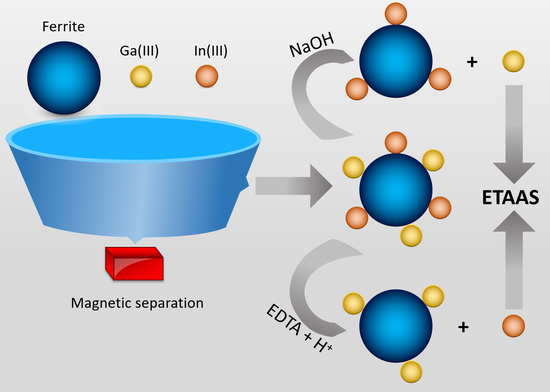
Using a Simple Magnetic Adsorbent for the Preconcentration and Determination of Ga(III) and In(III) by Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
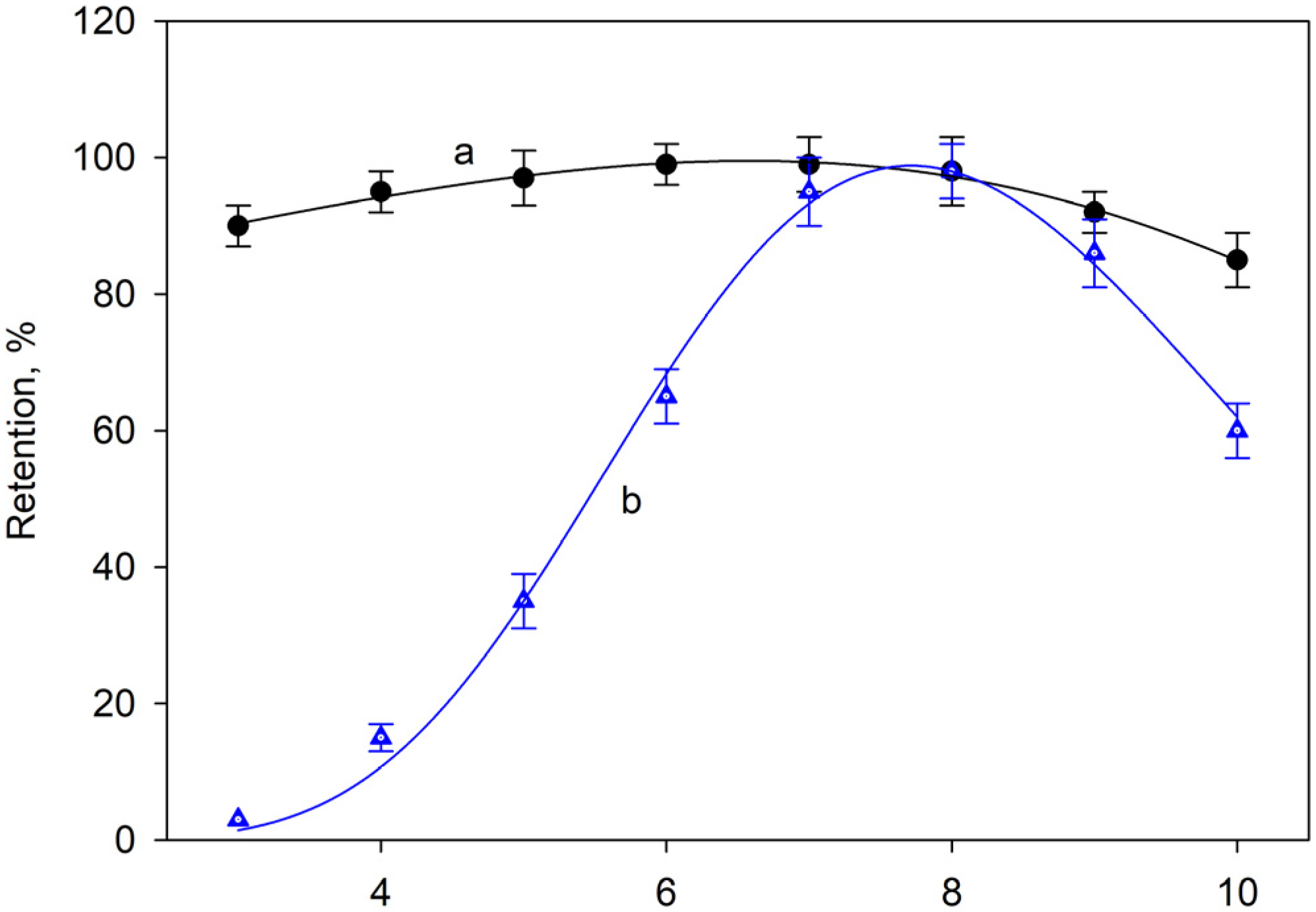
2.1. Effect of pH
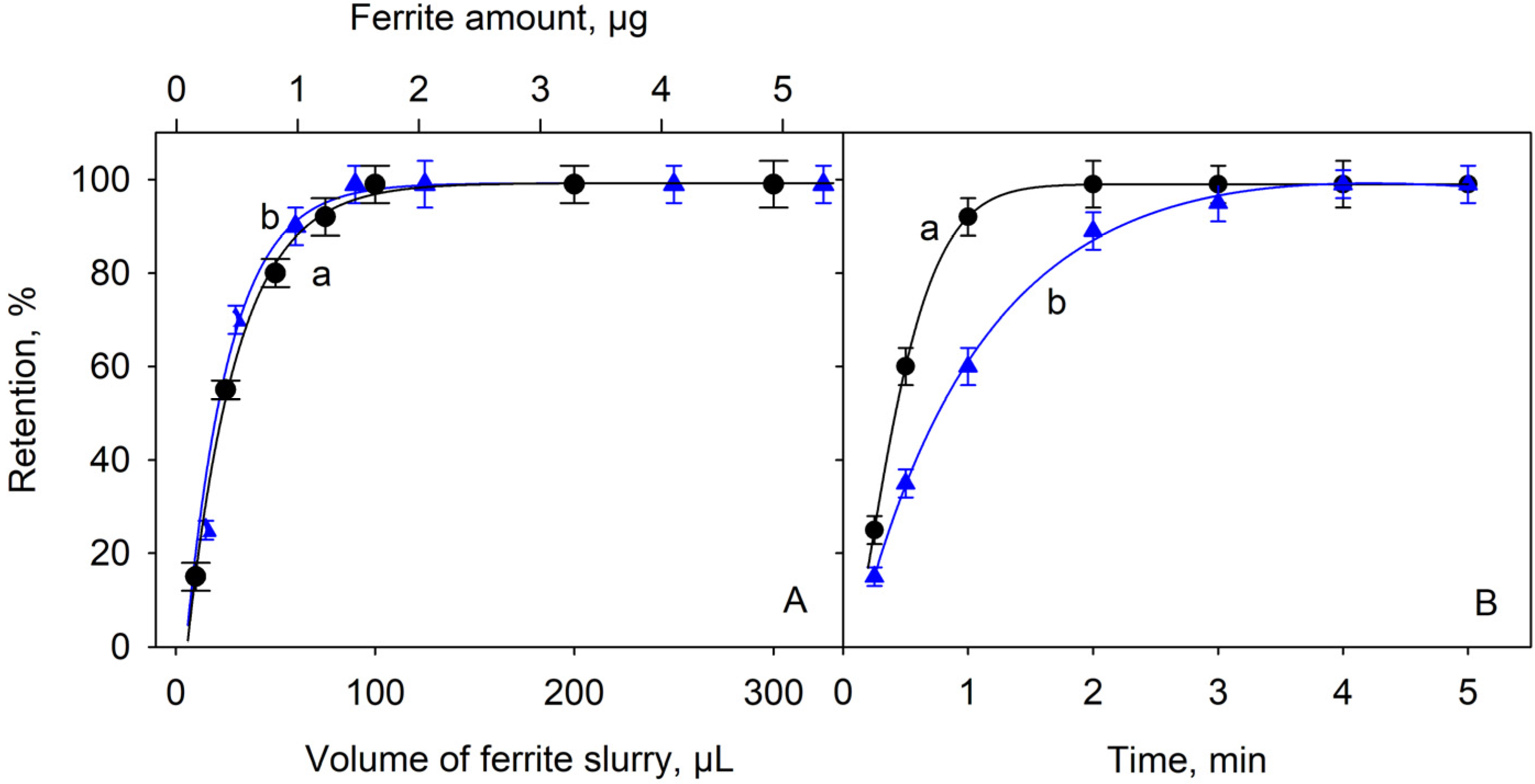
2.2. Effect of the Adsorbent Amount and the Time of Contact
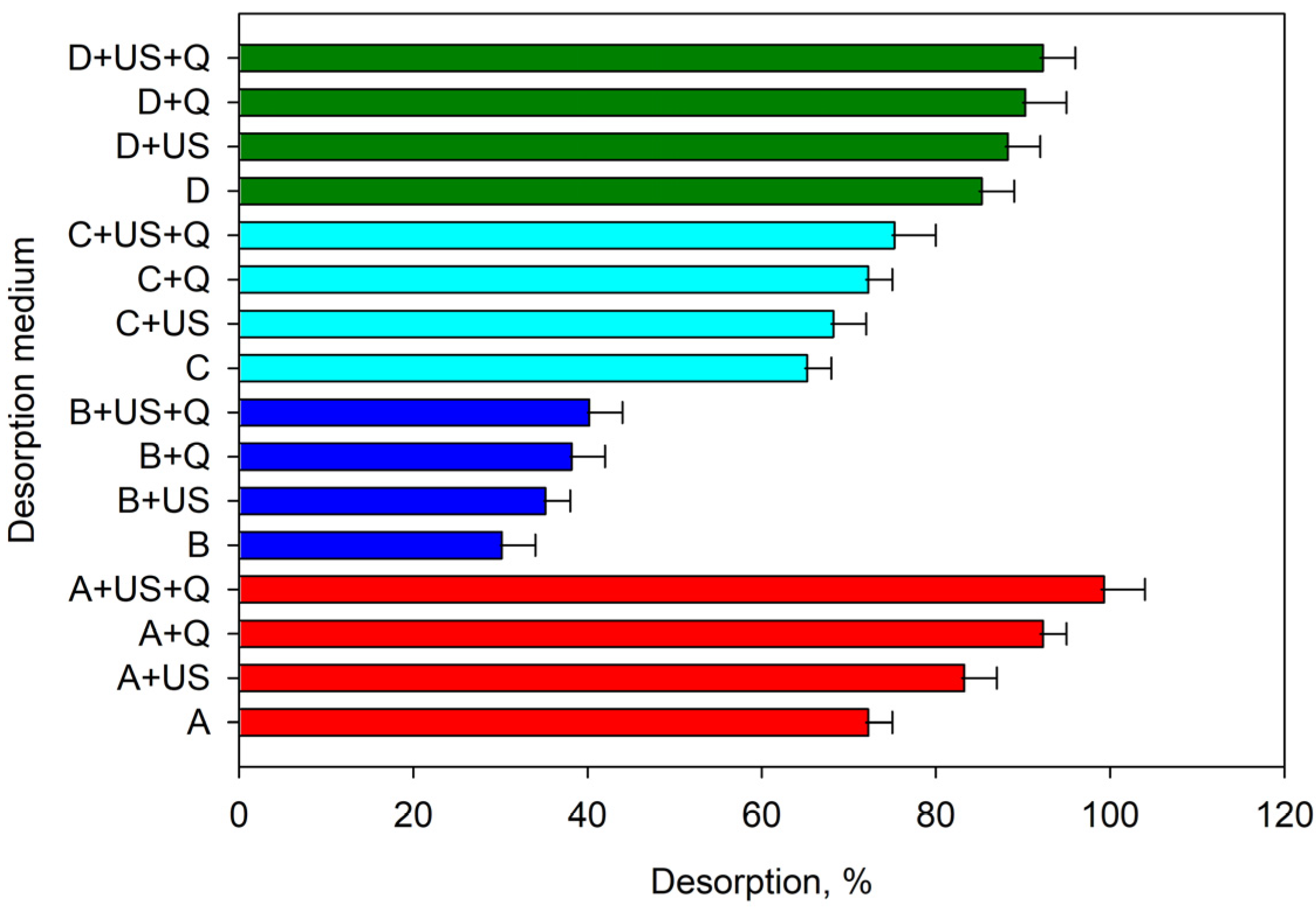
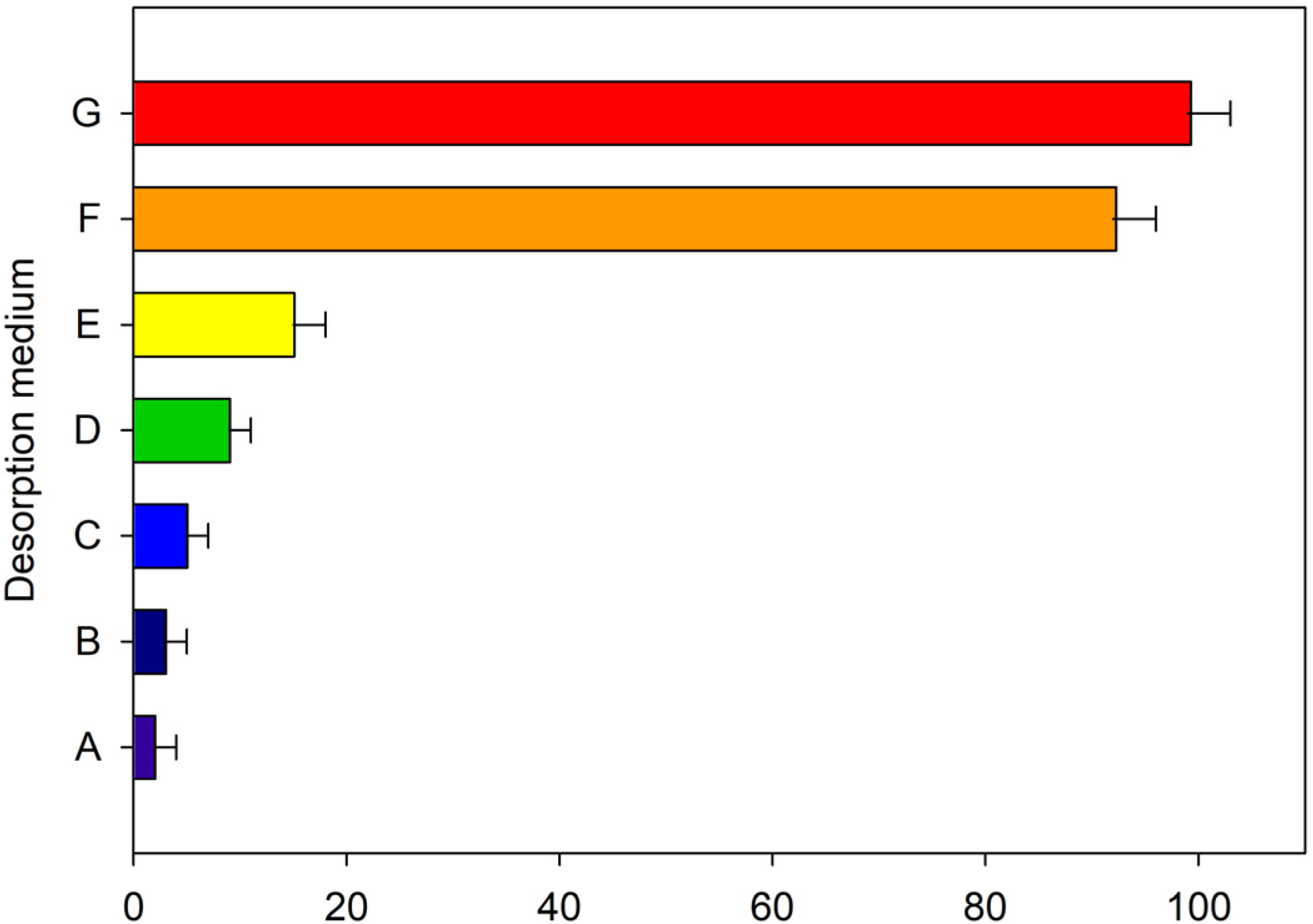
2.3. Study of the Desorption Conditions
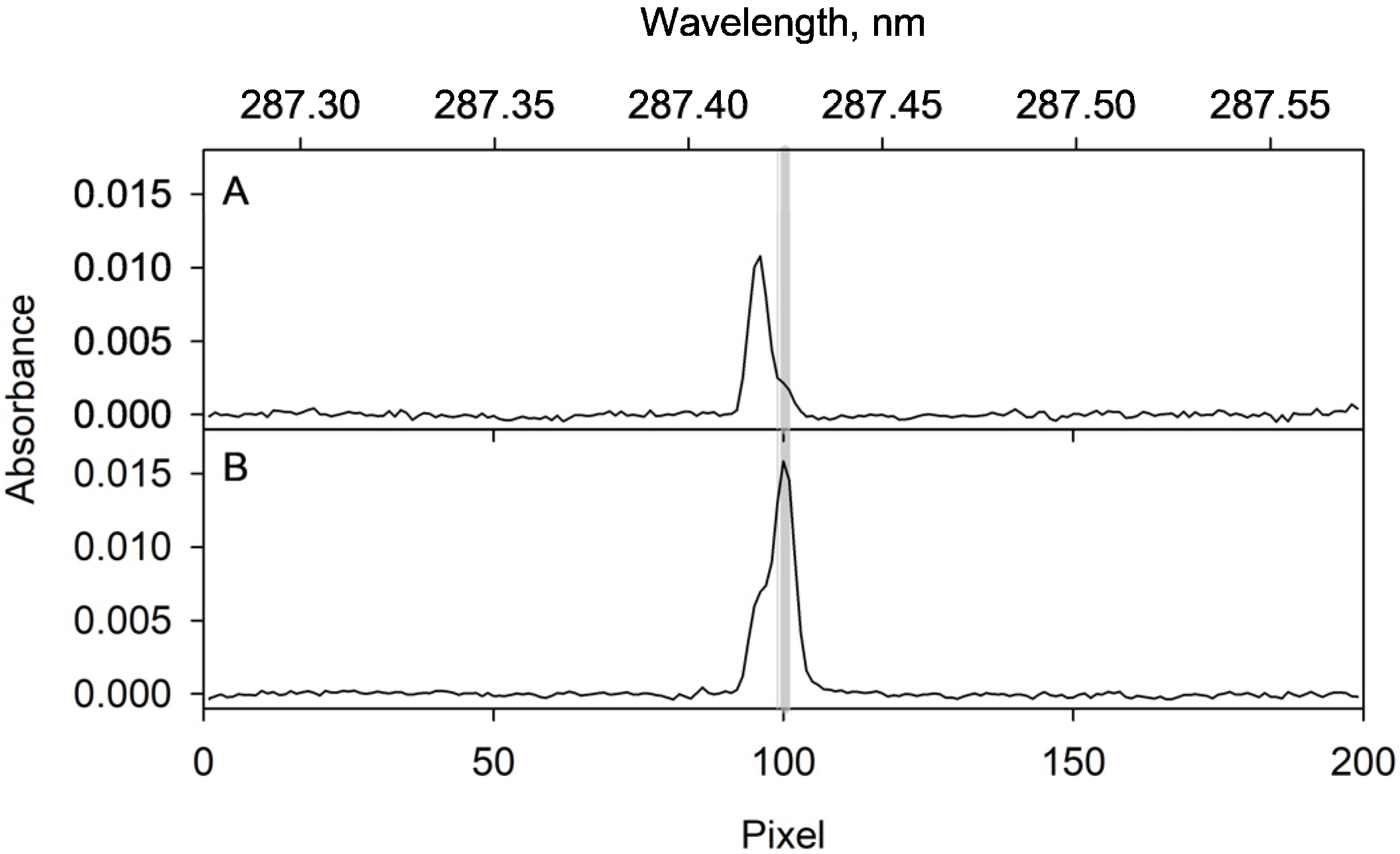
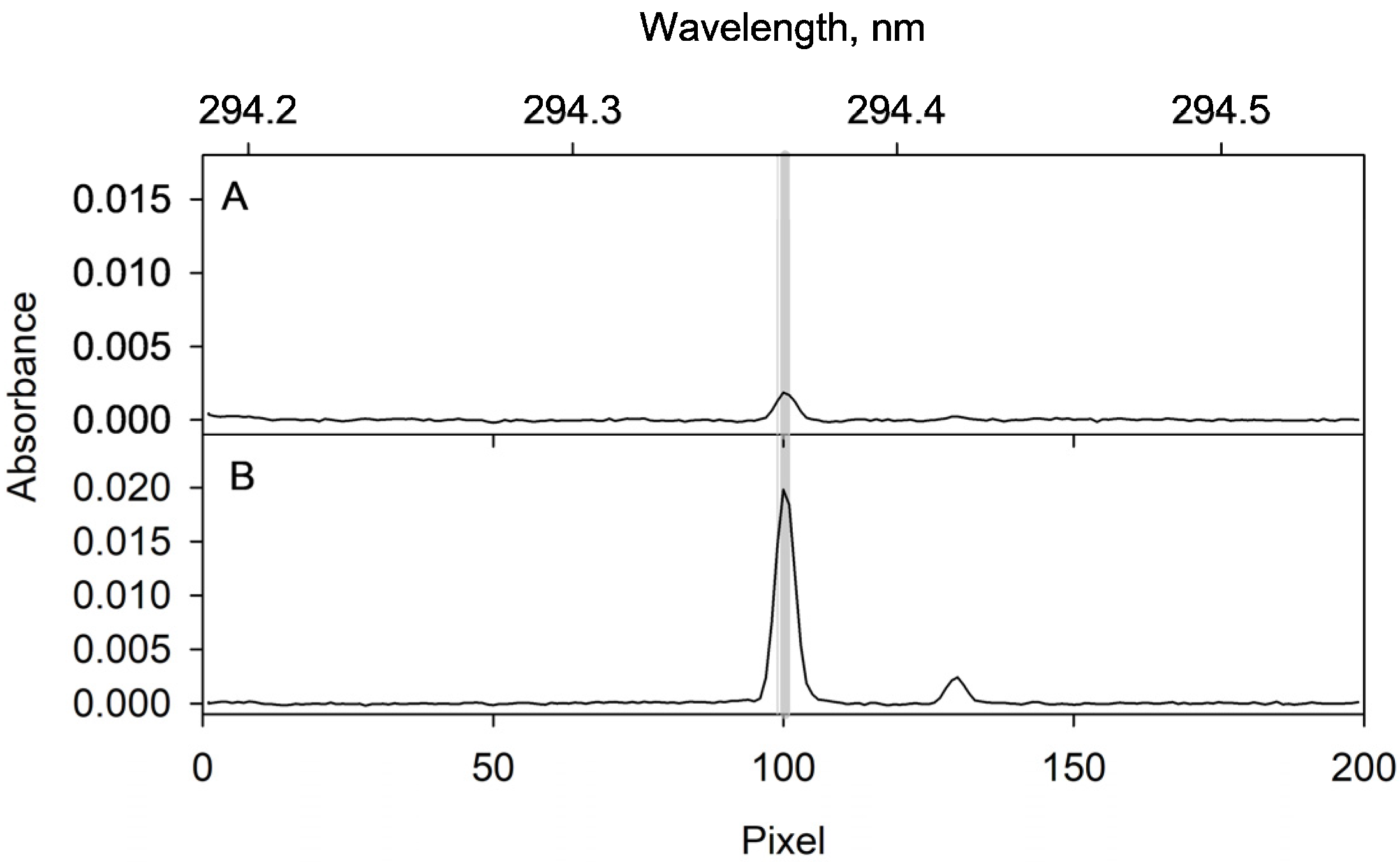
2.4. Optimization of the ETAAS Parameters
2.5. Analytical Figures of Merit: Applications
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instrumentation
3.2. Preparation of the Magnetic Material
3.3. Samples Treatment
3.4. Procedure for the Determination of Gallium and Indium
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Petrov, A.G. Liquid crystal physics and the physics of living matter. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1999, 332, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Keoleian, G.A. LCA of rare earth and critical metal recovery and replacement decisions for commercial lighting waste management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 159, 104846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomhard, E.M. The toxicology of indium oxide. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 58, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, T. Electronic waste management. Trans. IMF 2020, 98, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, E.; Gómez, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Bernabé, I.; Sáez, P.; Galán, J. A new mesoporous activated carbon as potential adsorbent for effective indium removal from aqueous solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 295, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.H.; Chuang, S.-H.; Huang, R.-Y.; Liu, P.-I.; Chang, M.-C.; Horng, R.-Y. Titanium Dioxide/Activated Carbon Electrode with Polyurethane Binder for the Removal of Indium Ions via Capacitive Deionization. Processes 2021, 9, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, C.Y.; Yap, S.S.; Ong, G.L.; Ong, T.S.; Chin, Y.T.; Lee, S.F.; Tou, T.Y.; Nee, C.H. Single pulse laser removal of indium tin oxide film on glass and polyethylene terephthalate by nanosecond and femtosecond laser. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shadman, F.; Ogden, K.L. Algae-based sorbents for removal of gallium from semiconductor manufacturing wastewater. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, S.; Sinharoy, A.; Lens, P.N. Adsorptive removal of gallium from aqueous solution onto biogenic elemental tellurium nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, S.; Costa, R.B.; Sinharoy, A.; Cunha, M.P.; Zaiat, M.; Lens, P.N. Selective removal and recovery of gallium and germanium from synthetic zinc refinery residues using biosorption and bioprecipitation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saez, P.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez, J.M.; Paramio, C.; Fraile, C.; Díez, E. H-Clinoptilolite as an Efficient and Low-Cost Adsorbent for Batch and Continuous Gallium Removal from Aqueous Solutions. J. Sustain. Met. 2021, 7, 1699–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.G.; Wang, H.Q.; Song, H.B.; Li, Z.H.; Li, X.P.; Ye, S.S.; Zhang, F.G.; Cui, S.W.; Yan, H.F.; Li, T. Occupational Exposure to Indium of Indium Smelter Workers. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AGS. Begründung zu Indium, Indium Oxid, Indium Hydroxid, Indium Phosphid in TRGS 900. 2017. Available online: https://www.baua.de/DE/Angebote/Rechtstexte-und-Technische-Regeln/Regelwerk/TRGS/pdf/900/900-indium-und-verbindungen.pdf?__%20blob=publicationFile&v=2 (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Chitambar, C.R. Medical Applications and Toxicities of Gallium Compounds. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2337–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladenberger, A.; Demetriades, A.; Reimann, C.; Birke, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Uhlbäck, J.; Andersson, M.; Jonsson, E. GEMAS: Indium in agricultural and grazing land soil of Europe—Its source and geochemical distribution patterns. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 154, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyersmann, D.; Hartwig, A. Carcinogenic metal compounds: Recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schen, S.; Zhao, R.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Toxicity and Biocompatibility of Liquid Metals. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 12, 2201924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomhard, E.M. The toxicology of gallium oxide in comparison with gallium arsenide and indium oxide. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 80, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata-Pendias, H.A.; Mukherjee, A.B. Trace Elements from Soil to Human; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Arain, G.; Devi, I.; Khuhawar, M.Y. Spectrophotometric determination of gallium(III) as bipyridylglyoxal bis(4-phenyl-3-thiosemicarbazone) derivative. Asian J. Chem. 2007, 19, 5169–5176. [Google Scholar]
- Avan, A.A. Spectrophotometric and colorimetric determination of gallium (III) with p-aminohippu- ric acid-functionalized citrate capped gold nanoparticles. Turk. J. Chem. 2021, 45, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Połedniok, J. Speciation of scandium and gallium in soil. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racheva, P.; Stojnova, K.T.; Lekova, V.; Dimitrov, A.N. Spectrophotometric Determination of Gallium(III) with 4-(2-Pyridylazo)-resorcinol and Nitron. Croat. Chem. Acta 2015, 88, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojnova, K.T.; Divarov, V.V.; Racheva, P.; Lekova, V.D. Extraction-Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Gallium(III) in the Form of Ion Associate with a Monotetrazolium Salt. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2015, 82, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.S.; Moalla, S.M.N. Utility of solid phase extraction for UV-visible spectrophotometric determination of gallium in environmental and biological samples. RSC Adv. 2015, 6, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, D.; Fisher, A.; Foulkes, M.; Hill, S.J. Determination of gallium at trace levels using a spectrofluorimetric method in synthetic U–Ga and Ga–As solutions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 75, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, W.I.; Kenawy, I.M.; Hassanien, M.M. A cloud point extraction procedure for gallium, indium and thallium determination in liquid crystal display and sediment samples. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashajanov, A.M.; Bayramov, S.M.; Abbasova, G.G.; Agamaliyeva, M.M.; Mamedova, Z.A. Extraction-Atomic-Absorption Determination of Gallium (III) with 2-hydroxy-5-T-butylphenol-4′-methoxy-azobenzene. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, Z.; Tyson, J.F. Slurry sampling for determination of lead in marine plankton by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2007, 86, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk-Coda, M. Sequential determination of gallium, indium, and thallium in environmental samples after preconcentration on halloysite nanotubes using ultrasound-assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 15444–15452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Liu, H.-M. Determination of gallium in human urine by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Peng, H.X. Determination of the Impurity Element Gallium in the Metallic Aluminum Products such as Aluminum and Aluminum Alloy by ICP-OES. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 706–708, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santana, F.A.; Barbosa, J.T.; Matos, G.D.; Korn, M.G.; Ferreira, S.L. Direct determination of gallium in bauxite employing ICP OES using the reference element technique for interference elimination. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Wei, X.; Wu, J.; Min, F.; Liu, Y.; Guan, Y. A solid phase extraction method for determination of trace gallium in aluminum–iron samples by atomic spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zu, W.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, C. Determination of gallium in water samples by atomic emission spectrometry based on solution cathode glow discharge. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2019, 152, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhin, M.; Zarubina, N.V.; Mikhailyk, P.E. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric measurement of gallium in ferromanganese crusts from the Sea of Japan. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 69, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatova, D.G.; Seregina, I.F.; Foteeva, L.S.; Pukhov, V.V.; Timerbaev, A.R.; Bolshov, M.A. Determination of gallium originated from a gallium-based anticancer drug in human urine using ICP-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.G.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Martínez, M.A. Determination of gallium by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Talanta 2004, 62, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabarczyk, M.; Wasąg, J. Determination of trace amounts of Ga(III) by adsorptive stripping voltammetry with in situ plated bismuth film electrode. Talanta 2015, 144, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, J.; Guin, S.K.; Pillai, J.S.; Aggarwal, S.K. Scope of detection and determination of gallium(III) in industrial ground water by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry on bismuth film electrode. Talanta 2011, 86, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvecky, L.; Briancin, J. Possibilities of simultaneous determination of indium and gallium in binary InGa alloys by anodic stripping voltammetry in acetate buffer. Chem. Pap.-Chem. Zvesti 2004, 58, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Pysarevska, S.; Dubenska, L. The advances in electrochemical determination of gallium (III). Chem. Met. Alloy 2018, 11, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, T. Separation of trace amounts of Ga and Ge in aqueous solution using nano-particles micro-column. Talanta 2011, 85, 2463–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divrikli, U.; Soylak, M.; Elci, L. Separation and Enrichment of Gallium(III) as 4-(2-Thiazolylazo) Resorcinol (TAR) Complex by Solid Phase Extraction on Amberlite XAD-4 Adsorption Resin. Anal. Lett. 2003, 36, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Martínez-Alfonso, N.; Bermejo-Barrera, A. Separation of gallium and indium from ores matrix by sorption on Amberlite XAD-2 coated with PAN. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2001, 369, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, M.M.; Kenawy, I.M.; El-Menshawy, A.M.; El-Asmy, A.A. Separation and Preconcentration of Gallium(III), Indium(III), and Thallium(III) Using New Hydrazone-modified Resin. Anal. Sci. 2008, 23, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanien, M.M.; Kenawy, I.M.; Mostafa, M.R.; El-Dellay, H. Extraction of gallium, indium and thallium from aquatic media using amino silica gel modified by gallic acid. Microchim. Acta 2010, 172, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Devi, N. Studies on extraction of gallium (III) from chloride solution using Cyphos IL 104 and its removal from photodiodes and red mud. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 171, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burylin, M.; Kopeyko, E.; Bokiy, E.; Konshin, V.; Konshina, D. Determination of indium in water samples using solid-phase extraction with modified silica gel and slurry sampling with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 5893–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, M.; Tateishi, I.; Katsumata, H.; Kaneco, S. Preconcentration of trace indium in aqueous samples using sodium dodecyl sulphate/activated carbon prior to electrothermal furnace absorption spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 101, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igosheva, V.S.; Zaitceva, P.V.; Vasil’Eva, N.L. Electrothermal atomic absorption indium determination. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2174, 020022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineza, N.; Barrera, A.B.; Bermejo, B.P. Indium determination in different environmental materials by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry with Amberlite XAD-2 coated with 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol. Talanta 2005, 66, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamisawa, H.; Murashima, K.; Minamisawa, M.; Arai, N.; Okutani, T. Determination of Indium by Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry after Coprecipitation with Chitosan. Anal. Sci. 2003, 19, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzen, M.; Soylak, M. A solid phase extraction procedure for Indium prior to its graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric determination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.L.; Nozal, M.J.; Deban, L.; Aller, A.J. Determination of indium in aluminium alloys by flame atomic-absorption spectroscopy and flame atomic-emission spectrometry. Talanta 1982, 29, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çelik, B.; Akkaya, E.; Bakirdere, S.; Aydin, F. Determination of indium using vortex assisted solid phase microextraction based on oleic acid coated magnetic nanoparticles combined with slotted quartz tube-flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2018, 141, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, G.L.; Kron, B.E.; Jones, B.T. Simultaneous determination of Cr, Ga, In and V in soil and water samples by tungsten coil atomic emission spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2009, 64, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, K.E.; Han, L.; Gwinn, W.M.; Morgan, D.L.; Ross, G.T.; Essader, A.S.; Fernando, R.A.; Haines, L.G.; Robinson, V.G. Development and Optimization of a Procedure for the Determination of Indium-Tin Oxide Particle Size and Concentration in Cellular Media. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 1614–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Synthesis and application of spherical macroporous epoxy-polyamide chelating resin for preconcentration and separation of trace Ga(III), In(III), Bi(III), V(V), Cr(III), and Ti(IV) from solution samples. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 2330–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfonoun, E.; Yousefi, S.R. Exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for on-line vortex-assisted dispersive micro-solid phase extraction of indium prior to determination by ICP-OES. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 4031–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibo, D.S.; Amakawa, H.; Nozaki, Y. Determination of indium in natural waters by flow injection inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 1998, 107, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Hu, Z.; Luo, T.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zong, K.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J. Determination of major and trace elements in geological samples by laser ablation solution sampling-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzke, K.; Timm, K.; Hebisch, R.; Brock, T.; Hartwig, A.; MAK Commission. Indium–Determination of indium and its compounds in workplace air using mass spectrometry with inductively coupled plasma (ICP-MS). MAK Collect. Occup. Health Saf. 2021, 6, Doc044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.D.M.M.; Morelli, T.; Moreira, I.M.N.S.; De Carvalho, M.S. Studies on indium sorption from iodide medium by polyurethane foam. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2004, 15, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, E.; Shokoufi, N.; Shemirani, F. Indium determination and preconcentration using fiber optic linear array detection spectrometry combined with dispersive liquid-liquid micro extraction. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 66, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połedniok, J. A Sensitive Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Trace Quantities of Indium in Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 186, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadmehri, E.A.; Abadi, M.D.M.; Chamsaz, M. Sensitive analysis In(III) in various matrices by spectrophotometry after dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic drop. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2014, 87, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, Z. Separation and preconcentration of trace indium(III) from environmental samples with nanometer-size titanium dioxide. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, E.A.; Taher, M.A.; Fazelirad, H.; Naghizadeh, M. Application of dispersive liquid–liquid–solidified floating organic drop microextraction and ETAAS for the preconcentration and determination of indium. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Zhu, X.; Wu, L.; Tan, X. Ultrasonic assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometry for determination of trace gallium in vanadium titanium magnetite. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; He, Q.; Zhou, G.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; Liu, M.; Fan, L. Determination of heavy metals in water samples using dual-cloud point extraction coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6732–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk-Coda, M.; Stanisz, E. Low cost adsorbents in ultrasound-assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction for simultaneous determination of indium and nickel by high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry in soils and sediments. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacht, B. Gallium(III) ion hydrolysis under physiological conditions. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, 29, 372–376. [Google Scholar]
- Baes, C.F.; Mesmer, R.E. The Hydrolysis of Cations; Robert, E., Ed.; Krieger: Malabar, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Brom, M.; Franssen, G.M.; Joosten, L.; Gotthardt, M.; Boerman, O.C. The effect of purification of Ga-68-labeled exendin on in vivo distribution. EJNMMI Res. 2016, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahri, Z.; Rezai, B.; Kowsari, E. Selective separation of gallium from zinc using flotation: Effect of solution pH value and the separation mechanism. Miner. Eng. 2016, 86, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, A.; Majumder, M.; Pal, M.; Das, N.S.; Chattopadhyay, K.K.; Saha, B. Enhanced Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium onto Magnetic Calcium Ferrite Nanoparticles: Kinetic, Isotherm, and Neural Network Modeling. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 1806–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Singh, N.B. Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by an adsorbent nickel ferrite-polyaniline nanocomposite. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2016, 23, 374–383. [Google Scholar]
- López-García, I.; Rivas, R.E.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Use of sodium tungstate as a permanent chemical modifier for slurry sampling electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometric determination of indium in soils. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, M.M.; Mortada, W.I.; Kenawy, I.M.; El-Daly, H. Solid Phase Extraction and Preconcentration of Trace Gallium, Indium, and Thallium Using New Modified Amino Silica. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 71, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-M.; Jiang, J.-K.; Lin, Y.-H. Simultaneous Determination of Gallium(III) and Indium(III) in Urine and Water Samples with Cloud Point Extraction and by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2012, 45, 2096–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitko, R.; Kocot, K.; Zawisza, B.; Feist, B.; Pytlakowska, K. Liquid-phase microextraction as an attractive tool for multielement trace analysis in combination with X-ray fluorescence spectrometry: An example of simultaneous determination of Fe, Co, Zn, Ga, Se and Pb in water samples. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, I.; Vicente-Martínez, Y.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Determination of ultratraces of mercury species using separation with magnetic core-modified silver nanoparticles and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 1980–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, A.; Fuchs, M.; Pinheiro, D.; Tanabe, E.; Bertuol, D. Recovery of indium from LCD screens of discarded cell phones. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.-F.; Tien, K.-W. Recovery of Gallium and Indium from Waste Light Emitting Diodes. J. Korean Inst. Resour. Recycl. 2020, 29, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Samson, I.M. The aqueous geochemistry of gallium, germanium, indium and scandium. Ore Geol. Rev. 2006, 28, 57–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength, nm | 294.364 (Ga)/303.935 (In) | ||
| Slit, nm | 0.7 | ||
| Atomizer | Transversal with L’Vov platform | ||
| Background correction | Zeeman effect | ||
| Injected sample volume, µL | 10 | ||
| Chemical modifier | 10 µL of 500 mg L−1 Pd(II) solution | ||
| Sample volume, mL | 10 | ||
| Heating program | |||
| Step | Temperature, °C | Ramp, °C s−1 | Hold, s |
| 1: Dry | 110 | 10 | 20 |
| 2: Dry | 130 | 9 | 10 |
| 3: Calcination | 1300 | 300 | 15 |
| 4: Atomization a,b | 2300 (Ga)/2200 (In) | 2300 (Ga)/1500 (In) | 5 |
| 5: Clean | 2450 | 500 | 4 |
| Analyte | Separation Technique | TD | V | FE | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ga, In | SPE with aminated silica gel functionalized with HBAAS | FAAS | 1000 | 200 | 4.1; 1.55 | [80] |
| Ga, In | SPE with aminated silica gel functionalized with gallic acid | FAAS | 50 | 250 | 5.8; 1.8 | [47] |
| In | SPE with TiO2 | Vis-UV | 25 | 25 | 450 | [68] |
| In | SPE with Chromosorb 108 and bathocuproine disulphonic acid | ETAAS | 100 | 30 | 0.012 | [54] |
| In | SPE with SDS-modified activated carbon | ETAAS | 200 | 363 | 0.0002 | [50] |
| In | DMSPE with exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets | ICP-OES | 10 | 75 | 0.32 | [60] |
| Ga, In | USA-DMSPE with halloysite nanotubes | ETAAS | 10 | 33; 37 | 0.02; 0.01 | [30] |
| In | VASPME with oleic acid coated ferrite | FAAS | 30 | 44 | 6.02 | [56] |
| In | DLSME with chitosan | ETAAS | 500 | 100 | 0.4 | [53] |
| Ga | CPE with 8-hydroxyquinoline and Triton X-114 | ICP-MS | 50 | 20 | 1.2 | [71] |
| Ga, In | CPE with gallic acid on Triton X-114 | FAAS | 25 | 54; 48 | 3.5; 1.25 | [27] |
| Ga, In | CPE with 5-Br-PADAP in the presence of Triton X-100 | ICP-OES | 25 | 12 | 0.7; 0.3 | [81] |
| Ga | DLLME with APDC | XRF | 5 | 250 | 1.7 | [82] |
| In | DLLME with PAN | Vis-UV | 10 | 160 | 0.3 | [65] |
| Ga | USA-DLLME with PAN in chlorobenzene | FAAS | 40 | 124 | 70 | [70] |
| In | SFOD-DLLME with dithizone and 1-undecanol | Vis-UV | 10 | 36 | 9 | [67] |
| In | SFOD-DLLME with PAN and 1-undecanol | ETAAS | 25 | 62,5 | 0.05 | [69] |
| Ga, In | MDSPE with ferrite | ETAAS | 10 | 163 | 0.02; 0.01 | TW |
| Ga(III), µg L−1 | In(III), µg L−1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RWS | Added | Found a | Rec., % | Added | Found a | Rec., % |
| M1 | 0 0.2 | <LOD 0.19 ± 0.02 | - 95 ± 6 | 0 0.1 | <LOD 0.10 ± 0.02 | - 103 ± 6 |
| M2 | 0.4 0 | 0.42 ± 0.02 <LOD | 105 ± 7 - | 0.3 0 | 0.29 ± 0.02 <LOD | 98 ± 7 - |
| 0.2 0.4 | 0.21 ± 0.03 0.38 ± 0.02 | 105 ± 6 95 ± 5 | 0.1 0.3 | 0.09 ± 0.02 0.31 ± 0.03 | 92 ± 5 104 ± 5 | |
| M3 | 0 0.2 | <LOD 0.21 ± 0.02 | - 105 ± 5 | 0 0.1 | <LOD 0.11 ± 0.02 | - 110 ± 6 |
| M4 | 0.4 0 | 0.39 ±0.03 <LOD | 98 ± 6 - | 0.3 0 | 0.32 ± 0.03 <LOD | 107 ± 7 - |
| 0.2 0.4 | 0.18 ± 0.03 0.41 ± 0.03 | 90 ± 6 103 ± 4 | 0.1 0.3 | 0.09 ± 0.02 0.31 ± 0.04 | 93 ± 6 103 ± 5 | |
| Ga(III), µg g−1 | In(III), µg g−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRM | Certificate | Found a | Certificate | Found |
| NIST SRM 2711 b (soil) | 15 | 15.8 ± 0.4 | 1.1 | 1.2 ± 0.1 |
| NCS DC 73319a (soil) | 18 ± 1.4 | 17.9 ± 0.3 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| Ga(III), µg L−1 | In(III), µg L−1 | |||
| SRM | Certificate | Found | Certificate | Found |
| TM-25.4 (water) | 32.6 ± 2.8 | 33.2 ± 0.5 | - | <LOD |
| TMDA-62.2 (water) | 9.03 ± 0.73 | 8.98 ± 0.23 | - | <LOD |
| Sample Treatment | Ga(III), µg g−1 | In(III), µg g−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Added | Found a | Rec., % | Added | Found a | Rec., % |
| LED light bulb | - 20 | 730 ± 3 749 ± 4 | - 99.8 ± 3.7 | - 20 | 20 ± 2 41 ± 2 | - 102.5 ± 4.7 |
| LCD Phone 1 | - 20 | 5.1 ± 0.2 25.3 ± 0.3 | - 100.8 ± 3.7 | - 20 | 160 ± 4 178 ± 5 | - 98.9 ± 2.8 |
| LCD Phone 2 | - 20 | 287 ± 2 306 ± 3 | - 99.7 ± 3.7 | - 20 | 412 ± 6 434 ± 6 | - 100.4 ± 1.4 |
| LCD Phone 3 | - 20 | 190 ± 2 212 ± 4 | - 100.9 ± 3.7 | - 20 | 580 ± 6 596 ± 5 | - 99.3 ± 0.9 |
| Laptop screen 1 | - 20 | 215 ± 3 236 ± 4 | - 100.4 ± 3.7 | - 20 | 360 ± 5 378 ± 5 | - 99.5 ± 1.3 |
| Laptop screen 2 | - 20 | 410 ± 2 432 ± 4 | - 100.4 ± 3.7 | - 20 | 265 ± 4 283 ± 5 | - 99.3 ± 1.7 |
| Ga(III), µg g−1 | In(III), µg g−1 | |||||
| Leaching | Added | Found a | Rec., % | Added | Found a | Rec., % |
| LED light bulb | - 20 | 730 ± 3 749 ± 4 | - 99.8 ± 0.5 | - 20 | 20 ± 2 41 ± 2 | - 102.5 ± 4.9 |
| LCD phone 1 | - 20 | 3.8 ± 0,2 23.3 ± 0,3 | - 97.9 ± 1.3 | - 20 | 112 ± 3 133 ± 4 | - 100.7 ± 3.0 |
| LCD phone 2 | - 20 | 280 ± 2 302 ± 3 | - 100.7 ± 0.9 | - 20 | 403 ± 6 424 ± 6 | - 102.0 ± 1.4 |
| LCD phone 3 | - 20 | 184 ± 2 205 ± 4 | - 100.5 ± 1.9 | - 20 | 551 ± 5 569 ± 5 | - 99.6 ± 0.9 |
| Laptop screen 1 | - 20 | 198 ± 4 223 ± 5 | - 102.3 ± 2.2 | - 20 | 327 ± 4 349 ± 5 | - 100.6 ± 1.4 |
| Laptop screen 2 | - 20 | 389 ± 4 411 ± 4 | - 100.5 ± 0.9 | - 20 | 252 ± 4 270 ± 5 | - 99.2 ± 1.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vicente-Martínez, Y.; Muñoz-Sandoval, M.J.; Hernández-Córdoba, M.; López-García, I. Using a Simple Magnetic Adsorbent for the Preconcentration and Determination of Ga(III) and In(III) by Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Molecules 2023, 28, 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062549
Vicente-Martínez Y, Muñoz-Sandoval MJ, Hernández-Córdoba M, López-García I. Using a Simple Magnetic Adsorbent for the Preconcentration and Determination of Ga(III) and In(III) by Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062549
Chicago/Turabian StyleVicente-Martínez, Yesica, María José Muñoz-Sandoval, Manuel Hernández-Córdoba, and Ignacio López-García. 2023. "Using a Simple Magnetic Adsorbent for the Preconcentration and Determination of Ga(III) and In(III) by Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062549
APA StyleVicente-Martínez, Y., Muñoz-Sandoval, M. J., Hernández-Córdoba, M., & López-García, I. (2023). Using a Simple Magnetic Adsorbent for the Preconcentration and Determination of Ga(III) and In(III) by Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Molecules, 28(6), 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062549