Descriptive Sensory Attributes and Volatile Flavor Compounds of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Ground Beef
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
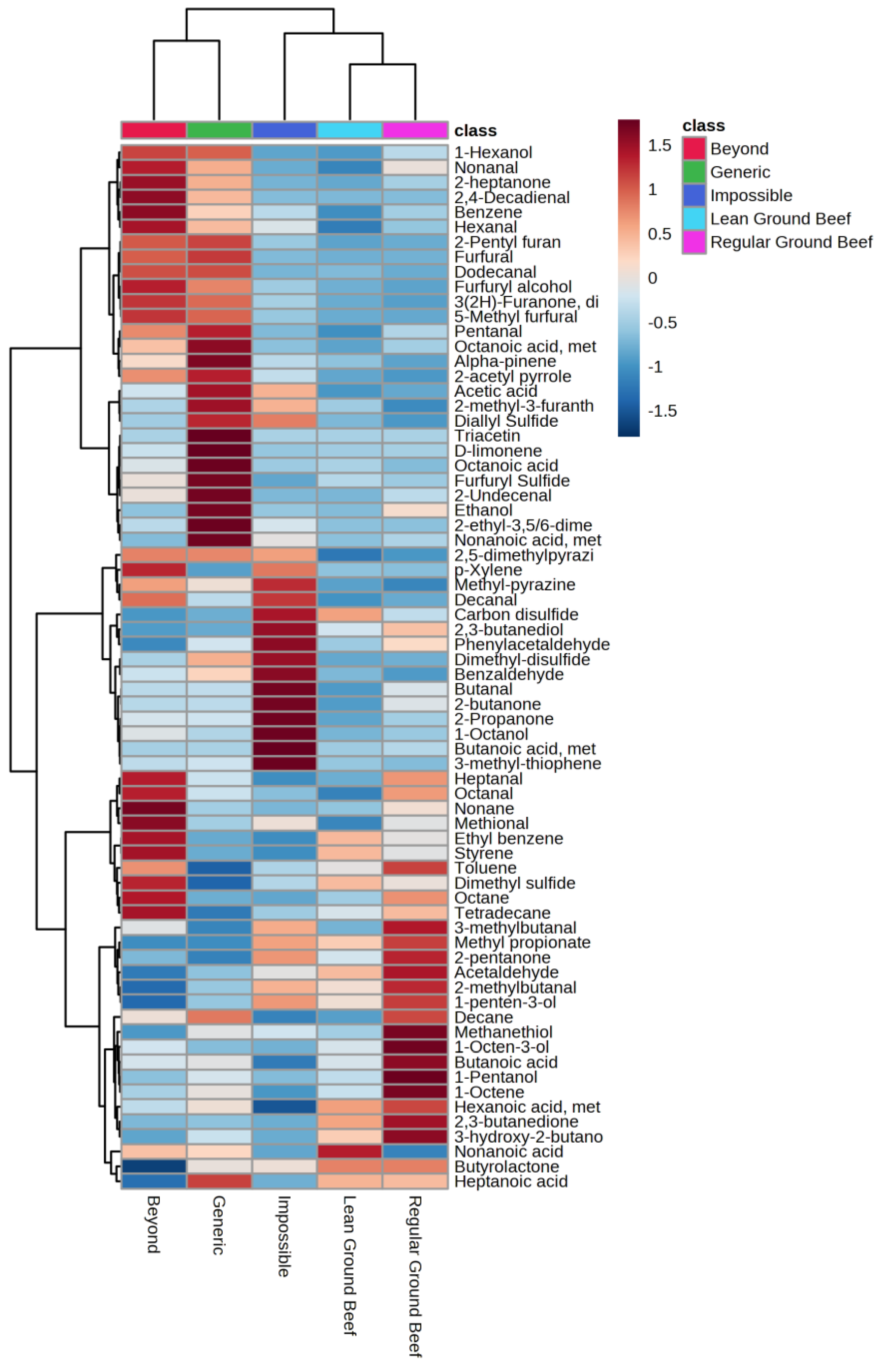
2.2. Volatile Compound Analysis
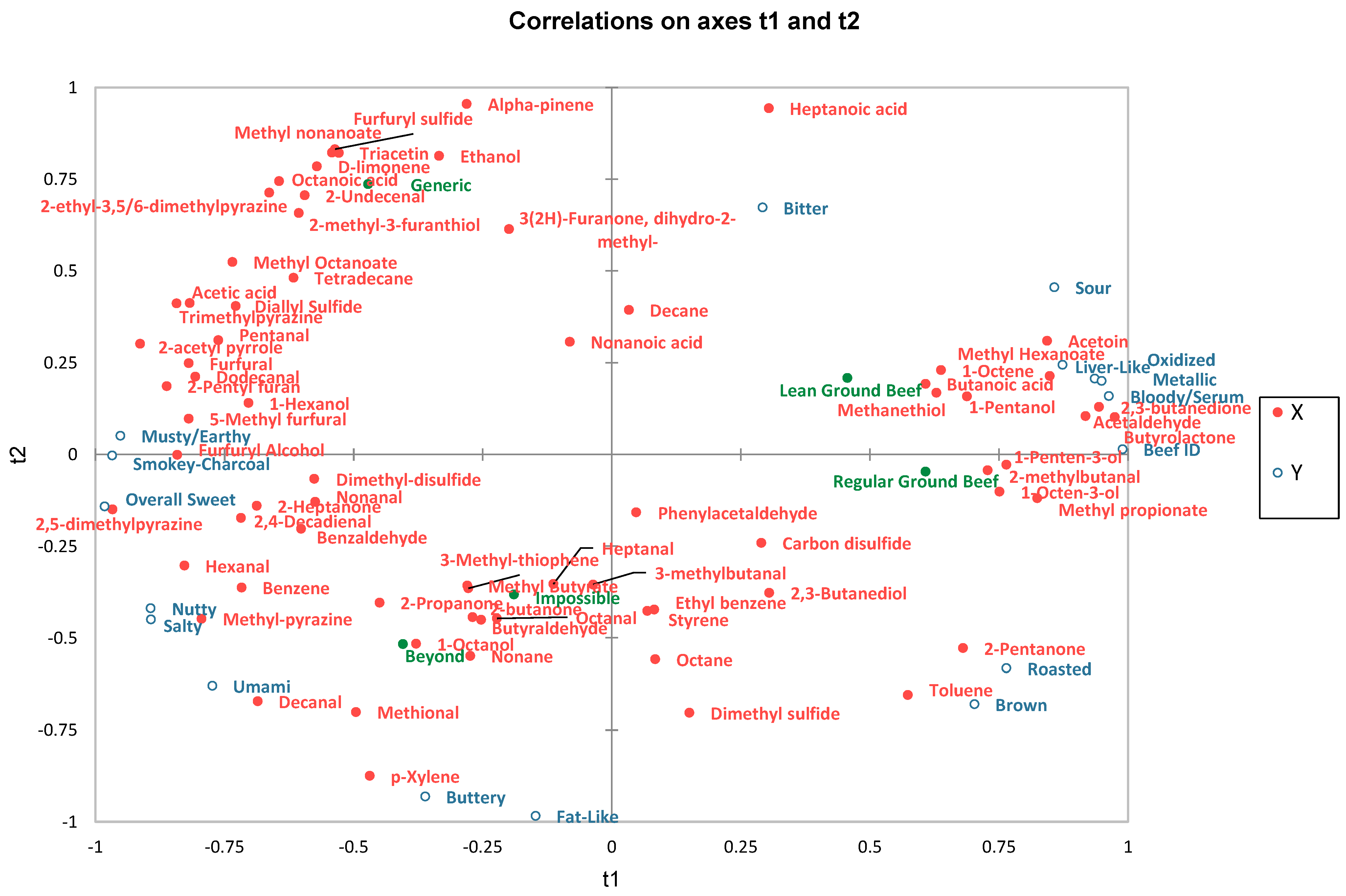
2.3. Relationship between Volatile Compounds and Sensory Attributes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Product Collection and Patty Manufacturing
4.2. Cooking Procedure
4.3. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
4.4. Volatile Compound Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- He, J.; Evans, N.M.; Liu, H.; Shao, S. A review of research on plant-based meat alternatives: Driving forces, history, manufacturing, and consumer attitudes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2639–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starowicz, M.; Kubara Poznar, K.; Zieliński, H. What are the main sensory attributes that determine the acceptance of meat alternatives? Curr. Opin. Food 2022, 48, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tuccillo, F.; Lampi, A.M.; Knaapila, A.; Pulkkinen, M.; Kariluoto, S.; Coda, R.; Edelmann, M.; Jouppila, K.; Sandell, M.; et al. Flavor challenges in extruded plant-based meat alternatives: A review. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food. Saf. 2022, 21, 2898–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.Z.; Shitut, M.; Agrawal, P.; Mendes, O.; Klapholz, S. Safety Evaluation of Soy Leghemoglobin Protein Preparation Derived from Pichia pastoris, Intended for Use as a Flavor Catalyst in Plant-Based Meat. Int. J. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godschalk-Broers, L.; Sala, G.; Scholten, E. Meat Analogues: Relating Structure to Texture and Sensory Perception. Foods 2022, 11, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J. The flavor of plant-based meat analogues. CFW 2020, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Chen, T.; Liu, X. Control of Beany Flavor from Soybean Protein Raw Material in Plant-Based Meat Analog Processing. Foods 2023, 12, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerth, C.R.; Miller, R.K. Beef flavor: A review from chemistry to consumer. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2783–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, C.R.; Hodgen, J.M. A fresh look at meat flavor. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottram, D.S. Flavour formation in meat and meat products: A review. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.G.; Harr, K.M.; Farmer, K.J.; Beyer, E.S.; Bigger, S.B.; Chao, M.D.; Tarpoff, A.J.; Thomson, D.U.; Vipham, J.L.; Zumbaugh, M.D.; et al. Quality of plant-based ground beef alternatives in comparison with ground beef of various fat levels. Meat Muscle Biol. 2021, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarska, K.; Taylor, M.; Piyasiri, U.; Frank, D. Flavor and metabolite profiles of meat, meat substitutes, and traditional plant-based high-protein food products available in Australia. Foods 2021, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, K.; Chambers, E., IV; Miller, R.; Vázquez-Araújo, L.; Bhumiratana, N.; Philip, C. Development of a lexicon for beef flavor in intact muscle. J. Sens. Stud. 2011, 26, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.K.; Pena, C.A.; Legako, J.F.; Woerner, D.R.; Brooks, C.; Schilling, B.; Nair, M.N.; Cramer, T.; Smith, P.; Wall, K.R.; et al. 2018 National Beef Flavor Audit: Consumer and Descriptive Sensory Attributes. Meat Muscle Biol. 2022, 6, 13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, H.; Balamurugan, S.; Shao, S. Fatty acids and volatile flavor compounds in commercial plant-based burgers. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Zhang, X.; Hayat, K.; Liu, P.; Jia, C.; Xia, S.; Xiao, Z.; Tian, H.; Niu, Y. Formation of the beef flavour precursors and their correlation with chemical parameters during the controlled thermal oxidation of tallow. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, K.W.; Bailey, M.E.; Clarke, A.D.; Chao, R.R. Concentration and identification of volatile compounds from heated beef fat using supercritical CO2 extraction-gas liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.T.N.; To, K.V.; Schilling, M.W. Fatty Acid Composition of Meat Animals as Flavor Precursors. Meat Muscle Biol. 2021, 5, 12251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Wu, W.; Soladoye, O.P.; Aluko, R.E.; Bak, K.H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Maillard reaction of food-derived peptides as a potential route to generate meat flavor compounds: A review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinkowska, M.A.; Jeleń, H.H. Role of Sulfur Compounds in Vegetable and Mushroom Aroma. Molecules 2022, 27, 6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, L.J.; Mottram, D.S.; Whitfield, F.B. Volatile compounds produced in maillard reactions involving cysteine, ribose and phospholipid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 49, 347–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, L.J.; Mottram, D.S. Interaction of lipid in the maillard reaction between cysteine and ribose: The effect of a triglyceride and three phospholipids on the volatile products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 53, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, Q.; Song, H.; Li, P.; Yao, J. Aroma-active components of yeast extract pastes with a basic and characteristic meaty flavour. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaere, J.; De Winne, A.; Dewulf, L.; Fraeye, I.; Šoljić, I.; Lauwers, E.; De Jong, A.; Sanctorum, H. Improving the Aromatic Profile of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: Effect of Myoglobin Addition on Volatiles. Foods 2022, 11, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swing, C.J.; Thompson, T.W.; Guimaraes, O.; Geornaras, I.; Engle, T.E.; Belk, K.E.; Gifford, C.L.; Nair, M.N. Nutritional composition of novel plant-based meat alternatives and traditional animal-based meats. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashdorj, D.; Amna, T.; Hwang, I. Influence of specific taste-active components on meat flavor as affected by intrinsic and extrinsic factors: An overview. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMSA. Research Guidelines for Cookery, Sensory Evaluation, and Instrumental Tenderness Measurements of Meat, 2nd ed.; American Meat Science Association: Champaign, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, M.S.; Woerner, D.R.; Brooks, J.C.; Wheeler, T.L.; Legako, J.F. Influence of aging temperature and duration on spoilage organism growth, proteolytic activity, and related chemical changes in vacuum-packaged beef longissimus. Meat Muscle Biol. 2022, 6, 13724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ha, M.; Frank, D.; McGilchrist, P.; Warner, R. Volatile profile of dry and wet aged beef loin and its relationship with consumer flavour liking. Foods 2021, 10, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdock, G.A. Fenaroli’s Handbook of Flavor Ingredients, 5th ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
| Ground Beef | Plant-Based Meat Alternatives | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attribute | Lean 2 | Regular 3 | Beyond Meat | Impossible Burger | Third Retail Brand | SEM 4 | p-Value 5 |
| Beef Flavor Identity | 46.8 b | 51.0 a | 16.7 c | 17.5 c | 11.5 d | 1.10 | <0.001 |
| Brown | 49.2 ab | 50.2 a | 48.3 b | 49.6 ab | 45.4 c | 0.67 | <0.001 |
| Roasted | 49.7 ab | 50.6 a | 49.0 b | 47.6 c | 44.0 d | 0.43 | <0.001 |
| Fat-Like | 15.8 d | 17.2 c | 19.6 a | 18.5 b | 14.5 e | 0.48 | <0.001 |
| Bloody/Serum | 0.8 a | 0.7 a | 0.0 b | 0.0 b | 0.0 b | 0.13 | <0.001 |
| Buttery | 1.4 bc | 2.0 b | 4.2 a | 3.6 a | 1.0 c | 0.28 | <0.001 |
| Overall Sweet | 2.1 b | 1.1 b | 13.1 a | 12.4 a | 12.7 a | 0.44 | <0.001 |
| Smokey-Charcoal | 4.1 c | 3.3 c | 9.6 b | 10.6 ab | 11.1 a | 0.73 | <0.001 |
| Umami | 14.4 d | 13.9 d | 24.9 a | 22.4 b | 17.5 c | 0.46 | <0.001 |
| Metallic | 1.5 a | 1.1 a | 0.1 b | 0.0 b | 0.1 b | 0.17 | <0.001 |
| Liver-Like | 1.5 a | 0.9 b | 0.1 c | 0.0 c | 0.2 c | 0.25 | <0.001 |
| Oxidized | 3.7 a | 3.3 a | 0.2 b | 0.1 b | 0.5 b | 0.38 | <0.001 |
| Nutty | 0.8 c | 0.0 c | 12.1 a | 11.8 a | 7.7 b | 0.51 | <0.001 |
| Musty/Earthy | 2.8 c | 2.3 c | 9.4 b | 11.8 a | 12.2 a | 0.60 | <0.001 |
| Bitter | 3.6 a | 2.9 ab | 1.8 b | 3.4 a | 3.5 a | 0.65 | 0.031 |
| Salty | 1.7 d | 0.7 d | 15.0 a | 12.1 b | 8.7 c | 0.48 | <0.001 |
| Sour | 0.6 a | 0.5 ab | 0.0 c | 0.1 c | 0.2 bc | 0.11 | <0.001 |
| Ground Beef | Plant-Based Meat Alternatives | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attribute | Lean 2 | Regular 3 | Beyond Meat | Impossible Burger | Third Retail Brand | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 |
| Juiciness | 51.3 b | 52.1 b | 55.1 a | 51.3 b | 42.9 c | 0.74 | <0.001 |
| Cohesiveness | 28.5 b | 29.4 ab | 24.5 c | 31.1 a | 28.5 b | 1.07 | <0.001 |
| Hardness | 29.9 a | 30.6 a | 27.9 b | 27.6 b | 25.5 c | 0.89 | <0.001 |
| Particle Size | 31.0 ab | 31.2 ab | 31.9 a | 30.1 b | 23.5 c | 0.58 | <0.001 |
| Ground Beef | Plant-Based Meat Alternatives | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volatile Compound (ng/g) | Lean 1 | Regular 2 | Beyond Meat | Impossible Burger | Third Retail Brand | SEM 3 | p-Value 4 |
| Furans | |||||||
| Furfural | 18.67 b | 20.99 b | 987.41 a | 64.71 b | 1093.54 a | 138.580 | <0.001 |
| 2-Furan methanol | 23.19 b | 16.25 b | 175.73 a | 39.18 b | 136.85 a | 19.454 | <0.001 |
| 2-Methyl-3-furanthiol | 21.33 abc | 1.58 c | 11.11 bc | 24.04 ab | 41.09 a | 9.246 | <0.001 |
| 5-Methyl furfural | 6.24 b | 5.76 b | 24.33 a | 6.99 b | 21.74 a | 2.194 | <0.001 |
| Ketones | |||||||
| Acetoin | 13.12 b | 24.93 a | 2.27 c | 2.76 c | 8.48 bc | 3.915 | <0.001 |
| 2,3-Butanedione | 30.15 ab | 42.01 a | 12.79 c | 11.84 c | 13.95 bc | 6.348 | 0.002 |
| Oxolanes | |||||||
| 2-Methyltetrahydro-3-furanone | 15.08 ab | 12.02 ab | 14.50 ab | 9.70 b | 15.95 a | 4.111 | 0.005 |
| Pyrazines | |||||||
| Methylpyrazine | 12.73 c | 10.26 c | 30.88 ab | 38.94 a | 24.18 b | 5.303 | <0.001 |
| Trimethylpyrazine | 2.98 d | 3.91 cd | 7.82 bc | 9.67 b | 15.56 a | 1.707 | <0.001 |
| 2,5-Dimethylpyrazine | 14.46 b | 16.97 b | 32.37 a | 30.92 a | 32.09 a | 5.203 | 0.017 |
| 2-Ethyl-3,5/6-dimethylpyrazine | 6.73 b | 7.35 b | 10.33 b | 12.48 b | 36.20 a | 6.338 | 0.001 |
| Pyrroles | |||||||
| 2-Acetylpyrrole | 169.69 c | 141.75 c | 559.78 ab | 306.20 bc | 725.88 a | 132.360 | <0.001 |
| Strecker Aldehydes | |||||||
| Acetaldehyde | 86.20 | 116.84 | 41.46 | 73.27 | 58.09 | 27.305 | 0.169 |
| Benzaldehyde | 36.67 c | 23.65 c | 62.07 bc | 164.42 a | 89.35 b | 17.477 | <0.001 |
| Butyraldehyde | 6.06 b | 6.49 b | 6.36 b | 7.41 a | 6.39 b | 0.309 | 0.013 |
| Methional | 2.28 b | 4.66 b | 8.38 a | 4.89 b | 3.77 b | 1.088 | 0.001 |
| Phenylacetaldehyde | 8.54 bc | 11.85 b | 6.10 c | 18.21 a | 10.10 bc | 1.803 | <0.001 |
| 2-Methylbutanal | 18.10 b | 23.51 a | 12.74 c | 20.74 ab | 15.56 bc | 1.915 | <0.001 |
| 3-Methylbutanal | 15.69 | 16.91 | 16.61 | 16.22 | 16.26 | 1.071 | 0.918 |
| Sulfides | |||||||
| Carbon disulfide | 53.96 ab | 32.46 bc | 15.59 c | 74.23 a | 20.58 c | 11.511 | <0.001 |
| Diallyl sulfide | 4.21 b | 2.91 b | 5.36 b | 13.61 a | 16.63 a | 2.249 | <0.001 |
| Dimethyl disulfide | 0.12 b | 0.12 b | 0.16 b | 0.39 a | 0.27 ab | 0.058 | 0.003 |
| Dimethyl sulfide | 11.74 | 10.98 | 13.46 | 10.21 | 8.80 | 2.020 | 0.535 |
| Furfuryl sulfide | 21.68 | 20.66 | 20.85 | 21.76 | 27.30 | 2.962 | 0.158 |
| Thiols | |||||||
| Methanethiol | 25.27 | 54.48 | 19.17 | 28.82 | 30.68 | 10.095 | 0.082 |
| Thiophenes | |||||||
| 3-Methyl thiophene | 2.47 b | 2.44 b | 2.46 b | 4.08 a | 2.46 b | 0.272 | <0.001 |
| Ground Beef | Plant-Based Meat Alternatives | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volatile Compound (ng/g) | Lean 1 | Regular 2 | Beyond Meat | Impossible Burger | Third Retail Brand | SEM 3 | p-Value 4 |
| Alcohols | |||||||
| Ethanol | 10.70 b | 21.01 b | 11.46 b | 11.97 b | 41.14 a | 7.085 | 0.009 |
| 1-Hexanol | 3.78 | 6.06 | 12.11 | 4.12 | 11.42 | 3.967 | 0.253 |
| 1-Octanol | 9.04 b | 11.52 b | 17.83 b | 43.89 a | 13.55 b | 4.271 | <0.001 |
| 1-Octen-3-ol | 7.19 b | 11.32 a | 7.11 b | 5.88 b | 6.10 b | 0.930 | <0.001 |
| 1-Pentanol | 5.76 b | 9.66 a | 5.16 b | 5.09 b | 6.01 b | 0.908 | <0.001 |
| 1-Penten-3-ol | 46.00 ab | 65.53 a | 19.90 c | 54.20 ab | 31.82 cb | 9.322 | 0.005 |
| 2,3-Butanediol | 16.44 | 19.67 | 12.41 | 25.89 | 13.17 | 3.997 | 0.052 |
| Aldehydes | |||||||
| Decanal | 9.89 | 10.82 | 19.03 | 20.54 | 13.11 | 3.850 | 0.132 |
| Dodecanal | 18.91 | 16.20 | 59.17 | 17.84 | 59.61 | 16.756 | 0.106 |
| Heptanal | 9.30 c | 20.42 ab | 26.36 a | 7.53 c | 13.50 bc | 2.591 | <0.001 |
| Hexanal | 39.98 c | 75.63 bc | 197.61 a | 103.87 b | 136.41 ab | 23.278 | <0.001 |
| Nonanal | 30.23 c | 48.12 abc | 69.56 a | 35.45 bc | 56.09 ab | 8.879 | 0.011 |
| Octanal | 11.81 c | 22.63 ab | 26.85 a | 14.89 bc | 17.31 bc | 3.145 | 0.005 |
| Pentanal | 3.85 b | 6.89 b | 12.90 a | 5.53 b | 15.49 a | 1.775 | <0.001 |
| 2-Undecenal | 16.80 b | 26.67 b | 34.83 b | 16.78 b | 81.79 a | 7.513 | <0.001 |
| (E,E)-2,4-Decadienal | 15.57 b | 17.22 b | 174.19 a | 17.73 b | 95.07 ab | 34.280 | 0.002 |
| Carboxylic acids | |||||||
| Acetic acid | 190.81 c | 236.92 c | 439.27 bc | 668.79 ab | 968.49 a | 131.410 | <0.001 |
| Butanoic acid | 9.40 ab | 15.43 a | 9.37 ab | 5.78 b | 9.69 ab | 2.387 | 0.049 |
| Heptanoic acid | 14.77 | 14.74 | 13.88 | 14.14 | 15.10 | 0.420 | 0.207 |
| Nonanoic acid | 8.38 | 6.51 | 7.65 | 6.73 | 7.52 | 1.117 | 0.755 |
| Octanoic acid | 76.96 b | 48.99 b | 124.33 b | 65.14 b | 396.33 a | 45.120 | <0.001 |
| Esters | |||||||
| Methyl butyrate | 4.56 b | 6.26 b | 5.07 b | 157.49 a | 23.02 b | 34.893 | <0.001 |
| Methyl hexanoate | 1.53 ab | 1.82 a | 1.27 ab | 1.12 b | 1.31 ab | 0.234 | 0.276 |
| Methyl nonanoate | 5.71 b | 5.73 b | 5.64 b | 5.71 b | 8.69 a | 0.567 | <0.001 |
| Methyl octanoate | 2.79 a | 2.88 bc | 3.10 ab | 2.84 bc | 3.40 a | 0.118 | <0.001 |
| Methyl propionate | 10.47 abc | 14.88 a | 4.09 c | 11.72 ab | 5.48 bc | 2.706 | 0.026 |
| Furans | |||||||
| 2-Pentyl furan | 3.24 b | 4.04 b | 24.17 a | 6.85 b | 25.46 a | 3.195 | <0.001 |
| Hydrocarbons | |||||||
| Benzene | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.059 | 0.244 |
| Decane | 4.84 | 7.94 | 6.28 | 4.47 | 7.51 | 1.438 | 0.303 |
| Ethylbenzene | 2.80 ab | 2.65 bc | 3.12 a | 2.33 c | 2.41 c | 0.144 | <0.001 |
| Nonane | 3.44 bc | 6.35 b | 13.21 a | 2.99 c | 3.93 b | 1.181 | <0.001 |
| Octane | 7.04 b | 15.81 a | 20.80 a | 4.59 b | 4.94 b | 2.429 | <0.001 |
| Styrene | 2.86 ab | 2.70 bc | 3.20 a | 2.38 c | 2.46 c | 0.149 | <0.001 |
| Tetradecane | 2.17 a | 2.66 ab | 3.71 a | 1.81 b | 4.64 a | 1.111 | 0.031 |
| Toluene | 4.37 | 4.89 | 4.67 | 4.22 | 3.81 | 0.456 | 0.364 |
| p-Xylene | 55.95 b | 53.18 b | 246.45 a | 200.66 a | 28.51 b | 29.375 | <0.001 |
| 1-Octene | 2.37 b | 5.60 a | 2.03 b | 1.23 b | 2.76 b | 0.688 | <0.001 |
| Ketones | |||||||
| 2-Butanone | 14.32 b | 19.34 b | 17.75 b | 30.33 a | 17.91 b | 3.589 | 0.012 |
| 2-Heptanone | 4.08 c | 6.76 c | 21.96 a | 4.70 c | 14.21 b | 2.019 | <0.001 |
| 2-Pentanone | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.035 | 0.627 |
| 2-Propanone | 129.65 b | 169.33 b | 200.67 b | 395.73 a | 207.80 b | 39.614 | <0.001 |
| Lactones | |||||||
| Butyrolactone | 15.54 | 15.97 | 13.37 | 12.77 | 12.70 | 4.664 | 0.904 |
| Terpenes | |||||||
| α-Pinene | 2.57 b | 2.53 b | 2.45 b | 2.38 b | 2.89 a | 0.131 | <0.001 |
| d-Limonene | 3.35 b | 3.44 b | 4.61 b | 2.92 b | 14.96 a | 1.376 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez, M.S.; Woerner, D.R.; Brooks, J.C.; Legako, J.F. Descriptive Sensory Attributes and Volatile Flavor Compounds of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Ground Beef. Molecules 2023, 28, 3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073151
Hernandez MS, Woerner DR, Brooks JC, Legako JF. Descriptive Sensory Attributes and Volatile Flavor Compounds of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Ground Beef. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073151
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez, Manuel Sebastian, Dale R. Woerner, J. Chance Brooks, and Jerrad F. Legako. 2023. "Descriptive Sensory Attributes and Volatile Flavor Compounds of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Ground Beef" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073151
APA StyleHernandez, M. S., Woerner, D. R., Brooks, J. C., & Legako, J. F. (2023). Descriptive Sensory Attributes and Volatile Flavor Compounds of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Ground Beef. Molecules, 28(7), 3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073151




