Temperature-Sensitive Modified Bentonite Based on NIPAM for Drilling Fluid: Experimental and Molecular Simulation Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Index Optimization
2.1.1. CMC-B
2.1.2. CMC-B-NIPAM
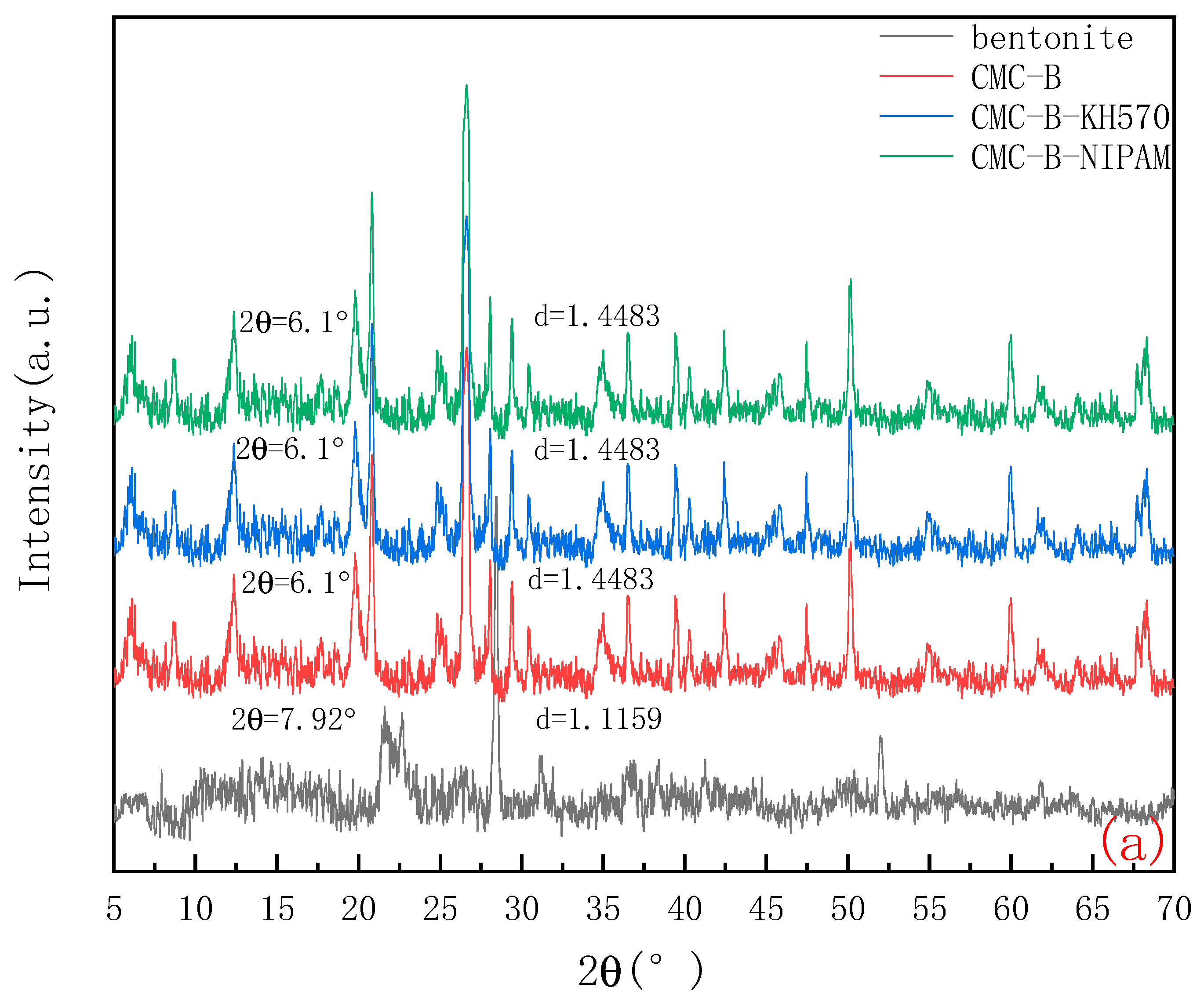
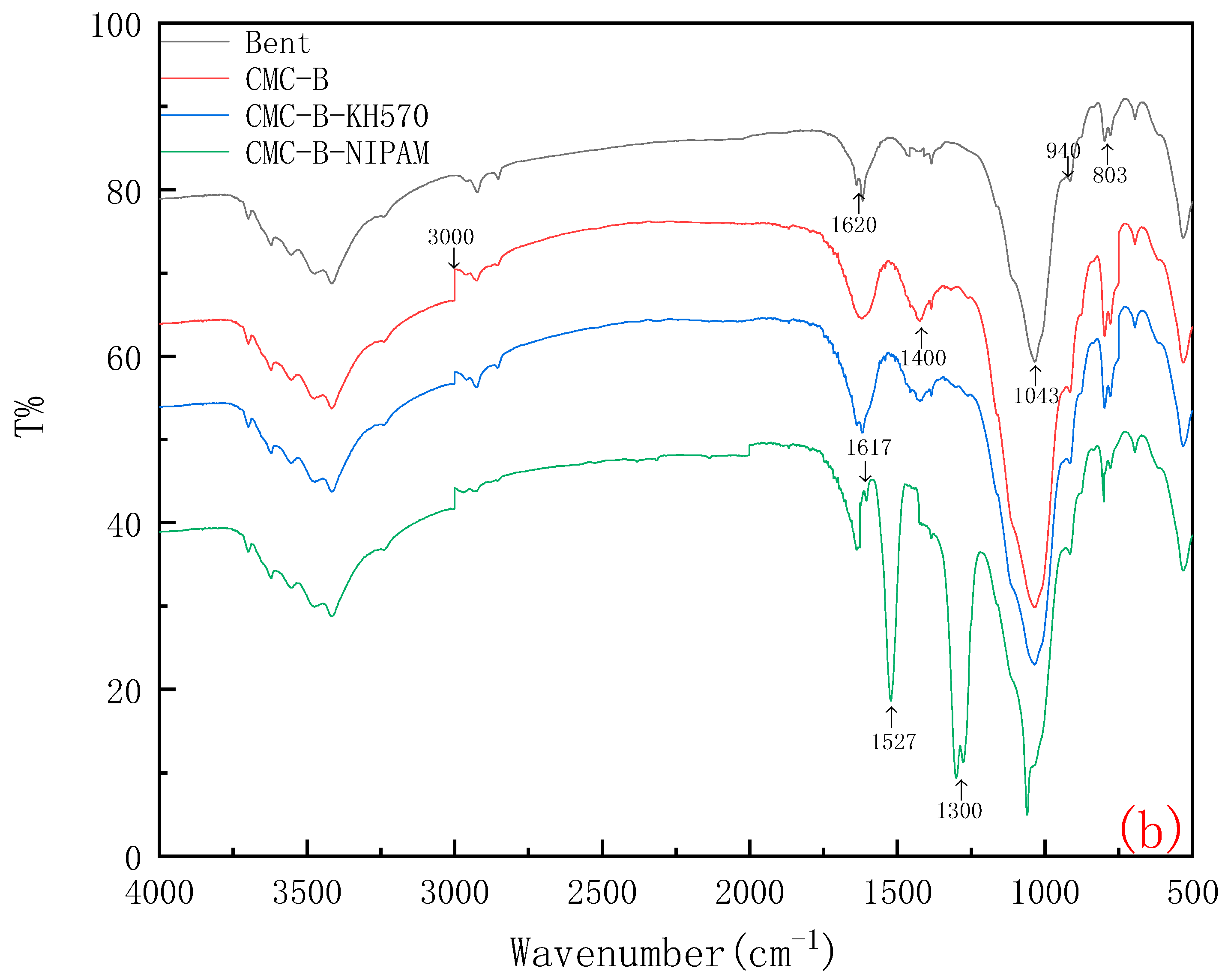
2.2. Characterization of CMC-B-NIPAM Composites
2.2.1. XRD
2.2.2. FTIR
2.3. Drilling Fluid Performance
2.3.1. Performance Evaluation
- (1)
- Thermosensitive
- (2)
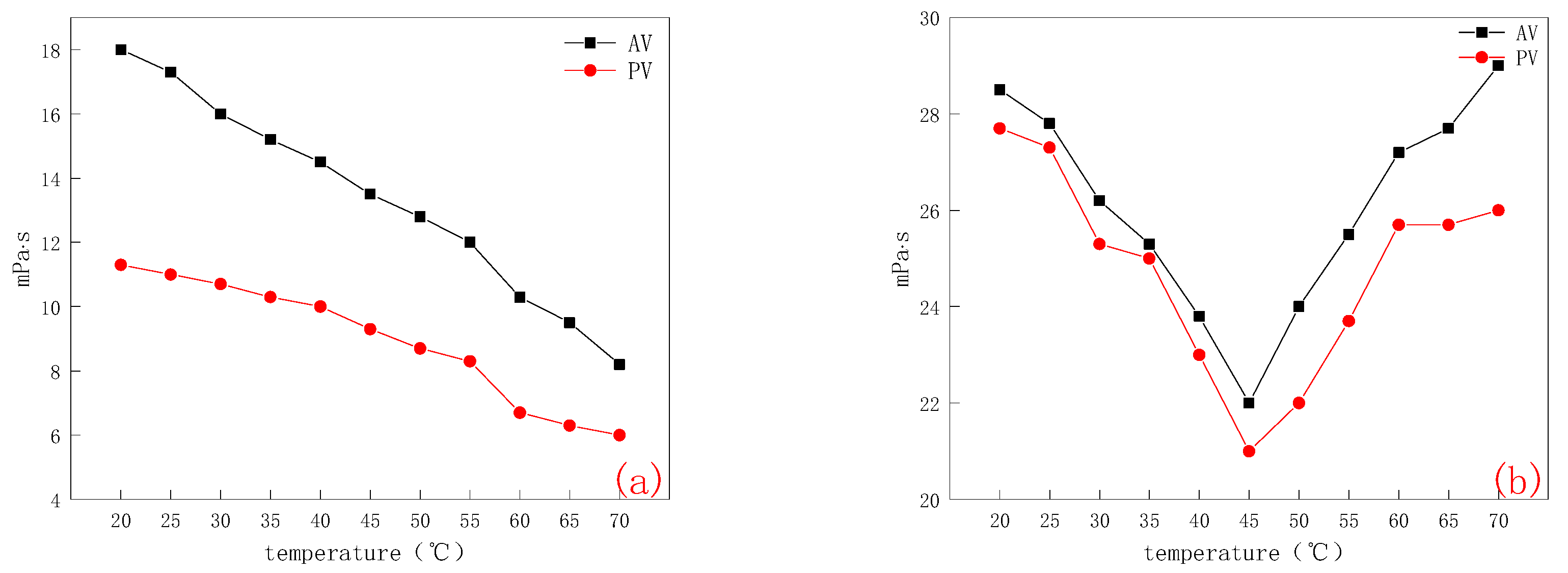
- Rheological property
- (3)
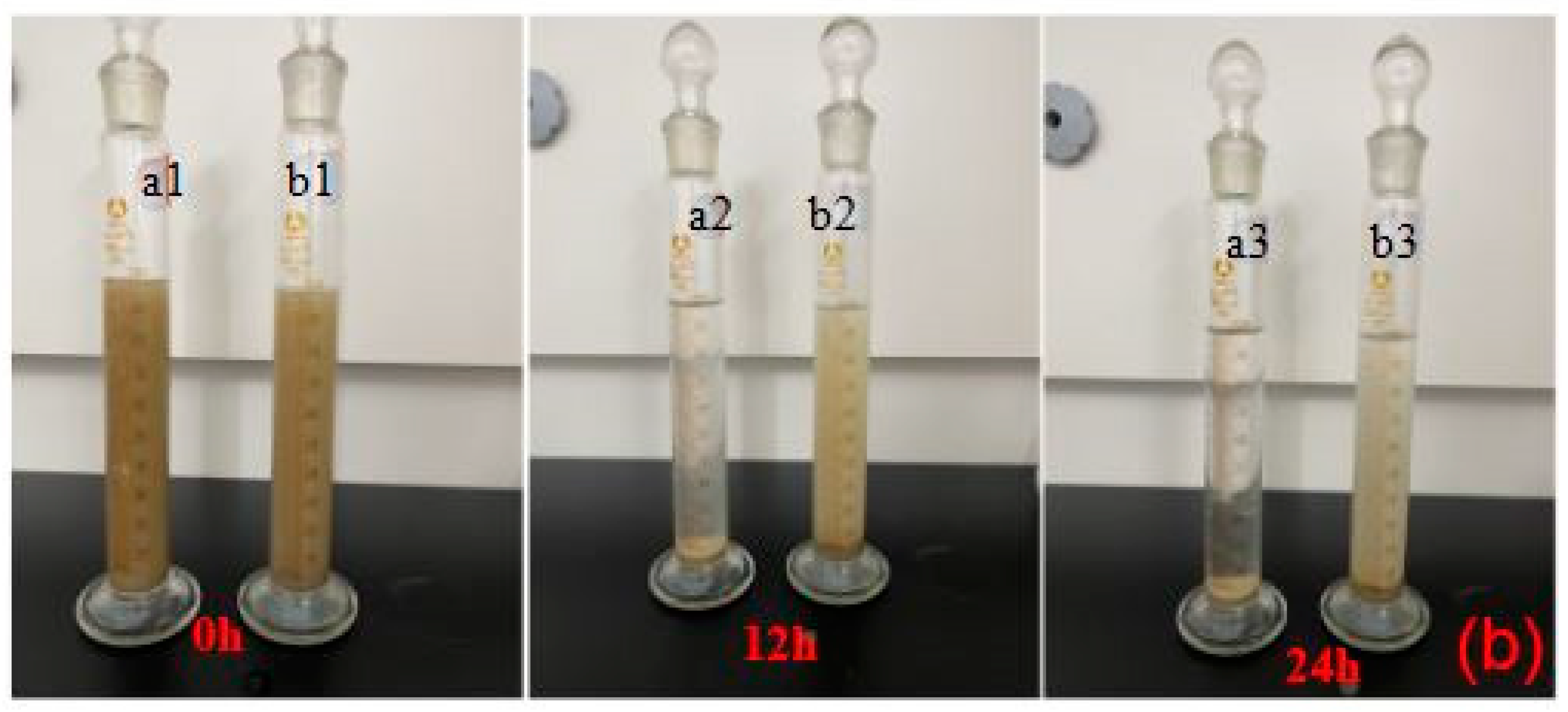
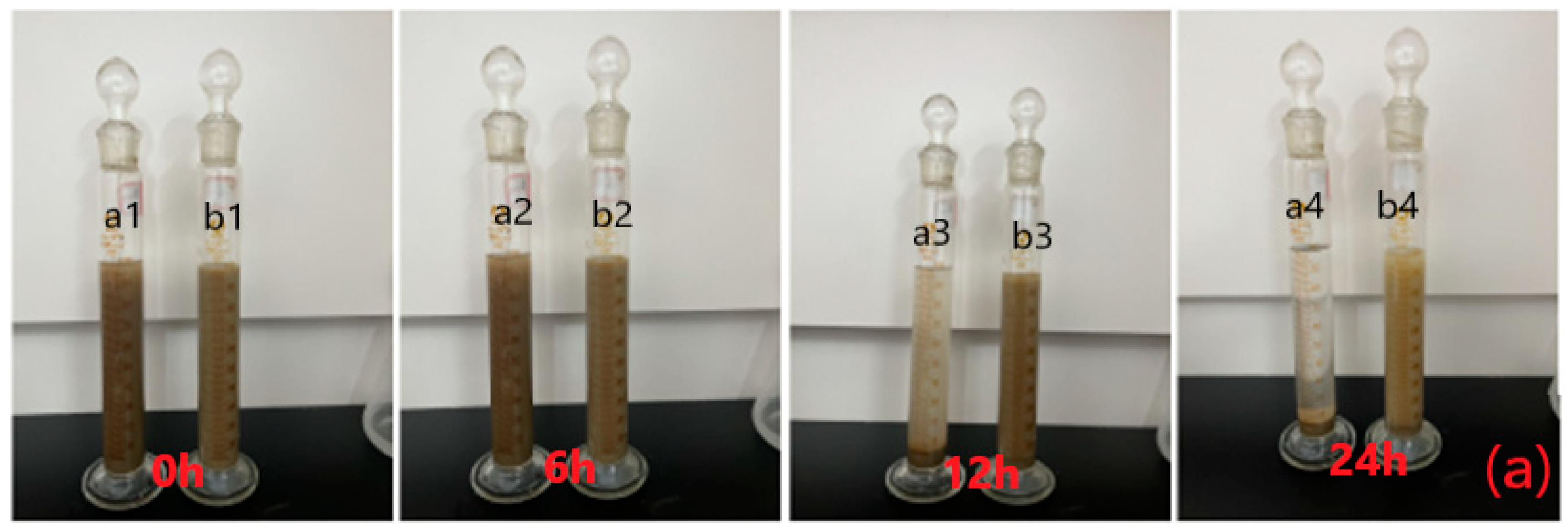
- Suspensibility
- (4)
- Expansion capacity
2.3.2. Comparison Test
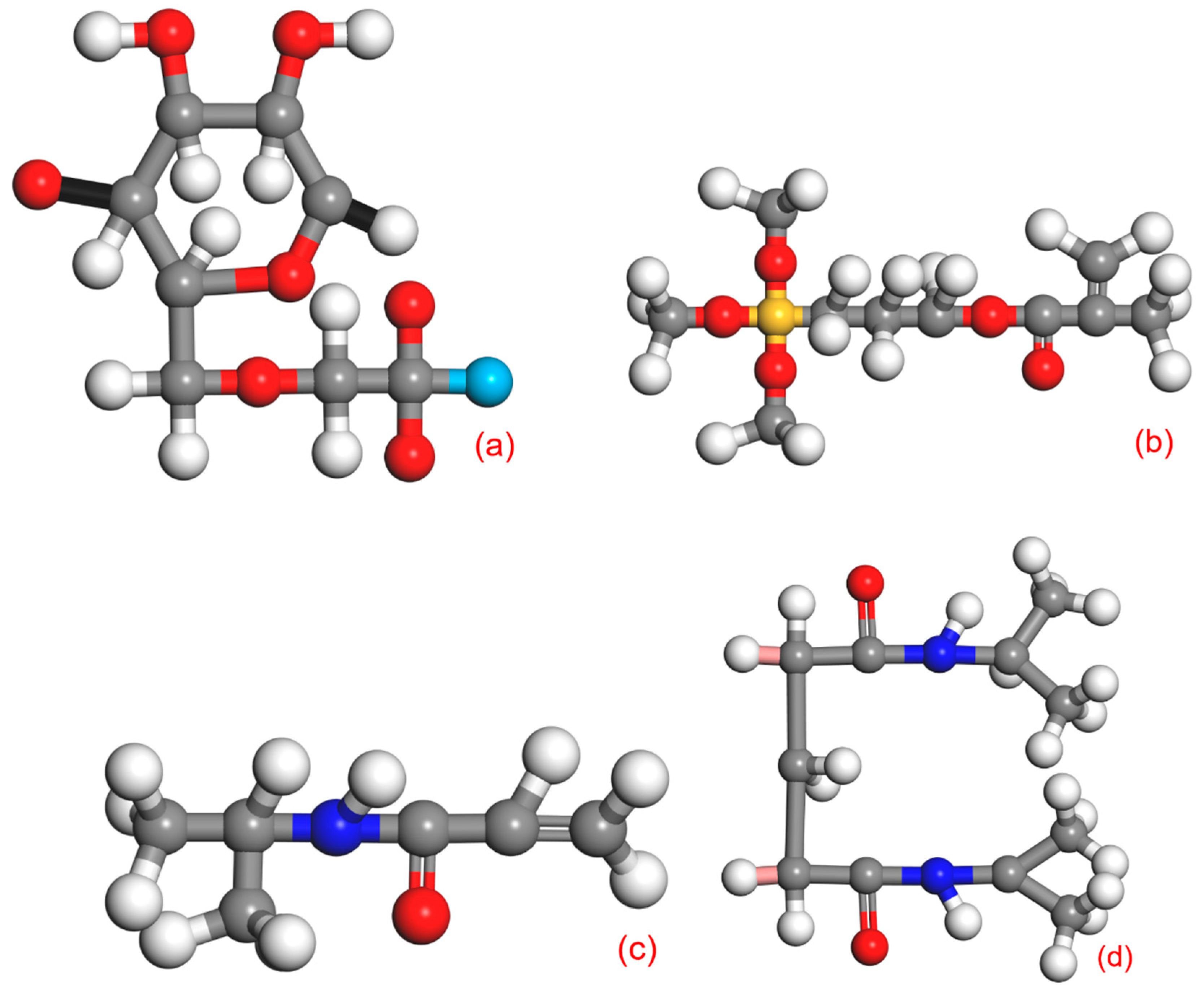
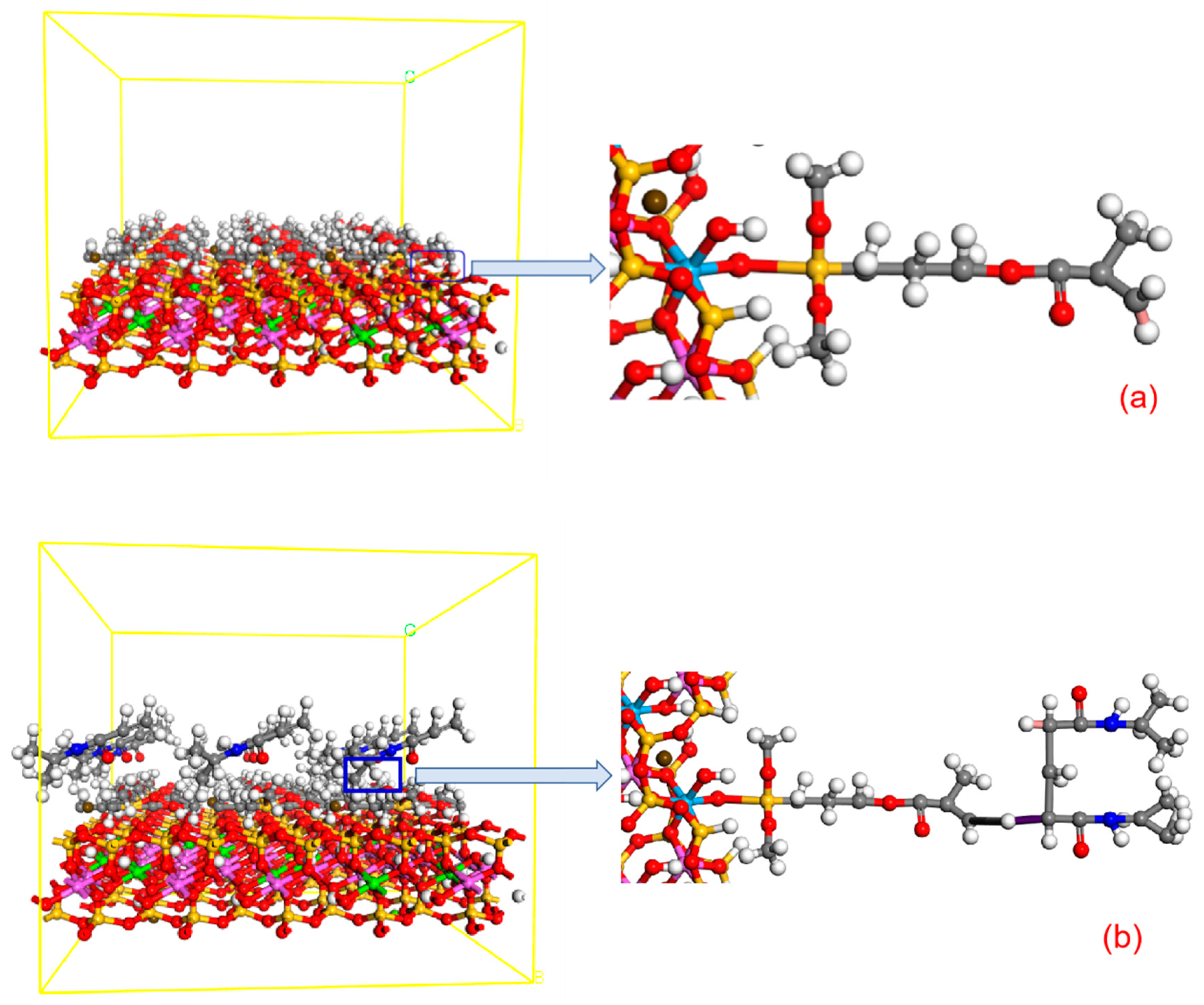
2.4. Molecular Simulation
2.4.1. CMC-B
2.4.2. CMC-B-KH570
2.4.3. CMC-B-NIPAM
3. Experiment
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Modified Bentonite
3.2.1. Preparation of Intercalated Bentonite (CMC-B)
3.2.2. Surface Modification Body Preparation (CMC-B-KH570)
3.2.3. Synthesis of Temperature-Sensitive Modified Bentonite Based on NIPAM (CMC-B-NIPAM)
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Indicator Optimization
3.3.2. Microscopic Characterization
3.3.3. Drilling Fluid Properties
- (1)
- Transmittance and absorbance
- (2)
- Rheological property
- (3)
- Suspensibility
- (4)
- Expansion capacity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| CMC | sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose |
| NIPAM | N-isopropyl acrylamide |
| CTMAB | Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium Bromide |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| CS | Chitosan |
| F | formaldehyde |
| UF | Urea-Formaldehyde resins |
| LCST | Lower Critical Solution Temperature |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer |
| SF | the static settlement factor |
| the density of the upper portion of the column (lower portion of the free liquid), g/cm3 | |
| the density at the bottom of the column, g/cm3 | |
| the expansion volume, ml/g | |
| v | the observed settlement volume of the sediment, ml |
| m | the amounts of sample added |
| RSiX3 | The general formula of silane coupling agent is RSiX3, R is alkyl group, X is alkoxy group, etc. |
| KH570 | γ-Methacryloxypropyl trimethoxy silane |
| AV | apparent viscosity |
| PV | plastic viscosity |
References
- Huang, W. Preparation, Characterization and Application Research of Modified Bentonite; Xiangtan University: Xiangtan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ratldevicius, L.A.; Jose, V.D.C.F.F.; Lins, D.B.N.E.; Santanna, V.C. Modification of bentonite clay by a cationic surfactant to be used as a viscosity enhancer in vegetable-oil-based drilling fluid. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L. Preparation of Organicbentonite and Its Adsorption Wastewater Thiocyanate Ions; Taiyuan University of Technology: Taiyuan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G. Development and Application of Water-Soluble Drilling Fluid Filtration Control Agent; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.C.; Wang, H.L.; Sun, D.S.; Zhu, Z.L. Microstructure and adsorption mechanism of intercalated modified Na-bentonite. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 4479–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.X.; Guan, H.; Li, J.J. Synthesis of Modified Chitosan Intercalated by Bentonite and Its Adsorption of Formaldehyde. Chem. World 2016, 265–267, 275. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y. Research on the Modification Mechanism of Organic Clay Used in Oil-based Drilling Fluids; China University of Petroleum (East China): Qingdao, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.S.; Wang, S.M.; Xu, Z.X.; Dong, B.H.; Sun, W.B. The surface graft modification and characterization of nanoparticles. New Chem. Mater. 2005, 33, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Biswas, D.R.; Datta, S.C.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Kumar, R.; Patra, A.K. Preparation of novel biodegradable starch/poly (vinyl alcohol)/bentonite grafted polymeric films for fertilizer encapsulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, M.S.; Sultan, A. Thermosensitive Water Soluble Polymers: A Solution to High Temperature and High Salinity Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Spe Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Technical Symposium & Exhibition, Dammam, Saudi Arabia, 26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reichenbach-Klinke, R.; Zimmermann, T.; Stavland, A.; Daniel, S. Temperature-Switchable Polymers for Improved Oil Recovery. In SPE Norway One Day Seminar; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2018; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulbaki, M.; Huh, C.; Sepehrnoori, K.; Delshad, M.; Varavei, A. A critical review on use of polymer microgels for conformance control purposes. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 122, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Luo, M. Application a novel thermo-sensitive copolymer as a potential rheological modifier for deep water water-based drilling fluids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 581, 123848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmeh, G.; Izadi, M.; Salehi, M.; Romero, J.L.; Manrique, E.J. Thermally Active Polymer to Improve Sweep Efficiency of Water Floods: Simulation and Pilot Design Approaches. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2011, 15, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Zhan, Q.R.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Benzeroual, N. Research progress on low-temperature rheology of high-performance ocean deepwater drilling fluids: An overview. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 218, 110978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Li, J.L.; Yang, N.W. Experimental research on affects the viscosity of carboxymethylcelluloses. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2011, 40, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Q.; Chen, F.J.; Liu, H.N.; Zhang, H.F.; Wu, Z.J.; Ye, X.S. Preparation of Poly(N-isopropylarymide) Hydrogel and Its Thermally Induced Aggregation Behavior. Mater. Rep. 2018, 32, 2491–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.Y. The Synthesis and Properties of Temperature-Sensitivity Acrylamide Copolymers; Sichuan University: Chengdu, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bertagnolli, C.; Kleinübing, S.J.; Silva, M. Preparation and characterization of a brazilian bentonite clay for removal of copper in porous beds. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.Y.; Li, T.T.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, B.; Liang, H.J. Effects of Temperature and Clay Content on Water-Based Drilling Fluids’ Rehological Property. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2008, 36, 3. [Google Scholar]
- García-García, S.; Wold, S.; Jonsson, M. Effects of temperature on the stability of colloidal montmorillonite particles at different pH and ionic strength. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, W.W. Study on Surface Modification of Bentonite with Coupling Agent; Guangxi University: Nanning, China, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xu, M.L.; Zhan, Q.R.; Hou, B.; Yang, S.C.; Li, N. Preparation and properties of N-isopropylacrylamide-based smart bentonite. Fine Chem. 2021, 38, 2057–2063+2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Geng, Y.; Discher, D.E.; Yang, S. Temperature-Controlled Assembly and Release from Polymer Vesicles of Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2905–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.X. Study on Synthesis and Properties of Modified Bentonite Sorbent; Guangxi University: Nanning, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, M.L.; Tong, L.; Yang, S.C.; Lebongo, E.Y.; Sun, X.L. Preparation and research of intelligent drilling fluid based on temperature-sensitive modified bentonite. Rev. Matéria 2023, 28, e20220269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
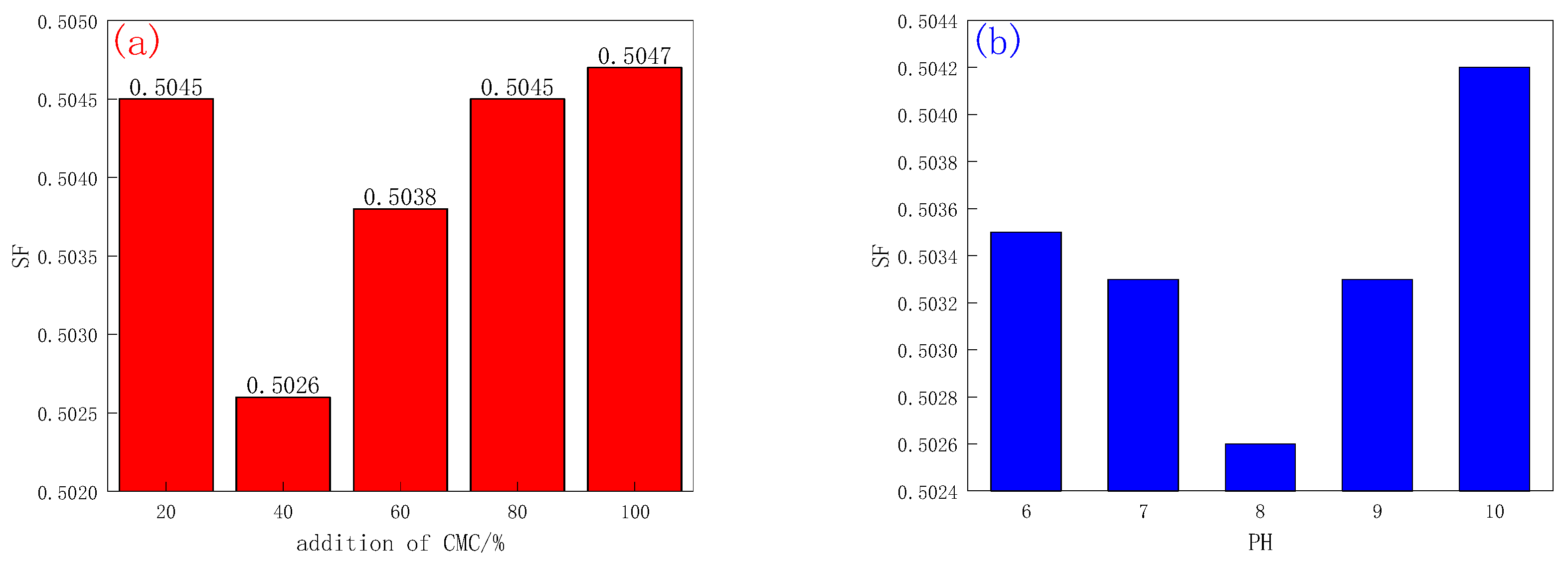
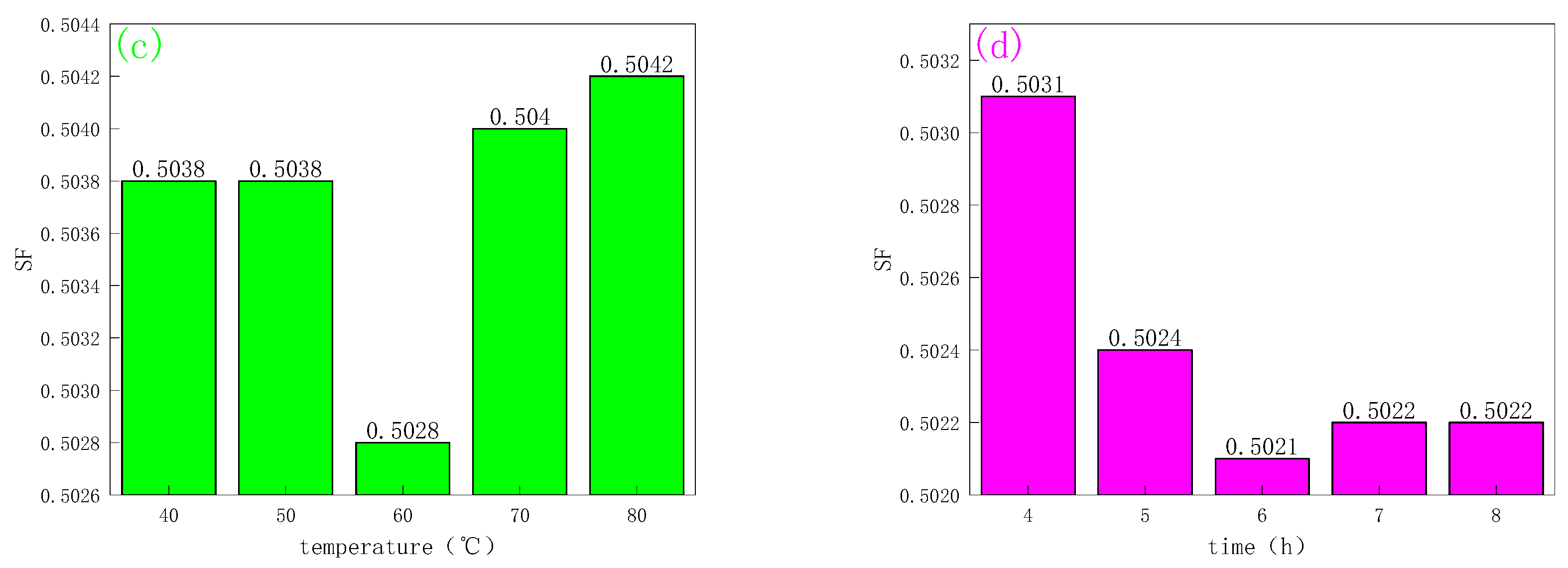
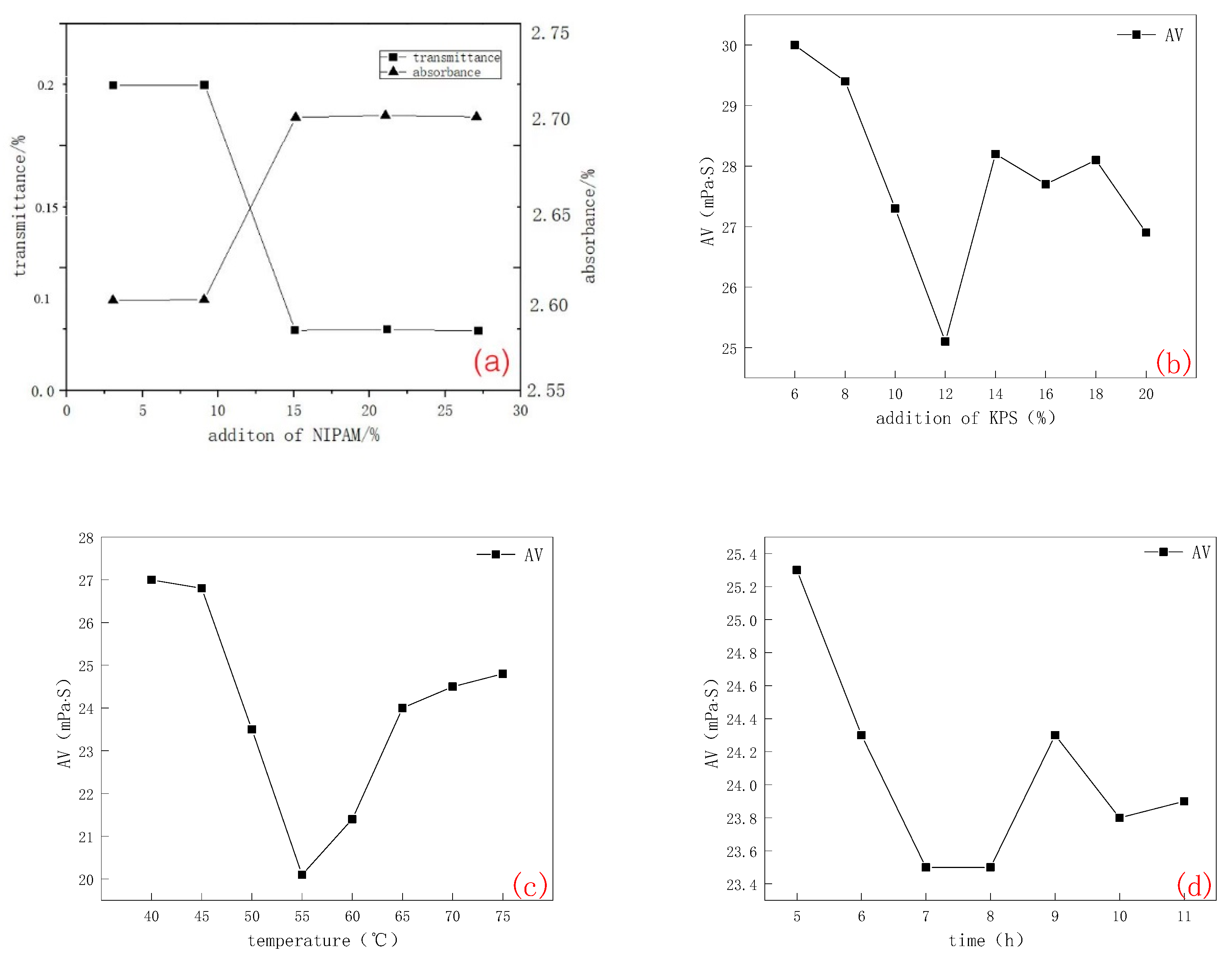



| Temperature (°C) | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmittance | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Absorbance | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
| Temperature (°C) | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmittance | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Absorbance | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| Temperature (°C) | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmittance | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Absorbance | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| Dispersion Type | SF | Evaluation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bentonite | 1.01 | 1.07 | 0.5144 | Good stability |
| CMC-B-NIPAM | 1.05 | 1.06 | 0.5023 | Good stability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Guan, J.; Yang, G.; Yang, P.; Qayum, Z.U.A. Temperature-Sensitive Modified Bentonite Based on NIPAM for Drilling Fluid: Experimental and Molecular Simulation Studies. Molecules 2023, 28, 3839. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093839
Pan Y, Zhang X, Zhan Q, Yang S, Wang Y, Guan J, Yang G, Yang P, Qayum ZUA. Temperature-Sensitive Modified Bentonite Based on NIPAM for Drilling Fluid: Experimental and Molecular Simulation Studies. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3839. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093839
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yi, Xinyue Zhang, Qianru Zhan, Shuangchun Yang, Yanchao Wang, Jian Guan, Gang Yang, Peng Yang, and Zain Ullah Abdul Qayum. 2023. "Temperature-Sensitive Modified Bentonite Based on NIPAM for Drilling Fluid: Experimental and Molecular Simulation Studies" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3839. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093839
APA StylePan, Y., Zhang, X., Zhan, Q., Yang, S., Wang, Y., Guan, J., Yang, G., Yang, P., & Qayum, Z. U. A. (2023). Temperature-Sensitive Modified Bentonite Based on NIPAM for Drilling Fluid: Experimental and Molecular Simulation Studies. Molecules, 28(9), 3839. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093839






