Computational Analysis of Histamine Protonation Effects on H1R Binding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
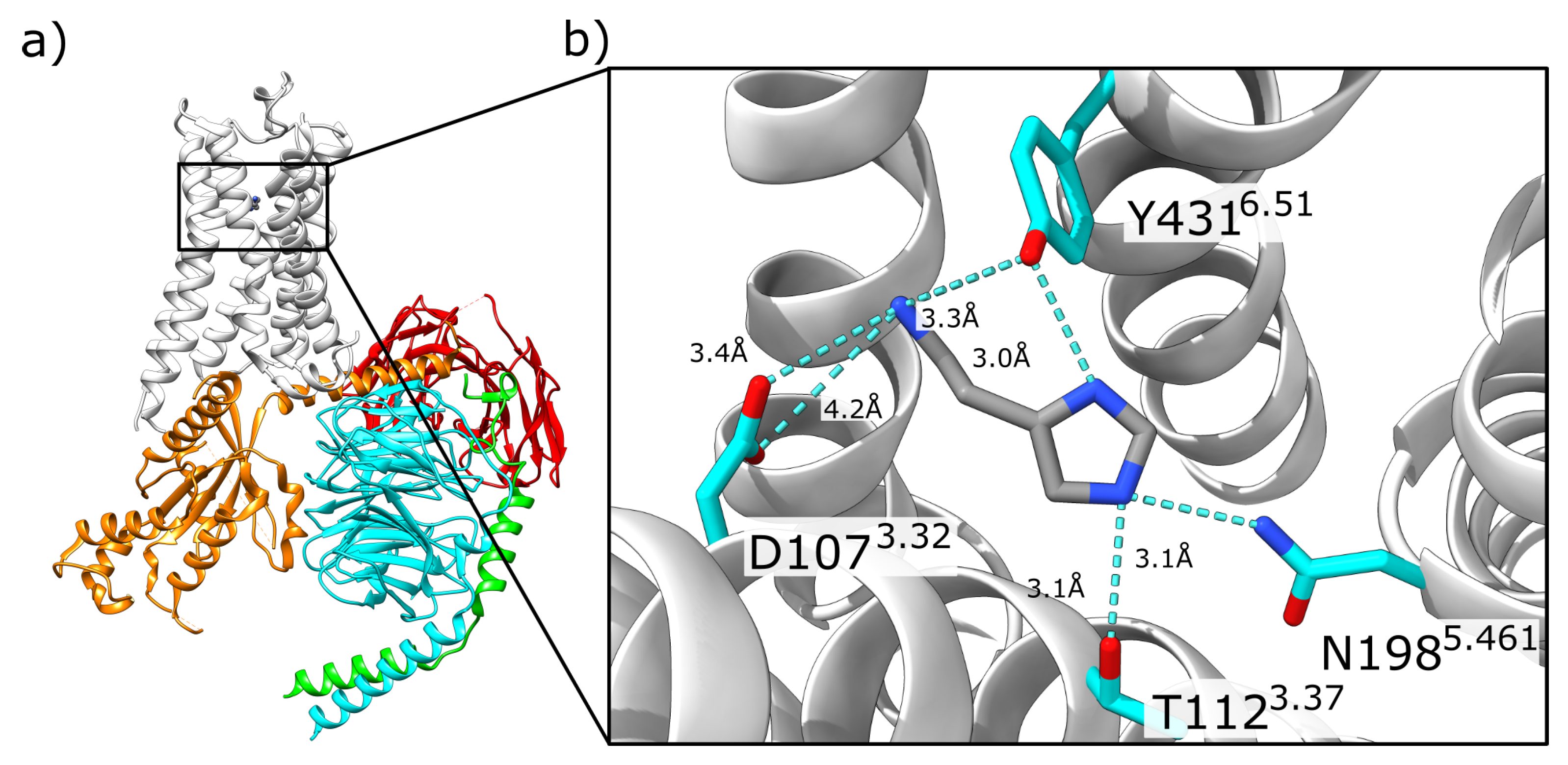
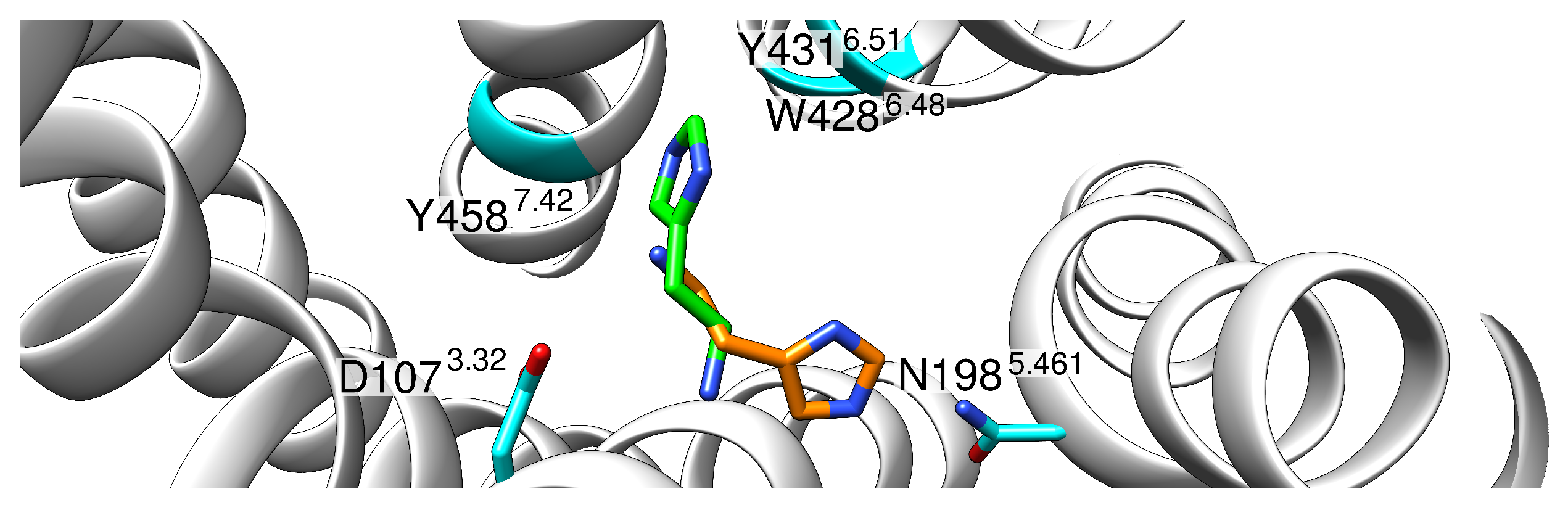
2.1. Initial Structural Analysis of the Histamine-HR-Gq Complex
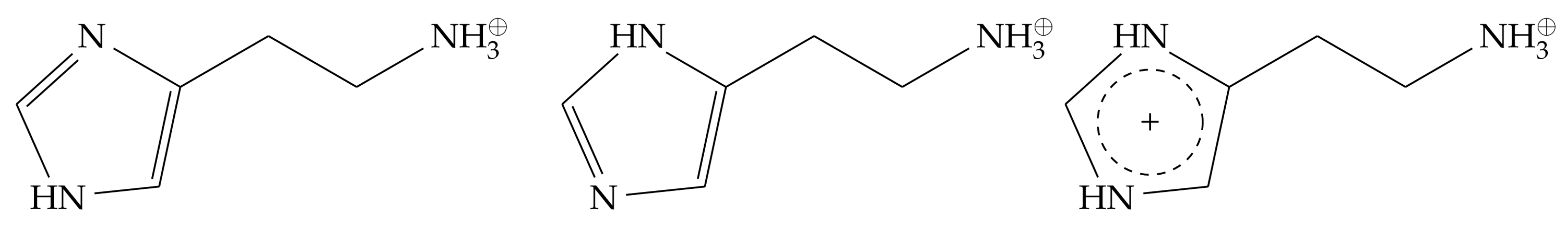
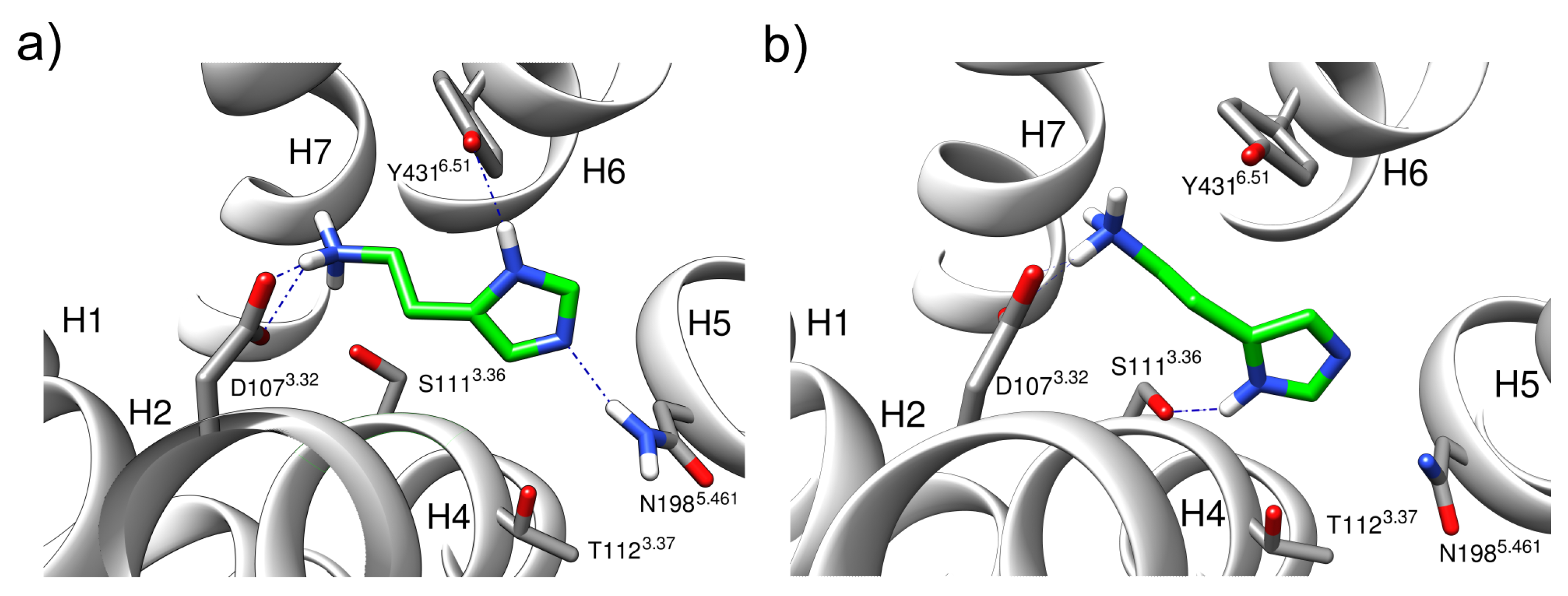
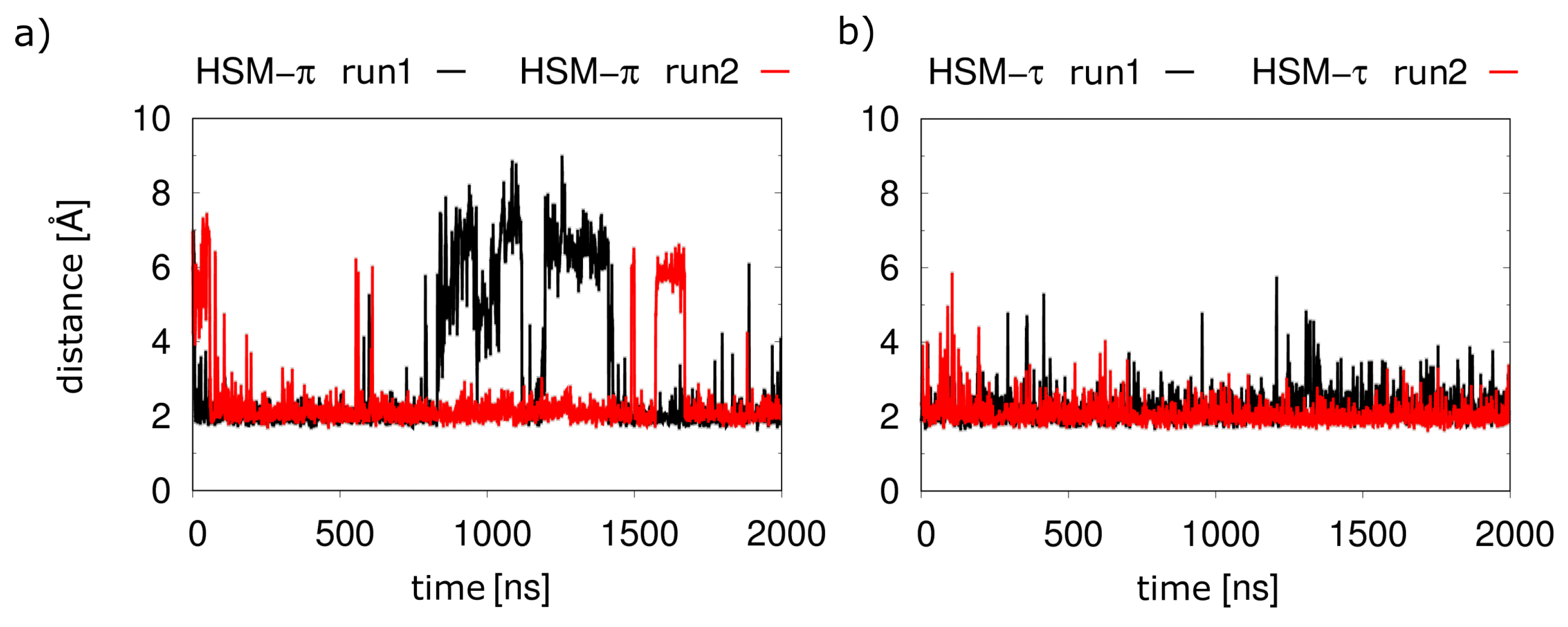
2.2. Monocationic Histamine Tautomers
- (i)
- The conformation of the -histamine fits better to the binding mode from the experimental structure, and no 180° rotational fluctuations of the ring are observed during the simulations as in the -tautomer.
- (ii)
- The hydrogen bond network of the imidazole ring is more stable for the -tautomer (Figure 6).
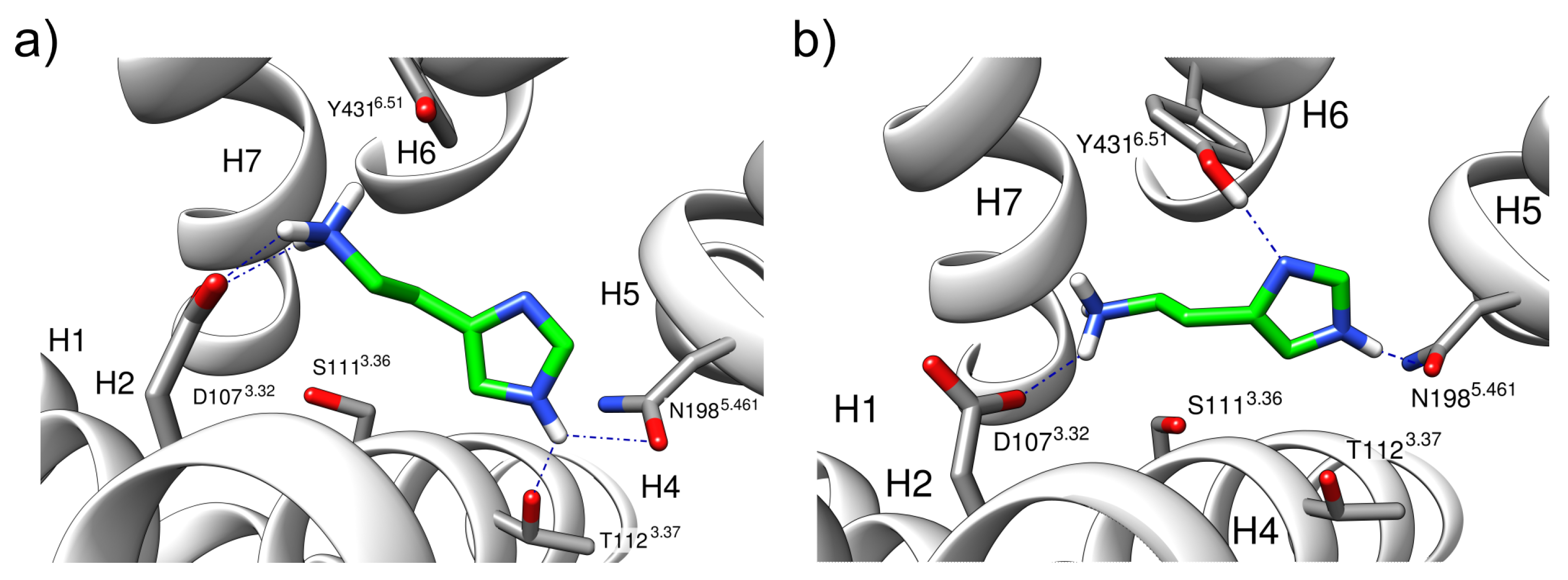
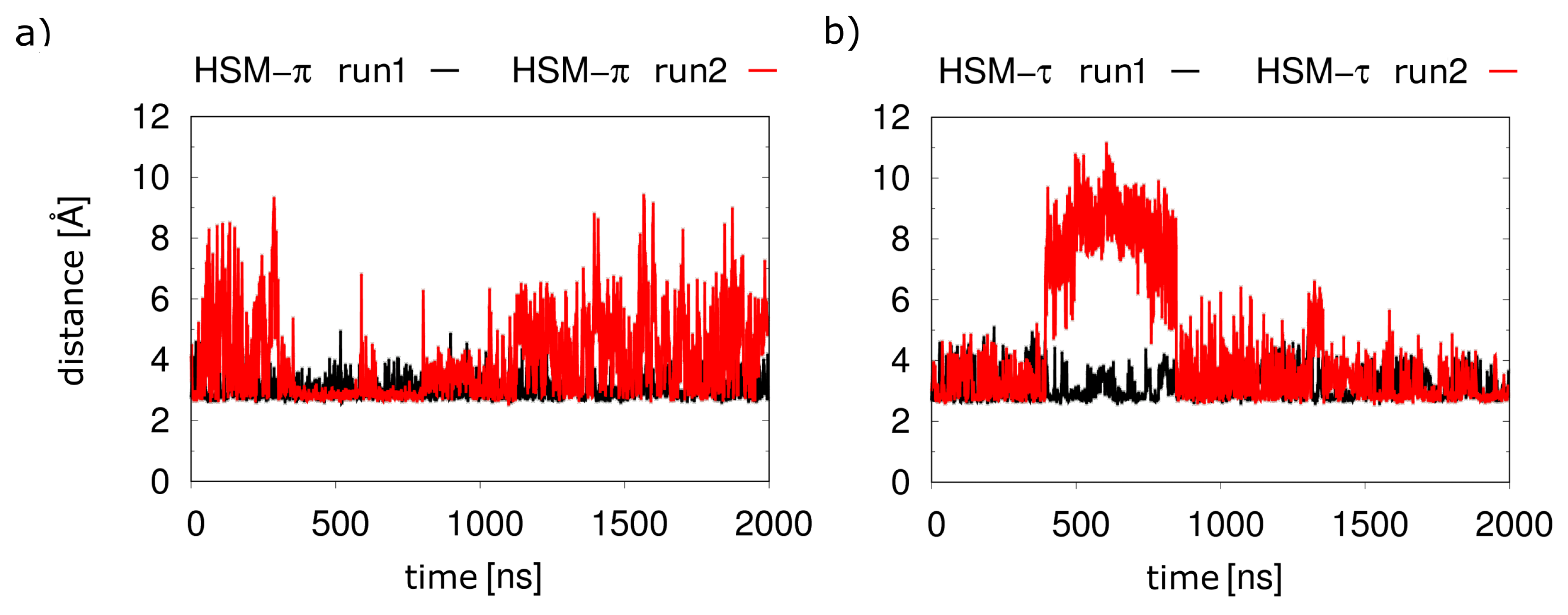
2.3. Dicationic Histamine
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hill, S.J. Distribution, properties, and functional characteristics of three classes of histamine receptor. Pharmacol. Rev. 1990, 42, 45–83. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, F.E.R. Advances in H1-antihistamines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2203–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, C.A.; Simons, F.E.R. Histamine receptors are hot in immunopharmacology. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 533, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 1993, 361, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewison, T.; Su, Y.; Disfany, F.M.; Liang, Y.; Knox, C.; Maciejewski, A.; Poelzer, J.; Huynh, J.; Zhou, Y.; Arndt, D.; et al. SMPDB 2.0: Big improvements to the Small Molecule Pathway Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D478–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Timmerman, H.; Leurs, R. Molecular properties and signalling pathways of the histamine H1 receptor. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Nogueira, P.; Noguera-Castells, A.; Fuster, G.; Recalde-Percaz, L.; Moragas, N.; López-Plana, A.; Enreig, E.; Jauregui, P.; Carbó, N.; Almendro, V.; et al. Histamine receptor 1 inhibition enhances antitumor therapeutic responses through extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 424, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, H.; Glaser, S.; DeMorrow, S.; Gaudio, E.; Ueno, Y.; Venter, J.; Dostal, D.; Onori, P.; Franchitto, A.; Marzioni, M.; et al. Small mouse cholangiocytes proliferate in response to H1 histamine receptor stimulation by activation of the IP3/CaMK I/CREB pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, C499–C513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Wang, N.; Xu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, A.; Guo, C.; He, Y. Cryo-EM structure of the human histamine H1 receptor/Gq complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganellin, C. The tautomer ratio of histamine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1973, 25, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söldner, C.A.; Horn, A.H.; Sticht, H. Binding of histamine to the H1 receptor—A molecular dynamics study. J. Mol. Model. 2018, 24, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, G.J.; Ganellin, C.R.; Parsons, M.E. Chemical differentiation of histamine H1-and H2-receptor agonists. J. Med. Chem. 1975, 18, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula, P.; Chazot, P.L.; Cowart, M.; Gutzmer, R.; Leurs, R.; Liu, W.L.S.; Stark, H.; Thurmond, R.L.; Haas, H.L. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCVIII. Histamine Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 601–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnala, V.R.; Kiihne, S.R.; Buda, F.; Leurs, R.; de Groot, H.J.; DeGrip, W.J. Solid-state NMR evidence for a protonation switch in the binding pocket of the H1 receptor upon binding of the agonist histamine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Weinstein, H. Integrated Methods for the Construction of Three-Dimensional Models and Computational Probing of Structure-Function Relations in G Protein-Coupled Receptors. In Methods in Neurosciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 25, pp. 366–428. [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura, T.; Shiroishi, M.; Weyand, S.; Tsujimoto, H.; Winter, G.; Katritch, V.; Abagyan, R.; Cherezov, V.; Liu, W.; Han, G.W.; et al. Structure of the human histamine H1 receptor complex with doxepin. Nature 2011, 475, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worth, G.A.; King, P.M.; Richards, W.G. Histamine tautomerism and its mode of action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 1990, 1036, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpińska, G.; Dobrowolski, J.C.; Mazurek, A.P. Tautomerism of histamine revisited. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 1996, 369, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruysters, M.; Pertz, H.H.; Teunissen, A.; Bakker, R.A.; Gillard, M.; Chatelain, P.; Schunack, W.; Timmerman, H.; Leurs, R. Mutational analysis of the histamine H1-receptor binding pocket of histaprodifens. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 487, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warne, T.; Edwards, P.C.; Doré, A.S.; Leslie, A.G.; Tate, C.G. Molecular basis for high-affinity agonist binding in GPCRs. Science 2019, 364, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, M.; Söldner, C.A.; Miao, Y.; Sticht, H. Agonist binding and G protein coupling in histamine H2 receptor: A molecular dynamics study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Ben-Shalom, I.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; et al. Amber 2021; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, C.J.; Madej, B.D.; Skjevik, Å.A.; Betz, R.M.; Teigen, K.; Gould, I.R.; Walker, R.C. Lipid14: The amber lipid force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Baldridge, K.K.; Boatz, J.A.; Elbert, S.T.; Gordon, M.S.; Jensen, J.H.; Koseki, S.; Matsunaga, N.; Nguyen, K.A.; Su, S.; et al. General atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J. Comput. Chem. 1993, 14, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupradeau, F.Y.; Pigache, A.; Zaffran, T.; Savineau, C.; Lelong, R.; Grivel, N.; Lelong, D.; Rosanski, W.; Cieplak, P. The R.E.D. Tools: Advances in RESP and ESP charge derivation and force field library building. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7821–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Song, L.F.; Merz, K.M., Jr. Systematic parameterization of monovalent ions employing the nonbonded model. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 1645–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.; Postma, J.v.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pándy-Szekeres, G.; Munk, C.; Tsonkov, T.M.; Mordalski, S.; Harpsøe, K.; Hauser, A.S.; Bojarski, A.J.; Gloriam, D.E. GPCRdb in 2018: Adding GPCR structure models and ligands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D440–D446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| System Name | Runs × Time | Histamine | 5 Helix | # Atoms | # DOPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR-HSM- | 2 × 2 s | × | 125,354 | 277 | |
| HR-HSM--5 | 2 × 2 s | ✓ | 125,794 | 277 | |
| HR-HSM- | 2 × 2 s | × | 124,943 | 278 | |
| HR-HSM--5 | 2 × 2 s | ✓ | 125,392 | 278 | |
| HR- | 2 × 2 s | × | 124,942 | 278 | |
| HR--5 | 2 × 2 s | ✓ | 125,391 | 278 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conrad, M.; Horn, A.H.C.; Sticht, H. Computational Analysis of Histamine Protonation Effects on H1R Binding. Molecules 2023, 28, 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093774
Conrad M, Horn AHC, Sticht H. Computational Analysis of Histamine Protonation Effects on H1R Binding. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093774
Chicago/Turabian StyleConrad, Marcus, Anselm H. C. Horn, and Heinrich Sticht. 2023. "Computational Analysis of Histamine Protonation Effects on H1R Binding" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093774
APA StyleConrad, M., Horn, A. H. C., & Sticht, H. (2023). Computational Analysis of Histamine Protonation Effects on H1R Binding. Molecules, 28(9), 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093774






