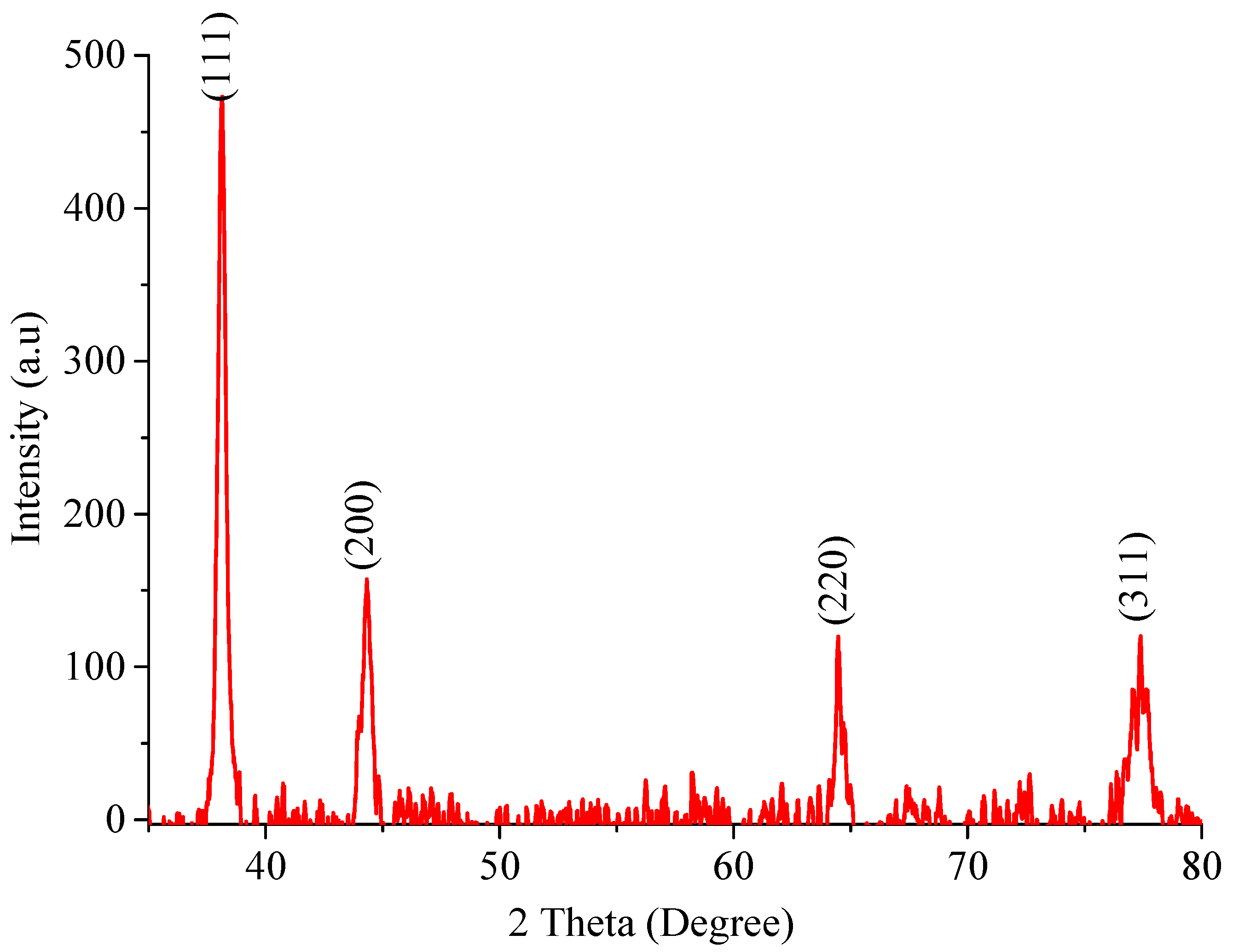

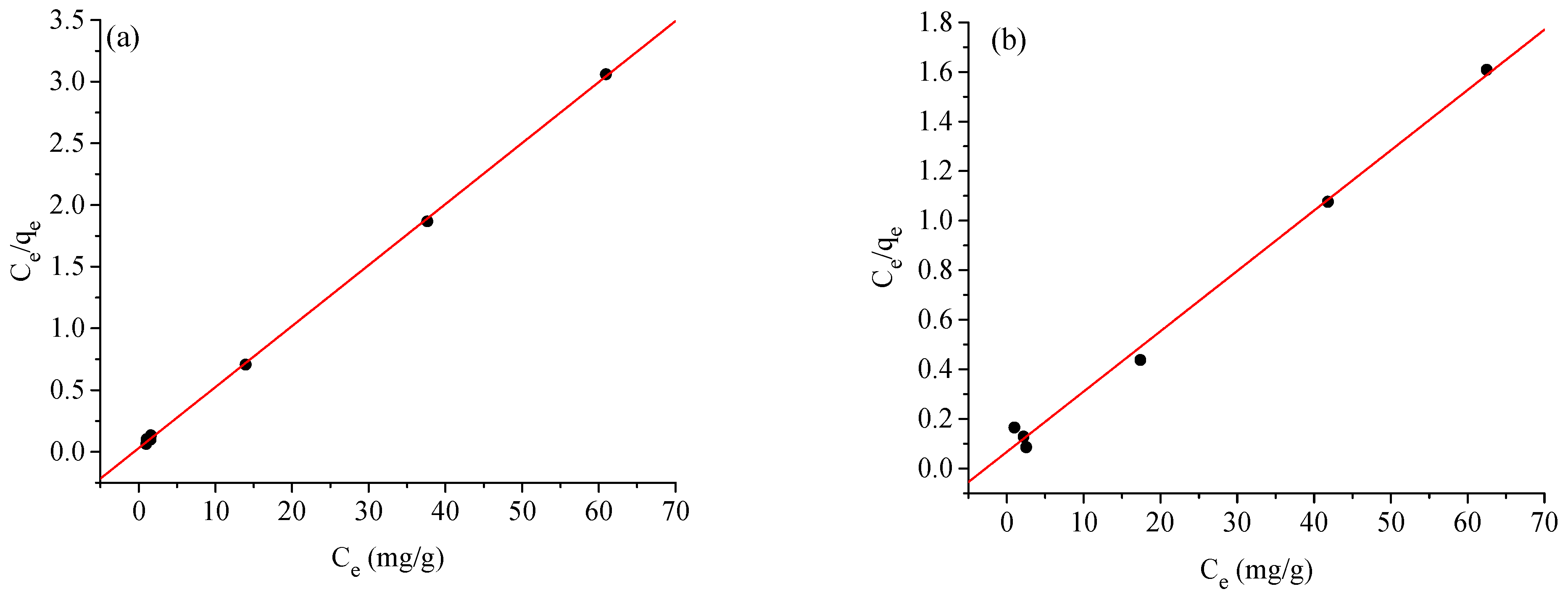
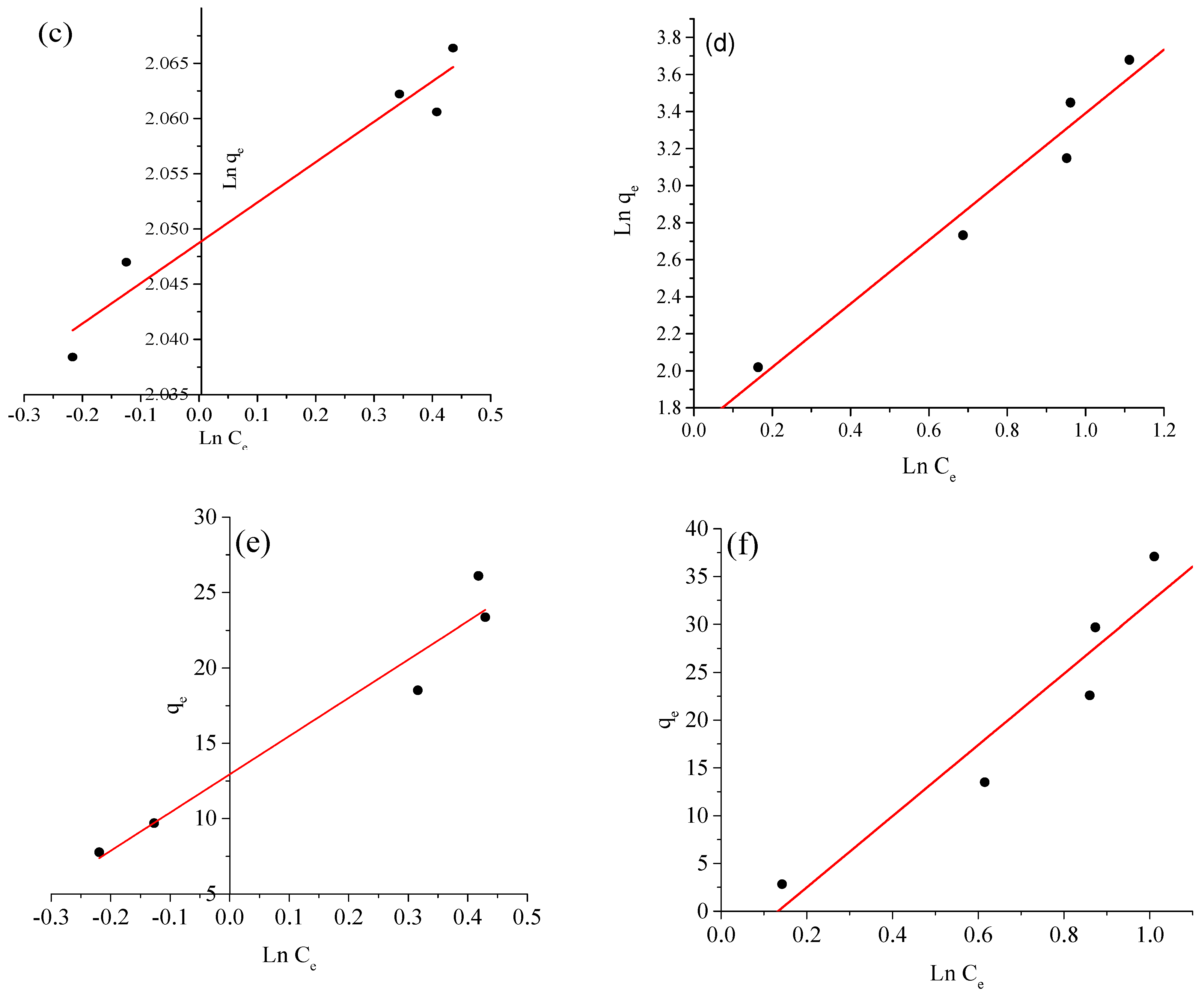
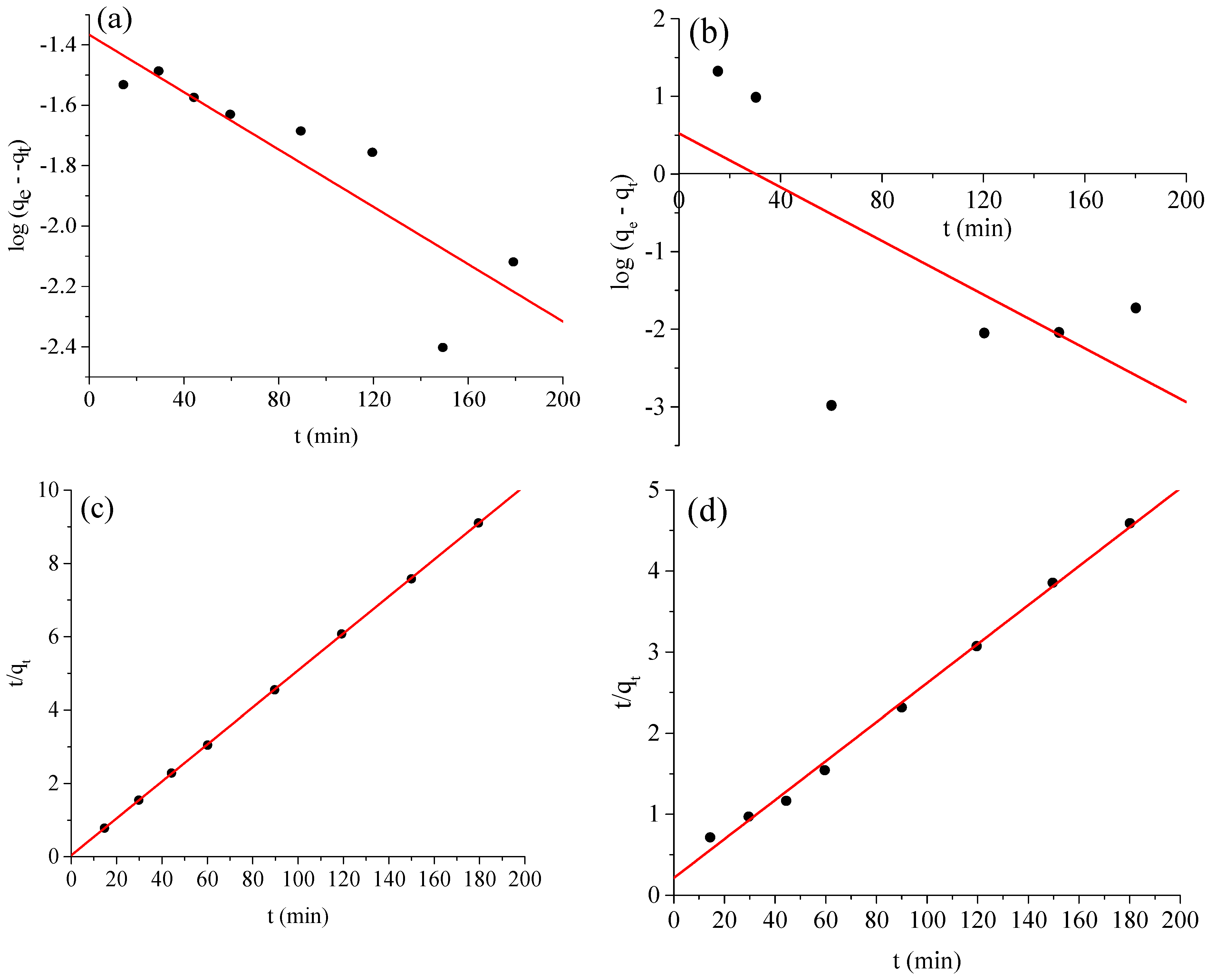
| No of Peaks | 2θ (Degree) | θ | FWHM | Height | d Value [Å] | (hkl) | t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38.05 | 19.07 | 0.4351 | 456.4 | 2 | 111 | 19.12 |
| 2 | 44.32 | 22.16 | 0.5428 | 143.9 | 2 | 200 | 15.64 |
| 3 | 64.70 | 32.26 | 0.4872 | 94.3 | 1 | 220 | 19.09 |
| 4 | 77.35 | 38.68 | 1.0103 | 94.4 | 1 | 311 | 09.97 |
| Isotherm Models | Variables | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCG | BPB | ||
| Langmuir | KL (L mg−1) | 01.2800 | 00.5329 |
| qm(cal) (mg g−1) | 20.4081 | 40.7166 | |
| R12 | 00.9981 | 00.9944 | |
| RL | 00.0077 | 00.0184 | |
| Freundlich | KF (mg g−1) (L mg−1)1/n | 07.7566 | 5.3924 |
| R22 | 00.8276 | 00.8276 | |
| n | 28.8350 | 00.5384 | |
| Temkin | BT (J. mol−1) | 25.2973 | 33.1412 |
| KT (L g−1) | 01.6521 | 00.9929 | |
| R32 | 00.8370 | 00.8327 | |
| Kinetic Models | Variables | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCG | BPB | ||
| Pseudo first order | k1 (min−1) | 9 × 10−5 | 0.0003 |
| qe(cal) (mg g−1) | 39.644 | 38.900 | |
| r12 | 0.7753 | 0.4335 | |
| qe(exp) (mg g−1) | 0.2832 | 1.468 | |
| Pseudo second order | k2 [g mg−1 min−1] | 1.600 | 0.0033 |
| qe(cal) (mg g−1) | 39.644 | 38.900 | |
| r22 | 1 | 0.9959 | |
| qe(exp) (mg g−1) | 39.821 | 41.0340 | |
| Temperature (K) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCG | BPB | BCG | BPB | BCG | BPB | BCG | BPB | |
| 288 | 1.3707 | 0.845 | −3.282 | −2.023 | 173.503 | 128.528 | 0.6125 | 0.4526 |
| 293 | 2.1248 | 1.508 | −5.176 | −0.004 | ||||
| 298 | 3.8078 | 2.649 | −9.434 | −0.006 | ||||
| Bromocresol Green, (BCG) | Bromophenol Blue, (BPB) | |
|---|---|---|
| Dye IUPAC name | 3,3-Bis(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)-3H-benzo [c] [1,2]oxathiole 1,1-dioxide | 3,3-Bis(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,1-benzoxathiole-1,1(3H)-dione |
| Chemical structure | 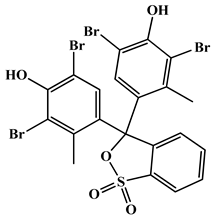 | 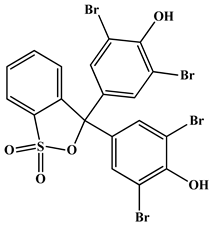 |
| Molecular formula | C21H14Br4O5S | C19H10Br4O5S |
| Chemical class | Sulfonephthaleins | Phenolphthaleins |
| λmax | 600 nm | 590 nm |
| Type | Anionic dye | Anionic dye |
| Solubility | Soluble in NaOH, water (6 mg/mL), ethanol (40 mg/mL), benzene, and diethyl ether. | Soluble in NaOH, methyl and ethyl alcohols, benzene, and acetic acid. Slightly soluble in water (0.4 g/100 g) at 20 °C. |
| CAS Number | Bromocresol green 76-60-8 | Bromophenol blue 115-39-9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljubiri, S.M.; El-Shwiniy, W.H.; Younes, A.A.O.; Alosaimi, E.H.; El-wahaab, B.A. Use of Euphorbia balsamifera Extract in Precursor Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Bromocresol Green and Bromophenol Blue Toxic Dyes. Molecules 2023, 28, 3934. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093934
Aljubiri SM, El-Shwiniy WH, Younes AAO, Alosaimi EH, El-wahaab BA. Use of Euphorbia balsamifera Extract in Precursor Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Bromocresol Green and Bromophenol Blue Toxic Dyes. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3934. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093934
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljubiri, Salha M., Walaa H. El-Shwiniy, Ayman A. O. Younes, Eid H. Alosaimi, and Badr Abd El-wahaab. 2023. "Use of Euphorbia balsamifera Extract in Precursor Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Bromocresol Green and Bromophenol Blue Toxic Dyes" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3934. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093934
APA StyleAljubiri, S. M., El-Shwiniy, W. H., Younes, A. A. O., Alosaimi, E. H., & El-wahaab, B. A. (2023). Use of Euphorbia balsamifera Extract in Precursor Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Bromocresol Green and Bromophenol Blue Toxic Dyes. Molecules, 28(9), 3934. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093934





