Evaluation of Selenomethionine Entrapped in Nanoparticles for Oral Supplementation Using In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
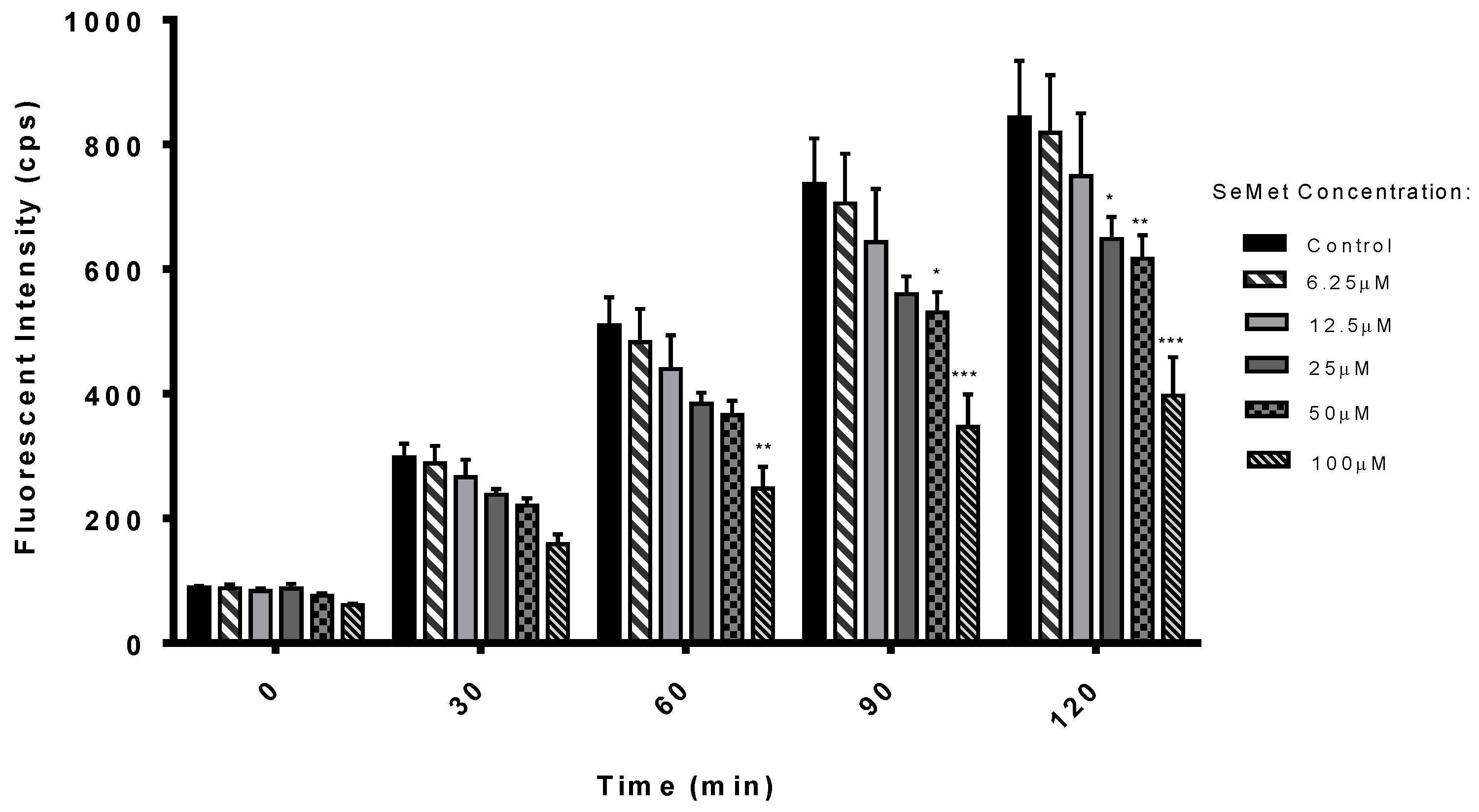
2.1. Antioxidant Potential of SeMet
2.2. SeMet Is Stable in Rat Intestinal and Liver Extracts
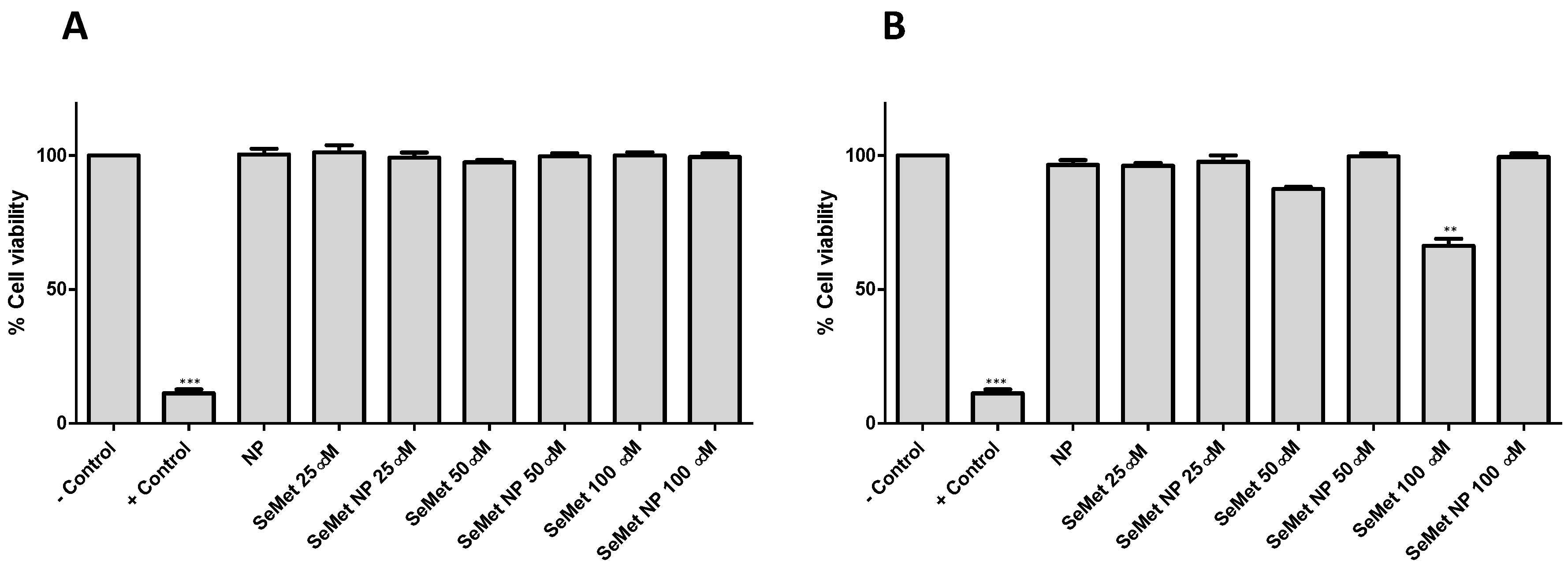
2.3. SeMet and SeMet-NPs Are Not Cytotoxic: MTS Assay
2.4. SeMet Does Not Effect Stimulated Isc in Rat Jejunal and Colonic Mucosae
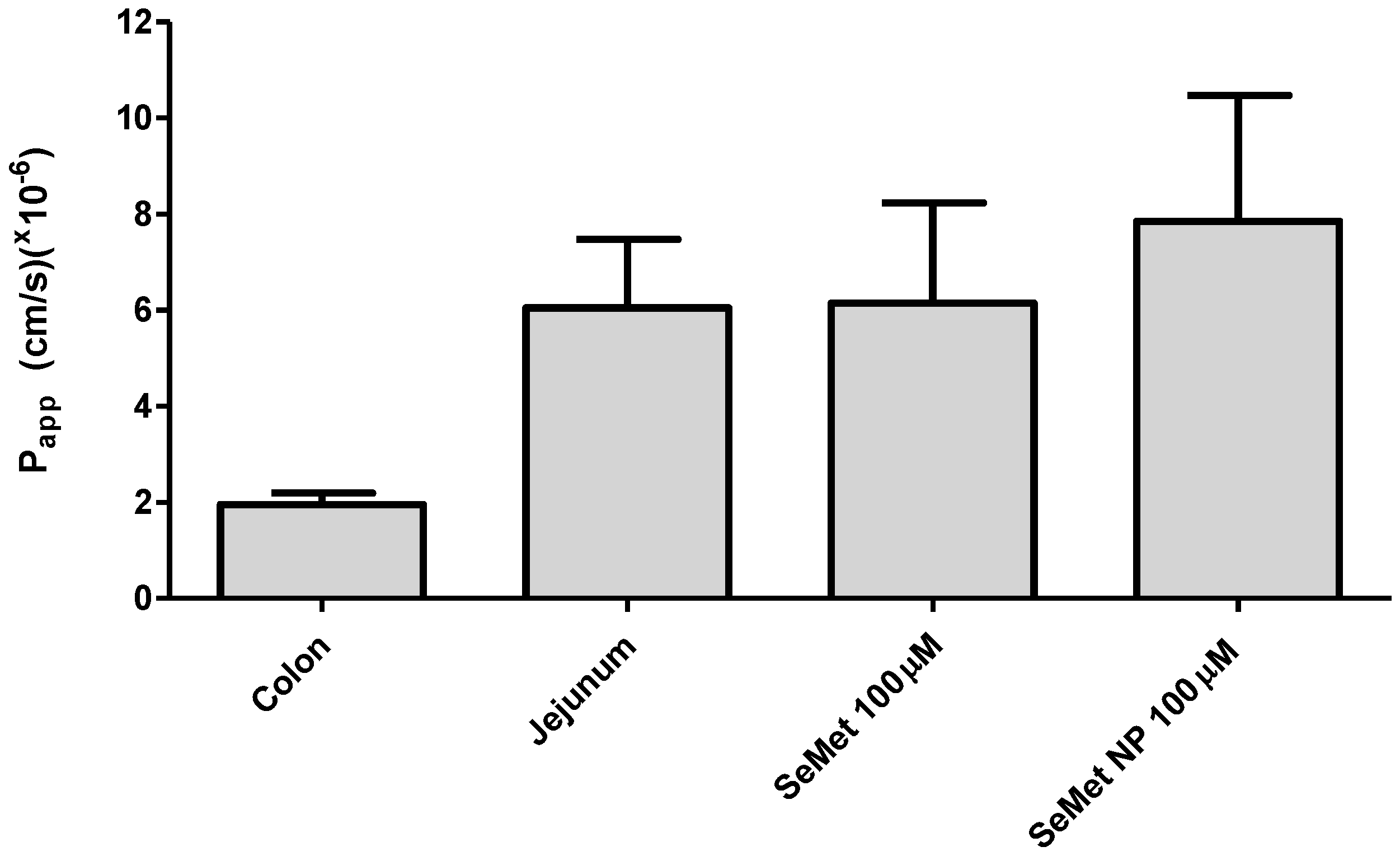
2.5. Transport of SeMet across Isolated Rat Jejunal Mucosae
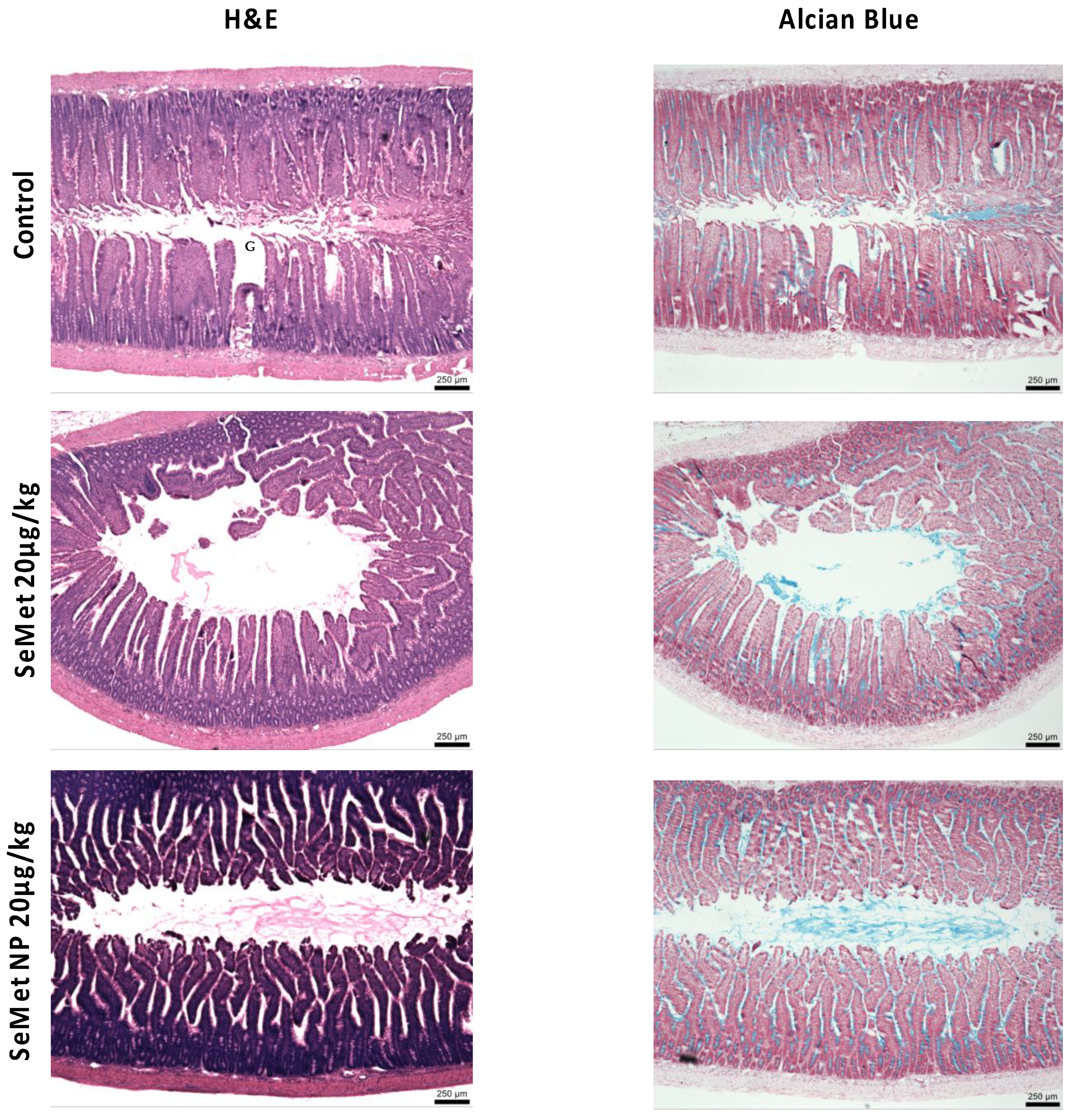
2.6. In Vivo Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Chemicals
4.2. ROS Assay
4.3. Preparation of Ex Vivo Rat Gastrointestinal Enzyme Fluids and Liver Homogenates
4.4. Stability Studies in Isolated Rat Intestinal and Liver Extracts
4.5. Reverse-Phase HPLC Analysis
4.6. Synthesis of SeMet-NPs
4.7. MTS Assay
4.8. Electrophysiology of Rat Intestinal Tissue Mucosae
4.9. Isolated Rat Intestinal Mucosae Transport Studies Using Adapted Horizontal Diffusion Chambers
4.10. LC-MS Analysis
4.11. Histology
4.12. In Vivo Instillation Studies in Rats
4.13. Anaesthesia and Euthanasia
4.14. Jejunal Instillations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rayman, M.P. Selenium intake, status, and health: A complex relationship. Hormones 2020, 19, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozmanova, J.; Manikova, D.; Vlckova, V.; Chovanec, M. Selenium: A double-edged sword for defense and offence in cancer. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 919–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderao, G.N.; Jadhav, S.E.; Pattanaik, A.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Lokesha, E.; Chaudhary, P.; Vaswani, S.; Singh, A.; Panigrahi, M.; et al. Dietary selenium levels modulates antioxidant, cytokine and immune response and selenoproteins mRNA expression in rats under heat stress condition. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 75, 127105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Bedmar, M.; Gil, F.; Olmedo, P.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Babio, N.; Fito, M.; Del Val Garcia, J.L.; Corella, D.; et al. Serum Selenium and Incident Cardiovascular Disease in the PREvencion con DIeta MEDiterranea (PREDIMED) Trial: Nested Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krohn, R.M.; Akhtar, E.; Kwong, G.P.S.; Raqib, R.; Smits, J.E.G. The effect of a high-selenium lentil diet on cardiovascular risk markers in an arsenic-exposed population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 772–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghiu, M.L.; Badiu, C. Selenium involvement in mitochondrial function in thyroid disorders. Hormones 2020, 19, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, K.H.; Rayman, M.P.; Bonnema, S.J.; Hegedus, L. Selenium in thyroid disorders—Essential knowledge for clinicians. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.R.; Roberts, B.R.; Bush, A.I.; Hare, D.J. Selenium, selenoproteins and neurodegenerative diseases. Metallomics 2015, 7, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muecke, R.; Schomburg, L.; Buentzel, J.; Kisters, K.; Micke, O.; German Working Group Trace Elements and Electrolytes in Oncology-AKTE. Selenium or no selenium—That is the question in tumor patients: A new controversy. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, H.J.; Sedlacek, S.M.; Fitzgerald, V.K.; Wolfe, P.; McGinley, J.N. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Investigation of Selenium Supplementation in Women at Elevated Risk for Breast Cancer: Lessons for Re-Emergent Interest in Selenium and Cancer. Biomedicines 2022, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rua, R.M.; Nogales, F.; Carreras, O.; Ojeda, M.L. Selenium, selenoproteins and cancer of the thyroid. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 76, 127115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiry, C.; Ruttens, A.; Pussemier, L.; Schneider, Y.J. An in vitro investigation of species-dependent intestinal transport of selenium and the impact of this process on selenium bioavailability. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 2126–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berntssen, M.H.G.; Sundal, T.K.; Olsvik, P.A.; Amlund, H.; Rasinger, J.D.; Sele, V.; Hamre, K.; Hillestad, M.; Buttle, L.; Ornsrud, R. Sensitivity and toxic mode of action of dietary organic and inorganic selenium in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 192, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Cao, W.; Zhang, X. Selenium-containing polymers: Promising biomaterials for controlled release and enzyme mimics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hedwig, S.; Schaffer, A.; Lenz, M.; Martinez, M. Sulfur Amino Acid Status Controls Selenium Methylation in Pseudomonas tolaasii: Identification of a Novel Metabolite from Promiscuous Enzyme Reactions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0010421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.; Jitaru, P.; Barbante, C. Selenium biochemistry and its role for human health. Metallomics 2014, 6, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Suzuki, N.; Ogra, Y. Bioavailability Comparison of Nine Bioselenocompounds In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdadi Sardou, H.; Akhgari, A.; Mohammadpour, A.H.; Beheshti Namdar, A.; Kamali, H.; Jafarian, A.H.; Afrasiabi Garekani, H.; Sadeghi, F. Optimization study of combined enteric and time-dependent polymethacrylates as a coating for colon targeted delivery of 5-ASA pellets in rats with ulcerative colitis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, A.A.; Saad, G.A.; El Maghraby, G.M. Permeation enhancers loaded bilosomes for improved intestinal absorption and cytotoxic activity of doxorubicin. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 630, 122427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Rewatkar, P.; Wang, R.; Hasnain, S.Z.; Popat, A.; Kumeria, T. Nanocarriers for oral delivery of biologics: Small carriers for big payloads. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, M.Z.; Liang, X.Y.; Nag, A.; Zeng, Q.Z.; Yuan, Y. Fabrication of food grade zein-dispersed selenium dual-nanoparticles with controllable size, cell friendliness and oral bioavailability. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, J.P.; Heade, J.; Ryan, S.M.; Brayden, D.J. Stability, toxicity and intestinal permeation enhancement of two food-derived antihypertensive tripeptides, Ile-Pro-Pro and Leu-Lys-Pro. Peptides 2015, 71, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vozza, G.; Danish, M.; Byrne, H.J.; Frias, J.M.; Ryan, S.M. Application of Box-Behnken experimental design for the formulation and optimisation of selenomethionine-loaded chitosan nanoparticles coated with zein for oral delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamba, G.; Friedman, P.A. Thick ascending limb: The Na+:K+:2Cl− co-transporter, NKCC2, and the calcium-sensing receptor, CaSR. Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2009, 458, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, J.; Baird, A.W.; O’Brien, L.M.; McElroy, M.; Callanan, J.J.; Bassett, H.F.; Campion, D.; Brayden, D.J. Rat, ovine and bovine Peyer’s patches mounted in horizontal diffusion chambers display sampling function. J. Control. Release 2006, 115, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noth, R.; Lange-Grumfeld, J.; Stuber, E.; Kruse, M.L.; Ellrichmann, M.; Hasler, R.; Hampe, J.; Bewig, B.; Rosenstiel, P.; Schreiber, S.; et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction disruption by altered expression and localization of occludin in a murine graft versus host disease model. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, D.; Enda, M.; Bond, T.; Moghaddam, S.P.; Conarton, J.; Scaife, C.; Volckmann, E.; Ghandehari, H. Transepithelial Transport of PAMAM Dendrimers Across Isolated Human Intestinal Tissue. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 4099–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentkowska, A.; Pyrzynska, K. Investigation of antioxidant activity of selenium compounds and their mixtures with tea polyphenols. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, S.G.; Purdie, N.G.; Osborne, V.R.; Coomber, B.L.; Cant, J.P. Selenomethionine increases proliferation and reduces apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cells under oxidative stress. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wei, L.; Lv, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. SeMet attenuates AFB1-induced intestinal injury in rabbits by activating the Nrf2 pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Jia, G.; He, H.; Ding, T.; Yu, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Yu, S.; Deng, H.; et al. Antiviral Effect of Selenomethionine on Porcine Deltacoronavirus in Pig Kidney Epithelial Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 846747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, F.; Müller, S.M.; Meyer, S.; Schwerdtle, T. Selenium and Toxicological Aspects: Cytotoxicity, Cellular Bioavailability, and Biotransformation of Se Species. In Selenium. Molecular and Integrative Toxicology; Michalke, B., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 373–391. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, S.; Iwataka, M.; Fuchigami, T.; Haratake, M.; Nakayama, M. In vitro assessment of bioavailability of selenium from a processed Japanese anchovy, Niboshi. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid Danish, M.; Gleeson, J.P.; Brayden, D.J.; Byrne, H.J.; Frias, J.M.; Ryan, S.M. Formulation, Characterisation and Evaluation of the Antihypertensive Peptides, Isoleucine-Proline-Proline and Leucine-Lysine-Proline in Chitosan Nanoparticles Coated with Zein for Oral Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.K.; Vozza, G.; Byrne, H.J.; Frias, J.M.; Ryan, S.M. Formulation, Characterization and Stability Assessment of a Food-Derived Tripeptide, Leucine-Lysine-Proline Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajander, E.O.; Harvima, R.J.; Eloranta, T.O.; Martikainen, H.; Kantola, M.; Karenlampi, S.O.; Akerman, K. Metabolism, cellular actions, and cytotoxicity of selenomethionine in cultured cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1991, 28, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, Y. Preparation and physicochemical properties of chitosan broadleaf holly leaf nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressman, J.B.; Reppas, C. In vitro-in vivo correlations for lipophilic, poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11 (Suppl. S2), S73–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, F.; Santos Dorneles, M.; Pelayo Zapata Norena, C. Accelerated stability testing and simulated gastrointestinal release of encapsulated betacyanins and phenolic compounds from Bougainvillea glabra bracts extract. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.J.; Yoshida, S.; Kamei, N.; Iwamae, R.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Olsen, J.; Rahbek, U.L.; Pedersen, B.L.; Takayama, K.; Takeda-Morishita, M. In vivo proof of concept of oral insulin delivery based on a co-administration strategy with the cell-penetrating peptide penetratin. J. Control. Release 2014, 189, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, L. Association Between Selenium Intake with Chronic Constipation and Chronic Diarrhea in Adults: Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 3205–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwipoerwantoro, P.G.; Lukito, W.; Aulia, D.; Arnaud, J.; Roussel, A.M. Selenium status and fungi in the protein-losing enteropathy of persistent diarrhea. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 26, S79–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manerov, F.K.; Gmoshinskii, I.V.; Mazo, V.K.; Zorin, S.N. Selenium safety in children with protracted diarrhea syndrome. Vopr. Pitan. 2004, 73, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bzik, V.A.; Medani, M.; Baird, A.W.; Winter, D.C.; Brayden, D.J. Mechanisms of action of zinc on rat intestinal epithelial electrogenic ion secretion: Insights into its antidiarrhoeal actions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.X. Calcium-sensing receptor inhibits secretagogue-induced electrolyte secretion by intestine via the enteric nervous system. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G60–G70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Coelho, M.A.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Ontogenic aspects of D1 receptor coupling to G proteins and regulation of rat jejunal Na+, K+ ATPase activity and electrolyte transport. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Fang, X.; Winesett, S.P.; Cheng, C.Y.; Binder, H.J.; Rivkees, S.A.; Cheng, S.X. Bumetanide increases Cl−-dependent short-circuit current in late distal colon: Evidence for the presence of active electrogenic Cl− absorption. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.B.; Rawlinson, L.A.; Baird, A.W.; Bzik, V.; Brayden, D.J. In vitro interactions between the oral absorption promoter, sodium caprate (C10) and S. typhimurium in rat intestinal ileal mucosae. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, P.; Artursson, P. Oral absorption of peptides and nanoparticles across the human intestine: Opportunities, limitations and studies in human tissues. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, J.P.; Brayden, D.J.; Ryan, S.M. Evaluation of PepT1 transport of food-derived antihypertensive peptides, Ile-Pro-Pro and Leu-Lys-Pro using in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo transport models. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 115, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammelgaard, B.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Gabel-Jensen, C.; Steffansen, B. Estimating intestinal absorption of inorganic and organic selenium compounds by in vitro flux and biotransformation studies in Caco-2 cells and ICP-MS detection. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 145, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, Y. Quantification of selenomethionine in plasma using UPLC-MS/MS after the oral administration of selenium-enriched yeast to rats. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokarnig, S.; Tsirigotaki, A.; Wiesenhofer, T.; Lackner, V.; Francesconi, K.A.; Pergantis, S.A.; Kuehnelt, D. Concurrent quantitative HPLC-mass spectrometry profiling of small selenium species in human serum and urine after ingestion of selenium supplements. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 29, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukawa, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Goto, H.; Shinohara, Y.; Shinohara, A.; Omori, Y.; Ichida, K.; Yokoyama, K. Evaluation of the metabolic chiral inversion of d-selenomethionine in rats by stable isotope dilution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 116, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encinar, J.R.; Schaumloffel, D.; Ogra, Y.; Lobinski, R. Determination of selenomethionine and selenocysteine in human serum using speciated isotope dilution-capillary HPLC-inductively coupled plasma collision cell mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 6635–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucera, O.; Endlicher, R.; Rousar, T.; Lotkova, H.; Garnol, T.; Drahota, Z.; Cervinkova, Z. The effect of tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress on lean and steatotic rat hepatocytes in vitro. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 752506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S. The use of biorelevant dissolution media to forecast the in vivo performance of a drug. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Niu, M.; Hu, F.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Yin, Z.; Wu, W. Integrity and stability of oral liposomes containing bile salts studied in simulated and ex vivo gastrointestinal media. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, P.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Vila-Jato, J.L.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan and chitosan/ethylene oxide-propylene oxide block copolymer nanoparticles as novel carriers for proteins and vaccines. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, A.W.; Margolius, H.S. Kinins stimulate net chloride secretion by the rat colon. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1982, 75, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjogren, E.; Eriksson, J.; Vedin, C.; Breitholtz, K.; Hilgendorf, C. Excised segments of rat small intestine in Ussing chamber studies: A comparison of native and stripped tissue viability and permeability to drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 505, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, T.A.; Rosa, M.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Coulter, I.; Brayden, D.J. Investigation of coco-glucoside as a novel intestinal permeation enhancer in rat models. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Treatment | ΔIsc Jejunum | ΔIsc Colon |
|---|---|---|
| FSK only (10 µM) | 79 | 225 |
| Preincubation with SeMet (10 µM) + FSK | 64 | 164 |
| Preincubation with SeMet (100 µM) + FSK | 38 | 168 |
| FSK + SeMet (10 µM) at plateau | 44 | 183 |
| FSK (BL) + SeMet (100 µM) at plateau | 15 | 134 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forde, S.; Vozza, G.; Brayden, D.J.; Byrne, H.J.; Frías, J.M.; Ryan, S.M. Evaluation of Selenomethionine Entrapped in Nanoparticles for Oral Supplementation Using In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models. Molecules 2023, 28, 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072941
Forde S, Vozza G, Brayden DJ, Byrne HJ, Frías JM, Ryan SM. Evaluation of Selenomethionine Entrapped in Nanoparticles for Oral Supplementation Using In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072941
Chicago/Turabian StyleForde, Shane, Giulianna Vozza, David J. Brayden, Hugh J. Byrne, Jesus M. Frías, and Sinéad M. Ryan. 2023. "Evaluation of Selenomethionine Entrapped in Nanoparticles for Oral Supplementation Using In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models" Molecules 28, no. 7: 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072941
APA StyleForde, S., Vozza, G., Brayden, D. J., Byrne, H. J., Frías, J. M., & Ryan, S. M. (2023). Evaluation of Selenomethionine Entrapped in Nanoparticles for Oral Supplementation Using In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models. Molecules, 28(7), 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072941










