Tackling the Challenging Determination of Trace Elements in Ultrapure Silicon Carbide by LA-ICP-MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
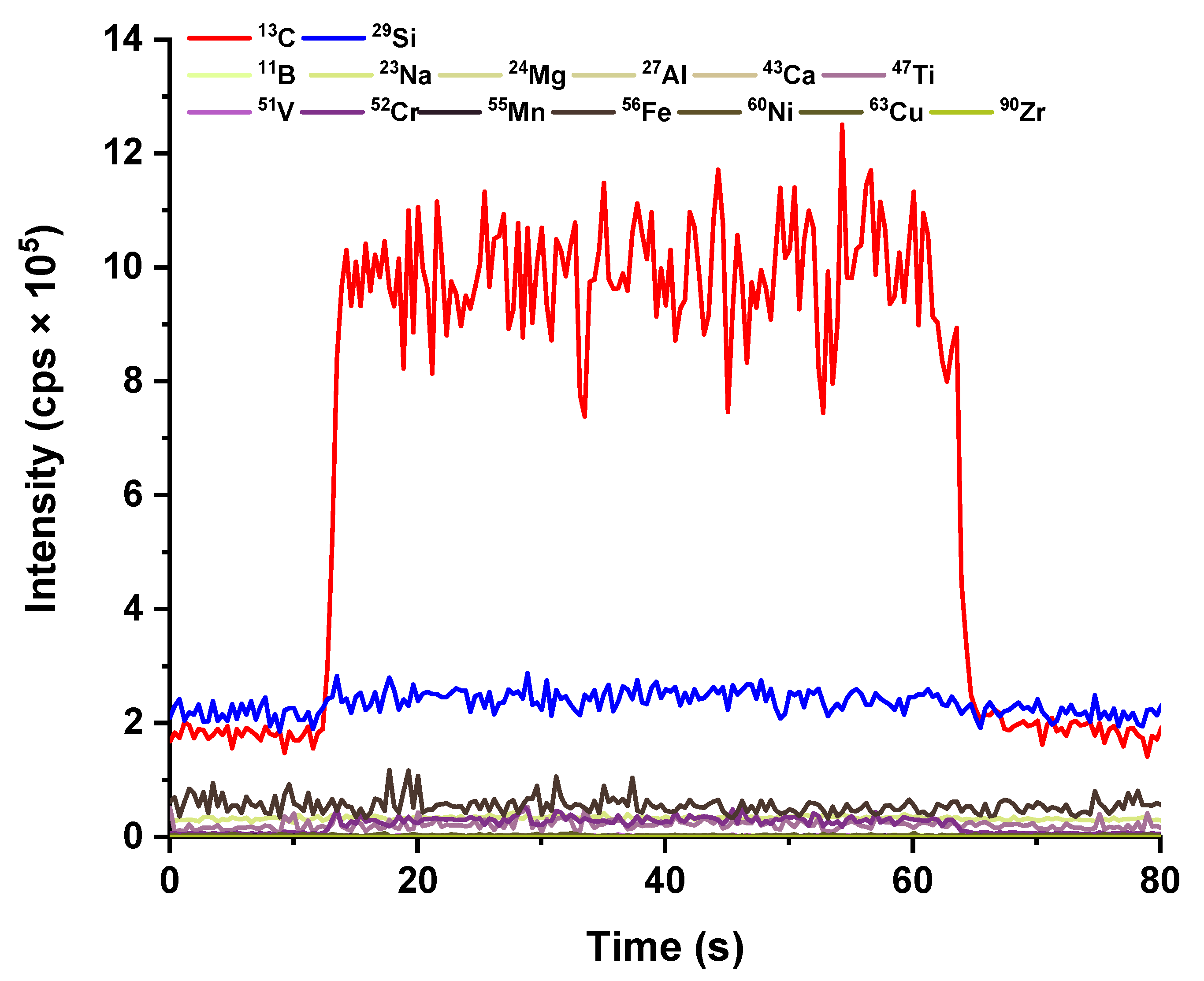
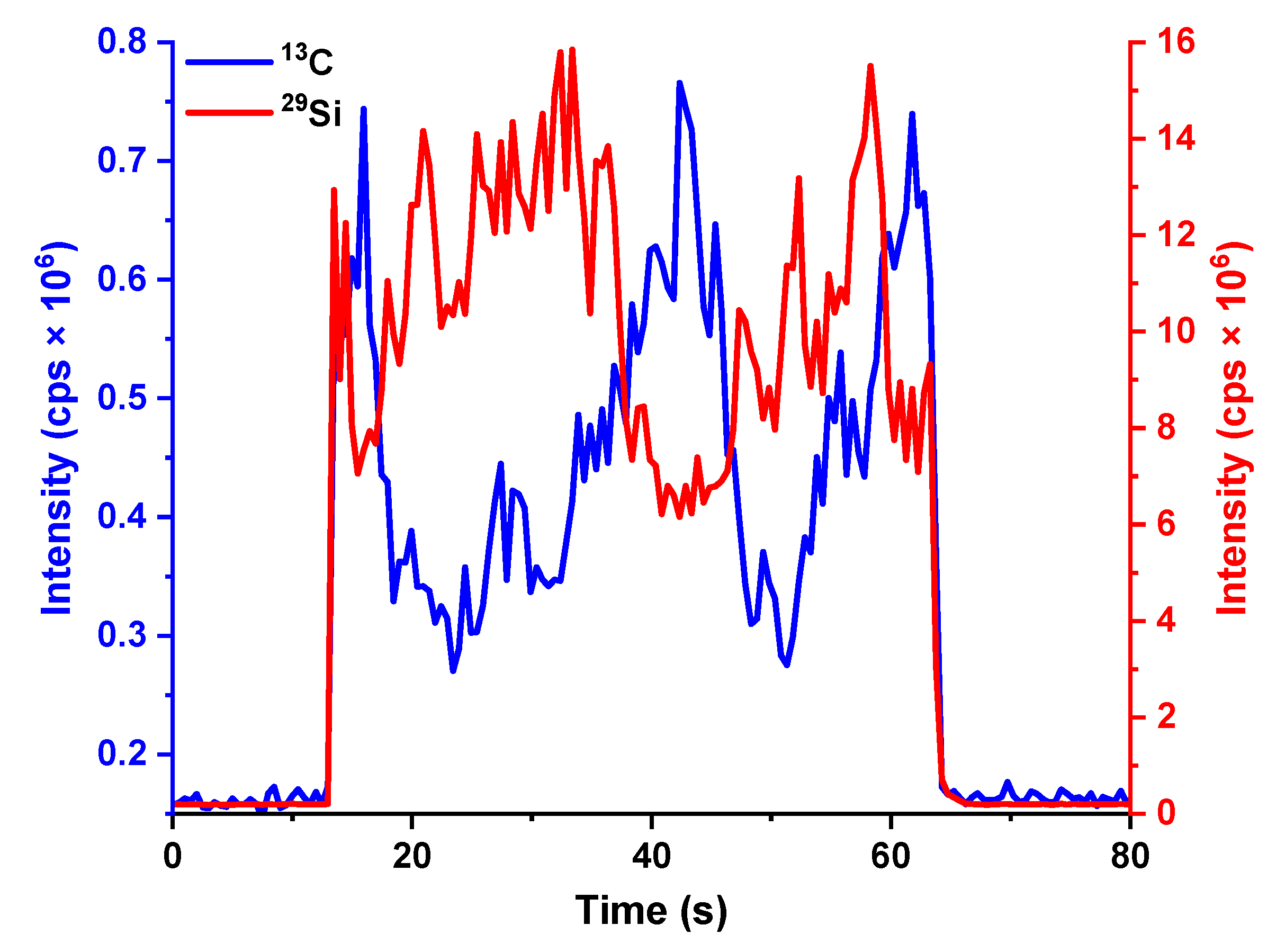
2.1. LA-ICP-MS Analysis
2.1.1. Fabrication of Binder-Free SiC Tablets and LA-ICP-MS Analysis
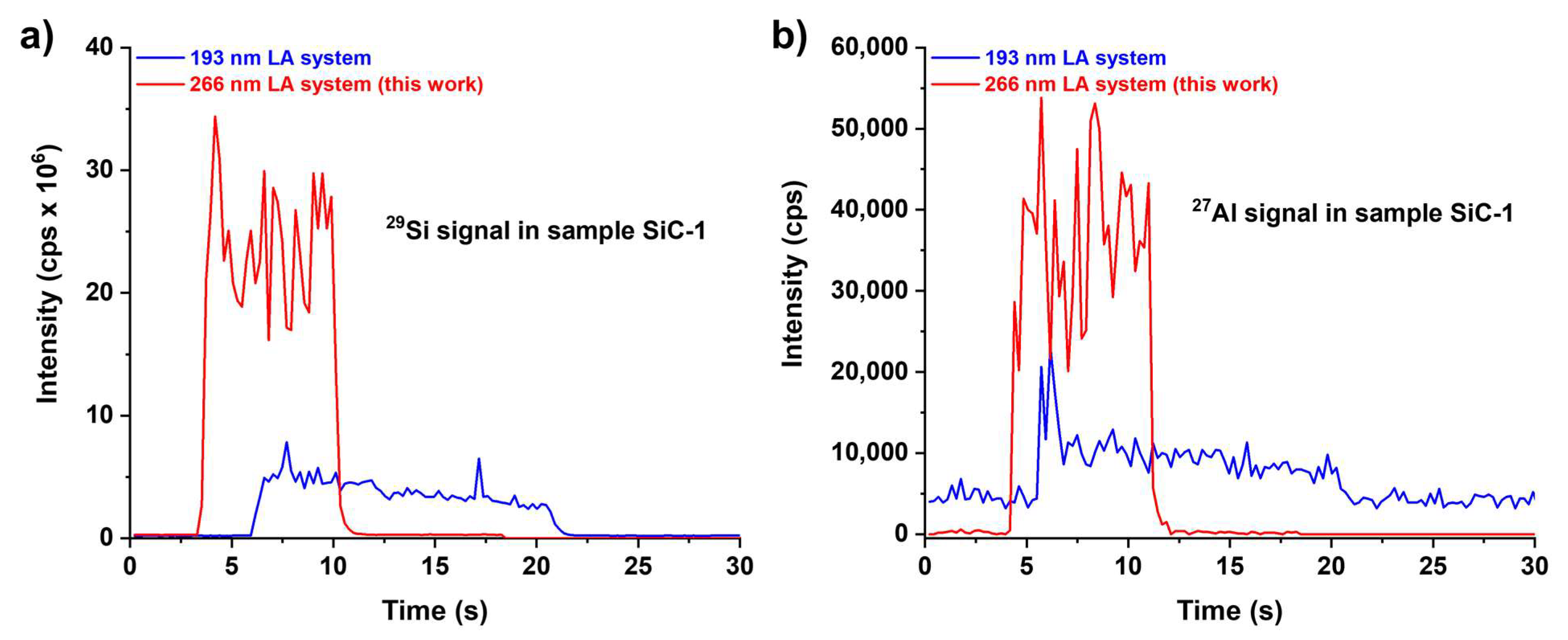
2.1.2. Embedding of SiC Powders in Epoxy Resin and Preliminary Observations
2.1.3. Analytical Performance of the Developed LA-ICP-MS Analytical Protocol
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Silicon Carbide Samples
3.2. Microwave-Assisted Acid Digestion
3.3. Sample Pretreatment for LA-ICP-MS Analysis
- Production of a SiC tablet: the sample was finely ground in an agate mortar and the obtained powder was pressed with a tablet press (Specac) to produce a compact SiC tablet (pressure = 9 × 103 kg/cm2, 30 min). With the aim of improving its mechanical stability, the tablet was sintered at 1000 °C for 2 h (ramp rate 5 °C/min) [16]. After this operation, the tablet was analyzed by LA-ICP-MS;
- Embedding in epoxy resin: the SiC sample without any mechanical pretreatment (i.e., in fine powder or grain form depending on the nature of the starting material) was embedded in an epoxy resin (Epofix Kit, Struers, Copenhagen, Denmark) as follows. The resin and the hardener were gently mixed with a volumetric ratio of 2:15 for 2 min, attempting to avoid the formation of air bubbles. Then, after 2 min of rest, the resin was poured on a small amount of sample previously placed (and eventually gently pressed) in the center of a cylindric mold until a cylinder of 3 or 4 cm was obtained. Immediately after resin pouring, the mold containing the sample and the fresh liquid resin was placed in a vacuum chamber to remove air bubbles and favor the penetration of the resin in SiC pores (pressure around 150 mbar for 15 min). After 24 h of hardening, the resin was cut into a 2.5 mm thin disc. If the sample was granular, a cut of about 750 µm was performed on the sample side to obtain a cross-section of exposed SiC grains. Then, the sample was polished with a 500-grit sandpaper and a pickling operation was applied in 0.1 M HCl for 45 min in a mechanical shaker at 130 rpm in order to remove any surface contamination due to sample handling.
3.4. LA-ICP-MS Analysis
- For the SiC tablets:
- Line analysis (spot from 20 to 40 µm, length from 1 at 2 mm, scanning speed = 40 µm/s, frequency = 10 Hz and fluence from 1 to 15 J/cm2). The ablation was performed up to 5 times along the same lines in order to evaluate surface contamination or any depth profiles inside the material.
- For the SiC powder embedded in epoxy resin:
- Spot analysis was performed (spot size = 120 µm, frequency = 10 Hz, ablation time = 10 s and fluence = 3.8 J/cm2). The ablation was performed 3 times on the same spot and the third ablation was used for quantitative purposes. Five replicate analyses were performed on spot in randomized positions.
- Line analysis was performed (spot size = 120 µm, length = 1 mm, scanning speed = 20 µm/s, frequency = 10 Hz and fluence = 3.8 J/cm2). The ablation was performed up to 5 times on the same line and the fifth line was used for quantitative purposes. Three replicate analyses were performed.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bechstedt, F.; Kackell, P.; Zywietz, A.; Karch, K.; Adolph, B.; Tenelsen, K.; Furthmüller, J. Polytypism and Properties of Silicon Carbide. Phys. Status Solidi 1997, 202, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhevskyi, V.A.; Genova, L.A.; Bressiani, J.C.; Bressiani, A.H.A. Review article: Silicon carbide. Structure, properties and processing. Cerâmica 2000, 46, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, X.; Huang, A.Q.; Lucia, O.; Ozpineci, B. Review of Silicon Carbide Power Devices and Their Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 8193–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, Y.; Snead, L.L. Silicon carbide and its composites for nuclear applications—Historical overview. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 526, 151849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Sohor, M.A.H.; Mustapha, M.; Chandra Kurnia, J. Silicon carbide—From synthesis to application: A review. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 131, 04003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docekal, B.; Broekaert, J.A.C.; Graule, T.; Tschöpel, P.; Tölg, G. Determination of impurities in silicon carbide powders. Fresenius. J. Anal. Chem. 1992, 342, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, Z. First-Principles Study of Metal Impurities in Silicon Carbide: Structural, Magnetic, and Electronic Properties. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 956675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukin, D.M.; Guidry, M.A.; Vučković, J. Integrated Quantum Photonics with Silicon Carbide: Challenges and Prospects. PRX Quantum 2020, 1, 020102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, J.P.R.; Roberts, J.; Ngoepe, N.; Tuling, A.S. Evaluation of the Phase Composition, Crystallinity, and Trace Isotope Variation of SiC in Experimental TRISO Coated Particles. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2009, 131, 062904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseynov, E.; Jazbec, A. Trace elements study of high purity nanocrystalline silicon carbide (3C-SiC) using k0-INAA method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2017, 517, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, M.; Hirosawa, K.; Nonose, N.; Nishida, S.; Furuta, N. Evaluation of measurement uncertainty in the elemental analysis of sintered silicon carbide using laser ablation in liquid—Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with external calibration and isotope dilution. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2019, 24, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senger, C.M.; Anschau, K.F.; Baumann, L.; Muller, A.L.H.; Mello, P.A.; Muller, E.I. Eco-friendly sample preparation method for silicon carbide using pyrohydrolysis for subsequent determination of tungsten by ICP-MS. Microchem. J. 2021, 171, 106781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschat, R.; Haßler, J.; Traub, H.; Dette, A. Multielement trace determination in SiC powders: Assessment of interlaboratory comparisons aimed at the validation and standardization of analytical procedures with direct solid sampling based on ETV ICP OES and DC arc OES. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qiu, D.; Ni, Z.; Tao, G.; Yang, P. Direct determination of impurities in high purity silicon carbide by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry using slurry nebulization technique. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 577, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianyou, P.; Gang, C.; Xiaohai, S.; Zucheng, J.; Bin, H. Electrothermal vaporization-inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry for the direct determination of trace amounts of impurities in slurries of silicon carbide. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 433, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zou, H.J.; Qu, H.Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Du, Y.P. Quantitative determination of trace metals in high-purity silicon carbide powder by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry without binders. Spectrochim. Acta—Part B Atca Spectrosc. 2013, 90, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Itoh, S.; Igarashi, S.; Naitoh, K.; Hasegawa, R. Determination of trace impurities in graphite and silicon carbide by total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry after homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, R.; Nishioka, R.; Fujiwara, M.; Furuta, N. Determination of trace elements in sintered and single-crystal silicon carbide by laser ablation in liquid inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Sci. 2017, 33, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, M.; Fukumura, H. Determination of impurities in silicon nitride and silicon carbide by microwave digestion. Bunseki Kagaku 1996, 45, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrea, M.T.; Gómez-pinilla, I.; Fariñas, J.C. Microwave-assisted Acid Dissolution of Sintered Advanced Ceramics for Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry. J. Anal. Atca Spectrom. 1997, 12, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilger, C.; Leis, F.; Tschöpel, P.; Broekaert, J.A.C.; Tölg, G. Analysis of silicon carbide powders with ICP-MS subsequent to sample dissolution without and with matrix removal. Fresenius. J. Anal. Chem. 1995, 351, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franek, M.; Krivan, V. Multielement characterization of silicon carbide powders by instrumental neutron activation analysis and ICP-atomic emission spectrometry. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1992, 342, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.C.; Nunes, T.S.; Muller, A.L.H.; Dressler, V.L.; Flores, E.M.M.; Muller, E.I. Determination of Boron in Silicon Carbide by ICP-OES and ICP-MS after Sample Preparation using Pyrohydrolysis. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2015, 26, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, R.; Saprykin, A.I.; Becker, J.S.; Dietze, H.-J.; Broekaert, J.A.C. Analysis of semiconducting materials by high-resolution radiofrequency glow discharge mass spectrometry. Mikrochim. Acta 1997, 125, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, V.; Kasik, M.; Robinson, P.K.; Venzago, C. Glow discharge mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 381, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisonero, J.; Fernández, B.; Günther, D. Critical revision of GD-MS, LA-ICP-MS and SIMS as inorganic mass spectrometric techniques for direct solid analysis. J. Anal. Atca Spectrom. 2009, 24, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Shi, K.; Xu, P.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Dai, Y.; Liu, H. Purification effect of the methods used for the preparation of the ultra-high purity graphite. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 120, 108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sabatino, M. Detection limits for glow discharge mass spectrometry (GDMS) analyses of impurities in solar cell silicon. Measurement 2014, 50, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, B.; Matschat, R.; Kipphardt, H. Enhancement of intensities in glow discharge mass spectrometry by using mixtures of argon and helium as plasma gases. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, W.; Bombach, G. A simple method of target preparation for the bulk analysis of powder samples by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2001, 370, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.; Lüdke, C.; Skole, J.; Stephanowitz, H.; Wagner, G. Studies on the quantitative analysis of trace elements in single SiC crystals using laser ablation-ICP-MS. J. Anal. Atca Spectrom. 1999, 14, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, I.D.; Gregson, D.; Shuttleworth, S. Laser Ablation ICP-MS Analysis of Ceramic Materials. In The Physics and Chemistry of Carbides, Nitrides and Borides; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Flórián, K.; Fischer, W.; Nickel, H. Direct solid sample analysis of silicon carbide powders by direct current glow discharge and direct current arc emission spectrometry. J. Anal. Atca Spectrom. 1994, 9, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldris Leon, L.; Thauront, J.L.; Hogmalm, K.J.; Hulthén, E.; Malmqvist, J. Evaluation of Refractory Metal Concentrations in Nano-Particulate Pressed-Powder Pellets Using LA-ICP-MS. Minerals 2022, 12, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazulla, M.F.; Rodrigo, M.; Ventura, M.J.; Orduña, M.; Andreu, C. Development and validation of a WD-XRF method for quantitative trace analysis: Application in the food industry. X-ray Spectrom. 2021, 50, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moxon, T. Agate in Thin Section. Rocks Miner. 2014, 89, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Wang, L.-K. Application of femtosecond laser micromachining in silicon carbide deep etching for fabricating sensitive diaphragm of high temperature pressure sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 309, 112017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbeck, A.; Galler, P.; Bonta, M.; Bauer, G.; Nischkauer, W.; Vanhaecke, F. Recent advances in quantitative LA-ICP-MS analysis: Challenges and solutions in the life sciences and environmental chemistry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6593–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, D.; Civati, D.; Giussani, B.; Dossi, C.; Spanu, D.; Recchia, S. A viscous film sample chamber for Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma—Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2018, 179, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.; Sánchez-Bajo, F.; Cumbrera, F.; Guiberteau, F. X-ray powder diffraction analysis of a silicon carbide-based ceramic. Mater. Lett. 2001, 49, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, M.; Signorelli, A.; Binda, G.; Dossi, C.; Rampazzi, L.; Spanu, D.; Recchia, S. How to Clean and Safely Remove HF from Acid Digestion Solutions for Ultra-Trace Analysis: A Microwave-Assisted Vessel-Inside-Vessel Protocol. Methods Protoc. 2022, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, D.; Butti, L.; Boldrocchi, G.; Bettinetti, R.; Monticelli, D. High-throughput, Multi-batch System for the Efficient Microwave Digestion of Biological Samples. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recchia, S.; Spanu, D.; Bianchi, D.; Dossi, C.; Pozzi, A.; Monticelli, D. Understanding microwave vessel contamination by chloride species. Talanta 2016, 159, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, D.; Castelletti, A.; Civati, D.; Recchia, S.; Dossi, C. How to Efficiently Produce Ultrapure Acids. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 2019, 5180610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Elements | SiC-1 (mg/kg) | SiC-2 (mg/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GD-MS | LA-ICP-MS (Tablet) | GD-MS | LA-ICP-MS (Tablet) | |
| Na | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 0.33 ± 0.07 | 0.4 ± 0.2 |
| Mg | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.28 ± 0.06 | 0.47 ± 0.05 |
| Al | 11 ± 2 | 16 ± 7 | 10 ± 2 | 8 ± 4 |
| Ca | <0.2 | 25 ± 2 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 6.2 ± 0.9 |
| Ti | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 4.5 ± 0.9 |
| Cr | <0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | <0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.2 |
| Mn | <0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | <0.05 | 0.1 ± 0.03 |
| Fe | 0.42 ± 0.08 | 13 ± 3 | 4.6 ± 0.9 | 9 ± 3 |
| Ni | <0.05 | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 25.3 ± 0.5 | 11 ± 4 |
| Cu | <0.05 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | <0.05 | 0.2 ± 0.4 |
| Zr | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 1.9 ± 0.4 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 2 |
| Elements | LOD (mg/kg) |
|---|---|
| B | 0.18 |
| Na | 0.13 |
| Mg | 0.001 |
| Al | 0.036 |
| Ca | 0.55 |
| Ti | 0.084 |
| V | 0.039 |
| Cr | 0.15 |
| Mn | 0.10 |
| Fe | 0.85 |
| Ni | 0.11 |
| Cu | 0.09 |
| Zr | 0.004 |
| ICP-MS Parameters | |
|---|---|
| RF power (kW) | 1.55 |
| Auxiliary gas flux (L/min) | 0.8 |
| Cooling gas flux (L/min) | 14 |
| Makeup gas flux (L/min) | 0.9 |
| Dwell time (ms) | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spanu, D.; Palestra, A.; Prina, V.; Monticelli, D.; Bonanomi, S.; Nanot, S.U.; Binda, G.; Rampazzi, L.; Sessa, G.; Callejo Munoz, D.; et al. Tackling the Challenging Determination of Trace Elements in Ultrapure Silicon Carbide by LA-ICP-MS. Molecules 2023, 28, 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062845
Spanu D, Palestra A, Prina V, Monticelli D, Bonanomi S, Nanot SU, Binda G, Rampazzi L, Sessa G, Callejo Munoz D, et al. Tackling the Challenging Determination of Trace Elements in Ultrapure Silicon Carbide by LA-ICP-MS. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062845
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpanu, Davide, Alessandro Palestra, Veronica Prina, Damiano Monticelli, Simone Bonanomi, Sandro Usseglio Nanot, Gilberto Binda, Laura Rampazzi, Gianluca Sessa, David Callejo Munoz, and et al. 2023. "Tackling the Challenging Determination of Trace Elements in Ultrapure Silicon Carbide by LA-ICP-MS" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062845
APA StyleSpanu, D., Palestra, A., Prina, V., Monticelli, D., Bonanomi, S., Nanot, S. U., Binda, G., Rampazzi, L., Sessa, G., Callejo Munoz, D., & Recchia, S. (2023). Tackling the Challenging Determination of Trace Elements in Ultrapure Silicon Carbide by LA-ICP-MS. Molecules, 28(6), 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062845









