Esterified Soy Proteins with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for the Stabilization of Nano-Emulsions under Acidic Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
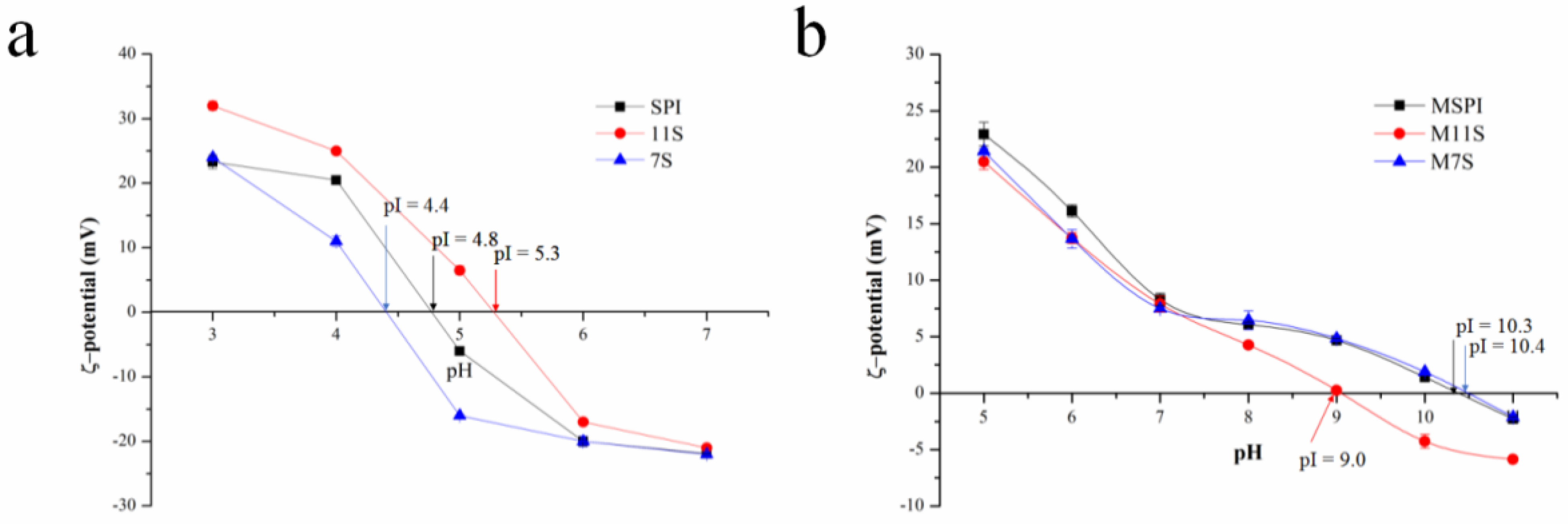
2.1. Protein Isoelectric Point (pI)
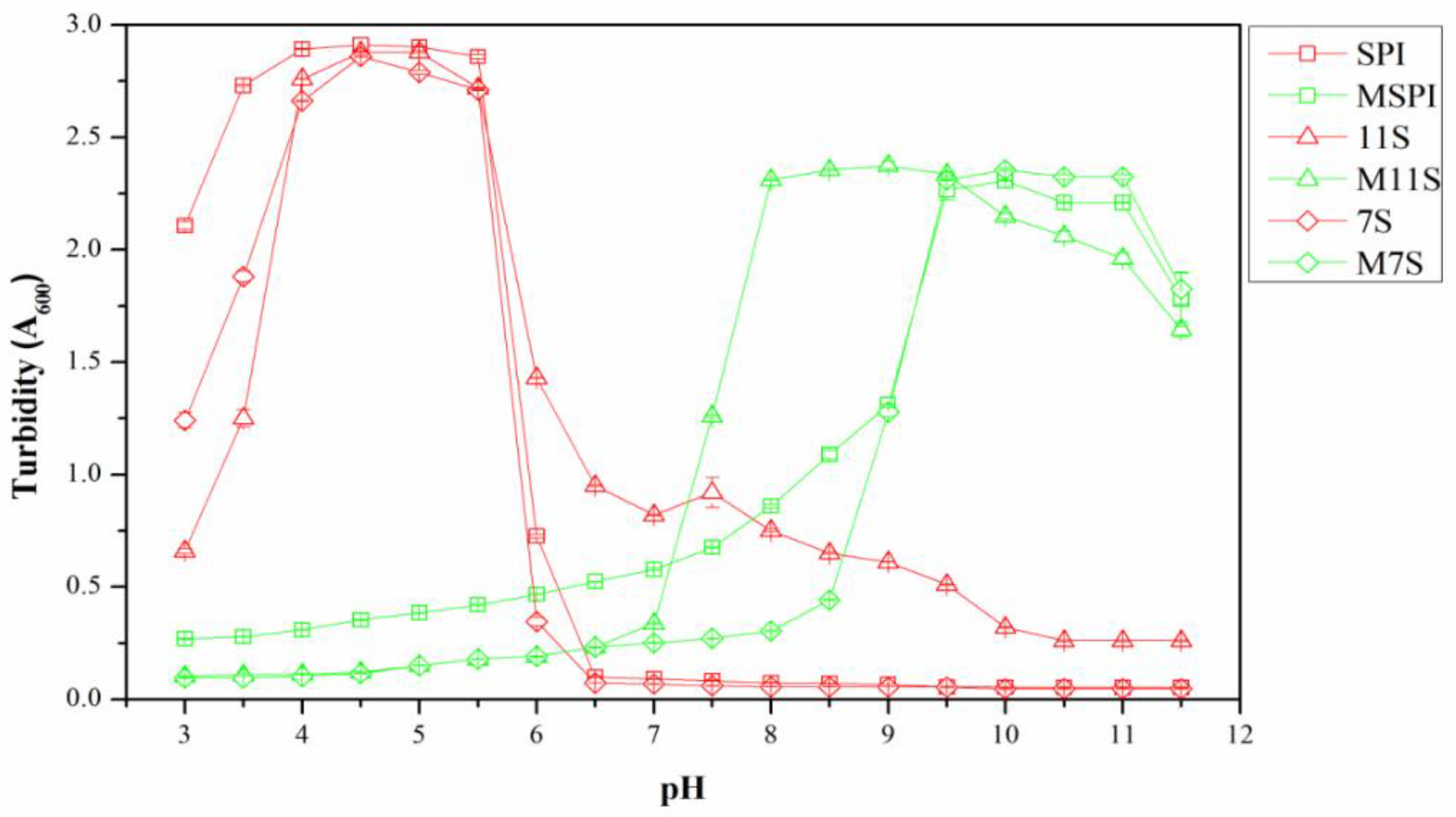
2.2. Turbidity
2.3. FTIR Spectra
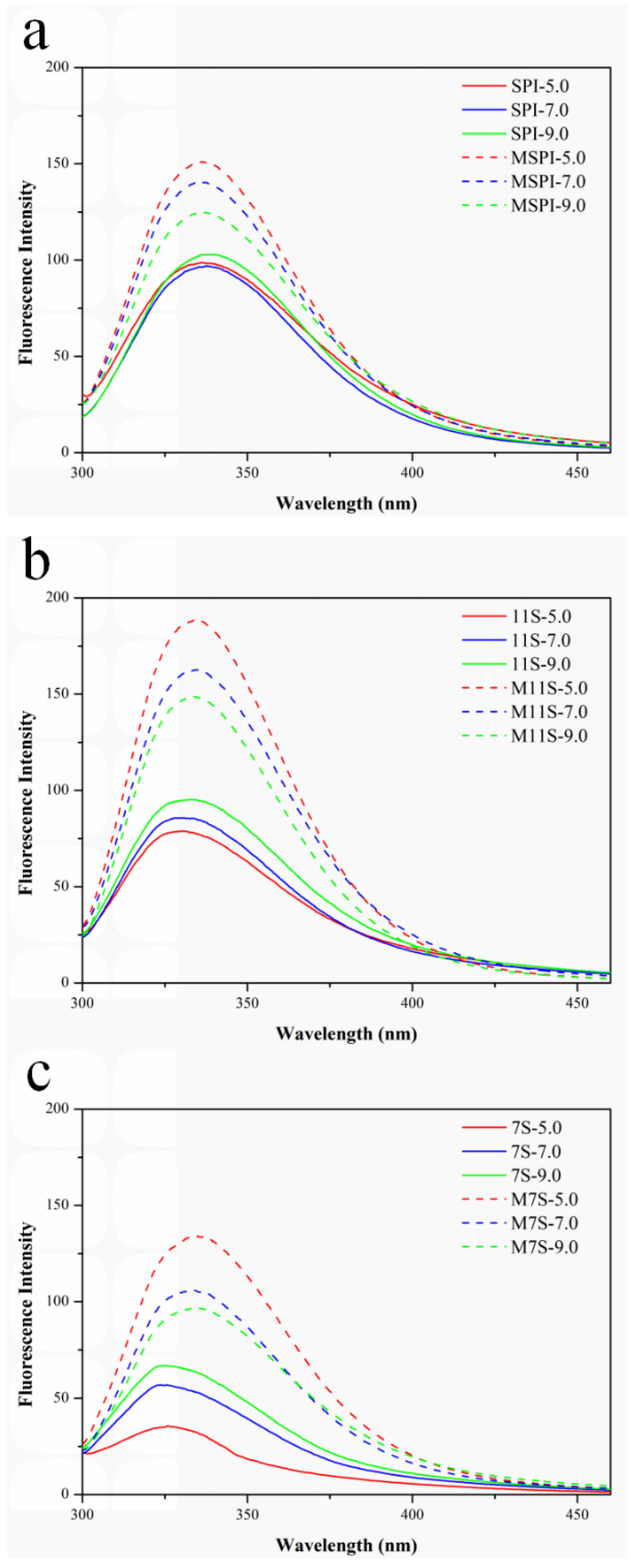
2.4. Fluorescence Spectra
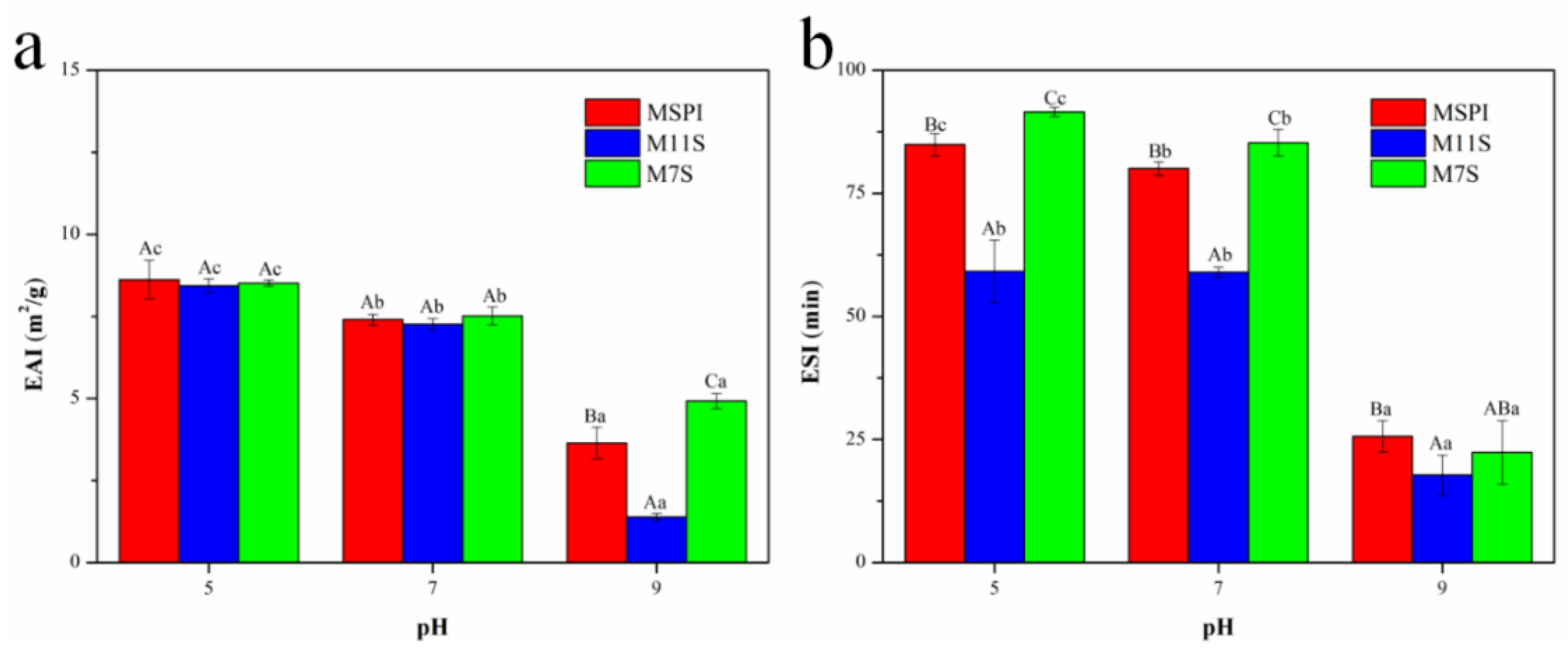
2.5. Emulsifying Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsion Stability Index (ESI)
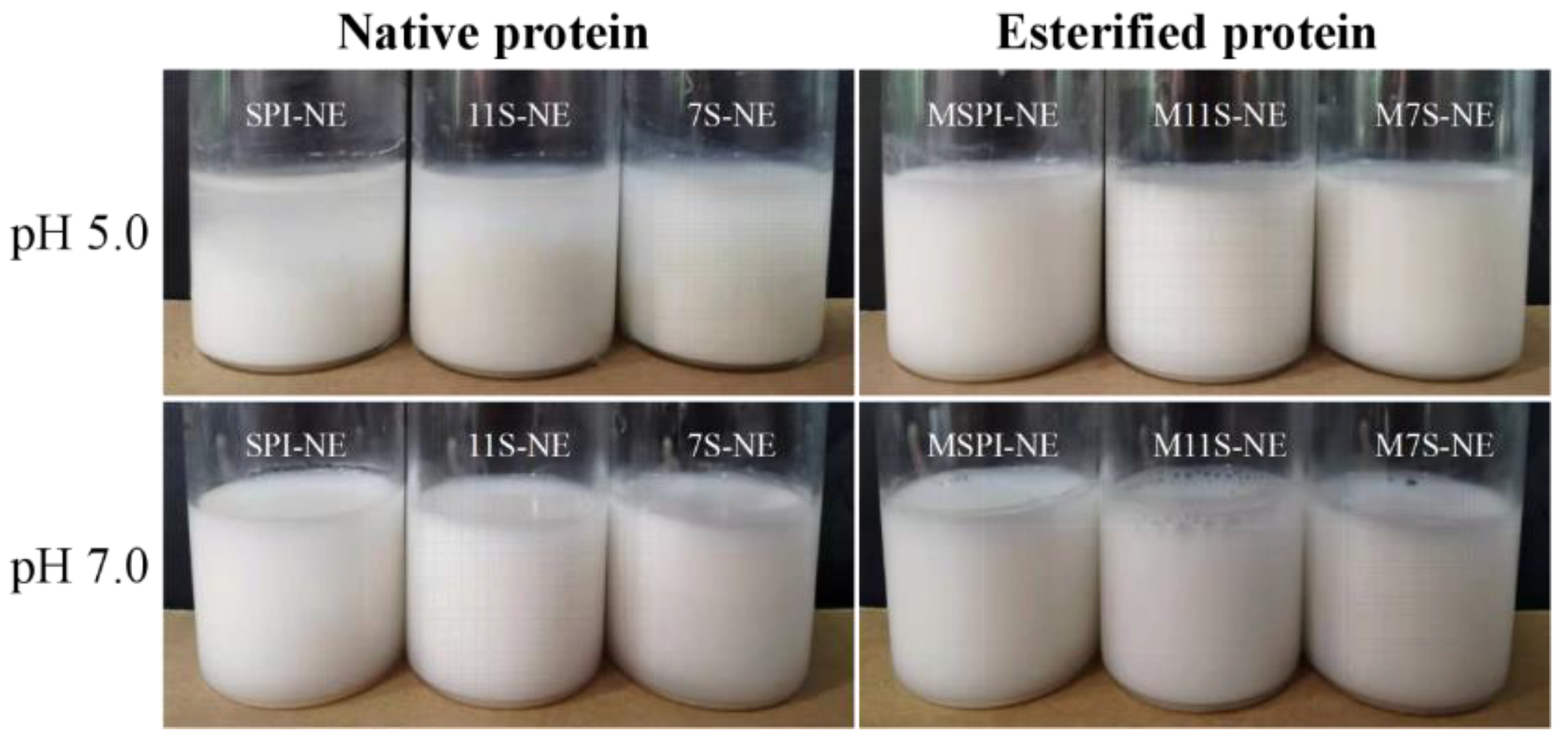
2.6. Physical Properties of Emulsions
2.6.1. Particle Size and ζ-Potential of Emulsions
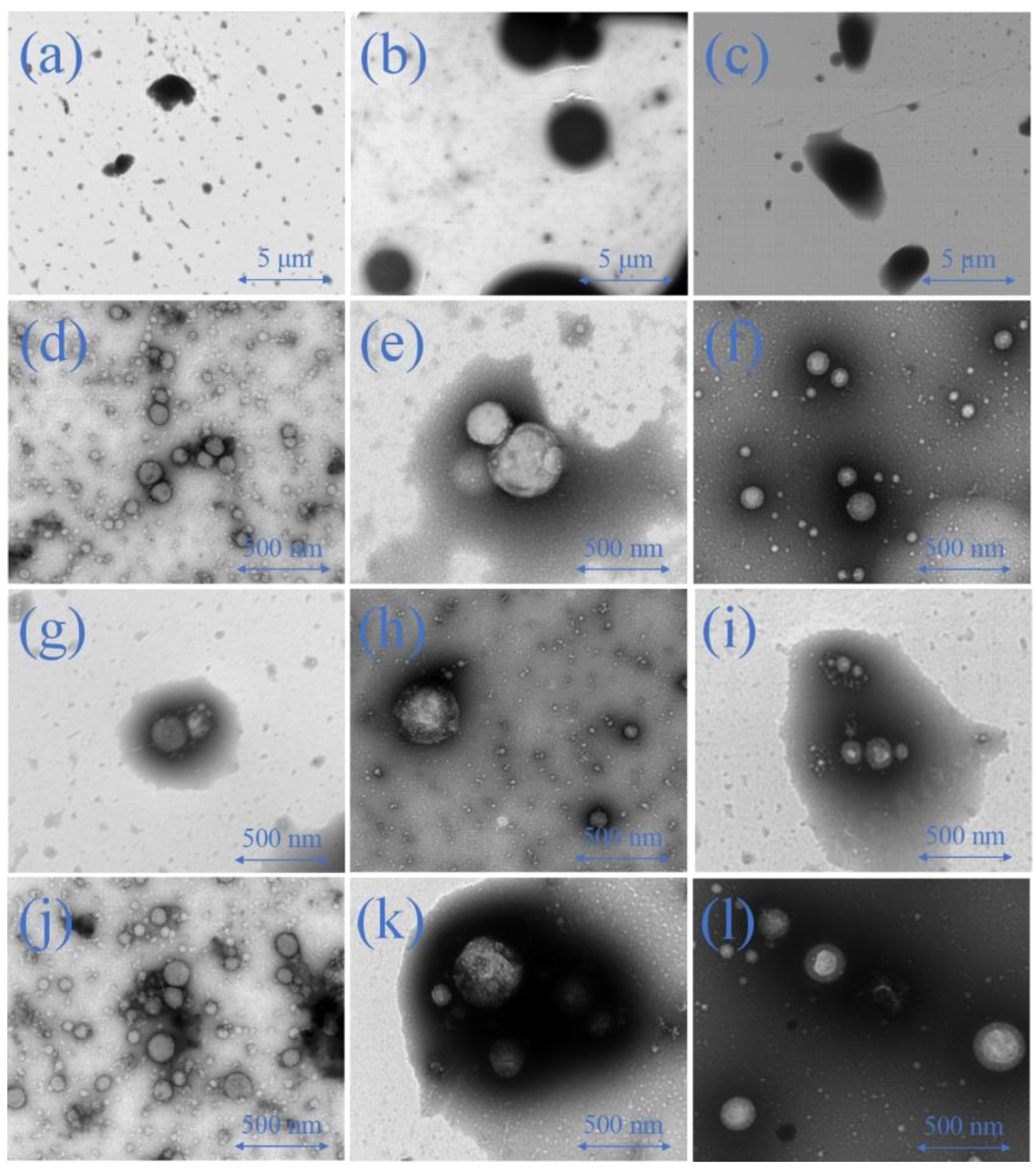
2.6.2. Emulsion Morphology
2.7. Emulsion Stability Analysis
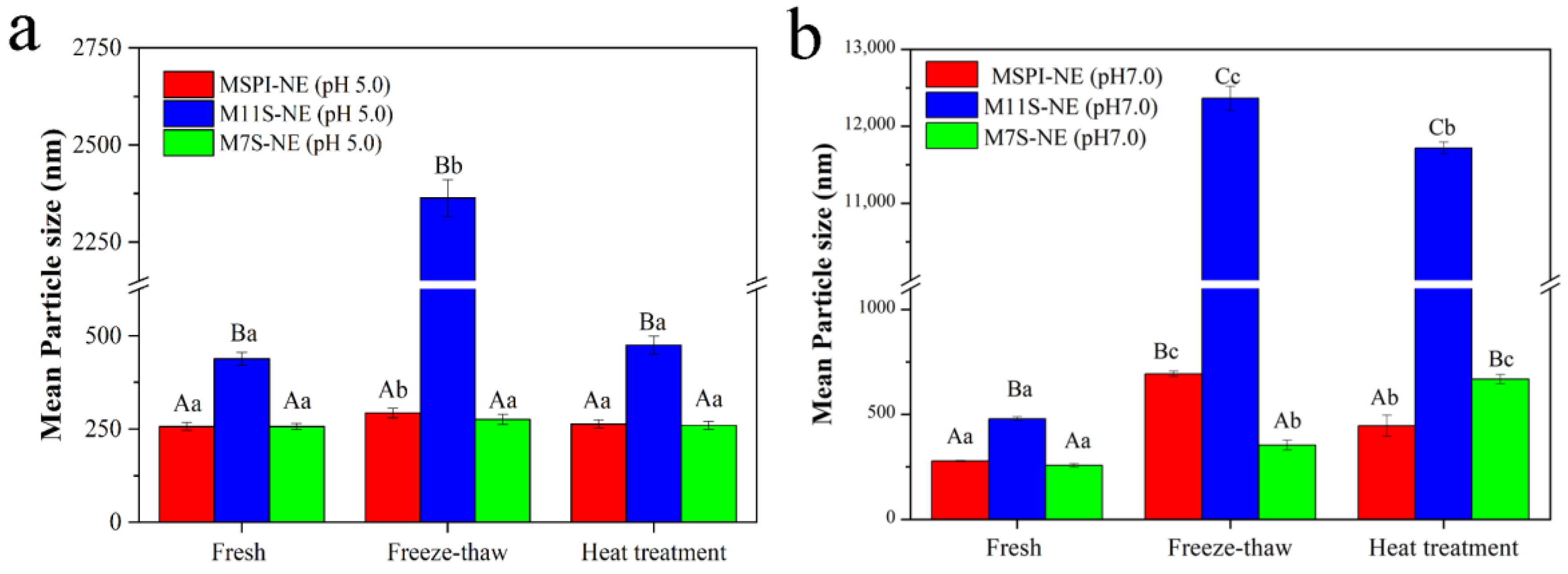
2.7.1. Storage Stability
2.7.2. Temperature Treatment
2.8. Bacteriostatic Analysis of Nano-Emulsion
3. Materials and Method
3.1. Materials
3.2. Protein Sample Preparation
3.3. Protein Esterification
3.4. Isoelectric Point (PI) Determination of Esterified Proteins
3.5. Turbidimetric Titration
3.6. Structural Analysis of Proteins
3.6.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
3.6.2. Intrinsic Fluorescence Spectra
3.7. Emulsifying Capacity of Proteins
3.8. Emulsion Properties
3.8.1. Preparation
3.8.2. Potential and Particle Size Measurements
3.8.3. Microstructure Observation
3.9. Stability of Emulsion
3.10. Agar Well Diffusion
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gharehbeglou, P.; Jafari, S.M.; Hamishekar, H.; Homayouni, A.; Mirzaei, H. Pectin-whey protein complexes vs. small molecule surfactants for stabilization of double nano-emulsions as novel bioactive delivery systems. J. Food Eng. 2019, 245, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Tan, T.B.; Tan, P.Y.; Abas, F.; Lai, O.M.; Nehdi, I.A.; Tan, C.P. Formation and characterization of thiol-modified fibrillated whey protein isolate solution with enhanced functionalities. J. Food Eng. 2017, 214, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Z.J.; Jin, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Q.S.; Liu, C.H.; Xu, J. Effect of enzymolysis and glycosylation on the curcumin nanoemulsions stabilized by beta-conglycinin: Formation, stability and in vitro digestion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Avila, C.; Arranz, E.; Guri, A.; Trujillo, A.J.; Corredig, M. Vegetable protein isolate-stabilized emulsions for enhanced delivery of conjugated linoleic acid in Caco-2 cells. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Sun, C.-X.; Mata, A.; Corke, H.; Gan, R.-Y.; Fang, Y. Physicochemical and pH-dependent functional properties of proteins isolated from eight traditional Chinese beans. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterenko, A.; Alric, I.; Silvestre, F.; Durrieu, V. Comparative study of encapsulation of vitamins with native and modified soy protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.C.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Chi, Y.J.; Xia, N.; Li, Z.S.; Jiang, L.W.; Zhang, X.N.; Rayan, A.M. Fabrication and digestive characteristics of high internal phase Pickering emulsions stabilized by ovalbumin-pectin complexes for improving the stability and bioaccessibility of curcumin. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 133055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Sanchez, L.G.; Jimenez-Fernandez, M.; Melgar-Lalanne, G.; Gutiarrez-Lopez, G.F.; Hernandez-Arana, A.; Reyes-Espinosa, F.; Hernandez-Sanchez, H. Chemical lipophilization of bovine alpha-lactalbumin with saturated fatty acyl residues: Effect on structure and functional properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3256–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitohy, M.; Osman, A. Antimicrobial activity of native and esterified legume proteins against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitohy, M.; Chobert, J.M.; Haertlé, T. Improvement of solubility and of emulsifying properties of milk proteins at acid pHs by esterification. Die Nahr. 2001, 45, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaije, R.; Hilgers, R.J.; Wierenga, P.A.; Gruppen, H. Relative contributions of charge and surface coverage on pH-induced flocculation of protein-stabilized emulsions. Colloid Surf. A 2017, 521, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitohy, M.; Mahgoub, S.; Osman, A. Controlling psychrotrophic bacteria in raw buffalo milk preserved at 4 degrees C with esterified legume proteins. LWT 2011, 44, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, X.G.; Wang, H.Y.; Xia, X.M.; Wang, K.Y. Effects of esterified lactoferrin and lactoferrin on control of postharvest blue mold of apple fruit and their possible mechanisms of action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6432–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, H.J.; Wang, Z.F.; Emara, A.M.; Hu, Y.; He, Z.F. Effects of in vitro oxidation on myofibrillar protein charge, aggregation, and structural characteristics. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Hua, Y.F.; Chen, Y.M.; Kong, X.Z.; Zhang, C.M. Effect of 7S/11S ratio on the network structure of heat-induced soy protein gels: A study of probe release. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 101981–101987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrih, N.P. Analytical techniques for the study of polyphenol-protein interactions. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. 2017, 57, 2144–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Dai, T.T.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Liu, C.M.; McClements, D.J. Protein-polyphenol functional ingredients: The foaming properties of lactoferrin are enhanced by forming complexes with procyanidin. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xu, C.Q.; Liu, F.G.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y.X. Native and Thermally modified protein-polyphenol coassemblies: Lactoferrin-based nanoparticles and submicrometer particles as protective vehicles for (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10816–10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lei, L.; Li, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Ming, J. Molecular interaction of soybean glycinin and β-conglycinin with (−)-epigallocatechin gallate induced by pH changes. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Sun, X.S. Effect of esterification on soy protein adhesive performance. In Proceedings of the 2005 ASAE Annual Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 17–21 July 2005; pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Wang, T.R.; Hu, Q.B.; Luo, Y.C. Caseinate-zein-polysaccharide complex nanoparticles as potential oral delivery vehicles for curcumin: Effect of polysaccharide type and chemical cross-linking. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Jain, N.; Bhasne, K.; Kumari, V.; Mukhopadhyay, S. pH-induced conformational isomerization of bovine serum albumin studied by extrinsic and intrinsic protein fluorescence. J. Fluoresc. 2011, 21, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijarotimi, O.S.; Malomo, S.A.; Fagbemi, T.N.; Osundahunsi, O.F.; Aluko, R.E. Structural and functional properties of Buchholzia coriacea seed flour and protein concentrate at different pH and protein concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattarella, N.L.; Richardson, T. Physicochemical and functional properties of positively charged derivatives of bovine β-lactoglobulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1983, 31, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, M.I.; Richardson, T. Selected functionality changes of β-lactoglobulin upon esterification of side-chain carboxyl groups. J. Dairy Sci. 1985, 68, 3189–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Wu, N.; Wu, F.; Yu, D.; Elfalleh, W. Effects of (+)-catechin on a rice bran protein oil-in-water emulsion: Droplet size, zeta-potential, emulsifying properties, and rheological behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tian, L.; Yi, J.; Zhu, Z.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Mixed plant-based emulsifiers inhibit the oxidation of proteins and lipids in walnut oil-in-water emulsions: Almond protein isolate-camellia saponin. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, J. Fabrication of β-conglycinin-stabilized nanoemulsions via ultrasound process and influence of SDS and PEG 10,000 co-emulsifiers on the physicochemical properties of nanoemulsions. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.N.; Yang, J.J.; Shao, G.Q.; Qu, D.N.; Zhao, H.K.; Zhu, L.J.; Yang, L.N.; Li, R.R.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; et al. Dilatational rheological and nuclear magnetic resonance characterization of oil-water interface: Impact of pH on interaction of soy protein isolated and soy hull polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, S.; Davidov-Pardo, G. Comparison of legume and dairy proteins for the impact of Maillard conjugation on nanoemulsion formation, stability, and lutein color retention. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.Y.; Jin, H.; Gao, Y.; Yan, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.S.; Xu, J. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on the structure and emulsifying properties of peanut protein isolates. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yin, P.; Xie, T.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Interaction between soyasaponin and soy β-conglycinin or glycinin: Air-water interfacial behavior and foaming property of their mixtures. Colloid Surf. B 2020, 186, 110707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshad, M.; Mohebbi, M.; Shahidi, F.; Koocheki, A. Freeze-thaw stability of emulsions with soy protein isolate through interfacial engineering. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 58, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Holmes, M.; Ettelaie, R.; Sarkar, A. Pea protein microgel particles as Pickering stabilisers of oil-in-water emulsions: Responsiveness to pH and ionic strength. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitohy, M.; Mahgoub, S.; Osman, A.; El-Masry, R.; Al-Gaby, A. Extent and mode of action of cationic legume proteins against listeria monocytogenes and salmonella enteritidis. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2013, 5, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Fang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Meng, Y. Mechanism of the antimicrobial activity of whey protein-epsilon-polylysine complexes against Escherichia coli and its application in sauced duck products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 328, 108663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafi, S.; Al-Mohammadi, A.-R.; Osman, A.; Enan, G.; Abdel-Hameid, S.; Sitohy, M. Characterization and antibacterial activity of 7S and 11S globulins isolated from cowpea seed protein. Molecules 2019, 24, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, K.; Chang, Y.; McLandsborough, L.; McClements, D.J. Influence of surfactant charge on antimicrobial efficacy of surfactant-stabilized thyme oil nanoemulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6247–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.T.; Wang, Z.J.; Handa, C.L.; Xu, J. Effects of ultrasound pre-treatment on the structure of β-conglycinin and glycinin and the antioxidant activity of their hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Jin, H.; Sun, X.T.; Sun, J.Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, C.H.; Xu, J. Physicochemical properties and storage stability of food protein-stabilized nanoemulsions. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Z.J.; Han, D.; Li, Y.Y.; Sun, X.T.; Wang, Z.J.; Jin, H. Structural and functional properties changes of-conglycinin exposed to hydroxyl radical-generating systems. Molecules 2017, 22, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Li, X.F.; Hua, Y.F.; Chen, Y.M.; Kong, X.Z.; Zhang, C.M.; Wang, Q. Mutual titration of soy proteins and gum arabic and the complexing behavior studied by isothermal titration calorimetry, turbidity and ternary phase boundaries. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 46, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.Y.; Jin, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zhao, Q.S.; Liu, C.H.; Xu, J. The effect of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate non-covalent interaction with the glycosylated protein on the emulsion property. Polymers 2019, 11, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, J.W.; Wang, H.W.; Jiang, L.Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H.; Fan, Z.J.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Q.S. Physicochemical antioxidative and emulsifying properties of soybean protein hydrolysates obtained with dissimilar hybrid nanoflowers. Foods 2022, 11, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellouze, M.; Lajnaf, R.; Zouari, A.; Attia, H.; Ayadi, M.A.; Vial, C. Camel alpha-lactalbumin at the oil-water interface: Effect of protein concentration and pH change on surface characteristics and emulsifying properties. Colloid Surf. B 2020, 189, 110654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Teng, F.; Wang, B.Q.; Ruan, X.X.; Ma, Y.F.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Z.J.; Jin, H. Gel property of soy protein emulsion gel: Impact of combined microwave pretreatment and covalent binding of polyphenols by alkaline method. Molecules 2022, 27, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wan, Z.L.; Yin, S.W.; Yang, X.Q. Stability and antimicrobial property of soy protein/chitosan mixed emulsion at acidic condition. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample | Mean Particle Size (nm) | ζ-Potential (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 5.0 | pH 7.0 | pH 5.0 | pH 7.0 | |
| SPI-NE | 3500 ± 100 c | 278.2 ± 5.5 a | −1.7 ± 0.1 b | −33.2 ± 1.8 a |
| MSPI-NE | 256.9 ± 10.1 a | 278.4 ± 3.0 a | 26.7 ± 0.5 e | 11.2 ± 0.3 d |
| 11S-NE | 5130 ± 170 e | 357.8 ± 8.2 b | 1.2 ± 0.1 c | −30.6 ± 0.5 b |
| M11S-NE | 438.7 ± 17.2 b | 479.0 ± 9.7 c | 22.7 ± 0.2 d | 6.3 ± 0.1 c |
| 7S-NE | 3840 ± 140 d | 273.6 ± 8.4 a | −1.4 ± 0.1 a | −32.6 ± 0.7 a |
| M7S-NE | 257.0 ± 8.1 a | 270.8 ± 7.5 a | 27.1 ± 0.1 e | 11.9 ± 0.6 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Yi, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, Z.; Jin, H.; Xu, J. Esterified Soy Proteins with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for the Stabilization of Nano-Emulsions under Acidic Conditions. Molecules 2023, 28, 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073078
Wang T, Yi K, Li Y, Wang H, Fan Z, Jin H, Xu J. Esterified Soy Proteins with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for the Stabilization of Nano-Emulsions under Acidic Conditions. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073078
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tingyu, Kehan Yi, Yang Li, Huan Wang, Zhijun Fan, Hua Jin, and Jing Xu. 2023. "Esterified Soy Proteins with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for the Stabilization of Nano-Emulsions under Acidic Conditions" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073078
APA StyleWang, T., Yi, K., Li, Y., Wang, H., Fan, Z., Jin, H., & Xu, J. (2023). Esterified Soy Proteins with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for the Stabilization of Nano-Emulsions under Acidic Conditions. Molecules, 28(7), 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073078







