Screening and Identification of ssDNA Aptamers for Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Receptor-Related Protein 6
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Aptamers of LRP6 Screened through CE-SELEX
2.2. Predicting Structure and Motif of Candidate Aptamers
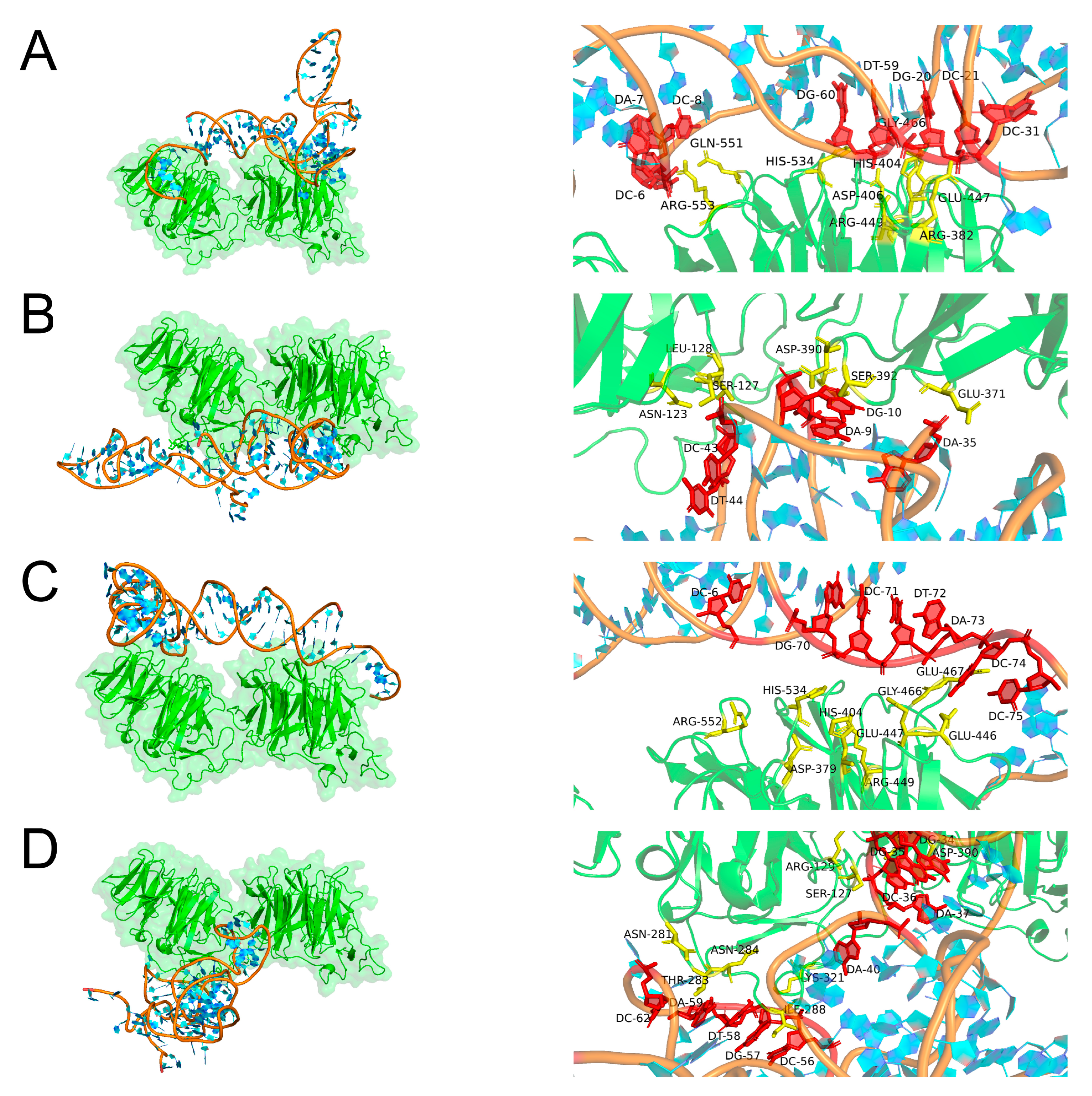
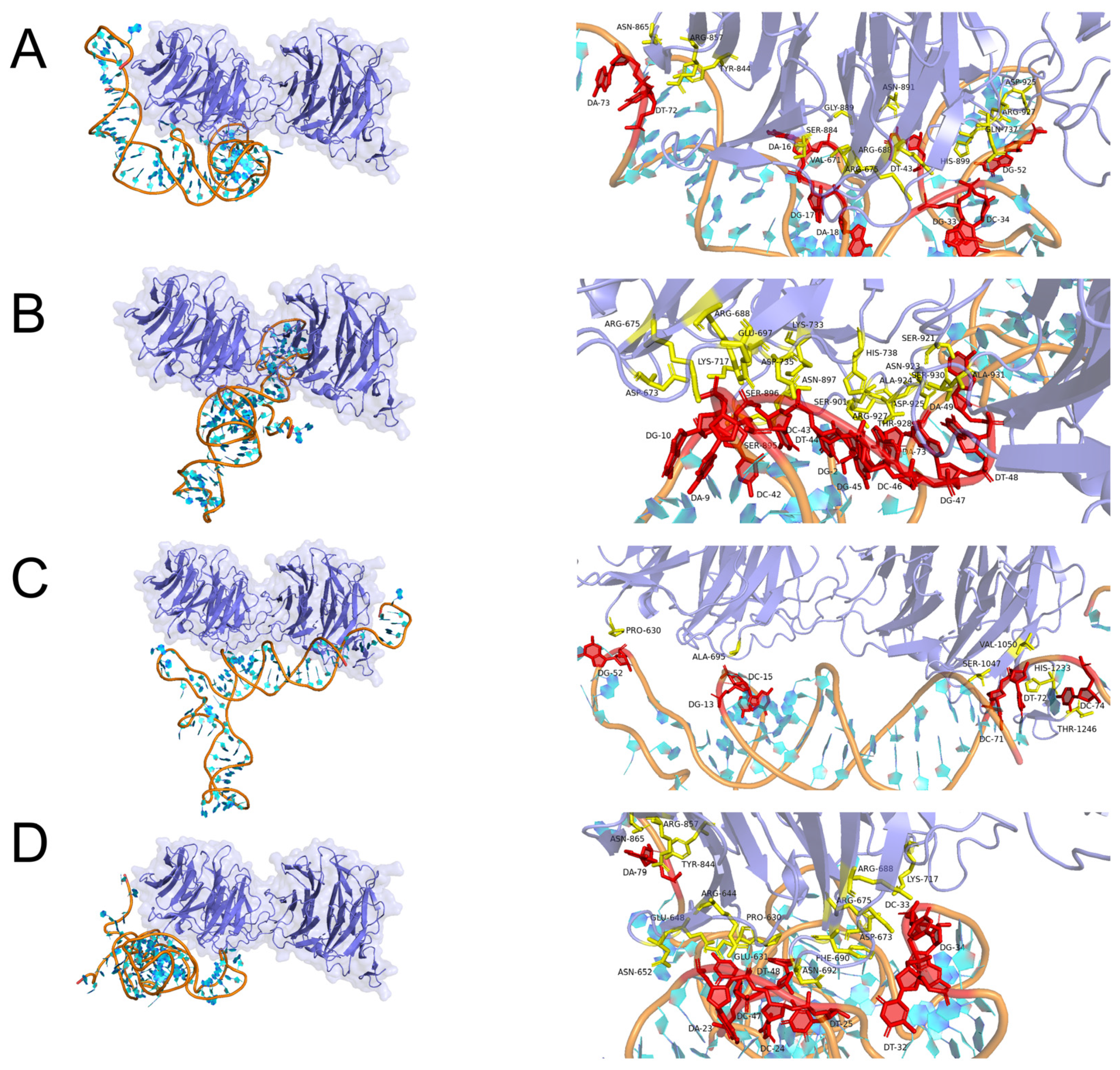
2.3. Molecular Docking Simulation
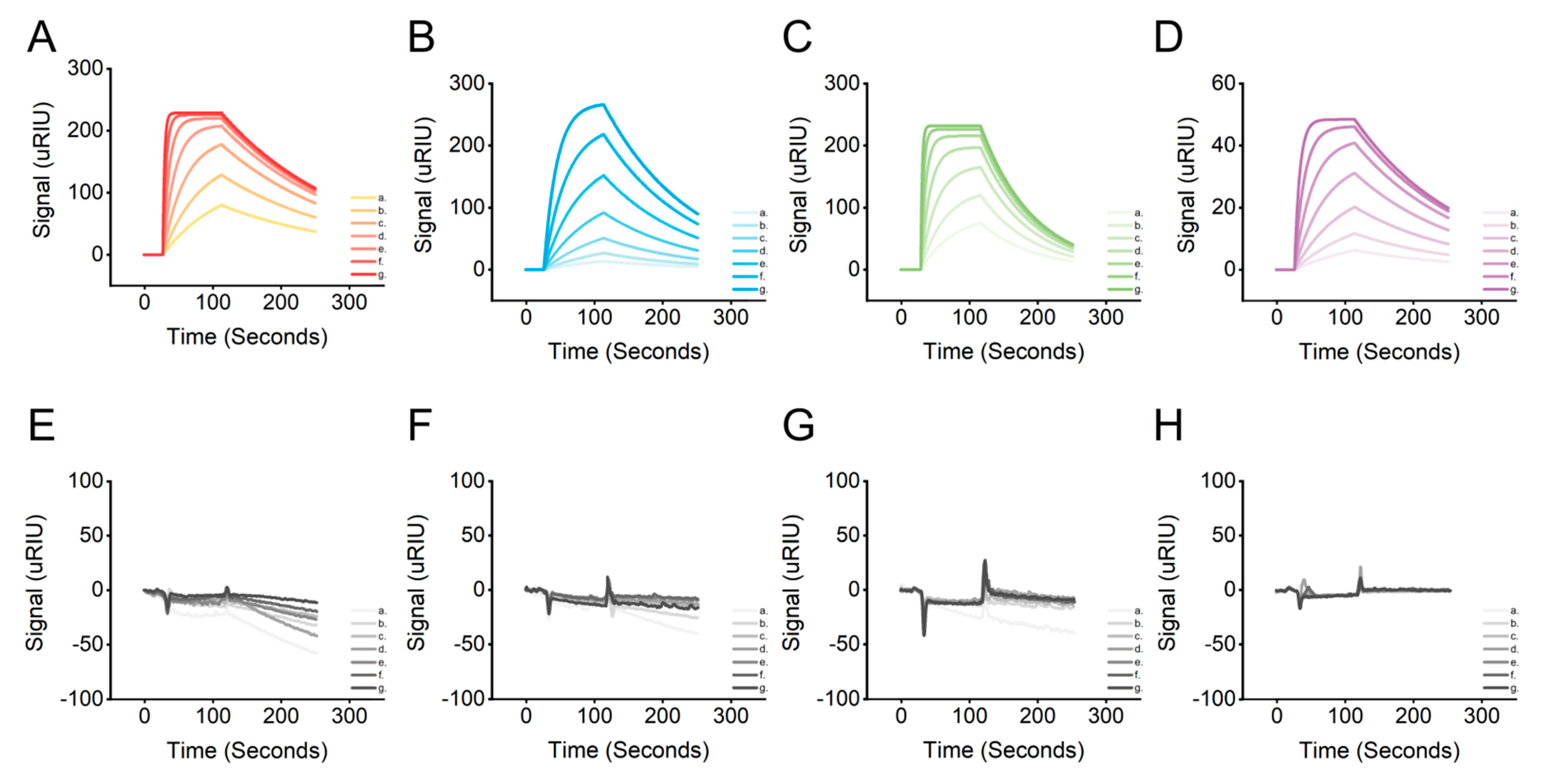
2.4. Affinity Characterization of Candidate Aptamers
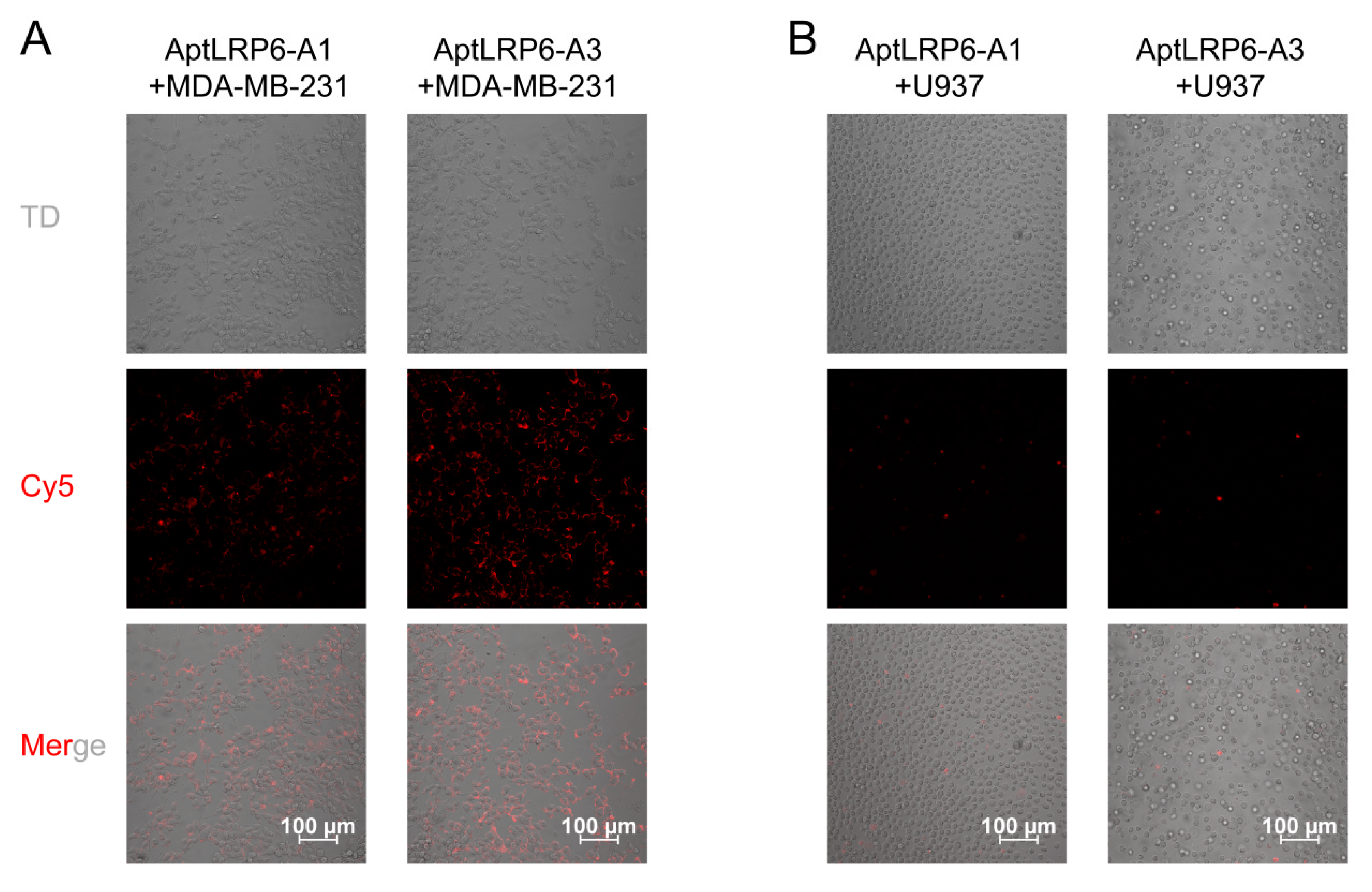
2.5. Binding Specificity of Candidate Aptamers to Target Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Cell Lines
3.2. CE-SELEX
3.3. Structure and Motif Predictions
3.4. Binding Mode Predictions
3.5. Affinity Characterization
3.6. Targeting of Aptamers to Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Huang, B.; Song, B.; Xu, C. Cholesterol metabolism in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raisch, J.; Côté-Biron, A.; Rivard, N. A Role for the WNT Co-Receptor LRP6 in Pathogenesis and Therapy of Epithelial Cancers. Cancers 2019, 11, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6-mediated signaling pathways and associated cardiovascular diseases: Diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, G. LRPs in WNT Signalling. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 269, 45–73. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, M.; Katoh, M. WNT signaling pathway and stem cell signaling network. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4042–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Joseph, J.; Zhang, X.; Ferdows, B.E.; Patel, D.N.; Chen, W.; Banfi, G.; Molinaro, R.; Cosco, D.; et al. Biomaterials and nanomedicine for bone regeneration: Progress and future prospects. Exploration 2021, 1, 20210011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, J.P.; Jordens, I.; Tauriello, D.V.F.; van ’t Land-Kuper, I.; Bugter, J.M.; Noordstra, I.; van der Kooij, J.; Low, T.Y.; Pimentel-Muiños, F.X.; Xanthakis, D.; et al. TMEM59 potentiates Wnt signaling by promoting signalosome formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3996–E4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, B.T.; Tamai, K.; He, X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev. Cell. 2009, 17, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Jho, E.H. Regulation of the Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein LRP6 and Its Association With Disease: Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Beyond. Front Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 714330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Prior, J.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Bu, G. LRP6 overexpression defines a class of breast cancer subtype and is a target for therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5136–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lu, W.; Chen, D.; Xu, B.; Li, Y. Role vof Wnt Co-Receptor LRP6 in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 2968–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindvall, C.; Zylstra, C.R.; Evans, N.; West, R.A.; Dykema, K.; Furge, K.A.; Williams, B.O. The Wnt co-receptor Lrp6 is required for normal mouse mammary gland development. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, E.K.; Wong, B.Y.; Yau, T.O.; Ng, I.O. Upregulation of the Wnt co-receptor LRP6 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis and enhances cell invasion. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; An, Y.; Hou, W.; Cao, Y.N.; Yao, M.F.; Ma, N.N.; Hou, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.J.; Zhang, B. LRP6 promotes invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer through cytoskeleton dynamics. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 109632–109645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, Y. Salinomycin suppresses LRP6 expression and inhibits both Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in breast and prostate cancer cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2014, 115, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Lin, C.; Li, Y. Rottlerin induces Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and suppresses both Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in prostate and breast cancer cells. Cell Signal 2014, 26, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shu, C.; Maimaiti, Y.; Wang, S.; Lu, C.; Zhou, J. LRP6 as a biomarker of poor prognosis of breast cancer. Gland Surg. 2021, 10, 2414–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xing, F.; Iiizumi-Gairani, M.; Okuda, H.; Watabe, M.; Pai, S.K.; Pandey, P.R.; Hirota, S.; Kobayashi, A.; Mo, Y.Y.; et al. N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 modulates Wnt-β-catenin signalling and pleiotropically suppresses metastasis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rismani, E.; Fazeli, M.S.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Movassagh, A.; Azami, S.; Karimipoor, M.; Teimoori-Toolabi, L. Pattern of LRP6 gene expression in tumoral tissues of colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 19, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Cai, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Sui, H.; Li, Q. MALAT1 regulates the transcriptional and translational levels of proto-oncogene RUNX2 in colorectal cancer metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 378. [Google Scholar]
- Nimjee, S.M.; White, R.R.; Becker, R.C.; Sullenger, B.A. Aptamers as Therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 57, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, Y.; Leslie, M.; Kameyama, H.; Volk, D.E.; Tanaka, T. Aptamer Therapeutics in Cancer: Current and Future. Cancers 2018, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonsa, S.D.; Bowser, M.T. In vitro evolution of functional DNA using capillary electrophoresis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, C.M.; Hayes, M.J.; Stettler, G.R.; Hickey, S.F.; Axelrod, T.M.; Giustini, N.P.; Suljak, S.W. Capillary electrophoretic development of aptamers for a glycosylated VEGF peptide fragment. Analyst 2010, 135, 2945–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, P.; Pai, R.B.; Storici, F. Real-Time PCR-Coupled CE-SELEX for DNA Aptamer Selection. ISRN Mol. Biol. 2012, 2012, 939083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Ghulam, M.; Li, L.; Qu, F. Evolution of multi-functional capillary electrophoresis for high-efficiency selection of aptamers. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, P.; Nosrati, R.; Alibolandi, M.; Rafatpanah, H.; Abnous, K.; Khedri, M.; Ramezani, M. SELEX methods on the road to protein targeting with nucleic acid aptamers. Biochimie 2018, 154, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmostuk, M.; Rimpelova, S.; Gbelcova, H.; Ruml, T. Current approaches in SELEX: An update to aptamer selection technology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1141–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.D.; Stephens, R.M. Sequence logos: A new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6097–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, D.M.; Ke, J.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, H.E.; Williams, B.O. LRP5 and LRP6 in development and disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Chin, E.N.; Fakhraldeen, S.A.; Berry, S.M.; Beebe, D.J.; Alexander, C.M. Both LRP5 and LRP6 receptors are required to respond to physiological Wnt ligands in mammary epithelial cells and fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16454–16466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Bubeck, D.; MacDonald, B.T.; Liang, W.X.; Mao, J.H.; Malinauskas, T.; Llorca, O.; Aricescu, A.R.; Siebold, C.; He, X.; et al. Structural and functional studies of LRP6 ectodomain reveal a platform for Wnt signaling. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Biechele, T.; Wei, Z.; Morrone, S.; Moon, R.T.; Wang, L.; Xu, W. Crystal structures of the extracellular domain of LRP6 and its complex with DKK1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adasme, M.F.; Linnemann, K.L.; Bolz, S.N.; Kaiser, F.; Salentin, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Schroeder, M. PLIP 2021: Expanding the scope of the protein-ligand interaction profiler to DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W530–W534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoatov, M.; Galievsky, V.A.; Krylova, S.M.; Cherney, L.T.; Jankowski, H.K.; Krylov, S.N. Using nonequilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures (NECEEM) for simultaneous determination of concentration and equilibrium constant. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, S.N.; Berezovski, M. Non-equilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures--appreciation of kinetics in capillary electrophoresis. Analyst 2003, 128, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezovski, M.; Krylov, S.N. Nonequilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures—A single experiment reveals equilibrium and kinetic parameters of protein-DNA interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13674–13675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

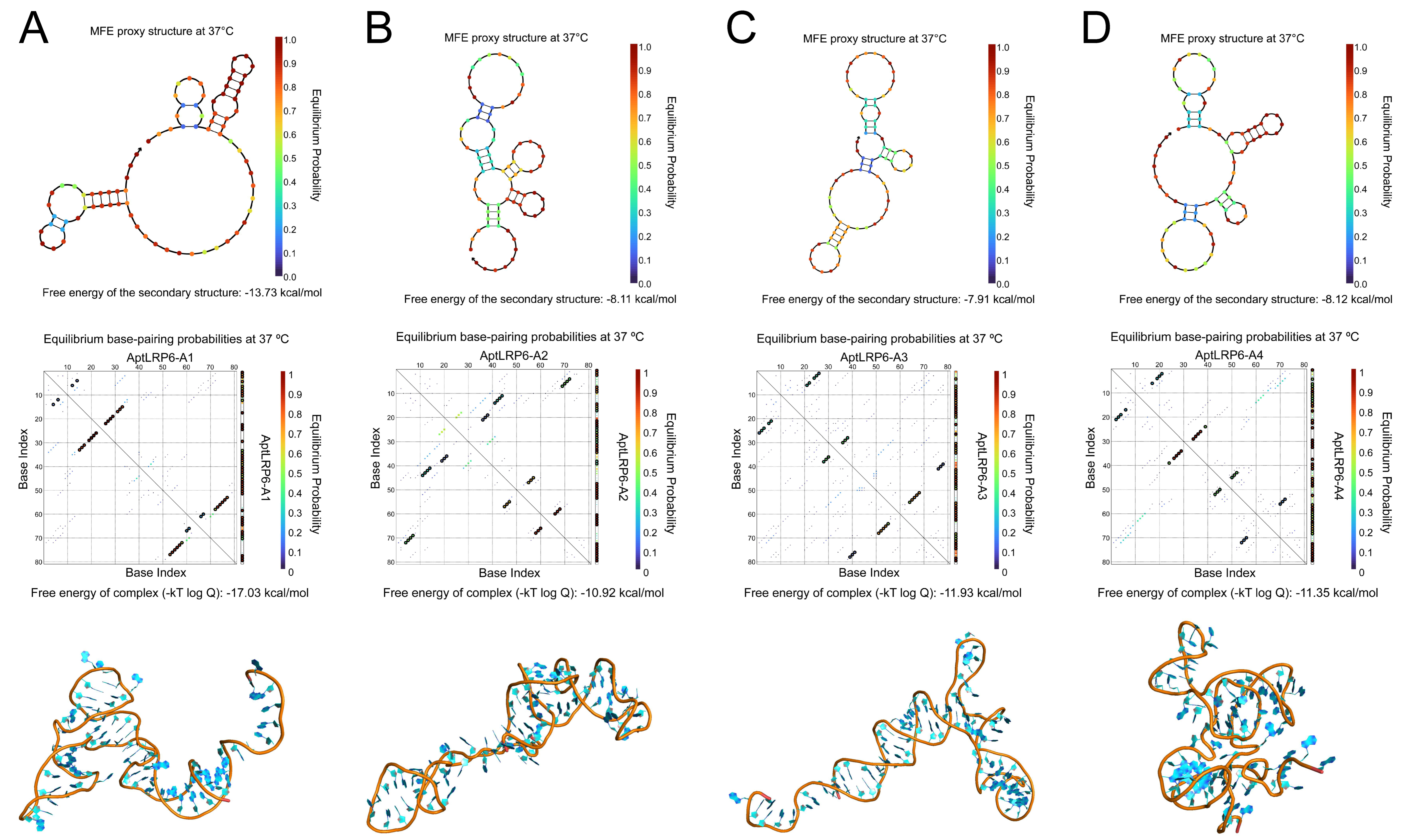

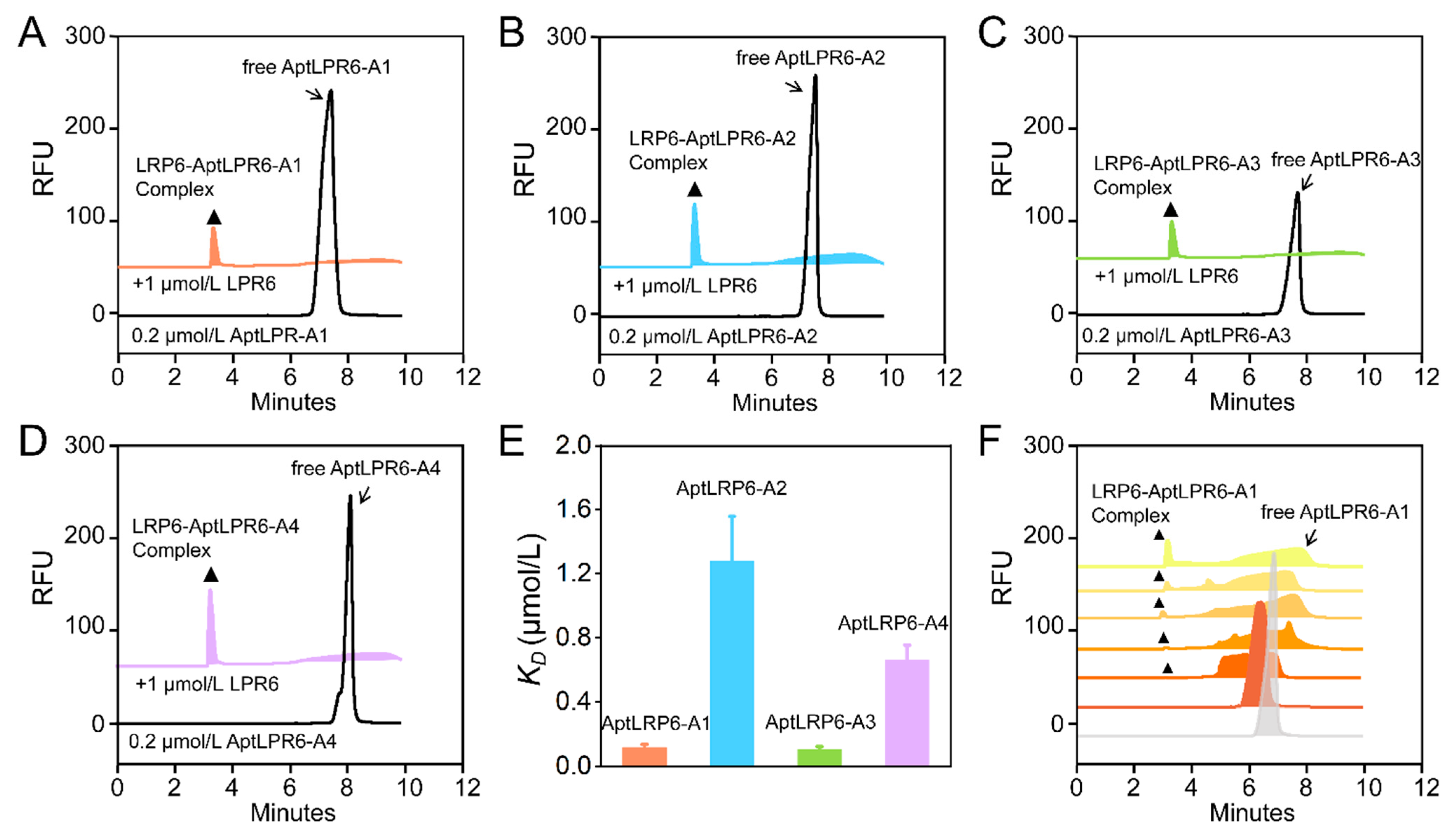
| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Frequency | ΔG (kcal/mol) | ΔH (kcal/mol) | ΔS (cal/K·mol) | Tm (°C) | KD (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AptLRP6-A1 | P1-CCGCAGGCAGCTGCCATTAGTCTCTATCCGTGACGGTATG-P2 | 1161 | −7.29 | −95.90 | −285.7 | 62.5 | 0.118 ± 0.019 |
| AptLRP6-A2 | P1-GCCACATTAGTCTCACCACTACCTGCGTACCTACCGCCGC-P2 | 306 | −1.78 | −55.00 | −171.5 | 47.3 | 1.279 ± 0.279 |
| AptLRP6-A3 | P1-GCAGCTAAGCAGGCGGCTCACAAAACCATTCGCATGCGGC-P2 | 133 | −3.07 | −83.00 | −257.7 | 48.9 | 0.105 ± 0.018 |
| AptLRP6-A4 | P1-CGACTTGCCTATCGGCATGACACAATCTTTTGGAGCGTAA-P2 | 45 | −1.54 | −51.80 | −162 | 46.5 | 0.661 ± 0.092 |
| Name | Bmax ([Signal (uRIU)]) | ka (1/(M · s)) | kd (1/s) | KD (mol/L) | U-Value: ka/kd (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AptLRP6-A1 | 231.71 | 4.12 × 105 | 5.53 × 10−3 | 1.34 × 10−8 | 10 |
| AptLRP6-A2 | 315.33 | 4.54 × 104 | 7.88 × 10−3 | 1.73 × 10−7 | 6.3 |
| AptLRP6-A3 | 237.77 | 5.02 × 105 | 1.29 × 10−2 | 2.57 × 10−8 | >50 |
| AptLRP6-A4 | 50.93 | 1.28 × 105 | 6.51 × 10−3 | 5.10 × 10−8 | 9.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Fan, K.; Qu, F.; Huang, Y. Screening and Identification of ssDNA Aptamers for Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Receptor-Related Protein 6. Molecules 2023, 28, 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093838
Zhang X, Yang G, Liu W, Liu Q, Wang Z, Fan K, Qu F, Huang Y. Screening and Identification of ssDNA Aptamers for Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Receptor-Related Protein 6. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093838
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaomin, Ge Yang, Wenjing Liu, Qing Liu, Zhuoran Wang, Kelong Fan, Feng Qu, and Yuanyu Huang. 2023. "Screening and Identification of ssDNA Aptamers for Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Receptor-Related Protein 6" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093838
APA StyleZhang, X., Yang, G., Liu, W., Liu, Q., Wang, Z., Fan, K., Qu, F., & Huang, Y. (2023). Screening and Identification of ssDNA Aptamers for Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Receptor-Related Protein 6. Molecules, 28(9), 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093838








