Enhanced Remdesivir Analogues to Target SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
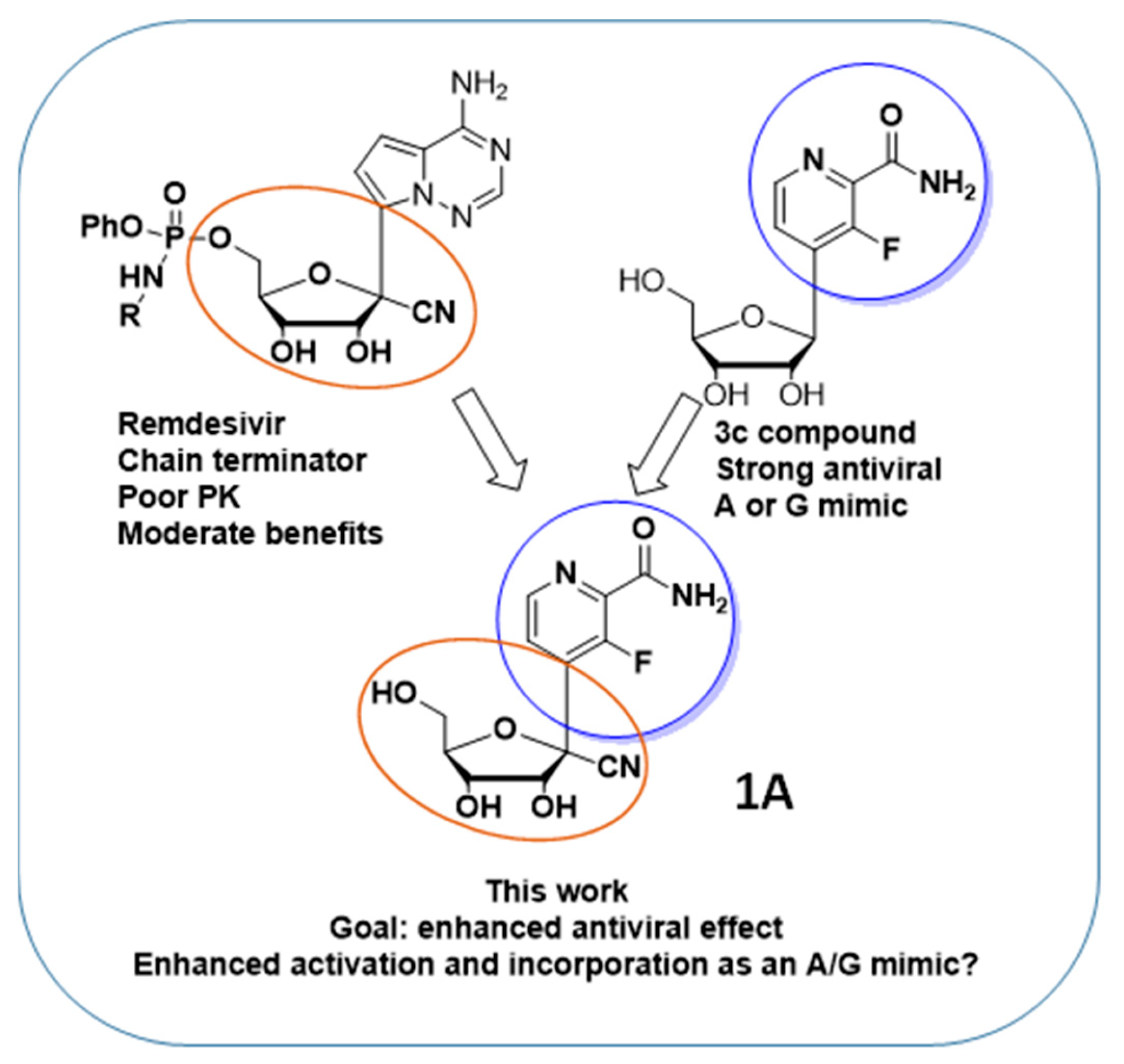
1. Introduction
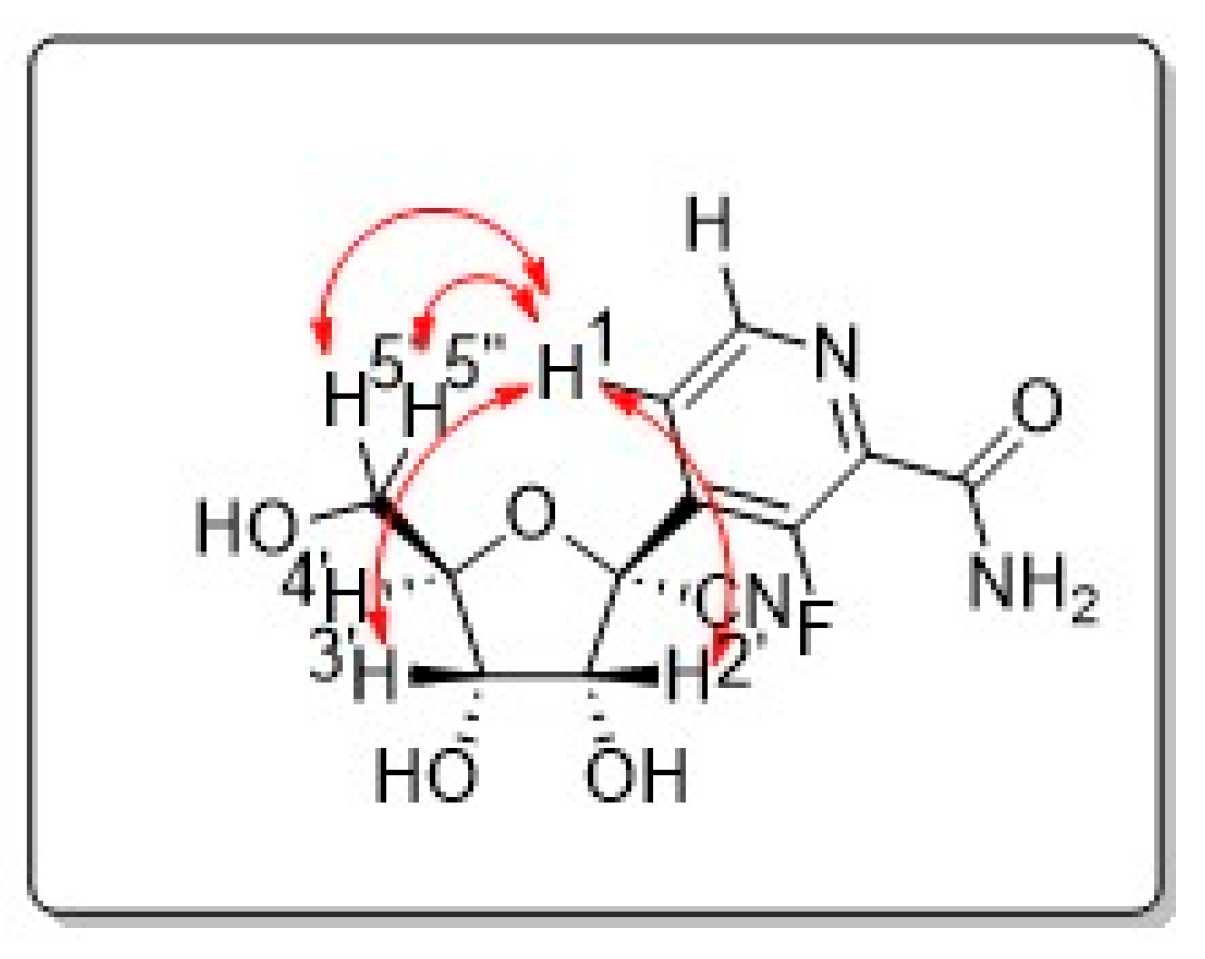
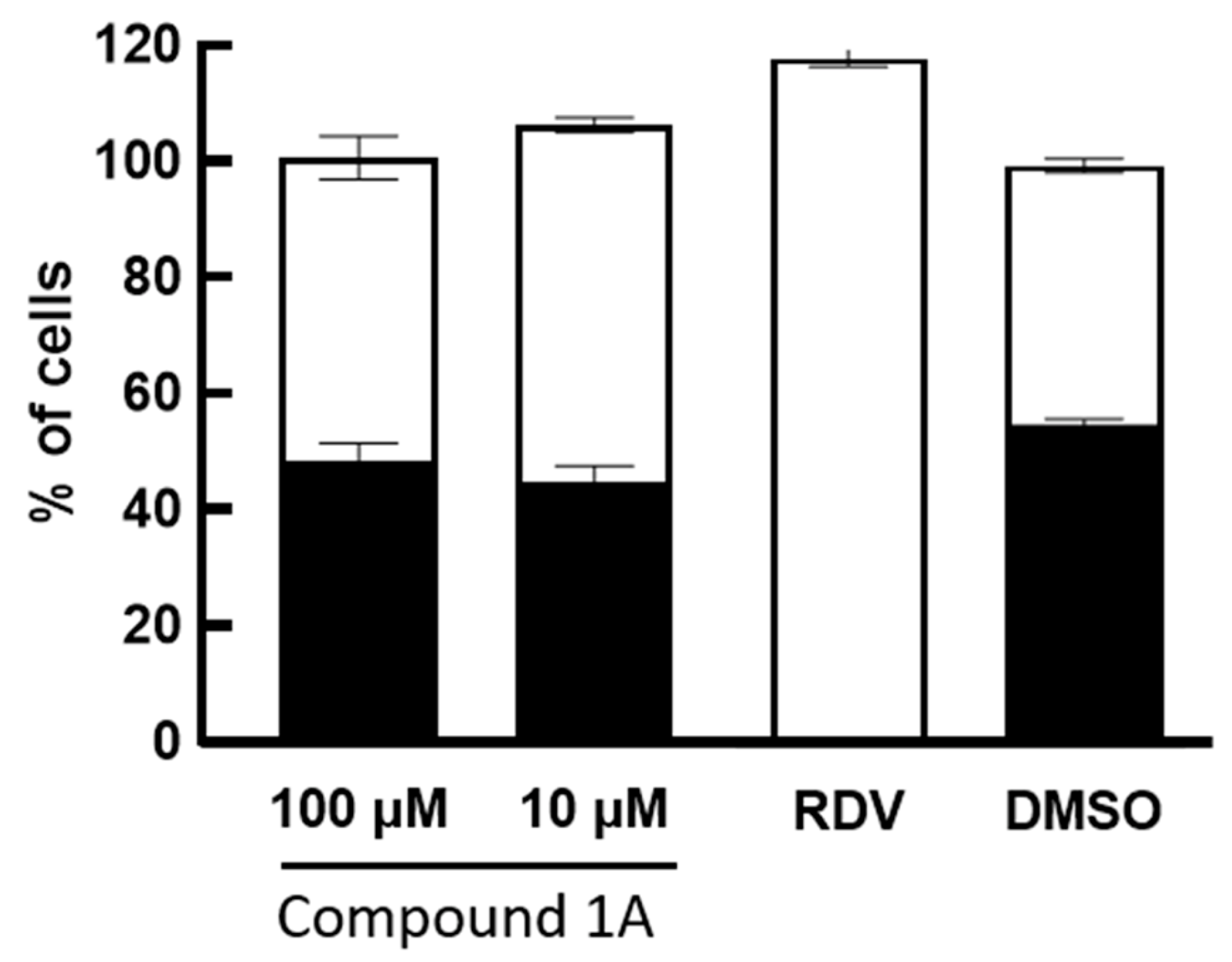
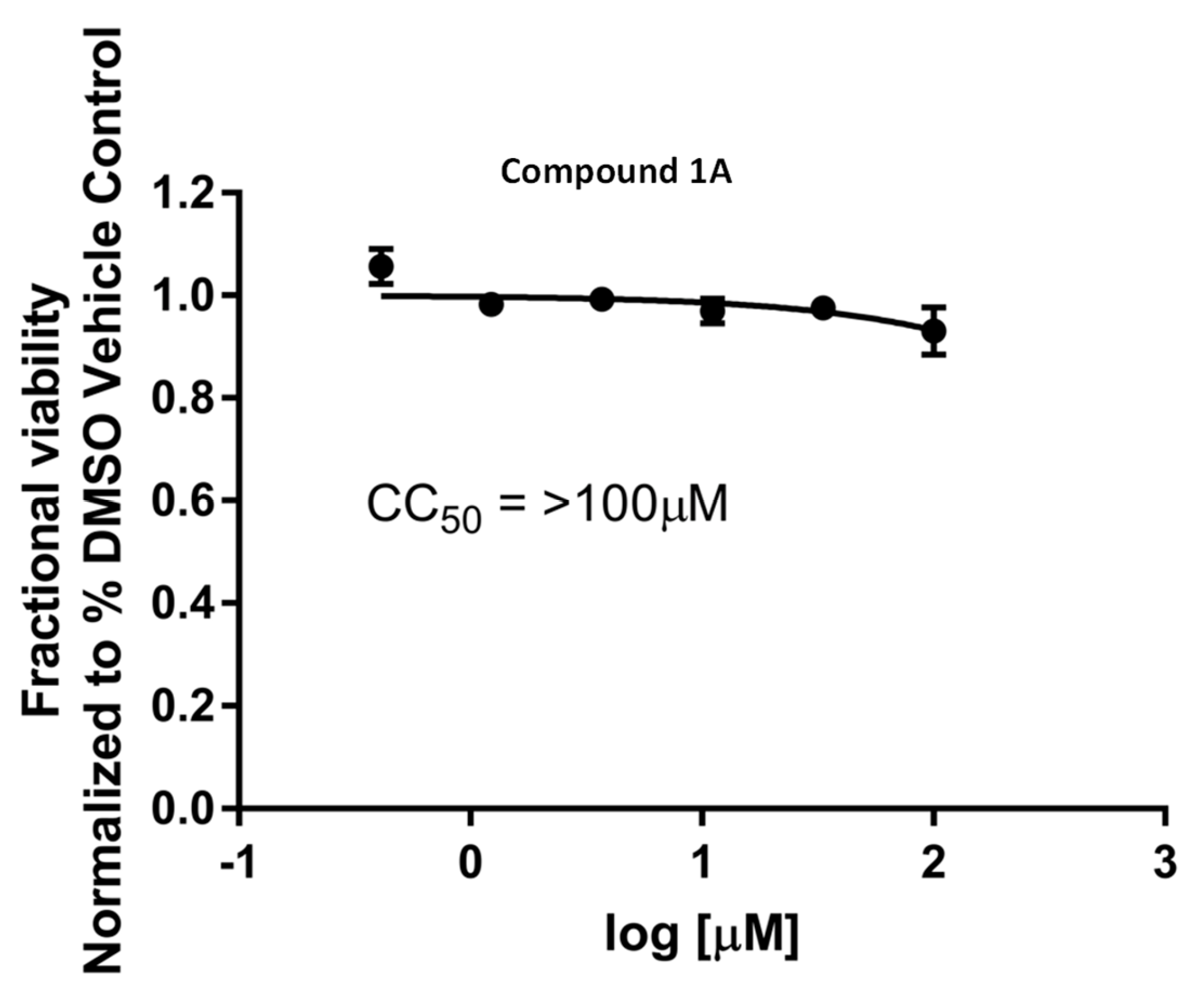
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Final Report. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraghty, R.J.; Geraghty, R.; Aliota, M.; Bonnac, L. Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Strategies and Nucleoside Analogues. Viruses 2021, 13, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Woolner, E.; Perry, J.K.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M. Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6785–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M. The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4773–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchesnokov, E.P.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M.; Tchesnokov, E.; Feng, J.; Porter, D. Mechanism of Inhibition of Ebola Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase by Remdesivir. Viruses 2019, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rompay, A.R.; Johansson, M.; Karlsson, A. Phosphorylation of nucleosides and nucleoside analogs by mammalian nucleoside monophosphate kinases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 87, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rompay, A.R.; Johansson, M.; Karlsson, A. Substrate specificity and phosphorylation of antiviral and anticancer nucleoside analogues by human deoxyribonucleoside kinases and ribonucleoside kinases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 100, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, T.K.; Jordan, R.; Lo, M.K.; Ray, A.S.; Mackman, R.L.; Soloveva, V.; Siegel, D.; Perron, M.; Bannister, R.; Hui, H.C.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 2016, 531, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wan, J.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X.; Prhavc, M.; Dyatkina, N.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Smith, D.B.; Jekle, A.; Kinkade, A.; et al. Synthesis and Anti-Influenza Activity of Pyridine, Pyridazine, and Pyrimidine C-Nucleosides as Favipiravir (T-705) Analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4611–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocek, M. C-Nucleosides: Synthetic Strategies and Biological Applications. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6729–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Simons, C. Synthetic Methodologies for C-Nucleosides. Synthesis 2004, 2004, 1533–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temburnikar, K.; Seley-Radtke, K.L. Recent advances in synthetic approaches for medicinal chemistry of C-nucleosides. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, K.J. Potassium trimethylsilanolate mediated hydrolysis of nitriles to primary amides. Int. Organ Rapid Publ. Prelim. Commun. Org. Chem. 2000, 41, 3747–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKillop, A.; Kemp, D. Further functional group oxidations using sodium perborate. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 3299–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnac, L.F.; Gao, G.Y.; Chen, L.; Patterson, S.E.; Jayaram, H.N.; Pankiewicz, K.W. Efficient synthesis of benzamide riboside, a potential anticancer agent. Nucl. Nucl. Nucleic Acids 2007, 26, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Acosta, R.; Edwards, T.C.; Dreis, C.D.; Krishna, V.D.; Cheeran, M.C.J.; Qiu, L.; Xie, J.; Bonnac, L.F.; Geraghty, R.J. Enhancing the Antiviral Potency of Nucleobases for Potential Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Therapies. Viruses 2021, 13, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, N.H.; Shi, K.; Demir, Ö.; Belica, C.; Banerjee, S.; Yin, L.; Durfee, C.; Amaro, R.E.; Aihara, H. Structure and dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 proofreading exoribonuclease ExoN. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2106379119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, C.; Harris, S.A.; Daluge, S.M.; Gudmundsson, K.S.; McLean, E.W.; Burnette, T.C.; Marr, H.; Hazen, R.; Condreay, L.D.; Johnson, L.; et al. Application of Phosphoramidate Pronucleotide Technology to Abacavir Leads to a Significant Enhancement of Antiviral Potency. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3504–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, C.; Kelleher, M.R.; Perrone, P.; Mulready, S.; Luoni, G.; Daverio, F.; Rajyaguru, S.; Le Pogam, S.; Najera, I.; Martin, J.A.; et al. The application of phosphoramidate ProTide technology to the potent anti-HCV compound 4′-azidocytidine (R1479). Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4250–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, C.; Perrone, P.; Madela, K.; Neyts, J. The phosphoramidate ProTide approach greatly enhances the activity of β-2′-C-methylguanosine against hepatitis C virus. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4316–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majima, R.; Edwards, T.C.; Dreis, C.D.; Geraghty, R.J.; Bonnac, L.F. Enhanced Remdesivir Analogues to Target SARS-CoV-2. Molecules 2023, 28, 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062616
Majima R, Edwards TC, Dreis CD, Geraghty RJ, Bonnac LF. Enhanced Remdesivir Analogues to Target SARS-CoV-2. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062616
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajima, Ryuichi, Tiffany C. Edwards, Christine D. Dreis, Robert J. Geraghty, and Laurent F. Bonnac. 2023. "Enhanced Remdesivir Analogues to Target SARS-CoV-2" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062616
APA StyleMajima, R., Edwards, T. C., Dreis, C. D., Geraghty, R. J., & Bonnac, L. F. (2023). Enhanced Remdesivir Analogues to Target SARS-CoV-2. Molecules, 28(6), 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062616




