Essential Oils Distilled from Colombian Aromatic Plants and Their Constituents as Penetration Enhancers for Transdermal Drug Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Essential Oil Characterization
2.2. Gel Characterization and Stability
2.3. Caffeine Model
2.4. EO as a Permeation Enhancer
2.5. PDM as a Permeation Enhancer for Caffeine
2.6. Skin Irritation Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material, Essential Oil Distillation, and Analysis
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Preparation of Gels and Caffeine Quantification
3.4. Mice
3.5. Permeation Studies
3.5.1. Skin Membrane
3.5.2. Transdermal Delivery of Caffeine
3.5.3. Experimental Data
3.6. Skin Adverse Effect Determination
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Madison, K.C. Barrier function of the skin: “la raison d’être” of the epidermis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal drug delivery: Innovative pharmaceutical developments based on disruption of the barrier properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, U.; Jain, K. Dermal and transdermal drug delivery through vesicles and particles: Preparation and applications. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 12, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.; Herman, A.P. Essential oils and their constituents as skin penetration enhancer for transdermal drug delivery: A review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Q.D.; Chai, Y.P.; Zhang, H.; Peng, P.; Yang, X.X. Natural terpenes as penetration enhancers for transdermal drug delivery. Molecules 2016, 21, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matos, S.P.; Teixeira, H.F.; de Lima, Á.A.N.; Veiga-Junior, V.F.; Koester, L.S. Essential oils and isolated terpenes in nanosystems designed for topical administration: A review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhasso, B.; Ghori, M.U.; Conway, B.R. Systematic review on the effectiveness of essential and carrier oils as skin penetration enhancers in pharmaceutical formulations. Sci. Pharm. 2022, 90, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, P.; Yao, J.; Yao, P.; Chen, J.; Duan, J. Development of essential oils as skin permeation enhancers: Penetration enhancement effect and mechanism of action. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, T.J. Percutaneous absorption on the relevance of in vitro data. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1975, 64, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, B.W. Lipid-Protein-Partitioning theory of skin penetration enhancement. J. Control. Release 1991, 15, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panico, A.; Serio, F.; Bagordo, F.; Grassi, T.; Idolo, A.D.E.; Giorgi, M.; Guido, M.; Congedo, M.D.E.; Donno, A. Skin safety and health prevention: An overview of chemicals in cosmetic products. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2019, 60, E50–E57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test no. 428: Skin absorption: In vitro method. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4: Health Effects; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H.; Piessens, S.; Bloem, A.; Pronk, H.; Finkel, P. Natural skin surface pH is on average below 5, which is beneficial for its resident flora. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 28, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhail, M.; Wu, P.C.; Minhas, M.U. Using carbomer-based hydrogels for control the release rate of diclofenac sodium: Preparation and in vitro evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla de Stéfano, J.C.; Abundis-Correa, V.; Herrera-Flores, S.D.; Alvarez, A.J. pH-Sensitive starch-based hydrogels: Synthesis and effect of molecular components on drug release behavior. Polymers 2020, 12, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd, E.; Namjoshi, S.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Roberts, M.S.; Grice, J.E. Synergistic skin penetration enhancer and nanoemulsion formulations promote the human epidermal permeation of caffeine and naproxen. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morteza-Semnani, K.; Saeedi, M.; Akbari, J.; Eghbali, M.; Babaei, A.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Nokhodchi, A. Development of a novel nanoemulgel formulation containing cumin essential oil as skin permeation enhancer. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stashenko, E.; Martínez, J.R. Study of essential oils obtained from tropical plants grown in Colombia. In Essential Oils of Nature, 1st ed.; El-Shemy, H.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, P.; Leal, S.M.; Herrera, L.V.; Martinez, J.R.; Stashenko, E. Chemical composition and antiprotozoal activities of Colombian Lippia spp essential oils and their major components. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2010, 105, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stashenko, E.E.; Martínez, J.R.; Ruíz, C.A.; Arias, G.; Durán, C.; Salgar, W.; Cala, M. Lippia origanoides chemotype differentiation based on essential oil GC-MS and principal component analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, K.; Zidorn, C. Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and bioactivity of the genus Turnera (Passifloraceae) with a focus on damiana-Turnera diffusa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 424–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, P.A.; Barry, B.W. Sesquiterpene components of volatile oils as skin penetration enhancers for the hydrophilic permeant 5-fluorouracil. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garlet, Q.I.; Pires, L.C.; Silva, D.T.; Spall, S.; Gressler, L.T.; Bürger, M.E.; Baldisserotto, B.; Heinzmann, B.M. Effect of (+)-dehydrofukinone on GABAA receptors and stress response in fish model. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, e4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Ma, L.; Wang, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Baldwin, I.T.; Wu, J. An ERF2-like transcription factor regulates production of the defense sesquiterpene capsidiol upon Alternaria alternata infection. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5895–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, B.; Zhang, N.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, R.; Chen, P.; Wang, W.; et al. Molecular targets of β-elemene, a herbal extract used in traditional Chinese medicine, and its potential role in cancer therapy: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, H.; Toyota, M.; Asakawa, Y.; Kawano, S. Naphthalene—A constituent of Magnolia flowers. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Pereira, I.; Fernandes-Ferreira, M. Essential oils and hydrocarbons from leaves and calli of Origanum vulgare spp. virens. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.A.; Suverkropp, C.; Kanekal, S.; Plopper, C.G.; Buckpitt, A.R. Tolerance to multiple doses of the pulmonary toxicant, naphthalene. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1989, 99, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanowska, M.; Olas, B. Biological Properties and prospects for the application of eugenol-a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, A.; Aqil, M.; Ali, A. The application of anethole, menthone, and eugenol in transdermal penetration of valsartan: Enhancement and mechanistic investigation. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Li, W.; Li, W. The Effect of clove oil on the transdermal delivery of ibuprofen in the rabbit by in vitro and in vivo methods. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondo, N.E.; Argenta, D.F.; Rauber, G.S.; Vitali, L.; Caon, T. Enhancing the skin permeation of testosterone with natural terpenes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 77, 103911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kararli, T.; Kirchhoff, C.; Penzotti, S. Enhancement of transdermal transport of azidothymidine (AZT) with novel terpene and terpene-like enhancers: In vivo-in vitro correlations. J. Control. Release 1995, 34, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantasart, D.; Pongjanyakul, T.; Higuchi, W.I.; Li, S.K. Effects of oxygen-containing terpenes as skin permeation enhancers on the lipoidal pathways of human epidermal membrane. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 3617–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombrea, A.; Antal, D.; Ardelean, F.; Avram, S.; Pavel, I.Z.; Vlaia, L.; Mut, A.M.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Dehelean, C.A.; Soica, C.; et al. A recent insight regarding the phytochemistry and bioactivity of Origanum vulgare L. essential oil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kattan, A.F.; Asbill, C.S.; Kim, N.; Michniak, B.B. The effects of terpene enhancers on the percutaneous permeation of drugs with different lipophilicities. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 215, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakeena, M.H.; Elrashid, S.M.; Muthanna, F.A.; Ghassan, Z.A.; Kanakal, M.M.; Laila, L.; Munavvar, A.S.; Azmin, M.N. Effect of limonene on permeation enhancement of keto epi-aristolochene. J. Oleo Sci. 2010, 59, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, L.F.; Matilla, J.C.; Stashenko, E.E.; Escobar, P. Toxicity, genotoxicity and anti-Leishmania activity of essential oils obtained of four chemotypes of Lippia genus. Bol. Latinoam. Caribe Plantas Med. Aromát. 2018, 17, 68–83. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-additives-petitions/substances-added-food-formerly-eafus (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Babushok, V.I.; Linstrom, P.J.; Zenkevich, I.G. Retention Indices for Frequently Reported Compounds of Plant Essential Oils. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2011, 40, 043101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, 4th ed.; Allured Publisher: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007; pp. 1–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, W. NIST Standard Reference Database 1A. Version 2.3; NIST: Gaithersburg, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]


| Code | Plant | Main Volatile Secondary Metabolites (>2%) |
|---|---|---|
| EO1 | Steiractinia aspera Cuatrec | α-Pinene (24.9), sabinene (4.6), β-pinene (14.8), α-phellandrene (6.3), p-cymene (4.5), limonene (2.4), β-phellandrene (10.1), α-copaene (2.6), trans-β-caryophyllene (3.1), germacrene D (13.1%). EO yield—0.1%. |
| EO2 | Turnera diffusa, Willd. ex Schult | p-Cymene (3.0), β-elemene (4.0), trans-β-caryophyllene (4.0), aristolochene (17.9%), β-selinene (5.2), premnaspirodiene (3.7), valencene (7.4), α-selinene (2.4), caryophyllene oxide (3.2), guaiol (3.5%), germacra-4,5,10-trien-1α-ol (3.5), dehydrofukinone (25.4). EO yield—0.3%. |
| EO3 | Lippia origanoides H.B.K. Phellandrene chemotype | α-Pinene (2.0), camphene (2.5), α-phellandrene (9.3), p-cymene (8.7), limonene (4.4), β-phellandrene (3.1), 1,8-cineole (6.5), trans-β-caryophyllene (18.6), α-humulene (10.2), germacrene D (2.2), δ-cadinene (2.0), caryophyllene oxide (3.8). EO yield—0.5%. |
| EO4 | Calycolpus moritzianus (O.Berg) Burret | α-Pinene (5.1), limonene (17.6), 1,8-cineole (19.1), linalool (1.3), α-copaene (3.2), trans-β-caryophyllene (6.3), viridiflorene (2.7), selina-3,7 (11)-diene (2.8), trans-nerolidol (3.5), viridiflorol (5.7), trans-geranyl-linalool (4.0). EO yield—0.2%. |
| EO5 | Piper aduncum Linnaeus | α-Pinene (4.6), α-phellandrene (4.4), p-cymene (3.0), limonene (6.0), 1,8-cineole (3.6), piperitone (14.8), α-copaene (2.9), trans-β-caryophyllene (7.4), 9-epi-trans-β-caryophyllene (1.1), δ-cadinene (5.5), caryophyllene oxide (3.8), viridiflorol (5.8). EO yield—0.2%. |
| EO8 | L. origanoides H.B.K. Carvacrol chemotype | β-Myrcene (2.5), p-cymene (14.4), 1,8-cineole (1.3), γ-terpinene (5.4), thymol (7.8), carvacrol (36.0), carvacryl acetate (2.0), trans-β-caryophyllene (4.4). EO yield—1.1%. |
| EO9 | L. origanoides H.B.K. Phellandrene chemotype | α-Phellandrene (7.1), p-cymene (12.6), limonene (2.1), 1,8-cineole (13.0), γ-terpinene (2.4), thymol (14.0), trans-β-caryophyllene (15.1), α-humulene (8.1), caryophyllene oxide (2.5), β-eudesmol (2.6). EO yield—0.6%. |
| EO19 | L. origanoides H.B.K. Thymol chemotype | β-Myrcene (2.1), p-cymene (10.7), γ-terpinene (2.0), thymyl methyl ether (1.0), thymol (72.3), carvacrol (4.4), EO yield—1.2%. |
| Gel | Color/Appearance/ Homogeneity | Caffeine Concentration (µg/mL) | pH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days after Preparation | |||||
| 1 | 7 | 15 | |||
| G-Vehicle-1 | Neutral/translucent | 11.46 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-Vehicle-2 | Neutral/translucent | 11.74 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-EO-1 | White/opaque | 11.90 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-EO-2 | White/opaque | 12.92 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-EO-3 | White/opaque | 11.68 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-EO-4 | White/opaque | 13.92 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-EO-5 | White/opaque | 9.71 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-EO-8 | White/opaque | 12.59 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-EO-9 | White/opaque | 14.63 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-EO-19 | White/opaque | 12.26 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-PDM-4 | White/opaque | 11.35 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-PDM-6 | White/opaque | 11.31 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-PDM-10 | Neutral/translucent | 11.26 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-PDM-19 | White/opaque | 17.79 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-PDM-22 | White/opaque | 16.12 | 5.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| G-PDM-35 | White/opaque | 14.01 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| G-PDM-41 | White/opaque | 11.41 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Gel | (Mean ± SD) | EI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flux (Jss) (µg cm−2 h−1) | Kp (cm h−1) | Tlag (h) | ||
| G-vehicle-1 | 34.57 ± 21.19 | 2.98 ± 1.83 | 2.08 ± 1.13 | 1.00 |
| G-Vehicle-2 | 29.98 ± 19.64 | 2.61 ± 1.71 | 2.55 ± 1.09 | 1.00 |
| G-EO-1 | 31.27 ± 14.30 | 2.58 ± 1.18 | 1.22 ± 1.71 | 0.87 |
| G-EO-2 | 105.92 ± 50.57 * | 8.81 ± 4.20 | 1.53 ± 1.36 | 2.96 |
| G-EO-3 | 39.68 ± 7.30 | 3.42 ± 0.63 | 0.52 ± 1.00 | 1.15 |
| G-EO-4 | 38.52 ± 18.30 | 2.77 ± 1.32 | 1.75 ± 1.27 | 0.93 |
| G-EO-5 | 26.25 ± 22.26 | 2.70 ± 2.29 | 2.51 ± 0.94 | 0.91 |
| G-EO-8 | 53.54 ± 16.06 | 4.71 ± 1.41 | 2.58 ± 0.48 | 1.58 |
| G-EO-9 | 61.38 ± 22.90 | 4.19 ± 1.57 | 2.40 ± 0.73 | 1.41 |
| G-EO-19 | 136.25 ± 21.04 * | 11.12 ± 1.72 | 0.27 ± 1.64 | 3.73 |
| G-PDM-4 | 40.86 ± 19.3 | 3.60 ± 1.70 | 2.74 ± 0.34 | 1.38 |
| G-PDM-6 | 85.21 ± 21.07 * | 6.83 ± 1.69 | 1.46 ± 1.22 | 2.61 |
| G-PDM-10 | 87.37 ± 45.77 * | 7.76 ± 4.07 | 2.24 ± 0.67 | 2.97 |
| G-PDM-19 | 91.58 ± 18.4 ** | 5.15 ± 1.03 | 1.81 ± 1.04 | 1.97 |
| G-PDM-22 | 100.24 ± 19.27 ** | 6.29 ± 1.21 | 2.40 ± 0.77 | 2.40 |
| G-PDM -35 | 51.29 ± 14.04 | 3.66 ± 1.00 | 2.38 ± 0.57 | 1.40 |
| G-PDM 41 | 36.80 ± 18.45 | 3.22 ± 1.71 | 1.90 ± 1.87 | 1.23 |
| Code | Name/Type | Structure | MW * (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDM-4 ** | (R)-(+)-Citronellal/ Acyclic monoterpenoid | 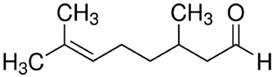 | 154.25 Log P 3.83 |
| PDM-6 | (R)-(+)-Limonene/ Monocyclic monoterpene | 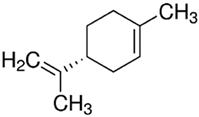 | 136.23 Log P 4.45 |
| PDM-10 | 1-Bromo naphthalene/Polyaromatic hydrocarbon | 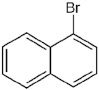 | 207.07 LogP 4.06 |
| PDM-19 | Carvacrol/ Phenolic monoterpene |  | 150.22 LogP 3.28 |
| PDM-22 | Eugenol/ Phenilpropanoid | 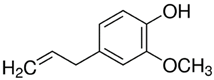 | 164.20 LogP 2.50 |
| PDM-35 | α-Phellandrene/ Hydrocarbon monoterpene |  | 136.23 LogP 4.43 |
| PDM-41 | trans-β-Caryophyllene/ Bicyclic sesquiterpene | 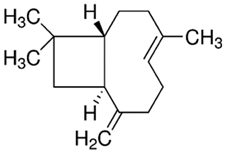 | 204.35 LogP 6.30 |
| Control | Caffeine | 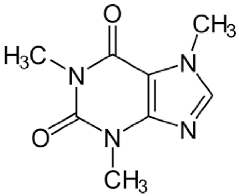 | 194.19 LogP −0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carreño, H.; Stashenko, E.E.; Escobar, P. Essential Oils Distilled from Colombian Aromatic Plants and Their Constituents as Penetration Enhancers for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Molecules 2023, 28, 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062872
Carreño H, Stashenko EE, Escobar P. Essential Oils Distilled from Colombian Aromatic Plants and Their Constituents as Penetration Enhancers for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062872
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarreño, Heider, Elena E. Stashenko, and Patricia Escobar. 2023. "Essential Oils Distilled from Colombian Aromatic Plants and Their Constituents as Penetration Enhancers for Transdermal Drug Delivery" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062872
APA StyleCarreño, H., Stashenko, E. E., & Escobar, P. (2023). Essential Oils Distilled from Colombian Aromatic Plants and Their Constituents as Penetration Enhancers for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Molecules, 28(6), 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062872







