Effect of Chemical Bath Deposition Variables on the Properties of Zinc Sulfide Thin Films: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current Trends in Research and Properties of ZnS Thin Films Utilizing the CBD
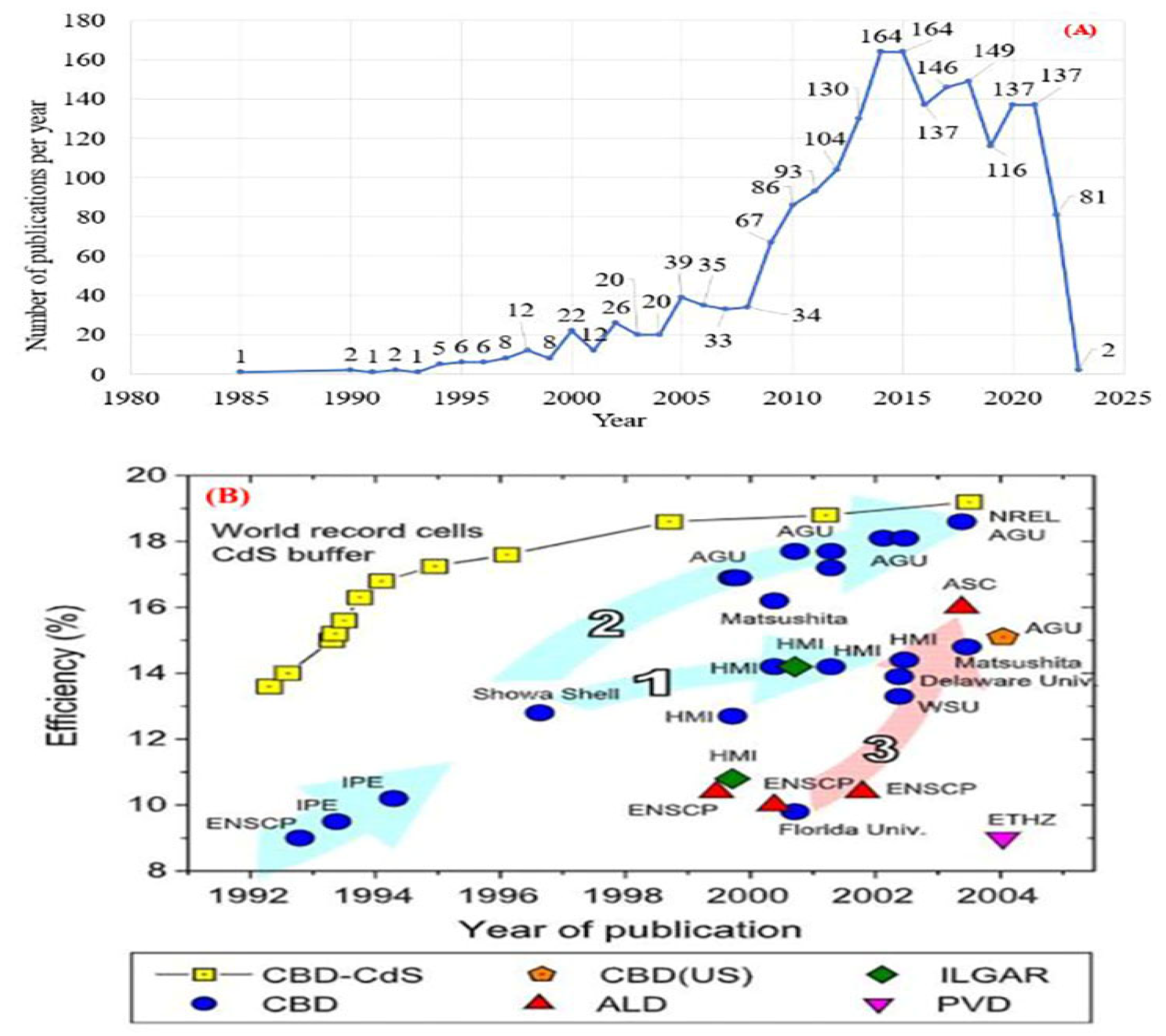
2.1. Current Research Trends
2.2. Properties of Zinc Sulfide Thin Film
3. Synthesis of ZnS Thin Films Using a Chemical Bath Deposition
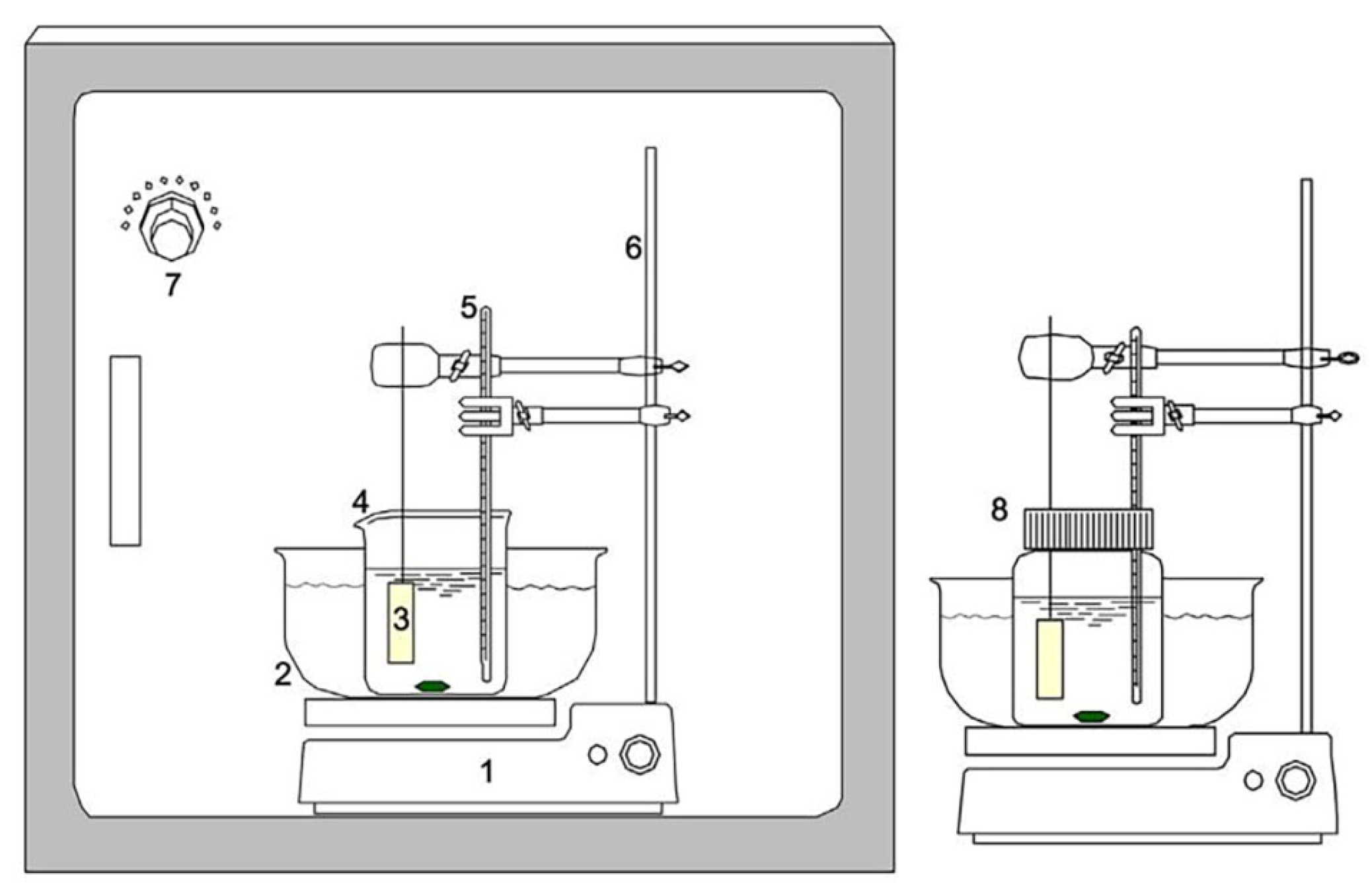
3.1. Basic Experimental Setup for CBD
3.2. Basic Principle of CBD
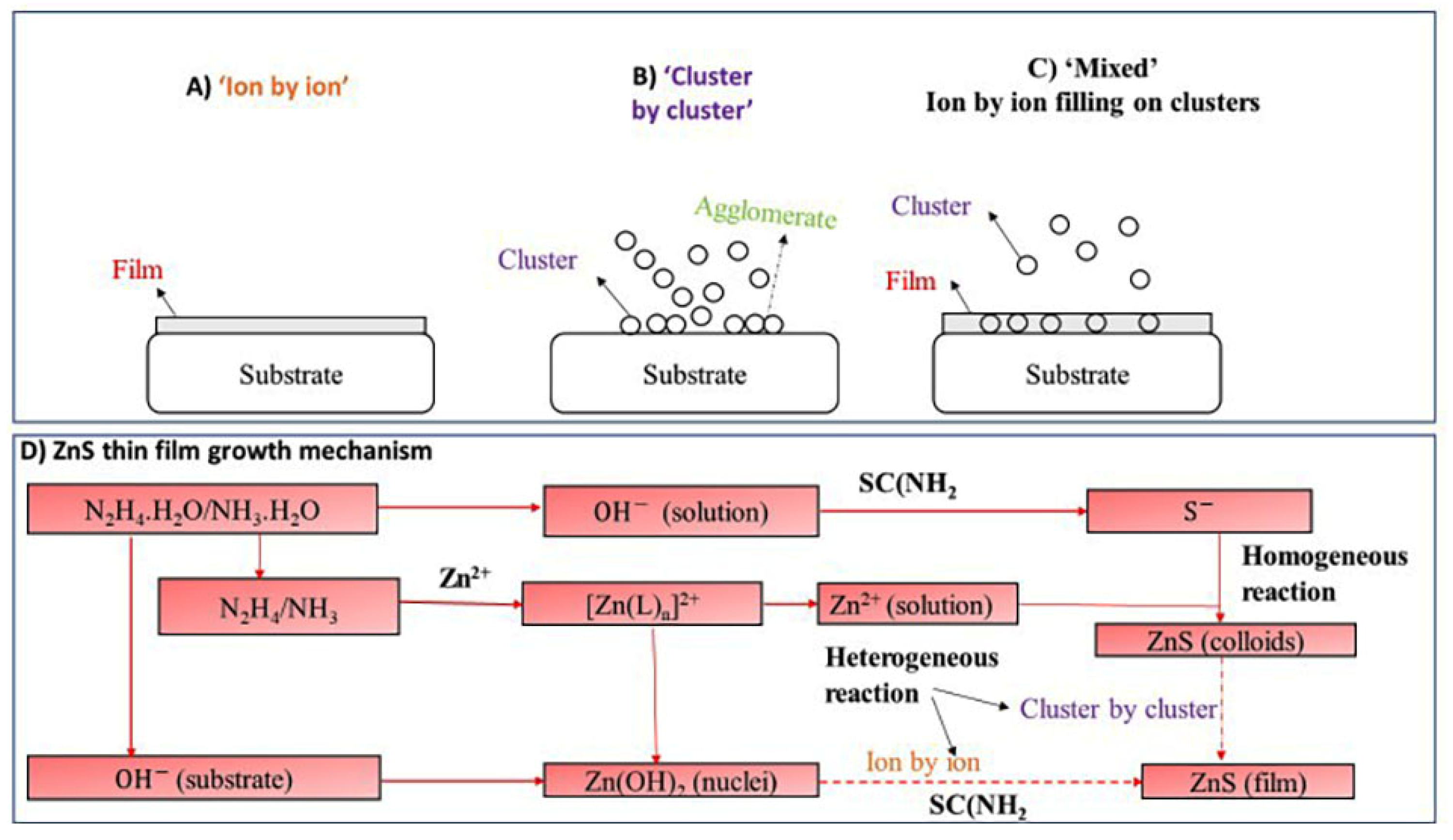
3.3. Reaction Mechanism for ZnS Deposition
3.4. Factors Will Affect the CBD for ZnS Thin Film Properties
| Ref | Years | Bath Composition & Molarity | Substrate | pH | Complexing Agent | Deposition of Temperature (°C) | Deposition of Time | Stirring Speed (rpm) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Annealing Environment | Properties Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (nm) | Transmittance (%) | Eg (eV) | |||||||||||
| [75] | 2012 | Glass | 10.0 | 80 | 4 h | - | - | - | 70–140 | 75–85% | 3.73–3.80 | ||
| [76] | 2012 | (1.5 M), KOH (0.8–1.4 M) | Glass | 10.0–12.0 | 90 | 60–120 min | - | - | - | 60–135 | >85% | 3.68–3.89 | |
| [58] | 2012 | (0.3–3 M) | ITO | - | 80 | - | 300 | 120 °C for 20 min | - | 40–90 | >80% | 3.73–3.79 | |
| [112] | 2012 | (0.2M), EDTA (0.4 M) | Glass | 10.0 | , EDTA | 80 | 4 h | - | - | - | >100 | 70–85% | 3.84–3.94 |
| [100] | 2012 | Glass, silicon | 11.0 | 80 | 10–60 min | - | - | - | 33.8–78.8 | >80% | 3.83–3.85 | ||
| [85] | 2013 | SLG | 8.3–10.6 | 70 | 2 h | - | 200 °C for 1 h | - | 80 | >70% | 3.76–3.87 | ||
| [105] | 2013 | Glass | 9.0–11.0 | 80 | 1 h | - | 550 °C for 2 h | - | 54–122 | 75–80% | 4.0–4.2 | ||
| [101] | 2013 | (2.9 M) | Glass | - | 75–95 | 2 h | - | 200 °C | - | 73–200 | 78% | - | |
| [90] | 2013 | urea (0.5 M) | Glass | 5.9–6.1 | 85 | 4 h | - | 500 °C | (5%) | 133–175 | >70% | 3.66–3.83 | |
| [91] | 2013 | (0.5M) | Glass, SiO2 | 10.0 | 79–80 | 30–90 min | - | - | - | 60 | >80% | 3.62 | |
| [18] | 2013 | SLG | 10.0–12.0 | 75–85 | 20–80 min | - | 400 °C for 1 h | 27–301 | 70.8–87.8% | 3.881–3.980 | |||
| [77] | 2014 | Glass | 10.0 | 80 | 1 h | - | 400 °C for 1 h 30 min | - | 60 | - | 3.099–3.215 | ||
| [106] | 2014 | SLG | 9.8–10.6 | 50–90 | 1.5–2.5 h | - | - | - | 40–160 | >80% | 3.93–4.06 | ||
| [69] | 2014 | SLG | 9.7 | 80 | 20–120 min | 650 | - | - | 50 | 77% | 3.78–3.96 | ||
| [102] | 2015 | (0.07 M) | SLG | 10.0 | 90 | - | - | 100–300 °C | - | - | 70–80% | 3.82–3.89 | |
| [78] | 2015 | (0.2 M) | Glass | - | 70–90 | - | - | - | - | 110 | 90–80% | 3.57–3.78 | |
| [11] | 2018 | (0.6 M), (7.5 M) | Glass | - | 70–90 | - | - | 250 °C for 10 min | - | 30–90 | - | 3.40–3.49 | |
| [104] | 2018 | Glass | 10.7 | 70 | 2–6 h | - | - | - | 68–134 | >80% | 3.69–3.77 | ||
| [99] | 2018 | Glass | 12 | 85 | 1 h | - | - | - | - | - | 3.36–3.69 | ||
| [103] | 2019 | Glass | - | 65–80 | 20–50 min | - | - | - | 70–160 | 93.7–99% | 3.97–4.05 | ||
| [96] | 2019 | Glass | 11.0 | 80 | 60–150 min | - | 500 °C for 2 h | - | - | 69–81% | 3.87–4.03 | ||
| [95] | 2019 | Glass | - | 70 | 30 min | 180 (2 h) | 500 °C for 1 h | Sulfur | - | 50–80% | - | ||
| [92] | 2020 | Glass | 9.0–10.6 | 80 | 3 h | - | - | - | 21–199 | >70% | 3.78–4.00 | ||
| [107] | 2020 | SLG | 9.0–10.8 | 80 | 0–2 h | - | 200 °C for 10 min | - | 37–75 | 70–80% | 3.64–3.75 | ||
| [108] | 2021 | Glass | 9.8 | 60 | 45 min | - | 100–300 °C for 1 h | - | 40–130 | 76% | 3.93–3.98 | ||
| [94] | 2021 | Glass | 5 | 80 | 90 min | - | - | - | - | - | 2.6–3.5 | ||
| [89] | 2021 | (5 M) | Glass, quartz | - | 90 (aged 1 h) | 60–70 min | - | 350 °C for 20 min | Nitrogen | 239–590 | >70% | 3.62–3.68 | |
| [110] | 2021 | , , . (3 M) | Glass | - | 80 | 1 h | - | - | - | - | 70% | 3.70 | |
| [97] | 2021 | Glass | 9 | - | 1 h | - | 150–300 °C | - | 450 | 77.32–79.43% | 3.34–3.45 | ||
| [98] | 2021 | Glass | 11.5–12.5 | 40–60 | - | - | - | - | - | 60–95% | 3.72 | ||
| [88] | 2022 | Glass | 6.5–7.0 | - | 10–60 min | - | - | - | 40–109 | 60–90% | 3.60–3.85 | ||
| [21] | 2022 | Glass | - | 80 | 60 min | - | - | - | - | 70% | 3.7 | ||
| [109] | 2022 | (0.1 M), | Glass | 75 | 90 min | - | - | - | 180–121 | >70% | 3.5–3.75 | ||
| [93] | 2022 | SLG | 5 | - | - | - | 500 °C for 30 min | vacuum | 90.44–101.32 | 15.82–75.782% | 4.15–4.56 | ||
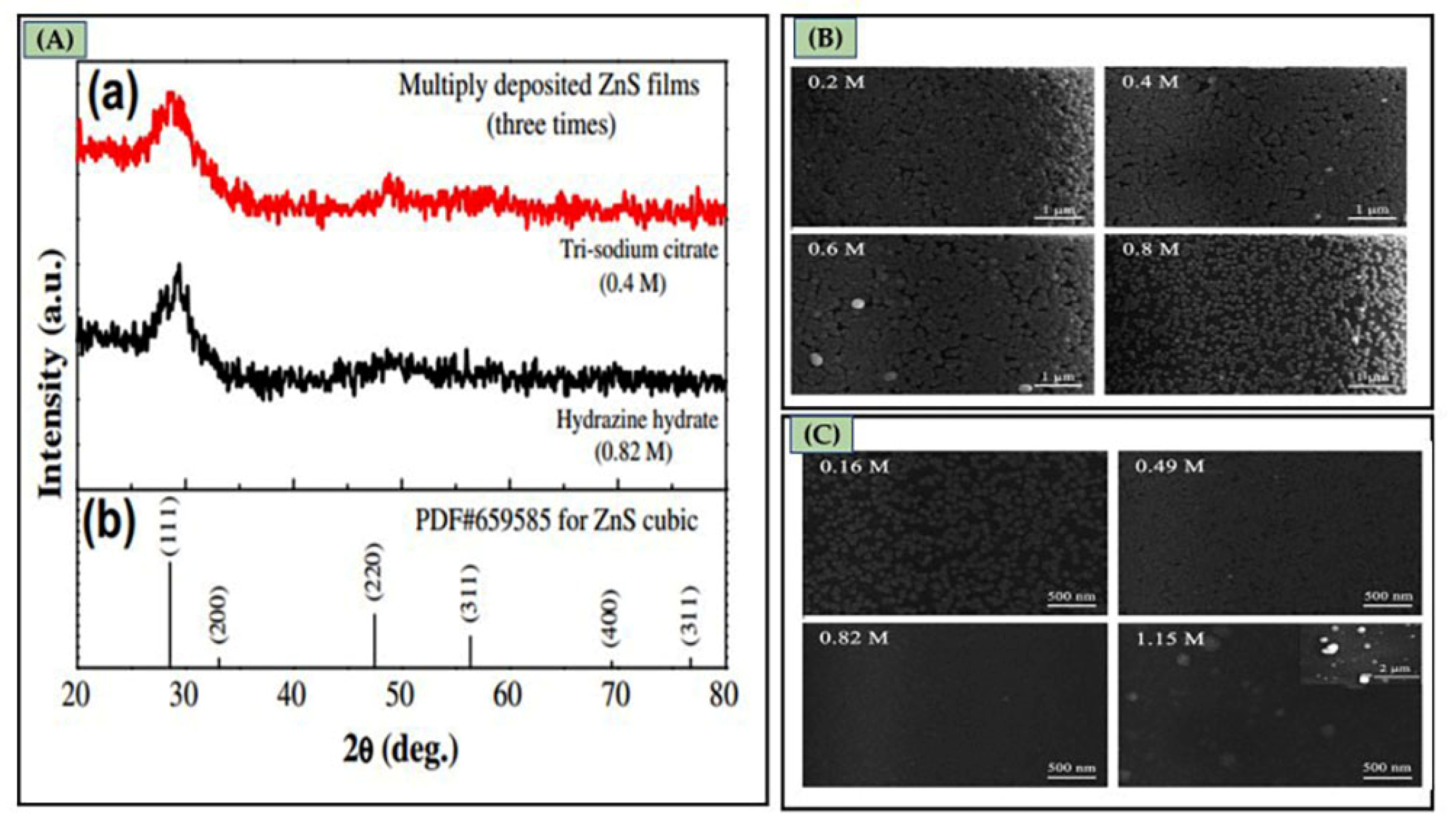
3.4.1. Influence of Complexing Agents
3.4.2. Influence of Concentration Ratio of the Reactants
3.4.3. Influence of Stirring Speed
3.4.4. Influence of Humidity
3.4.5. Influence of Deposition Temperature
3.4.6. Influence of Deposition Time
3.4.7. Influence of pH Value
3.4.8. Influence of Precursor Type
3.4.9. Influence of Annealing Temperature and Environment
3.4.10. Dopant Concentration Influence on ZnS Thin Film Properties
4. Applications of ZnS Thin Films
5. Limitations of CBD Method and Recommendations
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, P.; Ota, J.R.; Srivastava, S.K. Crystalline ZnS thin films by chemical bath deposition method and its characterization. Thin Solid Films 2006, 515, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elidrissi, B.; Addou, M.; Regragui, M.; Bougrine, A.; Kachouane, A.; Bernède, J.C. Structure, composition and optical properties of ZnS thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 68, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djelloul, A.; Adnane, M.; Larbah, Y.; Sharaoui, T.; Zegadi, T.; Maha, C.; Rahal, B. Properties Study of ZnS Thin Films Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis Method. J. Nano Electron. Phys. 2015, 7, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, S.K.; Chaudhuri, S.; Pal, A.K. Optical properties of nanocrystalline ZnS films prepared by high pressure magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 1999, 350, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.P.; Schaber, H. Matrix isolated II-VI molecules: Sulfides of Mg, Ca, Sr, Zn and Cd. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Spectrosc. 1982, 38, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Lu, M.; Chen, L. Metal sulfide nanostructures: Synthesis, properties and applications in energy conversion and storage. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trukhanov, S.V.; Bodnar, I.V.; Zhafar, M.A. Magnetic and electrical properties of (FeIn2S4)1-x(CuIn5S8)x solid solutions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 379, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, I.V.; Jaafar, M.A.; Pauliukavets, S.A.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Victorov, I.A. Growth, optical, magnetic and electrical properties of CuFe2.33In9.67S17.33single crystal. Mater. Res. Express 2015, 2, 85901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Kaur, S.; Singh, J.; Rawat, M. A Review on Zinc Sulphide Nanoparticles: From Synthesis, Properties to Applications. J. Bioelectron. Nanotechnol. 2016, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Cai, S.; Long, Z.; Fang, X. Design Principles and Material Engineering of ZnS for Optoelectronic Devices and Catalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Lim, D.; Eo, Y.J.; Choi, C. Chemical bath deposited ZnS buffer layer for Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 thin film solar cell. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 432, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.M. Role of Complexing Agent in Chemical Bath Deposition of Thin Films: A Review. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 9, 625–629. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Murmu, P.P.; Gupta, P.S.; Carder, D.A.; Chong, S.V.; Leveneur, J.; Rubanov, S. Effects of annealing on the structural and optical properties of zinc sulfide thin films deposited by ion beam sputtering. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 26, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, B.; Zeng, G. Effects of temperature on properties of ZnS thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Superlattices Microstruct. 2019, 130, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakerian, F.; Kafashan, H. Investigation the effect of annealing parameters on the physical properties of electrodeposited ZnS thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 2018, 124, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, R. Effect of substrate temperature on ZnS films prepared by thermal evaporation technique. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2015, 9, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Pivin, J.C.; Siva Kumar, V.V.; Tripathi, A.; Kanjilal, D.; Kumar, L. Grain growth and structural transformation in ZnS nanocrystalline thin films. Vacuum 2010, 85, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.L.; Yang, C.S.; Hsieh, S.H.; Chen, W.J.; Fern, C.L. Effect of deposition variables on properties of CBD ZnS thin films prepared in chemical bath of ZnSO4/SC(NH2)2/Na3C3H5O7/NH4OH. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 264, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, A.; Nagalingam, S.; Min, H.S.; Karrim, N. XRD and AFM studies of ZnS thin films produced by electrodeposition method. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 3, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugadoss, G. Luminescence properties of co-doped ZnS:Ni, Mn and ZnS:Cu, Cd nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 2043–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jrad, A.; Naouai, M.; Ammar, S.; Turki-Kamoun, N. Chemical composition, structural, morphological, optical and luminescence properties of chemical bath deposited Fe:ZnS thin films. Opt. Mater. 2022, 123, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trukhanov, A.V.; Turchenko, V.O.; Bobrikov, I.A.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Kazakevich, I.S.; Balagurov, A.M. Crystal structure and magnetic properties of the BaFe12-xAlxO19 (x = 0.1–1.2) solid solutions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 393, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdorovets, M.V.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Shlimas, D.I.; Borgekov, D.B. Phase transformations in FeCo–Fe2CoO4/Co3O4-spinel nanostructures as a result of thermal annealing and their practical application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 16694–16705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Zdorovets, M.V. Synthesis, structural, strength and corrosion properties of thin films of the type CuX (X = Bi, Mg, Ni). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 11819–11832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubar, T.I.; Usovich, T.I.; Tishkevich, D.I.; Kanafyev, O.D.; Fedkin, V.A.; Kotelnikova, A.N.; Panasyuk, M.I.; Kurochka, A.S.; Nuriev, A.V.; Idris, A.M.; et al. Features of Galvanostatic Electrodeposition of NiFe Films with Composition Gradient: Influence of Substrate Characteristics. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D.; Suthar, D.; Agarwal, R.; Patel, S.L.; Dhaka, M.S. Achieving desired quality of ZnS buffer layer by optimization using air annealing for solar cell applications. Phys. Lett. A 2020, 384, 126557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, R.; Gesheva, K.; Konstantinova, M.; Gogova, D. Investigations of a buffer layer grown on a CdTe surface. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1999, 11, 10003–10006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, R.; Alghoraibi, I. Effect of Deposition Time on Structural and Optical Properties of ZnS Nanoparticles Thin Films Prepared by CBD Method. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2014, 6, 3220–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briot, N.; Abounadi, A.; Gil, B.; Cloitre, T.; Aulombard, R.L. Reflectivity Analysis on GaAs and Si substrates by metal organic vapour-phase epitaxy. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 1994, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, K.; Kogure, O. Epitaxial growth of ZnS on Si by metal organic chemical vapor deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 24, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, Y.; Alam, M.J.; Cameron, D.C. The characteristics of thin film electroluminescent displays produced using sol-gel produced tantalum pentoxide and zinc sulfide. Thin Solid Films 2004, 447–448, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Pan, Z.; Bai, Z.; Kong, L.; Wang, J. Structural and optical properties of Nb-doped β-Ga2O3 thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2017, 146, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayou, V.L.; Salazar-Hernandez, B.; Constantino, M.E.; Andrés, E.R.; Díaz, T.; Macuil, R.D.; López, M.R. Structural studies of ZnS thin films grown on GaAs by RF magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2010, 84, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.M.; Tran, N.H.; Lamb, R.N. Growth of ZnS films by chemical vapor deposition of Zn[S2CN(CH3)2]2 precursor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 241, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.M.; Tran, N.H.; Russell, J.J.; Lamb, R.N. Structure evolution in chemical vapor-deposited ZnS films. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 5208–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Ishizuka, S.; Yamada, A.; Sakurai, K.; Niki, S.; Sakurai, T.; Akimoto, K. CIGS solar cell with MBE-grown ZnS buffer layer. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yun, S.J. Studies on polycrystalline ZnS thin films grown by atomic layer deposition for electroluminescent applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 229, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zeng, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, H. Phase controlled synthesis and optical properties of ZnS thin films by pulsed laser deposition. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 3843–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Nasr, T.; Kamoun, N.; Kanzari, M.; Bennaceur, R. Effect of pH on the properties of ZnS thin films grown by chemical bath deposition. Thin Solid Films 2006, 500, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, A.; Boyle, D.S.; O’Brien, P. In situ kinetic studies of the chemical bath deposition of zinc sulfide from acidic solutions. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 2940–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezekoye, B.A.; Offor, P.; Ezekoye, V.A.; Ezema, F.I. Chemical Bath Deposition Technique of Thin Films: A Review. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 2, 452–456. [Google Scholar]
- Shobana, T.; Venkatesan, T.; Kathirvel, D. A Comprehensive Review on Zinc Sulphide Thin Film by Chemical Bath Deposition Techniques. J. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2020, 9, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, T.; Lilhare, D.; Khare, A. Effects of Various Parameters on Structural and Optical Properties of CBD-Grown ZnS Thin Films: A Review. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 1730–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S.M.; Eid, A.H.; Salem, A.M.; Abou El-Khair, H.M. Nanocrystalline ZnS thin films by chemical bath deposition method and its characterization. Surf. Interface Anal. 2012, 44, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, R.S.; Lokhande, C.D. Chemical deposition method for metal chalcogenide thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2000, 65, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartale, S.D.; Sankapal, B.R.; Lux-Steiner, M.; Ennaoui, A. Preparation of nanocrystalline ZnS by a new chemical bath deposition route. Thin Solid Films 2005, 480–481, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, A.; Aval, G.M.; Sahraei, R.; Ahmadpoor, H. Ammonia-free chemical bath deposition of nanocrystalline ZnS thin film buffer layer for solar cells. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 4953–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, T.; Mizutani, M. 18% efficiency Cd-free Cu(In, Ga)Se2 thin-film solar cells fabricated using chemical bath deposition (CBD)-ZnS buffer layers. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 2 Lett. 2002, 41, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariskos, D.; Spiering, S.; Powalla, M. Buffer layers in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells and modules. Thin Solid Films 2005, 480–481, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Mao, G. Comparison of cds and Zns thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2009, 16, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Shi, J.H.; Liu, Q.Q.; Wang, Z.A.; Sun, Z.; Huang, S.M. Effect of [Zn]/[S] ratios on the properties of chemical bath deposited zinc sulfide thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Ra Kang, S.; Ho Yun, J.; Moholkar, A.V.; Moon, J.H.; Yong Lee, J.; Kim, J.H. Effect of different annealing conditions on the properties of chemically deposited ZnS thin films on ITO coated glass substrates. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.; Saadah, N.H.; Shaari, S.; Muchtar, A. Optical and structural properties of ZnS thin films grown by CBD technique. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 139–141, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göde, F.; Gümüş, C.; Zor, M. Investigations on the physical properties of the polycrystalline ZnS thin films deposited by the chemical bath deposition method. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 299, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Zdorovets, M.V. Effect of doping of Ce4+/3+ on optical, strength and shielding properties of (0.5-x)TeO2-0.25MoO-0.25Bi2O3-xCeO2 glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 263, 124444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.A.; Slimani, Y.; Algarou, N.A.; Vakhitov, M.G.; Klygach, D.S.; Baykal, A.; Zubar, T.I.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Attia, H.; et al. Tuning the structure, magnetic and high frequency properties of Sc-doped Sr0.5Ba0.5ScxFe12-xO19/NiFe2O4 hard/soft nanocomposites. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 8, 2101124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.S.; Lin, Y.J. Defect-induced magnetic properties of Cu-doped ZnS films with different copper contents. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 649, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.Y.; Cho, E.S.; Kwon, S.J. Characterization of the ZnS thin film buffer layer for Cu(In, Ga)Se 2 solar cells deposited by chemical bath deposition process with different solution concentrations. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 135, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, C.D.; Yermune, V.S.; Pawar, S.H. Electrodepositions of CdS, ZnS and Cd1-xZnxS films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1988, 20, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, J.; Ruckh, M.; Hariskos, D.; Ruhle, U.; Menner, R.; Schock, H.W. Interface engineering between CuInSe2 and ZnO. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the Twenty Third IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Louisville, KY, USA, 10–14 May 1993; pp. 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, T.; Furumi, K.; Kunioka, A. High-efficiency cadmium-free Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin-film solar cells with chemically deposited ZnS buffer layers. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1999, 46, 2093–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, A.K.; Kumbhakar, P. Cubic-to-hexagonal phase transition and optical properties of chemically synthesized ZnS nanocrystals. Results Phys. 2012, 2, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Chawla, A.K.; Chandra, R.; Prakash, J.; Kulriya, P.K.; Pivin, J.C.; Kanjilal, D.; Kumar, L. Structural phase transformation in ZnS nanocrystalline thin films by swift heavy ion irradiation. Solid State Commun. 2010, 150, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.Y.; Lu, Z.W.; Froyen, S.; Zunger, A. Zinc-blendewurtzite polytypism in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 10086–10097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakil, M.A.; Das, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Akther, U.S.; Hassan, M.K.; Rahman, M.K. A Review on Zinc Sulphide Thin Film Fabrication for Various Applications Based on Doping Elements. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2018, 09, 751–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodes, G. Semiconductor and ceramic nanoparticle films deposited by chemical bath deposition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 2181–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Aggarwal, R.; Raula, M. A review on chemical bath deposition of metal chalcogenide thin films for heterojunction solar cells. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 38, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugle, D.; Jadhav, G. Short review on chemical bath deposition of thin film and characterization. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1728, 20597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chao, Y.T.; Yao, P.C. Influence of humidity on the growth characteristics and properties of chemical bath-deposited ZnS thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; De Melo, O.; Vigil, O.; López, N.; Contreras-Puente, G.; Zelaya-Angel, O. Influence of magnetic field and type of substrate on the growth of ZnS films by chemical bath. Thin Solid Films 2002, 419, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, R.P.; Patel, A.J. Investigation of the effect of zinc precursors onto structural, optical and electrical properties of cbd deposited zns thin films. Nanosyst. Phys. Chem. Math. 2021, 12, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.; Murali, K.V.; Manoj, R.; Jayaraj, M.K. The effect of the pH value on the growth and properties of chemical-bath-deposited ZnS thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 90, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Il Lee, S. Deposition and optical properties of nanocrystalline ZnS thin films by a chemical method. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2007, 7, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernits, K.; Muska, K.; Danilson, M.; Raudoja, J.; Varema, T.; Volobujeva, O.; Altosaar, M. Anion effect of zinc source on chemically deposited ZnS(O,OH) films. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 2009, 372708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agawane, G.L.; Shin, S.W.; Moholkar, A.V.; Gurav, K.V.; Yun, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.H. Non-toxic complexing agent Tri-sodium citrate’s effect on chemical bath deposited ZnS thin films and its growth mechanism. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 535, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tec-Yam, S.; Rojas, J.; Rejón, V.; Oliva, A.I. High quality antireflective ZnS thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-khayatt, A.H.O.; Jaafer, M.D. Characteristics of Nanocrystalline ZnS thin films grown on glass with different Zn ion concentrations by CBD technique. IOSR J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 6, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Fan, P.; Chen, C.; Luo, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D. Improved microstructure and properties of CBD-ZnS thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 2230–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; Vigil, O.; De Melo, O.; López, N.; Zelaya-Angel, O. Influence of NH3 concentration and annealing in the properties of chemical bath deposited ZnS films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1999, 61, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doña, J.M.; Herrero, J. Process and Film Characterization of Chemical-Bath-Deposited ZnS Thin Films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hone, F.G.; Abza, T. Short review of factors affecting chemical bath deposition method for metal chalcogenide thin films. Int. J. Thin Film Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahouli, M.; Barhoumi, A.; Bouzid, A.; Al-Hajry, A.; Guermazi, S. Structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by direct precipitation method. Superlattices Microstruct. 2015, 85, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A.H.; Salim, S.M.; Sedik, M.B.; Omar, H.; Dahy, T.; Abou Elkhair, H.M. Preparation and characterization of ZnS thin films. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 6, 777–784. [Google Scholar]
- Brien, P.O.; Mcaleese, J. Developing an understanding of the processes controlling the chemical bath deposition of ZnS and CdS. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, M.; Zhao, Y. Preparation and characterization of ZnS thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2013, 16, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wei, A.; Zhao, Y. Effect of different complexing agents on the properties of chemical-bath-deposited ZnS thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 588, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benrezgua, E.; Deghfel, B.; Zoukel, A.; Basirun, W.J.; Amari, R.; Boukhari, A.; Yaakob, M.K.; Kheawhom, S.; Mohamad, A.A. Synthesis and properties of copper doped zinc oxide thin films by sol-gel, spin coating and dipping: A characterization review. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1267, 133639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, A.; Langroodi, S.M.; Arefkhani, M.; Samadani Langeroodi, N. Study of optical properties of ZnS and MnZnS (ZnS/MnS) nanostructure thin films; Prepared by microwave-assisted chemical bath deposition method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 275, 125103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Sahare, S.; Choubey, R.K. Influence of deposition time on the properties of ZnS/p-Si heterostructures. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 122, 105471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhang, B.L.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Zhao, S.R.; Cao, H.; Jiang, J.C.; Sun, Y.; Shen, Y. Effects of zinc salts on the structural and optical properties of acidic chemical bath deposited ZnS thin films. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, P.A.; Quevedo-Lopez, M.A.; Olivas, A. Influence of deposition time on ZnS thin film growth over SiO2 and glass substrates. Mater. Lett. 2013, 106, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arandhara, G.; Bora, J.; Saikia, P.K. Effect of pH on the crystallite size, elastic properties and morphology of nanostructured ZnS thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 241, 122277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, S.; Tahir, S.A.; Ashfaq, A.; Ahmad, W.; Baig, A.; ur Rehman, U.; Saeed, R.; Haneef, M.; Shabbir, K.; Khan, K.M. Effect of ammonia on the structural, morphological and optical properties of nanocrystalline ZnS thin film. Optik 2022, 261, 169088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Leta Tesfaye, J.; Kiran, R.; Deepak, T.; Ruby, A.U.; Venkatesh, S.; Krishnaraj, R. Studying the Effect of Metallic Precursor Concentration on the Structural, Optical, and Morphological Properties of Zinc Sulfide Thin Films in Photovoltaic Cell Applications. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 7443664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.; Yi, J.; Zhong, J.; Yang, S. Effect of sulphur pressure on properties of ZnS thin film prepared by chemical bath deposition technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 13230–13237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabou, N.; Birouk, B.; Aida, M.S.; Raskin, J.P. Deposition time and annealing effects on morphological and optical properties of ZnS thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2019, 37, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayeed, M.A.; Rouf, H.K.; Md Amjad Hussain, K. Doping and annealing effects on structural, optical and electrical characteristics of Sn-doped ZnS thin film. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 86401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Chan, I.J.; Pat-Herrera, A.; Trejo-Ramos, A.I.; Oliva, A.I. Synthesis and characterisation of ZnS thin films obtained without complexing agent by the chemical bath technique. Surf. Eng. 2021, 37, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathy, V.; Sankar, S.; Ponnuswamy, V. Influence of thiourea on the synthesis and characterization of chemically deposited nano structured zinc sulphide thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 7739–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.L.; Chen, W.J.; Hsieh, S.H.; Yu, J.H. Growth behavior of nanocrystalline ZnS thin films for solar cell using CBD technique. Procedia Eng. 2012, 36, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tang, N.; Wu, S. Influence of deposition temperature on ZnS thin film performance with chemical bath deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 228, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Um, Y. Post-annealing effects on ZnS thin films grown by using the CBD method. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2015, 67, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, R.; Alghoraibi, I. Influence of bath temperature and deposition time on topographical and optical properties of nanoparticles ZnS thin films synthesized by a chemical bath deposition method. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 7541863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Sohrabi, B.; Vaezi, M.R. Highly transparent, flexible and hydrophilic ZnS thin films prepared by a facile and environmentally friendly chemical bath deposition method. Thin Solid Films 2018, 651, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekiket, H.; Aida, M.S. Chemical bath deposition of nanocrystalline ZnS thin films: Influence of pH on the reaction solution. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2013, 16, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, H.; Duo, S.; Liu, T.; Sun, Q.; Ruan, C.; Fei, X.; Tan, J.; Zhan, S. Effect of temperature on structural and optical properties of ZnS thin films by chemical bath deposition without stirring the reaction bath. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 18, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, C.R.; Arepalli, V.K.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, W.J.; Chung, Y.D. Role of hydrazine in the enhanced growth of zinc sulfide thin films using chemical bath deposition for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cell application. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 105, 104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, R.Y. Annealing effect on the structure and optical properties of cbd-zns thin films for windscreen coating. Materials 2021, 14, 6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne Sarah Christinal, R.; Prakash, I.; Alex Arunmozhi, A.; Chakravarty, S.; Leo Rajesh, A. Variation of sulfur concentration on the effective deposition of solution processed ZnS thin films for buffer layer in thin film solar cells. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 68, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jrad, A.; Naouai, M.; Ammar, S.; Turki-Kamoun, N. Investigation of molybdenum dopant effect on ZnS thin films: Chemical composition, structural, morphological, optical and luminescence surveys. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 130, 105825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikova, N.S.; Maskaeva, L.N.; Markov, V.F.; Vorokh, A.S. Effect of chemical reaction mechanism on the formation of ZnS colloid particles with structure disordering. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 113, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Agawane, G.L.; Gang, M.G.; Moholkar, A.V.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.Y. Preparation and characteristics of chemical bath deposited ZnS thin films: Effects of different complexing agents. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 526, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaewdang, N.; Gaewdang, T. Investigations on chemically deposited Cd1-xZnxS thin films with low Zn content. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 3577–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.R.; Shin, S.W.; Choi, D.S.; Moholkar, A.V.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Effect of pH on the characteristics of nanocrystalline ZnS thin films prepared by CBD method in acidic medium. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, S473–S477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, K.; Preetha, K.C.; Murali, K.V.; Dhanya, A.C.; Ragina, A.J.; Remadevi, T.L. The effect of various complexing agents on the morphology and optoelectronic properties of chemically deposited ZnS Thin films: A comparative study. Optik 2014, 125, 5727–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladeji, I.O.; Chow, L. Synthesis and processing of CdS/ZnS multilayer films for solar cell application. Thin Solid Films 2005, 474, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dang, X.Y.; Jin, J.; Yu, T.; Li, B.Z.; He, Q.; Li, F.Y.; Sun, Y. ZnS thin film deposited with chemical bath deposition process directed by different stirring speeds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 6871–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, C.; Naghavi, N.; Roussel, O.; Etcheberry, A.; Hariskos, D.; Menner, R.; Powalla, M.; Kerrec, O.; Lincot, D. The Zn(S,O,OH)/ZnMgO Buffer in Thin Film Cu(In,Ga)(S,Se)2-Based Solar Cells Part I: Fast Chemical Bath Deposition of Zn(S,O,OH) Buffer Layers for Industrial Application on Co-evaporated Cu(In,Ga)Se2 and Electrodeposited CuIn(S,Se)2 Solar Cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2009, 17, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.; Altıokka, B. Effect of stirring on chemically deposited ZnO thin films. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2020, 137, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.; Jeon, J.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Ahn, H.S.; Kim, J.P.; Jeong, E.D.; Cho, C.R. Chemical bonding states and atomic distribution within Zn(S,O) film prepared on CIGS/Mo/glass substrates by chemical bath deposition. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jawad, S.M.H.; Alioy, F.H. Kinetics of Growth and Structural Characterization of Cd1-X ZnxS Thin Films Synthesized by CBD Method. Eng. Technol. J. 2013, 31, 505–519. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, H.; Chelouche, A.; Talantikite, D.; Merzouk, H.; Boudjouan, F.; Djouadi, D. Effects of deposition time in chemically deposited ZnS films in acidic solution. Thin Solid Films 2015, 589, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, C.; Naghavi, N.; Canava, B.; Etcheberry, A.; Lincot, D. Thermodynamic and experimental study of chemical bath deposition of Zn(S,O,OH) buffer layers in basic aqueous ammonia solutions. Cell results with electrodeposited CuIn(S,Se)2 absorbers. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 6032–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Chan, I.J.; Oliva, A.I. Physicochemical Analysis and Characterization of Chemical Bath Deposited ZnS Films at Near Ambient Temperature. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, D421–D427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Panzo, I.J.; Martín-Várguez, P.E.; Oliva, A.I. Physicochemical Conditions for ZnS Films Deposited by Chemical Bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, D181–D189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Ramos, A.I.; González-Chan, I.J.; Oliva, A.I. Physical properties of chemically deposited ZnS thin films: Role of the solubility curves and species distribution diagrams. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 118, 105207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xue, Y.; Li, J. Study on ZnS thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, S76–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.I.; González-Chan, I.; Rejón, V.; Rojas, J.; Patiño, R.; Aguilar, D. Chemical bath method for Zns thin films preparation. In Proceedings of the 2010 7th International Conference on Electrical Engineering Computing Science and Automatic Control, Tuxtla Gutierrez, Mexico, 8–10 September 2010; pp. 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.H.; Mohammed, R.Y.; Ibrahem, M.A. Influence of post annealing on CBD deposited ZnS thin films. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2660, 020038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göde, F. Annealing temperature effect on the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnS thin films. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2011, 406, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhova, L.V.; Konovalov, I.; Szargan, R.; Aschkenov, N.; Schubert, M.; Chassé, T. Composition and properties of ZnS thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition from acidic and basic solutions. Phys. Status Solidi C Conf. 2005, 2, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talantikite-Touati, D.; Merzouk, H.; Haddad, H.; Tounsi, A. Effect of dopant concentration on structural and optical properties Mn doped ZnS films prepared by CBD method. Optik 2017, 136, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, F.; Sahraei, R.; Soheyli, E.; Daneshfar, A. Dopant-Concentration Dependent Optical and Structural Properties of Cu-Doped Zns Thin Films. J. Nanostruct. 2022, 12, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jrad, A.; Ben Nasr, T.; Turki-Kamoun, N. Study of structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of indium-doped zinc sulfide thin films for optoelectronic applications. Opt. Mater. 2015, 50, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horoz, S.; Dai, Q.; Maloney, F.S.; Yakami, B.; Pikal, J.M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Tang, J. Absorption induced by Mn doping of ZnS for improved sensitized quantum-dot solar cells. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2015, 3, 24011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejjai, B.; Minnam Reddy, V.R.; Seku, K.; Kotte, T.R.R.; Park, C. Chemical bath deposition of Mn-doped ZnS thin films using greener complexing agents: Effect of Mn-doping on the optical properties. Optik 2017, 130, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Malik, M.A.; Alghamdi, Y.G.; Ahmad, K.S.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Chemical bath deposition of Fe-doped ZnS thin films: Investigations of their ferromagnetic and half-metallic properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 39, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Malik, M.A.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Room temperature ferromagnetism and half metallicity in nickel doped ZnS: Experimental and DFT studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 160, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Alghamdi, Y.G.; Azad Malik, M.; Arif Khalil, R.M.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Structural, optical, magnetic and half-metallic studies of cobalt doped ZnS thin films deposited via chemical bath deposition. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 6755–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, K.H.; Sultana, P.; Asfia, M.B. Chemical bath deposition of aluminum doped zinc sulfide thin films using non-toxic complexing agent: Effect of aluminum doping on optical and electrical properties. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 65315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummartyotin, S.; Infahsaeng, Y. A comprehensive review on ZnS: From synthesis to an approach on solar cell. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violas, A.F.; Oliveira, A.J.N.; Teixeira, J.P.; Lopes, T.S.; Barbosa, J.R.S.; Fernandes, P.A.; Salomé, P.M.P. Will ultrathin CIGS solar cells overtake the champion thin-film cells? Updated SCAPS baseline models reveal main differences between ultrathin and standard CIGS. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 243, 111792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kimoto, Y.; Yasaki, Y.; Kato, T.; Sugimoto, H. Cd-Free Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2 thin-film solar cell with record efficiency of 23.35%. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2019, 9, 1863–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Wu, J.L.; Hirai, Y.; Sugimoto, H.; Bermudez, V. Record Efficiency for Thin-Film Polycrystalline Solar Cells Up to 22.9% Achieved by Cs-Treated Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2019, 9, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.N.; Ramanathan, K. Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film solar cells with buffer layer alternative to CdS. Sol. Energy 2004, 77, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, U.; Kim, K.; Dhungel, S.K.; Mangalaraj, D.; Park, J.H.; Yi, J. Application of CBD Zinc Sulfide (ZnS) film to low cost antireflection coating on large area industrial silicon solar cell. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2003, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Olsen, L.C. Chemical bath deposited zinc sulfide buffer layers for copper indium gallium sulfur-selenide solar cells and device analysis. Thin Solid Films 2005, 471, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

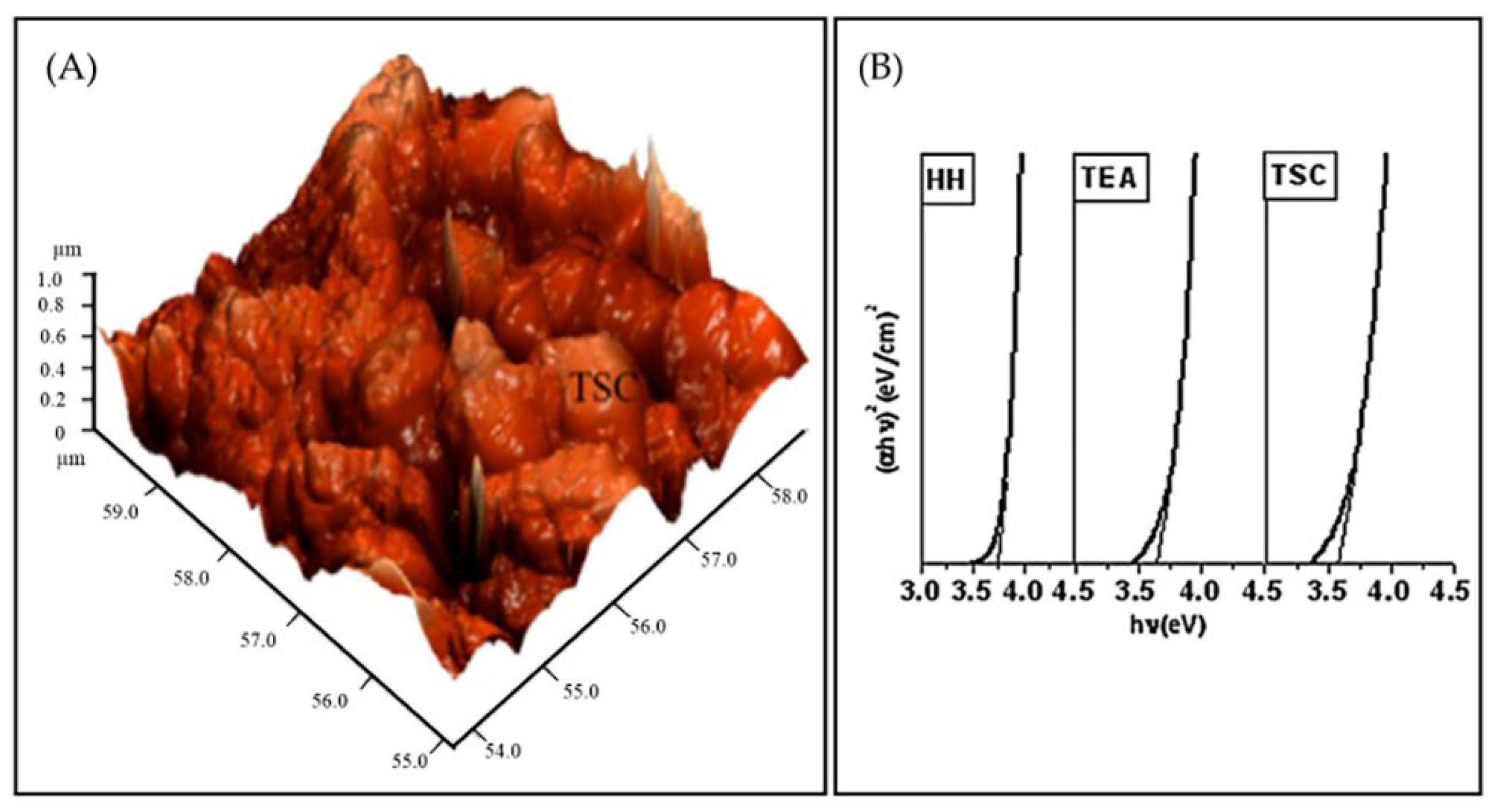
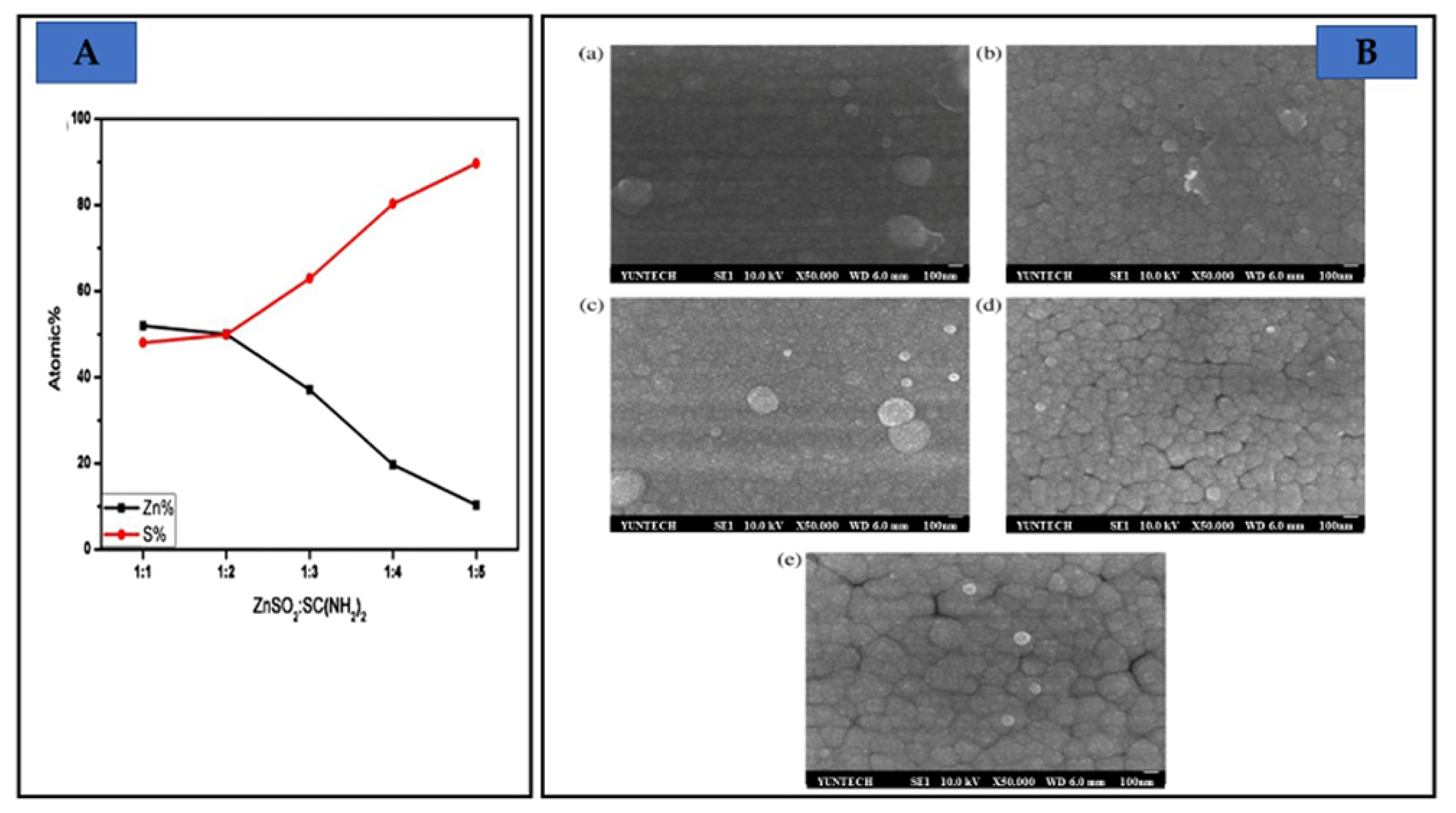
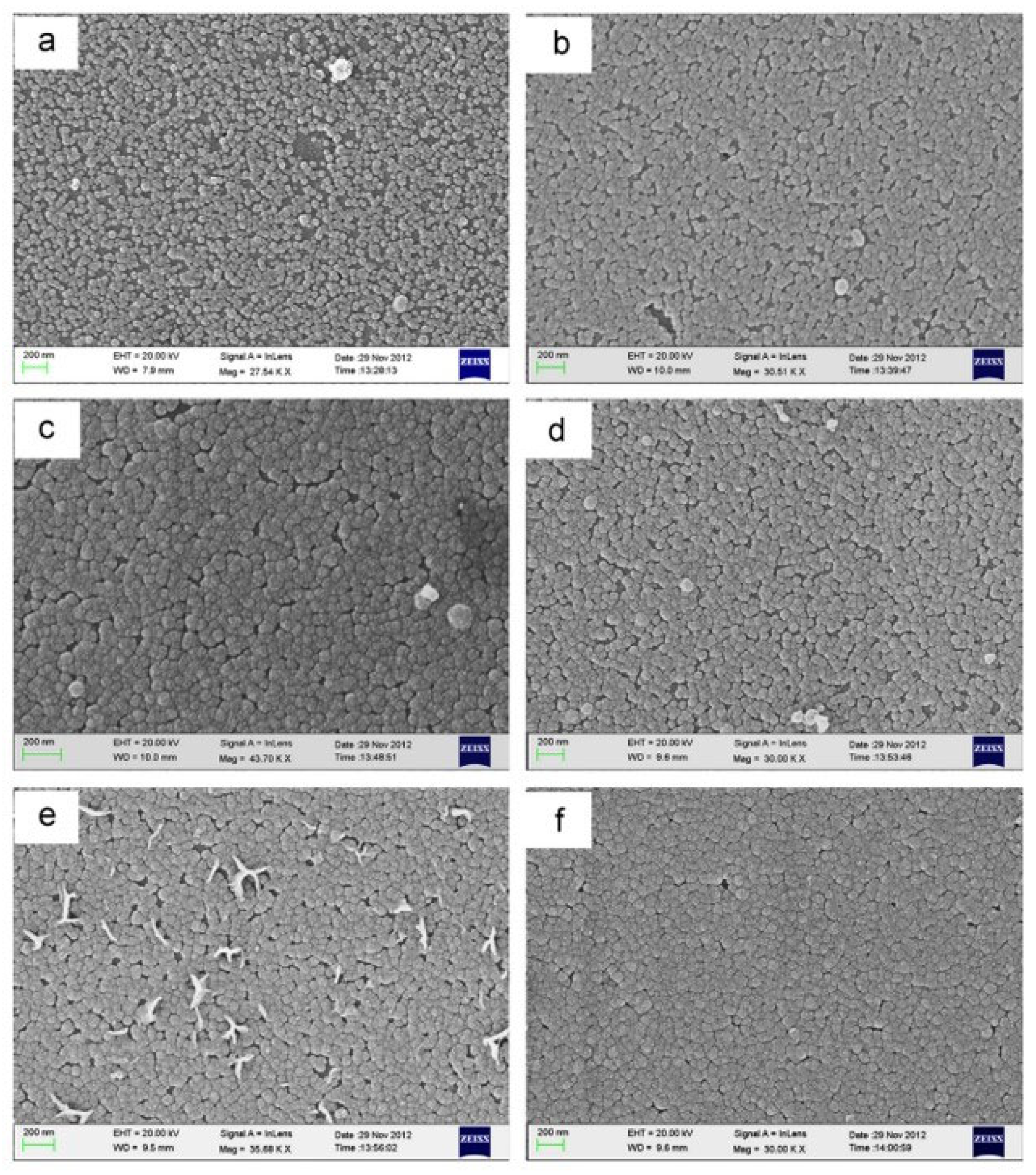

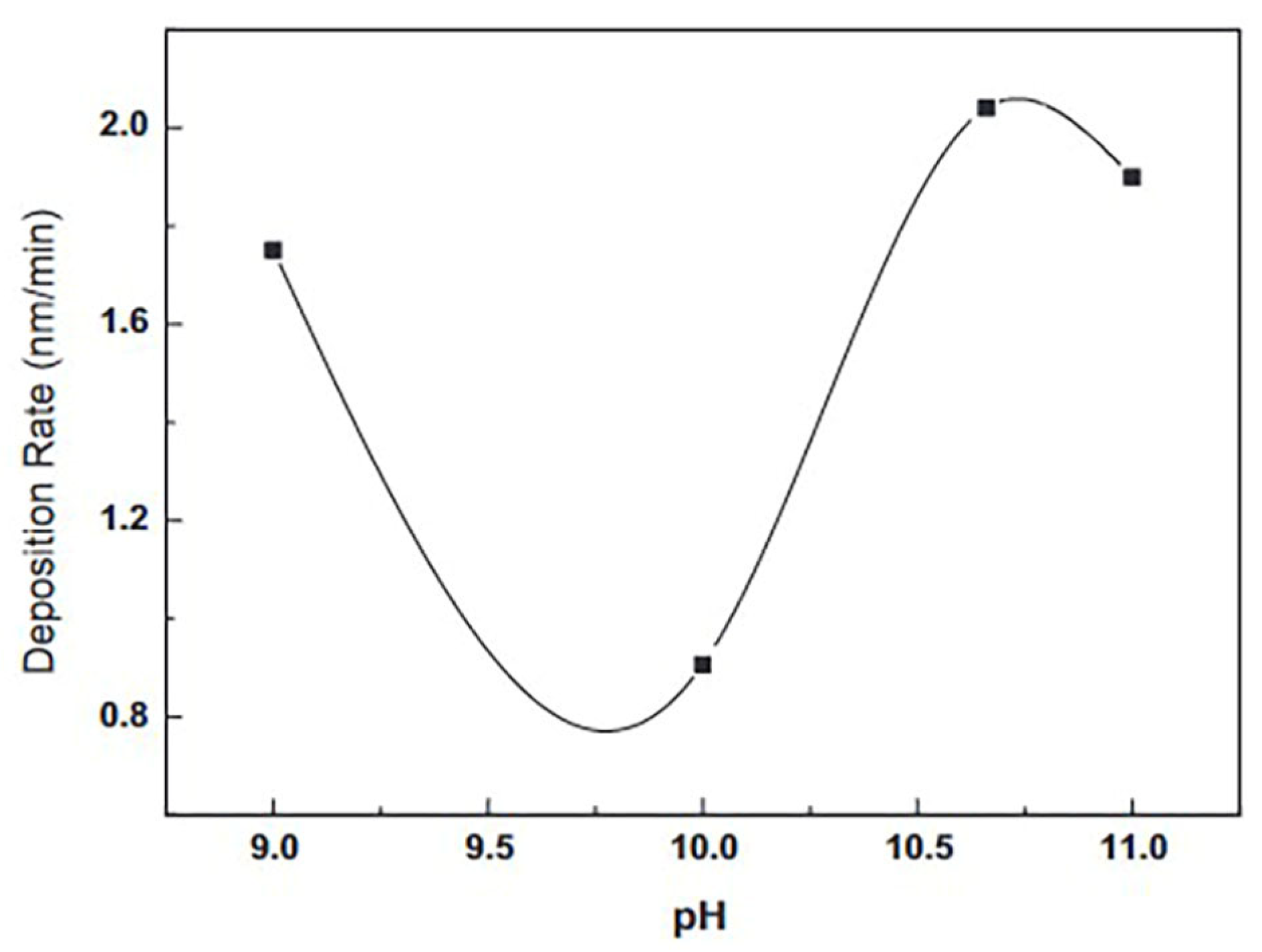
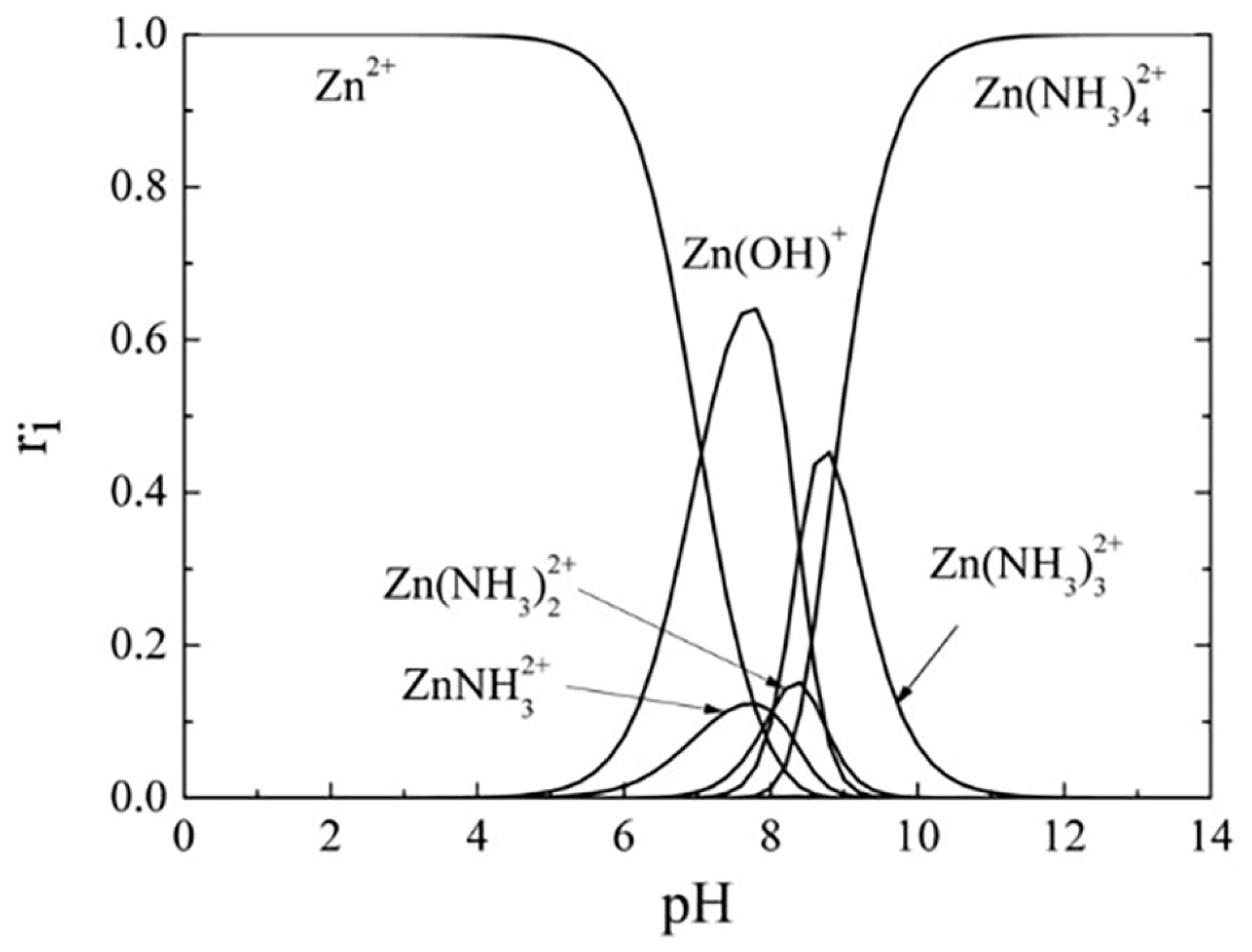
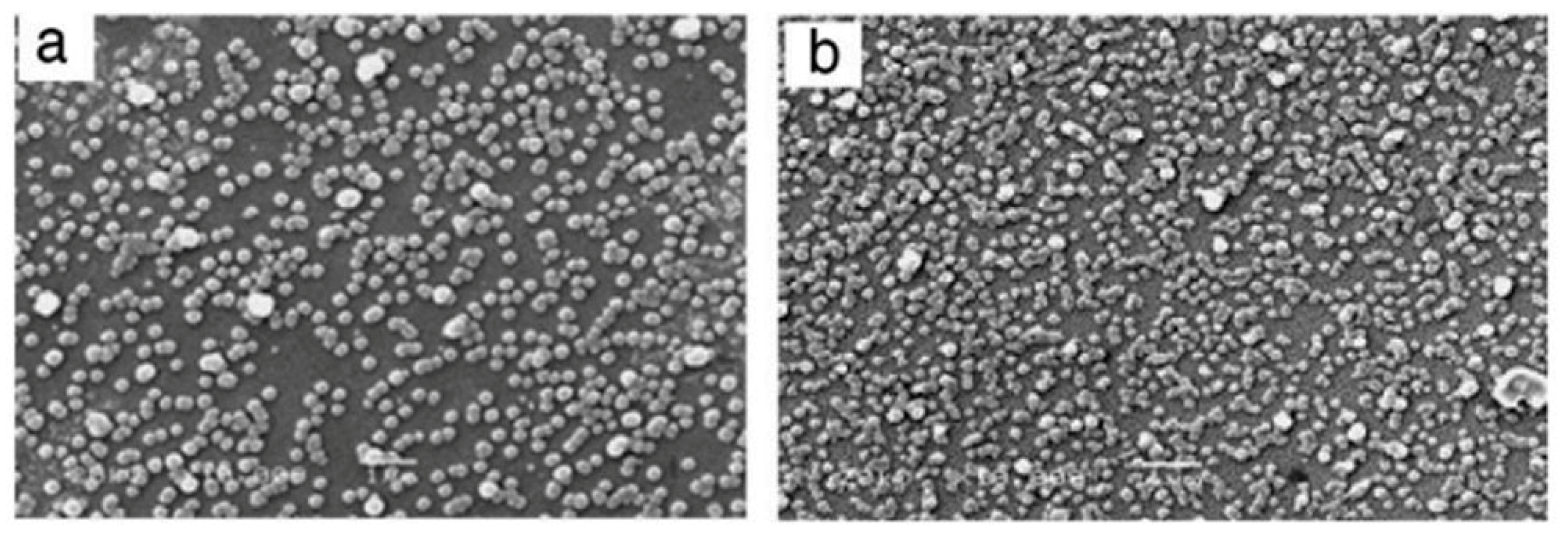
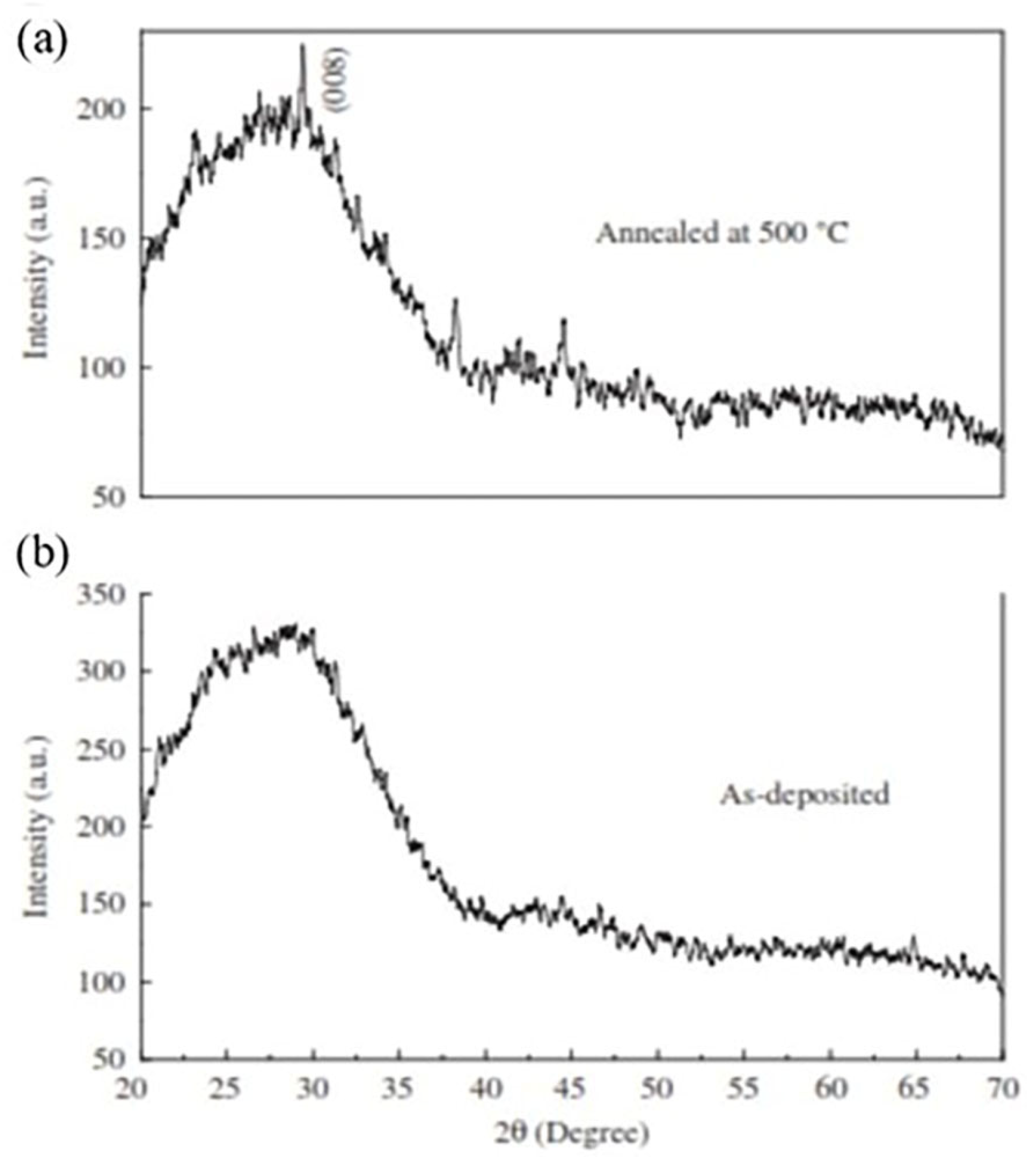



| Properties | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Odour | Sulfurous odour |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble | |
| Appearance | White-greyish to yellow powder | |
| Chemical | Empirical formula | ZnS |
| Molar mass | 97.46 g/mol | |
| Lattice constant | 5.4093 Å | |
| Crystal structure | Cubic | |
| Group | Zinc-12 | |
| Mechanical | Density | 4.079 g/cm3 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.27 | |
| Flexural Strength | 103 MPA | |
| Modulus elasticity | 75 GPA | |
| Boiling point | 1185 °C | |
| Melting point | 1850 °C | |
| Electric | Electronic configuration | Zinc: [Ar]3d104S2 |
| Dielectric constant | 8.9 | |
| Band gap | 3.54 eV | |
| Hole mobility | 5 cm2/Vs | |
| Electron mobility | 180 cm2/Vs | |
| Thermal | Heat of information | 477 KJ/mol |
| Heat of fusion | 390 J/g | |
| Thermal conductivity | 25.1 W/mk | |
| Specific heat capacity | 0.472 J/g°C | |
| Thermal coefficient of expansion | 6.36 µm/m °C | |
| Optical | Refractive index | 2.356 |
| Parameters of CBD | Affected Properties of ZnS Thin Films |
|---|---|
| Complexing agent | Crystalline characteristics, thickness, morphology, surface roughness, and optical transmittance |
| Zinc salt and [Zn]/[S] ratio | Crystalline characteristics, film growth, and morphology |
| Stirring speed | Film growth rate, thickness, and surface roughness |
| Humidity | Crystalline characteristics, morphology, and optical transmittance |
| Deposition temperature | Morphology, pH of the solution, thickness, and optical transmittance |
| Deposition time | Crystalline characteristics, thickness, and band gap |
| pH value | Crystalline characteristics, surface morphology, optical transmittance, film growth rate, and band-gap |
| Precursor types | Morphology, optical transmittance, and band gap |
| Annealing (environmental and temperature effect) | Crystalline characteristics, morphology, and optical transmittance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arsad, A.Z.; Zuhdi, A.W.M.; Abdullah, S.F.; Chau, C.F.; Ghazali, A.; Ahmad, I.; Abdullah, W.S.W. Effect of Chemical Bath Deposition Variables on the Properties of Zinc Sulfide Thin Films: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062780
Arsad AZ, Zuhdi AWM, Abdullah SF, Chau CF, Ghazali A, Ahmad I, Abdullah WSW. Effect of Chemical Bath Deposition Variables on the Properties of Zinc Sulfide Thin Films: A Review. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062780
Chicago/Turabian StyleArsad, Akmal Zaini, Ahmad Wafi Mahmood Zuhdi, Siti Fazlili Abdullah, Chien Fat Chau, Azrul Ghazali, Ibrahim Ahmad, and Wan Syakirah Wan Abdullah. 2023. "Effect of Chemical Bath Deposition Variables on the Properties of Zinc Sulfide Thin Films: A Review" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062780
APA StyleArsad, A. Z., Zuhdi, A. W. M., Abdullah, S. F., Chau, C. F., Ghazali, A., Ahmad, I., & Abdullah, W. S. W. (2023). Effect of Chemical Bath Deposition Variables on the Properties of Zinc Sulfide Thin Films: A Review. Molecules, 28(6), 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062780






