Combined Toxic Effects of BPA and Its Two Analogues BPAP and BPC in a 3D HepG2 Cell Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
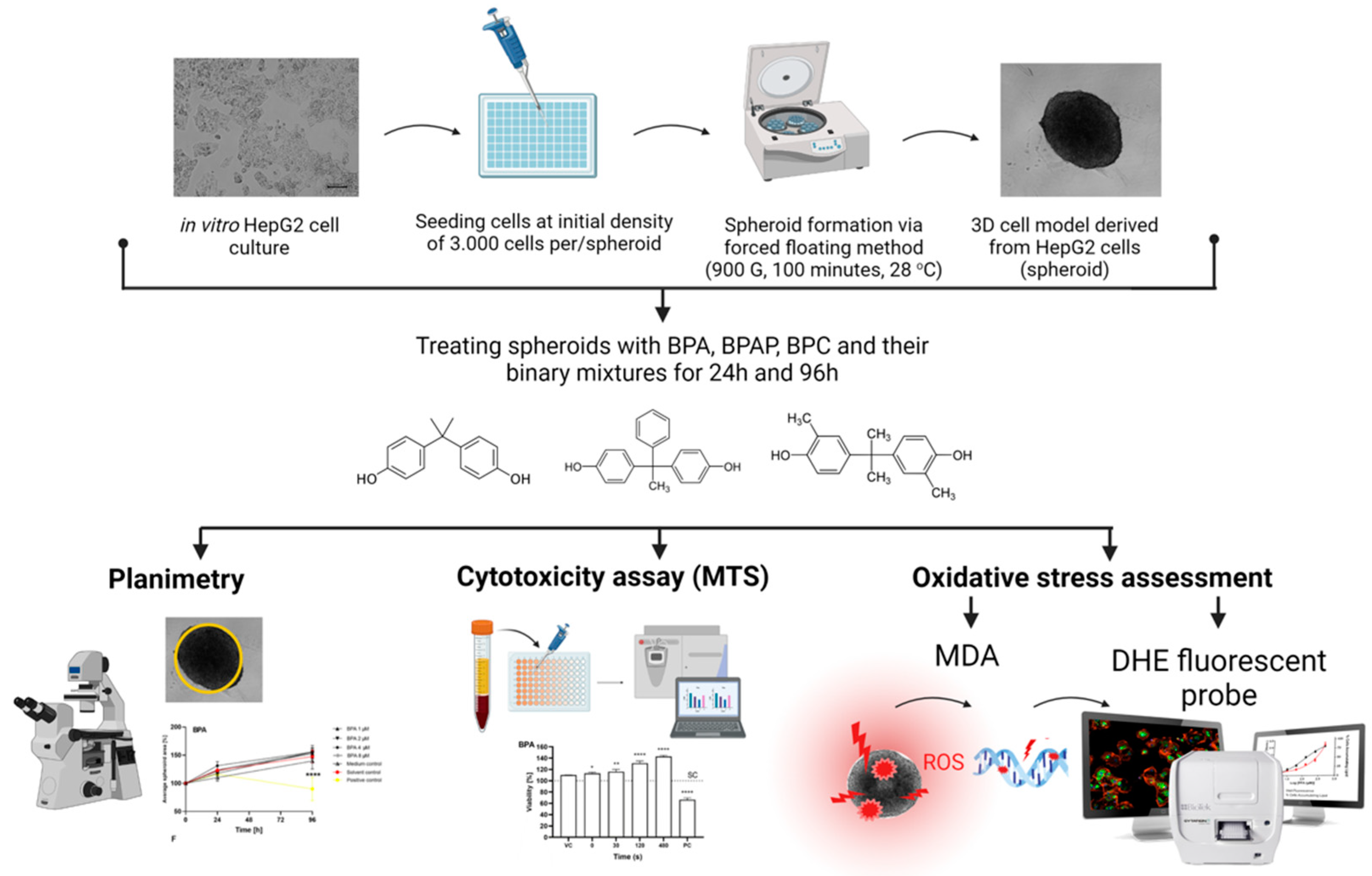
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Preparation of Bisphenol Standard Solution
| Compound Name | IUPAC Name | CAS No | Structural Formula | Molecular Weight [g/mol] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bisphenol A | 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane | 80-05-07 | 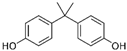 | 228.29 |
| Bisphenol AP | 4,4′-(1-phenylethylidene)bisphenol | 1571-75-1 |  | 290.36 |
| Bisphenol C | 4,4′-Isopropylidenedi-o-cresol | 79-97-0 | 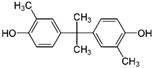 | 256.34 |
3.2. Cell Culture and Formation of In Vitro 3D Cell Model
3.3. Preparation of Complex BPs Mixtures and Treatment Conditions
| Time of Exposure | Single Compound or Binary Mixture | Concentrations |
|---|---|---|
| 24 h | BPA, BPAP, BPC | 10 µM, 20 µM, 40 µM, 80 µM |
| BPA + BPAP/BPC | 10 + 10 µM, 20 + 20 µM, 40 + 40 µM | |
| 96 h | BPA, BPAP, BPC | 1 µM, 2 µM, 4 µM, 8 µM |
| BPA + BPAP/BPC | 1 + 1 µM, 2 + 2 µM, 4 + 4 µM |
3.4. Cytotoxicity—The MTS Assay
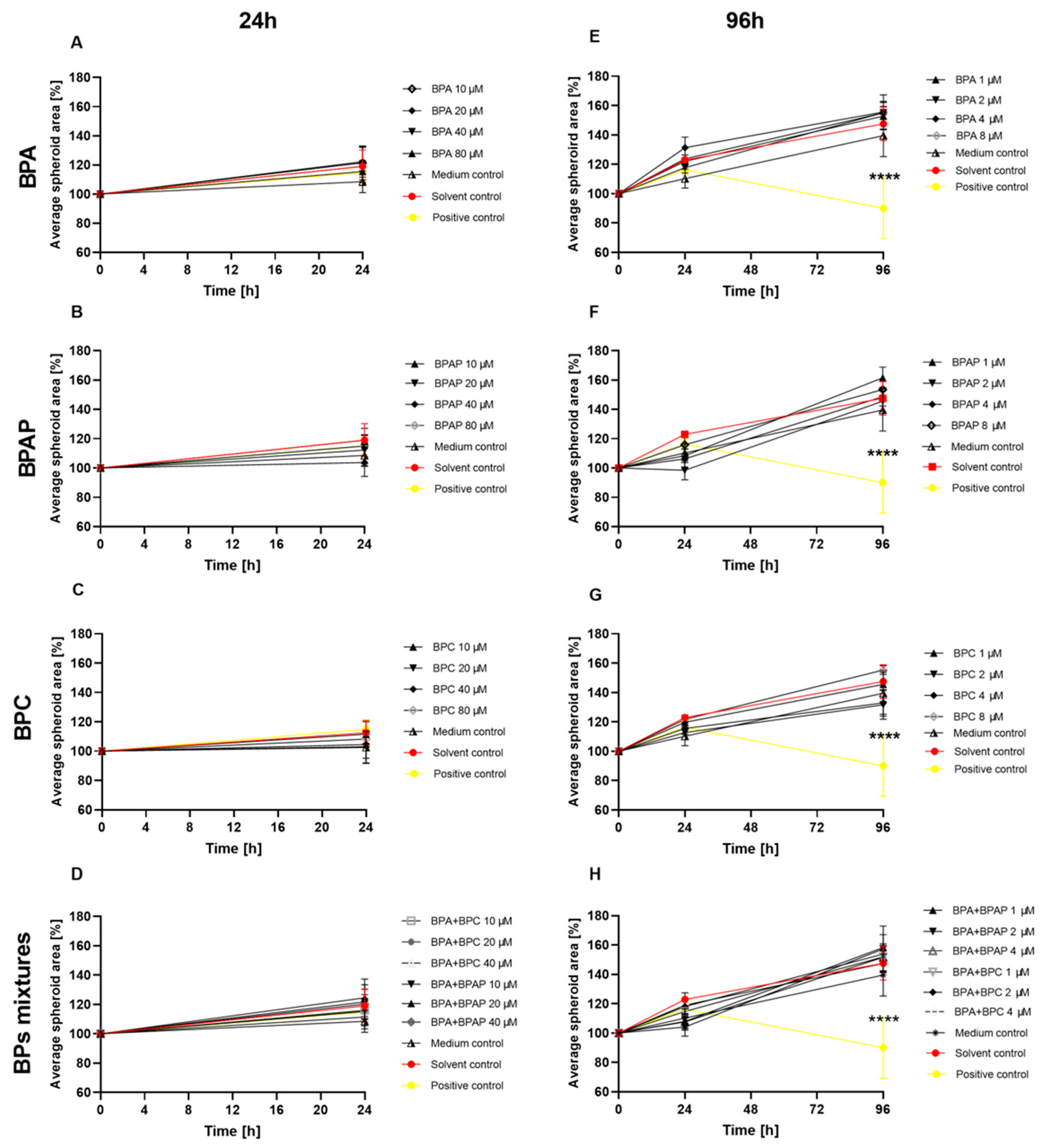
3.5. Planimetry—The Effects on the Average Surface Area
3.6. Oxidative Stress—The MDA Assay and ROS Production
3.6.1. Determination of MDA Level
3.6.2. Determination of ROS Production
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Arnold, S.M.; Clark, K.E.; Staples, C.A.; Klecka, G.M.; Dimond, S.S.; Caspers, N.; Hentges, S.G. Relevance of drinking water as a source of human exposure to bisphenol A. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chang, H.; Wiseman, S.; He, Y.; Higley, E.; Jones, P.; Wong, C.K.C.; Al-Khedhairy, A.; Giesy, J.P.; Hecker, M. Bisphenol A Disrupts Steroidogenesis in Human H295R Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 121, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V. Large effects from small exposures. II. The importance of positive controls in low-dose research on bisphenol A. Environ. Res. 2006, 100, 50–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Gómez, A.; Brandsma, S.H.; de Boer, J.; Leonards, P.E.G. Analysis of two alternative organophosphorus flame retardants in electronic and plastic consumer products: Resorcinol bis-(diphenylphosphate) (PBDPP) and bisphenol A bis (diphenylphosphate) (BPA-BDPP). Chemosphere 2014, 116, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-R.; Park, S.-J.; Jeong, M.-J.; Choi, J.C.; Kim, M. Fast and simple determination and exposure assessment of bisphenol A, phenol, p-tert-butylphenol, and diphenylcarbonate transferred from polycarbonate food-contact materials to food simulants. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmler, H.-J.; Liu, B.; Gadogbe, M.; Bao, W. Exposure to Bisphenol A, Bisphenol F, and Bisphenol S in U.S. Adults and Children: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2014. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6523–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Kannan, K.; Tan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.; Widelka, M. Bisphenol Analogues Other Than BPA: Environmental Occurrence, Human Exposure, and Toxicity—A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5438–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-H.; Zhang, X.-M.; Wang, F.; Gao, C.-J.; Chen, D.; Palumbo, J.R.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, E.Y. Occurrence of bisphenol S in the environment and implications for human exposure: A short review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassinari, R.; Tait, S.; Busani, L.; Martinelli, A.; Valeri, M.; Gastaldelli, A.; Deodati, A.; La Rocca, C.; Maranghi, F. Toxicological Assessment of Oral Co-Exposure to Bisphenol A (BPA) and Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) in Juvenile Rats at Environmentally Relevant Dose Levels: Evaluation of the Synergic, Additive or Antagonistic Effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, T.; Harner, T. Bisphenol A and its analogues in outdoor and indoor air: Properties, sources and global levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoner, J.R.; Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T.; Cozzarelli, I.M.; Gray, J.L.; Schwab, E.A. Contaminants of emerging concern in fresh leachate from landfills in the conterminous United States. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 2335–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantonwine, D.E.; Hauser, R.; Meeker, J.D. Bisphenol A and human reproductive health. Expert Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 8, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, P.; Romano, R.M.; Kizys, M.M.L.; Oliveira, K.C.; Kasamatsu, T.; Giannocco, G.; Chiamolera, M.I.; Dias-da-Silva, M.R.; Romano, M.A. Adult exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) in Wistar rats reduces sperm quality with disruption of the hypothalamic–pituitary–testicular axis. Toxicology 2015, 329, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Fang, F.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Z.-J.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J. Bisphenol A and Ovarian Reserve among Infertile Women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsdotter, M.K.; Jonker, W.; Legradi, J.; Kool, J.; Ballesteros-Gómez, A. Bisphenol A alternatives in thermal paper from the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden and Norway. Screening and potential toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Ahmad, M. From BPA to its analogues: Is it a safe journey? Chemosphere 2016, 158, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fic, A.; Žegura, B.; Sollner Dolenc, M.; Filipič, M.; Peterlin Mašič, L. Mutagenicity and DNA Damage of Bisphenol a and its Structural Analogues in Hepg2 Cells. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradesh, M.; Singh, I.R.; Talpade, J.; Shrman, K.; Sharma, R.K.; Gutham, V.; Singh, R.P.; Meena, N.S. Bisphenol a: An endocrine disruptor. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 394–397. [Google Scholar]
- Seachrist, D.D.; Bonk, K.W.; Ho, S.-M.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Keri, R.A. A review of the carcinogenic potential of bisphenol A. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 59, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, M.; Štampar, M.; Fras, K.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A.; Žegura, B. Adverse (geno)toxic effects of bisphenol A and its analogues in hepatic 3D cell model. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Colborn, T.; Hayes, T.B.; Heindel, J.J.; Jacobs, D.R.; Lee, D.-H.; Shioda, T.; Soto, A.M.; vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V.; et al. Hormones and Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: Low-Dose Effects and Nonmonotonic Dose Responses. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 378–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezg, R.; El-Fazaa, S.; Gharbi, N.; Mornagui, B. Bisphenol A and human chronic diseases: Current evidences, possible mechanisms, and future perspectives. Environ. Int. 2014, 64, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, M.; Pereiro, P.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. An integrative toxicogenomic analysis of plastic additives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Braver-Sewradj, S.P.; van Spronsen, R.; Hessel, E.V.S. Substitution of bisphenol A: A review of the carcinogenicity, reproductive toxicity, and endocrine disruption potential of alternative substances. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 128–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, T.S.; Lee, B.P.; Burić, I.; Steele, A.M.; BPA Schools Study Consortium; Kocur, A.L.; Pandeth, A.G.; Harries, L.W. Plastics Additives and Human Health: A Case Study of Bisphenol A (BPA). In Plastics and the Environment; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; pp. 131–155. [Google Scholar]
- EULC European Legislation on Chemicals—Bisphenol. Available online: http://www.bisphenol-a-europe.org/regulatory-framework/european-legislation-on-chemicals/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- US FDA. No Bisphenol A (BPA): Use in Food Contact Application. Public Health Focus 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- ECHA 4,4′-Isopropylidenedi-o-Cresol; European Chemicals Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2021.
- European Food Safety Authority Scientific opinion on bisphenol A (2015). Eur. Food Saf. Auth. 2015, 4, 1–4.
- FitzGerald, R.; Van Loveren, H.; Civitella, C.; Castoldi, A.F.; Bernasconi, G. Assessment of new information on Bisphenol S (BPS) submitted in response to the Decision 1 under REACH Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. EFSA Support. Publ. 2020, 17, 1844E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, F.; Krasniqi, T.; Bailat Rosset, G.; Roth, N.; Hopf, N.B.; Broillet, M.-C.; Staedler, D. Exposure to New Emerging Bisphenols Among Young Children in Switzerland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelch, K.; Wignall, J.A.; Goldstone, A.E.; Ross, P.K.; Blain, R.B.; Shapiro, A.J.; Holmgren, S.D.; Hsieh, J.-H.; Svoboda, D.; Auerbach, S.S.; et al. A scoping review of the health and toxicological activity of bisphenol A (BPA) structural analogues and functional alternatives. Toxicology 2019, 424, 152235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Barbato, F.; Mita, D.G.; Grumetto, L. Occurrence of Bisphenol A and its analogues in some foodstuff marketed in Europe. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Hong, Y.; Cai, Z. Occurrence and Partitioning of Bisphenol Analogues in Adults’ Blood from China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Liu, F.; Kannan, K. Bisphenol S, a New Bisphenol Analogue, in Paper Products and Currency Bills and Its Association with Bisphenol A Residues. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6515–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Q.H.; Ji, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, M.L. Synthesis and characterisation of 9,9-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-fluorene catalysed by cation exchanger. Pigment Resin Technol. 2008, 37, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J. Kinetics and thermal properties of epoxy resins based on bisphenol fluorene structure. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, P.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Rapid Method for the Separation and Recovery of Endocrine-Disrupting Compound Bisphenol AP from Wastewater. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3968–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Yu, T.; Zhou, L.; Fan, X.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Lv, J.; Jia, X.; et al. Bisphenol AP is anti-estrogenic and may cause adverse effects at low doses relevant to human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Suyama, K.; Nose, T.; Shimohigashi, M.; Shimohigashi, Y. Bisphenol-C is the strongest bifunctional ERα-agonist and ERβ-antagonist due to magnified halogen bonding. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlas, S.; Usman, A.; Ahmad, M. In vitro study to evaluate the cytotoxicity of BPA analogues based on their oxidative and genotoxic potential using human peripheral blood cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 60, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ren, M.L.; Feng, X.; Cai, Y.L.; Gao, Y.X.; Xu, Q. An evidence in vitro for the influence of bisphenol A on uterine leiomyoma. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2014, 178, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hercog, K.; Maisanaba, S.; Filipič, M.; Sollner-Dolenc, M.; Kač, L.; Žegura, B. Genotoxic activity of bisphenol A and its analogues bisphenol S, bisphenol F and bisphenol AF and their mixtures in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji-Youn, K.; Ho-Gyu, C.; Hae-Miru, L.; Geum-A, L.; Kyung-A, H.; Kyung-Chul, C. Effects of bisphenol compounds on the growth and epithelial mesenchymal transition of MCF-7 CV human breast cancer cells. J. Biomed. Res. 2017, 31, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonavane, M.; Gassman, N.R. Bisphenol A co-exposure effects: A key factor in understanding BPA’s complex mechanism and health outcomes. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2019, 49, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero-Casero, N.; Lunar, L.; Rubio, S. Analytical methods for the determination of mixtures of bisphenols and derivatives in human and environmental exposure sources and biological fluids. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 908, 22–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, M.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y. Rapid detection of four mycotoxins in corn using a microfluidics and microarray-based immunoassay system. Talanta 2018, 186, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, G.E.; Shah, U.-K.; Llewellyn, S.; Cervena, T.; Evans, S.J.; Al Ali, A.S.; Jenkins, G.J.; Clift, M.J.D.; Doak, S.H. Adaptation of the in vitro micronucleus assay for genotoxicity testing using 3D liver models supporting longer-term exposure durations. Mutagenesis 2020, 35, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elje, E.; Hesler, M.; Rundén-Pran, E.; Mann, P.; Mariussen, E.; Wagner, S.; Dusinska, M.; Kohl, Y. The comet assay applied to HepG2 liver spheroids. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2019, 845, 403033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elje, E.; Mariussen, E.; Moriones, O.H.; Bastús, N.G.; Puntes, V.; Kohl, Y.; Dusinska, M.; Rundén-Pran, E. Hepato(Geno)Toxicity Assessment of Nanoparticles in a HepG2 Liver Spheroid Model. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, S.V.; Conway, G.E.; Shah, U.-K.; Evans, S.J.; Jenkins, G.J.S.; Clift, M.J.D.; Doak, S.H. Advanced 3D Liver Models for In vitro Genotoxicity Testing Following Long-Term Nanomaterial Exposure. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 160, e61141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfuhler, S.; van Benthem, J.; Curren, R.; Doak, S.H.; Dusinska, M.; Hayashi, M.; Heflich, R.H.; Kidd, D.; Kirkland, D.; Luan, Y.; et al. Use of in vitro 3D tissue models in genotoxicity testing: Strategic fit, validation status and way forward. Report of the working group from the 7th International Workshop on Genotoxicity Testing (IWGT). Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2020, 850–851, 503135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, U.-K.; Verma, J.R.; Chapman, K.E.; Wilde, E.C.; Tonkin, J.A.; Brown, M.R.; Johnson, G.E.; Doak, S.H.; Jenkins, G.J. Detection of urethane-induced genotoxicity in vitro using metabolically competent human 2D and 3D spheroid culture models. Mutagenesis 2020, 35, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štampar, M.; Sedighi Frandsen, H.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A.; Wrzesinski, K.; Filipič, M.; Žegura, B. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2/C3A) cell-based 3D model for genotoxicity testing of chemicals. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štampar, M.; Tomc, J.; Filipič, M.; Žegura, B. Development of in vitro 3D cell model from hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line and its application for genotoxicity testing. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3321–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.C.; Hendriks, D.F.G.; Moro, S.M.L.; Ellis, E.; Walsh, J.; Renblom, A.; Fredriksson Puigvert, L.; Dankers, A.C.A.; Jacobs, F.; Snoeys, J.; et al. Characterization of primary human hepatocyte spheroids as a model system for drug-induced liver injury, liver function and disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilenberger, C.; Rothbauer, M.; Ehmoser, E.-K.; Ertl, P.; Küpcü, S. Effect of Spheroidal Age on Sorafenib Diffusivity and Toxicity in a 3D HepG2 Spheroid Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrzesinski, K.; Alnøe, S.; Jochumsen, H.H.; Mikkelsen, K.; Bryld, T.D.; Vistisen, J.S.; Willems Alnøe, P.; Fey, S.J. A Purpose-Built System for Culturing Cells as In Vivo Mimetic 3D Structures. In Biomechanics and Functional Tissue Engineering; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wrzesinski, K.; Fey, S.J. From 2D to 3D-a new dimension for modelling the effect of natural products on human tissue. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 5605–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, S.; Raposo, A.; Almeida-González, M.; Carrascosa, C. Bisphenol A: Food Exposure and Impact on Human Health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1503–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesinski, K.; Fey, S.J. After trypsinisation, 3D spheroids of C3A hepatocytes need 18 days to re-establish similar levels of key physiological functions to those seen in the liver. Toxicol. Res. 2013, 2, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fey, S.J.; Wrzesinski, K. Determination of Drug Toxicity Using 3D Spheroids Constructed From an Immortal Human Hepatocyte Cell Line. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 127, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.F.; No, D.Y.; Choi, Y.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Chung, B.G.; Lee, S.-H. Concave microwell based size-controllable hepatosphere as a three-dimensional liver tissue model. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8087–8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira Azevedo, L.; Masiero, M.M.; Cherkaoui, S.; Hornos Carneiro, M.F.; Barbosa Jr, F.; Zamboni, N. The alternative analog plasticizer BPS displays similar phenotypic and metabolomic responses to BPA in HepG2 and INS-1E cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 167, 113266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyurt, B.; Ozkemahli, G.; Yirun, A.; Ozyurt, A.B.; Bacanli, M.; Basaran, N.; Kocer-Gumusel, B.; Erkekoglu, P. Comparative evaluation of the effects of bisphenol derivatives on oxidative stress parameters in HepG2 cells. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 46, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Hu, K.; Yang, Z.; Song, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. Potent Clastogenicity of Bisphenol Compounds in Mammalian Cells—Human CYP1A1 Being a Major Activating Enzyme. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15267–15276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnett, K.G.; Chin, A.; Schuh, S.M. BPA and BPA alternatives BPS, BPAF, and TMBPF, induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in rat and human stem cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, G.; Capuozzo, A.; Barbato, F.; Irace, C.; Santamaria, R.; Grumetto, L. Cytotoxicity of seven bisphenol analogues compared to bisphenol A and relationships with membrane affinity data. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsui, T.; Tamura, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Hirose, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Nishimura, H.; Metzler, M.; Barrett, J.C. Mammalian cell transformation and aneuploidy induced by five bisphenols. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 86, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padberg, F.; Tarnow, P.; Luch, A.; Zellmer, S. Minor structural modifications of bisphenol A strongly affect physiological responses of HepG2 cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skledar, D.G.; Mašič, L.P. In vitro estrogenic activity of binary and multicomponent mixtures with bisphenol A. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Liang, X.; Song, Y.; Cai, Z. Mass Spectrometry Imaging Combined with Metabolomics Revealing the Proliferative Effect of Environmental Pollutants on Multicellular Tumor Spheroids. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11341–11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.G.; Jun, I.; Lee, S.; Ryu, C.S.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Han, H.; Park, H.; Manz, A.; Shin, H.; et al. Integration of Bioinspired Fibrous Strands with 3D Spheroids for Environmental Hazard Monitoring. Small 2022, 18, 2200757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, S.J.; Tarpley, M.; Shah, I.; Save, A.V.; Lyerly, H.K.; Patierno, S.R.; Williams, K.P.; Devi, G.R. Bisphenol A activates EGFR and ERK promoting proliferation, tumor spheroid formation and resistance to EGFR pathway inhibition in estrogen receptor-negative inflammatory breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, bgx003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Maiorino, M.; Ursini, F. Signaling Functions of Reactive Oxygen Species. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, H.; Wartenberg, M.; Hescheler, J. Reactive Oxygen Species as Intracellular Messengers During Cell Growth and Differentiation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2001, 11, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Huang, Q.-S.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.-Y.; Wu, S.-L.; Ni, B.-J. Polyvinyl Chloride Microplastics Affect Methane Production from the Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge through Leaching Toxic Bisphenol-A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourouma, A.; Quan, C.; Duan, P.; Qi, S.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K. Bisphenol A Induces Apoptosis in Liver Cells through Induction of ROS. Adv. Toxicol. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ďurovcová, I.; Kyzek, S.; Fabová, J.; Makuková, J.; Gálová, E.; Ševčovičová, A. Genotoxic potential of bisphenol A: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audebert, M.; Dolo, L.; Perdu, E.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Zalko, D. Use of the γH2AX assay for assessing the genotoxicity of bisphenol A and bisphenol F in human cell lines. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michałowicz, J.; Mokra, K.; Bąk, A. Bisphenol A and its analogs induce morphological and biochemical alterations in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (in vitro study). Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Shi, J.; Li, M.; Guo, Q.; Shao, B. Effects of bisphenol analogues on steroidogenic gene expression and hormone synthesis in H295R cells. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, R.; Zong, W. Bisphenol S Interacts with Catalase and Induces Oxidative Stress in Mouse Liver and Renal Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6630–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, S.; Wang, S.; Zhu, W.; Xie, C.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Curcumin attenuates BPA-induced insulin resistance in HepG2 cells through suppression of JNK/p38 pathways. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 272, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokra, K.; Kuźmińska-Surowaniec, A.; Woźniak, K.; Michałowicz, J. Evaluation of DNA-damaging potential of bisphenol A and its selected analogs in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (in vitro study). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 100, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterbauer, H.; Schaur, R.J.; Zollner, H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991, 11, 81–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seljeskog, E.; Hervig, T.; Mansoor, M.A. A novel HPLC method for the measurement of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS). A comparison with a commercially available kit. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 39, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domijan, A.-M.; Ralić, J.; Radić Brkanac, S.; Rumora, L.; Žanić-Grubišić, T. Quantification of malondialdehyde by HPLC-FL-application to various biological samples. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 29, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassman, N.R.; Coskun, E.; Stefanick, D.F.; Horton, J.K.; Jaruga, P.; Dizdaroglu, M.; Wilson, S.H. Bisphenol A Promotes Cell Survival Following Oxidative DNA Damage in Mouse Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huc, L.; Lemarié, A.; Guéraud, F.; Héliès-Toussaint, C. Low concentrations of bisphenol A induce lipid accumulation mediated by the production of reactive oxygen species in the mitochondria of HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Mun, G.; Choi, E.; Kim, M.; Jeong, J.S.; Kang, K.W.; Jee, S.; Lim, K.-M.; Lee, Y.-S. Submicromolar bisphenol A induces proliferation and DNA damage in human hepatocyte cell lines in vitro and in juvenile rats in vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, P.; Zhao, L. Effects of individual and combined toxicity of bisphenol A, dibutyl phthalate and cadmium on oxidative stress and genotoxicity in HepG 2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 105, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Yin, H.; Dang, Z.; Wu, P. Worldwide human daily intakes of bisphenol A (BPA) estimated from global urinary concentration data (2000–2016) and its risk analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meli, R.; Monnolo, A.; Annunziata, C.; Pirozzi, C.; Ferrante, M.C. Oxidative Stress and BPA Toxicity: An Antioxidant Approach for Male and Female Reproductive Dysfunction. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.J.; Bin Park, S.; Park, J.W.; Oh, S.R.; Han, M. Bisphenol A modulates inflammation and proliferation pathway in human endometrial stromal cells by inducing oxidative stress. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 81, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, C.; Li, L.; Pang, Q.; Wang, C.; Fan, R. In vitro and in silico assessment of GPER-dependent neurocytotoxicity of emerging bisphenols. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, B.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.; Wen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T. In vitro profiling of toxicity and endocrine disrupting effects of bisphenol analogues by employing MCF-7 cells and two-hybrid yeast bioassay. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajski, G.; Domijan, A.-M.; Žegura, B.; Štern, A.; Gerić, M.; Novak Jovanović, I.; Vrhovac, I.; Madunić, J.; Breljak, D.; Filipič, M.; et al. Melittin induced cytogenetic damage, oxidative stress and changes in gene expression in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Toxicon 2016, 110, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Štampar, M.; Ravnjak, T.; Domijan, A.-M.; Žegura, B. Combined Toxic Effects of BPA and Its Two Analogues BPAP and BPC in a 3D HepG2 Cell Model. Molecules 2023, 28, 3085. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073085
Štampar M, Ravnjak T, Domijan A-M, Žegura B. Combined Toxic Effects of BPA and Its Two Analogues BPAP and BPC in a 3D HepG2 Cell Model. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3085. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073085
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠtampar, Martina, Tim Ravnjak, Ana-Marija Domijan, and Bojana Žegura. 2023. "Combined Toxic Effects of BPA and Its Two Analogues BPAP and BPC in a 3D HepG2 Cell Model" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3085. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073085
APA StyleŠtampar, M., Ravnjak, T., Domijan, A.-M., & Žegura, B. (2023). Combined Toxic Effects of BPA and Its Two Analogues BPAP and BPC in a 3D HepG2 Cell Model. Molecules, 28(7), 3085. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073085







