Evaluation of the Impact of Two Thiadiazole Derivatives on the Dissolution Behavior of Mild Steel in Acidic Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis
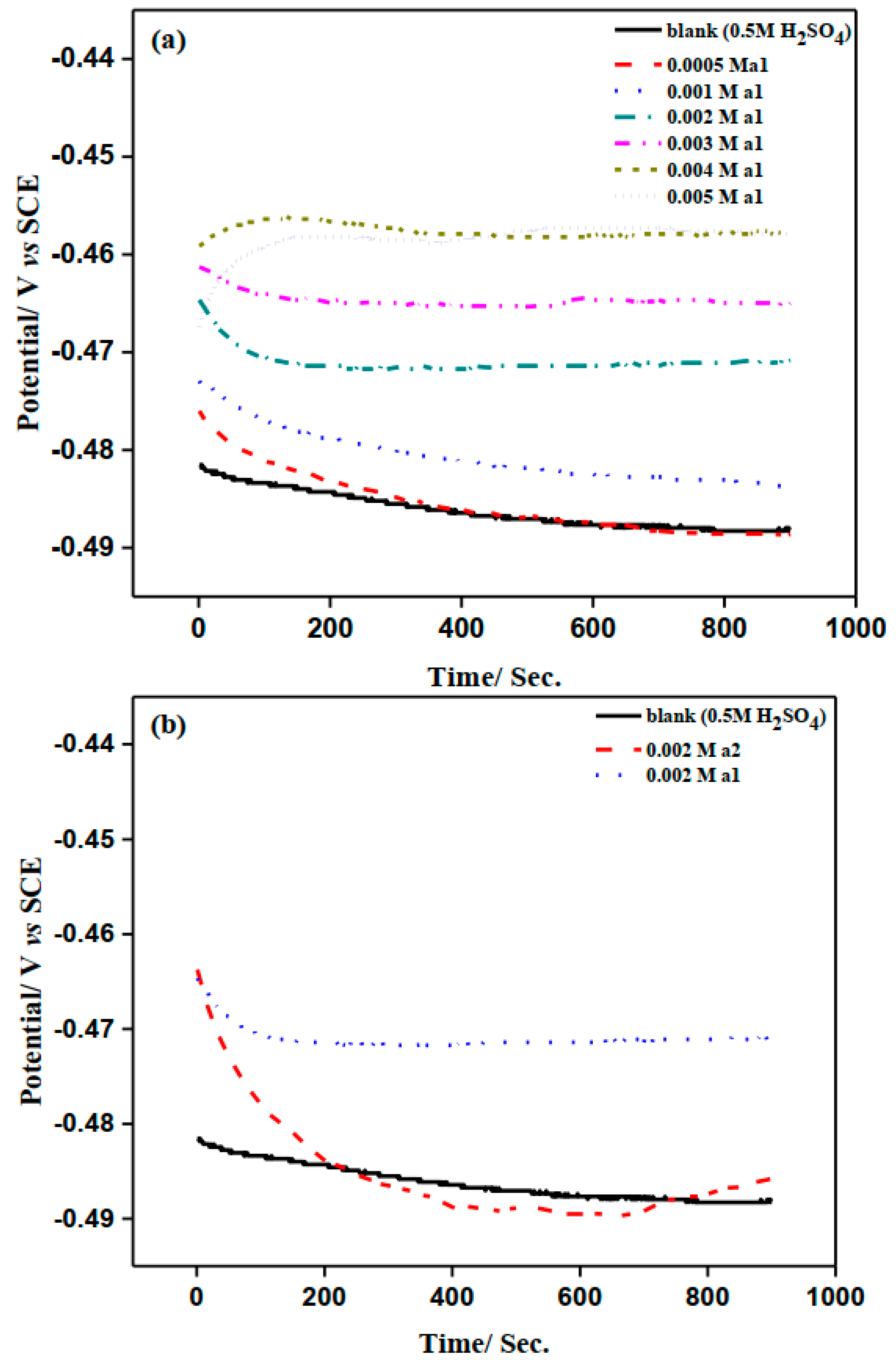
2.2. Open Circuit Potential Measurements
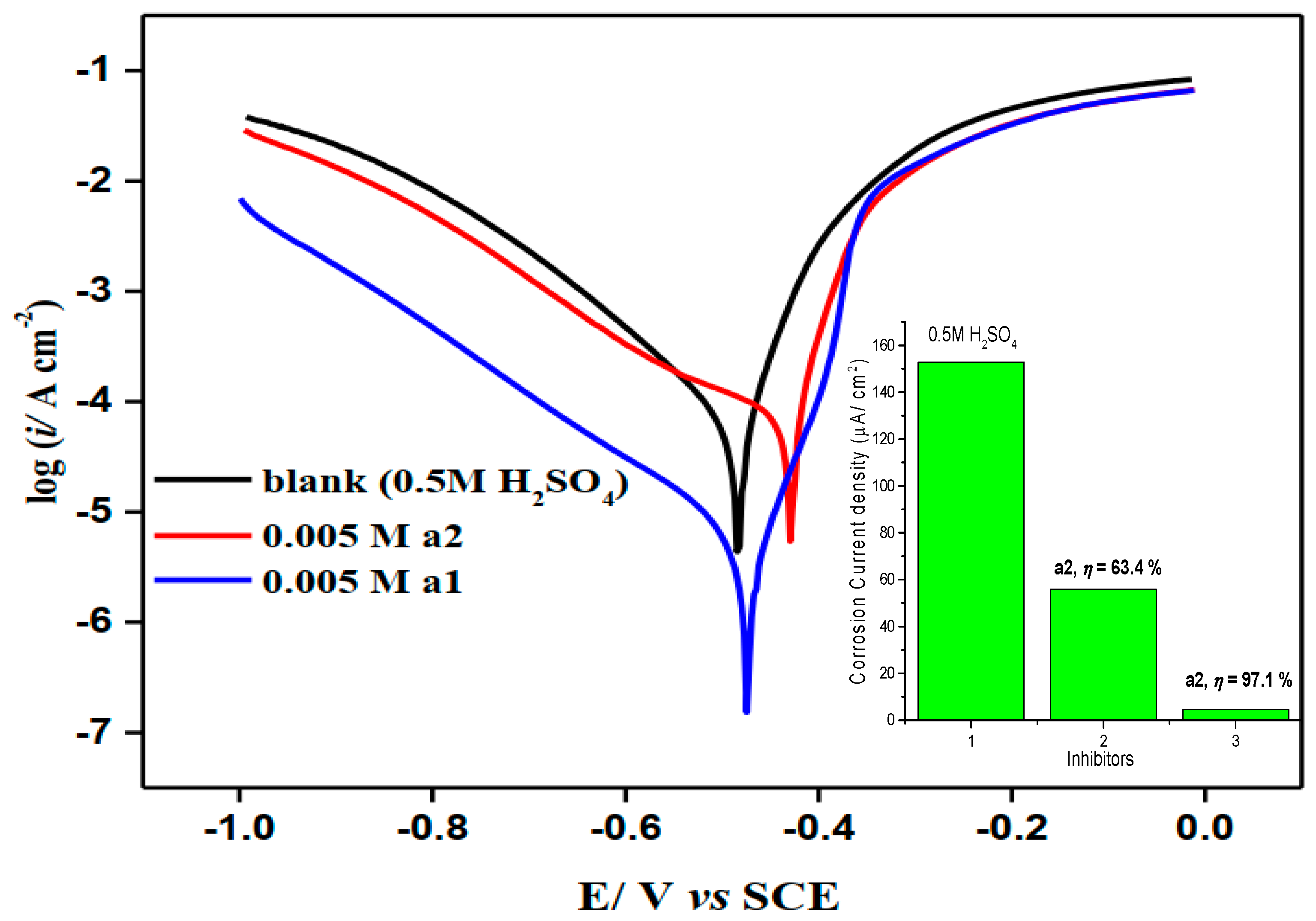
2.3. Potentiodynamic Polarization
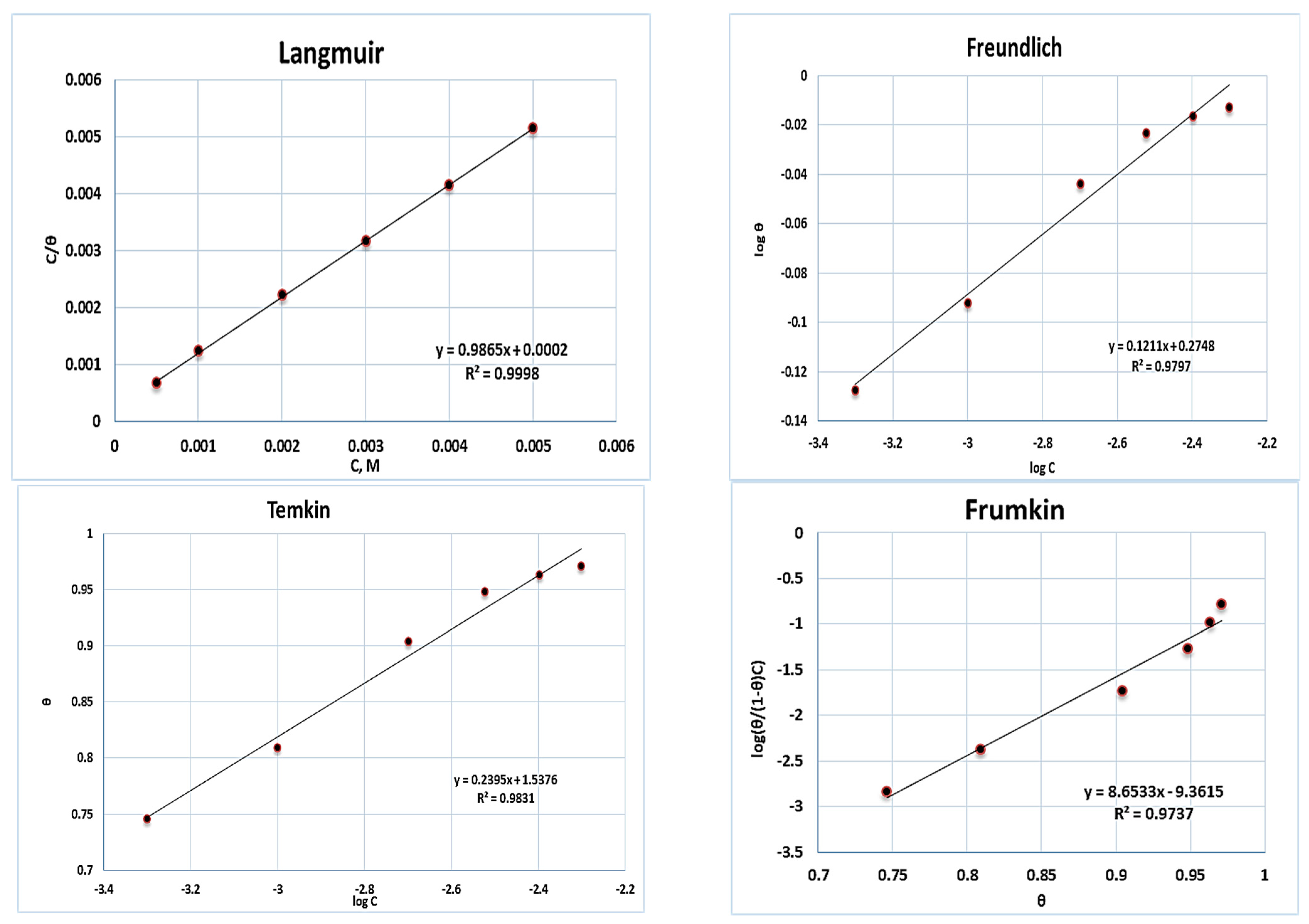
2.4. Adsorption Isotherm
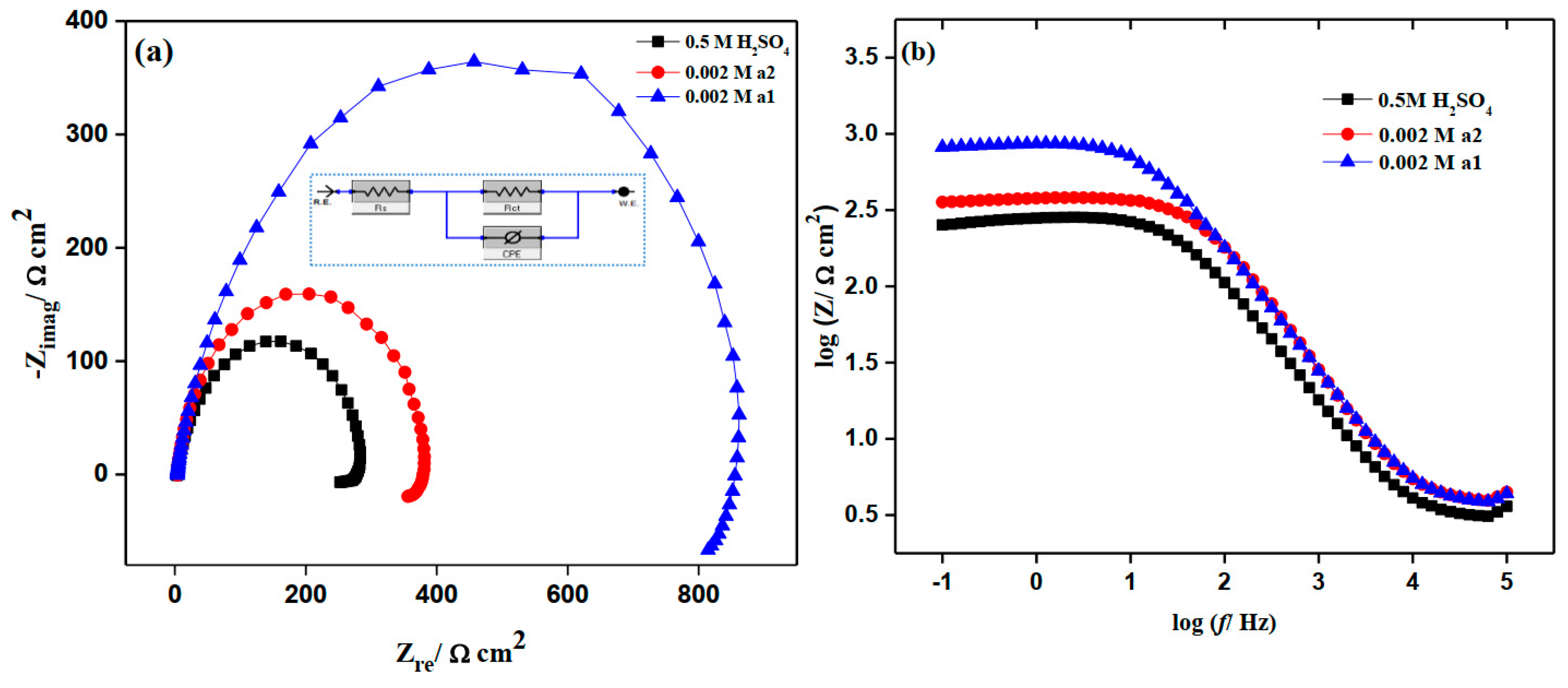
2.5. Electrochemical Impedance Study (EIS)
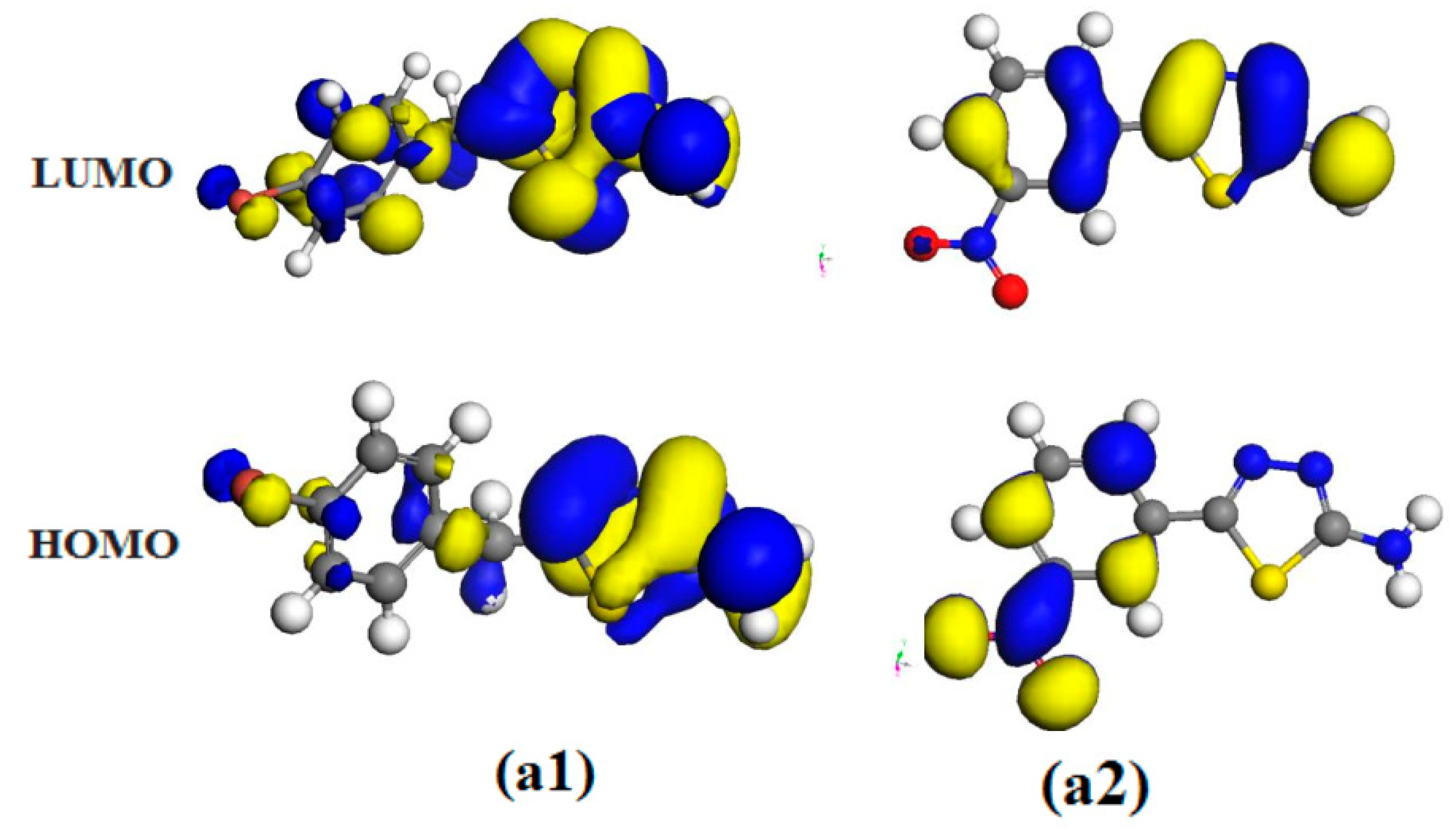
2.6. Theoretical Studies
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Equipment and Instrumentation
3.3. Synthesis of 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Derivatives
3.3.1. Synthesis of 2-Amino-5-(4-Bromobenzyl)-1,3,4-Thiadiazole
3.3.2. Synthesis of 2-Amino-5-(3-Nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-Thiadiazole
3.4. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Gopi, D.; Govindaraju, K.M.; Kavitha, L. Investigation of triazole derived Schiff bases as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, M.P.; Mohana, K.N. Adsorption and Corrosion Inhibition Characteristics of Some Nicotinamide Derivatives on Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. ISRN Corros. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Viburnum Sargentii Koehne Fruit Extract As Corrosion Inhibitor For Mild Steel In Acidic Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 5228–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manh, T.D.; Huynh, T.L.; Thi, B.V.; Lee, S.; Yi, J.; Dang, N.N. Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Environments Containing Sonneratia caseolaris Leaf Extract. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 8874–8886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faiz, M.; Zahari, A.; Awang, K.; Hussin, H. Corrosion inhibition on mild steel in 1 M HCl solution by Cryptocarya nigra extracts and three of its constituents (alkaloids). RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 6547–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odusote, J.K.; Ajayi, O.M. Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Acidic Medium by Jathropha Curcas Leaves Extract. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghzadeh, R.; Ejlali, L.; Eshaghi, M.; Basharnavaz, H.; Seyyedi, K. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel surface by isoxazoles in HCl solution: Electrochemical studies. Chem. Rev. Lett. 2021, 4, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haddad, M.A.M.; Radwan, A.B.; Sliem, M.H.; Hassan, W.M.I.; Abdullah, A.M. Highly efficient eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 5 M HCl at elevated temperatures: Experimental & molecular dynamics study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthamma, K.; Kumari, P.; Lavanya, M.; Rao, S.A. Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Acidic Media by N-[(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)Methyleneamino]-4-Hydroxy-Benzamide. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2020, 7, 3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Shukla, S.K.; Quraishi, M.A. Corrosion behaviour of mild steel in sulphuric acid solution in presence of ceftazidime. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 5802–5814. [Google Scholar]
- Ammal, P.R.; Prajila, M.; Joseph, A. Effective inhibition of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid using EBIMOT, a 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole derivative bearing a 2-ethylbenzimidazole moiety: Electro analytical, computational and kinetic studies. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviprabha, K.; Bhat, R.S. 5-(3-Pryridyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thiol as Potential Corrosion Inhibitor for AA6061 Aluminium Alloy in 0.1 M Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 2019, 55, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S. Measurement of Hydrogen Produced during Magnesium Corrosion in Hydrochloric Acid and the Effect of the Triton X-100 Surfactant on Hydrogen Production. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2018, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosari, A.; Moayed, M.; Davoodi, A.; Parvizi, R.; Momeni, M.; Eshghi, H.; Moradi, H. Electrochemical and quantum chemical assessment of two organic compounds from pyridine derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in HCl solution under stagnant condition and hydrodynamic flow. Corros. Sci. 2014, 78, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S. Expired Desloratidine Drug as Inhibitor for Corrosion of Carbon Steel Pipeline in Hydrochloric acid Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 150852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.G.N. Some new fundamental aspects in corrosion inhibition. In Corrosion Inhibitors; Nova Science Publisher: Ferrara, Italy, 1980; pp. 453–470. [Google Scholar]
- Aejitha, S.; Kasthuri, P.; Geethamani, P. Comparative Study of Corrosion Inhibition of Commiphora caudata and Digera muricata for Mild Steel in 1 M HCl Solution. Asian J. Chem. 2016, 28, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviprabha, K.; Bhat, R.S. Inhibition Effects of Ethyl-2-Amino-4-Methyl-1,3-Thiazole-5-Carboxylate on the Corrosion of AA6061 Alloy in Hydrochloric Acid Media. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2019, 19, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, S.; Bingham, R.; Mills, D. Advances in corrosion protection by organic coatings: What we know and what we would like to know. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 102, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, T.; Hauptmann, S. The Chemistry of Heterocycles: Structure, Reactions, Synthesis, and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Quraishi, M.; Rawat, J.; Ajmal, M. Dithiobiurets: A novel class of acid corrosion inhibitors for mild steel. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2000, 30, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Evaluation of 2-mercaptobenzimidazole as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in phosphoric acid. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Obot, I.B.; Zheng, X.; Shen, X.; Qiang, Y.; Kaya, S.; Kaya, C. Theoretical insight into an empirical rule about organic corrosion inhibitors containing nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur atoms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 406, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.A.; Simant, S.; Ankur, V.; Veerasamy, R.; Kishore, A.R. 1,3,4-Thiadiazole and its derivatives: A review on recent progress in biological activities. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 557–576. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Cui-Yun, L.; Xiao-Ming, W.; Yong-Hua, Y.; Hai-Liang, Z. 1,3,4-Thiadiazole: Synthesis, reactions, and applications in medicinal, agricultural, and materials chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5572–5610. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, S.; Liang, D.; Ba, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, S. Adsorption behavior of thiadiazole derivatives as anticorrosion additives on copper oxide surface: Computational and experimental studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 492, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.-P.; Cao, L.; Wang, L.-L. An investigation into the antiwear, antioxidation, and anticorrosion behaviour of some derivatives of 2,5-dimercapto -1,3,4-thiadiaxole. Lubr. Sci. 1995, 7, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. Electrophoretic deposition of graphene coating as a corrosion inhibitor for copper in NaCl solution. Results Surf. Interfaces 2022, 8, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.-L.; Shao, J.-J.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Lai, Y.-M.; Zhao, Z.-N. Adsorption and corrosion of renewable inhibitor of Pomelo peel extract for mild steel in phosphoric acid solution. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akande, I.; Oluwole, O.; Fayomi, O. Optimizing the defensive characteristics of mild steel via the electrodeposition of ZnSi3N4 reinforcing particles. Def. Technol. 2019, 15, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjaji, N.; Rico, I.; Srhiri, A.; Lattes, A.; Soufiaoui, M.; Ben Bachir, A. Effect of N-Alkylbetaines on the Corrosion of Iron in 1 M HCl Solution. Corrosion 1993, 49, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.; Kamar, E.; Eid, S.; El-Etre, A. Animal glue as green inhibitor for corrosion of aluminum and aluminum-silicon alloys in sodium hydroxide solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.; Kamar, E.M.; El-Etre, A.Y.; Eid, S. Gelatin as corrosion inhibitor for aluminum and aluminum silicon alloys in sodium hydroxide solutions. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surfaces 2016, 52, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadom, A.A.; Yaro, A.S. Mass transfer effect on corrosion inhibition process of copper–nickel alloy in hydrochloric acid by Benzotriazole. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Otaibi, N.; Hammud, H.H. Corrosion Inhibition Using Harmal Leaf Extract as an Eco-Friendly Corrosion Inhibitor. Molecules 2021, 26, 7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raviprabha, K.; Ramesh, S. Bhat, Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in 0.5 M HCL by substituted 1,3,4- oxadiazole. Egypt. J. Pet. 2023, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annon, I.A.; Abbas, A.S.; Al-Azzawi, W.K.; Hanoon, M.M.; Alamiery, A.A.; Isahak, W.N.R.W.; Kadhum, A.A.H. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid environment using thiadiazole derivative: Weight loss, thermodynamics, adsorption and computational investigations. South Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 41, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, Z.R.; Moustapha, M.E.; Anouar, E.H.; El-Hafeez, G.M.A. The inhibition tendencies of novel hydrazide derivatives on the corrosion behavior of mild steelin hydrochloric acid solution. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Sayyid, F.; Betti, N.; Shaker, L.; Hanoon, M.; Alamiery, A.; Kadhum, A.; Takriff, M. Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid environment by 1-amino-2-mercapto-5-(4-(pyrrol-1-yl)phenyl)-1,3,4-triazole. South Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 39, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozada, P.A.; Xometl, O.O.; Likhanova, N.V.; Lijanova, I.V.; García, J.R.V.; Ramıírez, R.E.H. Adsorption and performance of ammonium based ionic liquids as corrosion inhibitors of steel. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Liu, D.; Ding, H.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Gui, J. Task specific ionic liquids as corrosion inhibitors on carbon steel in 0.5 M HCl solution: An experimental and theoretical study. Case Stud. Fire Saf. 2019, 153, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Liu, D.; Ding, H.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Gui, J. Corrosion inhibition effects of a novel ionic liquid with and without potassium iodide for carbon steel in 0.5 M HCl solution: An experimental study and theoretical calculation. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 275, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashed, O.; Nazeeer, A.A. Effectiveness of some novel ionic liquids on mild steel corrosion protection in acidic environment: Experimental and theoretical inspections. Materials 2022, 15, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, N.H.; El-Hashemy, M.A.; Derafa, W.M.; Althobaiti, I.O.; Altaleb, H.A. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel by highly stable polydentate schiff base derived from 1,3- propanediamine in aqueous acidic solution. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2022, 26, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyam, D.F.; Tantawy, A.H.; Eid, S.; El-Etre, A.Y. Study of the inhibition effect of two novel synthesized amido-amine -based cationic surfactants on aluminum corrosion in 0.5 M HCl solution. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2022, 25, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, F.M.; Nobe, K. Theory of organic corrosion inhibitors: Adsorption and linear free energy relationships. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1965, 112, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, E.; Bellucci, F.; Latanision, R.M.; El-Ashry, E.S.H. Acid Corrosion Inhibition of Nickel by 2-(Triphenosphoranylidene) Succinic Anhydride. Corrosion 1991, 47, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, K.S.; Parameswaran, G. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution by Schiff base furoin thiosemicarbazone. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttner, K. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) of corrosion processes on inhomogeneous surfaces. Electrochimica Acta 1990, 35, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, M.H.; Kassim, M.J.; Razali, N.; Dahon, N.; Nasshorudin, D. The effect of Tinospora crispa extracts as a natural mild steel corrosion inhibitor in 1M HCl solution. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S616–S624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathina, A.; Rajalakshmi, R. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acid medium using canna indica as green corrosion inhibitor. Rasayan J. Chem. 2016, 9, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.A.; Khaled, K.; Mohsen, Q.; Arida, H. A study of the inhibition of iron corrosion in HCl solutions by some amino acids. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1684–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.; Hassan, W.M.I. Chemical and Theoretical Studies for Corrosion Inhibition of Magnesium in Hydrochloric Acid by Tween 80 Surfactant. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 8017–8027. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, M.M.; Soliman, K.A.; Eid, S.; Mabrouk, E.M. Experimental and theoretical study on some azo chromotropic acid dyes compounds as inhibitor for carbon steel corrosion in sulfuric acid. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2022, 19, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
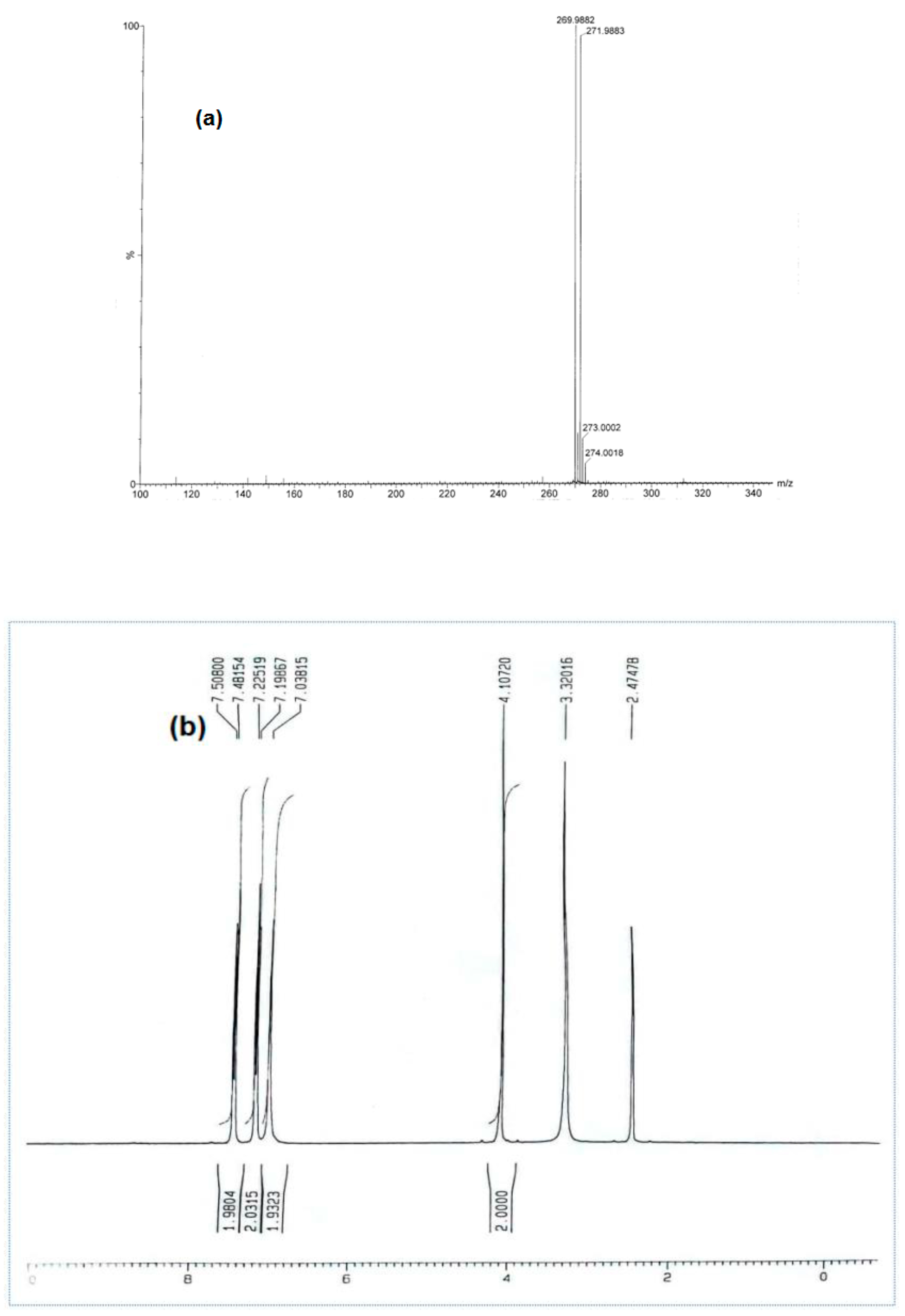
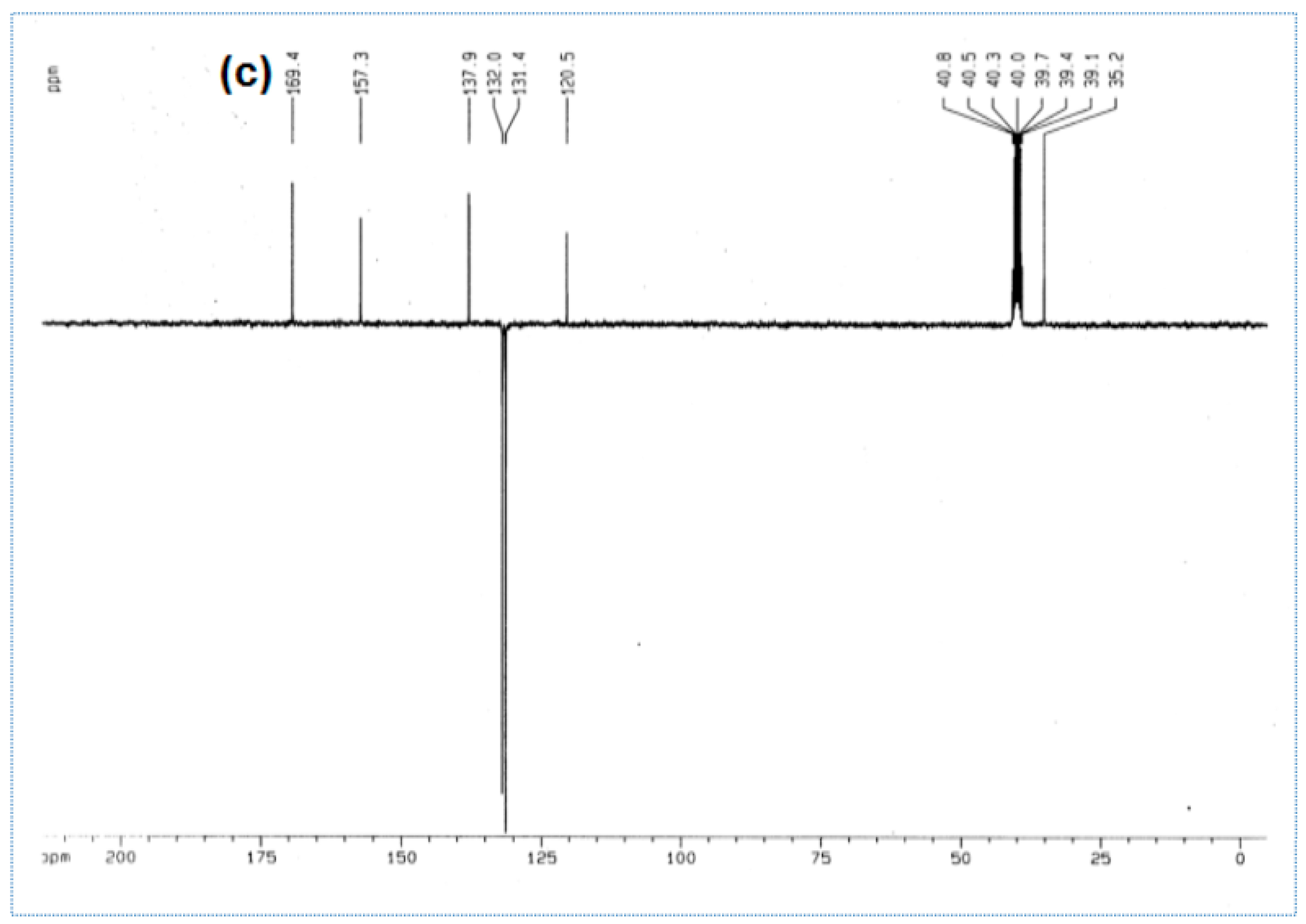




| Molecular Code | Molecular Structure | Molecular Name, Molecular Weight, Chemical Formula | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | 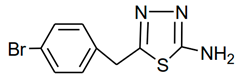 | 2-amino-5-(4- bromobenzyl)- 1,3,4-thiadiazole Molecular weight: 268.96 Chemical Formula: C9H8BrN3S | White crystal, Yield 65%; mp: 200–202 °C; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 4.10720 (s, 2H,-CH2-), 7.03815 (s, 2H, -NH2), 7.22519 (d, 2H, J = 8.18 Hz), 7.50800 (d, 2H, J = 8.079 Hz); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, δ ppm): (169.4, 157.3, 137.9, 132.0, 131.4, 120.5, 35.2); ESI-MS: 269.9 (100), 271.9 (98). |
| a2 |  | 2-amino-5-(3- nitrophenyl)-1,3,4- thiadiazole Molecular weight: 222.02 Chemical Formula: C8H6N4O2S | Yellow crystal. Yield 60%, mp:236- 238 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 7.62254 (s, 2H, -NH2), 7.71640–8.45752 (m, 4H, ArH); ESI-MS: 223 (100) |
| Inhibitor | Ecorr /mV | Icorr/ µA cm−2 | ßa/ mV dec−1 | ßc/ mV dec−1 | θ | IP% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | −503.1 | 152.7 | 91.2 | −174.4 | - | - |
| 0.005 M a1 | −459.4 | 4.5 | 41.9 | −169.7 | 0.971 | 97.1 |
| 0.005 M a2 | −434.7 | 55.9 | 39.1 | −201.6 | 0.634 | 63.4 |
| Inhibitor Conc/M | Ecorr /mV | Icorr / µA cm−2 | ßa/ mV dec−1 | ßc/ mV dec−1 | θ | IP% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | −503.1 | 152.7 | 91.2 | −174.4 | - | - |
| 0.0005 | −487.7 | 38.8 | 52.1 | −166.2 | 0.746 | 74.6 |
| 0.001 | −478.5 | 29.1 | 44.7 | −172.2 | 0.809 | 80.9 |
| 0.002 | −454.6 | 14.7 | 29.3 | −163.5 | 0.904 | 90.4 |
| 0.003 | −434.7 | 8.0 | 23.5 | −172.5 | 0.948 | 94.8 |
| 0.004 | −443.3 | 5.6 | 25.4 | −168.6 | 0.963 | 96.3 |
| 0.005 | −459.4 | 4.5 | 41.9 | −169.7 | 0.971 | 97.1 |
| Inhibitor | Concentration | Inhibition Efficiency | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5((6-Methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4yl)thiomethyl)-2((N-(3-methylquinoxalin-2(1H)one)yl) methyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole | 50 ppm | 84.85 | [36] |
| 1-(2-ethylamino-1,3,4-thiadiazol-5-yl)-3-phenyl-3-oxopropan (ETO) | 500 ppm | 98.4 | [37] |
| N-cyanoacetohydrazide (CAH) | 500 ppm | 48.24 | [38] |
| N-acryloylN0-cyanoacetohydrazide (ACAH) | 500 ppm | 91.1 | [38] |
| poly(N-acryloyl-N0-cyanoacetohydrazide) (PACAH) | 500 ppm | 96.57 | [38] |
| 1-Amino-2-mercapto-5-(4-(pyrrol-1-yl)phenyl)-1,3,4-triazole (AMPPT) | 500 ppm | 91.4 | [39] |
| N-trioctyl-N-methyl ammonium methylsulfate | 100 ppm | 92.0 | [40] |
| N-tetradecyl-N-trimethyl ammonium methylsulfate | 100 ppm | 94.0 | [40] |
| 1-(4-sulfonic acid) butyl-3-ethyl imidazolium hydrogen sulfate | 15 mM | 88.0 | [41] |
| 1,10 (1,4 phenylenebis (methylene))bis (3 (carboxymethyl) 1H imidazole 3 ium) chloride com KI (1:4) | 1 mM | 88.5 | [42] |
| 1-butyl-1-methyl-pyrrolidinium Imidazolate | 5 × 10−3 M | 92.32 | [43] |
| 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium Imidazolate | 5 × 10−3 M | 94.33 | [43] |
| 2-amino-5-(4-bromobenzyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole (a1) | 0.005 M | 97.1 | Our work |
| 2-amino-5-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole (a2) | 0.005 M | 63.4 | Our work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Althobaiti, I.O.; Eid, S.; El-Nasser, K.S.; Hashem, N.; Salama, E.E. Evaluation of the Impact of Two Thiadiazole Derivatives on the Dissolution Behavior of Mild Steel in Acidic Environments. Molecules 2023, 28, 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093872
Althobaiti IO, Eid S, El-Nasser KS, Hashem N, Salama EE. Evaluation of the Impact of Two Thiadiazole Derivatives on the Dissolution Behavior of Mild Steel in Acidic Environments. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093872
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlthobaiti, Ibrahim O., Salah Eid, Karam S. El-Nasser, Nady Hashem, and Eid Eissa Salama. 2023. "Evaluation of the Impact of Two Thiadiazole Derivatives on the Dissolution Behavior of Mild Steel in Acidic Environments" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093872
APA StyleAlthobaiti, I. O., Eid, S., El-Nasser, K. S., Hashem, N., & Salama, E. E. (2023). Evaluation of the Impact of Two Thiadiazole Derivatives on the Dissolution Behavior of Mild Steel in Acidic Environments. Molecules, 28(9), 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093872




